An Overview of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Particles: Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
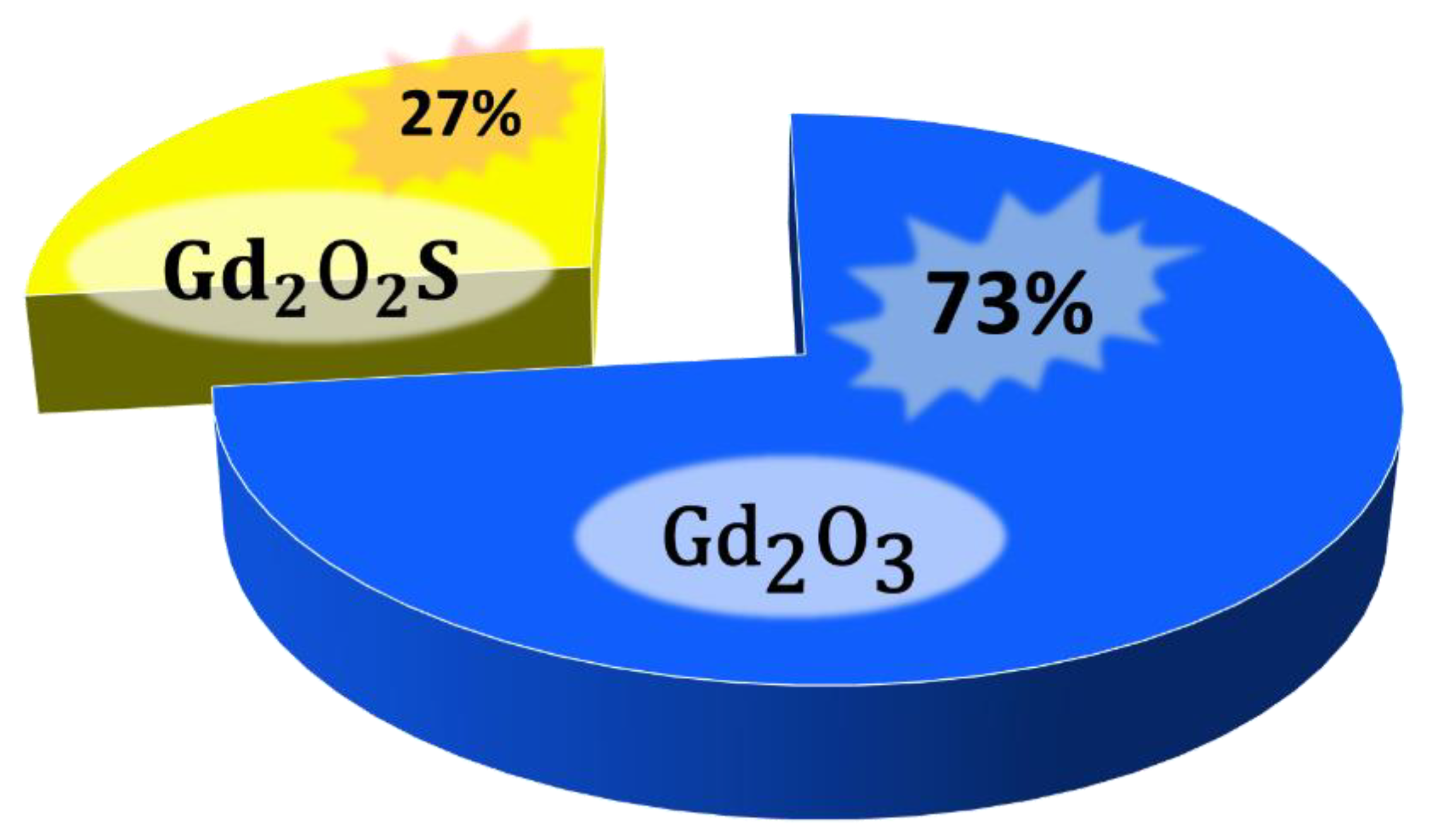
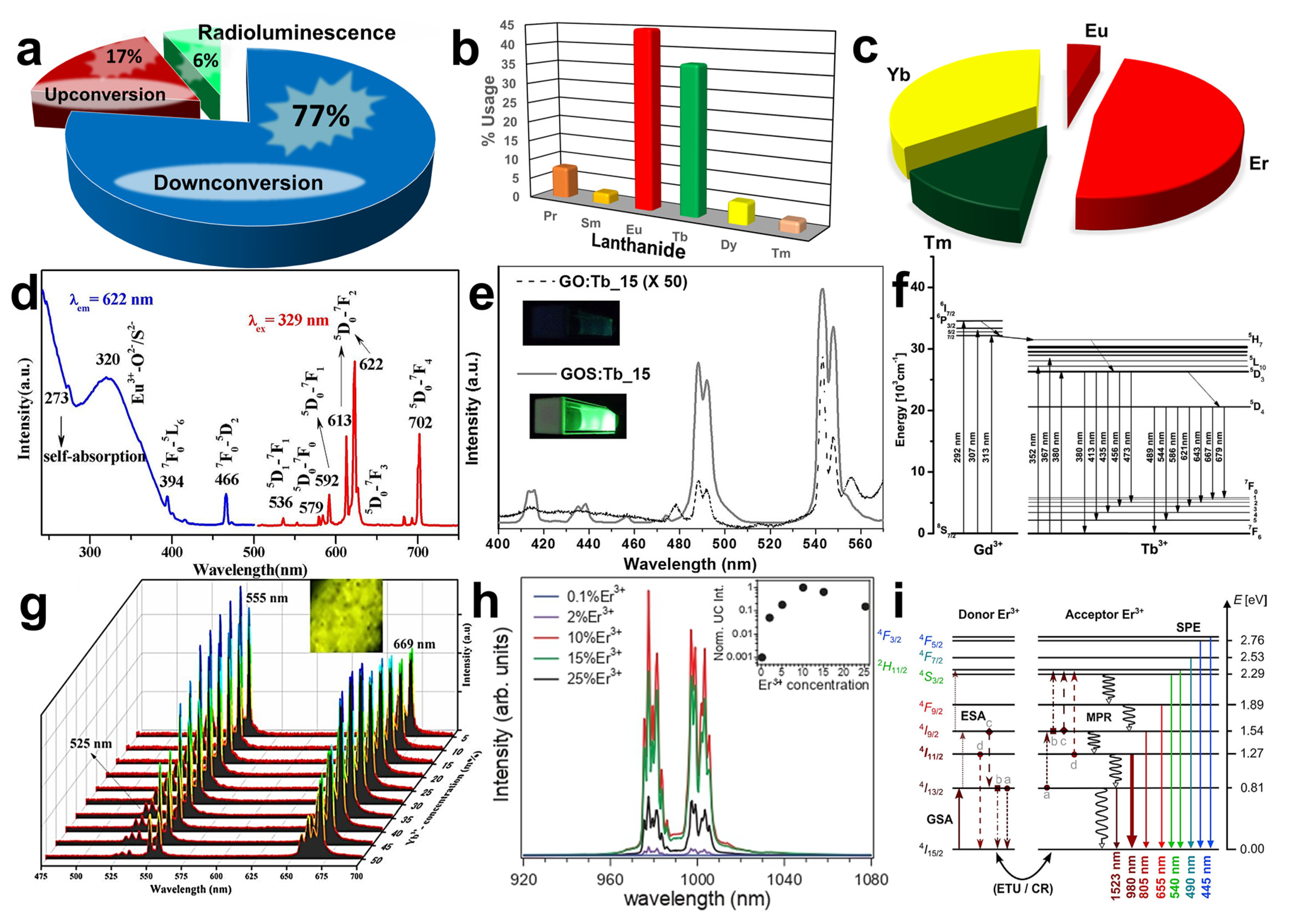
2. Optical Properties of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Materials
2.1. Gadolinium-Based Oxide
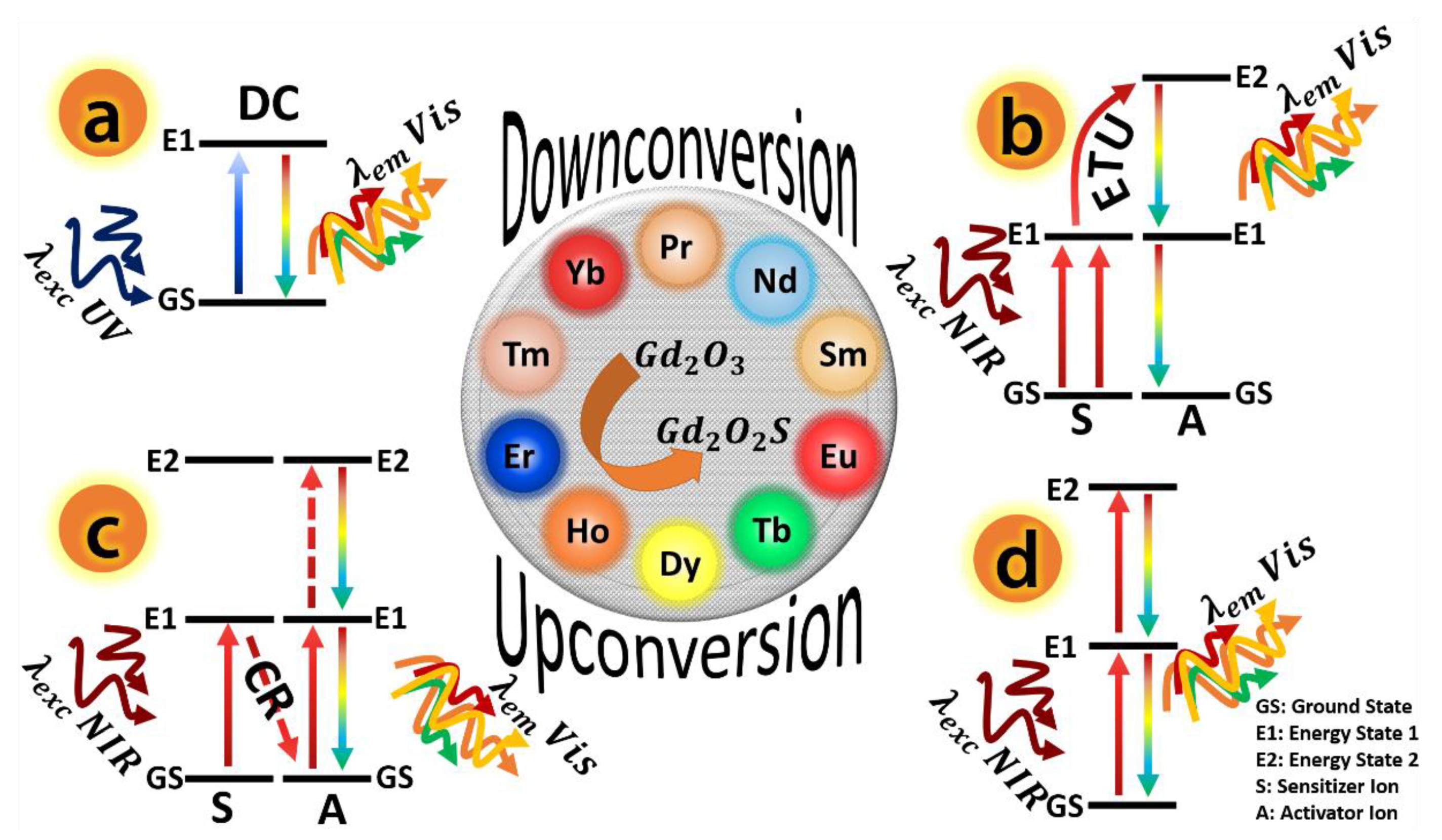
2.2. Down- and Up-Conversion Emission Processes
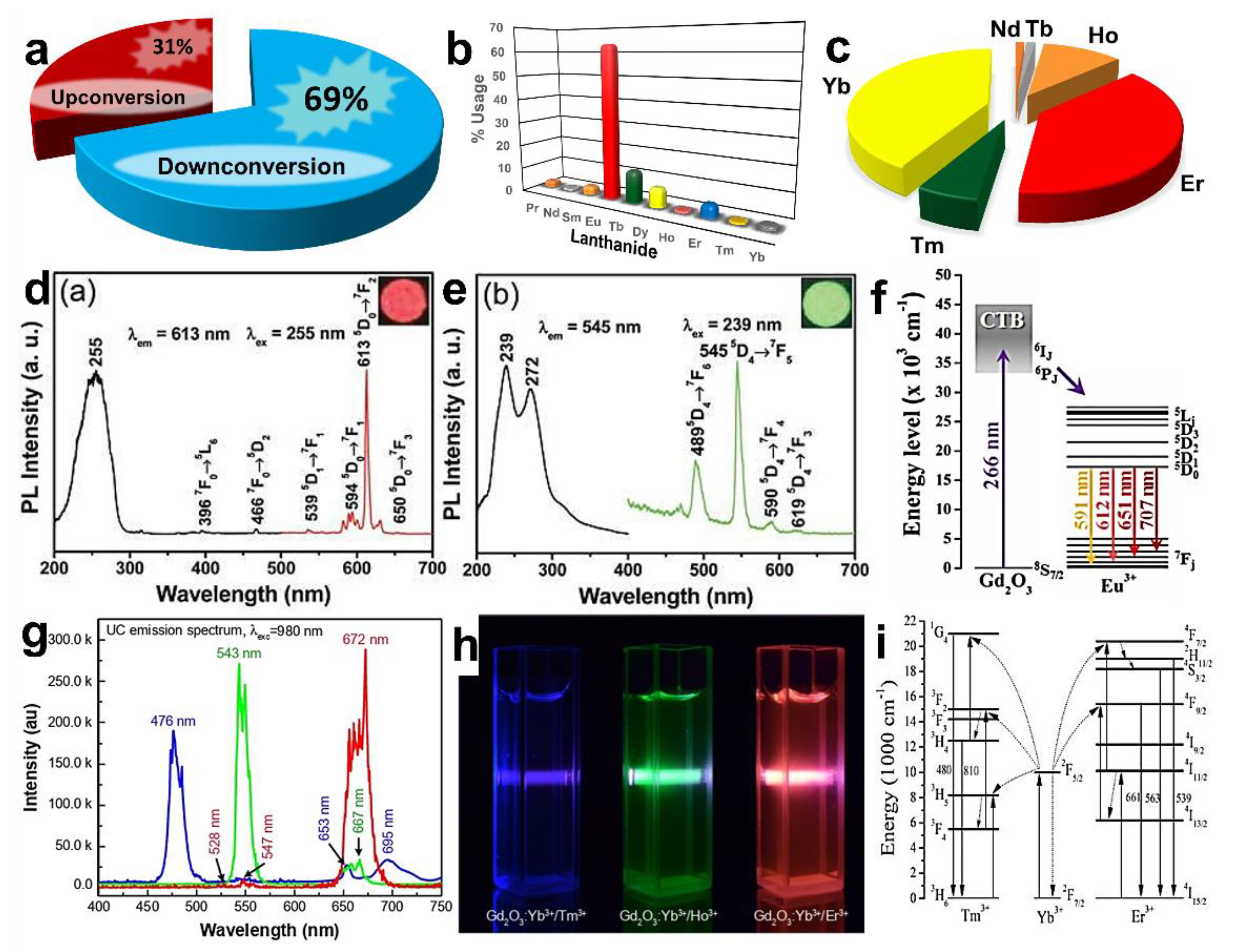
2.3. Dopants and Their Effect on the Photoluminescence Emission of Gd2O3
2.4. Dopants and Their Effect on the Photoluminescence of Gd2O2S
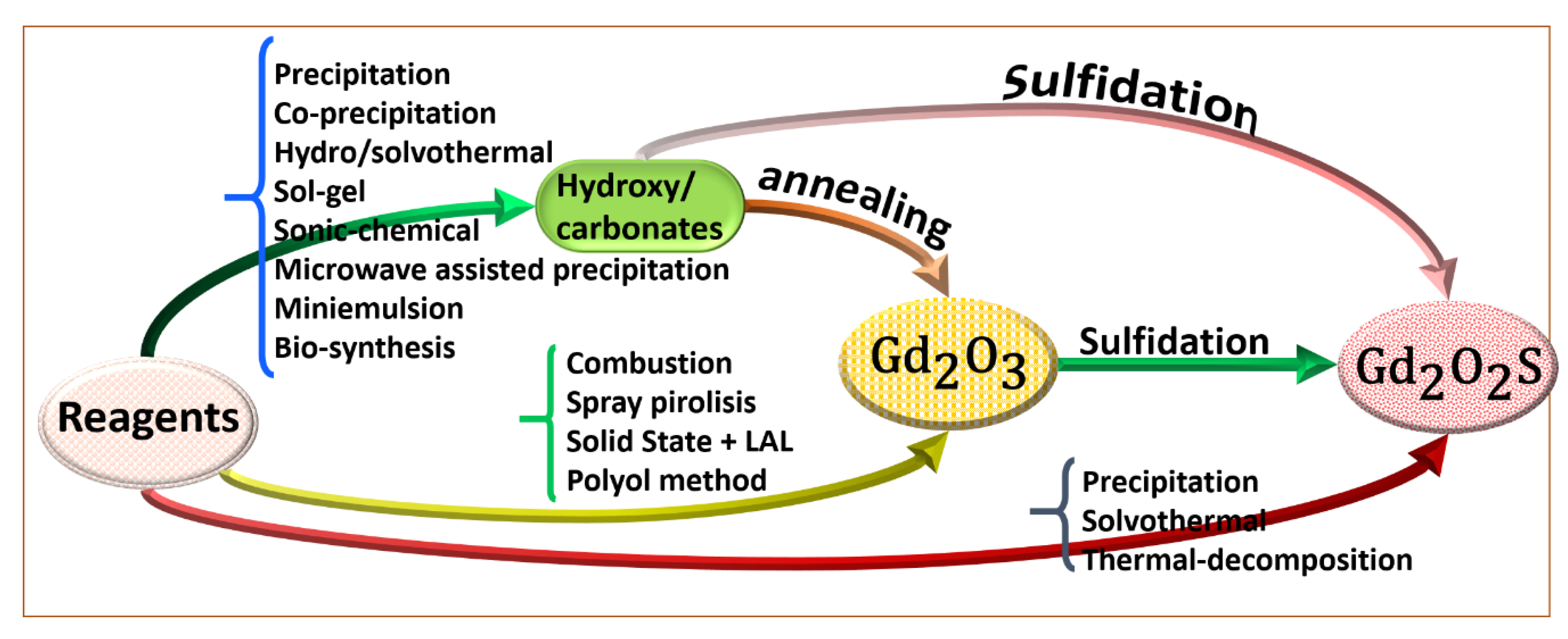
3. Status on Gadolinium-Based Nanoparticles Synthesis
3.1. Gd2O3 Synthesis Routes
3.1.1. Sonic-Chemical Method
3.1.2. Solid-State Technic
3.1.3. The Sol-Gel Method
3.1.4. Polyol Protocol
3.1.5. Hydrothermal Method
3.1.6. Microwave-Assisted Gd2O3 NPs Synthesis
3.1.7. The Mini Emulsion Technic
3.1.8. Biosynthesis
3.1.9. Thermal Decomposition
3.1.10. Combustion Method
3.1.11. Precipitation Method
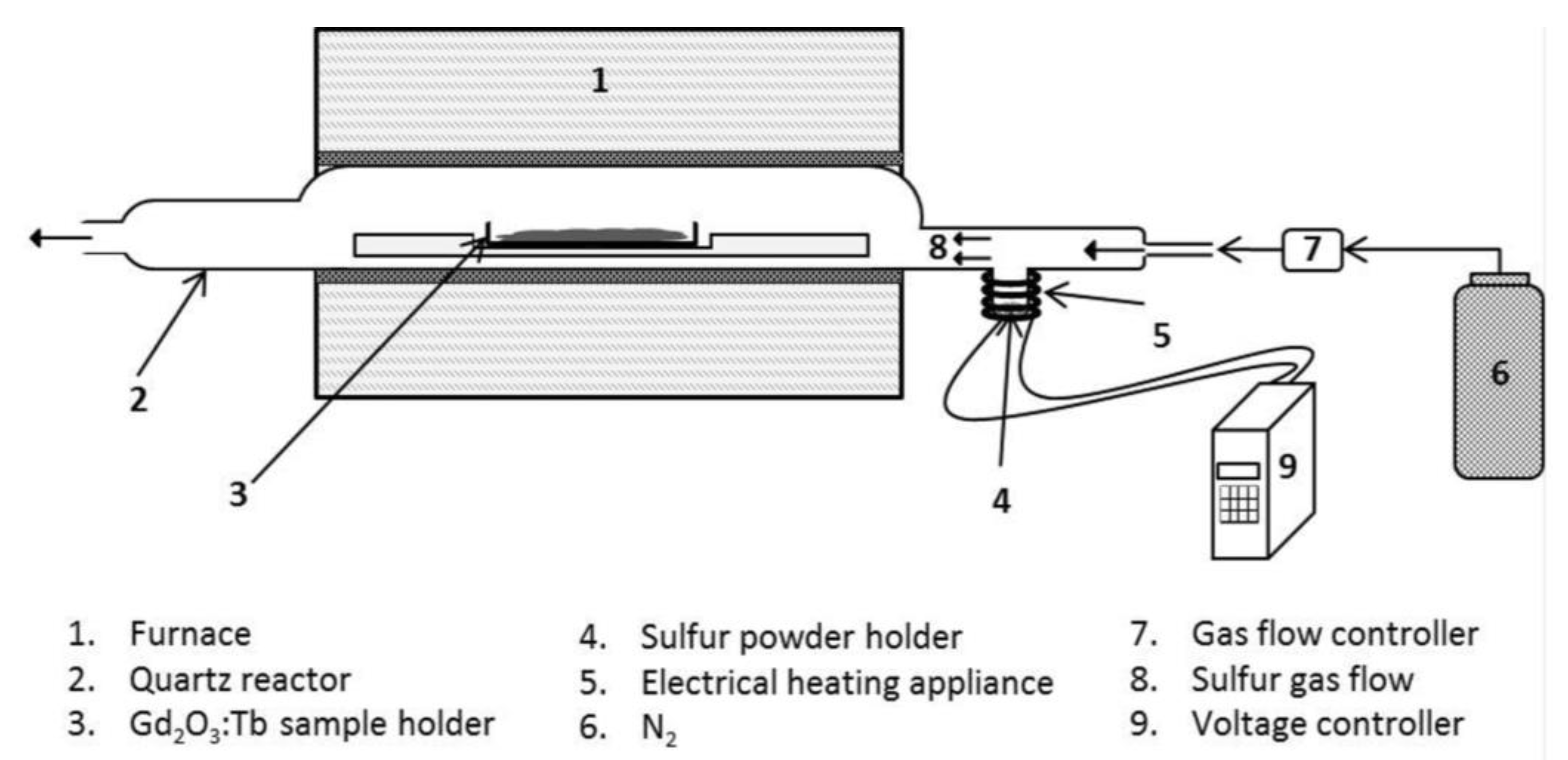
3.2. Gd2O2S Synthesis Routes
3.2.1. Sulfidation Process
3.2.2. Direct Precipitation of Oxysulfides
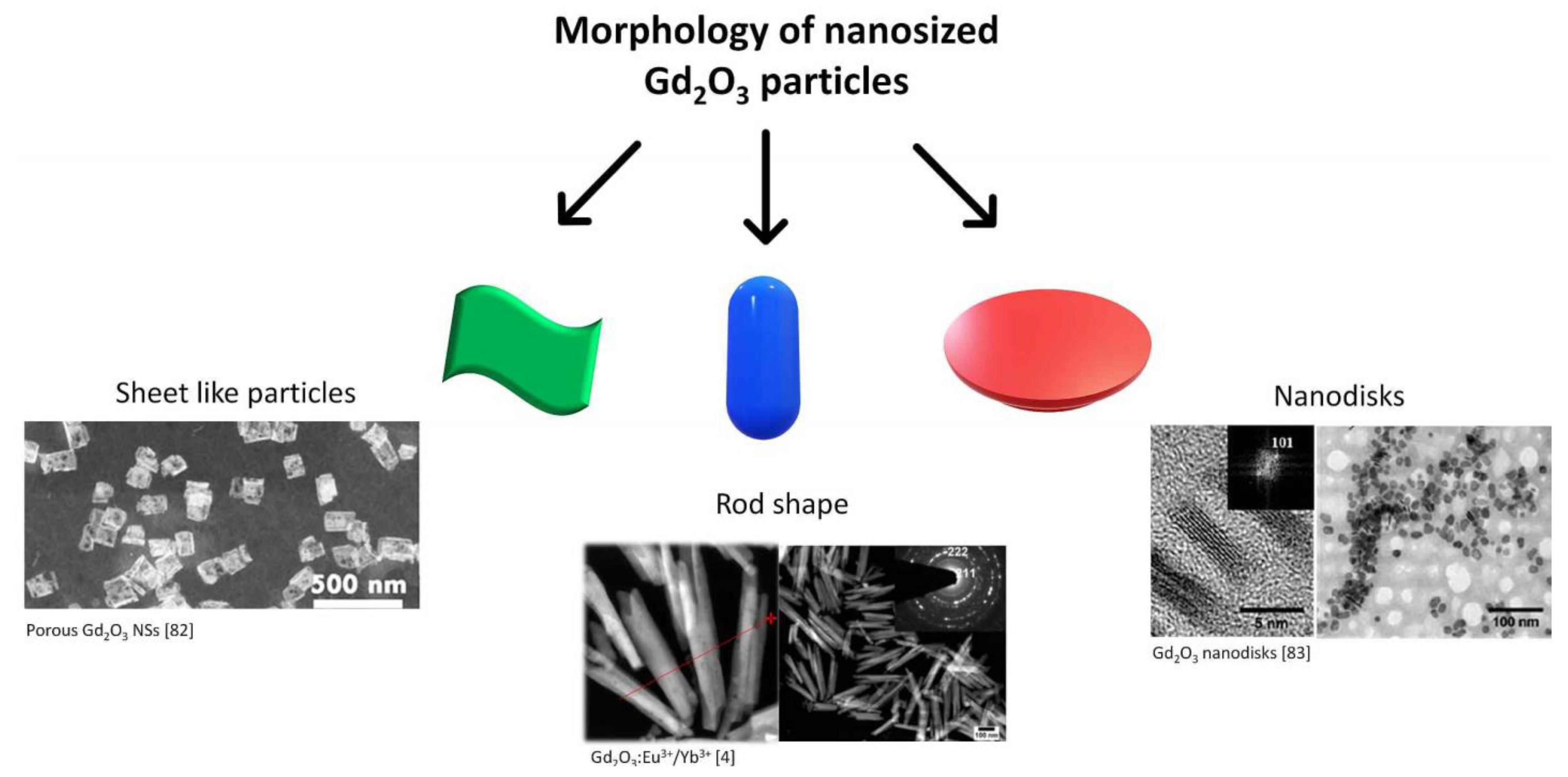
4. Texture, Shape, and Size of Gadolinium-Based Oxides and Oxysulfides
4.1. Gadolinium-Based Oxides
4.1.1. Porous Gadolinium-Based Sheet-like Particles
4.1.2. Gadolinium-Based Nanodisks
4.1.3. Gadolinium-Based Spherical NPs
4.1.4. Rod Shaped Gadolinium NPs
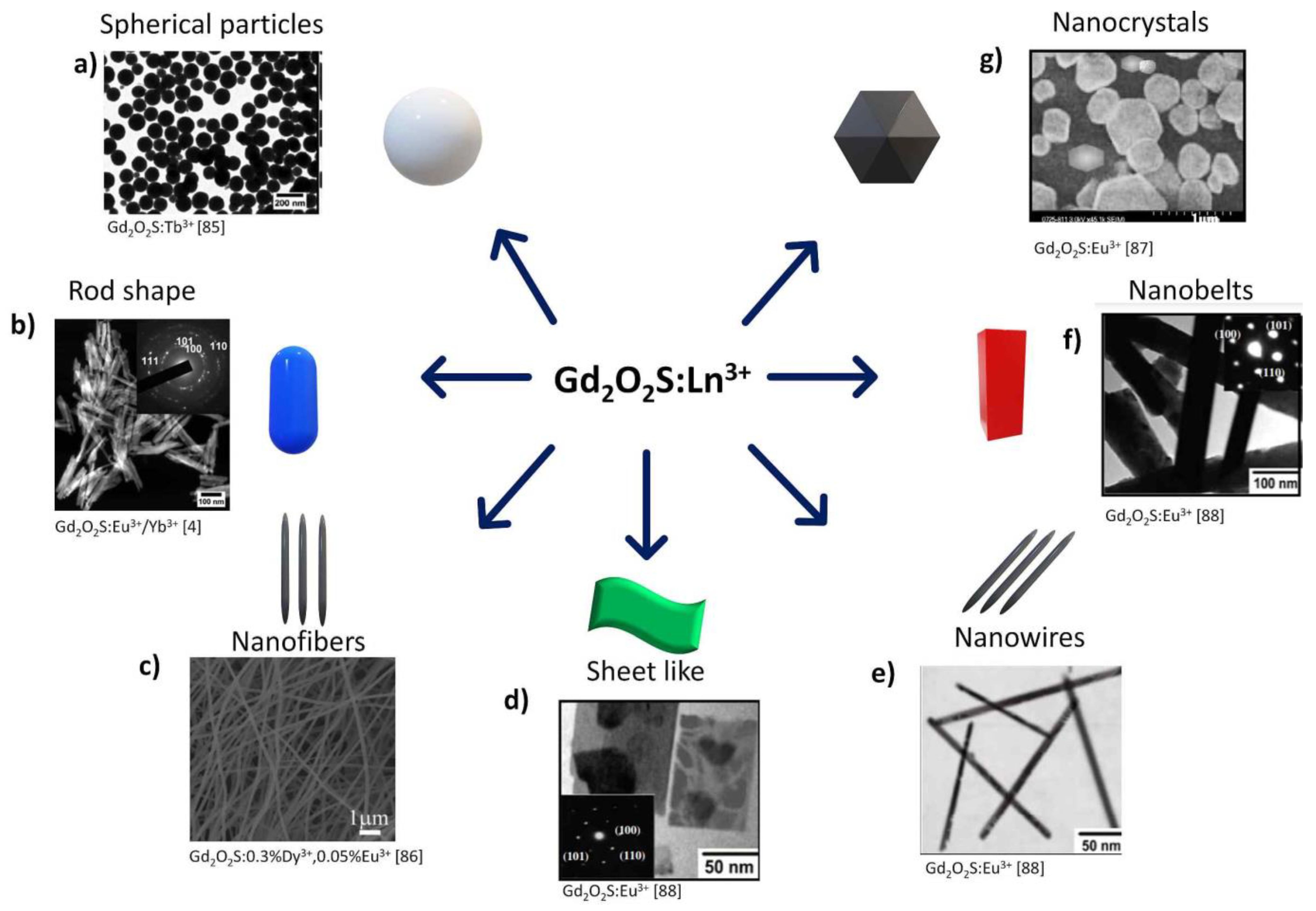
4.2. Gadolinium-Based Oxysulfides
4.2.1. Spherical Particles
4.2.2. Submicron Sized Spheres
4.2.3. Nanorods
4.2.4. Nanofibers
4.2.5. Hexagonal Shaped, Nanosheets, Nanobelts, Nanotubes, Nanorods, Nanowires Particles
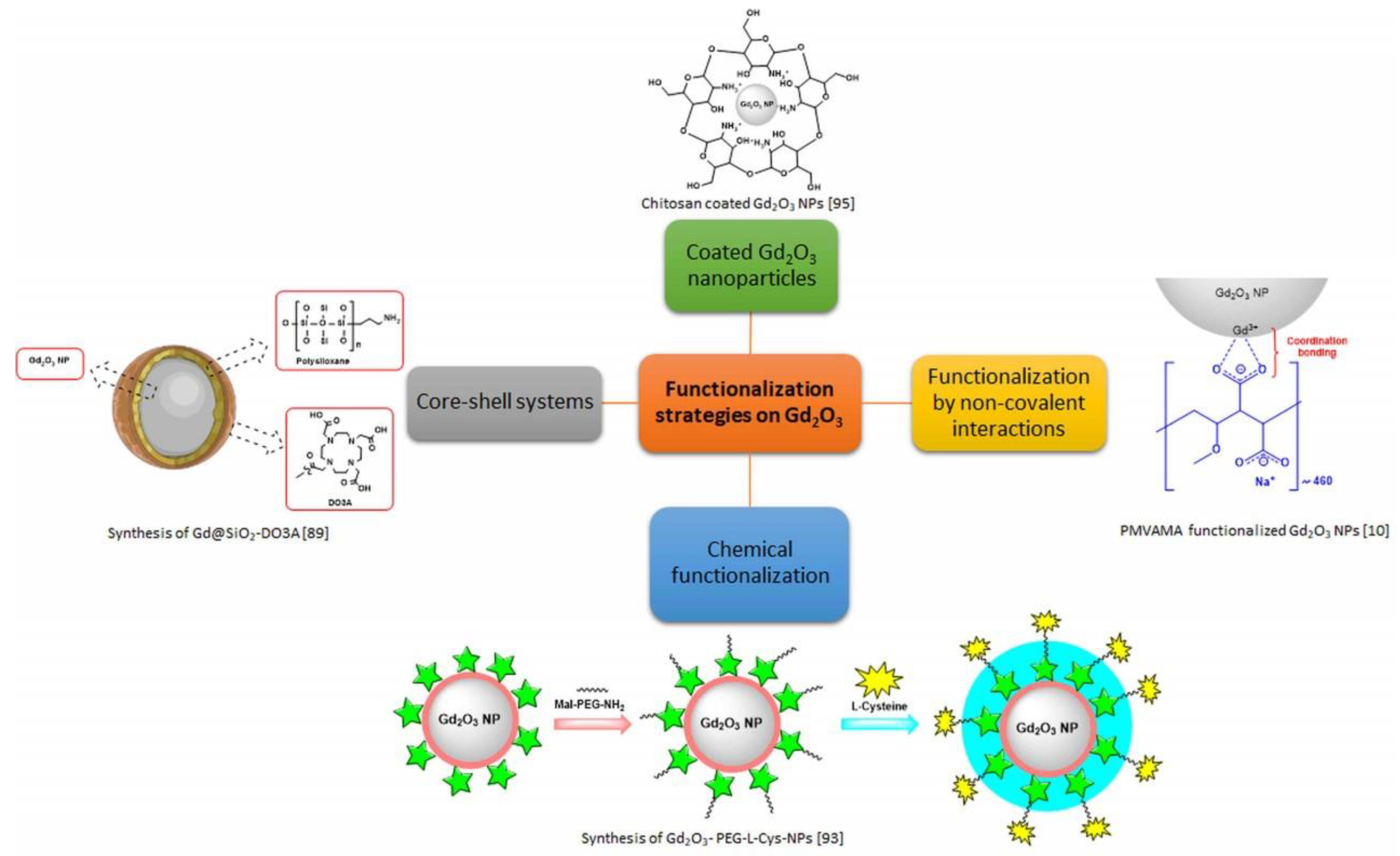
5. Surface Chemistry and Functionalization Strategies on Gadolinium-Based Oxides and Oxysulfides
5.1. Gadolinium-Based Oxides
5.1.1. Core-Shell Systems
5.1.2. Functionalization by Non-Covalent Interactions
5.1.3. Functionalization by Chemical Conjugation
5.1.4. Coated Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles
5.2. Gadolinium-Based Oxysulfides
5.2.1. PEGylation
5.2.2. Core-Shell Systems
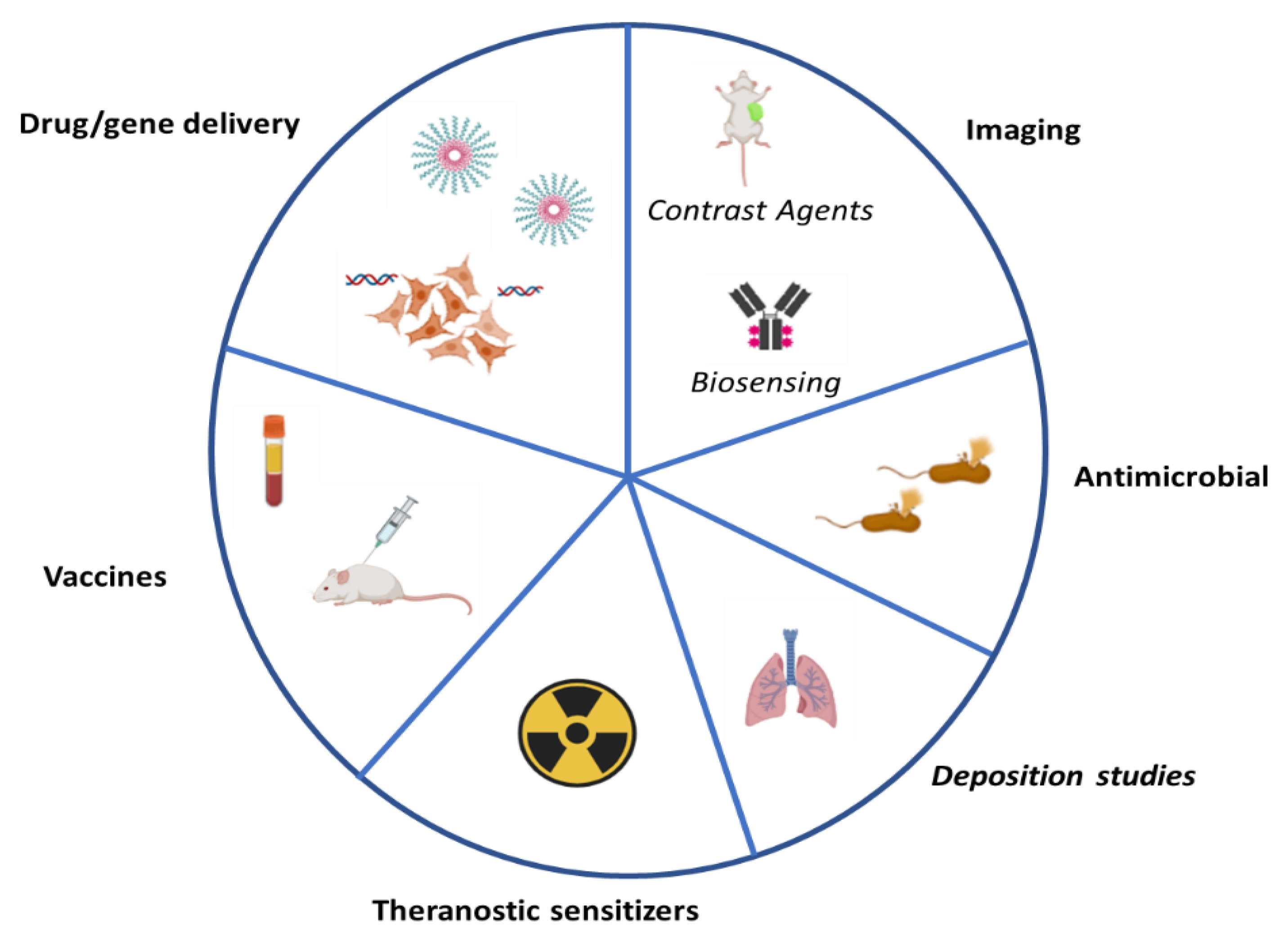
6. Biological Applications on Gadolinium-Based Particles
6.1. Imaging
6.1.1. Gd2O3 Particles
6.1.2. Gd2O2S Particles
| Particle | Synthesis Strategy | Size and Morphology | Biological Application | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd2O3 | Modified polyol protocol | Nanospheres | Imaging | Longitudinal proton relaxivities higher than the contrast agents commonly used for MRI | [99] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Polyol | Nanoplatelets | Imaging | Doping with Eu exhibits strong PL spectra, especially at 612 nm | [100] |
| Gd2O3 | One-pot | Ultrasmall nanospheres | Imaging | NPs showed high longitudinal relaxivities. These allowed the visualization of labeled cells implanted in vivo | [101] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Spray pyrolysis | Quasi-spherical | Imaging and immunosensing | Excellent matrix for antibody immobilization | [102] |
| Gd2O3 doped with Tb3+, Dy3+, Eu3+ | Gas-phase condensation | Fluffy morphology | Imaging and immunosensing | Strong emission lines and long lifetimes. Dy3+ was the most sensitive to concentration quenching | [31] |
| Gd2O3:Tb3+ | Spherical | Spherical | Imaging | Cellular fluorescence imaging in S18 cells clearly showed the green fluorescence from Gd2O3:Tb intracellular | [8] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Spray pyrolysis | Nearly-spherical | Imaging | NPs do not suffer any photobleaching and show significant excitation times | [103] |
| Gd2O3 | Organic synthesis | Ultrasmall nanospheres | Imaging | Improved longitudinal relaxivity r1 of 12.1 mM−1 s−1 at 7 T | [104] |
| Gd2O3 | Organic synthesis | Spherical | Imaging | NPs exhibited a longer longitudinal relaxation time (T1) and better biocompatibility with macrophage cell line | [105] |
| Gd2O3 | Polyol | Spherical | Theranostic sensitizers | The sensitizer enhancement ratio at the 10% survival level and elicited an increase in hydroxyl radical production, which led to DNA damage and cell cycle arrest. | [114] |
| Gd2O3 | Simple precipitation | Spherical | Antimicrobial agents | NPs had a potent antimicrobial effect against gram-negative and gram positives bacteria | [16] |
| Gd2O3 | Sonication technique | Spherical | Antimicrobial agents | NPs had antimicrobial and antifungal effects | [108] |
| Gd-NGO | Organic synthesis | Dendrimer | Drug and micro RNA delivery | NPs were able to deliver EPI and Let-7g miRNA into cells to destroy the DNA and then inhibited the cancer cell growth | [109] |
| Gd2O3 | Fungus based approach | Quasi-spherical | Drug delivery | Bioconjugation with taxol was potent in killing tumor/cancer cells | [70] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | High temperature solvothermal | Small triangular nanoplates | Drug delivery | Efficient delivery of drugs to the nuclei of cancer cells (HeLa and KB) with a high cytotoxic effect | [111] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Sol-gel process | Nanospheres | Drug delivery | The nanocomposite system exhibited more significant cytotoxicity compared to Dox free | [112] |
| Gd2O3 | Simple wet-chemical route | Rod-shaped | Drug delivery and imaging | Nanorods were internalized by cells more quickly than the control (DOX free) and displayed more cell cytotoxicity. Furthermore, these can serve as contrast agents for MRI | [17] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Flame pyrolysis | Spherical | Deposition studies | The dose of deposited particles was significantly greater in the juvenile rats at 2.22 ng/g body weight. The NPs did not show toxicity in any organ. | [18] |
| Gd2O3:Eu3+ | Spray flame pyrolysis | Quasi-spherical | Deposition, clearance, and translocation | NPs were detected in all the studied organs at low ppb levels; 59% of the particles remained in the lung. | [113] |
| Gd2O3:Tb3+/Er3+ | Hydrothermal | Spherical | Vaccines | Microparticles have shown an enhanced humoral (with a Th2-polarization) response compared with the control groups. | [19] |
| Gd2O3 | Polyol | Spherical | Imaging | The combination of NPs with CPC gives an injectable material that allowed the visualization of the implanted cement up to 8 weeks after implant | [115] |
| Gd2O2S: Er3+:Yb3+ | Hydroxycarbonate precursor precipitation. | Spherical | Imaging | NPs under infrared excitation (λex = 980 nm) show mainly red emission (≈650–680 nm). Consequently, they are more specifically designed for in vivo deep fluorescence imaging | [45] |
| Gd2O2S:Eu3+ | Hydroxycarbonate precursor precipitation | Spherical | Imaging | NPs demonstrated no toxic effects on whole organisms and their long-lasting tracking aptitude as well as their potential use as multimodal cell trace | [101] |
| Gd2O2S: Eu3+, Ti4+, Mg2+ | Hydrothermal | Nanoprobes | Imaging | NPs exhibited both persistent luminescence and paramagnetic properties. | [50] |
| Gd2O2S:Tb3+ | Urea homogenous precipitation | Hexagonal structure | Imaging | Emitting of green light from phosphor layer confirms its luminescence property. | [14] |
6.2. Antimicrobial Effects Gd2O3 Particles
6.3. Drug/Gene Delivery
Gd2O3 Particles
6.4. Deposition Studies
Gd2O3 Particles
6.5. Vaccines
Gd2O3 Particles
6.6. Theranostic Sensitizers
Gd2O3 Particles
7. Concluding Remarks and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escribano, P.; Julián-López, B.; Planelles-Aragó, J.; Cordoncillo, E.; Viana, B.; Sanchez, C. Photonic and Nanobiophotonic Properties of Luminescent Lanthanide-Doped Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 18, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gui, Q.; Ma, J.; Qi, L.; Bao, B.; Huang, Y. Upconversion Nanotubes with Tunable Fluorescence Properties Based on Gd2O2S:Ln3+ (Ln3+ = Yb3+, Er3+) and Derivatives for Photodynamic Therapy. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Lin, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Huang, G.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.-H. Gadolinium Oxysulfide-Coated Gold Nanorods with Improved Stability and Dual-Modal Magnetic Resonance/Photoacoustic Imaging Contrast Enhancement for Cancer Theranostics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Angel-Olarte, C.; Hernández-Adame, L.; Mendez-Blas, A.; Palestino, G. Eu3+/Yb3+ Co-Doped Gadolinium Oxysulfide Upconverting Nanorods: Morphological, Physicochemical and Optical Evaluation. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 787, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larquet, C.; Carenco, S. Metal Oxysulfides: From Bulk Compounds to Nanomaterials. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiro, V.; Parreira, P.; Freitas, S.C.; Martins, M.C.L.; Pêgo, A.P. Chapter 2-Conjugation Chemistry Principles and Surface Functionalization of Nanomaterials. In Biomedical Applications of Functionalized Nanomaterials; Sarmento, B., das Neves, J., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 35–66. ISBN 978-0-323-50878-0. [Google Scholar]
- Perdigon-Lagunes, P.; Estevez, O.; Zorrilla, C.; Gomez, A.; Herrera-Becerra, R. Alkaline Tannin Assisted Synthesis of β-Gd and Gd2O3nanoparticles at Room Temperature. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, N.; Yang, G.; Chen, D.; Li, L. Terbium-Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation in Liquid for Use as a Fluorescence and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Dual-Modal Contrast Agent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 17, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niftaliev, S.I.; Kuznetsova, I.V.; Saranov, I.A.; Zhundrikova, T.V.; Lygina, L.V.; Tuneekov, V.Y.; Chislova, I.V.; Zvereva, I.A. Synthesis of Nanosized Gadolinium Oxide. Glass Phys. Chem. 2019, 45, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Y.; Ahmad, M.W.; Yue, H.; Ho, S.L.; Park, J.A.; Jung, K.-H.; Cha, H.; Marasini, S.; Ghazanfari, A.; Liu, S.; et al. In Vivo Positive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications of Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Acid)-Coated Ultra-Small Paramagnetic Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, L.H.; Hoa, T.T.; Van Hieu, N.; Cuong, N.D. Facile Synthesis of Ultrafine Gd2O3 Nanoparticles by Polyol Microwave Method. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 3484–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevallier, S.; Hammer, P.; Caiut, J.M.A.; Mazeres, S.; Mauricot, R.; Verelst, M.; Dexpert, H.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Dexpert-Ghys, J. APTES-Modified RE2O3:Eu3+ Luminescent Beads: Structure and Properties. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamrakar, R.K.; Bisen, D.P.; Upadhyay, K.; Sahu, I.P. Upconversion and Colour Tunability of Gd2O3:Er3+ Phosphor Prepared by Combustion Synthesis Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 655, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M.; Sarabadani, P.; Hashemizadeh Aghda, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Gd2O2S:Tb3+ Phosphor Powder for X-ray Imaging Detectors. J. Nanostruct. 2019, 9, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, B.; Liu, D.; Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Dai, Y. Influence of Vacuum upon Preparation and Luminescence of Si4+ and Ti4+ Codoped Gd2O2S:Eu Phosphor. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 126, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Singh, S.; Mehta, S.K. Biocompatible Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles as Efficient Agent against Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 529, 496–504. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, M.; Jia, N. Facile Synthesis of Single-Phase Mesoporous Gd2O3:Eu Nanorods and Their Application for Drug Delivery and Multimodal Imaging. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.K.; Anderson, D.S.; Wallis, C.D.; Carratt, S.A.; Kennedy, I.M.; Van Winkle, L.S. Novel Multi-Functional Europium-Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticle Aerosols Facilitate the Study of Deposition in the Developing Rat Lung. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11518–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga, B.; Hernandez-Adame, L.; Angel-Olarte, C.; Aguilar, F.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Palestino, G. Optical and Biological Evaluation of Upconverting Gd2O3:Tb3+/Er3+ Particles as Microcarriers of a Zika Virus Antigenic Peptide. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Adame, L.; Cortez-Espinosa, N.; Portales-Pérez, D.P.; Castillo, C.; Zhao, W.; Juarez, Z.N.; Hernandez, L.R.; Bach, H.; Palestino, G. Toxicity Evaluation of High-Fluorescent Rare-Earth Metal Nanoparticles for Bioimaging Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyngrope, D.; Singh, L.R.; Prasad, A.I.; Bora, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Comparative Luminescence Studies of Rare-Earth-Doped Gd2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Ahmad, N.; Labis, J.P. Highly Colloidal Luminescent Porous Tb-Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles: Photophysical and Luminescent Properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2019, 371, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, S. Production and Optoelectronic Response of Tb3+ Activated Gadolinium Oxide Nanocrystalline Phosphors. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 62, 30401–30406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhao, X.; Tan, M.C. Synthesis of Uniform Rare Earth Doped Gd2O2S Sub-Micron Sized Spheres Using Gas-Aided Sulfurization and Their Optical Characteristics. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35738–35751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; You, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, N. Highly Uniform and Monodisperse Gd2O2S:Ln3+ (Ln = Eu, Tb) Submicrospheres: Solvothermal Synthesis and Luminescence Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 11499–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatsepin, A.; Kuznetsova, Y. Down-Conversion of UV Radiation in Erbium-Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldys, E.M.; Drozdowicz-Tomsia, K.; Jinjun, S.; Dosev, D.; Kennedy, I.M.; Yatsunenko, S.; Godlewski, M. Optical Characterization of Eu-Doped and Undoped Gd2O3 Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Hydrogen Flame Pyrolysis Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14498–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, R.; Ding, H.; Xiao, Q. Synthesis of Bifunctional Gd2O3:Eu3+ Nanocrystals and Their Applications in Biomedical Imaging. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Yang, P.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Niu, N.; He, F.; Li, X. Monodisperse Gd2O3:Ln (Ln = Eu3+, Tb3+, Dy3+, Sm3+, Yb3+/Er3+, Yb3+/Tm3+, and Yb3+/Ho3+) Nanocrystals with Tunable Size and Multicolor Luminescent Properties. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, K.; Tamrakar, R.K.; Bisen, D.P.; Sahu, I.P.; Sahu, M. Enhancement of Photoluminescence Behavior of Gd2O3:Er3+ Phosphor by Alkali Metal. Optik 2016, 127, 3693–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.O.; Carter, J.A.; Tissue, B.M. Long-Lifetime Luminescence of Lanthanide-Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Immunoassays. J. Lumin. 2004, 108, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I. Synthesis, Structural and Photophysical Properties of Gd2O3:Eu3+ Nanostructures Prepared by a Microwave Sintering Process. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 4, 374. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, D.; Contreras, O.; Hirata, G. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of Nanoparticles Y2O3 and Gd2O3 Co-Doped with Yb3+ and Er3+. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Guan, G.; Yao, B.; Teng, C.-P.; Liu, S.; Tee, S.Y.; Ong, B.C.; Dong, Z.; Han, M.-Y. Upconversion Luminescence of Gd2O3:Ln3+ Nanorods for White Emission and Cellular Imaging via Surface Charging and Crystallinity Control. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.; Oh, J.H.; Park, S.; Choi, H.; Moon, B.; Choi, B.; Jang, K.; Jeong, J.; Yi, S.; Hwan, K. Enhanced down and Upconversion Emission for Li+ Co-Doped Gd2O3:Er3+ Nanostructures. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoyue, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, L. Up-Conversion Luminescence of Yb3+/Er3+ Doped Gd2O3 Phosphors for Optical Temperature Sensing in Green and Red Regions. Opt. Commun. 2019, 452, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Suo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, C. Cross-Relaxation and Non-Steady-State Processes Induced up-Conversion Color Modulation in Gd2O3: Ln3+/Er3+ (Ln = Tm, Ho). Dyes Pigments 2018, 151, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pu, F.; Huang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Long-Circulating Gd2O3:Yb3+, Er3+ up-Conversion Nanoprobes as High-Performance Contrast Agents for Multi-Modality Imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 34, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.K.; Pandey, A.C. Fluorescent Magnetic Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Nanosci. Technol. 2015, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Das, G.K.; Heng, B.C.; Ng, S.-C.; White, T.; Loo, J.S.C.; D’Silva, L.; Padmanabhan, P.; Bhakoo, K.K.; Selvan, S.T.; Tan, T.T.Y. Gadolinium Oxide Ultranarrow Nanorods as Multimodal Contrast Agents for Optical and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8959–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhang, C.; Ding, S.; Wang, L. General Synthesis Route to Fabricate Uniform Upconversion Luminescent Gadolinium Oxide Hollow Spheres. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 6875–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, X.; Chen, H.; Shao, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, D. Near-Infrared to Visible and near-Infrared Upconversion of Monoclinic Gd2O3:Yb3+/Tm3+ Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation in Liquid for Fluorescence Imaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 348, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić, Ž.; Lojpur, V.; Nikolić, M.G.; Đorđević, V.; Ahrenkiel, P.S.; Dramićanin, M.D. Strong Emission via Up-Conversion of Gd2O3:Yb3+, Ho3+ Nanopowders Co-Doped with Alkali Metals Ions. J. Lumin. 2014, 145, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Tian, X.; Chen, X.; Shao, Y.; Xie, F.; Chen, D.; Li, L. Magnetic and Fluorescent Gd2O3:Yb3+/Ln3+ Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Upconversion Luminescence/MR Dual Modal Imaging and NIR-Induced Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Osseni, S.A.; Lechevallier, S.; Verelst, M.; Perriat, P.; Dexpert-Ghys, J.; Neumeyer, D.; Garcia, R.; Mayer, F.; Djanashvili, K.; Peters, J.A.; et al. Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanoparticles as Multimodal Imaging Agents for T2-Weighted MR, X-ray Tomography and Photoluminescence. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Zou, H.; Song, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sheng, Y. Solvothermal Synthesis of Columnar Gd2O2S:Eu3+ and a Comparative Study with Columnar Gd2O3:Eu3+. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Fröhlich, B.; Krämer, K.W.; Meijerink, A.; Goldschmidt, J.C. Upconversion Quantum Yield of Er3+-Doped β-NaYF4 and Gd2O2S: The Effects of Host Lattice, Er3+ Doping, and Excitation Spectrum Bandwidth. J. Lumin. 2014, 153, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Goel, S.; Zhan, Y.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Chen, F.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Intrinsically (89)Zr-Labeled Gd2O2S:Eu Nanophosphors with High in Vivo Stability for Dual-Modality Imaging. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5591–5600. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.-L.; Liu, T.-Y.; Lo, C.-L.; Wang, B.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lin, K.-Y.; Chang, C.A. Synthesis, Surface Modification, and Photophysical Studies of Ln2O2S:Ln׳3+ (Ln = Gd, Tb, Eu; Ln’ = Tb and/ or Eu) Nanoparticles for Luminescence Bioimaging. J. Lumin. 2016, 175, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, S.; Ayob, M.T.M.; Hasim, M.H.; Abdul Rahman, I.; Radiman, S. Physical and Optical Studies of Gd2O2S:Eu3+ Nanophosphors by Microwave Irradiation and γ-Irradiation Methods. Luminescence 2019, 34, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kou, H.; Zhang, W.; Ge, L.; Pan, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Multilayer Gd2O2S:Tb Phosphor Screen for X-ray Detection Application. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, A.; Pranjali, P.; Meher, M.K.; Chaturvedi, A.; Chakraborti, S.; Raj, R.; Poluri, K.M.; Kumar, D. Effect of Polyol Chain Length on Proton Relaxivity of Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 18061–18070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsrud, M.-A.; Grande, T. 1D Oxide Nanostructures from Chemical Solutions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J. Size-Tailored Synthesis and Luminescent Properties of One-Dimensional Gd2O3:Eu3+ Nanorods and Microrods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18148–18154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Wen, B.; Qian, C.; Wang, H.; Rao, L.; Liu, H.; Zeng, S. Intense Red Upconversion Emission and Shape Controlled Synthesis of Gd2O3:Yb/Er Nanocrystals. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhong, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, J. Phase Transformation and Spectroscopic Adjustment of Gd2O3:Eu3+ Synthesized by Hydrothermal Method. J. Lumin. 2014, 152, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, W.; Tian, G.; Yan, L.; Jin, S.; Ren, W.; Xing, G.; Li, W.; et al. Size-Tunable Synthesis of Lanthanide-Doped Gd2O3 Nanoparticles and Their Applications for Optical and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, G. Highly Uniform Gd(OH)3 and Gd2O3:Eu3+ Hexagram-like Microcrystals: Glucose-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis, Growth Mechanism and Luminescence Property. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6569–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Han, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T. Spectroscopic Properties of Gd2O3:Dy3+ Nanocrystals. J. Rare Earths 2013, 31, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, H.K. Multi Modality of Hollow Tube Gd2O3:Eu3+ Nanoparticles by Using Nonpolar Solvent. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaporev, A.; Sokolov, M.; Vanetsev, A.; Kulakova, A.; Tretyakov, Y. Solvothermal Synthesis of Colloidal Solutions of Gd2O3:Eu Luminescent Nanoplates. Dokl. Chem. 2011, 441, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yi, R.; Zhou, L.; Gao, G.; Shi, R.; Qiu, G.; Liu, X. Lanthanide Hydroxide Nanorods and Their Thermal Decomposition to Lanthanide Oxide Nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Wang, J.; Lin, N.; Huo, L.; Zhao, H.; Mountrichas, G. Template-Free Synthesis, Growth Mechanism and Photoluminescent Properties of Ln(OH)3 and Ln2O3 Nanorods (Ln: Lanthanide Ion). J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 507, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Mehta, S.K.; Umar, A. Ethylene Glycol Functionalized Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles as a Potential Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Hydrazine and P-Nitrophenol. Coatings 2019, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cai, R.; Zhao, T.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Jin, J.; Xu, L.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid-Functionalized Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Radiotherapy of Tumors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendra, T.V.; Roopan, S.M.; Khan, M.R. Biogenic Approach to Synthesize Rod Shaped Gd2O3 Nanoparticles and Its Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology-Box–Behnken Design Model. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahdatkhah, P.; Madaah Hosseini, H.R.; Khodaei, A.; Montazerabadi, A.R.; Irajirad, R.; Oghabian, M.A.; Delavari, H.H. Rapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of PVP-Coated Ultrasmall Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Phys. 2015, 453–454, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Martinelli, J.; Mayer, F.; Bonnet, C.S.; Szeremeta, F.; Djanashvili, K. Molecular Architecture Control in Synthesis of Spherical Ln-Containing Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69861–69869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Gambhir, S.; Ahmad, A. Extracellular Biosynthesis of Gadolinium Oxide (Gd2O3) Nanoparticles, Their Biodistribution and Bioconjugation with the Chemically Modified Anticancer Drug Taxol. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dědková, K.; Kuzníková, Ľ.; Pavelek, L.; Matějová, K.; Kupková, J.; Barabaszová, K.Č.; Váňa, R.; Burda, J.; Vlček, J.; Cvejn, D.; et al. Daylight Induced Antibacterial Activity of Gadolinium Oxide, Samarium Oxide and Erbium Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Aquatic Toxicity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 197, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, R.K.; Bisen, D.; Brahme, N. Combustion Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence Properties of Er3+, Yb3+ Doped Gadolinium Oxide Nanophosphor. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasimhadri, M.; Ratnam, B.V.; Jang, K.; Lee, H.S.; Chen, B.; Yi, S.-S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Rama Moorthy, L. Combustion Synthesis and Luminescent Properties of Nano and Submicrometer-Size Gd2O3:Dy3+ Phosphors for White LEDs. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2011, 8, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, R.; Bisen, D.P.; Upadhyay, K.; Brahme, N. Effect of Fuel on Structural and Optical Characterization of Gd2O3:Er3+ Phosphor. J. Lumin. Appl. 2014, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Hirata, G.A.; Farías, M.H.; Castillón, F.F. Synthesis and Characterization of (3-Aminopropyl)Trimethoxy-Silane (APTMS) Functionalized Gd2O3:Eu3+ red Phosphor with Enhanced Quantum Yield. Nanotechnology 2015, 27, 065601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijević, E.; Hsu, W.P. Preparation and Properties of Monodispersed Colloidal Particles of Lanthanide Compounds: I. Gadolinium, Europium, Terbium, Samarium, and Cerium(III). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 118, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qin, W.; Aidilibike, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Enhanced Upconversion Emission and Magnetization in Yb3+-Er3+/Ho3+ Codoped Gd2O3 Nanocrystals by Introducing Zn2+ Ions. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 675, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Adame, L.; Méndez-Blas, A.; Ruiz-García, J.; Vega-Acosta, J.R.; Medellín-Rodríguez, F.J.; Palestino, G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Gd:Tb Oxysulfide Colloidal Particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 258, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevallier, S.; Lecante, P.; Mauricot, R.; Dexpert, H.; Dexpert-Ghys, J.; Kong, H.-K.; Law, G.-L.; Wong, K.-L. Gadolinium−Europium Carbonate Particles: Controlled Precipitation for Luminescent Biolabeling. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6153–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichos, J.; Karbowiak, M.; Hreniak, D.; Stręk, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Monodisperse Eu3+ Doped Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanocrystals. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Qin, H.; Liang, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, F. Controllable Synthesis and Photoluminescence Properties of Gd2O2S:Pr3+ Microspheres Using an Urea-Ammonium Sulfate (UAS) System. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, J.; Chandramohan, R.; Vijayan, T.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Formation Mechanism of Monodispersed Gd2O2S:Eu3+ Nanocrystals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xu, L.; Xia, J.; Zhao, H.; Du, Y.; Lei, B. Synthesis of Porous Gadolinium Oxide Nanosheets for Cancer Therapy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; McDonagh, B.H.; Hak, S.; Peddis, D.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Sandvig, I.; Sandvig, A.; Glomm, W.R. Synthesis of Gadolinium Oxide Nanodisks and Gadolinium Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for MR Contrast Agents. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santelli, J.; Lechevallier, S.; Calise, D.; Marsal, D.; Siegfried, A.; Vincent, M.; Martinez, C.; Cussac, D.; Mauricot, R.; Verelst, M. Multimodal Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanoparticles for Bioimaging: A Comprehensive Biodistribution, Elimination and Toxicological Study. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Adame, L.; Palestino, G.; Meza, O.; Hernandez-Adame, P.L.; Vega-Carrillo, H.R.; Sarhid, I. Effect of Tb3+ Concentration in the Visible Emission of Terbium-Doped Gadolinium Oxysulfide Microspheres. Solid State Sci. 2018, 84, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, Q.; Dong, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. Investigating Efficient Energy Transfer in Novel Strategy-Obtained Gd2O2S:Dy3+, Eu3+ Nanofibers Endowed with White Emitting and Magnetic Dual-Functionality. J. Lumin. 2019, 206, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, J.; Chandramohan, R.; Divakar, R.; Mohandas, E.; Sekar, M.; Parameswaran, P. Eu3+ Doped Gadolinium Oxysulfide (Gd2O2S) Nanostructures—Synthesis and Optical and Electronic Properties. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 395703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumalai, J.; Chandramohan, R.; Valanarasu, S.; Vijayan, T.A.; Somasundaram, R.M.; Mahalingam, T.; Srikumar, S.R. Shape-Selective Synthesis and Opto-Electronic Properties of Eu3+-Doped Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 3889–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-K.; Lee, G.H.; Jung, K.-H.; Jung, J.-C.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Ryeom, H.-K.; Kim, T.-J.; Chang, Y. Gadolinium Nanoparticles Conjugated with Therapeutic Bifunctional Chelate as a Potential T 1 Theranostic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Agent. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórna, K.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Piotrowski, M.; Gajdošová, M.; Štěpánek, F.; Warszyński, P. Gadolinium Alginate Nanogels for Theranostic Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.L.; Choi, G.; Yue, H.; Kim, H.K.; Jung, K.H.; Park, J.A.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Miao, X.; et al. In Vivo Neutron Capture Therapy of Cancer Using Ultrasmall Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles with Cancer-Targeting Ability. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, W.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Li, L.; Bregadze, V.I.; et al. Small-Sized Gadolinium Oxide Based Nanoparticles for High-Efficiency Theranostics of Orthotopic Glioblastoma. Biomaterials 2020, 235, 119783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, S. Tumor-Specific Design of PEGylated Gadolinium-Based Nanoscale Particles: Facile Synthesis, Characterization, and Improved Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Metastasis Lung Cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 202, 111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Marasini, S.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Ho, S.L.; Cha, H.; Liu, S.; Jang, Y.J.; Tegafaw, T.; Ghazanfari, A.; Miao, X.; et al. Carbon-Coated Ultrasmall Gadolinium Oxide (Gd2O3@C) Nanoparticles: Application to Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Fluorescence Properties. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.Z.A.M.; Mohamed, F.; Rosli, N.R.A.M.; Rahman, I.A.; Idris, M.I.; Bradley, D.A.; Nor, M.M.; Mustafa, S.N.M. Effect of Gamma Irradiation on Magnetic Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles Coated with Chitosan (GdNPs-Cs) as Contrast Agent in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 165, 108407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezazadeh, T.; Gholibegloo, E.; Alam, N.R.; Dehghani, S.; Haghgoo, S.; Ghanaati, H.; Khoobi, M. Gadolinium (III) Oxide Nanoparticles Coated with Folic Acid-Functionalized Poly(β-Cyclodextrin-Co-Pentetic Acid) as a Biocompatible Targeted Nano-Contrast Agent for Cancer Diagnostic: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2019, 32, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezazadeh, T.; Gholibegloo, E.; Khoobi, M.; Alam, N.R.; Haghgoo, S.; Mesbahi, A. In Vitro and in Vivo Characteristics of Doxorubicin-Loaded Cyclodextrine-Based Polyester Modified Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles: A Versatile Targeted Theranostic System for Tumour Chemotherapy and Molecular Resonance Imaging. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Meena, V.K.; Hazari, P.P.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, R.K. Rose Bengal Attached and Dextran Coated Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Potential Diagnostic Imaging Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santelli, J.; Lechevallier, S.; Baaziz, H.; Vincent, M.; Martinez, C.; Mauricot, R.; Parini, A.; Verelst, M.; Cussac, D. Multimodal Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanoparticles: A Versatile Contrast Agent for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Labeling. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16775–16786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osseni, S.A.; Lechevallier, S.; Verelst, M.; Dujardin, C.; Dexpert-Ghys, J.; Neumeyer, D.; Leclercq, M.; Baaziz, H.; Cussac, D.; Santran, V.; et al. New Nanoplatform Based on Gd2O2S:Eu3+ Core: Synthesis, Characterization and Use for in Vitro Bio-Labelling. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18365–18372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Deng, Y.; Gu, D.; Che, R.; Zhao, D. Synthesis and Microwave Absorption of Uniform Hematite Nanoparticles and Their Core-Shell Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6706–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Dong, K.; Jiang, L.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Hybrid Mesoporous Gadolinium Oxide Nanorods: A Platform for Multimodal Imaging and Enhanced Insoluble Anticancer Drug Delivery with Low Systemic Toxicity. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14982–14990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzigues, C.; Gacoin, T.; Alexandrou, A. Biological Applications of Rare-Earth Based Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8488–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Cui, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Peng, B. Application of Rare Earth-Doped Nanoparticles in Biological Imaging and Tumor Treatment. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridot, J.-L.; Faure, A.-C.; Laurent, S.; Rivière, C.; Billotey, C.; Hiba, B.; Janier, M.; Josserand, V.; Coll, J.-L.; Vander Elst, L.; et al. Hybrid Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles: Multimodal Contrast Agents for in Vivo Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5076–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalej, N.M.; Qurashi, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Maalej, R.; Shaikh, M.N.; Ilyas, M.; Gondal, M.A. Synthesis of Gd2O3:Eu Nanoplatelets for MRI and Fluorescence Imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucher, L.; Tremblay, M.; Lagueux, J.; Gossuin, Y.; Fortin, M.-A. Rapid Synthesis of PEGylated Ultrasmall Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling and Tracking with MRI. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4506–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichkova, M.; Dosev, D.; Perron, R.; Gee, S.J.; Hammock, B.D.; Kennedy, I.M. Eu3+-Doped Gd2O3 Nanoparticles as Reporters for Optical Detection and Visualization of Antibodies Patterned by Microcontact Printing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosev, D.; Nichkova, M.; Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Liu, G.; Xia, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Kennedy, I.M. Application of Fluorescent Eu:Gd2O3 Nanoparticles to the Visualization of Protein Micropatterns. In Proceedings of the Imaging, Manipulation, and Analysis of Biomolecules and Cells: Fundamentals and Applications III, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–27 January 2005; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; 5699, pp. 473–481. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Liu, X.-L.; Yang, Y.; Lv, Y.-B.; Yang, C.-T.; Ding, J. Manipulating the Surface Coating of Ultra-Small Gd2O3 Nanoparticles for Improved T1-Weighted MR Imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, S.L.; Debele, T.A.; Tsai, H.-C. Encapsulation of Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticle (Gd2O3) Contrasting Agents in PAMAM Dendrimer Templates for Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6782–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrogiacomo, S.; Kownacka, A.E.; Dou, W.; Burke, B.P.; de Rosales, R.T.M.; Heerschap, A.; Jansen, J.A.; Archibald, S.J.; Walboomers, X.F. Bisphosphonate Functionalized Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles Allow Long-Term MRI/CT Multimodal Imaging of Calcium Phosphate Bone Cement. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosticher, C.; Viana, B.; Fortin, M.-A.; Lagueux, J.; Faucher, L.; Chanéac, C. Gadolinium Oxysulfide Nanoprobes with Both Persistent Luminescent and Magnetic Properties for Multimodal Imaging. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55472–55478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Singh, S.; Mehta, S.K. Ultrasonication Assisted Fabrication of L-Lysine Functionalized Gadolinium Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Biological Acceptability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Liu, H.-L.; Huang, C.-W.; Liao, S.-S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lu, Y.-J.; Wei, K.-C.; Ma, C.-C.M. Gadolinium-Functionalized Nanographene Oxide for Combined Drug and MicroRNA Delivery and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6534–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.S.; Razzak, R.; Bédard, E.; Guo, L.; Shaw, A.R.; Moore, R.B.; Roa, W.H. Layered Gadolinium-Based Nanoparticle as a Novel Delivery Platform for MicroRNA Therapeutics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 425102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Mohanta, S.C.; Deka, K.; Deb, P.; Devi, P.S. Surface-Engineered Multifunctional Eu:Gd2O3 Nanoplates for Targeted and PH-Responsive Drug Delivery and Imaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4126–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, P.; Lin, J.; Fang, J. A Luminescent and Mesoporous Core-Shell Structured Gd2O3:Eu3+@nSiO2@mSiO2 Nanocomposite as a Drug Carrier. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 4846–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.D.; Anderson, D.S.; Das, G.K.; Van Winkle, L.S.; Kennedy, I.M. Novel Lanthanide-Labeled Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Improve the Measurement of in Vivo Clearance and Translocation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, P.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, W.; Li, Q. Ultra-Small Gadolinium Oxide Nanocrystal Sensitization of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells toward X-ray Irradiation by Promoting Cytostatic Autophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, R.; Pandey, O.P.; Dhoble, S.J. Review on the Synthesis, Structural and Photo-Physical Properties of Gd2O3 Phosphors for Various Luminescent Applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 135, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlind, F.; Pedersen, H.; Petoral, R.M.; Käll, P.-O.; Uvdal, K. Synthesis and Characterisation of Gd2O3 Nanocrystals Functionalised by Organic Acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larquet, C.; Hourlier, D.; Nguyen, A.-M.; Torres-Pardo, A.; Gauzzi, A.; Sanchez, C.; Carenco, S. Thermal Stability of Oleate-Stabilized Gd2O2S Nanoplates in Inert and Oxidizing Atmospheres. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, B.; Dai, Y. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Pure and Doped Crystals: Gd2O2S, Gd2O2S:Eu3+ and Gd2O2S:Tb3+. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1020, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Moore, T.; Qi, B.; Colvin, D.C.; Jelen, E.K.; Hitchcock, D.A.; He, J.; Mefford, O.T.; Gore, J.C.; Alexis, F.; et al. Monitoring PH-Triggered Drug Release from Radioluminescent Nanocapsules with X-ray Excited Optical Luminescence. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Rogalski, M.M.; Anker, J.N. Advances in Functional X-ray Imaging Techniques and Contrast Agents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 13469–13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Direct Evidence of a Surface Quenching Effect on Size-Dependent Luminescence of Upconversion Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7456–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhuang, H.Z.; Liu, G.K.; Li, S.; Niedbala, R.S. Confinement on Energy Transfer between Luminescent Centers in Nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 5559–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Drug Safety Communication: FDA Warns That Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents (GBCAs) Are Retained in the Body; Requires New Class Warnings; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019.
- Byrne, H.L.; Le Duc, G.; Lux, F.; Tillement, O.; Holmes, N.M.; James, A.; Jelen, U.; Dong, B.; Liney, G.; Roberts, T.L.; et al. Enhanced MRI-Guided Radiotherapy with Gadolinium-Based Nanoparticles: Preclinical Evaluation with an MRI-Linac. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verry, C.; Sancey, L.; Dufort, S.; Duc, G.L.; Mendoza, C.; Lux, F.; Grand, S.; Arnaud, J.; Quesada, J.L.; Villa, J.; et al. Treatment of Multiple Brain Metastases Using Gadolinium Nanoparticles and Radiotherapy: NANO-RAD, a Phase I Study Protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e023591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega-Berlanga, B.; Betancourt-Mendiola, L.; del Angel-Olarte, C.; Hernández-Adame, L.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Palestino, G. An Overview of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Particles: Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Crystals 2021, 11, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091094
Ortega-Berlanga B, Betancourt-Mendiola L, del Angel-Olarte C, Hernández-Adame L, Rosales-Mendoza S, Palestino G. An Overview of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Particles: Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091094
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega-Berlanga, Benita, Lourdes Betancourt-Mendiola, César del Angel-Olarte, Luis Hernández-Adame, Sergio Rosales-Mendoza, and Gabriela Palestino. 2021. "An Overview of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Particles: Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091094
APA StyleOrtega-Berlanga, B., Betancourt-Mendiola, L., del Angel-Olarte, C., Hernández-Adame, L., Rosales-Mendoza, S., & Palestino, G. (2021). An Overview of Gadolinium-Based Oxide and Oxysulfide Particles: Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Crystals, 11(9), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091094