Abstract
A novel catalytic approach for the synthesis of symmetric and asymmetric azines has been developed. The environmentally benign protocol was achieved via condensation of 1-[(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (1) with different aromatic aldehydes 2a–h and acetyl heterocyclic compounds (4, 6, 8, 10, and 12) in the presence of cellulose sulfuric acid (CSA) as the green catalyst. These procedures offer an interesting method for the large-scale industrial manufacture of azines due to their high percentage yield, mild reaction conditions, broad substrate range, and utilization of an economical and environmentally acceptable catalyst. Additionally, the molecular docking of the products to the monoamine oxidase (MAO-A) target protein was achieved to highlight the possible binding interaction with the amino acid residues Arg51, Glu43, Gly22, Gly49, Gly443, Ala272, Ile335, and Tyr407 at the point of binding. The binding interaction energy was discovered to be (− 6.48 kcal/mol) for the protein MAO-A (PDB ID: 2Z5X). The most effective azine derivatives 7 and 13 revealed some major conserved interactions between the MAO-A protein’s binding site amino acid residues and the PDB co-crystal ligand 2Z5X. Moreover, azine derivatives 3a and 3f showed the lowest binding activity with the target MAO-A.
1. Introduction
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is overexpressed in dysthymia, which leads to neurological system disorders including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease and inhibits the amounts of monoaminergic transmitters, and as a result, the nerve system’s ability to communicate. MAO inhibitors can keep MAO levels within cells and in communication [1]. A significant enzyme called MAO, which is found on the membrane enclosing the mitochondria in neuronal cells, contains flavins. The C-terminal transmembrane polypeptide loop provides the connection [2], and it is inserted into the membrane via ubiquitin, with ATP acting as the source of energy [3], controlling monoaminergic homeostasis and perhaps neurotransmission in neuronal, glial, and other cells. The deficiency of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin, leads to depression and other mental problems. A key finding in the monoamine theory of depression was the discovery in the 1950s of the antidepressant effects of MAO inhibitors (MAOIs). However, earlier MAOIs that were used in care medicine were terminated because of unfavorable side effects, including hepatotoxicity, orthostatic hypotension, and the reported “cheese effect” that had hypertensive crises as its feature. The first-generation antidepressants being used were MAOIs, for decades, in the treatment for those who suffered from unusual depression [4], a tremendous range of depression, bipolar, anxiety resistant to therapy depression [5], specific phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and migraines that did not respond to other therapies [6]. The research of MAOIs was sparked by the unexpected result of antidepressant effects in patients taking iproniazid, a hydrazine-based antitubercular drug chemically related to isoniazid. This discovery, coupled with evidence that iproniazid was a potent MAOI [7], sparked the development of further MAOIs, such as phenelzine. Among the family of MAOs is monoamine oxidase A, which has the ability to accelerate the deamination of serotonin, noradrenaline, and adrenaline. Dopamine, tryptamine, and tyramine can also be metabolized by monoamine oxidases A [8]. Cordyline and other drugs are used to administer monoamine oxidases (MAO-A) [9], and moclobemide (MAO-A) [10]. The MAO-A inhibitor is suggested for the treatment of anxiety and depression in the brain [11,12,13]. An entirely new family of chemicals has emerged as a result of recent efforts to find reversible and selective MAOIs.
Sustainable green catalysts with environmental and economical advantageousness are considered to be of interest in the development of green chemistry. In synthetic organic chemistry, the utilization of green techniques is supportive to reduce the usage of hazardous toxic chemicals [14], minimize the reaction time, and increase selectivity [15]. That simplifies the purification and isolation of the isolated products rather than conventional methods [16]. Cellulose sulfuric acid (CSA) is an attractive sustainable candidate in green technology because it is a biodegradable material and has a renewable source. It has emerged as a biopolymeric solid support acid catalyst for the synthesis of pyridotriazolopyrimidines [17], dihydropyrimidinones [18], pyrazoles [19], and α-aminonitriles [20]. On the other hand, aldazines and ketazines with the conjugated hydrazone system (C=N–N=C) have been widespread and employed in pharmacological research and the industrial field. Both symmetric and asymmetric azines have revealed biological activities as antimicrobial [21], antibacterial [22], and antitumor [23] agents. In addition, azines were used as building blocks for the construction of nonlinear optical materials [24] and covalent organic frameworks (COFs) which served as chemo-sensing detectors [25].
Based on the aforementioned precedents and in continuation of our efforts in green chemistry research [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35], we have presently employed cellulose sulfuric acid as a catalyst for the synthesis of symmetric and asymmetric azines in this context. Additionally, it was also shown that molecular modelling may be used to estimate the binding affinity and determine the interactions of the tested compounds at the MAO-A (PDB: 2Z5X) binding site where the synthesized azines were established.
2. Results and Discussion
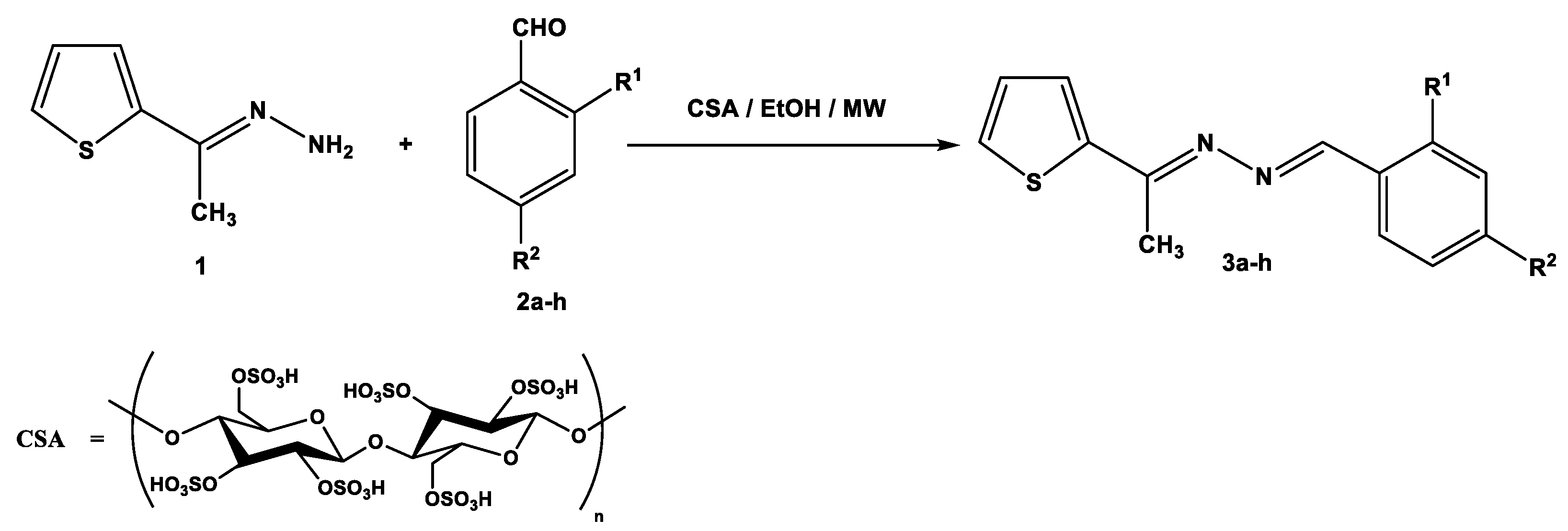
Recently, environmentally benign protocols for the condensation of carbonyl compounds and amines were achieved in the presence of meglumine [36], L-tyrosine [37], and citric acid [38] as green catalysts. These reports encouraged us to synthesize symmetric and asymmetric azines by using CSA as a biodegradable and reusable catalyst. Thus, the condensation of 1-[(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (1) with aromatic aldehydes 2a–h in ethanolic solution, containing 0.05 g of CSA, under microwave irradiation at 120 °C for 20–30 min, gave the corresponding azines 3a–h (Scheme 1). The required products were separated in good to excellent yields regardless of the kind of substituents (electron-withdrawing or electron-donating group). The reaction was slightly sensitive to the steric hindrance of 2-substituted benzaldehydes 2f–2h which decreased the reactivity and yield percentage of products 3f–3h (Table 1).
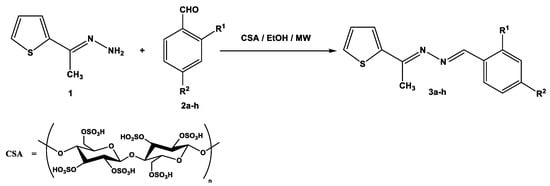
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of unsymmetric azines 3a–h.

Table 1.
Yield percentage of azine derivatives 3a–h.
The structural elucidation of azines 3a–h was characterized by elemental and spectroscopic data. In IR spectra, the stretching absorption of the (C=N) group was observed at about 1599–1904 cm−1. In the 1H-NMR spectra of compounds, the Schiff base proton (N=CH) was determined at about δ = 8.54–8.96 ppm and the aromatic protons were assigned at the expected region.
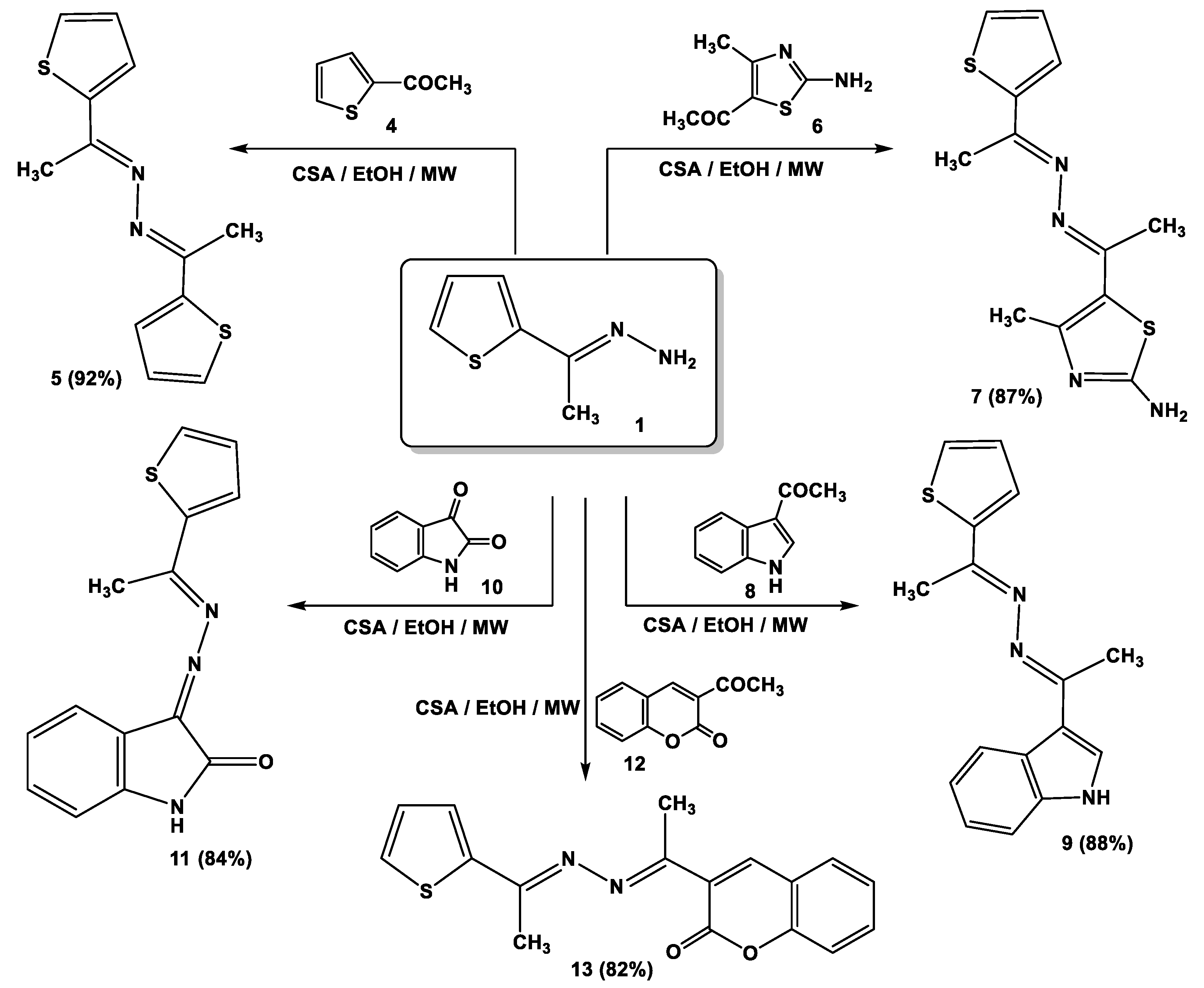
Notably, the catalytic activity of cellulose sulfuric acid was applicable for the preparation of symmetric and asymmetric ketazines. Thus, different acetyl heterocyclic compounds (4, 6, 8, 10, and 12) were subjected to react with 1-[(2-thienyl)ethylidene] hydrazine (1) under the employed conditions to give the respective bis-hydrazones (5, 7, 9, 11, and 13) in good yields (Scheme 2).
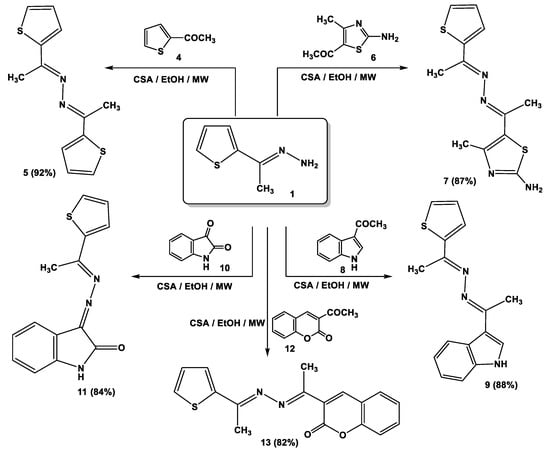
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of ketazine derivatives 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13.
3. Molecular Docking
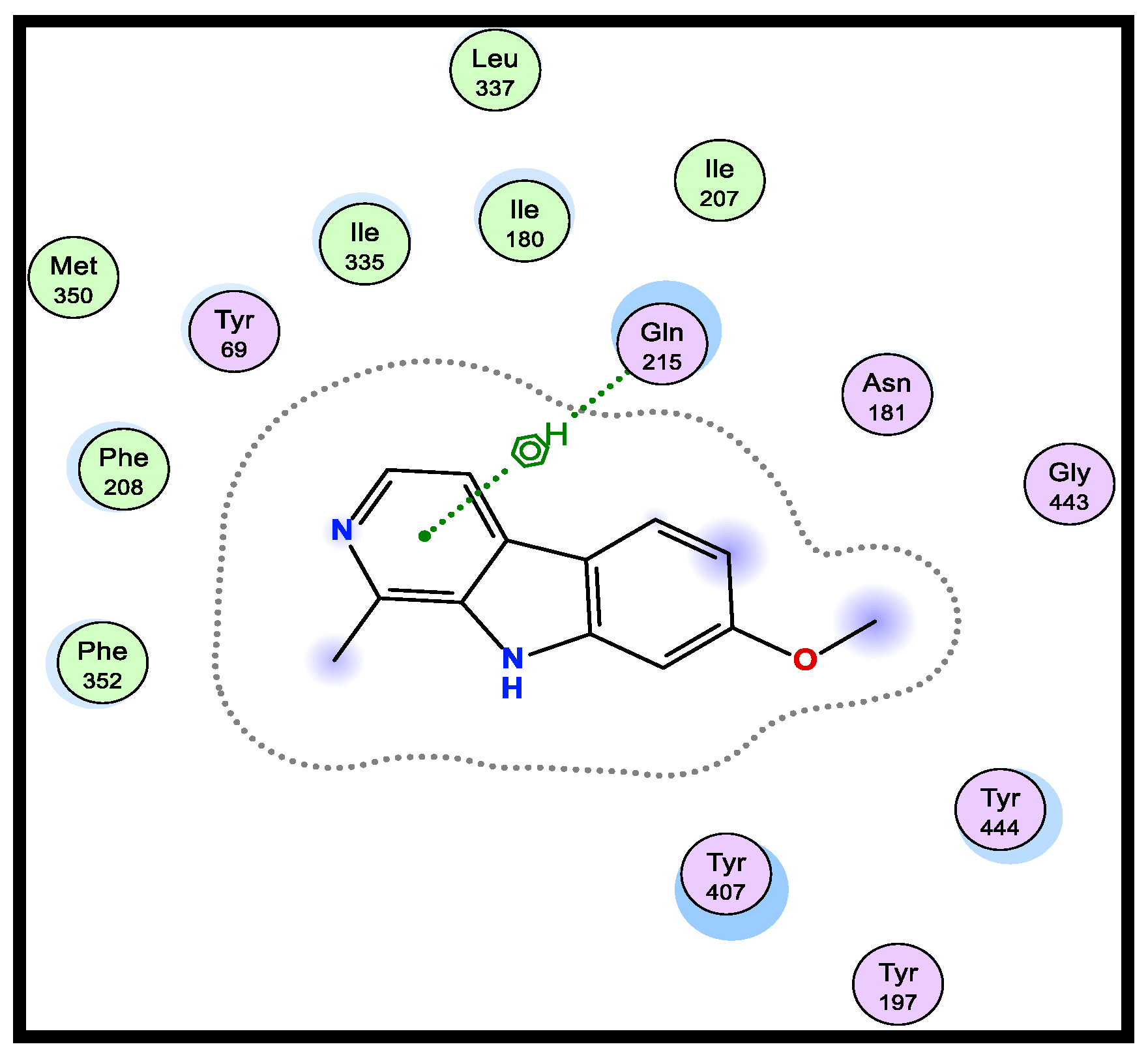
A version of the Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software 2015.10 was used to conduct the molecular docking and validated through the re-docking of the native ligand high-resolution melt (HRM) within the active site of MAO-A, giving docked scores of −6.48 kcal/mol with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) value of 0.84 A˚ between the docked configurations and the co-crystallized ligand. HRM demonstrated the important interactions with the residues at the active site of MAO-A (Figure 1).
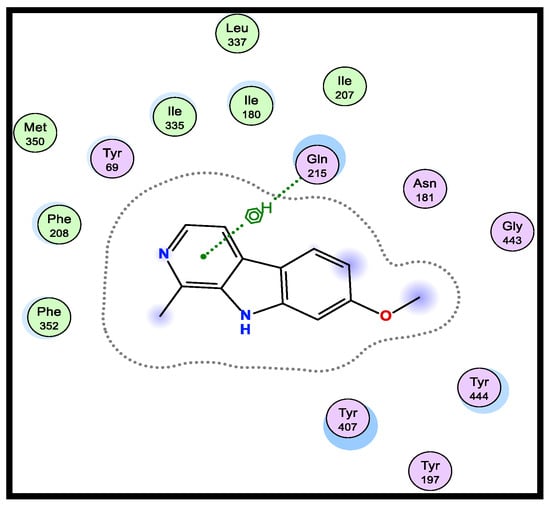
Figure 1.
2D-binding of HRM (a reference ligand) with MAO-A.
Therefore, using the native co-crystallized ligand HRM700 as a docking partner into the appropriate MAO-A binding sites, the verification of the MAO-A docking accuracy was examined (PDB: 2Z5X). After being re-docked into the binding site, the co-crystallized ligand HRM700 interacted hydrophobically with Gln215, an essential amino acid for MAO-A. Within an RMSD of 0.84 Å, this auto-dock success rate was extraordinarily good (Figure 1).
Hydrazones, as a moiety open chain with aryl or bioactive azoles, were reported as MAO-inhibiting agents [39,40]. The synthesized azines all showed excellent inhibitory potency and selectivity towards MAO-A in general. Molecular docking studies showed that the synthesized azines (3a–h, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13) have binding energy values between −8.09 and −6.36 kcal/mol. According to the molecular docking analysis, docking scores for compounds 7 and 13 were the highest (−7.32 kcal/mol and −8.09, respectively) (Table 2).

Table 2.
RMSD (A˚) and energy scores (kcal/mol) for azine derivatives (3a–h, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13) compared to the native ligand (HRM).
3.1. SAR Analysis for a Series of 1-(arylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3a–h)
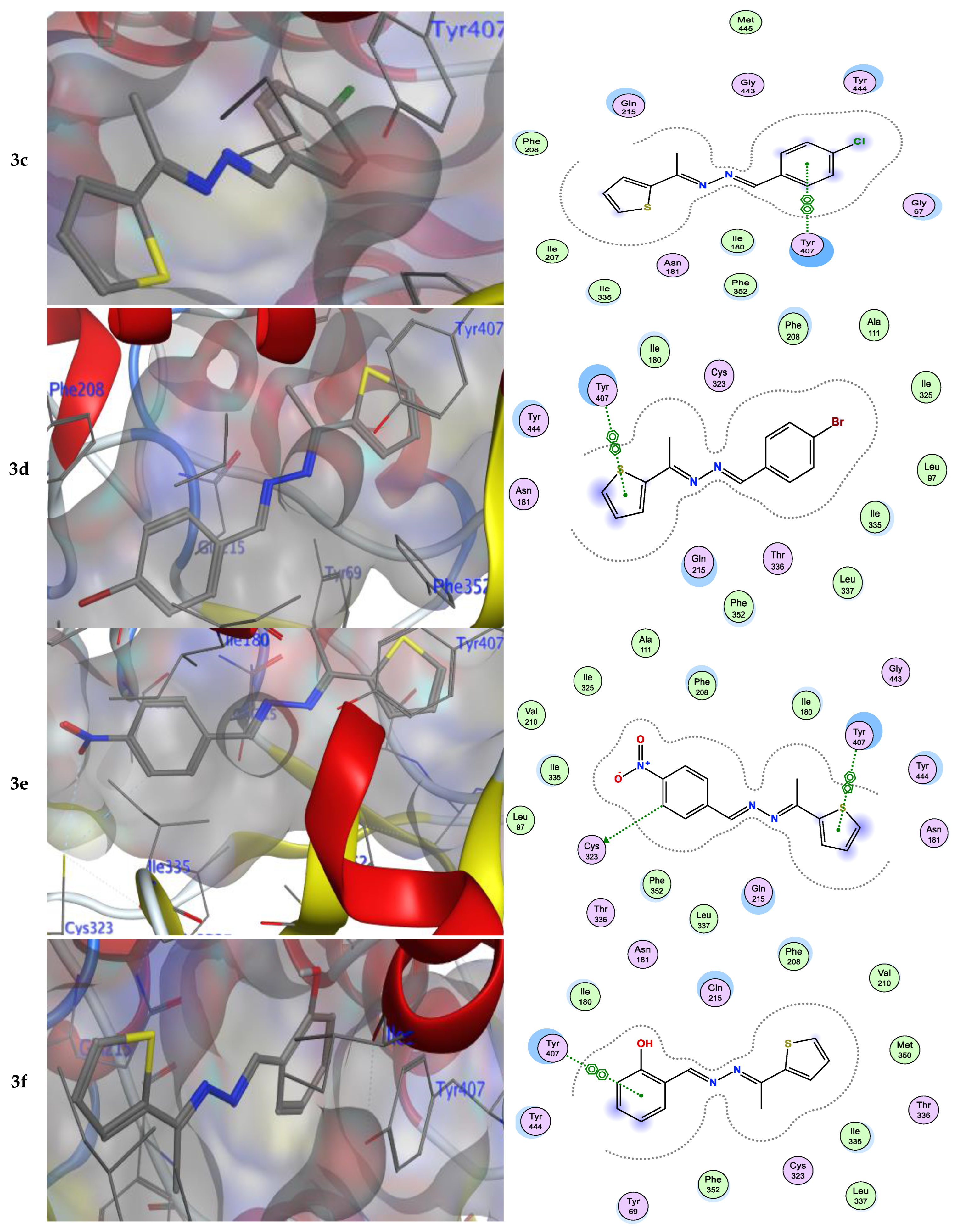
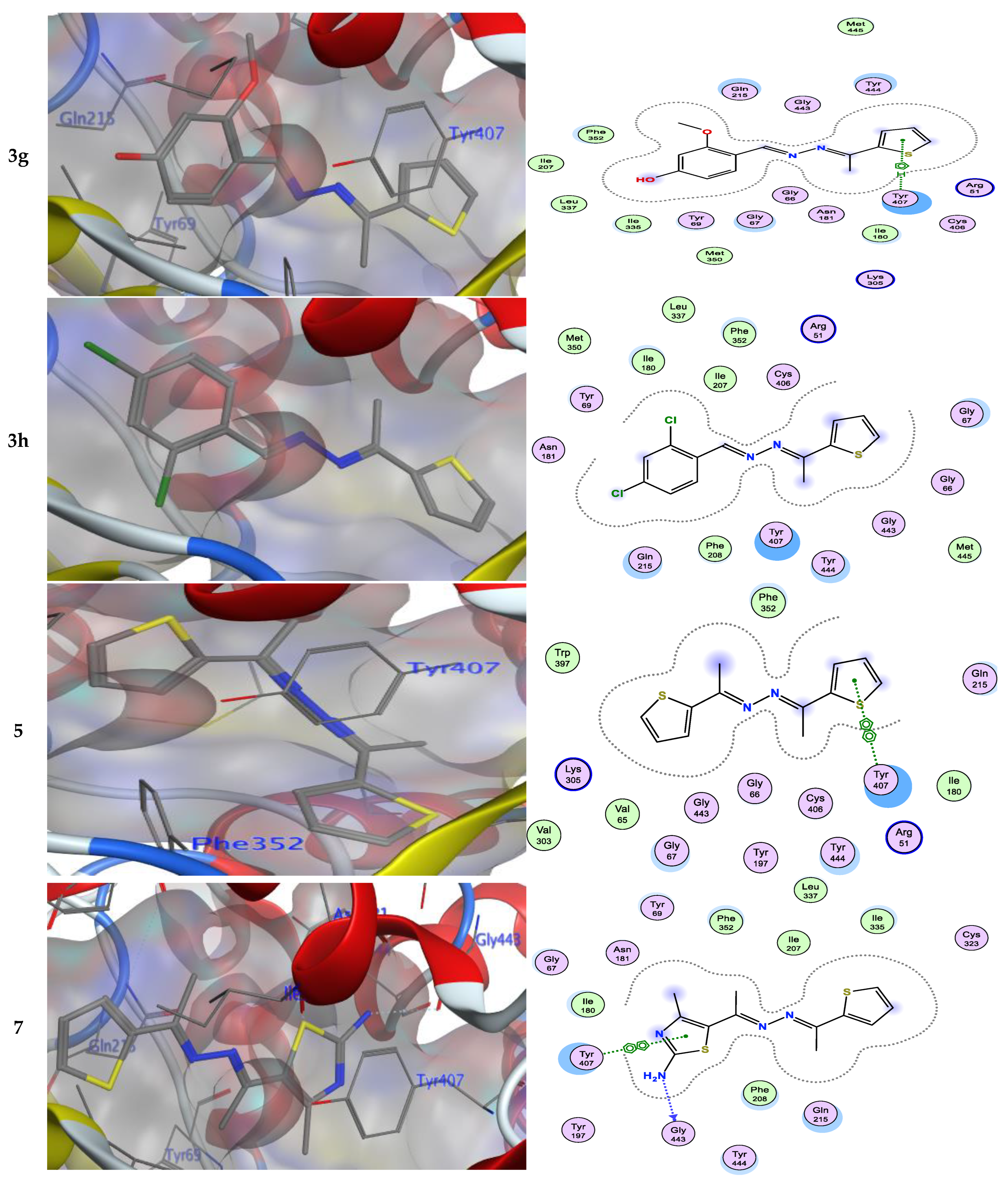
The substituted phenyl ring was preferred over an unsubstituted one. Thus, compound (3a) (−6.36 kcal/mol) displayed the least decrease in the activity for the investigated series. The para substitution of the electron-donating methoxy group (3b) (−7.16 kcal/mol) or electron-withdrawing moiety such as the NO2 group (3e) (−7.15 kcal/mol) was found to have a significant impact on the inhibition of the receptor. The activity indicated that the alkoxy (-OCH3)-substituted compound (3b) (−7.16 kcal/mol) was more active when compared to the halogen (Cl and Br)-substituted ones (3c and 3d) (−6.94 and −6.83 kcal/mol, respectively). The small size electron-withdrawing moiety of Cl was less than that of Br; thus, compound (3c) showed more activity than bulk compound (3d) (−6.94 and −6.83 kcal/mol, respectively). The presence of the hydroxy group at the ortho position in (3f) (−6.65 kcal/mol) derivative was not favorable for binding, and thus showed poor inhibition activity. The monosubstituted derivative (3c) (−6.94 kcal/mol) was a better MAO-A inhibitor as compared to the disubstituted one’s steric groups (3h) (−6.78 kcal/mol).
3.2. SAR Analysis for a Series of Symmetric and Asymmetric Azines (5, 7, 9, 11, and 13)
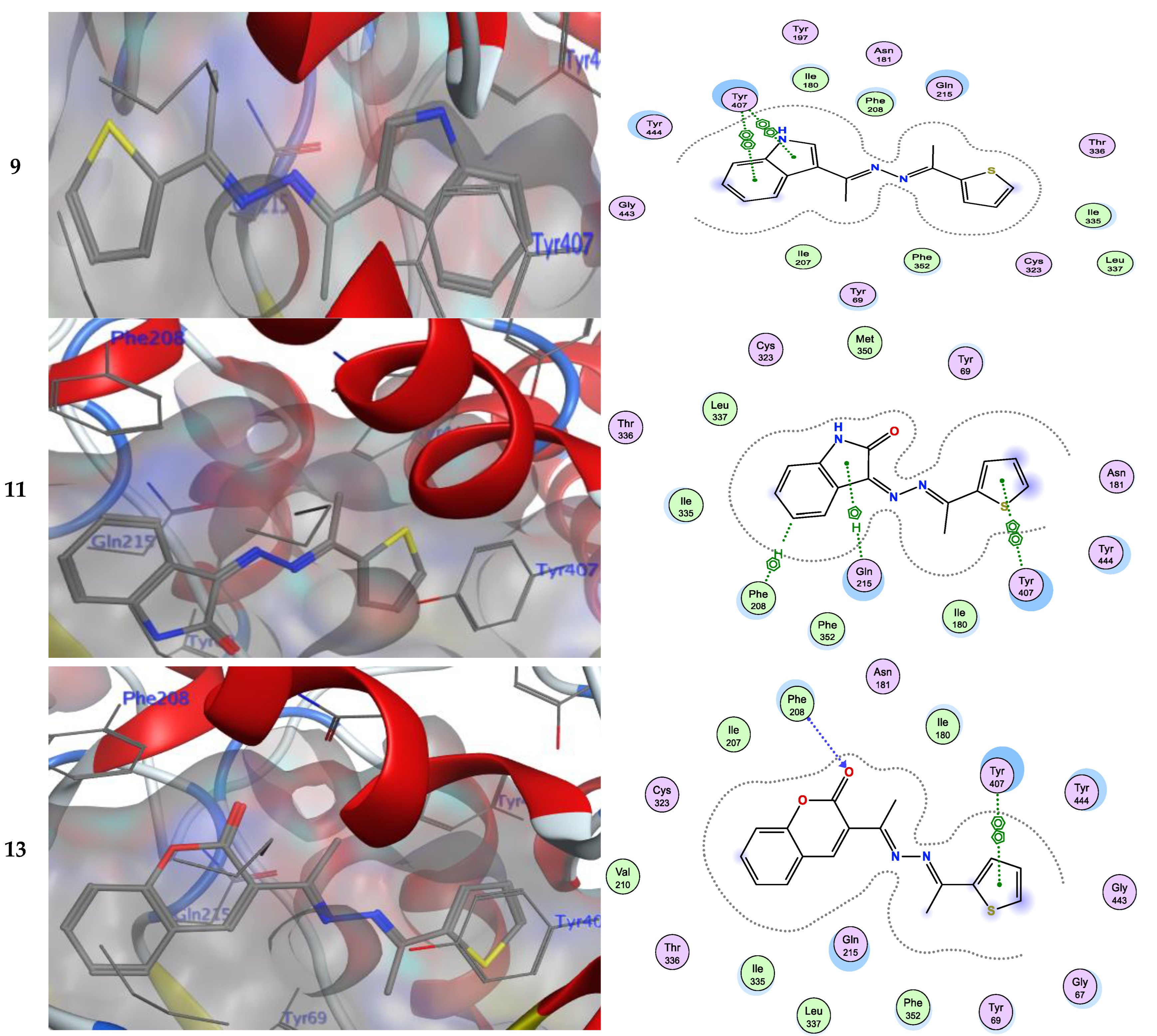
It was found that compound 7 (−7.32 kcal/mol), with different hetero atoms such as sulfur and nitrogen in the thiazole ring, had more inhibitory activity than compound 5 (−7.18 kcal/mol) possessing only the sulfur atom in the thiophen ring. From another structural viewpoint, the azine derivative 9 with indole moiety (−7.28 kcal/mol) exhibited improved inhibitory properties over compound 11 with isatin moiety (−7.19 kcal/mol) [41,42]. The most potent azine derivative was compound 13 because the synthetic coumarin derivative has been characterized as MAOIs [43,44].
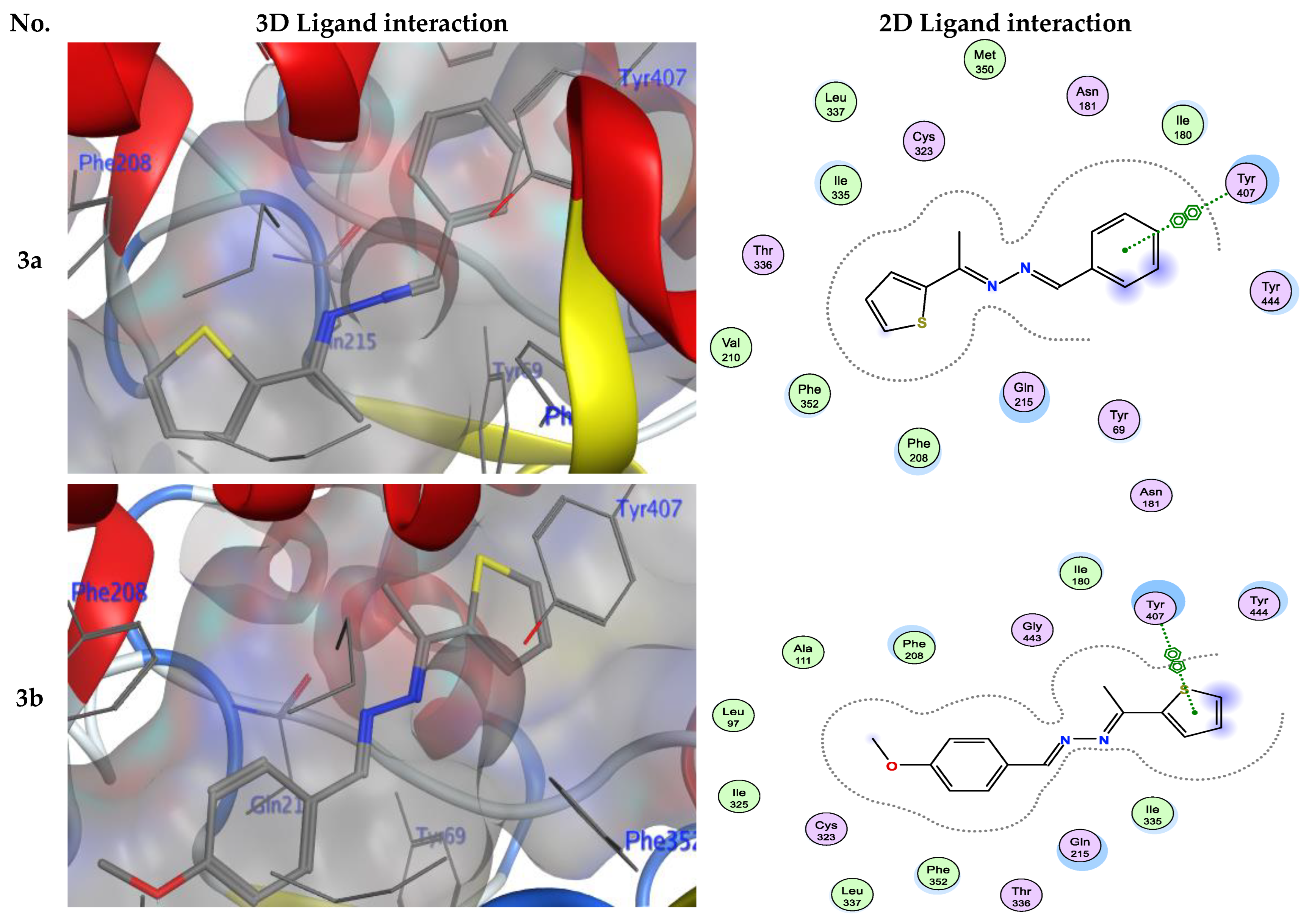
Numerous hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between the azine derivatives and the receptor’s active residues were the cause of the binding affinity as shown in Figure 2. As demonstrated, compounds 3a, 3c, 3f and 3b, 3d, 3e, 5, and 13 provided the π-π interaction between the phenyl and thiophene ring with the essential amino acid Try407, respectively. Additionally, in compound 3e, the carbon atom of the phenyl ring interacted as an H-bond donor with the Cys323. Moreover, compound 3g showed the π-H interaction between the thiophene ring with the essential amino acid Try407. The 3D model of the binding mode of compound 7 showed one H-bond was between the nitrogen of the amino group afforded the H-bond donor and the use of the side chain of Gly443, and additionally the π-π interaction between the thiazole ring and the essential amino acid Try407. As demonstrated, compound 9 provided two π-π interactions between the indole ring and Try407. The 3D model of the binding mode of compound 11 showed three π- interactions, one of which was between the thiophene ring and permitted the π-π to utilize the side chain of Try407, and the other two π-H interactions were between indolin-2-one moiety and the side chain of Gln215 and Phe208. Moreover, compound 13 showed the H-bond acceptor between the oxygen atom of coumarin moiety and the side chain of Phe208. The results showed that the examined ligands were positioned and oriented similarly inside the predicted binding site of HRM (Figure 2).
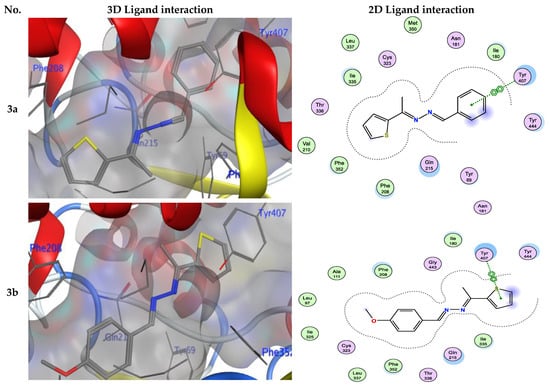
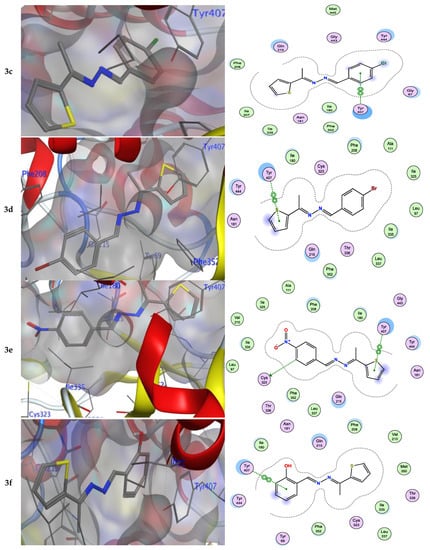
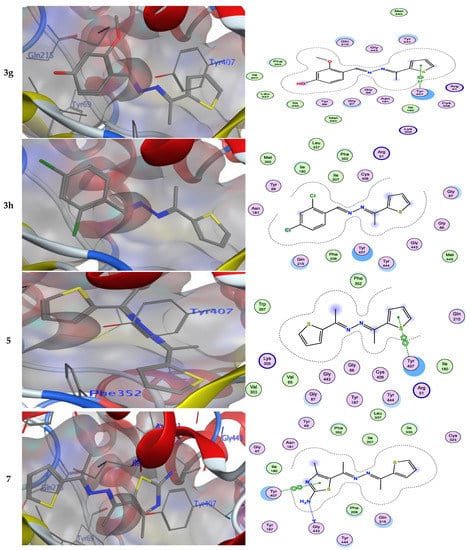
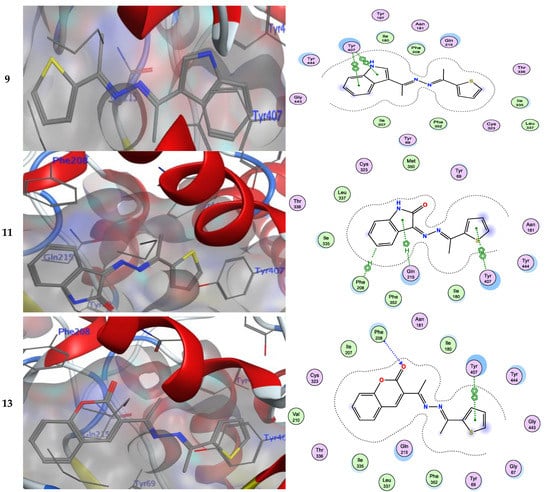
Figure 2.
3D- and 2D-ligand interactions within the binding site of 2Z5X for azine derivatives (3a–h, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13).
4. Experimental Section
The 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were measured using a Varian Mercury VXR-300 spectrometer (300 MHz and 75 MHz for 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR, respectively). The melting temperatures of the newly formed azine derivatives were measured using an electrothermal Gallenkamp device. The mass spectra of the azine derivatives were measured using a GCMS 5988-A HP spectrometer at 70 eV of ionizing voltage. IR spectra were measured using a Pye-Unicam SP300 device in KBr discs. The CEM Discover Labmate microwave device was used for the microwave tests (Discover, SP, NC, USA, 300 W). At the Microanalytical Center at Cairo University in Giza, Egypt, elemental studies were performed.
4.1. General Reactions of 1-[(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (1) with Aldehydes (2a–h) or Ketones (4, 6, 8, 10, and 12)
The 1-[(2-Thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (1) (0.14 g, 1 mmol) was allowed to react with arylaldehydes (2a–h) or acetylthiophene (4), or 2-amino-4-methyl-5-acetylthiazole (6) or 3-acetylindole (8), or isatin (10) or 3-acetylcoumarine (12) (1 mmol of each) in EtOH (10 mL) containing 0.05 g of CSA. The reaction mixture was irradiated by MW at 120 °C in a closed Teflon vessel until completeness (20–30 min). CSA was carefully removed by filtration of the hot solution. The excess solvent was removed, and the reaction mixture was triturated with methanol. The separated product was then filtered and finally recrystallized from EtOH to give the products 3a–h or 5 or 7 or 9 or 11 or 13, respectively.
- 1-(Benzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3a)
Pale yellow crystals, mp 117–120 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2917 (CH), 1602 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 228 (M+, 30); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.48 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.42–7.86 (m, 8H, Ar-H), 8.68 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.3 (CH3), 123.4, 125.8, 127.5, 128.9, 129.7, 130.2, 134.1, 143.8, 158.4, 162.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H12N2S (228.07): C, 68.39; H, 5.03; N, 12.27; S, 14.04. Found: C, 68.44; H, 4.92; N, 12.41; S, 14.18%.
- 1-(4-Methoxybenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3b)
Yellow crystals, mp 159–161 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2919 (CH), 1601 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 258 (M+, 43); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.49 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.78 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.01–7.78 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 8.59 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.3 (CH3), 56.1 (OCH3), 114.9, 127.1, 128.2, 129.7, 130.1, 130.5, 144.2, 157.5, 160.9, 162.2 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C14H14N2OS (258.08): C, 65.09; H, 5.46; N, 10.84; S, 12.41. Found: C, 64.94; H, 5.22; N, 10.71; S, 12.58%.
- 1-(4-Chlorobenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3c)
Pale yellow crystals, mp 207–209 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2921 (CH), 1599 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 262 (M+, 18); 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ = 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.11–7.87 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 8.68 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 15.7 (CH3), 124.4, 125.6, 127.4, 128.8, 129.5, 131.1, 134.5, 144.2, 158.8, 162.7 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H11ClN2S (262.03): C, 59.43; H, 4.22; N, 10.66; S, 12.20. Found: C, 59.54; H, 4.12; N, 10.40; S, 12.38%.
- 1-(4-Bromobenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3d)
Pale yellow crystals, mp 228–230 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2918 (CH), 1600 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 305 (M+, 12); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.11–7.87 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 8.67 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.8 (CH3), 124.8, 125.7, 127.9, 128.5, 130.1, 132.1, 134.2, 145.2, 158.7, 162.9 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H11BrN2S (305.98): C, 50.83; H, 3.61; N, 9.12; S, 10.44. Found: C, 50.69; H, 3.52; N, 9.24; S, 10.32%.
- 1-(4-Nitrobenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3e)
Brown crystals, mp 285–287 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2917 (CH), 1601 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 273 (M+, 32); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.52–8.34 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 8.68 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.7 (CH3), 124.4, 125.8, 126.5, 127.9, 129.3, 133.2, 138.1, 144.8, 157.8, 162.6 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H11N3O2S (273.06): C, 57.13; H, 4.06; N, 15.37; S, 11.73. Found: C, 57.34; H, 3.92; N, 15.41; S, 11.88%.
- 1-(2-Hydroxybenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3f)
Yellow crystals, mp 173–175 °C IR (KBr) υ = 3420 (OH), 2920 (CH), 1604 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 244 (M+, 28); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.36 (s, 3H, CH3), 6.93–7.66 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 8.96 (s, 1H, CH=N), 11.12 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.9 (CH3), 118.9, 123.1, 124.2, 125.8, 126.7, 128.1, 130.5, 132.2, 133.8, 156.5, 160.1, 163.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H12N2OS (244.07): C, 63.91; H, 4.95; N, 11.47; S, 13.12. Found: C, 63.74; H, 5.12; N, 11.61; S, 13.28%.
- 1-(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3g)
Yellow crystals, mp 144–146 °C IR (KBr) υ = 3425 (OH), 2918 (CH), 1602 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 274 (M+, 46); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.78 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.40–8.54 (m, 6H, Ar-H), 8.66 (s, 1H, CH=N), 11.32 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.8 (CH3), 56.8 (OCH3), 108.9, 112.1, 116.7, 124.2, 125.8, 126.7, 128.1, 130.5, 133.8, 155.8, 160.1, 164.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C14H14N2O2S (274.08): C, 61.29; H, 5.14; N, 10.21; S, 11.69. Found: C, 61.44; H, 5.19; N, 10.41; S, 11.48%.
- 1-(2,4-Dichlorobenzylidene)-2-[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (3h)
Yellow crystals, mp 108–110 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2921 (CH), 1599 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 295 (M+, 16); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.48 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.10–7.62 (m, 6H, Ar-H), 8.54 (s, 1H, CH=N); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.4 (CH3), 124.4, 125.4, 126.2, 127.5, 128.1, 128.7, 129.5, 130.1, 131.5, 134.2, 158.8, 162.7 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C13H10Cl2N2S (295.99): C, 52.54; H, 3.39; N, 9.43; S, 10.79. Found: C, 52.44; H, 3.22; N, 9.52; S, 10.88%.
- 1,2-Bis[1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine (5)
Orange powder, mp 97–99 °C, lit mp = 95–96 °C [45]; IR (KBr) υ = 2918 (CH), 1596 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 248 (M+, 6); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.36 (s, 6H, 2CH3), 7.09–7.61 (m, 6H, Ar-H); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.2 (CH3), 125.5, 126.9, 128.7, 129.2, 162.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C12H12N2S2 (248.04): C, 58.03; H, 4.87; N, 11.28; S, 25.82. Found: C, 58.14; H, 4.92; N, 11.42; S, 25.68%.
- 4-Methyl-5-{1-[((1-(2-thienyl)ethylidene)hydrazono]ethyl}thiazol-2-amine (7)
Yellow crystals, mp 95–97 °C IR (KBr) υ = 3342, 3218 (NH2), 2923 (CH), 1601 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 278 (M+, 30); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.35 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.36 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.11–7.73 (m, 5H, Ar-H + NH2); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 14.9 (CH3), 15.3 (CH3), 16.9 (CH3), 124.8, 125.5, 126.9, 127.7, 128.2, 129.6, 131.2, 160.4, 162.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C12H14N4S2 (278.07): C, 51.77; H, 5.07; N, 20.13; S, 23.03. Found: C, 51.64; H, 4.99; N, 20.31; S, 23.18%.
- 3-{1-[((1-(2-Thienyl)ethylidene)hydrazono]ethyl}-1H-indole (9)
Yellow crystals, mp 284–286 °C IR (KBr) υ = 3214 (NH), 2920 (CH), 1600 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 281 (M+, 24); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.42 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.48 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.12–8.48 (m, 8H, Ar-H), 11.39 (s, 1H, NH); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.4 (CH3), 16.1 (CH3), 112.1, 116.6, 120.8, 122.6, 123.6, 125.6, 126.4, 127.8, 128.4, 129.3, 130.4, 137.7, 158.3, 160.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C16H15N3S (281.10): C, 68.30; H, 5.37; N, 14.93; S, 11.39. Found: C, 68.14; H, 5.19; N, 14.81; S, 11.19%.
- 3-{[(1-(2-Thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazono}indolin-2-one (11)
Orange crystals, mp 196–198 °C IR (KBr) υ = 3210 (NH), 2922 (CH), 1660 (C=O), 1599 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 269 (M+, 51); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 6.93–7.33 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 10.63 (s, 1H, NH); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.8 (CH3), 120.1, 125.9, 126.8, 127.6, 128.6, 129.6, 130.4, 131.8, 132.4, 137.7, 139.4, 141.3, 160.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C14H11N3OS (269.06): C, 62.44; H, 4.12; N, 15.60; S, 11.90. Found: C, 62.64; H, 4.19; N, 15.81; S, 12.09%.
- 3-{1-[1-((2-Thienyl)ethylidene)hydrazono]ethyl}-2H-chromen-2-one (13)
Orange crystals, mp 221–223 °C IR (KBr) υ = 2917 (CH), 1703 (C=O), 1604 (C=N) cm−1; MS, m/z (%) 310 (M+, 25); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ = 2.42 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.44–8.79 (m, 8H, Ar-H); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ = 15.6 (CH3), 16.4 (CH3), 116.1, 118.6, 119.8, 123.8, 124.6, 125.6, 126.6, 127.4, 128.8, 129.4, 130.3, 132.4, 147.7, 158.3, 161.5 (Ar-C and C=N). Anal. calcd for C17H14N2O2S (310.08): C, 55.79; H, 4.55; N, 9.03; S, 10.33. Found: C, 55.84; H, 4.69; N, 9.18; S, 10.19%.
4.2. Molecular Docking
Chemdraw 12.0 was used to sketch out the chemical structures of the most active compounds. To further refine the findings, London dG force and force field energy were employed. Using Merck molecular force field 94 (MMFF 94), all minimizations were carried out until an RMSD gradient of 0.1 kcal·mol−1Å−1 was reached. The MOE software’s scoring function and dock function (S, kcal/mol) were used to assess the ligand’s binding affinity. The protein data bank was used to download the X-ray crystal structure of the enzyme in PDB format (PDB ID: 2Z5X, resolution: 2.2 Å) [46]. The enzyme was prepared for docking studies: (i) The waters were eliminated from the protein. (ii) The structure was then supplied with hydrogen atoms in their typical geometries, then the broken bonds were reconnected and the potential fixed [47]. (iii) MOE Alpha Site Finder was utilized for the large site search in the enzyme structure, and dummy atoms were generated from the alpha spheres that were produced [48]. (iv) The interaction of the ligand with the amino acids of the active site was analyzed. The active ligands’ largest negative value yielded the highest docking score. All docking procedures and scoring were recorded according to established protocols [49,50,51]. Overall docking results were compared to the crystal structure of the bound natural ligand-protein complex (HRM700). The London dG score tool and Triangle Matcher placement method were used for docking. After docking, the 2D and 3D interactions with residues of amino acids were visualized.
5. Conclusions
Novel series of symmetric and asymmetric azines have been synthesized via the condensation of 1-[(2-thienyl)ethylidene]hydrazine with different aromatic aldehydes and acetyl heterocyclic compounds in the presence of CSA as green catalysts with environmental and economical advantageousness. The attractive features of this protocol are the mild reaction conditions, high percentage yield, wide substrate scope, and use of an inexpensive and environmentally friendly catalyst, all of which make it an attractive strategy for the large-scale industrial preparation of azines. Additionally, the binding interaction energies between azines and the monoamine oxidase (MAO-A) target protein were determined using molecular docking techniques. The ligand in discussion exhibits a binding interaction energy of (−6.48 kcal/mol) for protein 2Z5X. The visual representation of the intermolecular interactions between the designated ligand and protein is investigated.
Author Contributions
S.M.G., S.M.R. and B.F.: Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Formal analysis, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing; R.A.K.A., M.E.A.Z. and T.Z.A.: Resources, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Leonetti, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Stefanachi, A.; Campagna, F.; Carotti, A. Targeting monoamine oxidases with multipotent ligands: An emerging strategy in the search of new drugs against neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4568–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoma, J.-Y.; Ito, A. Mitochondrial targeting signal of rat liver monoamine oxidase B is located at its carboxy terminus. J. Biochem. 1992, 111, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Marks, B.; Mc-Cauley, R.B. The insertion of monoamine oxidase A into the outer membrane of rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletscher, A. The discovery of antidepressants: A winding path. Experientia 1991, 47, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thase, M.E. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in depression treatment guidelines. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareri, P.; Falconi, U.; De Fazio, P.; De Sarro, G. JPin. Conventional and new antidepressant drugs in the elderly. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 61, 353–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeller, E.; Barsky, J. In vivo inhibition of liver and brain monoamine oxidase by 1-Isonicotinyl-2-isopropyl hydrazine. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1952, 81, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.J.; Mantle, T.J.; Tipton, K.F. The nature of the inhibition of rat liver monoamine oxidase types A and B by the acetylenic inhibitors clorgyline, l-deprenyl and pargyline. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1982, 15, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, A.N.; Mirzaei, M. Flavonoid derivatives for monoamine oxidase–A inhibition. Adv. J. Chem. B 2019, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesura, A.M.; Pletscher, A. The new generation of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Prog. Drug. Res. 1992, 38, 171–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrey, M.G.; Gomha, S.M.; Arafa, W.A.A.; Abdulla, M.M. An approach to polysubstituted triazipines, thiadiazoles and thiazoles based on benzopyran moiety through the utility of versatile hydrazonoyl halides as in vitro monoamine oxidase inhibitors. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Yasuhara, H. Clinical pharmacology of MAO inhibitors: Safety and future. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cue, B.W. Green Techniques for Organic Synthesis and Medicinal Chemistry; A John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J. Organic reaction in aqueous media with a focus on carbon-carbon bond formations: A decade update. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3095–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, G.W.V.; Raston, C.L.; Scott, J.L. Recent advances in solventless organic reactions towards benign synthesis with remarkable versatility. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M. Cellulose Sulfuric Acid as an Eco-Friendly Catalyst for Novel Synthesis of Pyrido[2,3-d][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidin-5-ones. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.N.; Reddy, Y.T.; Reddy, M.M.; Rajitha, B.; Crooks, P.A. Cellulose Sulfuric Acid: An Efficient Biodegradable and Recyclable Solid Acid Catalyst for the One-Pot Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-ones. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, M.A.; Salmi, M.; Esmaeili, A.A. Cellulose sulfuric acid as a bio-supported and efficient solid acid catalyst for synthesis of pyrazoles in aqueous medium. RCS Adv. 2014, 4, 61139–61199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, A.; Maleki, A. Cellulose sulfuric acid as a bio-supported and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the one-pot three-component synthesis of a-amino nitriles. App. Cat. A Gen. 2007, 331, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, K.; Ramaiah, M.; Shashikaladevi, K.; Avinash, T.S.; Vaidya, V.P. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of asymmetrical azines derived from naphtho[2,1-b]furan. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Veena, K.; Ramaiah, M.; Vanita, G.K.; Avinash, T.S.; Vaidya, V.P. Synthesis of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Azines Encompassing Naphtho[2,1-b]furan by a Novel Approach. E.-J. Chem. 2011, 8, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xia, J.; Lei, D.; Li, X.; Yao, Q.; Gao, J. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of symmetrical bis-Schiff base derivatives of isatin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choytun, D.D.; Langlois, L.D.; Johansson, T.P.; Macdonald, C.L.B.; Leach, G.W.; Weinberg, N.; Clyburne, J.A.C. Azines possessing strong push–pull donors/acceptors. Chem. Commun. 2004, 16, 1842–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, S.; Jin, S.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Nagai, A.; Jiang, D. An Azine-Linked Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17310–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.A.; Riyadh, S.M.; Al-Kaff, N.; Nayl, A.A.S.; Khalil, K.D.; Bräse, S.; Gomha, S.M. Synthesis and greener pastures biological study of bis-thiadiazoles as potential covid-19 drug candidates. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Melha, S.; Gomha, S.M.; Abouzied, A.S.; Edrees, M.M.; Abo Dena, A.S.; Muhammad, Z.A. Microwave-assisted one pot three-component synthesis of novel bioactive thiazolyl-pyridazinediones as potential antimicrobial agents against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Molecules 2021, 26, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Melha, S.; Edrees, M.M.; Riyadh, S.M.; Abdelaziz, M.R.; Elfiky, A.A.; Gomha, S.M. Clean grinding technique: A facile synthesis and in silico antiviral activity of hydrazones, pyrazoles, and pyrazines bearing thiazole moiety against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Molecules 2020, 25, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.R.; Gomha, S.M.; Taher, E.A.; Muhammad, Z.A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Gaber, H.M.; Ahmed, M.M. One-pot synthesis of novel thiazoles as potential anti- cancer agents. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M. Synthesis of triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazines and triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazines using chitosan as ecofriendly catalyst under microwave irradiation. Arkivoc 2009, 11, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashdan, H.R.M.; Gomha, S.M.; El-Gendey, M.S.; El-Hashash, M.A.; Soliman, A.M.M. Eco-friendly one-pot synthesis of some new pyrazolo[1,2-b]phthalazinediones with antiproliferative efficacy on human hepatic cancer cell lines. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Abdelaziz, M.; Serag, N. Eco-friendly one-pot synthesis and antiviral evaluation of pyrazolyl pyrazolines of medicinal interest. Turk. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M.; Mahmmoud, E.A.; Elaasser, M.M. Synthesis and anticancer activities of thiazoles, 1,3-thiazines, and thiazolidine using chitosan-grafted-poly(vinylpyridine) as basic catalyst. Heterocycles 2015, 91, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, H.K.; Gomha, S.M.; Abdelhady, H.A.; Elaasser, M.M.; Hassain, D.Z.H. Microwave-assisted one-pot three component synthesis of some thiazolyl(hydrazonoethyl)thiazoles as potential anti-breast cancer agents. Polycyc. Aromat. Compd. 2022, 42, 7232–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Gomha, S.M.; Ahmed, H.A. Three-component synthesis of some new coumarin derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 762248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shang, Z.-R.; Li, X.-T.; Zhang, J.-N.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H. A simple and efficient approach for synthesis of hydrazones from carbonyl compounds and hydrazides catalyzed by meglumine. Synth. Commun. 2017, 47, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Hao, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Hua, Y. A Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of N-Arylsulfonylhydrazone Compounds. Heterocycl. Commun. 2019, 25, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinore, J.M.; Yelwande, A.A.; Palve, M.P.; Sapkal, A.V. Citric Acid Catalyzed Synthesis of Hydrazones Schiff Bases of 2,4-Dinirtophenyl Hydrazine. Int. J. Pharm. Pham. Res. 2016, 6, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, A.; Khan, K.M.; Ateeq, H.S.; Khan, S.; Rahat, S.; Perveen, S.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase–A activity in rat brain by synthetic hydrazines: Structure-activity relationship (SAR). J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2005, 20, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, D.; Carradori, S.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Yáñez, M.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S. Synthesis and selective human monoamine oxidase inhibition of 3-carbonyl, 3-acyl, and 3-carboxyhydrazido coumarin derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4846–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Regina, G.; Silvestri, R.; Gatti, V.; Lavecchia, A.; Novellino, E.; Befani, O.; Turini, P.; Agostinelli, E. Synthesis, structure–activity relationships and molecular modeling studies of new indole inhibitors of monoamine oxidases A and B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9729–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, L.H.; Petzer, J.P.; Malan, S.F. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by indole and benzofuran derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4458–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.J.; Viña, D.; Picciau, C.; Orallo, F.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Synthesis and evaluation of 6-methyl-3-phenylcoumarins as potent and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5053–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenti, F.; Secci, D.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Bizzarri, B.; Granese, A.; Carradori, S.; Yanez, M.; Orallo, F.; Ortuso, F.; et al. Synthesis, molecular modeling, and selective inhibitory activity against human monoamine oxidases of 3-carboxamido-7-substituted coumarins. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alali, A.; Al-Kamali, A.S. Reactions of 1,3-dipolar aldazines and ketazines with the dipolarophile dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate. Can. J. Chem. 2002, 80, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-Å resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdúch, M.; Havlíèek, L.; Veselý, J.; Novotný, R.; Mihál, V.; Strnad, M. Synthetic cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 457, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Labute, P. Protonate3D: Assignment of ionization states and hydrogen coordinates to macromolecular structures. Proteins 2009, 75, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan, S.W.; Nafie, M.S.; Elmgeed, G.A.; Alelwani, W.; Badar, M.; Tantawy, M.A. Molecular docking, anti-proliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in human liver cancer cells treated with androstane derivatives: Implication of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 198, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, M.A.; Sroor, F.M.; Mohamed, M.F.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Saleh, F.M.; Hassaneen, H.M.; Abdelhamid, I.A. Molecular docking study, cytotoxicity, cell cycle arrest and apoptotic induction of novel chalcones incorporating thiadiazolyl isoquinoline in cervical cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, M.S.; Tantawy, M.A.; Elmgeed, G.A. Screening of different drug design tools to predict the mode of action of steroidal derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Steroids 2019, 152, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).