The Structural Basis of DL0410, a Novel Multi-Target Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
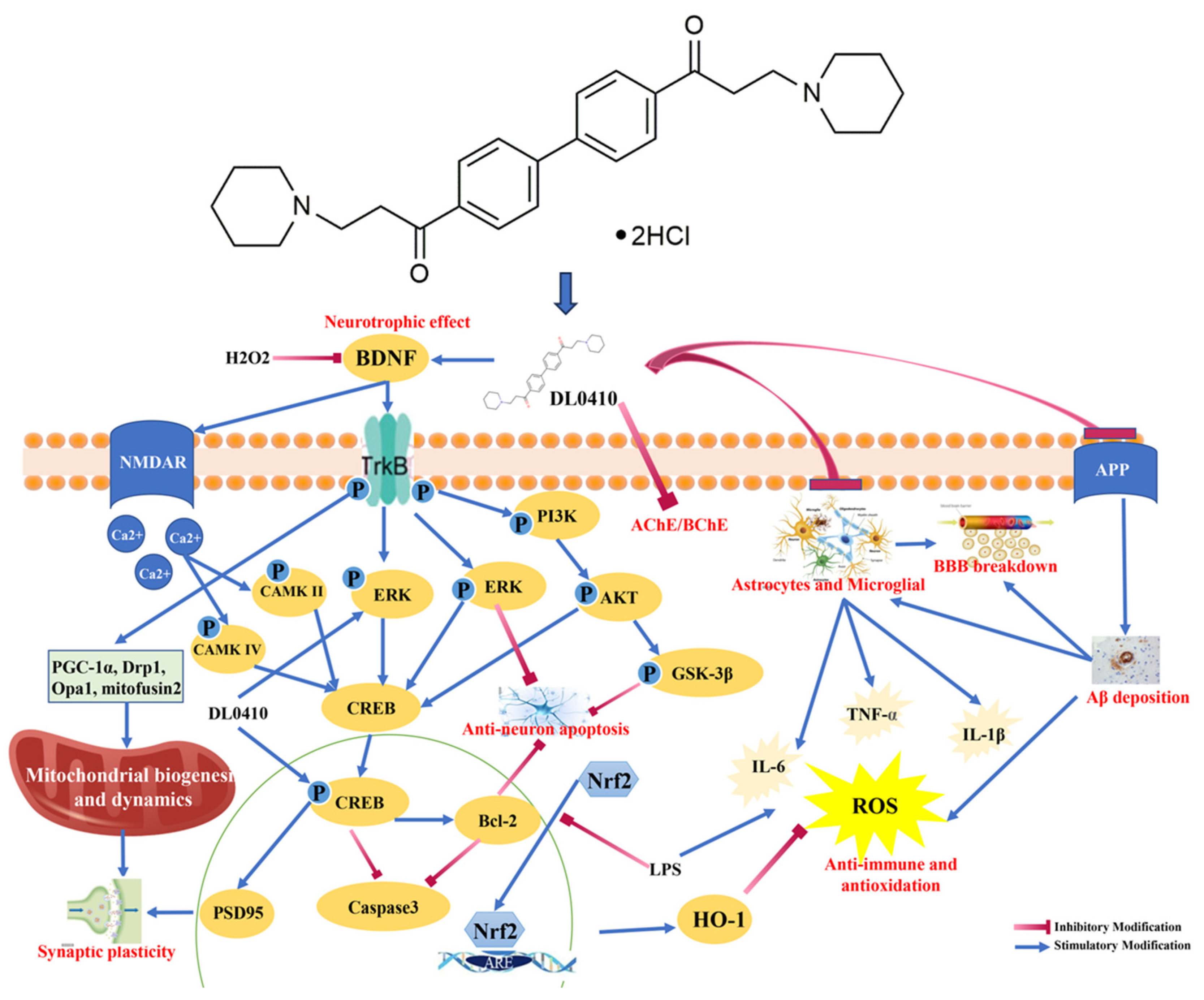
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Crystal Preparation
2.3. Single Crystal Detection
2.4. Thermal Analyses
2.5. Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. The Crystal Structure of DL0410
3.2. Thermal Analyses
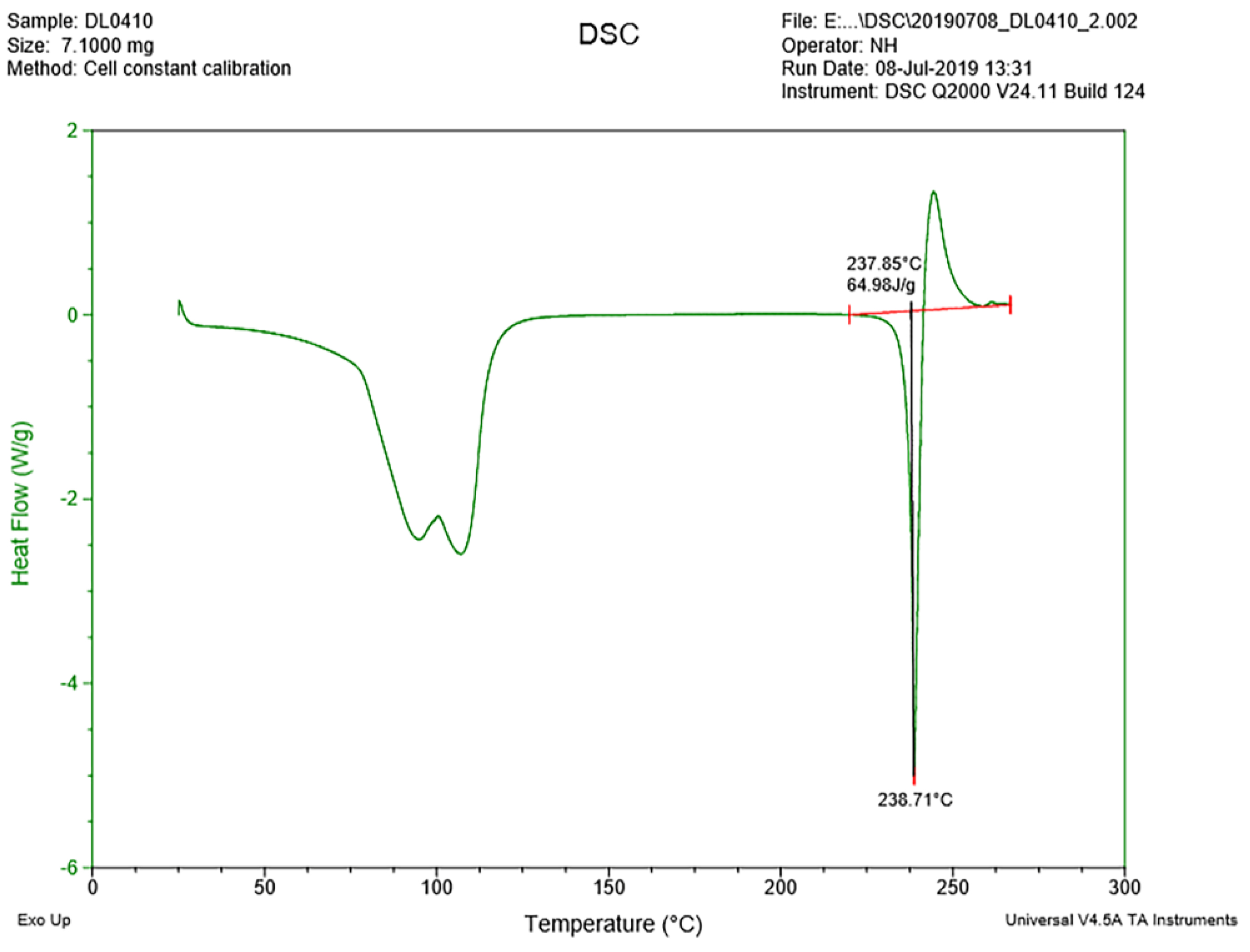
3.2.1. DSC Analysis
3.2.2. TGA Result
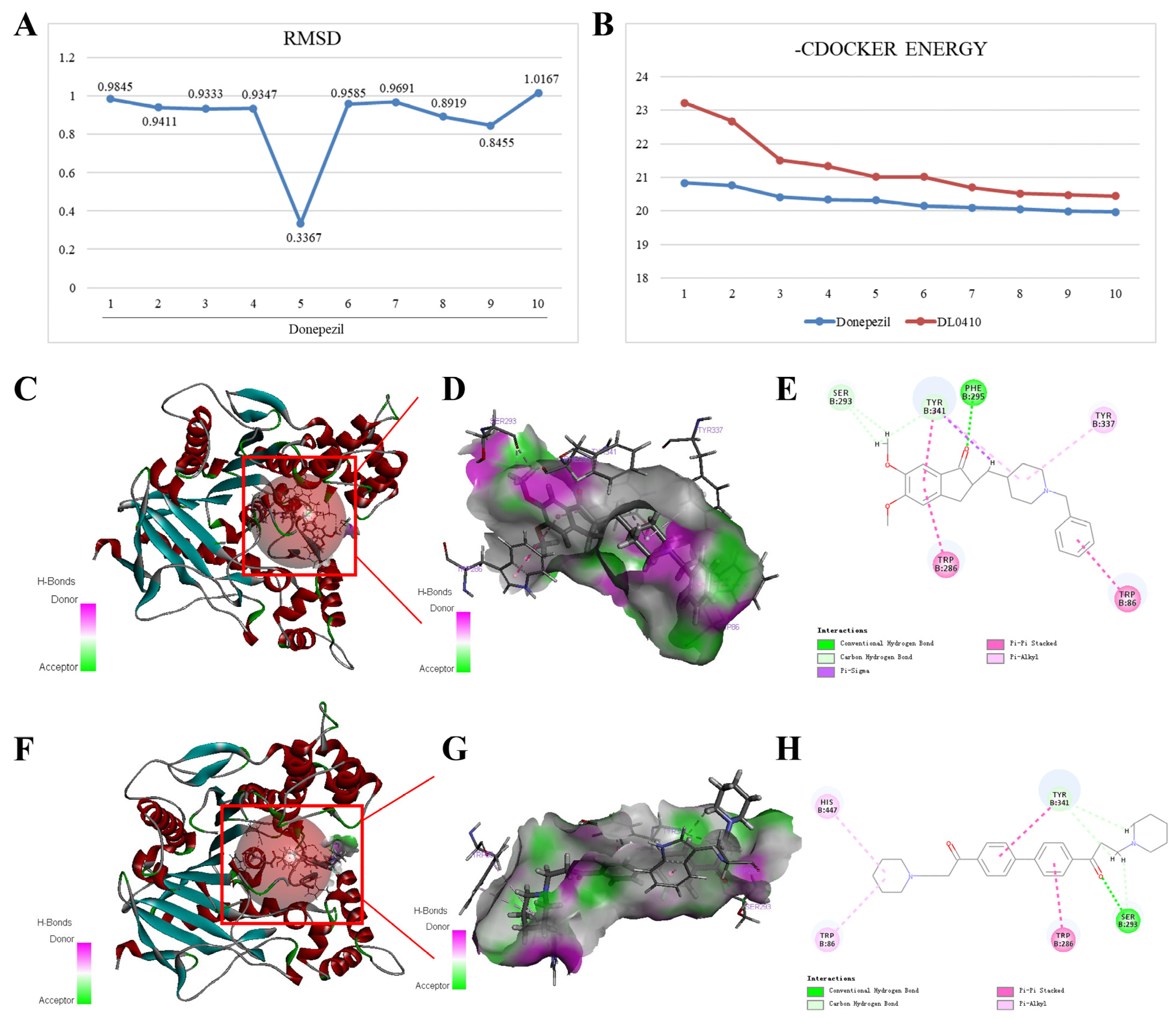
3.3. Molecular Docking of DL0410 with AChE, BuChE, and H3R
3.3.1. Molecular Docking of DL0410 with AChE
3.3.2. Molecular Docking of DL0410 with BuChE
3.3.3. Molecular Docking of DL0410 with H3R
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chetelat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, Z.; Afrashteh, N.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Hearing loss and impaired short-term memory in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model of amyloid-beta pathology. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 365, 114413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Se Thoe, E.; Fauzi, A.; Tang, Y.Q.; Chamyuang, S.; Chia, A.Y.Y. A review on advances of treatment modalities for Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Wang, L. Multi-resolution 3D-HOG feature learning method for Alzheimer’s Disease diagnosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 214, 106574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsteinsson, A.P.; Isaacson, R.S.; Knox, S.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Rubino, I. Diagnosis of Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Practice in 2021. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 8, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostagno, A.A. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. Available online: https://www.alz.org/media/documents/alzheimers-facts-and-figures.pdf. (accessed on 7 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Aisen, P.S.; DuBois, B.; Frolich, L.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Jones, R.W.; Morris, J.C.; Raskin, J.; Dowsett, S.A.; Scheltens, P. Drug development in Alzheimer’s disease: The path to 2025. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, D.P.; Fillit, H.; Neumann, P. Accelerating Alzheimer’s disease drug innovations from the research pipeline to patients. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Farlow, M.R.; Giacobini, E.; Grossberg, G.T.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Cavedo, E.; Snyder, P.J.; et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2018, 141, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Sorbi, S. The complexity of Alzheimer’s disease: An evolving puzzle. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1047–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benek, O.; Korabecny, J.; Soukup, O. A Perspective on Multi-target Drugs for Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Tam, K.Y. Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lian, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, A.; Du, G. DL0410 Alleviates Memory Impairment in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Rats by Suppressing Neuroinflammation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6521146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocci, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Leuci, R.; Carrieri, A.; Brunetti, L.; Laghezza, A.; Catto, M.; Limongelli, F.; Chaves, S.; Tortorella, P.; et al. Novel Phenothiazine/Donepezil-like Hybrids Endowed with Antioxidant Activity for a Multi-Target Approach to the Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.X.; Dai, C.L.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Multi-Targets: An Unconventional Drug Development Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 837649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, B.; de Morais, L.A.; Viana, M.C.; Carneiro, G. Promising strategies for improving oral bioavailability of poor water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.R.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A. Quercetin derivatives: Drug design, development, and biological activities, a review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 229, 114068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crampon, K.; Giorkallos, A.; Deldossi, M.; Baud, S.; Steffenel, L.A. Machine-learning methods for ligand-protein molecular docking. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.R.; Moon, H.K. Gravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetric studies on glycerin-induced skin hydration. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, S.P.; Nethercott, M.J.; Mays, C.J.; Winquist, N.T.; Arthur, D.; Calahan, J.L.; Sethi, M.; Pardue, D.S.; Kim, J.; Amidon, G.; et al. Characterization of Synthesized and Commercial Forms of Magnesium Stearate Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry, Thermogravimetric Analysis, Powder X-ray Diffraction, and Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sabbarwal, S.; Mishra, P.K.; Upadhyay, S.N. Thermal degradation kinetics of sugarcane leaves (Saccharum officinarum L.) using thermo-gravimetric and differential scanning calorimetric studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L., 3rd; Vieth, M. Detailed analysis of grid-based molecular docking: A case study of CDOCKER-A CHARMm-based MD docking algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Pang, X.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; He, Y.; Lian, W.; Liu, A.L.; Du, G.H. Discovery of multitarget-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease through systematic prediction of chemical-protein interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, R.; Gao, L.; Zhou, D.; Yang, S.; Liu, A.L.; Du, G.H. Predictions of BuChE inhibitors using support vector machine and naive Bayesian classification techniques in drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Bolanos, J.G.; Lopez, O. Butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors as potential anti-Alzheimer’s agents: An updated patent review (2018-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2022, 32, 913–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Kishi, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Iwata, N. Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Barve, K.H.; Kumar, M.S. Recent Advancements in Pathogenesis, Diagnostics and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1106–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Atluri, V.; Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Nair, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Length [Å] | |
| O1–C3 | 1.2184 (12) |
| O2–H2C | 0.851 (16) |
| O2–H2D | 0.829 (16) |
| O3–H3A | 0.869 (15) |
| O3–H3B | 0.873 (15) |
| O4–H4A | 0.833 (15) |
| O4–H4B | 0.869 (15) |
| O5–H5A | 0.806 (17) |
| O5–H5B | 0.856 (17) |
| N1–C1 | 1.4943 (12) |
| N1–C10 | 1.5012 (12) |
| N1–C14 | 1.5055 (12) |
| N1–H1 | 0.935 (14) |
| C1–C2 | 1.5199 (13) |
| C2–C3 | 1.5166 (13) |
| C3–C4 | 1.4878 (13) |
| C4–C5 | 1.3950 (12) |
| C4–C9 | 1.3962 (12) |
| C5–C6 | 1.3928 (12) |
| C5–H5 | 0.9500 |
| C6–C7 | 1.4024 (12) |
| C6–H6 | 0.9500 |
| C7–C8 | 1.4046 (12) |
| C7–C7 #1 | 1.4907 (17) |
| C8–C9 | 1.3853 (12) |
| C8–H8 | 0.9500 |
| C9–H9 | 0.9500 |
| C10–C11 | 1.5217 (14) |
| C11–C12 | 1.5190 (16) |
| C12–C13 | 1.5251 (16) |
| C13–C14 | 1.5145 (14) |
| Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle [°] |
| H2C–O2–H2D | 110 (2) |
| H3A–O3–H3B | 105.6 (18) |
| H4A–O4–H4B | 99.2 (18) |
| H5A–O5–H5B | 108 (2) |
| C1–N1–C10 | 113.63 (7) |
| C1–N1–C14 | 108.41 (7) |
| C10–N1–C14 | 111.26 (7) |
| C1–N1–H1 | 109.1 (8) |
| C10–N1–H1 | 106.4 (8) |
| C14–N1–H1 | 107.8 (8) |
| N1–C1–C2 | 114.96 (7) |
| H1A–C1–H1B | 107.5 |
| C3–C2–C1 | 108.96 (7) |
| H2A–C2–H2B | 108.3 |
| O1–C3–C4 | 120.20 (8) |
| O1–C3–C2 | 120.17 (8) |
| C4–C3–C2 | 119.61 (8) |
| C5–C4–C9 | 118.89 (8) |
| C5–C4–C3 | 122.89 (8) |
| C9–C4–C3 | 118.20 (8) |
| C6–C5–C4 | 120.27 (8) |
| C6–C5–H5 | 119.9 |
| C4–C5–H5 | 119.9 |
| C5–C6–C7 | 121.35 (8) |
| C5–C6–H6 | 119.3 |
| C7–C6–H6 | 119.3 |
| C6–C7–C8 | 117.50 (8) |
| C6–C7–C7 #1 | 121.54 (9) |
| C8–C7–C7 #1 | 120.96 (9) |
| C9–C8–C7 | 121.25 (8) |
| C9–C8–H8 | 119.4 |
| C7–C8–H8 | 119.4 |
| C8–C9–C4 | 120.64 (8) |
| C8–C9–H9 | 119.7 |
| C4–C9–H9 | 119.7 |
| N1–C10–C11 | 111.03 (8) |
| H10A–C10–H10B | 108.0 |
| C12–C11–C10 | 111.99 (9) |
| H11A–C11–H11B | 107.9 |
| C11–C12–C13 | 109.94 (9) |
| H12A–C12–H12B | 108.2 |
| C14–C13–C12 | 110.60 (9) |
| H13A–C13–H13B | 108.1 |
| N1–C14–C13 | 111.77 (8) |
| H14A–C14–H14B | 107.9 |
| Atom–Atom–Atom–Atom | Torsion Angle [°] |
|---|---|
| C10–N1–C1–C2 | 56.79 (11) |
| C14–N1–C1–C2 | −178.96 (8) |
| N1–C1–C2–C3 | 173.39 (8) |
| C1–C2–C3–O1 | 2.52 (14) |
| C1–C2–C3–C4 | −178.57 (8) |
| O1–C3–C4–C5 | 170.80 (10) |
| C2–C3–C4–C5 | −8.12 (14) |
| O1–C3–C4–C9 | −7.68 (15) |
| C2–C3–C4–C9 | 173.40 (9) |
| C9–C4–C5–C6 | 2.69 (15) |
| C3–C4–C5–C6 | −175.78 (9) |
| C4–C5–C6–C7 | −0.77 (16) |
| C5–C6–C7–C8 | −2.02 (14) |
| C5–C6–C7–C7 #1 | 178.07 (11) |
| C6–C7–C8–C9 | 2.94 (14) |
| C7 #1–C7–C8–C9 | −177.15 (10) |
| C7–C8–C9–C4 | −1.07 (15) |
| C5–C4–C9–C8 | −1.79 (14) |
| C3–C4–C9–C8 | 176.75 (9) |
| C1–N1–C10–C11 | 177.47 (8) |
| C14–N1–C10–C11 | 54.78 (11) |
| N1–C10–C11–C12 | −55.33 (12) |
| C10–C11–C12–C13 | 55.63 (13) |
| C11–C12–C13–C14 | −55.86 (12) |
| C1–N1–C14–C13 | 178.11 (8) |
| C10–N1–C14–C13 | −56.24 (11) |
| C12–C13–C14–N1 | 56.78 (12) |
| D–H⋯A [Å] | d(D–H) [Å] | d(H⋯A) [Å] | d(D⋯A) [Å] | <(DHA) [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2–H2C⋯O4 #1 | 0.851 (16) | 1.975 (17) | 2.824 (8) | 175 (3) |
| O2–H2D⋯Cl5 #2 | 0.829 (16) | 2.282 (18) | 3.079 (9) | 161 (3) |
| O3–H3A⋯Cl5 | 0.869 (15) | 2.120 (15) | 2.981 (4) | 171 (2) |
| O3–H3B⋯O2 #3 | 0.873 (15) | 2.023 (17) | 2.874 (9) | 165 (2) |
| O4–H4A⋯Cl5 | 0.833 (15) | 2.281 (15) | 3.079 (2) | 161 (2) |
| O4–H4B⋯O2 | 0.869 (15) | 2.095 (18) | 2.956 (9) | 171 (2) |
| O5–H5A⋯Cl4 | 0.806 (17) | 2.05 (2) | 2.820 (11) | 161 (3) |
| O5–H5B⋯Cl3 | 0.856 (17) | 2.166 (19) | 2.974 (6) | 157 (3) |
| N1–H1⋯O3 | 0.935 (14) | 1.802 (14) | 2.736 (4) | 175.4 (12) |
| N1–H1⋯Cl3 | 0.935 (14) | 2.063 (14) | 2.995 (4) | 174.1 (12) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, A.; Zhao, J.; Huls, N.J.; Zeller, M.; Wang, L.; Li, T. The Structural Basis of DL0410, a Novel Multi-Target Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Crystals 2024, 14, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010059
Liu A, Zhao J, Huls NJ, Zeller M, Wang L, Li T. The Structural Basis of DL0410, a Novel Multi-Target Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Crystals. 2024; 14(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ailin, Jun Zhao, Nicholas J. Huls, Matthias Zeller, Lin Wang, and Tonglei Li. 2024. "The Structural Basis of DL0410, a Novel Multi-Target Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease" Crystals 14, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010059
APA StyleLiu, A., Zhao, J., Huls, N. J., Zeller, M., Wang, L., & Li, T. (2024). The Structural Basis of DL0410, a Novel Multi-Target Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Crystals, 14(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14010059





