Highlights
- Na-aluminosilicate glasses containing La2O3 and LaF3 were obtained.
- Na-aluminosilicate glasses provide a thermally stable matrix for the incorporation of lanthanides, either in the form of oxides or fluorides.
- The addition of La2O3 or LaF3 instead of Na2O increases the glass transition temperature.
- For glass containing 7.5 mol% LaF3, a low-phonon phase can be obtained through a controlled crystallization process.
Abstract
This study examines the impact of varying the content of lanthanum oxide and lanthanum fluoride on the formation of glass-ceramics and their effect on the thermal stability of Na-aluminosilicate glasses, depending on the type and concentration of the raw material used. The aim of this study is to obtain a fluoride crystalline phase in the glassy matrix. Such a phase, due to its low phonon energy, increases the probability of radiative transitions (decay) of optically active lanthanide dopants, thereby enhancing luminescence. The scope of the work included the preparation of two glass series with varying amounts of La2O3 and LaF3 to determine the glass-forming range and to identify the characteristic temperatures of the glasses using Differential Thermal Analysis. It was found that increasing the La2O3 content above 10 mol% in this glass leads to exceeding the target melting temperature (1400 °C) of the glass batch. In contrast, the introduction of 10 mol% LaF3 prevents the formation of homogeneous glass. Based on these results, a controlled crystallization process was designed, and the resulting crystalline phases were identified using X-ray diffraction (XRD). In the base glass, two crystalline phases were identified: Na2O·Al2O3·SiO2 and Na2SiO3. For the La-oxide series, the crystallization of NaAlSiO4 and La2SiO5 was confirmed. In the case of the La-fluoride series, the formation of LaF3 was observed. It was found that by introducing an appropriate amount of LaF3 (7.5 mol%) into the aluminosilicate network, it is possible to obtain a glass suitable for controlled crystallization, leading to the formation of a low-phonon LaF3 phase.
1. Introduction
Aluminosilicate glasses are characterized by good thermal stability [1], high thermal [2] and chemical resistance [3], as well as high mechanical strength [4]. Due to the significant polymerization of the glass network and the strong bonding within [SiO4] and [AlO4] tetrahedra, these glasses exhibit high phonon energy (~1100 cm−1) [5]. As a result, when doped with optically active ions, they show low luminescence efficiency because the probability of non-radiative relaxation processes is high [6,7].
On the other hand, fluoride glasses [8] (such as ZBLAN [9]), which have low phonon energy [10] (<600 cm−1), serve as excellent host matrices for the development of optically active glasses [11]. However, their poor thermal stability [12] and the complexity of their melting process, which requires highly pure raw materials and an oxygen-free atmosphere, pose significant challenges in their fabrication [13].
The development of oxyfluoride glasses [14] could represent a step forward in creating materials that combine the advantages of both glass types, provided that controlled crystallization of the fluoride phase can be achieved. This crystalline phase, in the form of nanocrystals, can serve as a suitable host for optically active lanthanide dopants [15]. Although lanthanum itself does not exhibit luminescent properties, in the form of LaF3 it can act as an excellent host for doping with other optically active lanthanides [16,17,18].
Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the influence of lanthanum addition on the thermal stability of aluminosilicate glass and to determine the differences resulting from the use of La2O3 and LaF3 as lanthanum-containing raw materials in the context of forming low-phonon phases based on fluorides. The formation of such phases would enable the incorporation of optically active lanthanide ions into their structure.
The study focused on examining the impact of varying the content of lanthanum oxide and lanthanum fluoride on the formation of glass-ceramics and their effect on the thermal stability of aluminosilicate glasses, depending on the type and concentration of the raw material used.
The scope of the work included the preparation of two glass series with varying amounts of La2O3 and LaF3 to determine the glass-forming range and to identify the characteristic temperatures of the glasses using Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA). Based on these results, a controlled crystallization process was designed, and the resulting crystalline phases were identified using X-ray diffraction (XRD). This study also included structural analysis based on Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR).
2. Methods
The crystallization behavior of aluminosilicate glasses modified with La2O3 or LaF3 was investigated using a PerkinElmer DTA-7 system (PerkinElmer, Connecticut, USA) operating in DSC heat flux mode. The DTA curves enabled the identification of distinct thermal regions associated with crystallization, annealing, and phase transitions. For each measurement, approximately 50 mg of powdered glass was placed in a platinum crucible and heated at a constant rate of 10 K·min−1 under a nitrogen atmosphere.
The crystalline phases formed after thermal treatment were identified by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), performed on a Philips X’Pert diffractometer (Philips Analytical X-Ray B.V., Amsterdam, Netherlands) using CuKα radiation. Prior to analysis, glass-ceramic samples were finely ground to particle sizes below 1 μm to ensure adequate resolution.
Mid-infrared (MIR) spectra were acquired using a Bruker Vertex 70v FTIR spectrometer (Bruker, Massachusetts, USA). Measurements were conducted at room temperature over the 4000–400 cm−1 range, with a resolution of 4 cm−1. Each spectrum was averaged over 128 scans to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio. Samples were prepared via the standard potassium bromide (KBr) pellet technique to ensure reproducibility. All spectra were normalized to standardize the integrated intensities of absorption bands, allowing for consistent comparison across different samples.
3. Materials
All glass samples were synthesized using a conventional melt-quenching method. The batches were prepared by thoroughly mixing high-purity reagents (SiO2, Al2O3, Na2CO3, La2O3, and LaF3) with a purity of at least 99%, procured from Sigma-Aldrich, for the synthesis of the glasses. Prior to melting, the raw materials were homogenized using a ceramic mortar to ensure compositional uniformity. Each 30 g batch was melted in a covered platinum crucible, heated in an electric furnace up to 1400 °C over a period of 2 h, and held at that temperature for 90 min. The melting process was carried out in an air atmosphere. The resulting melts were cast onto a preheated brass plate, producing bulk glass samples with a thickness of 2–3 mm. The glasses were subsequently annealed at 500 °C to relieve internal stresses.
The chemical compositions of the synthesized glasses are provided in Table 1. The La2O3 content was recalculated to LaO1.5 in order to maintain the same lanthanum concentration as in the glass series containing LaF3.

Table 1.
Nominal composition of aluminosilicate glasses with the addition of La2O3 or LaF3.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Composition
For this study, a glass system composed of SiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, La2O3, and LaF3 was selected. The key variable was the increasing content of lanthanum-containing compounds, introduced at the expense of sodium carbonate, which served as the source of Na2O in the glass composition. Sodium oxide is essential for obtaining aluminosilicate glass, as it balances the charge of the aluminum ion (Al3+) within the tetrahedral unit [19]. Additionally, it lowers the melting temperature of the batch. Two series of glass samples were prepared: one series in which lanthanum was added in the form of La2O3, and another in which LaF3 served as the dopant. The purpose of the La2O3-based series was to provide a reference system, while the LaF3-containing series enabled the evaluation of the effect of fluoride incorporation on glass properties. This approach allowed for a comparative assessment of whether substituting La2O3 with LaF3 yields similar structural and thermal behavior and to what extent the presence of fluoride influences the overall characteristics of the resulting glasses.
It was found that increasing the La2O3 content above 10 mol% in this glass leads to exceeding the target melting temperature (1400 °C) of the glass batch. In contrast, the introduction of 10 mol% LaF3 prevents the formation of homogeneous glass.
4.2. Thermal Analysis
Analysis of DTA curves indicates that the obtained glasses do not exhibit sharp crystallization effects (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Instead, the structural ordering process proceeds slowly, as evidenced by broad exothermic effects. This behavior results from a strong, polymerized aluminosilicate network characterized by robust covalent–ionic bonding. The strength of this network decreases with the introduction of LaF3, as indicated by the increase in crystallization enthalpy (ΔH).
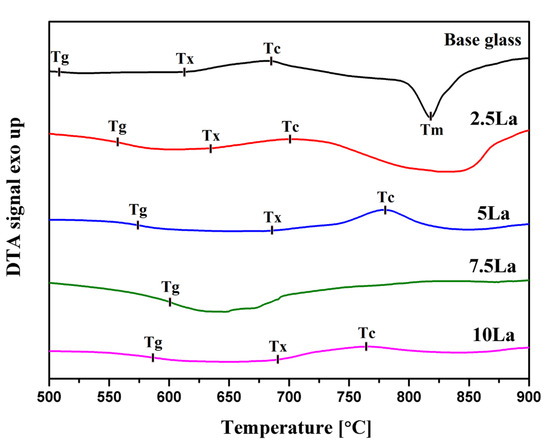
Figure 1.
DTA curves of aluminosilicate glasses for the La-oxide series. Tg—the glass transformation temperature; Tx—the onset of crystallization temperature; Tc—the peak crystallization temperature; Tm—the melting temperature.
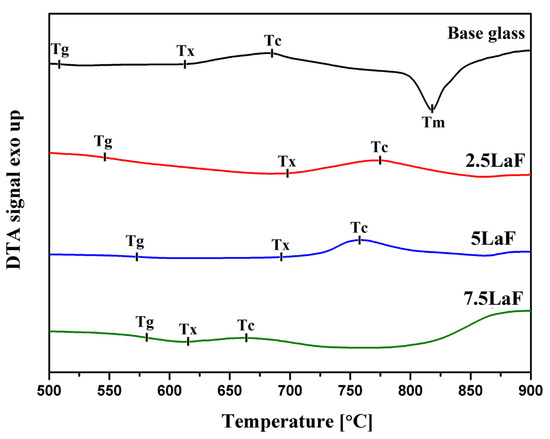
Figure 2.
DTA curves of aluminosilicate glasses for the La-fluoride series. Tg—the glass transformation temperature; Tx—the onset of crystallization temperature; Tc—the peak crystallization temperature; Tm—the melting temperature.
The base glass exhibits good thermal stability. It is generally accepted that if ΔT exceeds 100 °C, the glass is considered stable and suitable for forming processes. In the case of the glass series with La2O3, a non-monotonic change in this parameter is observed. The addition of 2.5 mol% La2O3 lowers the ΔT value below 100 °C, but with 7.5 mol% La2O3, the threshold is exceeded again (Table 2).

Table 2.
Thermal parameters for aluminosilicate glasses with the addition of La2O3.
In contrast, the glass series containing LaF3 shows the opposite trend. A small addition of lanthanum fluoride increases thermal stability, which is then gradually reduced, reaching a minimum value of 35 °C for the sample with 7.5 mol% LaF3 (Table 2).
Additionally, the introduction of lanthanum significantly increases Δcp. This increase is more pronounced in the series with lanthanum oxide than in the one with lanthanum fluoride. This parameter serves as an indicator of stress relaxation within the glass network during the transformation process.
4.3. XRD Characterization
Based on the obtained DTA curves (Figure 1 and Figure 2), the heat-treatment temperature was determined for each glass composition in order to induce glass-ceramic formation. Figure 3 presents an example of the 7.5 La sample before and after ceramization.

Figure 3.
Effect of heat treatment of the 7.5 La glass at 800 °C for 30 min.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the diffraction patterns of the heat-treated glass samples. All glasses were crystallized at the maximum crystallization temperature determined from the DTA. In the base glass, two crystalline phases were identified: Na2O·Al2O3·SiO2 and Na2SiO3. Due to the high Na2O content in the glass, the first one crystallizes as the main phase. This results from the strong affinity of sodium ions for aluminum and their role in compensating the charge deficiency of Al3+ in the [AlO4] tetrahedron. The remaining sodium acts as a network modifier, breaking the oxygen bridges between [SiO4] tetrahedra. During the crystallization process, this leads to the formation of sodium silicate. In the 10 La sample, two different crystalline phases were identified: NaAlSiO4 and La2SiO5. NaAlSiO4 (nepheline) exhibits a zeolite-like structure based on a three-dimensional tetrahedral network of [SiO4] and [AlO4] units [20], with Na+ ions occupying interstitial sites within the framework. La2SiO5 is of particular interest due to its well-known application as a host matrix for rare-earth dopant ions such as Eu3+, Ce3+, Tb3+, and Dy3+ [21,22], which impart photoluminescent properties. For example, La2SiO5:Eu3+ is a widely studied red phosphor used in LED technologies and display screens [18]. For the glass-ceramic 2.5 LaF and 5 LaF samples were observed to have crystallization of the NaAlSiO4 and NaLa4(SiO4)3F, respectively. The latter belongs to the apatite group. Apatite structures are known for their flexible crystal frameworks, allowing for extensive ionic substitution, making them attractive for applications in optics [23], ceramics [24], biomaterials [25], and as phosphor hosts [26]. The silicate units [SiO4]4− form a stable tetrahedral backbone, while La3+ and Na+ occupy highly symmetric crystallographic sites. This structure facilitates the incorporation of various ions, especially rare-earth elements (e.g., Eu3+, Ce3+, Tb3+, and Sm3+), making this apatite a promising host for optically active ions. Finally, in the sample labeled 7.5 LaF, lanthanum fluoride (LaF3) was identified as the only phase present. Thus, for this glass, a low-phonon phase can be obtained through controlled crystallization. Increasing the amount of LaF3 in the glass batch composition leads to spontaneous crystallization of LaF3 during melt cooling.
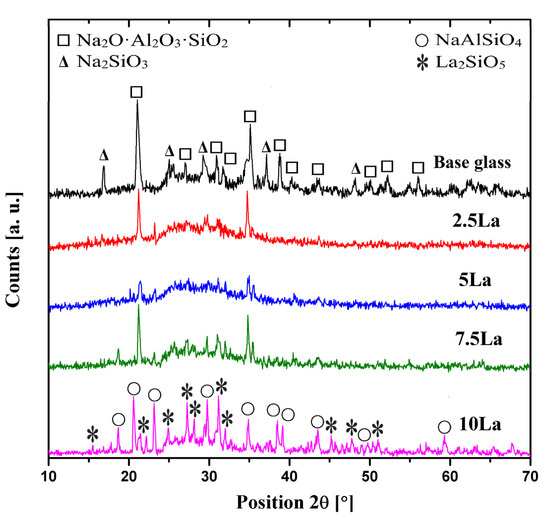
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of aluminosilicate glass-ceramics for the La-oxide series.
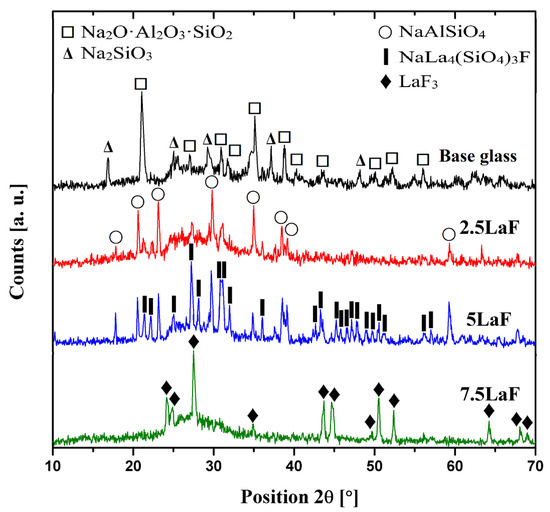
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of aluminosilicate glass-ceramics for the La-fluoride series.
According to our findings, fluoride can modify the glass structure by influencing the anionic subnetwork. Introducing fluorine into the glass matrix reduces its degree of polymerization, which leads to the weakening of network bonds and increased ion mobility. Fluorine forms weaker bonds with network-forming cations (e.g., Si4+ and P5+), resulting in a more open and less ordered glass structure. This allows for the formation of lanthanide fluoride phases [27].
4.4. FT-IR Study
In all the glass spectra there appear three bands (Figure 6a). They derive from the bridging oxygen atom vibrations: stretching (at about 1000 cm−1), bending (700–800 cm−1), and rocking (about 500–420 cm−1). The first of these bands is the most intensive, and it usually represents a superposition of some bands situated close to each other, which is visible for glass-ceramics (Figure 6b).
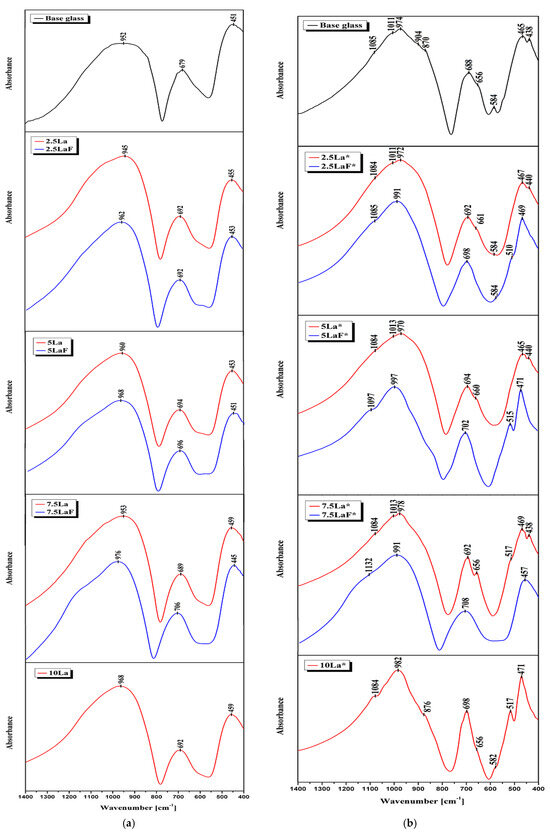
Figure 6.
FT-IR spectra of the glass series (a) and glass-ceramic series (b), showing the evolution of vibrational bands with varying composition. * represents glass-ceramic series.
For silicate glasses, the position of the Si–O–Si band, typically observed around 1100 cm−1, varies depending on the type and concentration of network-modifying cations (Na+, Ca2+, and La3+) [28,29]. In our samples, this band appears as a right-hand shoulder of the main absorption band. Silicate glasses generally exhibit higher wavenumber values compared to aluminosilicate glasses [30]. The introduction of modifiers in the form of oxides (e.g., Na2O and CaO) also leads to the appearance of bands at lower wavenumbers, attributed to symmetric stretching vibrations of terminal Si–O bonds [31,32]. The presence of a band near 980 cm−1 is characteristic of orthosilicates [33], while bending vibrations typically appear around 660 cm−1 [34], as observed in the spectra of the glass-ceramics. With increasing La2O3 content—but not in the case of LaF3—these bands become more pronounced.
By comparing the spectra of glasses from the La2O3 and LaF3 series, it can be observed that the shift of the main band maximum toward lower wavenumbers is less pronounced for the LaF3 series. This is attributed to the weaker interaction between lanthanum ions and oxygen ions in terminal Si–O ··· and Al–O ··· bonds. Spectral analysis confirms that lanthanum is surrounded by fluoride ions, and the crystallization of lanthanum fluoride can occur in this glass.
5. Conclusions
Aluminosilicate glasses provide a thermally stable matrix for the incorporation of lanthanides, either in the form of oxides or fluorides. Increasing the content of either lanthanum oxide or lanthanum fluoride at the expense of Na2O leads to an increase in the melting temperature of the glass batch. However, these dopants exhibit distinct effects on the glass transition temperature (Tg), thermal stability (ΔT), and crystallization tendency, as indicated by the enthalpy of crystallization (ΔH).
A small amount of lanthanum fluoride improves the thermal stability of the glass; however, higher concentrations also result in spontaneous crystallization of the LaF3 phase during melt quenching.
It was found that by introducing an appropriate amount of LaF3 (7.5 mol%) into the aluminosilicate network, it is possible to obtain a glass suitable for controlled crystallization, leading to the formation of a low-phonon LaF3 phase. Thanks to the chemical affinity of lanthanide ions for fluorine, it becomes possible for rare-earth dopants to incorporate into the LaF3 nanocrystals, leading to the formation of transparent materials with enhanced luminescence.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Ś.; methodology, M.Ś.; validation, S.Ś.; formal analysis, M.Ś.; investigation, M.Ś. and M.S.; data curation, S.Ś.; writing—original draft, M.Ś. and S.Ś. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported by the statutory funds of AGH University of Krakow, Faculty of Materials Science and Ceramics, No. 16.16.160.557 (2025).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included within this article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ma, Y.; Peng, X.; Fei, M.; Zhang, W.; Teng, L.; Hu, F.; Wei, R.; Guo, H. Adjustable white luminescence and high thermal stability in Eu2+/Eu3+/Tb3+/Al co-doped aluminosilicate oxyfluoride glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, L. Thermal conductive networks constructed by Sialon fibers in-situ synthesized in barium aluminosilicate glass–ceramic. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 192, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ding, Y.; Sun, J.; Cao, M.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, G. Investigation on the tensile properties of annealed and chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 493, 143317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cai, Y.; Xu, F.; Tian, P.; Yuan, J.; Peng, Z. Structure, mechanical properties, and diffusion kinetics of chemical strengthening ultra-thin aluminosilicate glass by two-step method. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 27660–27669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, N.T.Q.; Van Tuyen, H.; Nogami, M. Effects of Na/Al ratio on phonon sideband spectra and luminescent characteristics of Eu3+ doped sodium aluminosilicate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 312, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, M.; Safonova, A.; Mariotto, G.; Daldosso, N.; You, S.; Kumar, P.; Vomiero, A.; Ben Zaied, M.Y.; Bouaicha, M.; Enrichi, F. Fe-dependent optical properties of peralkaline soda aluminosilicate glasses: A combined Raman and photoluminescence study. Opt. Mater. 2025, 165, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vařák, P.; Kamrádek, M.; Mrázek, J.; Podrazký, O.; Aubrecht, J.; Peterka, P.; Nekvindová, P.; Kašík, I. Luminescence and laser properties of RE-doped silica optical fibers: The role of composition, fabrication processing, and inter-ionic energy transfers. Opt. Mater. X 2022, 15, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, L. Research on ultra-smooth surface processing of mid-infrared indium fluoride-based fiber glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1027, 180590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumachev, K.; Savikin, A.; Egolin, V. Enhanced 1.5-μm luminescence of Er3+ in ZBLAN glasses by additional doping with Tb3+ and Yb3+ ions. Opt. Mater. 2025, 160, 116688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, K.; Jusza, A.; Komorowski, P.; Andrejuk, P.; Piramidowicz, R. Short wavelength up-converted emission studies in Er3+ and Yb3+ doped ZBLAN glasses. J. Lumin. 2018, 201, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Xia, K.; Gui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, N.; Cao, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, S.; Liu, Z. High content Er3+ doped ZBLAN glass: The spectral characteristics and high slope efficiency MIR laser investigation. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 865, 158170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Delben, J.; Delben, A.; Andrade, L.; Lima, S. Thermal stability and crystallization behavior of TiO2 doped ZBLAN glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 2907–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashdeep; Subbiah, S. Use of magnetic fields to impact glass-transition and crystallization during manufacturing of ZBLAN optical fibers. Manuf. Lett. 2024, 41, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniak, M.; Starzyk, B.; Zając, P.; Szymczak, P.; Jimenez, G.L.; Szumera, M.; Ziąbka, M.; Kochanowicz, M.; Miluski, P.; Żmojda, J.; et al. Structural and luminescent properties of Er3+-doped tellurite-phosphate oxide/oxyfluoride glasses and glass-ceramics modified with Sr2+. Opt. Mater. 2025, 167, 117328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secu, C.; Negrea, R.; Secu, M. Eu3+ probe ion for rare-earth dopant site structure in sol–gel derived LiYF4 oxyfluoride glass–ceramic. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, M.; Zheng, X.; Qiao, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J. Controllable growth of Ce3+-doped fluoride nanocrystals (LaF3/KLaF4) in fluorosilicate glass. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 116740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermillac, M.; Fneich, H.; Lupi, J.-F.; Tissot, J.-B.; Kucera, C.; Vennéguès, P.; Mehdi, A.; Neuville, D.R.; Ballato, J.; Blanc, W. Use of thulium-doped LaF3 nanoparticles to lower the phonon energy of the thulium’s environment in silica-based optical fibres. Opt. Mater. 2017, 68, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, T.; Garber, E.; Edmonson, D.; Hawkins, T.; Chen, Y.; Turri, G.; Bass, M.; Ballato, J. Spectral engineering of optical fiber preforms through active nanoparticle doping. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalahe, J.; Onodera, Y.; Takimoto, Y.; Hijiya, H.; Ono, M.; Miyatani, K.; Kohara, S.; Urata, S.; Du, J. Influence of interatomic potential and simulation procedures on the structures and properties of sodium aluminosilicate glasses from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 588, 121639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zan, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, T.; Xu, K.; Goel, A. Structure and crystallization behavior of phosphorus-containing nepheline (NaAlSiO4) based sodium aluminosilicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 560, 120719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Simantilleke, A.P.; Singh, D. Synthesis, structural and photoluminescence behaviour of novel La2SiO5:Eu3+/Tb3+ nanomaterials for UV-LEDs. Optik 2020, 221, 165324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugua, S.N.; Shaat, S.K.; Swart, H.C.; Ntwaeaborwa, O.M. The influence of Dy3+ ions concentration and annealing on the properties of LaGdSiO5:Dy3+ nanophosphors. J. Lumin. 2016, 179, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douzi, A.; Slimi, S.; Madirov, E.; Serres, J.M.; Solé, R.M.; Ben Salem, E.; Turshatov, A.; Richards, B.S.; Mateos, X. Investigation of luminescence properties and ratiometric thermometry through yellow-to-blue Dy3+ emission in Ca3La7(SiO4)5(PO4)O2 apatite. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 19623–19639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Echeweozo, E.; Kirkbinar, M.; Al-Buriahi, M. Synthesis and radiation attenuation properties of polymethyl methacrylate/apatite-wollastonite composites for advanced shielding applications. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2025, 219, 111466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ban, C.; Hao, X. Influence of the substitution of CaO by SrO on the structure, degradation and in vitro apatite formation of sol–gel derived SiO2–CaO–SrO–P2O5 system bioactive glasses. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 55906–55919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xin, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Ding, X.; Geng, W. Geng. Recent development in rare earth doped phosphors for white light emitting diodes. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fneich, H.; Vermillac, M.; Neuville, D.R.; Blanc, W.; Mehdi, A. Highlighting of LaF3 Reactivity with SiO2 and GeO2 at High Temperature. Ceramics 2022, 5, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacasulu, L.; Biesuz, M.; Pastorelli, V.; Vakifahmetoglu, C.; Sglavo, V.M.; Ferraris, M.; Sorarù, G.D. Pressureless joining of soda lime silicate glass using polysilazane-derived silica at near-room temperature. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 5747–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Matsuura, F. Effects of heat treatment of silica-based glasses on their static and dynamic wettability. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 314, 128871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoch, L.; Środa, M. Infrared spectroscopy in the investigation of oxide glasses structure. J. Mol. Struct. 1999, 511–512, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, A.; Lubas, M.; Przerada, I. Application of Mössbauer spectroscopy and FT-IR to describe coordination of amphoteric ions in structure of glasses from the SiO2–Na2O–MgO–CaO–Al2O3–Fe2O3 system. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1285, 135368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G. Structural characterization of glass–ceramics made from fly ash containing SiO2–Al2O3–Fe2O3–CaO and analysis by FT-IR–XRD–SEM methods. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1019, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.G.V.M.; Kumar, A.R.; Rao, B.H.; Veeraiah, N.; Reddy, M.R. Optical absorption, ESR, FT-IR spectral studies of iron ions in lead oxyfluoro silicate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1021, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloraini, D.A.; Almuqrin, A.; Albarzan, B.; Wahab, E.A.; Shaaban, K.S. Studying structural, mechanical, and radiation shielding properties for BaO–Li2B4O7–SiO2–MgO glasses. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2025, 10, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).