Wetting of Graphite and Platinum Substrate by Oxide System with Graded B2O3 Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Samples
2.2. Determination of Liquidus Temperatures
2.3. High-Temperature Wettability Test
2.4. SEM, EDX, FTIR, and XRD Methods
3. Results and Discussion
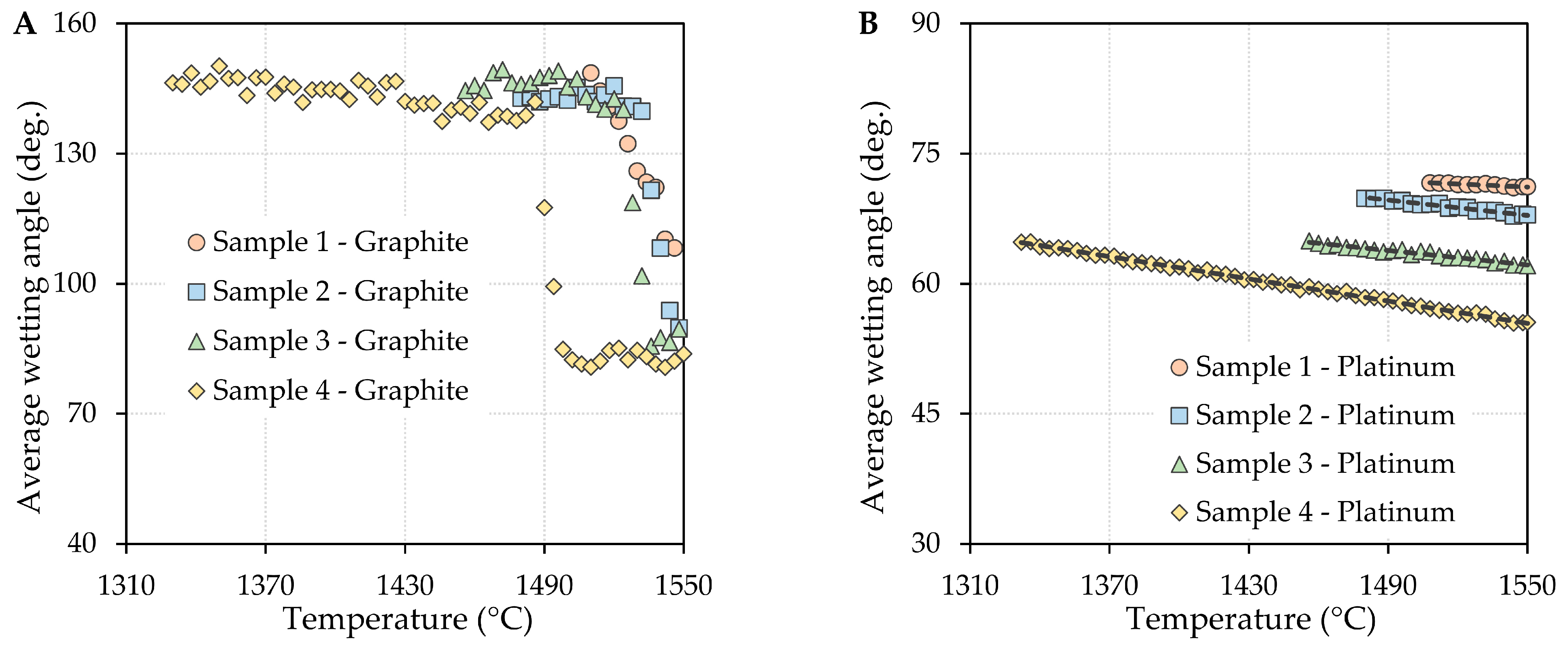
3.1. Determination of Wetting Angles
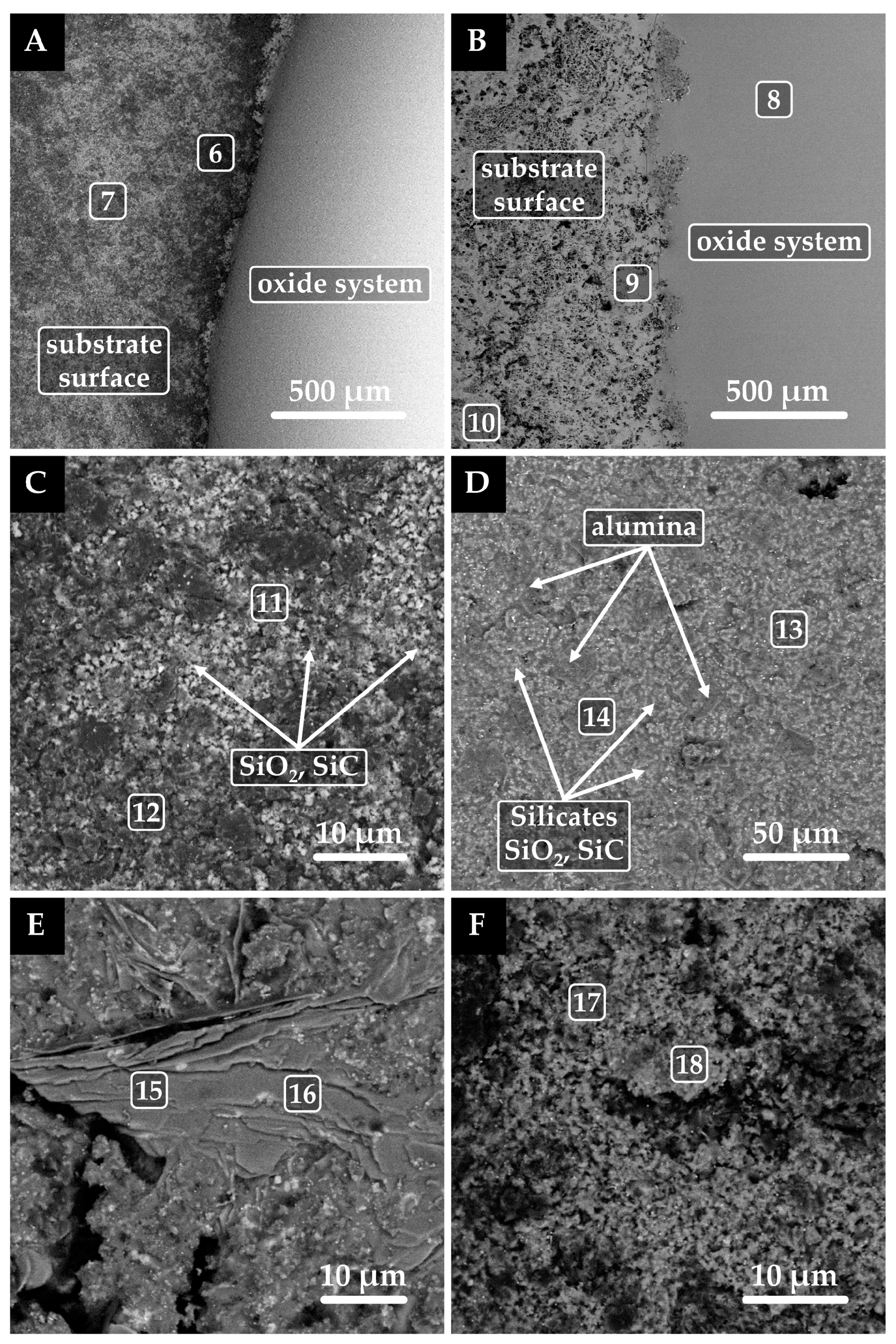
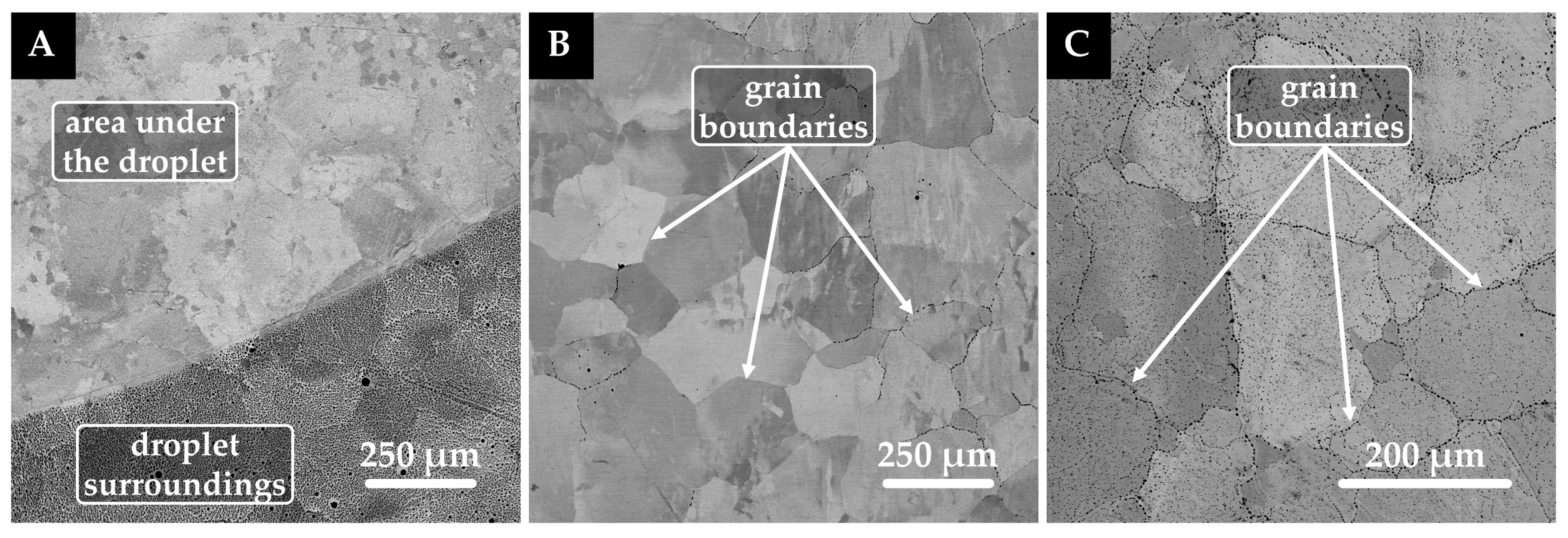
3.2. Oxide System/Graphite (Platinum) Substrate Interaction
4. Conclusions
- The contact angle values decreased with increasing temperature for the oxide system/graphite substrate system, and the effect of the boric oxide content on the contact angle values was negligible. The wetting of the graphite substrate by the investigated oxide system can be considered reactive. The strong interaction of the two contacting phases was accompanied by the formation of reaction products at the phase interface, and the interaction intensity increased with increasing boron oxide content.
- In the case of the oxide system/platinum substrate system, it can be stated that the contact angles decreased with increasing temperature, as well as with increasing boron oxide content. The wettability of these systems can be considered non-reactive based on the supporting SEM/EDX analyses.
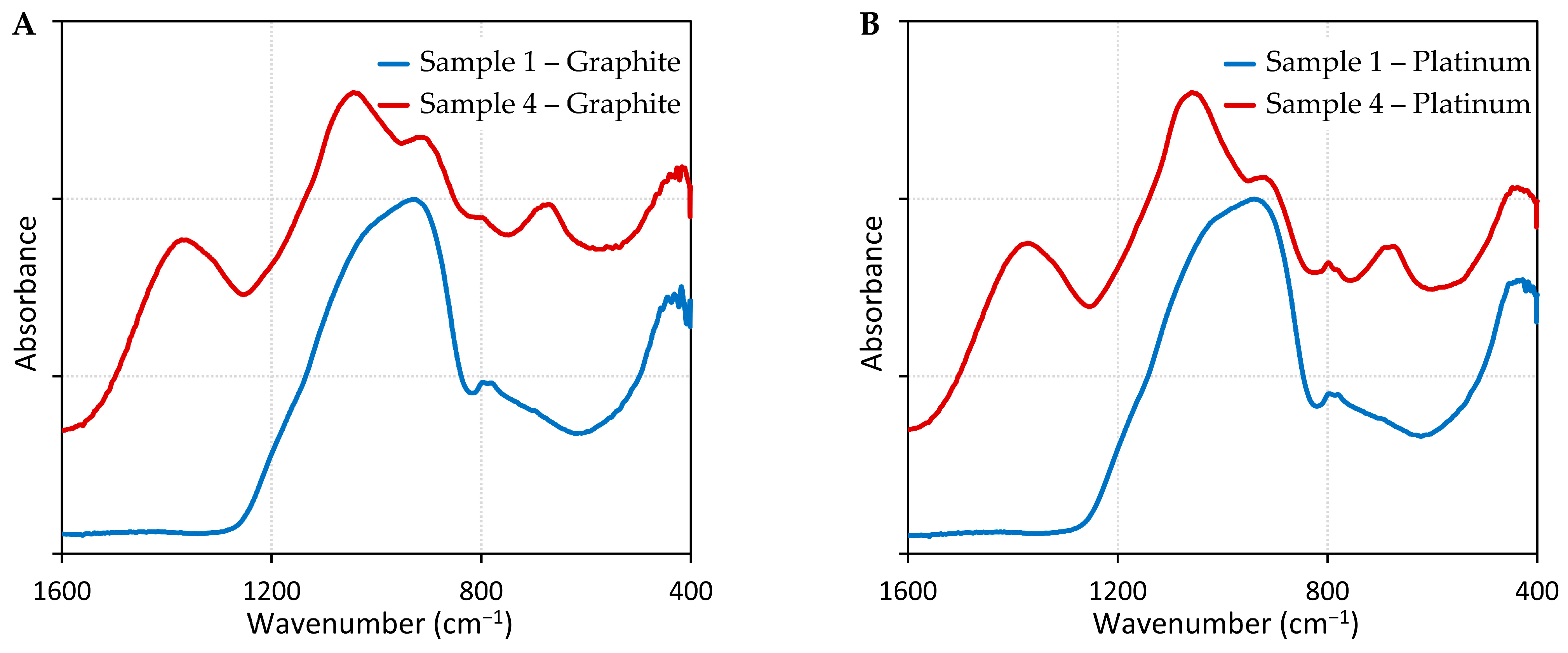
- FTIR analysis showed that oxide system samples, after high-temperature wettability tests on both graphite and platinum substrates, contain a minimum crystalline phase. It was further confirmed that adding boron oxide changed the structure of the sample.
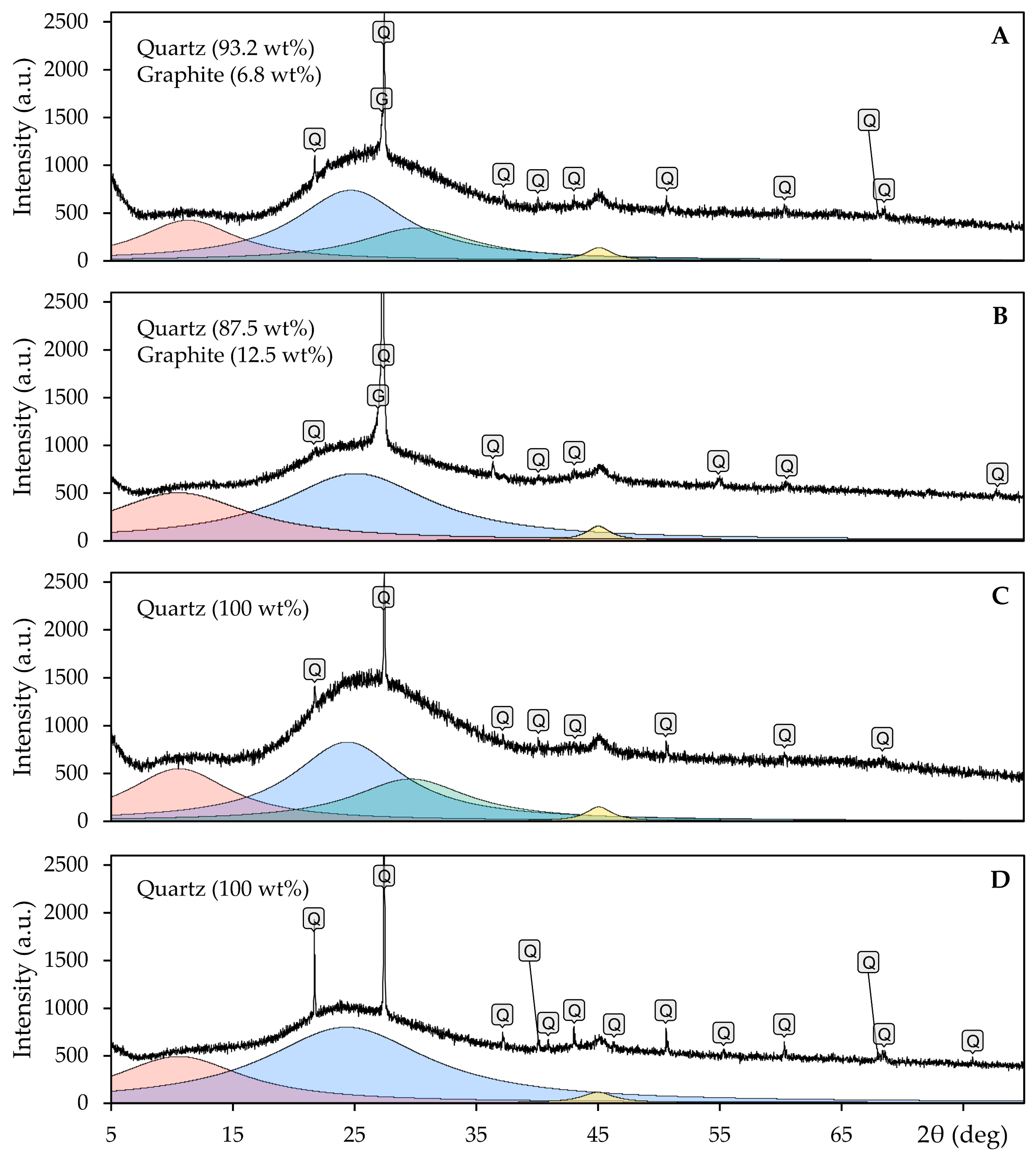
- The results of XRD analysis confirmed the highly amorphous nature of all the investigated oxide system samples, with a small fraction of the crystalline phase identified as quartz. The oxide system samples that wetted the graphite substrate were slightly contaminated with graphite due to the high adhesion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADSA | Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Powder Diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
References
- Bengisu, M. Borate glasses for scientific and industrial applications: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2199–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, S.; Abdelouas, A.; Criscenti, L.J.; Ebert, W.L.; Ferrand, K.; Geisler, T.; Harrison, M.T.; Inagaki, Y.; Mitsui, S.; Mueller, K.T.; et al. An international initiative on long-term behavior of high-level nuclear waste glass. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reben, M.; Li, H. Thermal Stability and Crystallization Kinetics of MgO-Al2O3-B2O3-SiO2 Glasses. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2011, 2, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Richards, C.; Watson, J. High-performance glass fiber development for composite applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2014, 5, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Guo, W. Influence of compositions on sealing temperature and properties of lead borate non-crystallizing sealing glasses. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 464, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of B2O3 on melting temperature, viscosity and desulfurization capacity of CaO-based refining flux. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-M.; Yang, L.-L.; Li, G.-R.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.-T. Effects of B2O3 and CaF2 on Melting Temperatures of CaO-SiO2-Fe2O3 System Fluxes. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Prabhu, K.N. Review of non-reactive and reactive wetting of liquids on surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 133, 61–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezellus, O.; Eustathopoulos, N. Fundamental issues of reactive wetting by liquid metals. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4256–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Rauch, N.; Scheu, C.; Ruehle, M.; Benhassine, M.; Seveno, D.; De Coninck, J.; Lopez-Esteban, S. Nonreactive spreading at high temperature: Molten metals and oxides on molybdenum. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 041602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, G.J.; Rivers, A.D.; Smith, R. Contact angle measurements of E-glass with platinum group metals. J. Mater. Sci. 1975, 10, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, W.-T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Tang, H.-Y.; Dai, Y.; Wei, G.-B.; Xie, W.-D. Research on high-temperature wettability between SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO glass melt droplets and platinum–rhodium alloy. Vacuum 2019, 160, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.; Ostrovski, O. Wettability of solid metals by Molten CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 slag. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Fujii, H.; Nogi, K. Wettability of some refractory materials by molten SiO2-MnO-TiO2-FeOx slag. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.F.; Lee, J.; Hessling, O.; Glaser, B. Reactions Between Liquid CaO-SiO2 Slags and Graphite Substrates. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Antonini, C. Contact angle measurements: From existing methods to an open-source tool. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustathopoulos, N.; Sobczak, N.; Passerone, A.; Nogi, K. Measurement of contact angle and work of adhesion at high temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, S.J.; Carroll, N.T.; Nicholas, M.G. Some effects of substrate roughness on wettability. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 714–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, N.; Singh, M.; Asthana, R. High-temperature wettability measurements in metal/ceramic systems—Some methodological issues. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.; Ostrovski, O. Wettability of solid metals by molten MnO-SiO2 slag. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raask, E. Mineral Impurities in Coal Combustion: Behavior, Problems, and Remedial Measures, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, G.; Ostrovski, O. Wetting of solid iron, nickel and platinum by liquid MnO-SiO2 and CaO-AI2O3-SiO2. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustathopoulos, N.; Nicholas, M.G.; Drevet, B. Wettability at High Temperatures; Pergamon, Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, A.S.; Sahajwalla, V. Influence of temperature on the wettability at the slag/carbon interface during pulverised coal injection in a blast furnace. Scand. J. Metall. 2001, 30, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.S.; Sahajwalla, V. Coal-char/Slag Interactions during Pulverised Coal Injection in a Blast Furnace: Reaction Kinetics and Wetting Investigations. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.S.; Sahajwalla, V. Influence of composition of slag and carbonaceous materials on the wettability at the slag/carbon interface during pulverised coal injection in a blast furnace. Scand. J. Metall. 2000, 29, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, N.; Bhoi, B.; Paramguru, R.K.; Sahajwalla, V.; Ostrovski, O. Slag-graphite wettability and reaction kinetics. Part 2. Wettability influenced by reduction kinetics. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2000, 27, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, N.; Bhoi, B.; Paramguru, R.K.; Sahajwalla, V.; Ostrovski, O. Slag-graphite wettability and reaction kinetics Part 1 kinetics and mechanism of molten FeO reduction reaction. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2000, 27, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Lee, J. Composition-dependent reactive wetting of molten slag on coke substrates. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, N.; Sahajwalla, V.; Ostrovski, O.; Belton, G.R. Wettability of graphite by CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-FeO-MgO slag. High Temp. Mater. Proc. 1997, 16, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, M.A.; Hughes, R.W. Slag density and surface tension measurements by the constrained sessile drop method. Fuel 2017, 188, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, X.; Bai, C.; Li, B. Wettability of pyrolytic graphite by molten blast furnace slag bearing TiO2. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řeháčková, L.; Novák, V.; Rosypalová, S.; Heger, M.; Zimný, O.; Matýsek, D.; Leinweberová, S.; Novák, D. On rheological properties of environmentally friendly inorganic systems and their modeling by artificial neural networks. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řeháčková, L.; Novák, V.; Váňová, P.; Matýsek, D.; Tkadlečková, M.; Konečná, K.; Sniegoň, M.; Smetana, B.; Rosypalová, S.; Kawuloková, M.; et al. Interfacial phenomena between alumina substrate and nickel containing low-alloy steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 900, 163376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, V.; Řeháčková, L.; Rosypalová, S.; Matýsek, D. Wetting of Refractory Ceramics with High-Manganese and Structural Steel and Description of Interfacial Interaction. Crystals 2022, 12, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubberstein, T.; Heller, H.-P.; Klostermann, J.; Schwarze, R.; Brillo, J. Surface tension and density data for Fe–Cr–Mo, Fe–Cr–Ni, and Fe–Cr–Mn–Ni steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7227–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustathopoulos, N.; Drevet, B. Determination of the nature of metal-oxide interfacial interactions from sessile drop data. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 249, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech, J.; Braccini, M.; Mortensen, A.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wetting, interfacial interactions and sticking in glass/steel systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 384, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G. Wetting: Statics and dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Xu, J. Viscosity and structure of MgO–SiO2-based slag melt with varying B2O3 content. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Sitarz, M.; Król, M. Spectroscopic Characterization of Silicate Amorphous Materials. In Molecular Spectroscopy—Experiment and Theory, 1st ed.; Koleżyński, A., Król, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 26, pp. 457–481. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.R. Application of infrared spectroscopy to studies of silicate glass structure: Examples from the melilite glasses and the systems Na2O-SiO2 and Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 1990, 99, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | B2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | 64.6 | 15.9 | 10.0 | 9.5 |
| 2 | 5.0 | 61.1 | 14.4 | 10.0 | 9.5 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 53.9 | 11.6 | 10.0 | 9.5 |
| 4 | 30.0 | 43.2 | 7.3 | 10.0 | 9.5 |
| Sample | Liquidus Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1510 |
| 2 | 1482 |
| 3 | 1456 |
| 4 | 1332 |
| Sample | (°C) | (deg.) | (deg·°C−1) | (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1510 | 72 | −11.60 × 10−3 | 1510–1550 |
| 2 | 1482 | 70 | −29.33 × 10−3 | 1482–1550 |
| 3 | 1456 | 65 | −27.56 × 10−3 | 1456–1550 |
| 4 | 1332 | 65 | −42.72 × 10−3 | 1332–1550 |
| Point | Caption | C | O | Mg | Al | Si | Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt%) | |||||||
| 1 | Oxides | 31.9 | 40.3 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 19.0 | 2.1 |
| 2 | Oxides | 36.6 | 35.0 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 21.6 | 1.7 |
| 3 | Silicates, SiO2, SiC, reduced metals | 51.3 | 28.2 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 11.4 | 2.3 |
| 4 | Silicates, SiO2, SiC, reduced metals | 48.2 | 24.2 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 18.8 | 2.3 |
| 5 | Silicates, SiO2, SiC, reduced metals | 52.2 | 16.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 25.3 | 1.5 |
| 6 | SiO2, SiC | 72.6 | 4.5 | ― | ― | 22.9 | ― |
| 7 | SiO2, SiC | 66.7 | 4.2 | ― | ― | 29.1 | ― |
| 8 | Oxides | 8.7 | 39.2 | 7.4 | 7.8 | 27.3 | 9.6 |
| 9 | Silicates/SiO2/Al2O3, reduced metals | 11.4 | 44.4 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 28.6 | 4.6 |
| 10 | Silicates/SiO2/Al2O3, reduced metals | 25.8 | 32.9 | 10.3 | 8.4 | 15.6 | 7.0 |
| 11 | SiO2, SiC, Si | 64.1 | 2.7 | ― | ― | 33.2 | ― |
| 12 | SiO2, SiC, Si | 80.1 | 4.2 | ― | ― | 15.7 | ― |
| 13 | Silicates/SiO2/SiC | 41.5 | 19.6 | 1.5 | 5.2 | 27.7 | 4.5 |
| 14 | Al2O3, oxides, SiO2, SiC | 28.6 | 32.0 | 9.1 | 19.7 | 9.7 | 0.9 |
| 15 | Al2O3 > silicates, SiO2, SiC | 44.5 | 24.3 | ― | 19.4 | 6.4 | 5.4 |
| 16 | Al2O3 > silicates, SiO2, SiC | 39.8 | 23.7 | ― | 22.0 | 8.5 | 6.0 |
| 17 | SiO2, SiC | 42.5 | 5.6 | ― | ― | 51.9 | ― |
| 18 | SiO2, SiC > Al2O3 | 59.4 | 4.7 | ― | 0.7 | 35.2 | ― |
| 0 wt% B2O3 on Graphite | 30 wt% B2O3 on Graphite | 0 wt% B2O3 on Pt | 30 wt% B2O3 on Pt | IR Assignment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | |||||
| ― | 1370 | ― | 1371 | B–O stretching vibration of varied borate groups in [BO3] units | [40] |
| ― | 1044 | ― | 1057 | [SiO4]-tetrahedral stretching and [BO4]-tetrahedral stretching | [40] |
| 928 | 914 | 938 | 919 | Si–O bonds occurring in Si–O–Si (νas S–O–Si) and Si–O–Al bridges (νas S–O–Al) | [41] |
| 799/779 | 796 | 795/780 | 797/781 | The motions of Si atoms against tetrahedral oxygen cage | [42] |
| ― | 672 | ― | 674 | B–O–B bending vibration | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novák, D.; Řeháčková, L.; Novák, V.; Matýsek, D.; Peikertová, P. Wetting of Graphite and Platinum Substrate by Oxide System with Graded B2O3 Content. Crystals 2023, 13, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13121618
Novák D, Řeháčková L, Novák V, Matýsek D, Peikertová P. Wetting of Graphite and Platinum Substrate by Oxide System with Graded B2O3 Content. Crystals. 2023; 13(12):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13121618
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovák, Dalibor, Lenka Řeháčková, Vlastimil Novák, Dalibor Matýsek, and Pavlína Peikertová. 2023. "Wetting of Graphite and Platinum Substrate by Oxide System with Graded B2O3 Content" Crystals 13, no. 12: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13121618
APA StyleNovák, D., Řeháčková, L., Novák, V., Matýsek, D., & Peikertová, P. (2023). Wetting of Graphite and Platinum Substrate by Oxide System with Graded B2O3 Content. Crystals, 13(12), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13121618






