Impact-Initiation Sensitivity of High-Temperature PTFE-Al-W Reactive Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
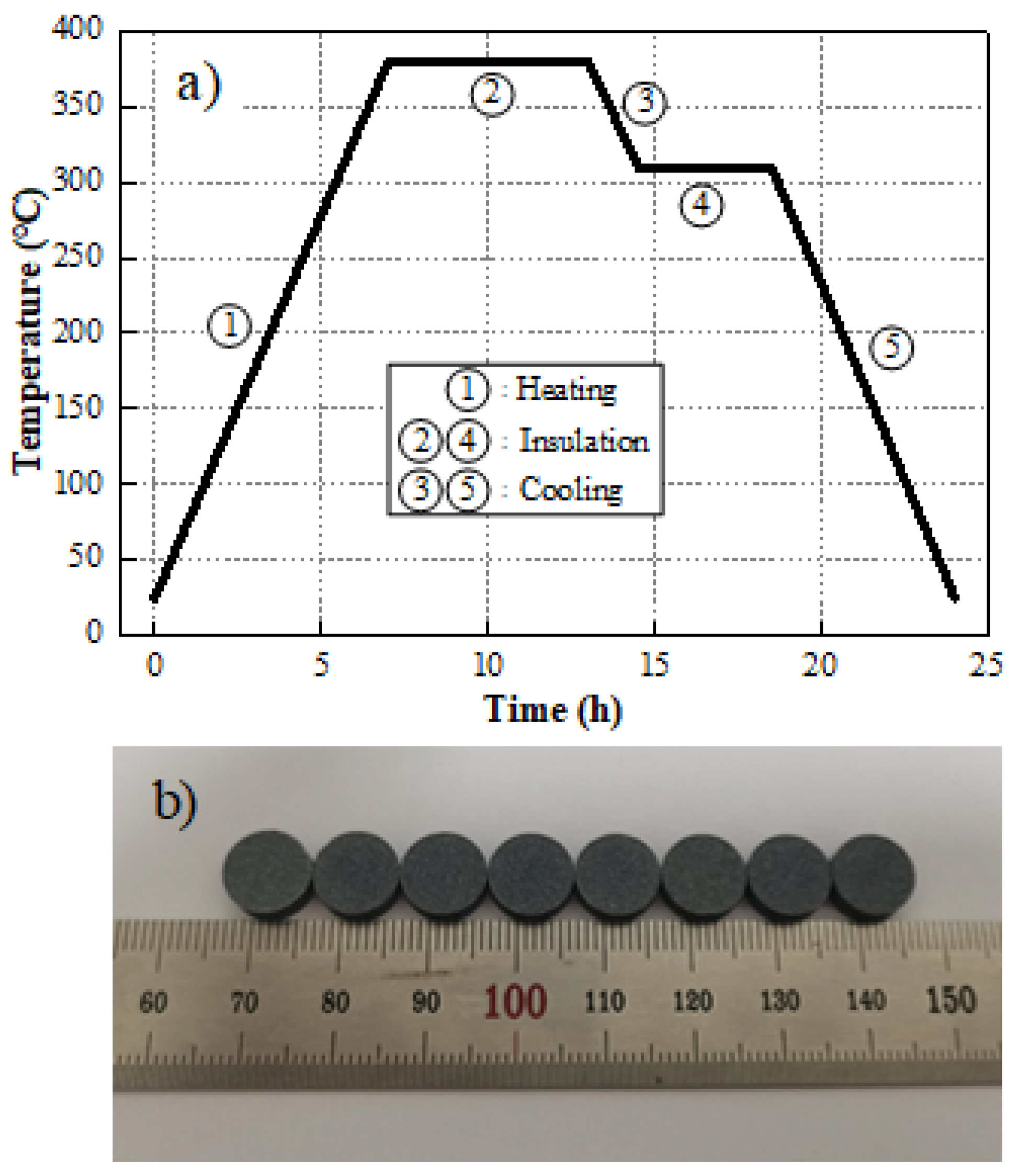
2.1. Sample Preparation
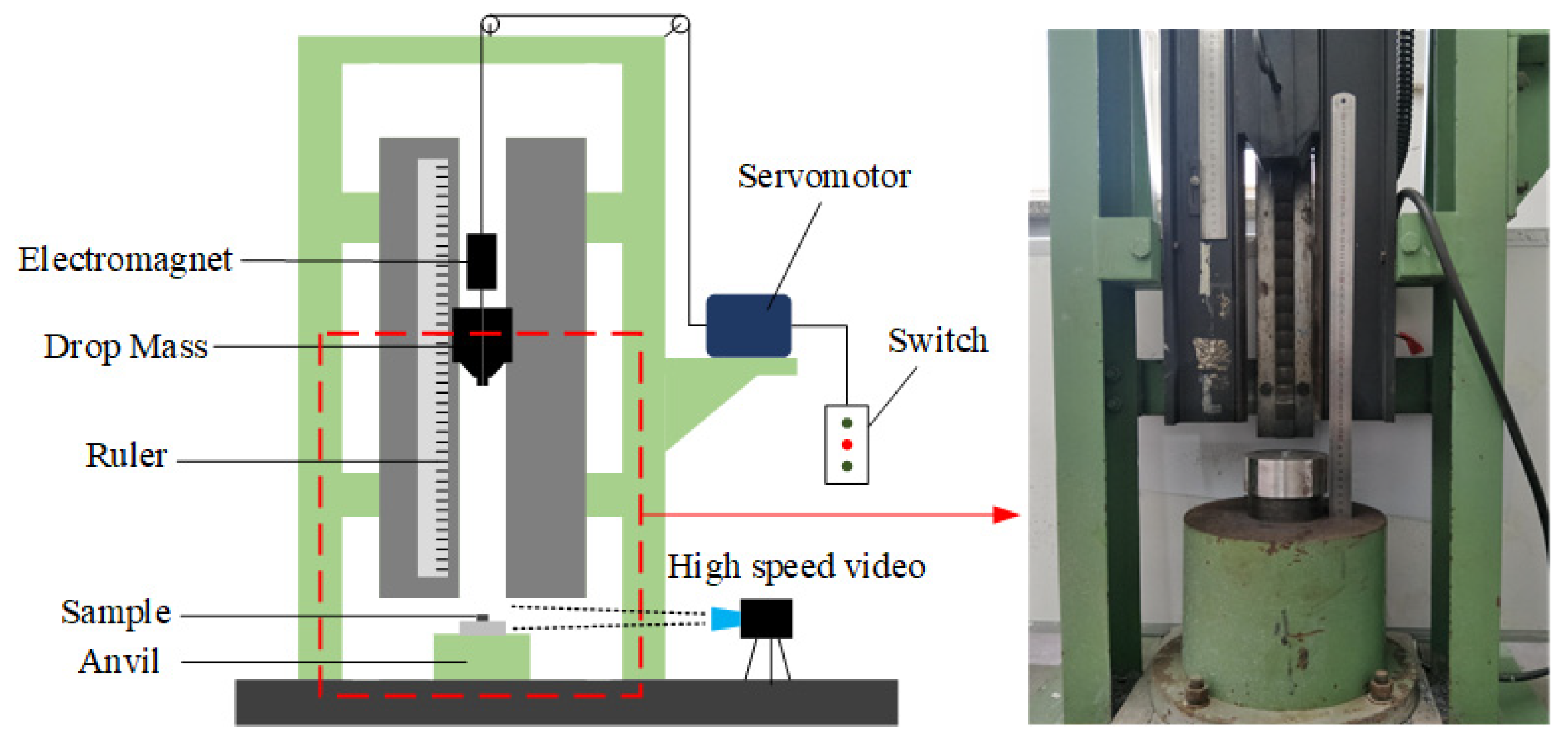
2.2. Drop-Weight Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crack-Induced Initiation Mechanism
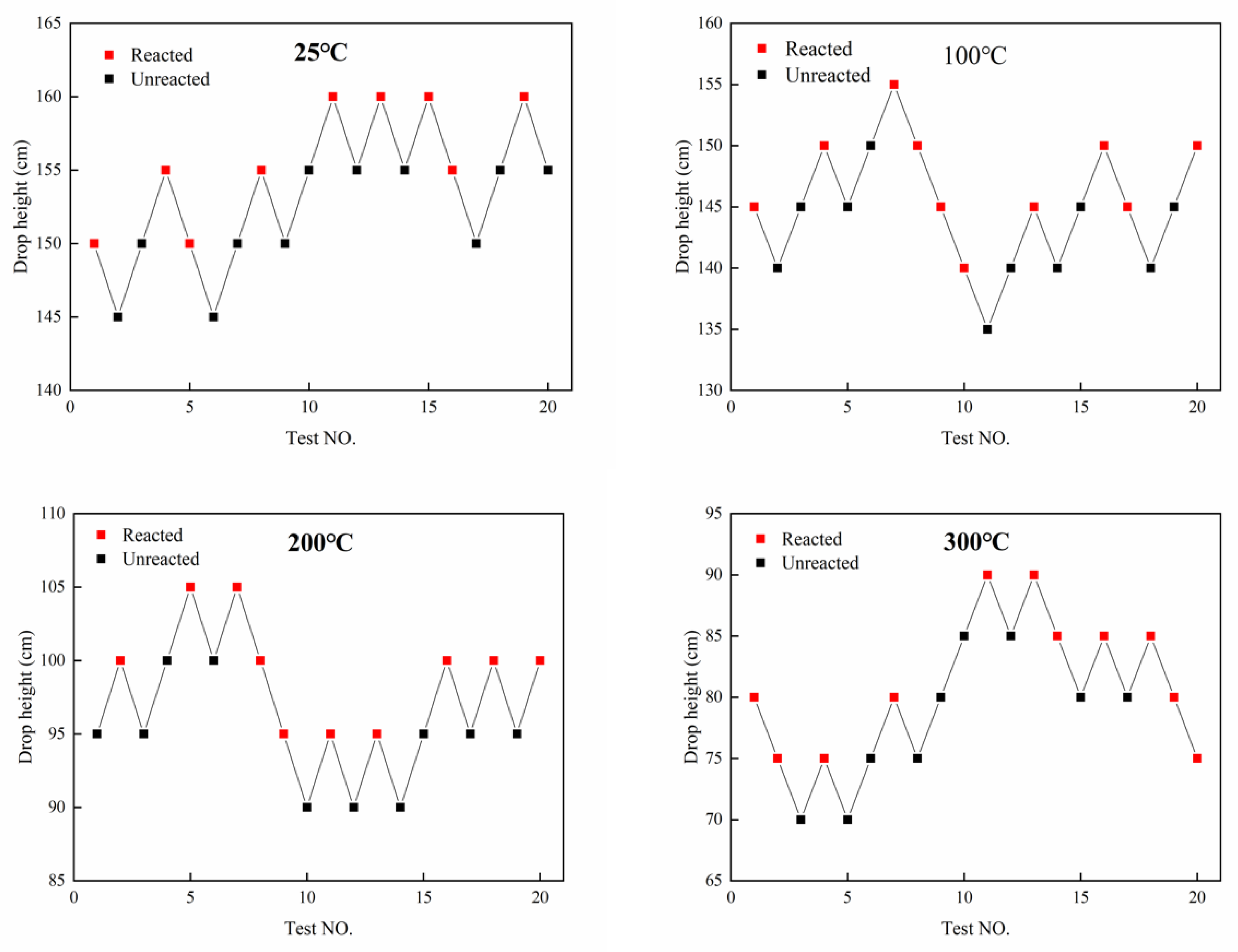
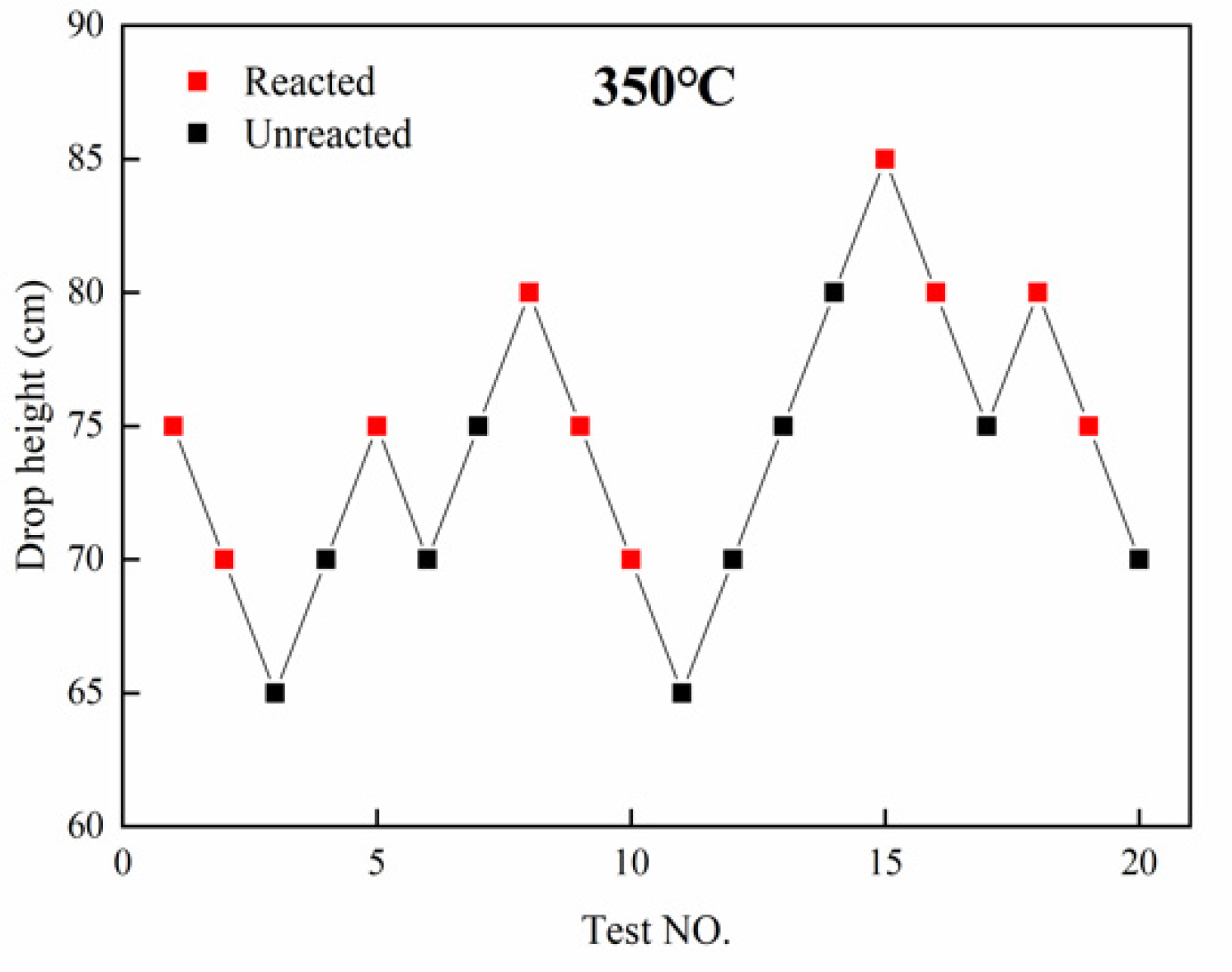
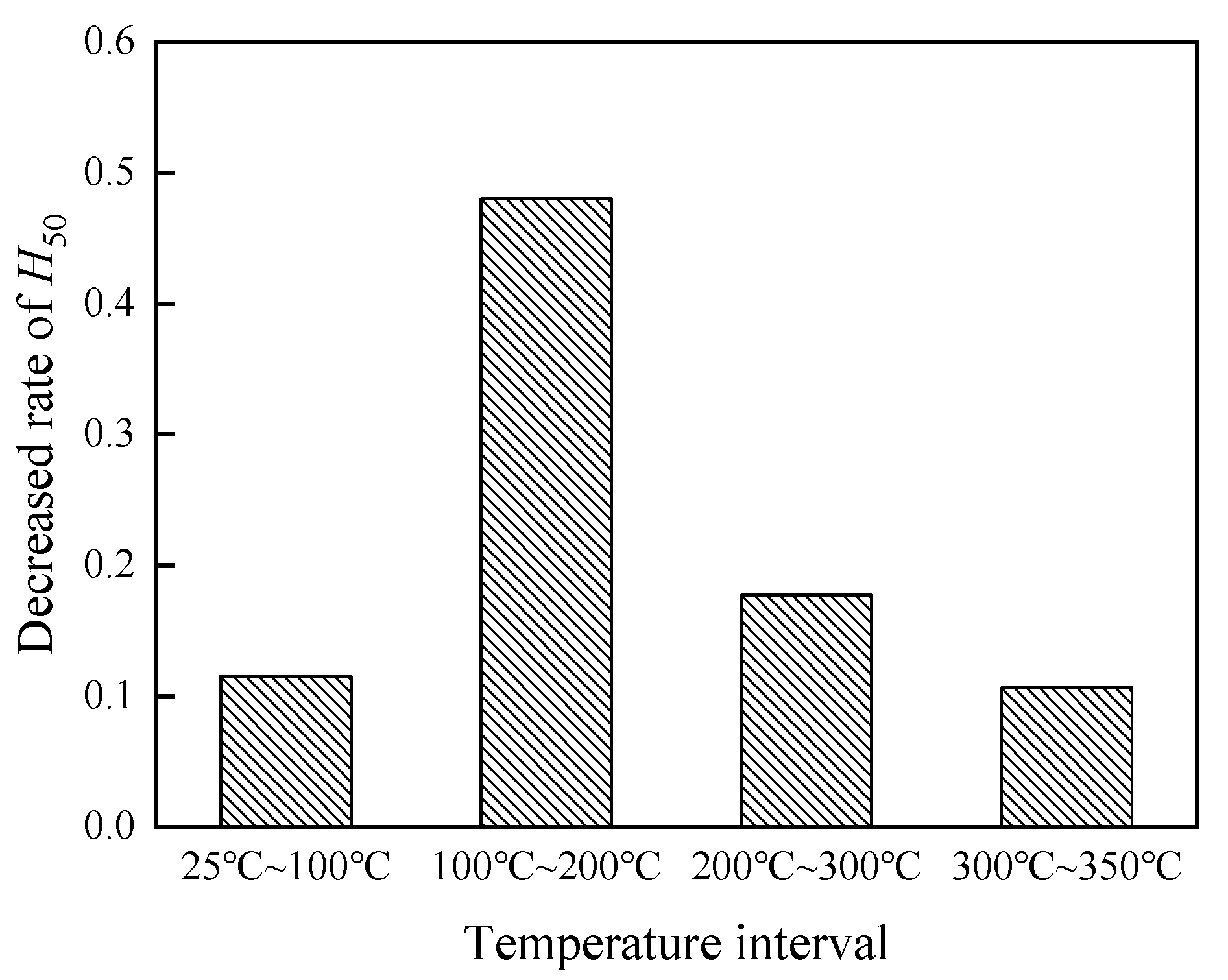
3.2. Influence of Temperature on Impact Sensitivity
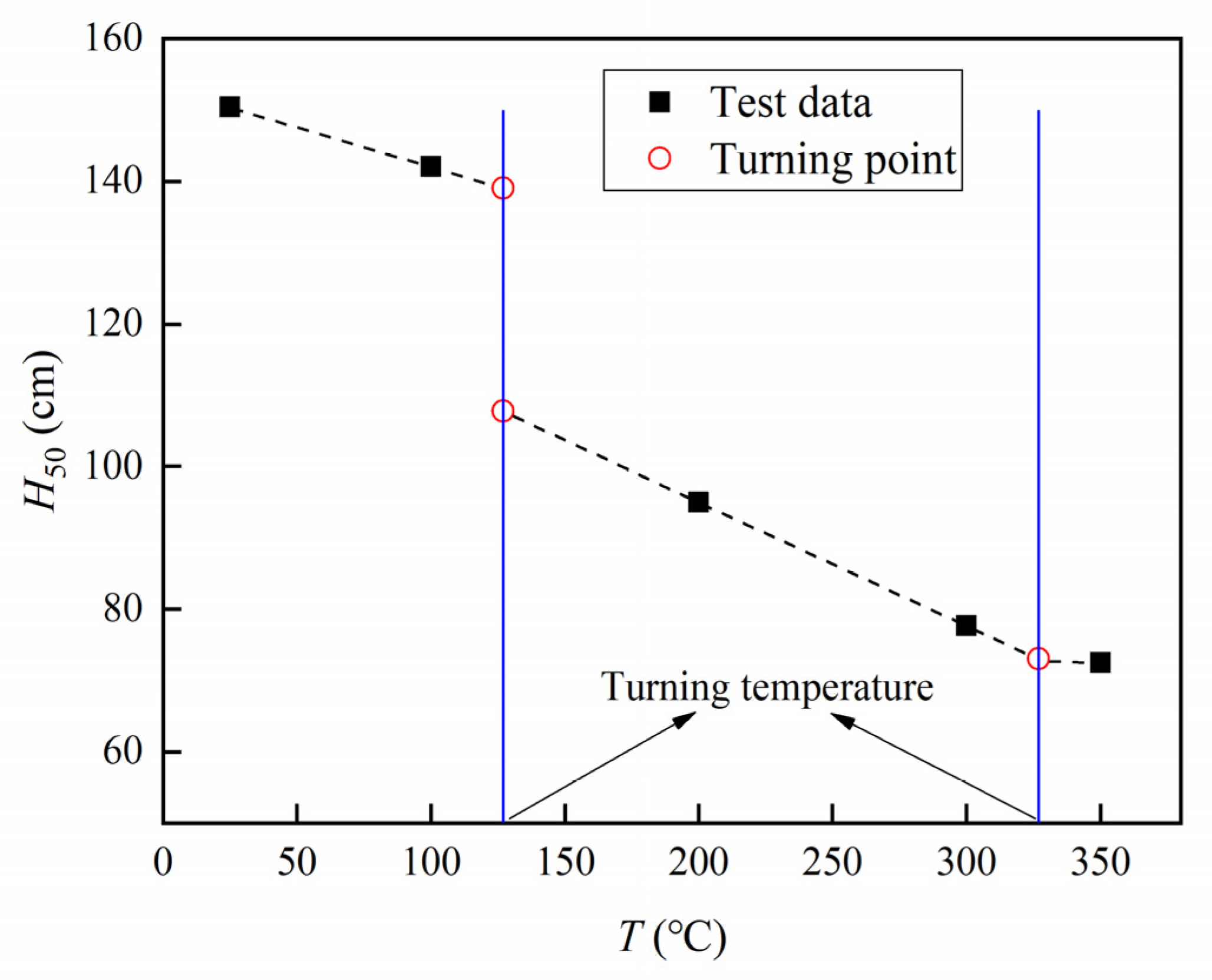
3.3. Thermal Sensitivity
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- The crack of the materials subjected to dynamic loading provided a high-temperature and aerobic environment, in which Al reacted violently with PTFE, thus inducing the initiation.
- (b)
- The impact-initiation sensitivity of the materials significantly depends on temperature. The sensitivity more than doubled with increasing the sample temperature from 25 to 350 °C.
- (c)
- The impact-initiation sensitivity of the materials showed a temperature interval effect. The sensitivity increased more rapidly in the temperature interval from 127 to 327 °C, but hardly changed after the temperature reached 327 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DE Technologies, Inc. Reactive Fragment Warhead for Enhanced Neutralization of Mortar, Rocket, & Missile Threats. ONR-SBIR 2006. N04-903. Available online: http://www.detk.com (accessed on 15 May 2006).
- Technologies Committee on Advanced Energetic Materials and Manufacturing, National Research Council. Advanced Energetic Materials; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Joshi Vasant, S. Process for Making Polytetrafluoroethylene-Aluminum Composite and Product Made. U.S. Patent 6547993 B1, 15 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Fang, X.; Wang, H.X.; Dong, W.; Li, Y.C. The effect of crystallinity on compressive properties of Al-PTFE. Polymers 2016, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, C.; Dong, Y.; Maimaitituersun, W.; Ren, Y.; Feng, S. Experimental study on impact-induced initiation thresholds of polytetrafluoroethylene/aluminum composite. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.G. Energy Release Characteristics of Impact-Initiated Energetic Materials. In MRS Proceeding; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, B.R.; Kimsey, K.D.; Love, B.M. High-velocity impact of low-density projectiles on structural aluminum armor. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Walley, S.M.; Hunt, R.J.A.; Proud, W.G.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Meyers, M.A. High-strain, high-strain-rate flow and failure in PTFE/Al/W granular composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, L.; Shi, A.S.; Zhang, Y.G.; He, Y.; Guan, Z.W. Experimental study of the compression properties of Al/W/PTFE granular composites under elevated strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 581, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, H.F. Damage effects of aluminum plate by reactive material projectile impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 104, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, H.F. Experimental study on penetration behavior of reactive material projectile impacting aluminum plate. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 95, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftenberg, M.N.; Mock, W.; Kirby, G.C. Modeling the impact deformation of rods of a pressed PTFE/Al composite mixture. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, S.Z.; Wang, H.X.; Tao, Z.M.; Fang, X. A crack-induced initiation mechanism of Al-PTFE under quasi-static compression and the investigation of influencing factors. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E.M.; Malcolm, S.; Pantoya, M.L.; Davis, F. Impact ignition of nano and micron composite energetic materials. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X. Investigation on reaction energy, mechanical behavior and impact insensitivity of W-PTFE-Al composites with different W percentage. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Maimaitituersun, W.; Dong, Y.; Tian, C. A study on the mechanical properties and impact-induced initiation characteristics of brittle PTFE/Al/W reactive materials. Materials 2017, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbold, E.B.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Benson, D.J.; Cai, J.; Vecchio, K.S.; Jiang, F.; Addiss, J.W.; Walley, S.M.; Proud, W.G. Particle size effect on strength, failure, and shock behavior in polytetrafluoroethylene-Al-W granular composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Geng, B.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, H. Experimental study on behind-plate overpressure effect by reactive material projectile. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q.M.; Long, R.R. Potential space debris shield structure using impact-initiated energetic materials composed of polytetrafluoroethylene and aluminum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 135–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, W.R.; Baber, B.B.; Ku, P.M. New test techniques for evaluating the compatibility of materials with liquid oxygen under impact. Tribol. Trans. 1968, 11, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speerschneider, C.J.; Li, C.H. A correlation of mechanical properties and microstructure of polytetrafluoroethylene at various temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 3004–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, K.N.G.; Fox, P.G.; Field, J.E. The temperature rise at the tip of fast-moving cracks in glassy polymers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1975, 341, 537–557. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, P.J.; Dattelbaum, D.M. The properties of poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE) in compression. Polymer 2004, 45, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, P.J.; Brown, E.N. The properties of poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE) in tension. Polymer 2005, 46, 8128–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakama, S.; Takemura, T. Transitions and phases of polytetrafluoroethylene. Jpn. J. App. Phys. 1969, 8, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccrum, N.G. An internal friction study of polytetrafluoroethylene. J. Polym. Sci. 1959, 34, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Temperature (°C) | 25 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 350 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unreacted |  |  | 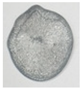 |  |  |
| Reacted |  |  | 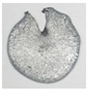 |  |  |
| T (°C) | 25 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 350 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H50 (cm) | 153.6 | 145 | 97 | 79.3 | 74 |
| Ec (J) | 150.5 | 142.1 | 95 | 77.7 | 72.5 |
| vc (m/s) | 5.5 | 5.3 | 4.4 | 3.9 | 3.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H. Impact-Initiation Sensitivity of High-Temperature PTFE-Al-W Reactive Materials. Crystals 2022, 12, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010030
Sun T, Zheng Y, Yuan Y, Wang H. Impact-Initiation Sensitivity of High-Temperature PTFE-Al-W Reactive Materials. Crystals. 2022; 12(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tao, Yuanfeng Zheng, Ying Yuan, and Haifu Wang. 2022. "Impact-Initiation Sensitivity of High-Temperature PTFE-Al-W Reactive Materials" Crystals 12, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010030
APA StyleSun, T., Zheng, Y., Yuan, Y., & Wang, H. (2022). Impact-Initiation Sensitivity of High-Temperature PTFE-Al-W Reactive Materials. Crystals, 12(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010030







