Synthesis and X-ray Structure Combined with Hirshfeld and AIM Studies on a New Trinuclear Zn(II)-Azido Complex with s-Triazine Pincer Ligand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of [Zn3(PMT)2(Cl4)(N3)2]
2.2. Physicochemical Characterizations
2.3. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
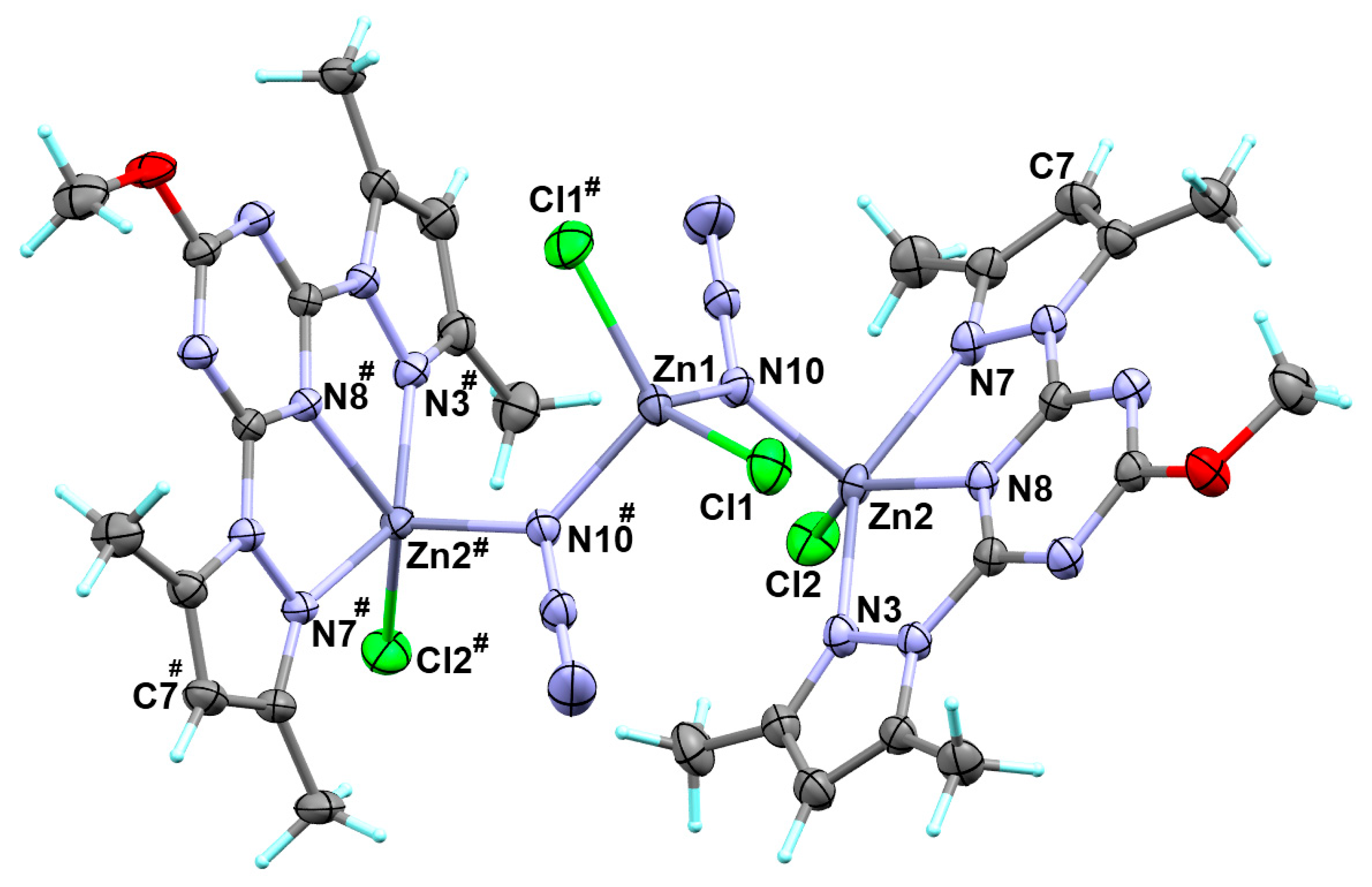
3.2. Crystal Structure Description
3.3. Analysis of Molecular Packing
3.4. Natural Charge Distribution
3.5. The Atoms in Molecules (AIM) Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, S.; Zhou, H.-C. A Metal−Organic Framework with Entatic Metal Centers Exhibiting High Gas Adsorption Affinity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11734–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hee, K.C.; Jaheon, K.; Olaf, D.F.; Michael, O.; Omar, M.Y. Design of Frameworks with Mixed Triangular and Octahedral Building Blocks Exemplified by the Structure of [Zn4O(TCA)2] Having the Pyrite Topology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3907–3909. [Google Scholar]
- Kepert, C.J.; Rosseinsky, M.J. Zeolite-like crystal structure of an empty microporous molecular framework. Chem. Comm. 1999, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-N.; Xing, H.; Li, Y.-Z. Unprecedented interweaving of single-helical and unequal double-helical chains into chiral metal–organic open frameworks with multiwalled tubular structures. Chem. Comm. 2007, 2293–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Updegraff, I.H.; Moore, S.T.; Herbes, W.F.; Roth, P.B. Amino Resins and Plastics, in Kirk-Othmer’s Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd ed.; Grayson, M., Eckroth, D., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 2, pp. 440–469. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.W.A. Ecology of Pesticides; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 10–11, 329–339, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, S.E. Applications of Triazine Chemistry: Education, Remediation, and Drug Delivery. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tobe, A.; Kobayashi, T. Pharmacological studies on triazine derivatives V. Sedative and neuroleptic actions of 2-amino-4-(4-(2hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-trifluoromethyl-s-triazine (TR10). Jpn. J. Aerosp. Med. Psychol. 1976, 26, 559–570. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.V.; Kumari, P.; Rajani, D.P.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Chikhalia, K.H. Antimicrobial, anti-TB, anticancer and anti-HIV evaluation of new s-triazine-based heterocycles. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vathanaruba, M.; Tharmaraj, P.; Sheela, C.D. Studies on A Novel s-triazine based ONO donor heterocyclic ligand and its transition Metal(II) complexes. Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 2014, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Marandi, F.; Moeini, K.; Arkak, A.; Mardani, Z.; Krautscheid, H. Docking studies to evaluate the biological activities of the Co(II) and Ni(II) complexes containing the triazine unit: Supported by structural, spectral, and theoretical studies. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 71, 3893–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katugampala, S.; Perera, I.C.; Nanayakkara, C.; Perera, T. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of novel sulfonated copper-triazine complexes. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 2530851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kala, R.S.; Tharmaraja, P.; Sheela, C.D. Synthesis, spectral studies, NLO, and biological studies on metal(II) complexes of s-triazine-based ligand. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2014, 44, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Thakur, R.; Kumar, V. Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes derived from 4-[{3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ylmethylene}-amino]-3-mercapto-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazine. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic App. Sci. 2016, 5, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, A.; Shrivastav, K.; Puri, S.K.; Chauhan, M.S. Syntheses of 2,4,6-trisubstituted triazines as antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldaniya, B.B.; Patel, P.K. Synthesis, antibacterial and antifungal activities of s-triazine derivatives. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, A.M.; Agrawal, M.; Sharma, S.; Dwivedi, J.; Kishore, D. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of some novel trisubstituted s-triazine derivatives based on isatinimino, sulphonamido, and azacarbazole. J. Chem. 2012, 2013, 925439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.H. Synthesis and characterization of cobalt(II) and nickel(II) complexes of some Schiff bases derived from 3-hydrazino-6-methyl[1,2,4] triazin-5(4H)one. Transit. Met. Chem. 2006, 31, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Shi, L.; Wei, H.Y.; Wang, X.Y. Field-induced single-ion magnet behavior in two new cobalt(II) coordination polymers with 2,4,6-tris(4-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine. Inorganics 2017, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgharpour, Z.; Farzaneh, F.; Abbasi, A. Synthesis, characterization and immobilization of a new cobalt(ii) complex on modified magnetic nanoparticles as catalyst for epoxidation of alkenes and oxidation of activated alkanes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95729–95739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, D.; Dayaker, G.; Bachu, P. Cobalt mediated C–H bond functionalization: Emerging tools for organic synthesis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 2756–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Cobalt-catalyzed C(sp3)−H functionalization reactions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pototschnig, G.; Maulide, N.; Schnürch, M. Direct functionalization of C−H bonds by iron, nickel, and cobalt catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9206–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordin, E.; List, M.; Monkowius, U.; Schindler, S.; Knör, G. Synthesis and characterization of cobalt, nickel and copper complexes with tripodal 4N ligands as novel catalysts for the homogeneous partial oxidation of alkanes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 402, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aktaş, A.; Saka, E.T.; Bıyıklıoğlu, Z.; Acar, İ.; Kantekin, H. Investigation of catalytic activity of new Co(II) phthalocyanine complexes in cyclohexene oxidation using different type of oxidants. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 745, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.; Papa, V.; Beller, M. Cobalt–pincer complexes in catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judy-Azar, A.R.; Mohebbi, S.J. A novel magnetic hybrid nanomaterial as a highly efficient and selective catalyst for alcohol oxidation based on new Schiff base complexes of transition metal ions. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 397, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menati, S.; Rudbari, H.A.; Askari, B.; Farsani, M.R.; Jalilian, F.; Dini, G. Synthesis and characterization of insoluble cobalt(II), nickel(II), zinc(II) and palladium(II) Schiff base complexes: Heterogeneous catalysts for oxidation of sulfides with hydrogen peroxide. C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahiez, G.R.; Moyeux, A. Cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1435–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebrard, F.; Kalck, P. Cobalt-catalyzed hydroformylation of alkenes: Generation and recycling of the carbonyl species, and catalytic cycle. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4272–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omae, I. Three characteristic reactions of organocobalt compounds in organic synthesis. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 21, 318–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkheil, M.; Lashanizadegan, M. Schiff base ligand derived from (±)trans-1,2-cyclohexane-diamine and its Cu(II), Co(II), Zn(II) and Mn(II) Complexes: Synthesis, characterization, styrene oxidation and a hydrolysis study of the imine bond in the Cu(II) Schiff base complex. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2016, 81, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; El-Faham, A. One pot synthesis of two Mn(II) perchlorate complexes with s-triazine NNN-pincer ligand; molecular structure, Hirshfeld analysis and DFT studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1164, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; El-Faham, A. Synthesis, characterization, and structural studies of two heteroleptic Mn(II) complexes with tridentate N,N,N-pincer type ligand. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 71, 2373–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Almarhoon, Z.; Sholkamy, E.N.; El-Faham, A. Bis-pyrazolyl-s-triazine Ni(II) pincer complexes as selective gram positive antibacterial agents; synthesis, structural and antimicrobial studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1195, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; El-Faham, A. Synthesis, X-ray structure, and DFT studies of five and eight-coordinated Cd(II) complexes with s-triazine N-pincer chelate. J. Coord. Chem. 2019, 72, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Almarhoon, Z.; El-Faham, A. Synthesis, Molecular and Supramolecular Structures of New Cd(II) Pincer-Type Complexes with s-Triazine Core Ligand. Crystals 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhowmik, P.; Biswas, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Diaz, C.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Ghosh, A. Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of two alternating double μ 1, 1 and μ 1, 3 azido bridged Cu(II) and Ni(II) chains. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12414–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mukherjee, P.S. Cu II–azide polynuclear complexes of Cu4 building clusters with Schiff-base co-ligands: Synthesis, structures, magnetic behavior and DFT studies. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 4019–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, F.A.; Fischer, R.C.; Williams, B.R.; Massoud, S.S.; Salem, N.M. Hexanuclear cadmium (II) cluster constructed from tris (2-methylpyridyl) amine (TPA) and azides. Crystals 2020, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mautner, F.A.; Fischer, R.C.; Reichmann, K.; Gullett, E.; Ashkar, K.; Massoud, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of 1D and 2D cadmium (II)-2, 2′-bipyridine-N, N′-dioxide coordination polymers bridged by pseudohalides. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1175, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonmak, J.; Nakano, M.; Chaichit, N.; Pakawatchai, C.; Youngme, S. Spin canting and metamagnetism in 2D and 3D cobalt (II) coordination networks with alternating double end-on and double end-to-end azido bridges. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 7324–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, F.A.; Louka, F.R.; Hofer, J.; Spell, M.; Lefèvre, A.; Guilbeau, A.E.; Massoud, S.S. One-dimensional cadmium polymers with alternative di (EO/EE) and di (EO/EO/EO/EE) bridged azide bonding modes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4518–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, S.S.; Louka, F.R.; Obaid, Y.K.; Vicente, R.; Ribas, J.; Fischer, R.C.; Mautner, F.A. Metal ions directing the geometry and nuclearity of azido-metal (II) complexes derived from bis (2-(3, 5-dimethyl-1 H-pyrazol-1-yl) ethyl) amine. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 3968–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, P.; Guha, P.M.; Drew, M.G.; Ishida, T.; Ghosh, A. Spin-Canted Antiferromagnetic Phase Transitions in Alternating Phenoxo-and Carboxylato-Bridged MnIII-Salen Complexes. Eur. J. Chem. 2011, 2011, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Poulter, N.; Donaldson, M.; Mulley, G.; Duque, L.; Waterfield, N.; Shard, A.G.; Spencer, S.; Jenkins, A.T.A.; Johnson, A.L. Plasma deposited metal Schiff-base compounds as antimicrobials. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, S.; Kamalraj, S.; Varghese, B.; Muthumary, J.; Kandaswamy, M. A series of oxyimine-based macrocyclic dinuclear zinc(II) complexes enhances phosphate ester hydrolysis, DNA binding, DNA hydrolysis, and lactate dehydrogenase inhibition and induces apoptosis. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 5580–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Yasui, H.; Yoshikawa, Y. Development of a novel antidiabetic zinc complex with an organoselenium ligand at the lowest dosage in KK-Ay mice. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 121, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.V. Determination of the antifouling agent zinc pyrithione in water samples by copper chelate formation and high-performance liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 833, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xub, H. Zinc(II) and copper(II) complexes of β-substituted hydroxylporphyrins as tumor photosensitizers. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3030–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Hosseinimehr, S.J.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Akhlaghpoor, S. Kojic acid and its manganese and zinc complexes as potential radioprotective agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-P.; Gan, X.-P.; Li, X.-L.; Liu, Z.-D.; Geng, W.-Q.; Zhou, F.-X.; Ke, W.-Z.; Wang, P.; Kong, L.; Hao, F.-Y.; et al. Anion-Induced Assembly of Five-Coordinated Mercury(II) Complexes and Density Functional Theory Calculations to Study Bond Dissociation Energies of Long Hg−N Bonds. Crystal Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Elsilk, S.E.; El-Faham, A. Synthesis, structure and biological activity of zinc (II) pincer complexes with 2, 4-bis (3, 5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-6-methoxy-1, 3, 5-triazine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2020, 508, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, H.M.; Alotaibi, A.A.M.; Dege, N.; El-Faham, A.; Soliman, S.M. Synthesis, Structure and Biological Evaluations of Zn(II) Pincer Complexes Based on S-Triazine Type Chelator. Molecules 2022, 27, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAINT; Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1995.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS; University of Goettingen: Goettingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; Spackman, P.R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. Crystal Explorer17; University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. GAUSSIAN 09; Revision A02; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Glendening, E.D.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Weinhold, F. NBO Version 3.1; CI, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Exchange functionals with improved long-range behavior and adiabatic connection methods without adjustable parameters: The mPW and mPW1PW models. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comp. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.M.; Elsilk, S.E.; El-Faham, A. Novel one-dimensional polymeric Cu(II) complexes via Cu(II)-assisted hydrolysis of the 2,4-bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-6-methoxy-1,3,5-triazine pincer ligand: Synthesis, structure, and antimicrobial activities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Al-Rasheed, H.H.; Elsilk, S.E.; El-Faham, A.A. Novel Centrosymmetric Fe(III) Complex with Anionic Bis-pyrazolyl-s-triazine Ligand; Synthesis, Structural Investigations and Antimicrobial Evaluations. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, H.M.; Alotaibi, A.A.M.; Dege, N.; El-Faham, A.; Soliman, S.M. Syntheses, X-ray structure and biological studies of binuclear μ-oxo diiron complexes with s-triazine pincer ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 543, 121196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(I) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: Structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, τ4. Dalton Trans. 2007, 9, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, N.T.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua [1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 7, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlous, K.A.; Soliman, S.M.; El-Faham, A.; Massoud, R.A. Synthesis, Molecular and Supramolecular Structures of Symmetric Dinuclear Cd(II) Azido Complex with bis-Pyrazolyl s-Triazine Pincer Ligand. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, C.F.; Hernandez-Trujillo, J.; Tang, T.-H.; Bader, R.F.W. Hydrogen–Hydrogen Bonding: A Stabilizing Interaction in Molecules and Crystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, S.J.; Pfitzner, A.; Zabel, M.; Dubis, A.T.; Palusiak, M. Intramolecular H···H Interactions for the Crystal Structures of [4-((E)-But-1-enyl)-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl]pyridine-3-carboxylate and [4-((E)-Pent-1-enyl)-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl]pyridine-3-carboxylate; DFT Calculations on Modeled Styrene Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, C.F.; Castillo, N.; Boyd, R.J. Characterization of a Closed-Shell Fluorine−Fluorine Bonding Interaction in Aromatic Compounds on the Basis of the Electron Density. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 3669–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendás, A.M.; Francisco, E.; Blanco, M.A.; Gatti, C. Bond Paths as Privileged Exchange Channels. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 9362–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.G.; Pereira, F.S.; de Araujo, R.C.M.C.; Ramos, M.N. The hydrogen bond strength: New proposals to evaluate the intermolecular interaction using DFT calculations and the AIM theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 427, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, D.; Kraka, E. Chemical Bonds without Bonding Electron Density—Does the Difference Electron-Density Analysis Suffice for a Description of the Chemical Bond? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1984, 23, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| CCDC | 2219487 | |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C28H34Cl4N20O2Zn3 | |
| F.Wt | 1020.66 g/mol | |
| T | 293(2) K | |
| λ | 0.71073 Å | |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | |
| Space group | C2/c | |
| Unit cell dimensions | a = 18.549(11) Å | α = 90° |
| b = 11.371(7) Å | β = 97.098(11)° | |
| c = 20.123(11) Å | γ = 90° | |
| V | 4212.0(4) Å3 | |
| Z | 4 | |
| D (calc.) | 1.610 g/cm3 | |
| Absorption coefficient | 2.003 mm−1 | |
| F(000) | 2064 | |
| θ range for data collection | 2.21 to 30.58° | |
| Index ranges | −23 ≤ h ≤ 26, −16 ≤ k ≤ 16, −28 ≤ l ≤ 28 | |
| Reflections collected | 29,481 | |
| Independent reflections | 6452 [R(int) = 0.0365] | |
| Completeness to θ = 25.35° | 99.50% | |
| Refinement method | Full-matrix least-squares on F2 | |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 6452/0/264 | |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.04 | |
| Final R indices [I > 2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0414, wR2 = 0.1215 | |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0632, wR2 = 0.1363 | |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 1.456 and −0.639 | |
| Bond | Distance | Bond | Distance |
| Zn1–N10 | 2.040(2) | Zn2–N3 | 2.181(3) |
| Zn1–Cl1 | 2.2305(12) | Zn2–Cl2 | 2.1924(14) |
| Zn2–N10 | 2.036(2) | Zn2–N7 | 2.279(2) |
| Zn2–N8 | 2.072(2) | ||
| Bonds | Angle | Bonds | Angle |
| N10–Zn1–N10 # | 105.87(14) | N10–Zn2–Cl2 | 111.83(8) |
| N10–Zn1–Cl1 | 110.55(8) | N8–Zn2–Cl2 | 142.79(7) |
| N10–Zn1–Cl1 # | 105.46(8) | N3–Zn2–Cl2 | 103.76(7) |
| Cl1–Zn1–Cl1 # | 118.35(7) | N10–Zn2–N7 | 94.69(9) |
| N10–Zn2–N8 | 104.77(10) | N8–Zn2–N7 | 71.66(8) |
| N10–Zn2–N3 | 102.91(9) | N3–Zn2–N7 | 143.96(8) |
| N8–Zn2–N3 | 73.53(8) | Cl2–Zn2–N7 | 98.30(6) |
| Bond | BD | ρ | G(r) a | V(r) b | H(r) | V(r)/G(r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1–Cl1 | 2.230 | 0.0431 | 0.0864 | −0.0803 | 0.0060 | 0.930 |
| Zn1–N10 | 2.040 | 0.0568 | 0.1138 | −0.1111 | 0.0027 | 0.976 |
| Zn2–N3 | 2.181 | 0.0335 | 0.0505 | −0.0507 | −0.0002 | 1.004 |
| Zn2–N7 | 2.279 | 0.0277 | 0.0537 | −0.0485 | 0.0052 | 0.903 |
| Zn2–N8 | 2.072 | 0.0520 | 0.1044 | −0.1012 | 0.0031 | 0.969 |
| Zn2–N10 | 2.036 | 0.0572 | 0.1172 | −0.1141 | 0.0031 | 0.974 |
| Zn2–Cl2 | 2.193 | 0.0461 | 0.0960 | −0.0889 | 0.0071 | 0.926 |
| N10–N1 | 1.210 | 0.4607 | 0.3902 | −1.0560 | −0.6658 | 2.706 |
| N1–N11 | 1.129 | 0.5725 | 0.5704 | −1.5492 | −0.9788 | 2.716 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahlous, K.A.; Soliman, S.M.; El-Faham, A.; Massoud, R.A. Synthesis and X-ray Structure Combined with Hirshfeld and AIM Studies on a New Trinuclear Zn(II)-Azido Complex with s-Triazine Pincer Ligand. Crystals 2022, 12, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121786
Dahlous KA, Soliman SM, El-Faham A, Massoud RA. Synthesis and X-ray Structure Combined with Hirshfeld and AIM Studies on a New Trinuclear Zn(II)-Azido Complex with s-Triazine Pincer Ligand. Crystals. 2022; 12(12):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121786
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahlous, Kholood A., Saied M. Soliman, Ayman El-Faham, and Raghdaa A. Massoud. 2022. "Synthesis and X-ray Structure Combined with Hirshfeld and AIM Studies on a New Trinuclear Zn(II)-Azido Complex with s-Triazine Pincer Ligand" Crystals 12, no. 12: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121786
APA StyleDahlous, K. A., Soliman, S. M., El-Faham, A., & Massoud, R. A. (2022). Synthesis and X-ray Structure Combined with Hirshfeld and AIM Studies on a New Trinuclear Zn(II)-Azido Complex with s-Triazine Pincer Ligand. Crystals, 12(12), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12121786







