Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Time on the Structure and Optical Properties of ZnO/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites
(This article belongs to the Section Inorganic Crystalline Materials)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
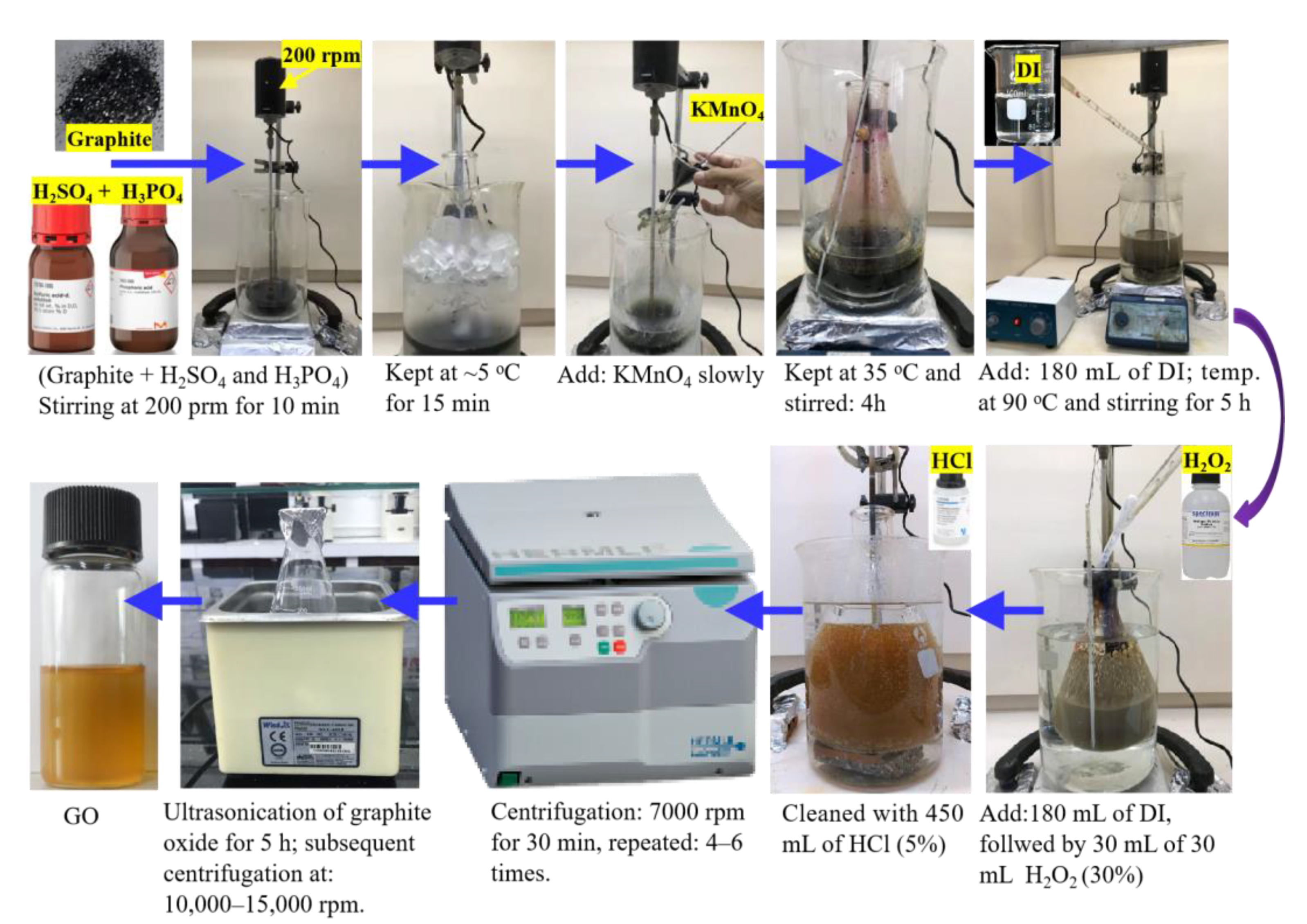
2.2. Preparation of Graphene Oxide (GO)
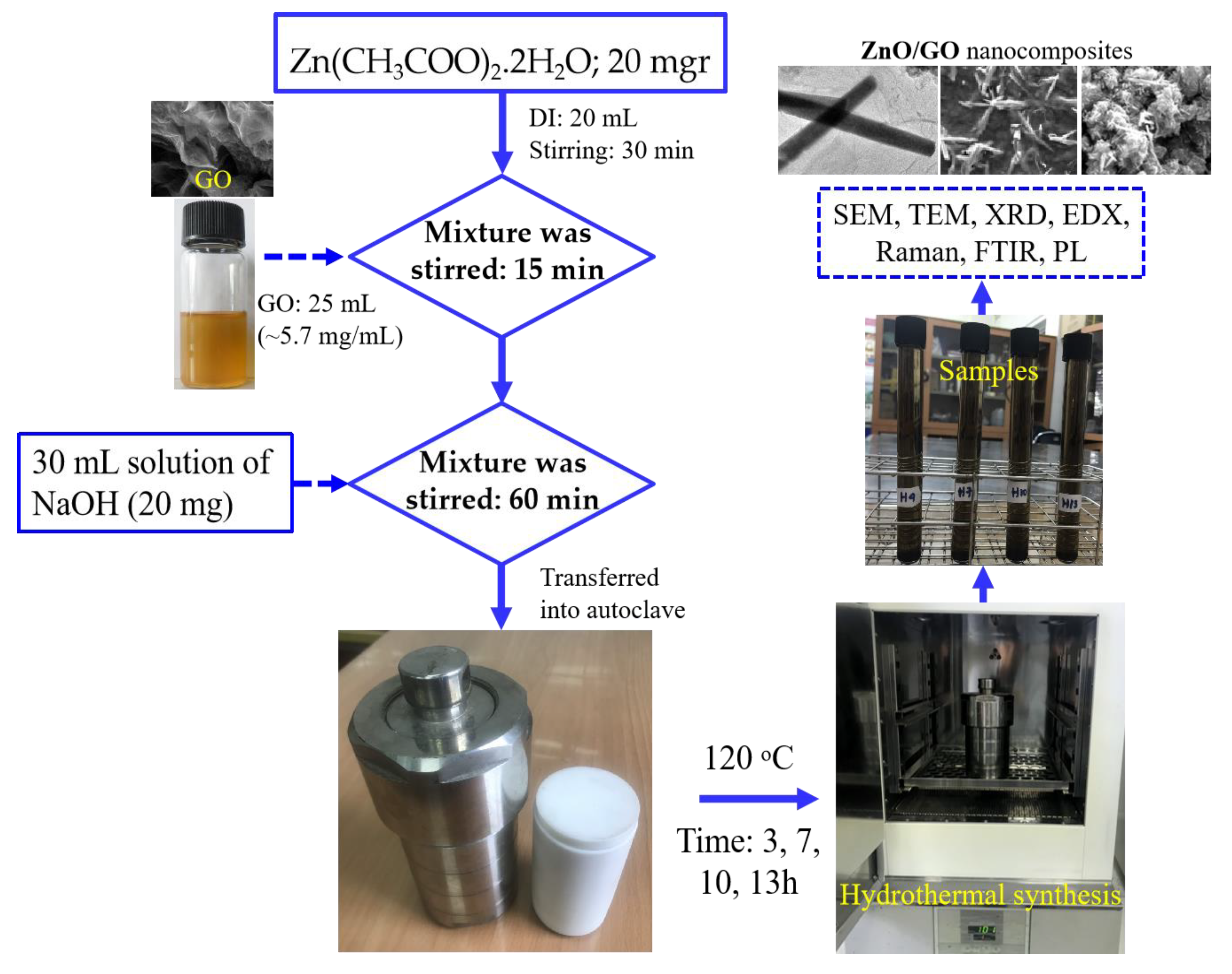
2.3. Fabrication of ZnO/GO Nanocomposites
2.4. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
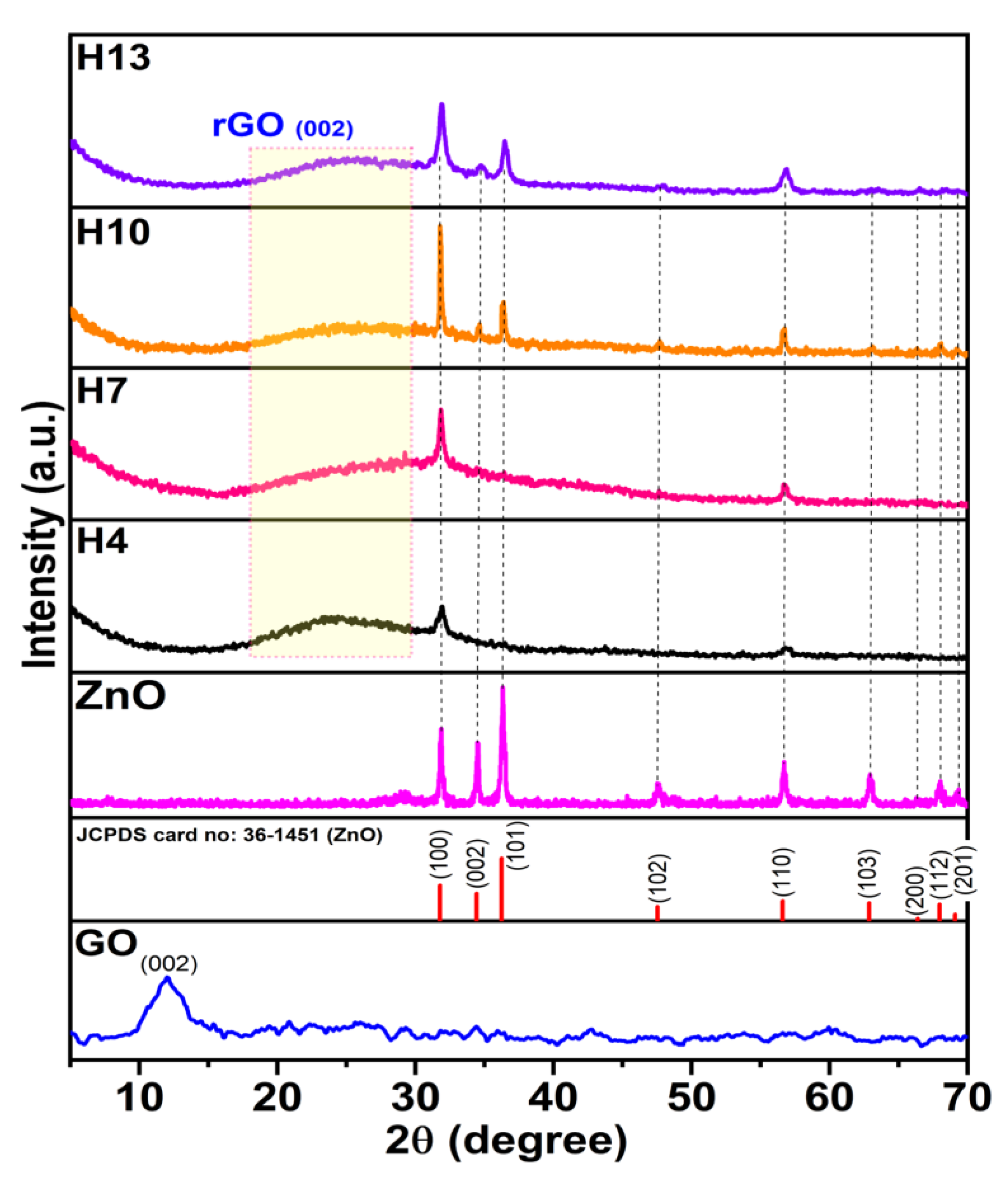
3.1. Structural Characterization of ZnO/GO Nanocomposites
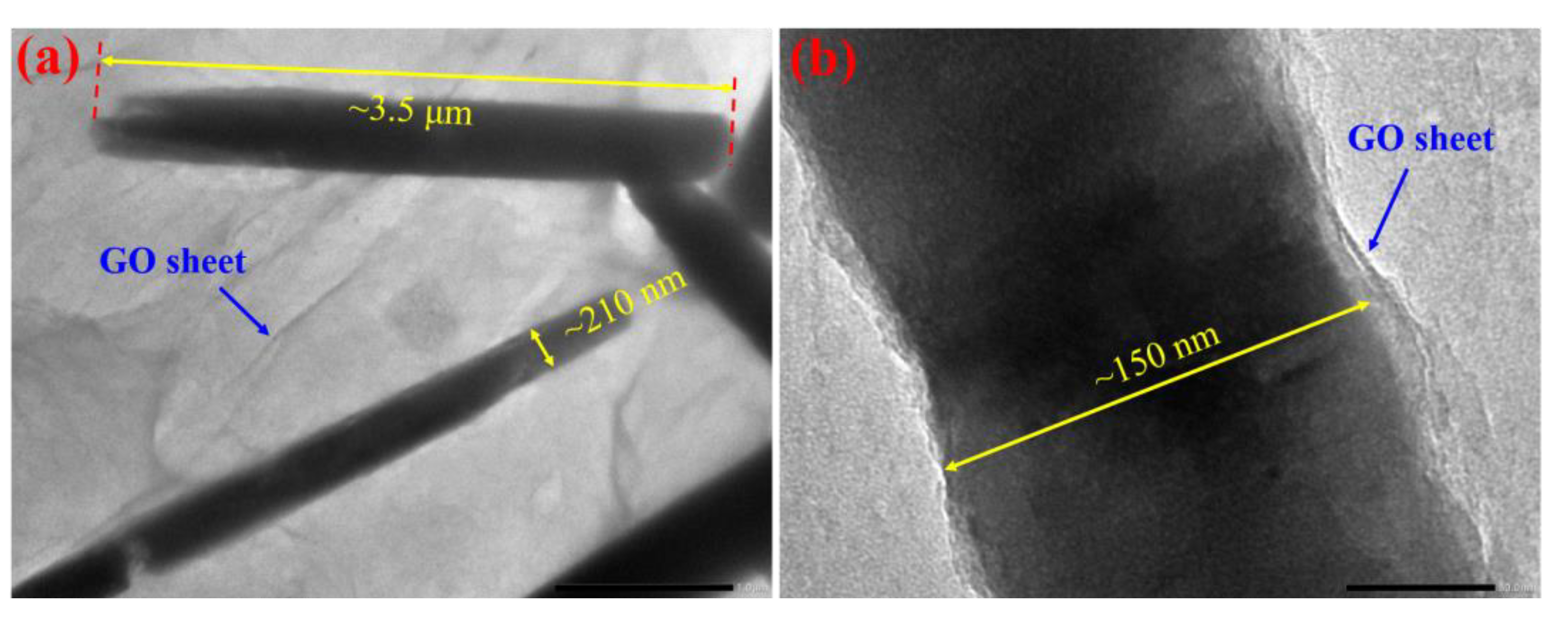
3.2. Morphology, Microstructure and Chemical Composition of ZnO/GO Nanocomposites
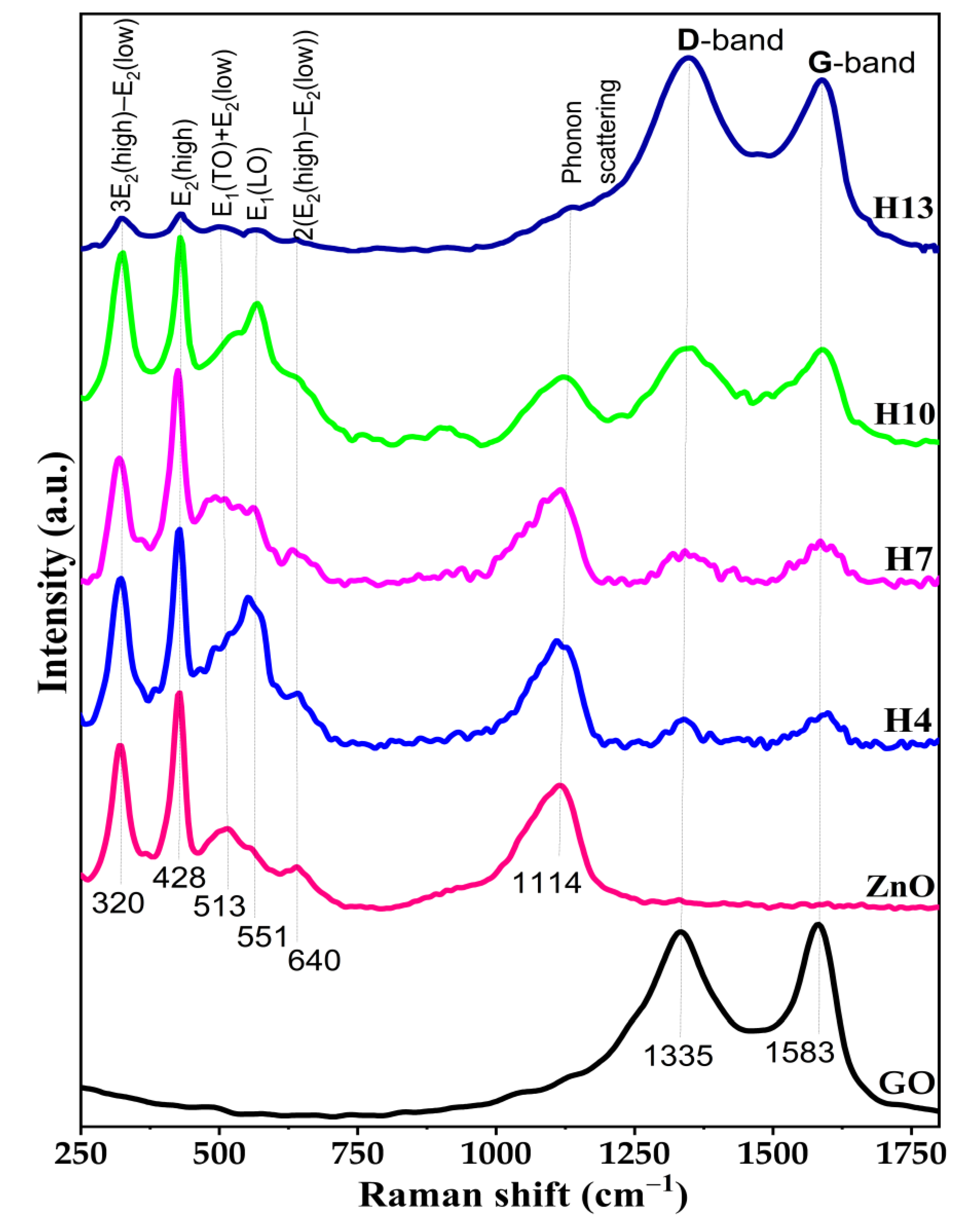
3.3. Raman Analysis of GO, ZnO and Synthesized ZnO/GO Nanocomposites
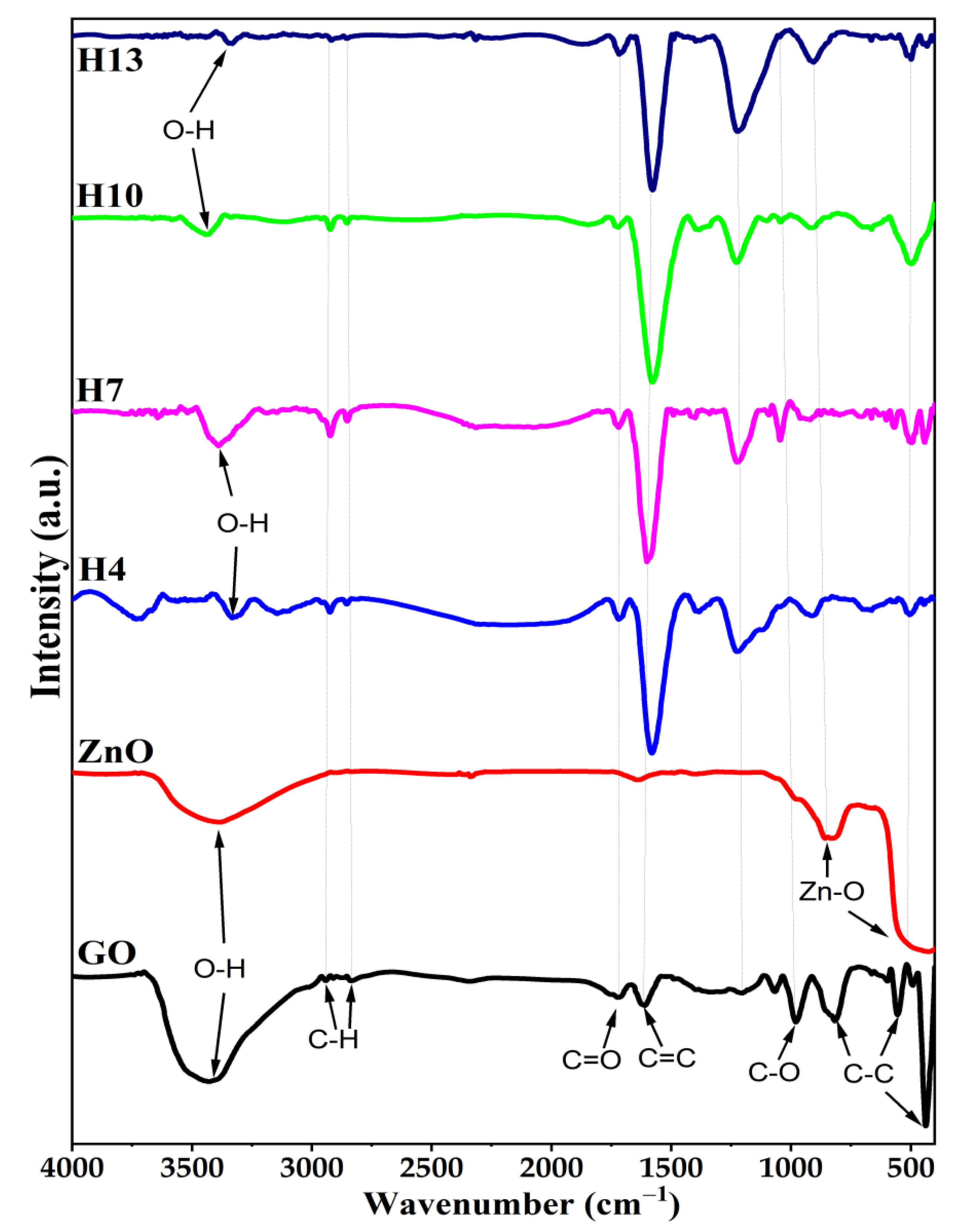
3.4. Feature Chemical Functional Groups Using Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectra (FTIR)
3.5. Optical Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zon, R.; He, G.; Xu, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J. ZnO nanorods on reduced graphene sheets with excellent field emission, gas sensor and photocalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8445–8452. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Ruby, D.S.; Peters, D.W.; McKenzie, B.B.; Hsu, J.W.P. ZnO nanostructures as efficient antireflection layers in solar cells. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khai, T.V.; Maneeratanasarn, P.; Choi, B.G.; Ham, H.; Shim, K.B. Diameter-and density-controlled synthesis of well-aligned ZnO nanowire arrays and their properties using a thermal evaporation technique. Phys. Status Solidi A 2012, 209, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, T.V.; Thu, L.V.; Lam, T.D. Vertically well-aligned ZnO nanowire arrays directly synthesized from Zn vapor deposition without catalyst. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2601–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Nanostructures of zinc oxide. Mater. Today 2004, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.Y.; Wen, J.G.; Ren, Z.F. Hierarchical ZnO nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.C.; Wang, C.; Park, W. ZnO nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S22–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.G.; Santana, G.; Güell, F.; Martínez-Alanis, P.R.; Dutt, A. Photoluminescence of ZnO nanowires: A review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Huang, Y.; Boland, J.J. Controllable growth of ZnO nanostructures by a simple solvothermal process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ramu, A.G.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Jeon, H.; Sathishkumar, V.E.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Al-onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Choi, D. Fabrication of ZnO nanorods based gas sensor pattern by photolithography and lift off techniques. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Lian, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, G.; Shen, D.; Yan, Q. Highly efficient field emission from large-scale and uniform monolayer graphene sheet supported on patterned ZnO nanorod arrays. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3965–3971. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, D.; Chang, P.-C.; Tseng, W.-Y.; Lu, J.G. ZnO nanowire field-effect transistor and oxygen sensing property. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5923–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banszerus, L.; Schmitz, M.; Engels, S.; Dauber, J.; Oellers, M.; Haupt, F.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Beschoten, B.; Stampfer, C. Ultrahigh-mobility graphene devices from chemical vapor deposition on reusable copper. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, M.J.; Tung, V.C.; Kaner, R.B. Honeycomb carbon: A review of graphene. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.; Gayen, R.N.; Biswas, S.; Bhat, S.V.; Bhunia, R. Enhanced UV detection by transparent graphene oxide/ZnO composite thin films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61661–61672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Robinson, J.T.; Li, Y.; Jackson, A.; Cui, Y.; Dai, H. Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium–sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2644–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Fang, Y.; Wen, D.; Dong, S. One-pot synthesis of functional two-dimensional graphene/SnO2 composite nanosheets as a building block for self-assembly and an enhancing nanomaterial for biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16911–16917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Graphene-based semiconductor photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Lin, J.-S. Synthesis of ZnO@Graphene composites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cote, L.J.; Huang, J. Two dimensional soft material: New faces of graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, P.P.; Siaj, M. Harvesting graphene oxide—Years 1859 to 2019: A review of its structure, synthesis, properties and exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Hu, Z.-A.; Chang, Y.-Q.; Wang, H.-W.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wu, H.-Y. Zinc oxide/reduced graphene oxide composites and electrochemical capacitance enhanced by homogeneous incorporation of reduced graphene oxide sheets in zinc oxide matrix. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2563–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessalli, B.A.; Zito, C.A.; Perfecto, T.M.; Volanti, D.P.; Mazon, T. ZnO nanorods/graphene oxide sheets prepared by chemical bath deposition for volatile organic compounds detection. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 696, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.T.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Development of polysulfone-nanohybrid membranes using ZnO-GO composite for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial control. Desalination 2017, 402, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rokhsat, E.; Akhavan, O. Improving the photocatalytic activity of graphene oxide/ZnO nanorod films by UV irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Afarideh, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Geranmayeh, S.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Ehsani, M.H. Preparation and characterization of GO-ZnO nanocomposite for UV detection application. Opt. Mater. 2019, 92, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zong, Y.; Men, Y. Room-temperature synthesis of ZnO@GO nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramshahi, V.; Karamdel, J.; Yousefi, R. High acetic acid sensing performance of Mg-doped ZnO/rGO nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7034–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Pan, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Electrochemical behaviors of graphene–ZnO and graphene–SnO2 composite fifilms for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4170–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Pan, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, G.; Lv, T.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, T.; Chua, D.H.C. Microwaveassisted synthesis of graphene ZnO nanocomposite for electrochemical supercapacitors. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 5488–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, G.C. Vertically aligned ZnO nanostructures grown on graphene layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 213101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Shen, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, K. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of sandwich-like graphene/ZnO nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 2826–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlinda, A.R.; Huang, N.M.; Muhamad, M.R.; Ańamt, M.N.; Chang, B.Y.S.; Yusoff, N.; Harrison, I.; Lim, H.N.; Chia, C.H.; Kumar, S.V. Highly effificient preparation of ZnO nanorods decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2012, 80, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, U.; Zhoub, W.; Belay, A.B.; Krueger, R.; Davis, K.O.; Hickman, N.S. Optical and structural properties of ZnO nanorods grown on graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide film by hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Kwon, J.B.; Lee, J.G.; Beom-Hoan, O.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, E.H.; Park, S.G. Novel fabrication of various size ZnO nanorods using hydrothermal method. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2009, 10, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almamari, M.R.; Ahmed, N.M.; Holi, A.M.; Yam, F.K.; Kyaw, H.H.; Almessiere, M.A.; Al-Abr, M.Z. Some distinct attributes of ZnO nanorods arrays: Effects of varying hydrothermal growth time. Materials 2022, 15, 5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Q. Growth of flower-like ZnO via surfactant-free hydrothermal synthesis on ITO substrate at low temperature. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 5996–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Han, B.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y.; Djerdj, I. Hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanorods on Zn substrates and their application in degradation of azo dyes under ambient conditions. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 7761–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, T.V.; Lam, T.D.; Thu, L.V.; Kim, H.W. A two-step method for the preparation of highly conductive graphene film and its gas-sensing property. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2015, 6, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khai, T.V.; Kwak, D.S.; Kwon, Y.J.; Kim, S.S.; Shim, K.B.; Kim, H.W. High-quality graphene thin films synthesized by H2 ambient-annealing of reduced graphene oxide sheets. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2013, 14, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janotti, A.; van de Walle, C.G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, P.K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.K. Chemical growth of hexagonal zinc oxide nanorods and their optical properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.J.; Shi, E.W.; Zhong, W.Z.; Yin, Z.W. Growth mechanism and growth habit of oxide crystal. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 203, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barret, C.S.; Massalski, T.B. Structure of Metals: Crystallographic Methods, Principles and Data; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1980; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Boukhoubza, I.; Khenfouch, M.; Achehboune, M.; Mothudi, B.M.; Zorkani, I.; Jorio, A. Graphene oxide/ZnO nanorods/graphene oxide sandwich structure: The origins and mechanisms of photoluminescence. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 797, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Fang, L.; Ruan, H.B.; Wu, F.; Huang, Q.L.; Xu, C.L.; Kong, C.Y. Effect of zinc acetate concentration on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by Sol-Gel method. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 7, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudin, K.N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H.C.; Prud’Homme, R.K.; Aksay, I.A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Singh, F.; Gautam, S.K.; Singh, R.G.; Ojha, S.; Kapoor, A. Growth of highly transparent CdxZn1−xO (CZO) thin films: Structural and optical studies. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 650, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettumperumal, R.; Kalyanaraman, S.; Santoshkumar, B.; Thangavel, R. Estimation of electron–phonon coupling and Urbach energy in group-I elements doped ZnO nanoparticles and thin films by sol–gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 77, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.-Q. Preparation and characterization of Ag/ZnO composites via a simple hydrothermal route. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaibhav, K.; Lokesh, S.; Malik, M.M. Effect of NaOH concentration on optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci.-Poland 2016, 34, 819–827. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, M.; Safa, S.; Azimirad, R.; Mokhtari, S. Graphene oxide incorporated ZnO nanostructures as a powerful ultraviolet composite detector. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 6919–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Srivastava, V.C. Simple synthesis of large graphene oxide sheets via electrochemical method coupled with oxidation process. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 10233–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.; Shen, M. A low-cost method for preliminary separation of reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, N.; Hussain, I.; El-Naggar, A.M.; Albassam, A.A. Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for optoelectronics applications. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, E.; Mekawy, M.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical-sensor applications of zinc oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposite. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Ran, C. Photoluminescence investigation about zinc oxide with graphene oxide & reduced graphene oxide buffer layers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 416, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, T. Fabrication and characterization of graphene oxide/zinc oxide nanorods hybrid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8950–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.I.; Kwon, B.W.; Yang, J.D.; Park, D.H.; Seo, W.S.; Lee, H.; Yi, Y.; Lee, C.L.; Choi, W.K. Charge separation and ultraviolet photovoltaic conversion of ZnO quantum dots conjugated with graphene nanoshells. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Diffraction Plane | Intensity (a.u.) | Calculated TChkl for 3 Main Peaks | FWHM (Radian) | Peak Position (Degree) | Crystallite Size: D (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 ((JCPDS-ICDD:36-1451) | I (Measured) | ||||||
| ZnO | (100) | 57 | 66 | 1.02 | 0.00443 | 31.85 | 32.57 |
| (002) | 44 | 54 | 1.09 | 0.00398 | 34.50 | 36.53 | |
| (101) | 100 | 100 | 0.89 | 0.00543 | 36.30 | 29.06 | |
| H4 | (100) | 57 | 100 | 2.40 | 0.01144 | 31.80 | 12.61 |
| (002) | 44 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| (101) | 100 | 43 | 0.60 | - | - | - | |
| H7 | (100) | 57 | 100 | 2.92 | 0.00502 | 31.84 | 28.71 |
| (002) | 44 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| (101) | 100 | 40 | 0.08 | - | - | - | |
| H10 | (100) | 57 | 100 | 1.77 | 0.00297 | 31.81 | 48.60 |
| (002) | 44 | 33 | 0.76 | 0.00576 | 34.62 | 25.24 | |
| (101) | 100 | 47 | 0.47 | 0.00506 | 36.32 | 28.86 | |
| H13 | (100) | 57 | 100 | 1.54 | 0.00698 | 31.91 | 20.70 |
| (002) | 44 | 66 | 0.86 | 0.01221 | 34.70 | 11.90 | |
| (101) | 100 | 54 | 0.60 | 0.00733 | 36.47 | 19.90 | |
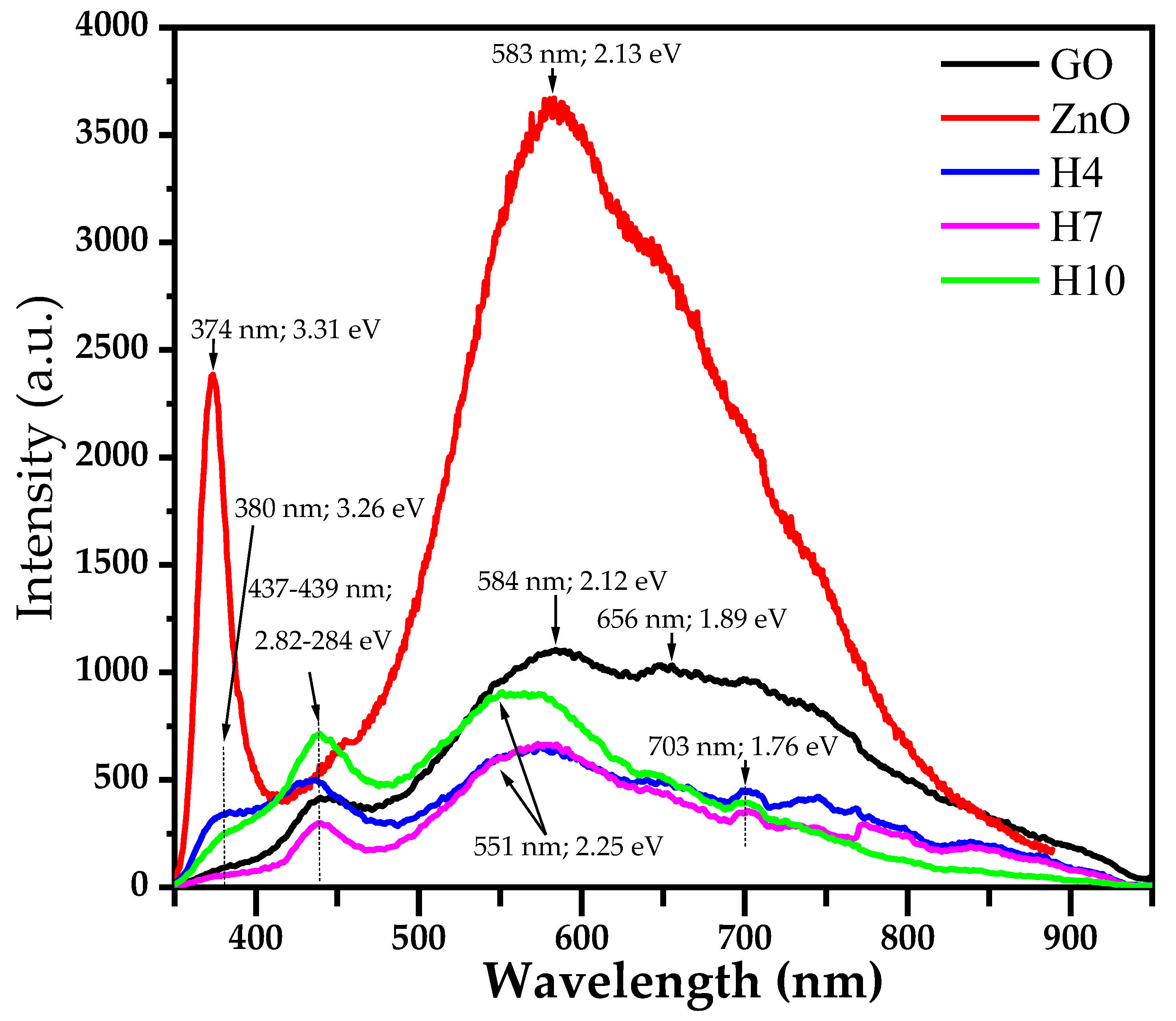
| Sample | Wavelength (nm) | Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| GO | 439 | 2.82 |
| 584 656 | 2.12 1.89 | |
| ZnO | 374 | 3.31 |
| 583 | 2.12 | |
| H4 | 380 | 3.26 |
| 437 | 2.84 | |
| 551 703 | 2.25 1.76 | |
| H7 | 380 | 3.26 |
| 439 | 2.82 | |
| 560 703 | 2.21 1.76 | |
| H10 | 380 | 3.26 |
| 439 | 2.82 | |
| 551 703 | 2.25 1.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khai, T.V.; Long, L.N.; Khoi, N.H.T.; Hoc Thang, N. Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Time on the Structure and Optical Properties of ZnO/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Crystals 2022, 12, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121825
Khai TV, Long LN, Khoi NHT, Hoc Thang N. Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Time on the Structure and Optical Properties of ZnO/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Crystals. 2022; 12(12):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhai, Tran Van, Le Ngoc Long, Nguyen Hoang Thien Khoi, and Nguyen Hoc Thang. 2022. "Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Time on the Structure and Optical Properties of ZnO/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites" Crystals 12, no. 12: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121825
APA StyleKhai, T. V., Long, L. N., Khoi, N. H. T., & Hoc Thang, N. (2022). Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Time on the Structure and Optical Properties of ZnO/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Crystals, 12(12), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121825






