Coal Fly Ash as Raw Material for Immobilization of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Microwave Heating: Mechanism and Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
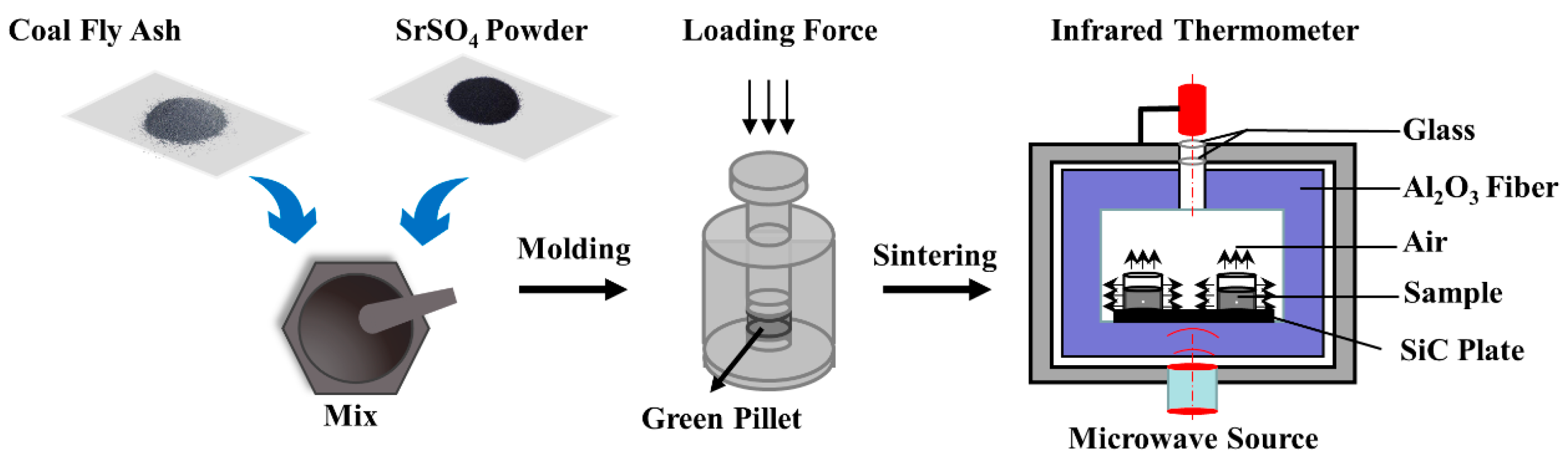
2.2. Experiment Procedures
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
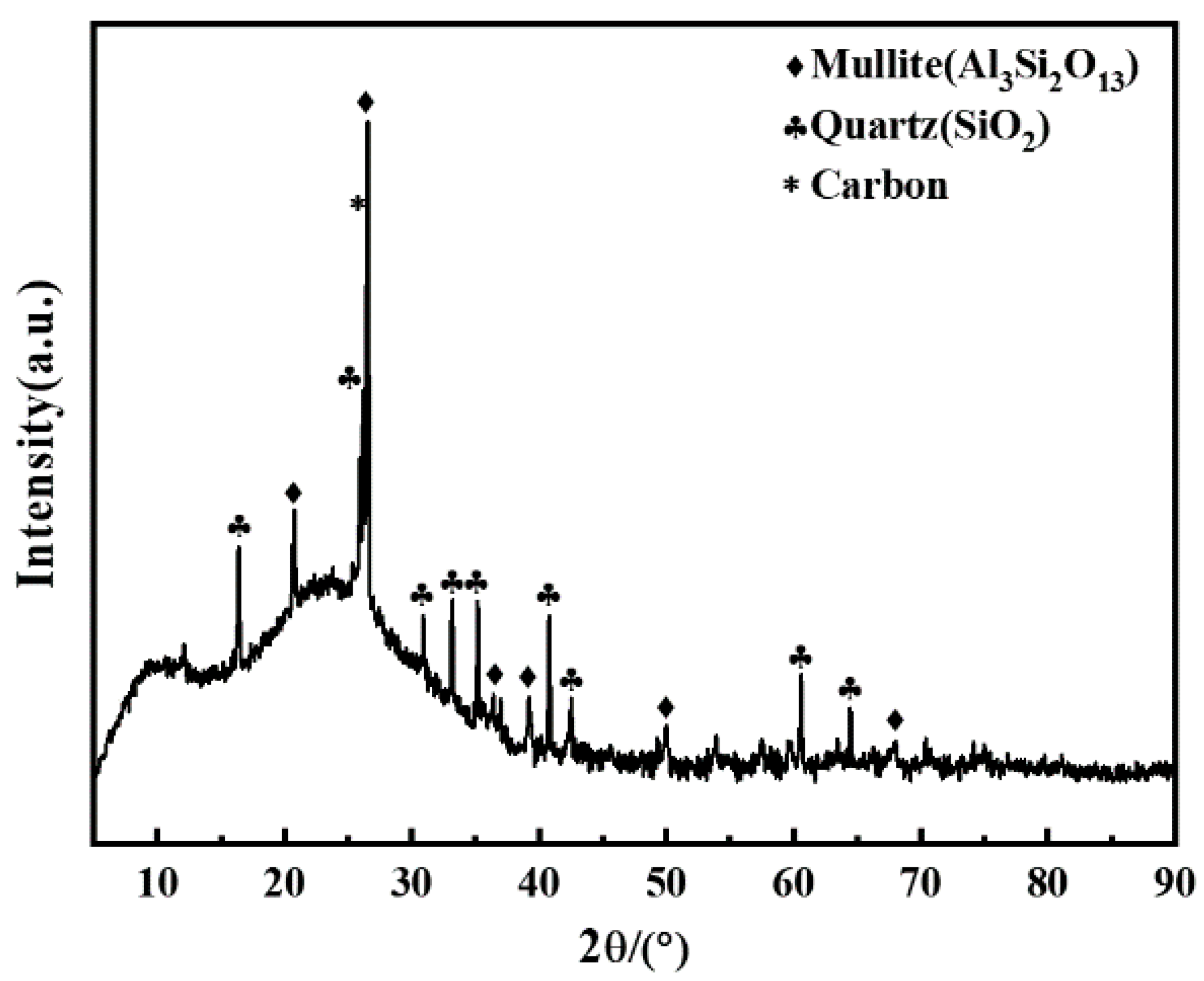
3.1. Phase Evolution Analysis
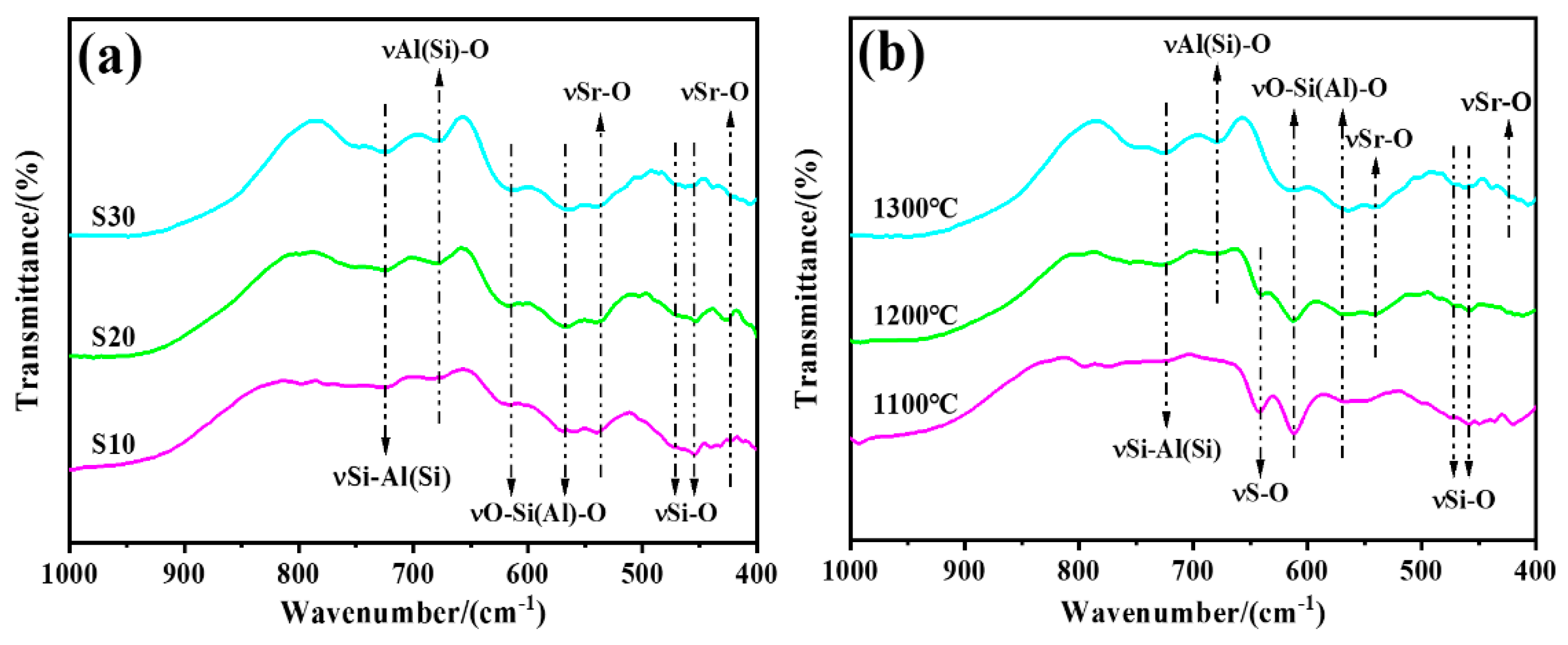
3.2. Microstructural Analysis
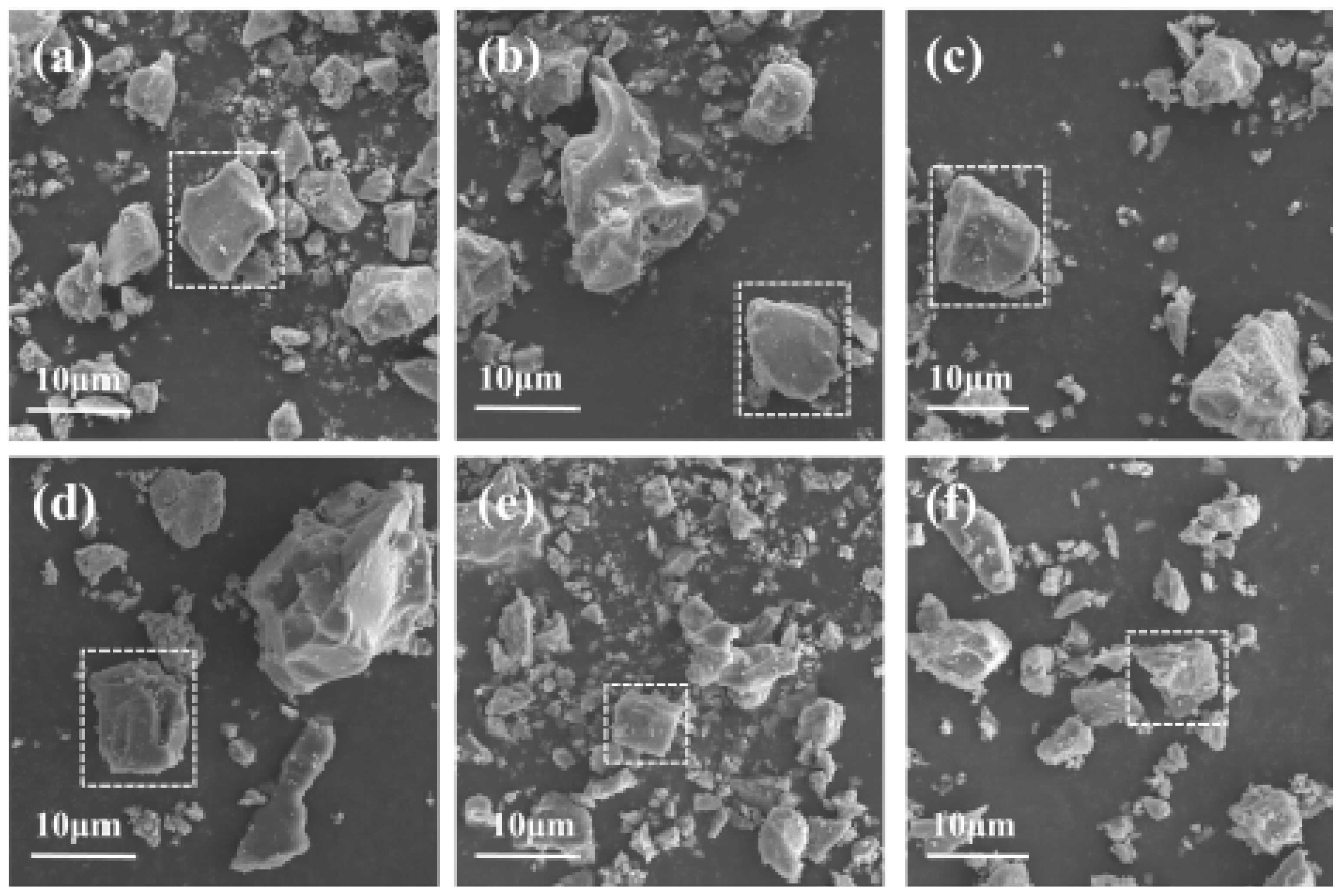
3.3. Micromorphology Analysis
3.4. Physical Property Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.F.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.X.; Wen, J.W.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, J. Microwave-sintering preparation, phase evolution and chemical stability of Na1-2xSrxZr2(PO4)(3) ceramics for immobilizing simulated radionuclides. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 540, 152366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.W.; Navrotsky, A.; Stefanovsky, S.; Vance, E.R.; Vernaz, E. Materials science of high-level nuclear waste immobilization. MRS Bull. 2009, 34, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Shu, X.; Huang, W.; Miao, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Luo, F.; Xie, Y.; Shao, D.; et al. Rapid solidification of Sr-contaminated soil by consecutive microwave sintering: Mechanism and stability evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Stohl, A.; Hayano, R.S.; Burkhart, J.F.; Eckhardt, S.; Yasunari, T. Cesium-137 deposition and contamination of Japanese soils due to the Fukushima nuclear accident. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 108, 19530–19534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, H.; Onda, Y.; Teramage, M. Depth distribution of 137Cs, 134Cs, and 131I in soil profile after Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident. J. Environ. Radioact. 2012, 111, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojovan, M.I.; Lee, W.E. Glassy Wasteforms for Nuclear Waste Immobilization. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 42, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gin, S.; Jollivet, P.; Tribet, M.; Peuget, S.; Schuller, S. Radionuclides containment in nuclear glasses: An overview. Radiochim. Acta 2017, 105, 927–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Li, W.Q.; Ren, C.R.; Zhao, J.C. Structure and chemical durability studies of powellite ceramics Ca1-xLix/2Gdx/2MoO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) for radioactive waste storage. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, I.W.; Metcalfe, B.L.; Taylor, R.N.J.J.J.o.M.e. The immobilization of high level radioactive wastes using ceramics and glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 5851–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X. Preparation of Mullite Ceramics with Fly Ash and Clay by Pickling Process. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2015, 12, E132–E137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.S.; Rowson, N.A. A review of the multi-component utilisation of coal fly ash. Fuel 2012, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X. Effect of particle size and alkali activation on coal fly ash and their role in sintered ceramic tiles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.; Bergmann, C.P. Fly ash of mineral coal as ceramic tiles raw material. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Shi, M.; Xu, C.; Shu, X.; Luo, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Lu, X. Mechanical and leaching properties of neodymium-contaminated soil glass-ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y. Preparation of zircon-matrix material for dealing with high-level radioactive waste with microwave. Mater. Lett. 2014, 131, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; Mao, X.; Song, M. Rapid and efficient disposal of radioactive contaminated soil using microwave sintering method. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shu, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, H.; Hou, C.; Mao, X.; Chi, F.; Song, M.; Lu, X. Rapid Immobilization of Simulated Radioactive Soil Waste by Microwave Sintering. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 337, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Lu, X. Rapid vitrification of uranium-contaminated soil: Effect and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghbaei, M.; Mirzaee, O. Microwave versus conventional sintering: A review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 494, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Xiong, T.; Bai, Z.; Zhao, D.; Yang, W.; Peng, Y.; Dan, H.; Ding, Y.; Duan, T. Effect of Si/Zr molar ratio on the sintering and crystallization behavior of zircon ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4605–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, S.A.; Schardt, C.R.; Masiello, D.J.; Simmons, J.H. Dispersion analysis of FTIR reflection measurements in silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 275, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Egili, K. Infrared studies of Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2003, 325, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrosko, M.; Koch-Muller, M.; Schade, U. In-situ mid/far micro-FTIR spectroscopy to trace pressure-induced phase transitions in strontium feldspar and wadsleyite. Am. Mineral. 2011, 96, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manam, J.; Das, S. Preparation, characterization and thermally stimulated luminescence studies of undoped, Cu and Mn doped SrSO4 compounds. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J. Characterization of radioactive waste forms and packages: Technical Reports Series No. 383, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1997, 138 pages, ISBN 92-0-100497-4, US$ 55. Waste Manag. 1998, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | K2O | Fe2O3 | Na2O | MgO | TiO2 | SO3 | P2O5 | ZnO | |
| CFA | 29.13 | 57.06 | 3.05 | 2.88 | 2.36 | 1.15 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.02 | 0.522 | 0.465 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Zhu, A.; Chen, M.; Dai, B.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y. Coal Fly Ash as Raw Material for Immobilization of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Microwave Heating: Mechanism and Performance. Crystals 2022, 12, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010055
Xie Y, Zhu A, Chen M, Dai B, Wang B, Liu Y. Coal Fly Ash as Raw Material for Immobilization of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Microwave Heating: Mechanism and Performance. Crystals. 2022; 12(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yupeng, Ailian Zhu, Min Chen, Bing Dai, Bin Wang, and Yong Liu. 2022. "Coal Fly Ash as Raw Material for Immobilization of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Microwave Heating: Mechanism and Performance" Crystals 12, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010055
APA StyleXie, Y., Zhu, A., Chen, M., Dai, B., Wang, B., & Liu, Y. (2022). Coal Fly Ash as Raw Material for Immobilization of Sr-Contaminated Soil by Microwave Heating: Mechanism and Performance. Crystals, 12(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010055






