Semiconductive Tendency of the Passive Film Formed on Super Austenitic Stainless Steel SR-50A in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Alloy and Test Solution
2.2. Anodic Polarization Test
2.3. Potentiostatic EIS Test
2.4. Mott–Schottky Anlysis
2.5. XPS
3. Results
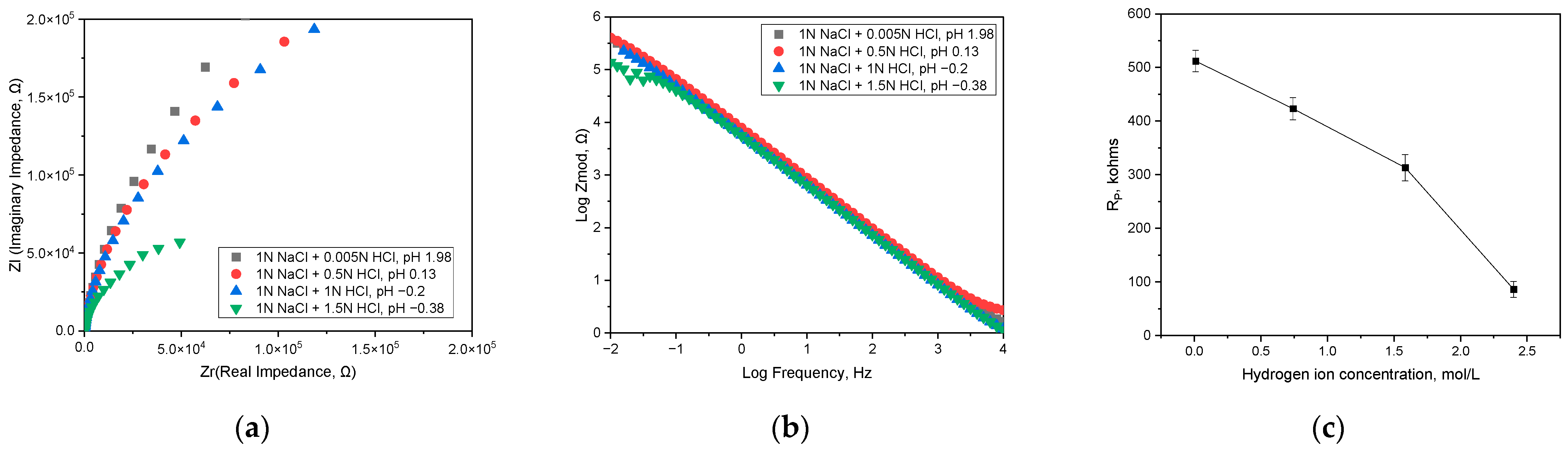
3.1. Effect of pH on Corrosion Behavior and Semiconductive Properties
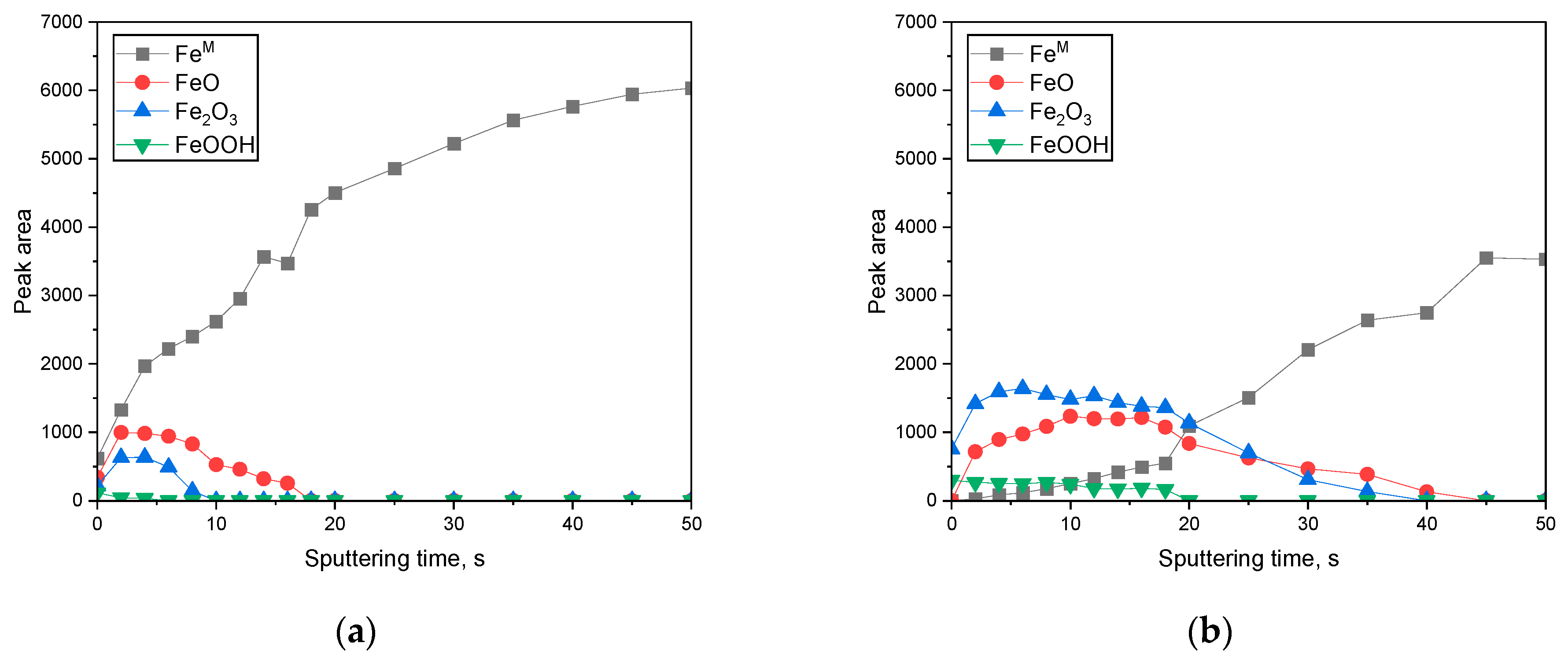
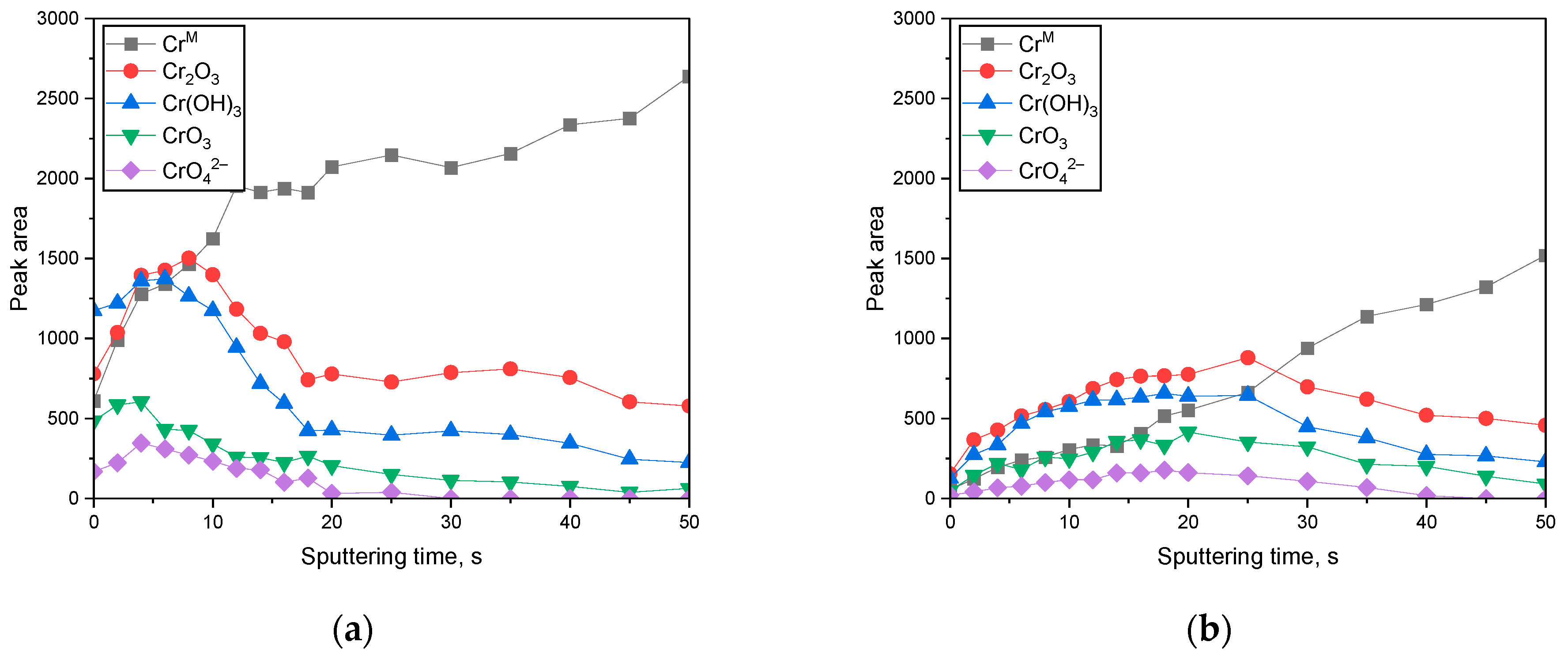
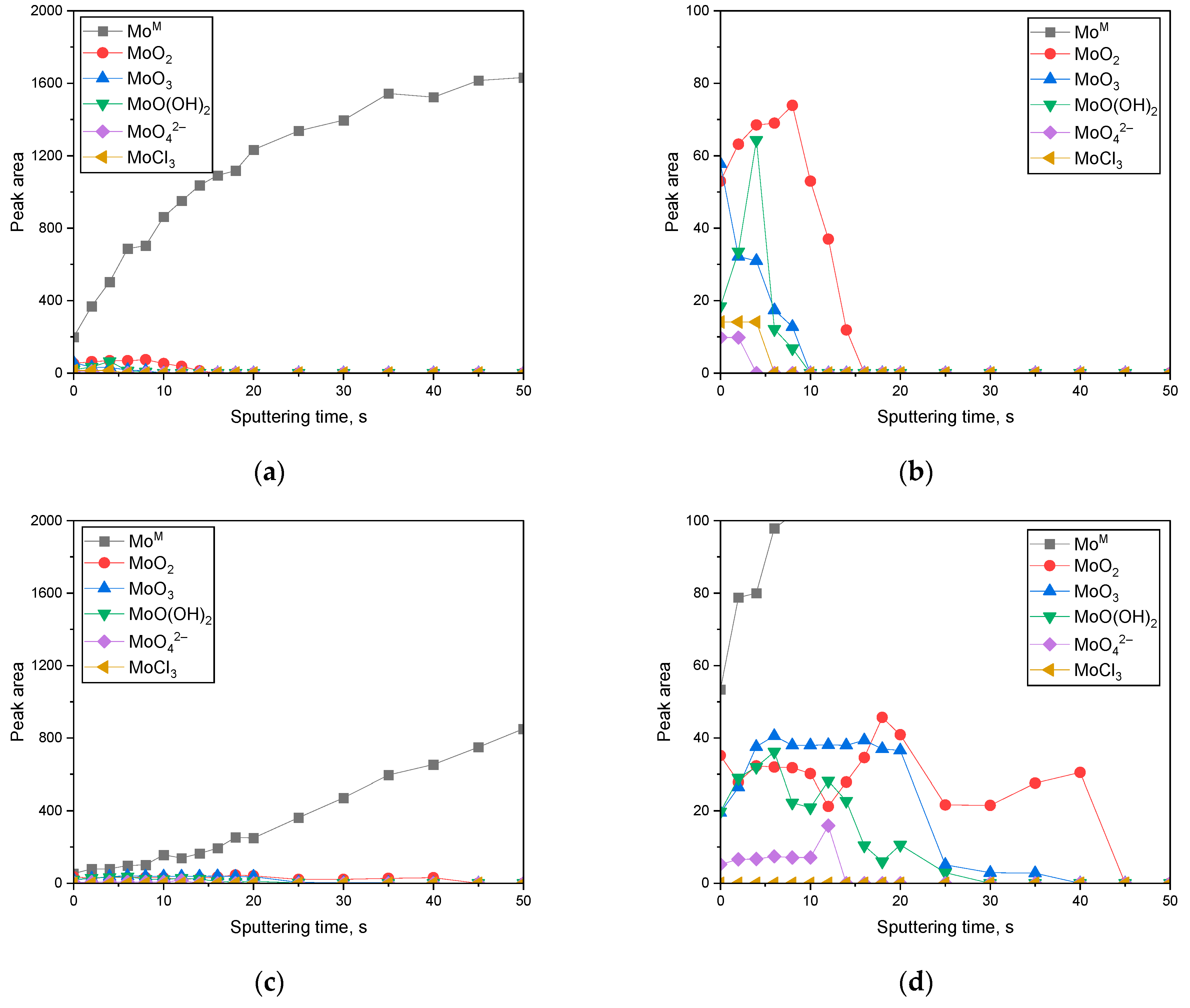
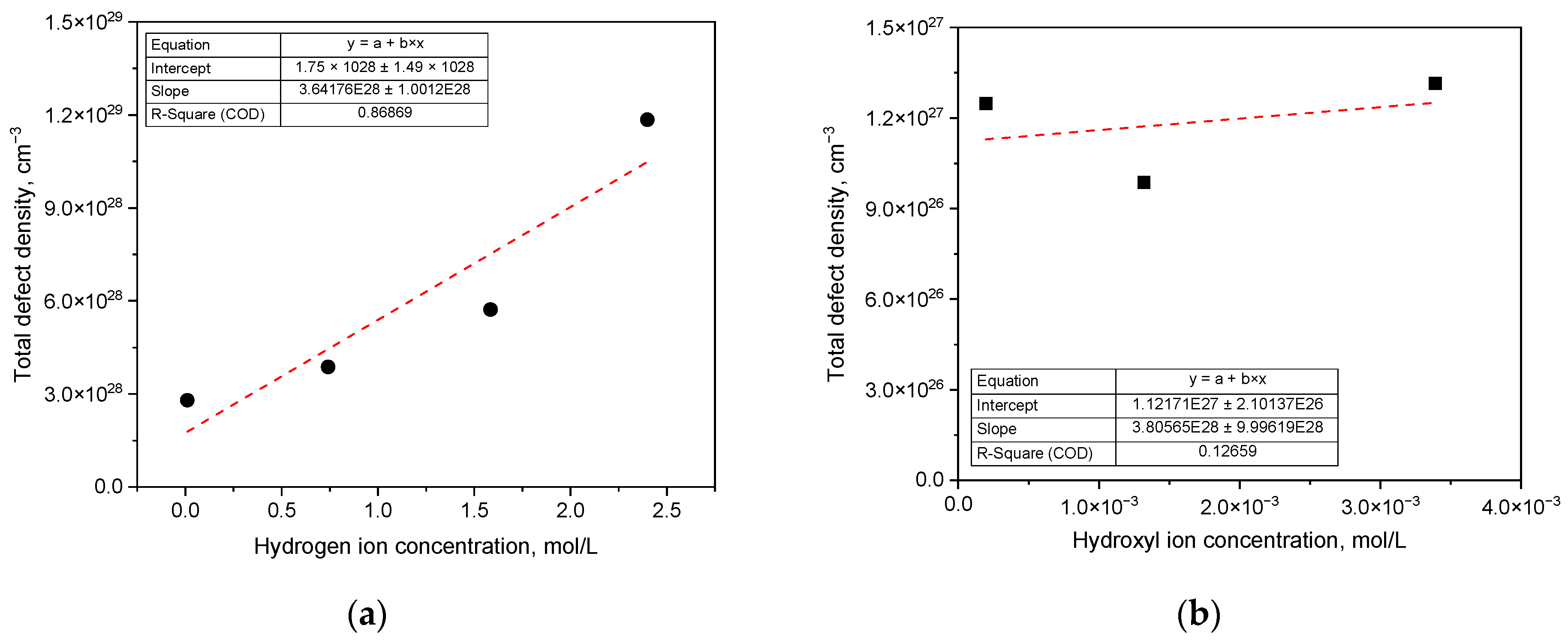
3.2. Surface Analysis on the Passive Film Formed in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions
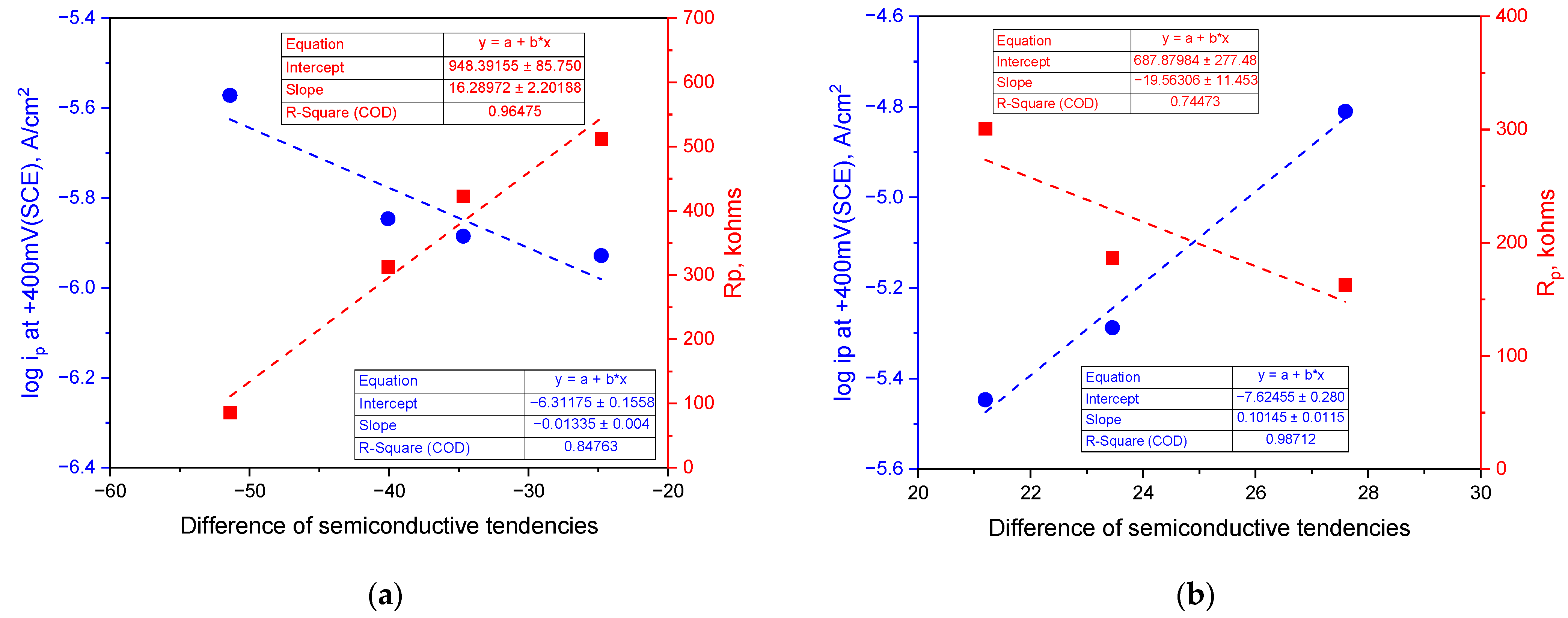
4. Discussion
- (1)
- p-type semiconductive tendency, % = |p|/(|p| + |n|) × 100;
- (2)
- n-type semiconductive tendency, % = |n|/(|p| + |n|) × 100;
- (3)
- Difference in semiconductive tendencies = (1) − (2).
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the concentration of hydrogen ions or hydroxyl ions increases in either acidic or alkaline chloride solutions, the passive current density escalates and the polarization resistance diminishes. The passive film formed at a constant potential consists of an outer layer primarily containing metal hydroxides and metal oxyanions, and an inner layer mainly composed of metallic oxides, exhibiting semiconductive properties;
- (2)
- The surface of the stainless steel develops a passive film comprising two layers with p-type and n-type semiconductive properties regardless of the solution’s pH. When the concentration of hydrogen ions or hydroxyl ions in the environment fluctuates, the semiconductive tendencies of the passive film change, leading to either a weakening or strengthening of the passive film’s properties. Notably, the corrosion resistance improves as the p-type and n-type semiconductive tendencies become more balanced, enhancing the properties of the passive film.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olefjord, I. The passive state of stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1980, 42, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannani, A.; Kermiche, F.; Pourbaix, A.; Belmokre, K. Characterisation of passive film on AISI304 stainless steel. Trans. IMF 1997, 8, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, S.; Strehblow, H.H. A combined surface analytical and electrochemical study of the formation of passive layers on Fe/Cr alloys in 0.5 M H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaQue, F.L.; Copson, H.R. Corrosion Resistance of Metal and Alloys, 2nd ed.; Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1963; p. 375. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Revie, R.W. Corrosion and Corrosion Control; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheim, R.; Heine, B.; Fischmeister, H.; Hofmann, S.; Knote, H.; Stolz, U. The passivity of iron-chromium alloys. Corros. Sci. 1989, 29, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, M.; Adachi, H.; Satoko, C. Theory of electronic structure of oxide surfaces. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1983, 14, 113–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromhold, A.T., Jr.; Kruger, J. Space-charge and concentration-gradient effects on anodic oxide film formation. Electrochem. Soc. 1973, 120, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N. An overview on the passivity of metals. Corros. Sci. 1990, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, A.M.P.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Rondot, B.; da Cunha Belo, M. Study of passive films formed on AISI 304 stainless steel by impedance measurements and photoelectrochemistry. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, V.; Yang, W.P.; Marcus, P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy study of passive films formed on (100) Fe-18Cr-13Ni single-crystal surfaces. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorang, G.; Belo, M.D.C.; Simões, A.M.P.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Chemical composition of passive films on AISI 304 stainless steel. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, P.; Bussell, M.E. XPS study of the passive films formed on nitrogen-implanted austenitic stainless steels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1992, 59, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vito, E.D.; Marcus, P. XPS study of passive films formed on molybdenum-implanted austenitic stainless steels. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 19, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Fujimoto, S. Semiconductor properties of passive films formed on sputter-deposited Fe–18Cr alloy thin films with various additive elements. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2004, 5, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Tsuchiya, H. Semiconductor properties and protective role of passive films of iron base alloys. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, R.; Metikoš, H.M. Semiconducting properties of passive films on AISI 304 and 316 stainless steels. Electroanal. Chem. 1993, 358, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiki, N.E.; Montemor, M.F.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; da Cunha Belo, M. Semiconducting properties of thermally grown oxide films on AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Cheng, X.; Dong, C.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Passivity of 316L stainless steel in borate buffer solution studied by Mott–Schottky analysis, atomic absorption spectrometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Dong, C.F.; Cheng, X.Q.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.G. Electrochemical behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steel in NaCl solution with different chromate contents. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, T.P.; Mears, D.C.; Rothwell, G.P. The relationships between anodic passivity, brightening and pitting. Corros. Sci. 1965, 5, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D. Passivity—The key to our metals-based civilization. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 951–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Kwon, H.S. In situ study on the effects of Ni and Mo on the passive film formed on Fe–20Cr alloys by photoelectrochemical and Mott–Schottky techniques. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2006, 590, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningshen, S.; Mudali, U.K. Hydrogen effects on pitting corrosion and semiconducting properties of nitrogen-containing type 316L stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 6374–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Cheng, X.; Dong, C.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Effects of dissolved oxygen on electrochemical and semiconductor properties of 316L stainless steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 407, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsanya, I.G.; Hansson, C.M. The semiconductor properties of passive films and corrosion behavior of stainless steel reinforcing bars in simulated concrete pore solution. Materialia 2019, 6, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmezim, M.J.; Simões, A.M.; Montemor, M.F.; da Cunha Belo, M. Capacitance behaviour of passive films on ferritic and austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Vafaeian, S. Comparison of electrochemical behavior between coarse-grained and fine-grained AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel by Mott–Schottky analysis and EIS measurements. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zou, J.; Wang, F. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and corrosion behavior of a Fe-18Cr-15Mn-0.66N stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 107, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. The effect of molybdate anion on the ion-selectivity of hydrous ferric oxide films in chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 1977, 17, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. Ion-selectivity of nickel chromate, molybdate, and tungstate precipitate membranes. Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku 1976, 44, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. Ion Selectivity of Chromium Hydroxide and Chromium-Nickel Mixed Hydroxide Precipitate Membranes. Corros. Eng. 1976, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. Ion selectivity of precipitate films affecting passivation and corrosion of metals. Corrosion 1979, 35, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. Membrane potentials of nickel hydroxide precipitate membranes. Corros. Sci. 1975, 24, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Clayton, C.R.; Lu, Y.C. A bipolar model of the passivity of stainless steel: The role of Mo addition. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.R.; Clayton, C.R.; Doss, K.; Lu, Y.C. On the role of Cr in the passivity of stainless steel. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Clayton, C.R.; Brooks, A.R. A bipolar model of the passivity of stainless steels—II. The influence of aqueous molybdate. Corros. Sci. 1989, 29, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, C.R.; Lu, Y.C. A bipolar model of the passivity of stainless steels—III. The mechanism of MoO42− formation and incorporation. Corros. Sci. 1989, 29, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Park, Y.S. A study on effects of Mo addition on the corrosion resistance of stainless steels. J. Corros. Sci. Soc. Korea 1989, 18, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Park, Y.S. A study on effects of N addition on the passivating mechanism of stainless steels. J. Corros. Sci. Soc. Korea 1989, 18, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- ASTMG3-2004; Standard Practice for Conventions Applicable to Electrochemical Measurements in Corrosion Testing. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Qiao, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.G.; Okafor, P.C.; Ke, W. Electrochemical behaviour of high nitrogen bearing stainless steel in acidic chloride solution: Effects of oxygen, acid concentration and surface roughness. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, M.J.K.; Deen, K.M.; Haider, W. Corrosion behavior of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel in acidic media. Materialia 2018, 54, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, A.; Raslan, A.M.; Mohamed, L.Z. Corrosion characteristics of 304 stainless steel in sodium chloride and sulfuric acid solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, S.; Bastidas, D.M.; Criado, M.; Bastidas, J.M. Electrochemical study on the corrosion behaviour of a new low-nickel stainless steel in carbonated alkaline solution in the presence of chlorides. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 129, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.; Carmezim, M.J.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Montemor, M.F. The passive behaviour of AISI 316 in alkaline media and the effect of pH: A combined electrochemical and analytical study. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6174–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Vafaeian, S. Passivation behavior of a ferritic stainless steel in concentrated alkaline solutions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Du, C. Corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel in acetic acid by EIS and Mott-Schottky. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2008, 23, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taveira, L.V.; Montemor, M.F.; da Cunha Belo, M.; Ferreira, M.G.; Dick, L.F.P. Influence of incorporated Mo and Nb on the Mott–Schottky behaviour of anodic films formed on AISI 304L. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2813–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Luo, J.L. Electronic structure and pitting susceptibility of passive film on carbon steel. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 2947–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Kuron, D.; Hofmann, S.; Kirchheim, R. AES analysis of pits and passive films formed on Fe-Cr, Fe-Mo and Fe-Cr-Mo alloys. Corros. Sci. 1990, 31, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, A.E.; Lumsden, J.B.; Staehle, R.W. The composition of passive films on ferritic stainless steels. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1977, 124, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S. The influence of nitrogen, and NO3−, NO2− and NH4+ ions on the corrosion properties and passive film composition of stainless steels. J. Corros. Sci. Soc. Korea 1992, 21, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S. Influences of alloyed molybdenum and molybdate addition on the corrosion properties and passive film composition of stainless steels. Met. Mater. 1998, 4, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S. Synergistic effect of nitrogen and molybdenum on localized corrosion of stainless steels. Corros. Sci. Technol. 2010, 9, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, K.N. Properties of super stainless steels for orthodontic applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 69, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J. The Influence of W and Mo Addition on the pitting resistance and the Passivation of Ferritic Stainless Steels. J. Corros. Sci. Soc. Korea 1997, 26, 6. [Google Scholar]











| Material | Chemical Compositions, wt. % | * PREN30 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNS S32050 (SR-50A) | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | Cu | N | C | P | Fe | 52.1 |
| 23.52 | 22.01 | 6.24 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 0.016 | 0.023 | bal. | ||
| Hydrogen Ion Concentration, mol/L | ER, V (SCE) | iR, A/cm2 | iC, A/cm2 | iP at +400 mV (SCE), A/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0105 (pH −0.38) | −0.26 | 3.548 × 10−7 | 1.349 × 10−6 | 1.175 × 10−6 |
| 0.7413 (pH −0.2) | −0.27 | 5.248 × 10−7 | 3.388 × 10−6 | 1.288 × 10−6 |
| 1.5849 (pH 0.13) | −0.32 | 6.457 × 10−6 | 1.288 × 10−4 | 1.413 × 10−6 |
| 2.3988 (pH 1.98) | −0.29 | 4.266 × 10−6 | 2.630 × 10−4 | 2.692 × 10−6 |
| Hydroxyl Ion Concentration, mol/L | ER, V (SCE) | iR, A/cm2 | Etr, V (SCE) | iP at +400 mV (SCE), A/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.95 × 10−4 (pH 10.29) | −0.069 | 8.318 × 10−9 | 0.74 | 3.548 × 10−6 |
| 1.318 × 10−3 (pH 11.12) | −0.14 | 6.166 × 10−8 | 0.64 | 5.129 × 10−6 |
| 3.388 × 10−3 (pH 11.53) | −0.48 | 1.318 × 10−7 | 0.54 | 1.549 × 10−5 |
| Hydrogen/Hydroxyl Ion Concentration, mol/L | 2.3988 | 1.5849 | 0.7413 | 1.05 × 10−2 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 1.32 × 10−3 | 3.39 × 10−3 |
| Efb by N slope, V (SCE) | 0.045 | 0.046 | 0.047 | −0.1 | −0.55 | −0.63 | −0.65 |
| Efb by P slope, V (SCE) | −0.05 | −0.14 | 0.03 | −0.51 | −0.97 | −0.99 | −0.1 |
| Hydrogen Ion Concentration, mol/L | Hydroxyl Ion Concentration, mol/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.3988 | 1.5849 | 0.7413 | 0.0105 | 1.95 × 10−4 | 1.318 × 10−3 | 3.388 × 10−3 | |
| ND (cm−3) | 2.88 × 1028 | 1.71 × 1028 | 1.26 × 1028 | 1.05 × 1028 | 0.076 × 1028 | 0.061 × 1028 | 0.084 × 1028 |
| NA (cm−3) | 8.97 × 1028 | 4.01 × 1028 | 1.75 × 1028 | 1.75 × 1028 | 0.049 × 1028 | 0.038 × 1028 | 0.048 × 1028 |
| Total defect density (cm−3) | 11.8 × 1028 | 5.72 × 1028 | 3.87 × 10+ | 2.80 × 1028 | 0.12 × 1028 | 0.099 × 1028 | 0.13 × 1028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-H.; Yoo, Y.-R.; Kim, Y.-S. Semiconductive Tendency of the Passive Film Formed on Super Austenitic Stainless Steel SR-50A in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions. Crystals 2024, 14, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090766
Choi S-H, Yoo Y-R, Kim Y-S. Semiconductive Tendency of the Passive Film Formed on Super Austenitic Stainless Steel SR-50A in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions. Crystals. 2024; 14(9):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090766
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seung-Heon, Young-Ran Yoo, and Young-Sik Kim. 2024. "Semiconductive Tendency of the Passive Film Formed on Super Austenitic Stainless Steel SR-50A in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions" Crystals 14, no. 9: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090766
APA StyleChoi, S.-H., Yoo, Y.-R., & Kim, Y.-S. (2024). Semiconductive Tendency of the Passive Film Formed on Super Austenitic Stainless Steel SR-50A in Acidic or Alkaline Chloride Solutions. Crystals, 14(9), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14090766







