Abstract
In this manuscript, the effect of Mo addition on the corrosion resistance of the low-alloy steel in a simulated tropical marine atmospheric environment has been studied through microstructure characterization, corrosion immersion experiments, electrochemical measurement, and a series of microscopic characterization methods. The results show that Mo has the ability to reduce the corrosion rate of low-alloy steel in a marine atmospheric environment, with a more pronounced reduction effect observed over longer corrosion periods. The addition of Mo enhances the corrosion product film’s compactness when coupled with Cr, subsequently improving corrosion resistance. Simultaneously, MoO42−, acting as a slow-release ion, can effectively suppress localized corrosion in low-alloy steel. The research findings can offer data support and a theoretical foundation for the design of low-alloy steels with enhanced corrosion resistance in a tropical marine atmospheric environment.
1. Introduction
Chromium-containing steel is extensively utilized in various fields, including bridges, construction, and offshore platforms due to its excellent resistance to atmospheric and seawater corrosion [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Research [4,8,9,10] has shown that the addition of trace amounts of chromium can increase the steel’s corrosion potential, facilitating the densification of corrosion product films, and promote the formation of protective corrosion products, thereby enhancing the steel’s resistance to uniform corrosion. However, with the continuous increase in chromium content, in environments with high chloride ion concentrations, the chromium content can accelerate the hydrolysis reactions of Cr3+ and Fe3+, leading to a decrease in pH at the rust layer/matrix interface, making localized corrosion of the steel more pronounced [8,11,12,13]. To address this issue, there is a growing focus on the microalloying of chromium-containing steel to improve its corrosion resistance.
The addition of Mo has a dual effect on enhancing the corrosion resistance of steel [14,15,16,17,18,19]. On one hand, it can improve the composition of the passivation film to enhance the steel’s passivation capability. On the other hand, it can slow down the anodic dissolution process in the pitting corrosion area by forming insoluble oxides. Consequently, Mo is widely applied in stainless steel to enhance the material’s resistance to localized corrosion. Sakashita et al. [20] discovered that that Cl− ions can penetrate through the corrosion product film and accumulate beneath the film. The enrichment of Cl− ions can lead to localized acidification, thereby reducing the pH beneath the film and accelerating corrosion. However, the properties of iron oxide films adsorbed with MoO42− can transition from anion-selective to cation-selective, allowing H+ to diffuse out of the film, preventing Cl− from diffusing into the film and significantly improving the corrosion resistance of the steel.
Hesham et al. [5] conducted research on the corrosion behavior of T22 steel and T92 steel in hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid solutions. They found that T22 steel can form insoluble molybdenum chloride complexes in hydrochloric acid, promoting the densification of the steel’s surface oxide layer, thereby exhibiting improved corrosion resistance. Xiao et al. [21] discovered that the addition of Mo can increase the content of M-A islands in the steel, enhancing its corrosion resistance in the early stages of corrosion. In the long term, Mo accumulates in the internal rust layer of the steel in the form of MoO3, increasing the rate of formation of a dense rust layer and inhibiting the steel’s anodic dissolution process.
In summary, in the marine atmospheric environment, the addition of Cr can enhance the corrosion resistance performance of low-alloy steel. However, an excessively high Cr content increases the risk of localized corrosion [22]. With the growing demand for material sustainability and cost-effectiveness, there is an urgent need to comprehensively improve the corrosion resistance of low-alloy steel. This study aims to draw insights from the role of Mo in stainless steel. However, due to the current concentration of research on Mo in high Cr or high Mo passivation systems, it remains unclear whether the mechanisms of Mo in these systems differ from the corrosion resistance mechanism of Mo in low-Cr alloy steel under tropical marine atmospheric conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the impact of adding Mo to low-Cr alloy steel on corrosion resistance performance.
This study utilized vacuum smelting technology to prepare two different low-alloy steels with varying Mo content. It simulated a tropical marine atmospheric environment through indoor immersion tests and characterization techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), laser confocal microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and an electrochemical workstation to investigate the corrosion behavior and corrosion mechanisms of these two steel types. The results are expected to provide research foundations and ideas for optimizing the corrosion resistance performance for the low-alloy steel.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation and Microstructural Characterization
The experimental materials consisted of two different low-alloy steels with varying Mo content, developed in-house and named based on their elemental distinctions. The specific chemical compositions are detailed in Table 1. Both steel types were prepared using vacuum induction melting, and after casting into ingots, they were heated to 1200 °C and held for 2 h in a box-type furnace [22,23,24]. Subsequently, a two-stage rolling process was applied to reduce the ingots into 15 mm thick steel plates, which were then air-cooled to room temperature.

Table 1.
The chemical compositions of the two chromium-containing steels (wt.%).
Using wire cutting, specimens with dimensions of 10 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm were cut perpendicular to the rolling direction of the steel plate. One of the 10 mm × 10 mm surfaces was designated as the working surface. This working surface was progressively polished using SiC sandpaper until a 2000# finish was achieved. Subsequently, it was water polished to a mirror finish using 1.5 μm and 0.5 μm polishing paste. The polished surface was etched with a 4 vol.% nitric acid + 96 vol.% alcohol solution, and its microstructure was observed using SEM (Quanta 250, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
For the other polished sample, electrolytic polishing was performed using a 10% perchloric acid and 90% glacial acetic acid mixture [23,25,26]. The polishing parameters included a voltage of 15 V, a current of 1.5 A, and a polishing time of 10 s. After completion, the sample was quickly rinsed with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol and observed using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD-Lumis, Thermo Fisher Scientific) for microstructure examination.
Figure 1 displays the microstructure of the two steel types. From the SEM images, it is evident that the 0 Mo steel exhibits a typical granular bainite microstructure, while the 1 Mo steel displays a typical lamellar bainite structure. The addition of Mo elements results in a delay in the transformation from austenite to ferrite and a reduction in the phase transition temperature, and it favors the formation of granular bainite [27,28,29,30]. The EBSD images reveal that the addition of Mo has no significant impact on the structural orientation of the steel; there is still no evident preferred orientation, and the internal grain orientation differences are relatively small.
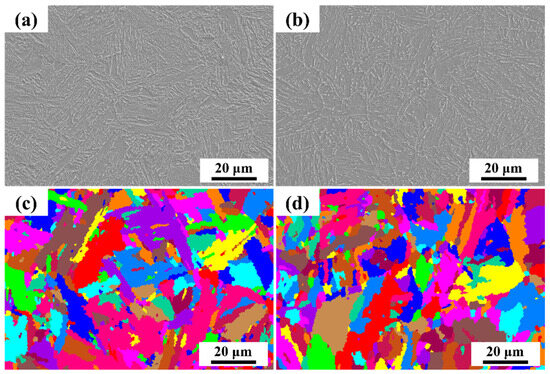
Figure 1.
SEM and EBSD morphology of two steels: (a) and (c) 0 Mo, (b) and (d) 1 Mo.
2.2. Simulation of Tropical Marine Atmospheric Corrosion Testing
To elucidate the impact of Mo content on the corrosion resistance of low-alloy steel in a tropical marine atmospheric environment, this study conducted a simulated investigation through indoor immersion tests. Rectangular specimens, sized at 50 mm × 25 mm × 3 mm, were fabricated, polished to a P800 finish, and subsequently washed with deionized water and alcohol. After drying, they were weighed and dimensionally measured. The testing was conducted at a temperature of 35 ± 1 °C, using a test solution [22] designed to accelerate the simulation of tropical marine atmospheric conditions: 5 wt.% NaCl + 0.05 wt.% CaCl2 + 0.05 wt.% Na2SO4. The immersion test periods included 7 days, 15 days, and 30 days. To improve test precision, three replicate samples were prepared for each type of steel at each time point, and the testing solution was replaced every 7 days.
2.3. Corrosion Performance Testing
2.3.1. Corrosion Rate Testing
At the end of each test period, the samples were removed and subjected to ultrasonic derusting using a derusting solution composed of 500 mL H2O + 500 mL HCl + 3.5 g hexamethylenetetramine. Subsequently, the samples were extensively rinsed thoroughly with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol, dried, and then weighed to calculate the corrosion loss and corrosion rate. The formulas for calculating the corrosion loss and corrosion rate are as follows [31,32,33,34]:
where w represents the corrosion loss in grams per square centimeter (g/cm2), v denotes the corrosion rate in millimeters per year (mm/y), m0 stands for the initial weight of the sample in grams (g), mt indicates the weight of the sample after rust removal in grams (g), S is the exposed surface area of the sample in square centimeters (cm2), ρ is the density of the steel (7.8 g/cm3), and t is the exposure time in hours (h).
2.3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Measurements
The electrochemical measurement applied a conventional three-electrode system, where the test steel acted as the working electrode, Pt served as the auxiliary electrode, and an SCE functioned as the reference electrode [35]. The dimensions of the working electrode were 10 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm. Copper wires were spot welded to the backside of the working electrode, and epoxy resin was used to embed it, retaining a working area of 1 cm2. The working surface was polished to a P2000 finish using sandpaper, rinsed with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol, and then dried quickly.
The electrochemical immersion samples were conducted in parallel with the immersion tests, with testing periods of 1 day, 3 days, 7 days, 15 days, and 30 days. An electrochemical workstation (Auto-Lab Nova 2, Metrohm Autolab, Utrecht, The Netherland) was used to measure the AC impedance of the two steel types. All tests were conducted with the open-circuit potential stabilized. The frequency range for AC impedance testing was 100 kHz to 10 mHz, with an AC sine wave amplitude of 10 mV. Data fitting was performed using ZsimpWin 3.5 software.
2.3.3. Corrosion Product Analysis
SEM was utilized to observe the surface and cross-sectional morphology of the rust layers on the test steel, and EDS was applied for element distribution analysis. The rust layers from the surfaces of each steel sample were scraped off with a blade, and the rust layer particles were ground into powder using a quartz mortar and pestle. XRD (Bruker D8 Advance, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) was used to determine the phase composition of the corrosion products on the two types of steel after corrosion immersion. The X-ray source used was Cu Kα radiation, with current and voltage set at 40 mA and 40 kV, respectively. The scanning range for the diffraction angle was from 25° to 90°, with a scanning rate of 4°/min. The post-derusting corrosion morphology was characterized using a Laser Confocal Microscope (BZ, KEYENCE, Osaka, Japan) to examine its 3D morphology.
3. Results
3.1. Corrosion Rate
In order to study the influence of Mo on the atmospheric corrosion behavior of Cr-containing steel, a 30-day indoor immersion test was conducted, and the corrosion rate is illustrated in Figure 2. As shown in the figure, with the extension of the test time, the corrosion rate of 1 Mo steel consistently remains at a lower level compared to 0 Mo steel. This indicates that adding approximately 0.21 wt.% Mo to Cr-containing steel can significantly enhance its resistance to uniform corrosion in a tropical marine atmospheric environment.
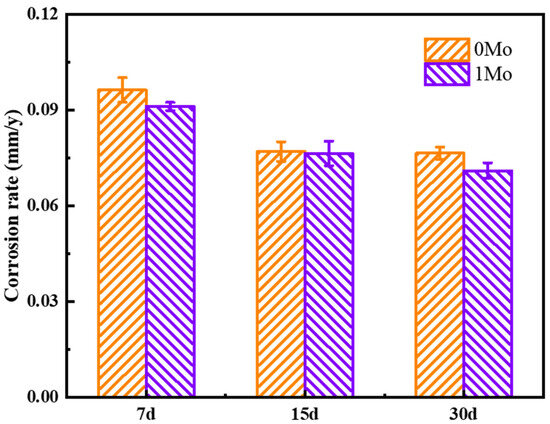
Figure 2.
Corrosion rate of two Cr-containing steels in a simulated tropical marine atmospheric environment.
3.2. Corrosion Product Layer Morphology
The variation in corrosion rate is closely related to the performance of the corrosion product layer on the steel surface during the test period. Therefore, a detailed analysis of the corrosion product layer is essential. Figure 3 depicts the macroscopic morphology of the corrosion products on the two types of steel submitted to different immersion times.
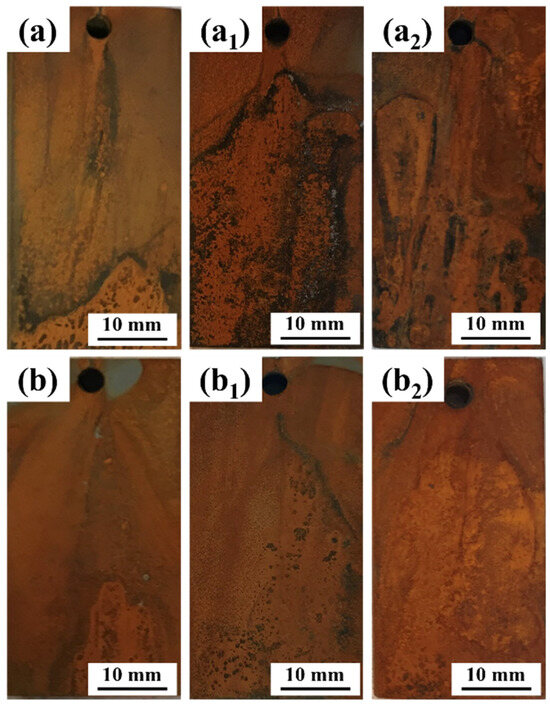

Figure 3.
Macroscopic morphology of corrosion products on two steel types after different immersion durations: (a) 0 Mo—7 d, (a1) 0 Mo—15 d, (a2) 0 Mo—30 d, (b) 1 Mo—7 d, (b1) 1 Mo—15 d and (b2) 1 Mo—30 d.
From Figure 3a,a1,a2, it is evident that the corrosion product layer on 0 Mo steel appears light yellow after 7 days of immersion. As the immersion period is extended, corrosion products progressively coat the entire sample surface, transitioning to a reddish-brown hue, with some areas turning black. Observing the macroscopic morphology of the corrosion products on 1 Mo steel after 7 days, 15 days, and 30 days of immersion, it is apparent that the corrosion products already exhibit a reddish-brown color in the early stages of corrosion. In the middle stage, small amounts of black corrosion products can be observed, while in the later stages, the corrosion products are mainly reddish-brown and orange. This indicates that the addition of Mo leads to differences in the corrosion products formed on the steel.
To further clarify the differences in the performance of the corrosion product layers on both steel types, the microscopic morphology of the products was observed. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the microscopic morphology of the corrosion products on 0 Mo steel and 1 Mo steel after different immersion durations. From the corrosion product layer morphology after 7 days of immersion for both steel types, it can be observed that they consist of two distinct layers. The outer layer of the products is relatively loose, easily peeled off, and does not form a complete covering. The outer layer appears dense but exhibits a cracked appearance due to drying-induced embrittlement.
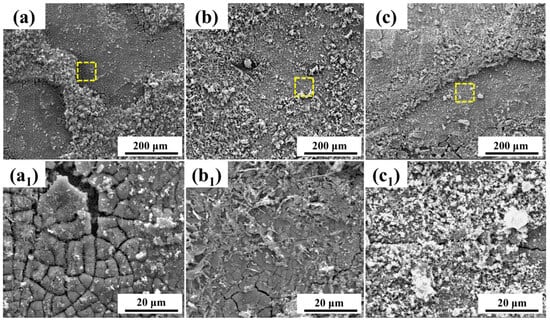
Figure 4.
Microscopic morphology of corrosion products on 0 Mo steel after different immersion durations: (a–c) depict the microscopic morphology of the corrosion products after 7 days, 15 days, and 30 days of immersion, respectively. (a1–c1) represent localized magnifications of the areas outlined by yellow dashed lines in (a–c).
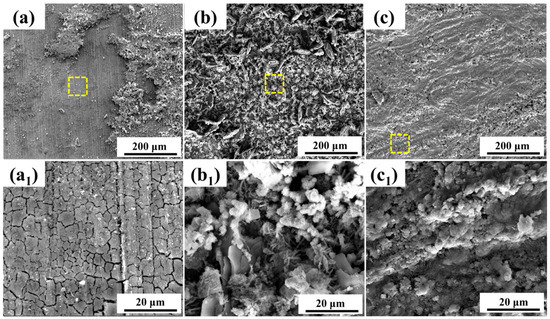
Figure 5.
Microscopic morphology of corrosion products on 1 Mo steel after different immersion durations: (a–c) depict the microscopic morphology of the corrosion products after 7 days, 15 days, and 30 days of immersion, respectively. (a1–c1) represent localized magnifications of the areas outlined by yellow dashed lines in (a–c).
As the immersion period extends, combined with localized magnifications, it is apparent that the outer corrosion product layer of 0 Mo steel remains relatively loose. In contrast, the outer corrosion product layer of 1 Mo steel shows a significant improvement in density, covering almost the entire sample surface by the 30-day immersion mark. After 15 days of immersion, the corrosion product morphology on 1 Mo steel is varied, but by the 30-day mark, the surface of 1 Mo steel is overall smooth and dense. There is almost no visible loose area, and magnified views reveal the thorough evolution of the corrosion products. No distinct product morphology is discernible, as the particles merge with each other, forming a more complete and dense corrosion product layer. This layer effectively impedes the intrusion of the corrosive medium, greatly reducing the corrosion rate of the steel substrate. As a result, the corrosion rate of 1 Mo steel is significantly lower than that of 0 Mo steel.
Cross-sectional observations of the corrosion product layers on both steel types are shown in Figure 6. It is evident from the figure that the corrosion product layers on both steel types exhibit a dual-layer structure: a relatively dense inner rust layer and a looser outer rust layer. The inner rust layer of 0 Mo steel is more brittle and prone to developing penetrating cracks during the drying process. These cracks can serve as fast pathways for the corrosive medium, accelerating the corrosion process.
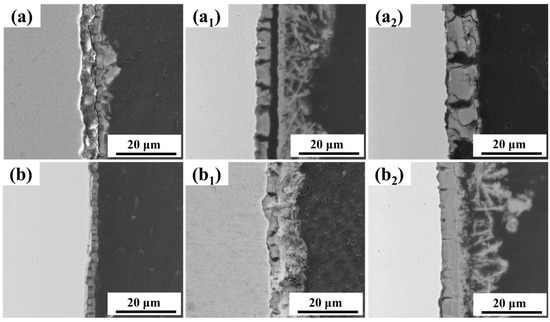
Figure 6.
Cross-sectional morphology of corrosion product layers on both steel types after different immersion durations: (a) 0 Mo—7 d, (a1) 0 Mo—15 d, (a2) 0 Mo—30 d, (b) 1 Mo—7 d, (b1) 1 Mo—15 d and (b2) 1 Mo—30 d.
In contrast, the inner rust layer of 1 Mo steel exhibits significantly fewer cracks compared to 0 Mo steel. After 30 days of immersion, the product layer on 1 Mo steel shows no significant cracks due to dehydration and displays excellent adhesion to the substrate. Considering the surface morphology of the corrosion products shown in Figure 5c1, it can be inferred that the addition of Mo to the steel enhances the early-stage transformation of corrosion products into stable ones, leading to the rapid growth and fusion of corrosion products into a dense and complete layer. This layer acts as a barrier to prevent the intrusion of the corrosive medium. Furthermore, the higher Mo content significantly improves the toughness of the corrosion products.
Figure 7 shows the elemental distribution within the cross-section of the corrosion product layers on both steel types after 30 days of immersion. It is apparent that O is evenly distributed throughout the entire corrosion product layer, while Cr and Mo are only enriched in the inner rust layer. This indicates that the corrosion products rich in Cr and Mo are concentrated within the inner rust layer.
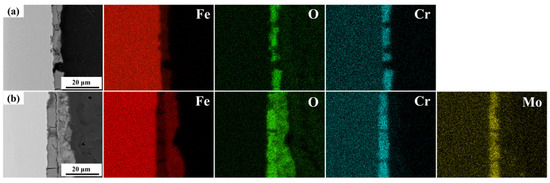
Figure 7.
Elemental distribution in the cross-section of corrosion product layers on both steel types after 30 days of immersion: (a) 0 Mo steel, (b) 1 Mo steel.
3.3. Corrosion Product Analysis
Clearly, the differences in corrosion rates and the morphology of the corrosion product layers are attributed to the changes in the corrosion products resulting from the addition of Mo. Therefore, XRD phase analysis was conducted on the corrosion products of both steel types, as shown in Figure 8. The analysis reveals that the corrosion products on both steel types primarily consist of α-FeOOH, Fe3O4, γ-FeOOH, and Fe, with the Fe peak reflecting the substrate due to the thinness of the corrosion product layer. Comparing the peak intensities of the various phases on both steel types, it is evident that the Fe peak for 1 Mo steel is significantly weaker than that of 0 Mo steel. This indicates that the corrosion product layer of 1 Mo steel is denser and more uniform, resulting in less X-ray penetration. Additionally, compared to 0 Mo steel, 1 Mo steel shows a decrease in the peak intensity of γ-FeOOH and Fe3O4, while the peak intensity of α-FeOOH is enhanced.
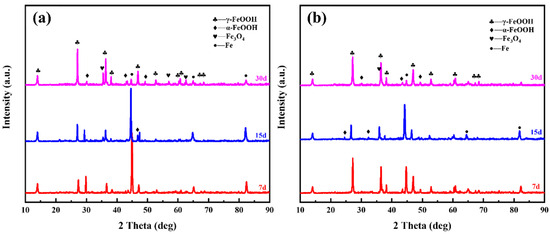
Figure 8.
Phase composition of corrosion products on both steel types after different immersion durations: (a) 0 Mo steel, (b) 1 Mo steel.
To provide a clearer characterization of the differences in steel phases, a semi-quantitative analysis of the corrosion product phase proportions for both steel types after 30 days of immersion is presented in Figure 9. It can be observed that the proportion of α-FeOOH in 1 Mo steel is increased to nearly 30%, while it is only 5% in 0 Mo steel. This indicates that with the addition of Mo, a greater portion of γ-FeOOH transforms into the stable α-FeOOH, leading to increased stability and protection in the corrosion product layer.
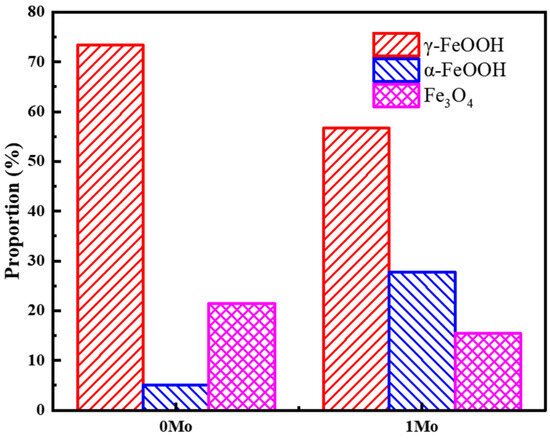
Figure 9.
Phase proportions of corrosion products on both steel types after 30 days of immersion.
3.4. Immersion Electrochemical Analysis
Some studies [6,31,36,37] have found that EIS is an effective method for characterizing the protective properties of corrosion product layers on low-alloy steel. Therefore, EIS results for both steel types after different immersion durations in the simulated tropical marine atmosphere were determined, as shown in Figure 10. Figure 10 displays the Nyquist plots for two types of steel. In terms of the overall effect, during the initial immersion period (7 days), there was little difference in the impedance arc radii between the two steel types, and there was no significant change over time. When the immersion time reached 15 days, both steel types showed a noticeable increase in the radii of the impedance arcs, indicating an enhanced resistance of the corrosion product layers of both steel types to the external corrosive medium during this period. After 30 days of immersion, the impedance arc radius of the 0 Mo steel exhibited a slight increase compared to the 15-day result. In contrast, the 1 Mo steel displayed a more pronounced increase, with the impedance arc approaching a straight line. This observation suggests a clear diffusion-controlled phenomenon. This suggests that as the immersion time extends, the addition of Mo significantly enhances the protective and compact nature of the corrosion products on the steel surface. The process of corrosion medium diffusion into the corrosion product layer and its contact with the substrate is noticeably inhibited.
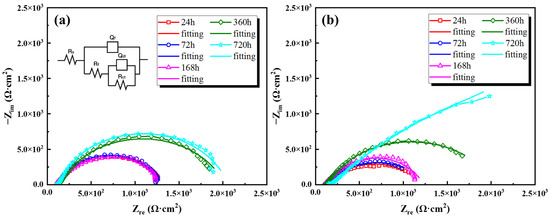
Figure 10.
Nyquist plots of both steel types after different immersion durations: (a) 0 Mo steel, (b) 1 Mo steel.
Using the equivalent circuit from Figure 10a, the electrochemical impedance spectra of both steel types were fitted. In the circuit, Rs represents solution resistance, Qf and Rf denote the constant phase element and pore resistance of the corrosion product layer, and Qdl and Rct correspond to the double-layer constant phase element and charge transfer resistance at the metal interface. The fitting results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Fitting results of impedance spectra for both steel types after different immersion durations.
The results indicate that for both steel types, the pore resistance and charge transfer resistance of the corrosion product layer did not change significantly during the first 7 days of immersion. As the immersion time increased, there was a noticeable increase in resistance values, suggesting an enhanced hindrance effect of the corrosion product layer on the corrosive medium. When comparing the two steel types, it is evident that the Rf and Rct values for 1 Mo steel are significantly higher than those for 0 Mo steel. After 30 days of immersion, the Rf and Rct values for 1 Mo steel reach 92.3 and 799.4 Ω·cm2, indicating a substantial improvement in the denseness of the corrosion product layer in response to the addition of Mo. This results in reduced ion exchange and material transport pathways within and outside the layer increased diffusion resistance and enhanced protective properties of the corrosion product layer.
3.5. The Corrosion Morphology Analysis
To clarify the impact of Mo addition on the pitting corrosion resistance of Cr-containing steel in harsh tropical marine atmospheric conditions, the morphology of the two Cr-containing steels was characterized using SEM and laser confocal microscopy after 30 days of immersion. The results are shown in Figure 11. Observing the corrosion morphology of the two steels after 30 days of immersion reveals that the 0 Mo steel substrate has numerous pores, which are narrow and deep, indicating localized corrosion characteristics. This finding is further confirmed by the 3D morphology in Figure 11a1,a2, where the pitting corrosion depth reaches 9.411 μm. In contrast, the 1 Mo steel substrate corrodes more uniformly, with only localized areas showing wide and shallow pits, indicative of typical uniform corrosion characteristics. The 3D morphology images do not show any significant pits, and the highest corrosion depth is only 4.493 μm. This indicates that the addition of Mo effectively mitigates the localized corrosion of Cr-containing steel.
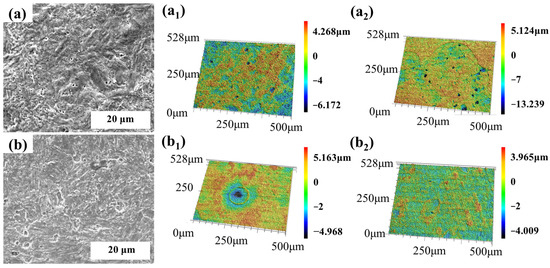
Figure 11.
Microstructural morphology of the two steels after 30 days of immersion and 3D morphology after 7 and 30 days of immersion: (a) 0 Mo—30 d and (b) 1 Mo—30 d, (a1) 0 Mo—7 d; and (a2) 0 Mo—30 d, (b1) 1 Mo—7 d and (b2) 1 Mo—30 d.
4. Discussion
The standard electrode potential of Mo (vs SHE) is −0.22 V [31]. This indicates that, compared to Fe (−0.44 V) and Cr (−0.74 V), Mo exhibits lower electrochemical activity in the corrosive environment. As a result, the corrosion resistance of the steel matrix is improved. As corrosion progresses, Mo undergoes oxidation reactions and exists in ionic form. With the gradual densification of the corrosion product layer, the mass transfer process becomes more challenging. Mo ions further react with oxygen to form a stable higher-oxidation-state product, MoO42−. This compound acts as an insoluble product that can effectively fill defects. such as cracks in the corrosion product layer, enhancing its density [38,39]. The relevant chemical reactions are represented by Equations (3)–(5).
Based on the cross-sectional morphology of the rust layer and the distribution of alloy elements in 1 Mo steel, it is evident that the compactness of the corrosion product layer gradually increases with prolonged immersion time. Moreover, Mo and Cr accumulate only in the inner layer. The synergistic effect of Mo and Cr will further promote the electrochemical conversion of γ-FeOOH, which is an electrochemically active substance, into thermodynamically stable α-FeOOH. α-FeOOH is nearly non-reactive and acts as a highly stable insulating product. This greatly enhances the stability and protectiveness of the corrosion product layer, significantly improving the overall electrochemical stability of the corrosion product layer. As the compactness of the corrosion product layer increases, ion diffusion within the steel becomes more challenging, leading to a significant accumulation of Mo and Cr in the corrosion product layer, resulting in a uniform corrosion characteristic on the steel surface.
Furthermore, it has been reported in the literature [16,40,41] that due to the generation of MoO42− in solution, which can stably exist in near-neutral or high-pH environments, Mo serves as a typical anodic corrosion inhibitor. It preferentially adsorbs on the steel surface, reducing the adsorption sites for Cl− ions and inhibiting the active dissolution of steel. Additionally, near existing pits, it can suppress further pit propagation. The combined effects described above lead to Mo enhancing the steel’s resistance to local corrosion.
Therefore, in a tropical marine atmospheric environment, the addition of Mo in Cr-containing steel can enhance the corrosion resistance of the steel matrix. The coupling effect with Cr further increases the content of α-FeOOH, improving the compactness, protectiveness, and toughness of the corrosion product layer. This results in uniform corrosion characteristics on the steel surface. Additionally, Mo can generate the slow-release ion MoO42− to mitigate the localized acidification phenomenon that occurs at the interface between the steel matrix and the corrosion product layer due to difficult medium diffusion, effectively inhibiting localized corrosion on the steel.
5. Conclusions
This study utilized vacuum melting combined with controlled rolling and cooling techniques to prepare two Cr-containing steels with different Mo contents. Through immersion tests, microscopic analysis of corrosion product layers and electrochemical experiments, the impact mechanism of Mo on the corrosion resistance of Cr-containing low-alloy steel in a simulated tropical marine atmospheric environment has been elucidated. The main conclusions are as follows:
- The addition of Mo reduces the corrosion rate of Cr-containing steel in a simulated tropical marine atmospheric environment, and this effect becomes more pronounced with longer exposure times.
- Mo and Cr simultaneously accumulate in the inner corrosion product layer. The synergistic effect of these elements promotes the formation of α-FeOOH, which exhibits excellent thermodynamic stability. This leads to enhanced compactness and protectiveness of the corrosion product layer.
- MoO42−, a product of Mo, acts as a slow-release ion and accumulates on the inner side of the corrosion product layer. It effectively mitigates the acidification effects at the interface between the corrosion product layer and the substrate, resulting from the diffusion challenges of a dense corrosion product layer. Consequently, localized corrosion in Cr-containing steel is significantly inhibited.
Author Contributions
Resources, X.X.; data curation, J.G.; writing–original draft, N.W. and X.X.; writing–review and editing, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number SDBX2023016, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2023M733875.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kamimura, T.; Stratmann, M. The influence of chromium on the atmospheric corrosion of steel. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Z.; Zuo, X.M.; Cheng, X.Q.; Li, X.G. The role of chromium content in the long-term atmospheric corrosion process. NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2020, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.H.; Ma, C.H.; Niu, D.; Xu, J.J.; Li, M.S. Influence of alloyed chromium on the atmospheric corrosion resistance of weathering steels. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, T.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Banthukul, W. Optimize Ni, Cu, Mo element of low Cr-steel rebars in tropical marine atmosphere environment through two years of corrosion monitoring. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fatah, H.T.; Hassan, A.A.; Shetify, M.M.; El-Sehiety, H.E.; Abdel-Samad, H.S.; Zohdy, K.M. Effect of Cr and Mo on the corrosion behavior of some low alloy steels in acidic media. Chem. Sci. Rev. Lett. 2012, 1, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, X.X.; Li, Y.; Lv, X.W. The function of Cr on the rust formed on weathering steel performed in a simulated tropical marine atmosphere environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Banthukul, W.; Zhao, Y.G.; Zhang, T.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Li, X.G. Comparison of the characteristics of corrosion scales covering 3Cr steel and X60 steel in CO2-H2S coexistence environment. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 80, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, I.; Cano, H.; Lopesino, P.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Jimenez, J.A.; Medina, S.F.; Morcillo, M. Five-year atmospheric corrosion of Cu, Cr and Ni weathering steels in a wide range of environments. Corros. Sci. 2018, 141, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszczyk, A.; Banaś, J.; Pisarek, M.; Seyeux, A.; Marcus, P.; Światowska, J. Effect of Cr Content on Corrosion Resistance of Low-Cr Alloy Steels Studied by Surface and Electrochemical Techniques. Electrochem 2021, 2, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of Cr, Ni and Cu on the corrosion behavior of low carbon microalloying steel in a Cl− containing environment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, K.; Sugae, K.; Kamimura, T.; Miyuki, H.; Kudo, T. Effect of Chromium Contents on Atmospheric Corrosion of Steel in Chloride Environment. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. Mater. 2013, 77, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Indira, K.; Nishimura, T. SECM Study of Effect of Chromium Content on the Localized Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloy Steels in Chloride Environment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, H.; Diaz, I.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Morcillo, M. Effect of Cu, Cr and Ni alloying elements on mechanical properties and atmospheric corrosion resistance of weathering steels in marine atmospheres of different aggressivities. Mater. Corros. Werkst. Und Korros. 2018, 69, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Dong, J.H.; Ke, W. A study of the evolution of rust on Mo-Cu-bearing fire-resistant steel submitted to simulated atmospheric corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Merino, M.C.; Coy, A.E.; Viejo, F.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Effect of Mo and Mn additions on the corrosion behaviour of AISI 304 and 316 stainless steels in H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Ha, H.-Y.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, T.-H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Han, H.N.; Hong, H.-U. Effect of Mo and Cr additions on the microstructure, mechanical properties and pitting corrosion resistance of austenitic Fe-30Mn-10.5 Al-1.1 C lightweight steels. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Hao, J.; Yang, F.L.; Chen, H.D.; Liang, N.N.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Ma, H.; Klu, E.E.; Gao, B.; et al. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of Cr-Mo alloyed steel: Role of ferrite/bainite duplex microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 809, 151787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayat, M.; Morales, M.; Moradi, M.; Mateo, A. Laser wobbling surface texturing of AISI 301LN steel for enhancement of the corrosion resistance at high temperature. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 171, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargas, G.; Zapata, A.; Roa, J.J.; Sapezanskaia, I.; Mateo, A. Correlation Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties Before and After Reversion of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, M.; Sato, N. The effect of molybdate anion on the ion-selectivity of hydrous ferric oxide films in chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 1977, 17, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.M.; Peng, Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Tian, Z.L. Effects of Alloy Element and Microstructure on Corrosion Resistant Property of Deposited Metals of Weathering Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2016, 23, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.H.; Du, C.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, X.G.; Wu, Y.M. Fundamental understanding on the effect of Cr on corrosion resistance of weathering steel in simulated tropical marine atmosphere. Corros. Sci. 2021, 186, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Wu, W.; Li, N.N.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, X.G. Effect of 0.1 wt% Nb on the microstructure and corrosion fatigue performance of high strength steels. Corros. Sci. 2023, 219, 111242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, X.G. Improving the resistance of high-strength steel to SCC in a SO2-polluted marine atmosphere through Nb and Sb microalloying. Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, T.L.; Cui, Q.Q.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, X.G. Corrosion fatigue behavior of Fe-16Mn-0.6C-1.68Al twinning-induced plasticity steel in simulated seawater. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Cheng, H.L.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, X.G. Stress corrosion cracking behavior and mechanism of Fe-Mn-Al-C-Ni high specific strength steel in the marine atmospheric environment. Corros. Sci. 2021, 191, 109760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostryzhev, A.; Singh, N.; Chen, L.; Killmore, C.; Pereloma, E. Comparative Effect of Mo and Cr on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in NbV-Microalloyed Bainitic Steels. Metals 2018, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.J.; Xu, G.; Zhou, M.X.; Yuan, Q. Effect of Mo Content on Microstructure and Property of Low-Carbon Bainitic Steels. Metals 2016, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.K.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Hwang, B. Effect of finish cooling temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength bainitic steels containing Cr, Mo, and B. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct 2015, 624, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Y.; Xin, J.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z. Combined effect of cathodic potential and sulfur species on calcareous deposition, hydrogen permeation, and hydrogen embrittlement of a low carbon bainite steel in artificial seawater. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.H.; Pang, Y.J.; Du, C.W.; Li, X.G.; Wu, Y.M. Optimization of Mo on the corrosion resistance of Cr-advanced weathering steel designed for tropical marine atmosphere. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Cheng, X.Q.; Zhao, J.B.; Li, X.G. Benefit of the corrosion product film formed on a new weathering steel containing 3% nickel under marine atmosphere in Maldives. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.J.; Dong, B.J.; Yang, W.J.; Fan, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.G. On how the corrosion behavior and the functions of Cu, Ni and Mo of the weathering steel in environments with different NaCl concentrations. Corros. Sci. 2021, 192, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, W.; Chowwanonthapunya, T.; Dong, B.J.; Zhao, Y.G.; Yang, Y.M. Corrosion Evolution and Analysis of Welded Joints of Structural Steel Performed in a Tropical Marine Atmospheric Environment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 5057–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wu, W.; Jiang, S.; Yang, J.W.; Liu, Z.Y. Optimizing the resistance of Ni-advanced weathering steel to marine atmospheric corrosion with the addition of Al or Mo. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, X.Q.; Zhao, J.B.; Li, X.G. Effect of Sn on the corrosion behavior of weathering steel in a simulated tropical marine atmosphere. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2020, 67, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, W.Z.; Cheng, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, K.M.; Liu, M. Effects of niobium and rare earth elements on microstructure and initial marine corrosion behavior of low-alloy steels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ni, R.-C.; Hua, H.-Z.; Pourbaix, A. The behavior of chromium and molybdenum in the propagation process of localized corrosion of steels. Corros. Sci. 1984, 24, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfrouh, A.; Masson, C.; Vouagner, D.; De Becdelievre, A.; Prakash, N.; Audouard, J. The cumulative effect of alloying elements N, W, Mo and Cu on the corrosion behaviour of 17Cr-13Ni stainless steel in 2 N H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Asami, K.; Kawashima, A.; Habazaki, H.; Akiyama, E. The role of corrosion-resistant alloying elements in passivity. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Ambrose, J. Effect of molybdate ion on the repassivation kinetics of iron in solutions containing chloride ions. Corrosion 1977, 33, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).