Effects of theTiB2-SiC Volume Ratio and Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Preparation of the TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Powder
2.2. Preparation of TiB2-BN-SiC Multiphase Ceramics
2.3. Testing and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of the TiB2-SiC Volume Ratio on the Material Properties, Microstructure, and Phase Composition
3.1.1. Effects of the TiB2-SiC Volume Ratio on the Material Properties
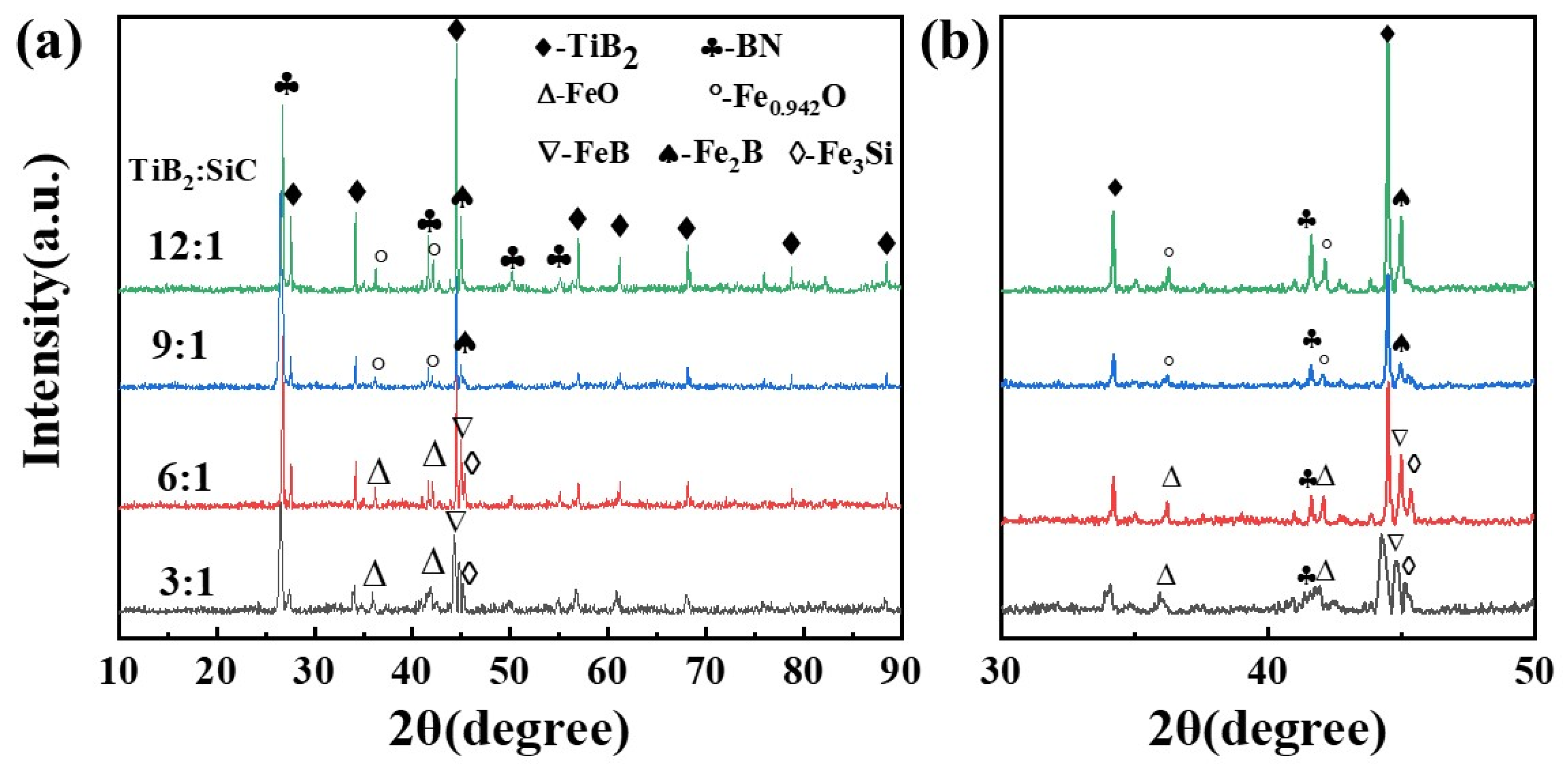
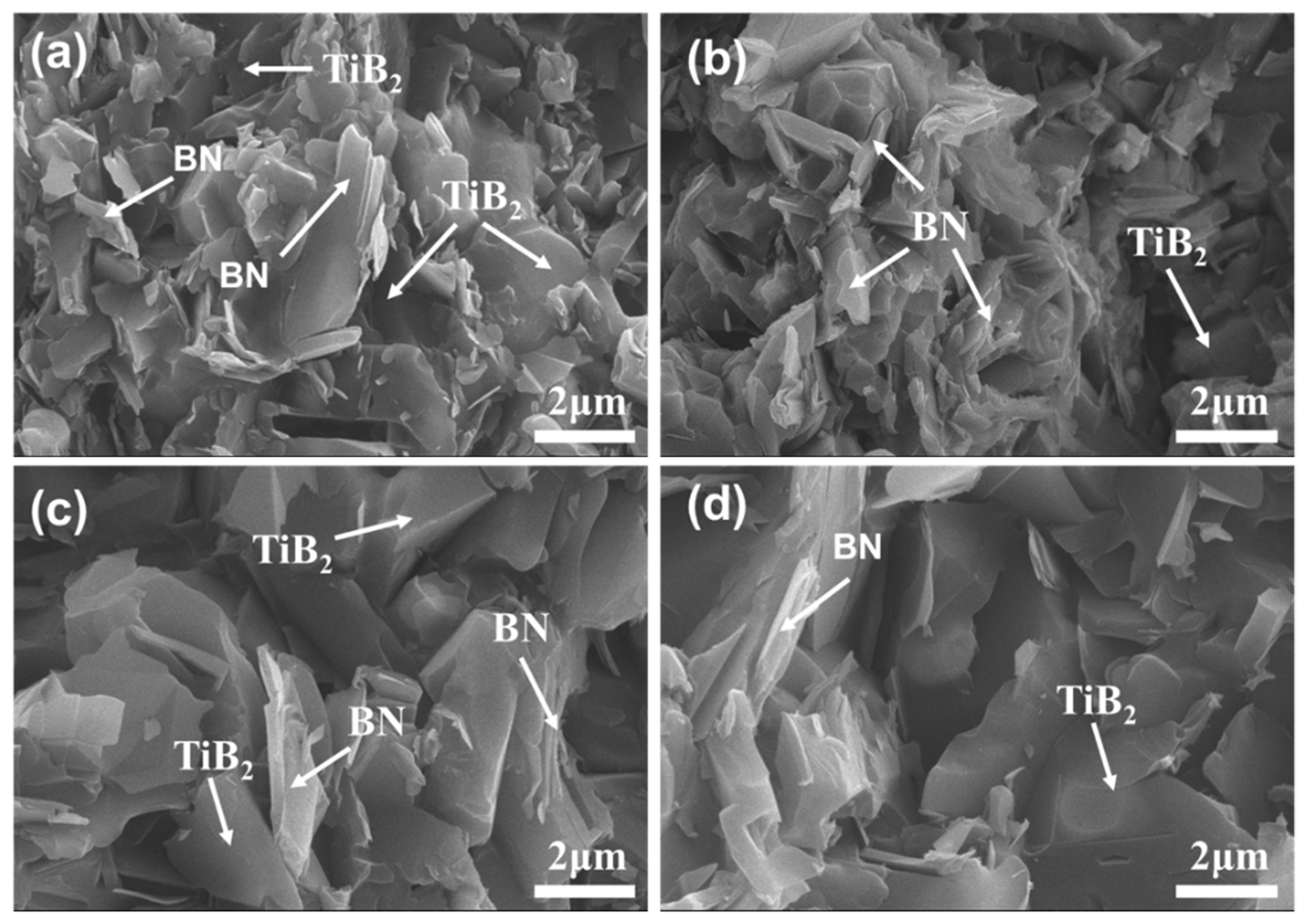
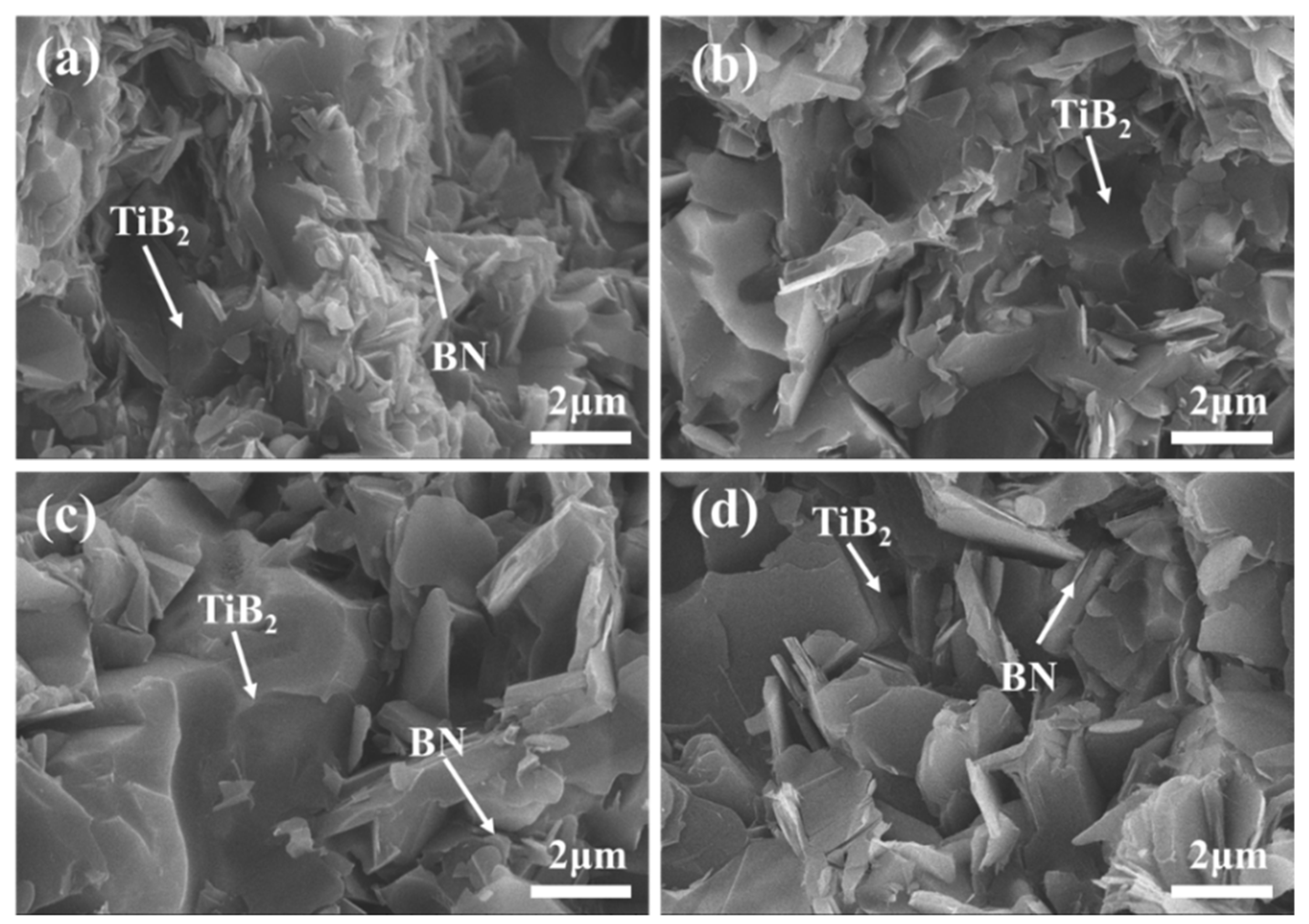
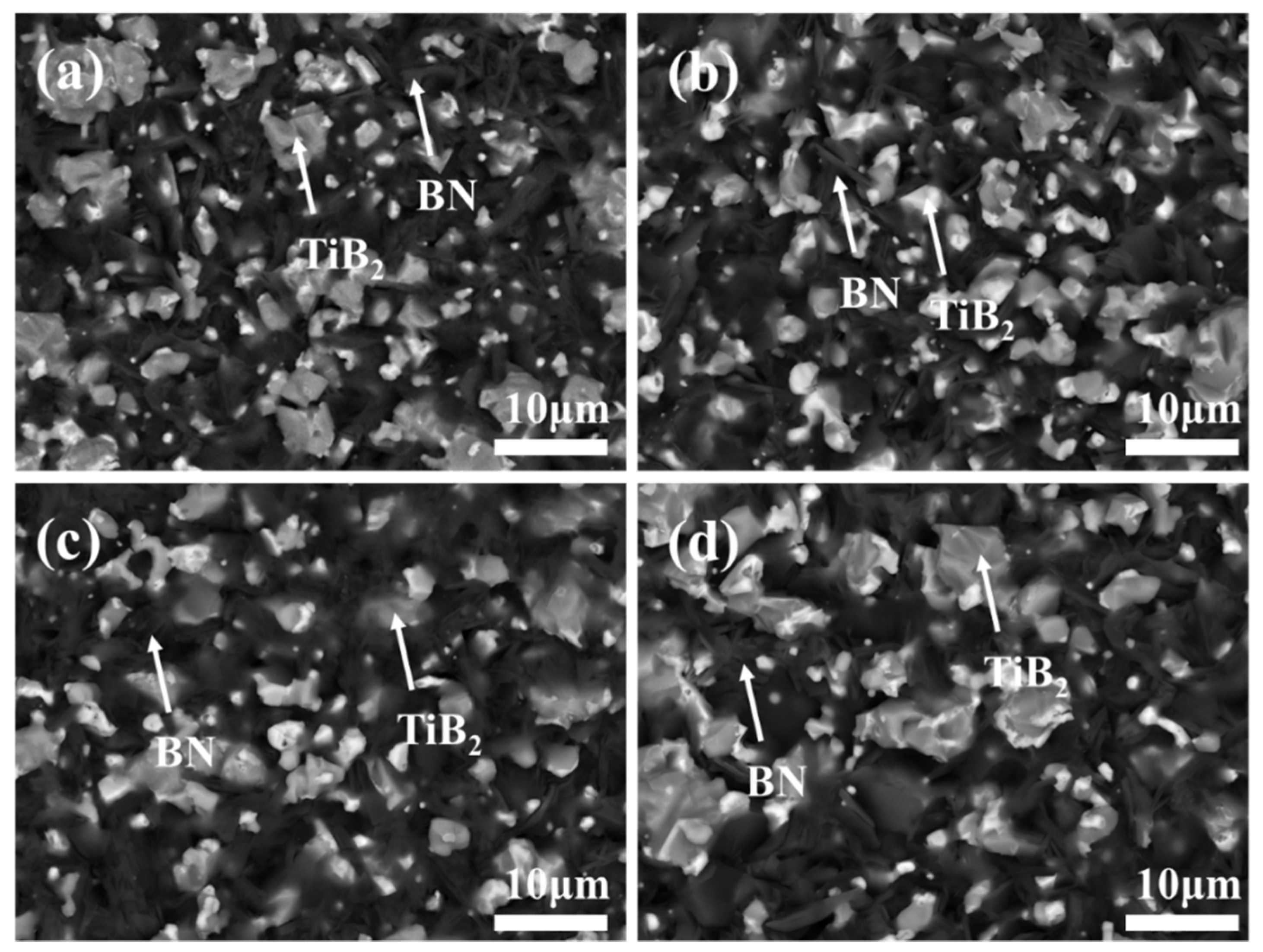
3.1.2. Influence of the TiB2-SiC Ratio on the Material Phase and Microstructure
3.2. Effects of the Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Material Properties, Microstructure, and Phase Composition
3.2.1. Effects of the Sintering Temperature on the Material Properties
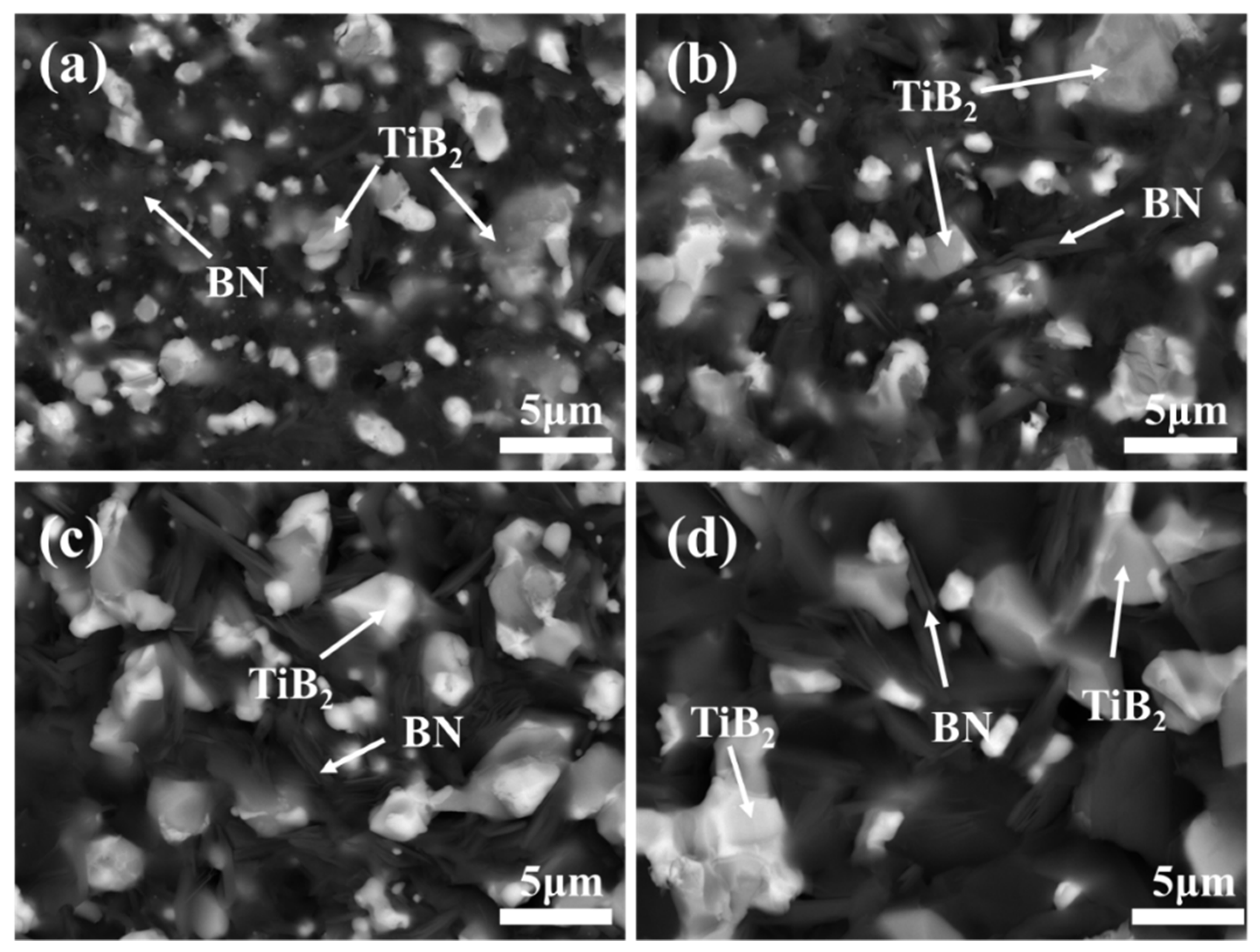
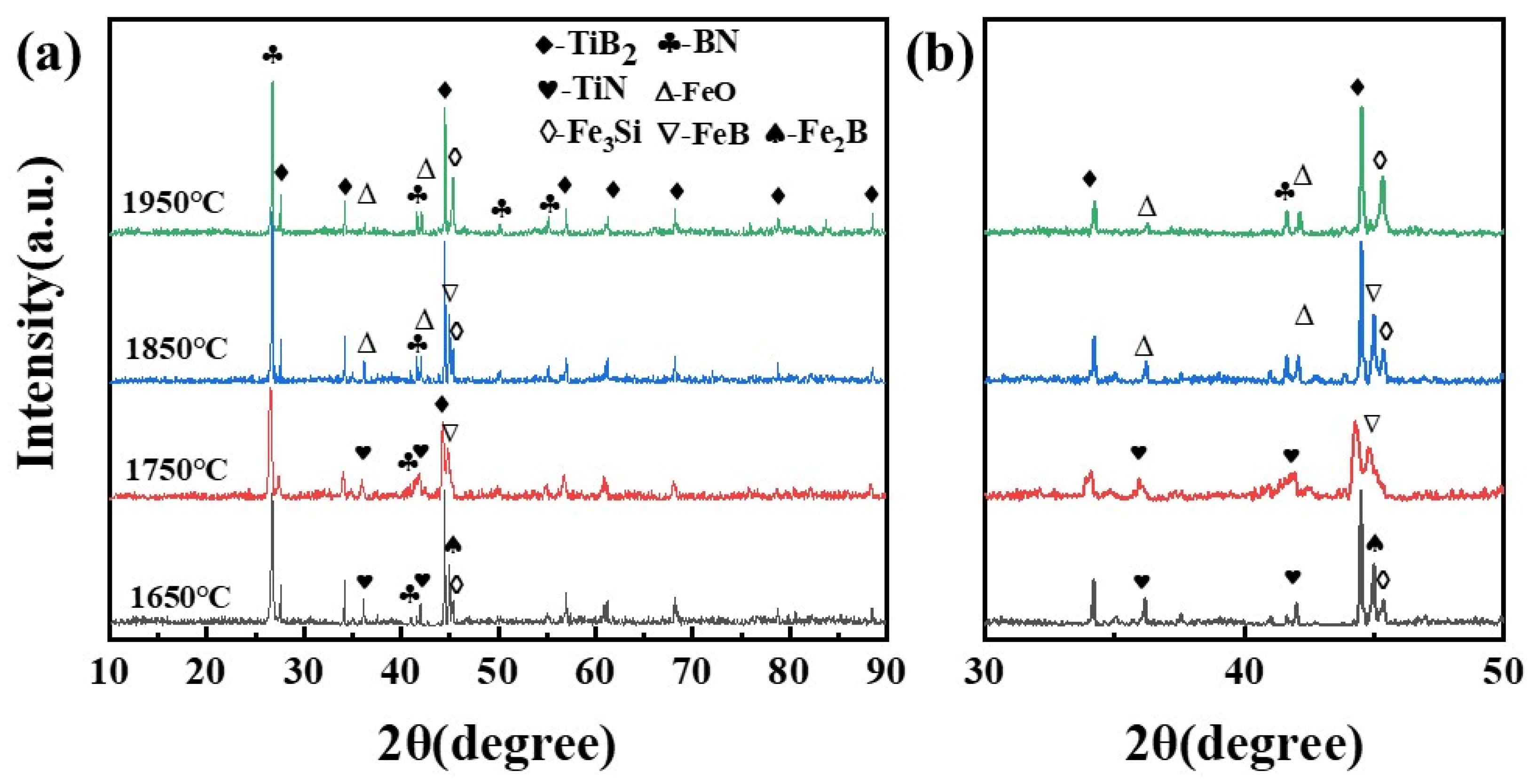
3.2.2. Influence of the Sintering Temperature on the Phase and Microstructure
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- As the ratio of TiB2-SiC increases, the electrical resistivity of the TiB2-BN-SiC composite ceramics decreases, the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient gradually increase, and the grain size of the ceramic cross-section increases significantly. When the ratio is increased from 3:1 to 12:1, the resistivity drops from 8000 to 5000 μΩ·cm; the thermal conductivity rises from 28.8 to 34.2 W/m·K; and the thermal expansion coefficient increases from 7.36 × 10−6/K to 10.80 × 10−6/K.
- (b)
- The increase in the sintering temperature of the multiphase ceramics promotes the relative density and mechanical properties of the ceramics. The electrical resistance initially increases and subsequently decreases at 1950 °C. The thermal conductivity and thermal expansion also gradually increase.
- (c)
- The small amount of Fe that is introduced in the process of mechanically alloying the composite powder reacts with the main powder and the impurities in the powder during the sintering process to produce FeB and FeO, among other products, and melts into a liquid phase at high temperature to promote the sintering of the ceramics. The earlier the liquid phase is formed, the higher the densification performance of the ceramic.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Ping, H.; Fu, Z. Large-scale synthesis and growth mechanism of boron nitride nanocomposite assembled by nanosheets and nanotubes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 5594–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Hamidzadeh Mahaseni, Z.; Dashti Germi, M.; Delbari, S.A.; Le, Q.V.; Ahmadi, Z.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Shahedi Asl, M.; Sabahi Namini, A. Densification behavior and microstructure development in TiB2 ceramics doped with h-BN. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 18970–18975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Xing, R.; Babapoor, A. Hot-pressing and characterization of TiB2–SiC composites with different amounts of BN additive. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16652–16660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-H.; Delbari, S.A.; Sabahi Namini, A.; Ahmadi, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Shahedi Asl, M.; Mohammadi, M. Microstructural evolution of TiB2–SiC composites empowered with Si3N4, BN or TiN: A comparative study. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Germi, M.D.; Mahaseni, Z.H.; Delbari, S.A.; Le, Q.V.; Ahmadi, Z.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Namini, A.S.; Asl, M.S. Enhanced densification of spark plasma sintered TiB2 ceramics with low content AlN additive. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 22127–22133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, T.; Xie, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, R.; Zhen, Q. Growth behavior of TiB2 hexagonal plates prepared via a molten-salt-mediated carbothermal reduction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-H.; Shahedi Asl, M.; Hamidzadeh Mahaseni, Z.; Dashti Germi, M.; Delbari, S.A.; Le, Q.V.; Ahmadi, Z.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Sabahi Namini, A.; Mohammadi, M. Role of co-addition of BN and SiC on microstructure of TiB2-based composites densified by SPS method. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 25341–25350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, J.; Lesniak, C. Boron nitride (BN) and BN composites for high-temperature applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, D.J.; Zhang, S.; Yan, J.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Gao, C.K.; Wang, N.; Liu, G.Q.; Gu, H.Q.; Wan, R.X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-deposited and annealed TiB2/BN superlattice coatings. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 5328–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, R.; Grasso, S.; Tudball, A.; Reece, M.J. Flash spark plsma sintering of cold-Pressed TiB2-hBN. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 2787–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, D.; Xue, C.; Niu, B.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Li, D.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Preparation and mechanical properties of laminated B4C–TiB2/BN ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31214–31221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Ping, H.; Fu, Z. Surface-diffusion mechanism for synthesis of substrate-free and catalyst-free boron nitride nanosheets. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 5324–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.; Räthel, J.; Höhn, S.; Eichler, J.; Michaelis, A. Interaction of titanium diboride/boron nitride evaporation boats with aluminium. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wang, Q.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C. Effects of ZrB2 addition on properties of BN-AlN-TiB2 composite ceramics. Naihuo Cailiao 2020, 54, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Yamashita, S.; Kubota, M.; Kita, H. B4C-SiC Ceramics with Interfacial Nanorelief Morphologies and Low Underwater Friction and Wear. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, L.K.; Xu, C. Hot pressing and microstructural characterization of SiC and TiN added TiB2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 3946–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Kita, H.; Hyuga, H.; Kondo, N.; Nagaoka, T. Reaction joining of SiC ceramics using TiB2-based composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 3203–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, T. Effect of sintering temperature on the mechanical properties and microstructures of pressureless-sintered B4C/SiC ceramic composite with carbon additive. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; He, R.; Cheng, X.; Fang, D. Fabrication and characterization of B4C–ZrB2–SiC ceramics with simultaneously improved high temperature strength and oxidation resistance up to 1600 °C. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 8000–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, H.; Wang, G.L.; Zhi, W. Oxidation mechanism and resistance of ZrB2-SiC composites. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Tian, S.; Xie, J.; Xiang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z. Microstructure and anisotropic mechanical properties of B6.5C-TiB2-SiC-BN composites fabricated by reactive hot pressing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, M.; Karunanithi, R.; RasoolMohideen, S.; Sivasankaran, S. A comprehensive exploration on the development of nano Y2O3 dispersed in AA 7017 by mechanical alloying and hot-pressing technique. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22924–22938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zarezadeh Mehrizi, M. Direct synthesis of NiAl intermetallic matrix composite with TiC and Al2O3 reinforcements by mechanical alloying of NiO–Al–Ti–C powder mixture. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 26863–26868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimba, Y.; Kondo, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Okuno, Y.; Kasada, R. Effect of mechanically alloyed sintering aid on sinterability of TiB2. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 21660–21667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Numerical simulation of the temperature field in sintering of TiB2-BN by SPS. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2006, 21, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.R.; Zhou, M. Effect of Microstructure on Dynamic Failure Resistance of Titanium Diboride/Alumina Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlup, Z.; Bača, Ľ.; Halasová, M.; Neubauer, E.; Hadraba, H.; Stelzer, N.; Roupcová, P. Effect of metallic dopants on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S. Fabrication and Characteristics of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kalita, M.P.C.; Peramal, A.; Srinivasan, A. Structural analysis of mechanically alloyed nanocrystalline Fe75Si15Al10 powders. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Akhlaghi, M. Microstructural characterization of TiB2–SiC–BN ceramics prepared by hot pressing. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29174–29182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Dong, L.; Gao, C.K.; Li, D.J. A study of structure, energy and electronic properties of TiB2/c-BN interface by first principles calculations. Opt. Mater. 2014, 36, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.W.; Berthebaud, D.; Yubuta, K.; Yoshikawa, A.; Shishido, T.; Suzuta, K.; Mori, T. New Synthesis Route for Complex Borides; Rapid Synthesis of Thermoelectric Yttrium Aluminoboride via Liquid-Phase Assisted Reactive Spark Plasma Sintering. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| TiB2-SiC | TiB2 (Vol%) | SiC (Vol%) |
|---|---|---|
| 3:1 | 21 | 7 |
| 6:1 | 24 | 4 |
| 9:1 | 25.2 | 2.8 |
| 12:1 | 25.8 | 2.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, S.; Liao, Z.; Guo, W.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Effects of theTiB2-SiC Volume Ratio and Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics. Crystals 2022, 12, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010029
Tian S, Liao Z, Guo W, He Q, Wang H, Wang W. Effects of theTiB2-SiC Volume Ratio and Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics. Crystals. 2022; 12(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Shi, Zelin Liao, Wenchao Guo, Qianglong He, Heng Wang, and Weimin Wang. 2022. "Effects of theTiB2-SiC Volume Ratio and Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics" Crystals 12, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010029
APA StyleTian, S., Liao, Z., Guo, W., He, Q., Wang, H., & Wang, W. (2022). Effects of theTiB2-SiC Volume Ratio and Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on the Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-BN-SiC Composite Ceramics. Crystals, 12(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010029





