Patterns in Nature—S-Layer Lattices of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
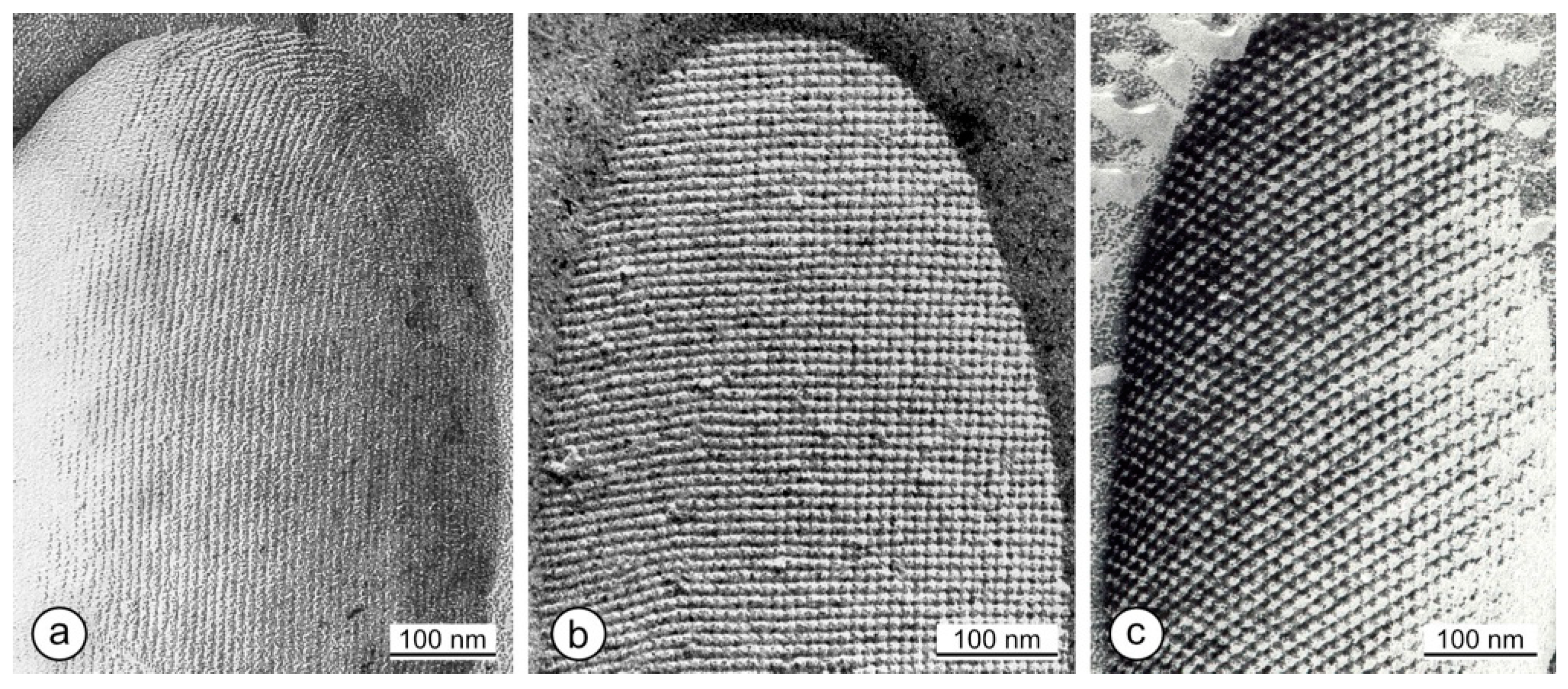
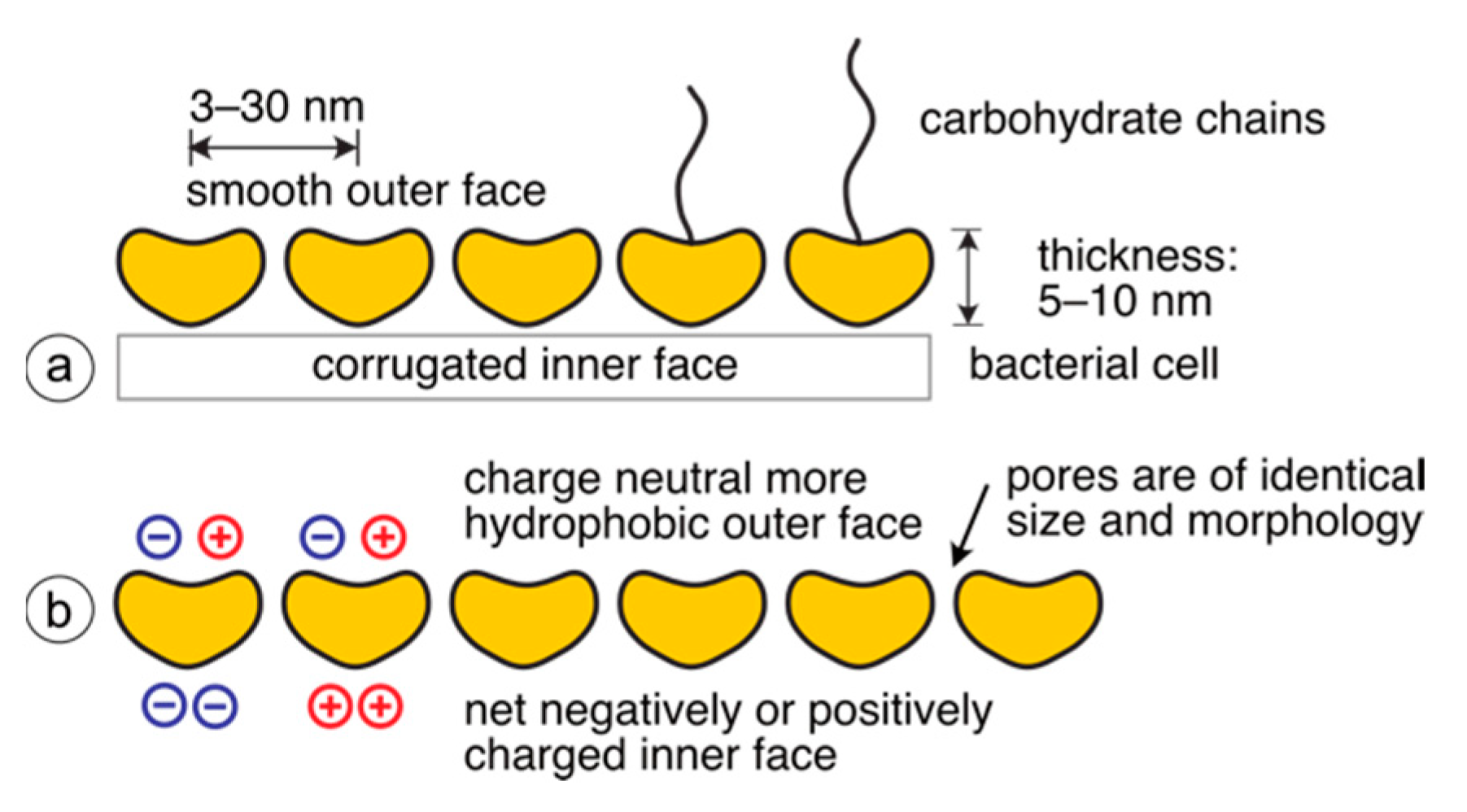
2. Occurrence and Ultrastructure of S-Layers
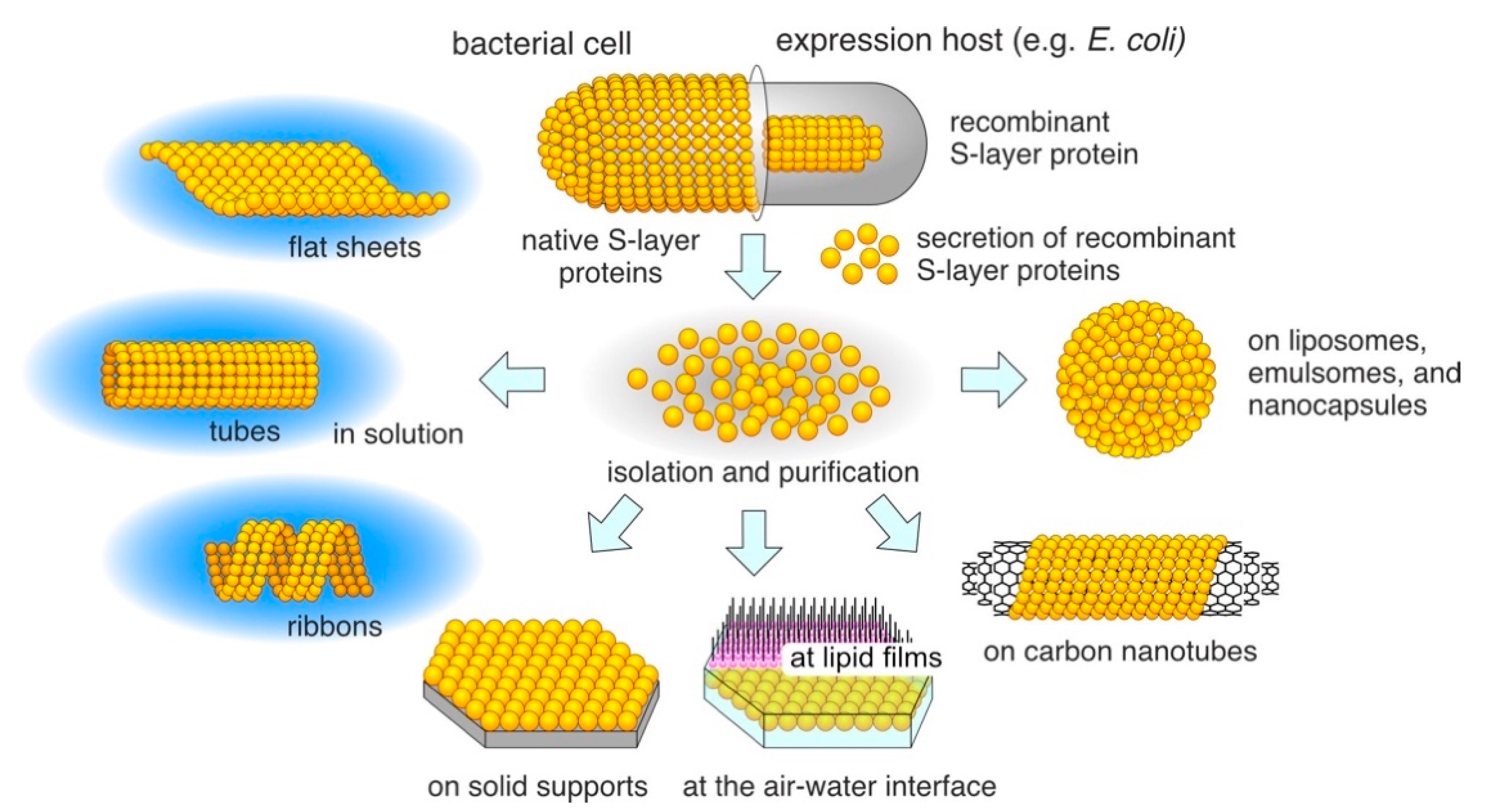
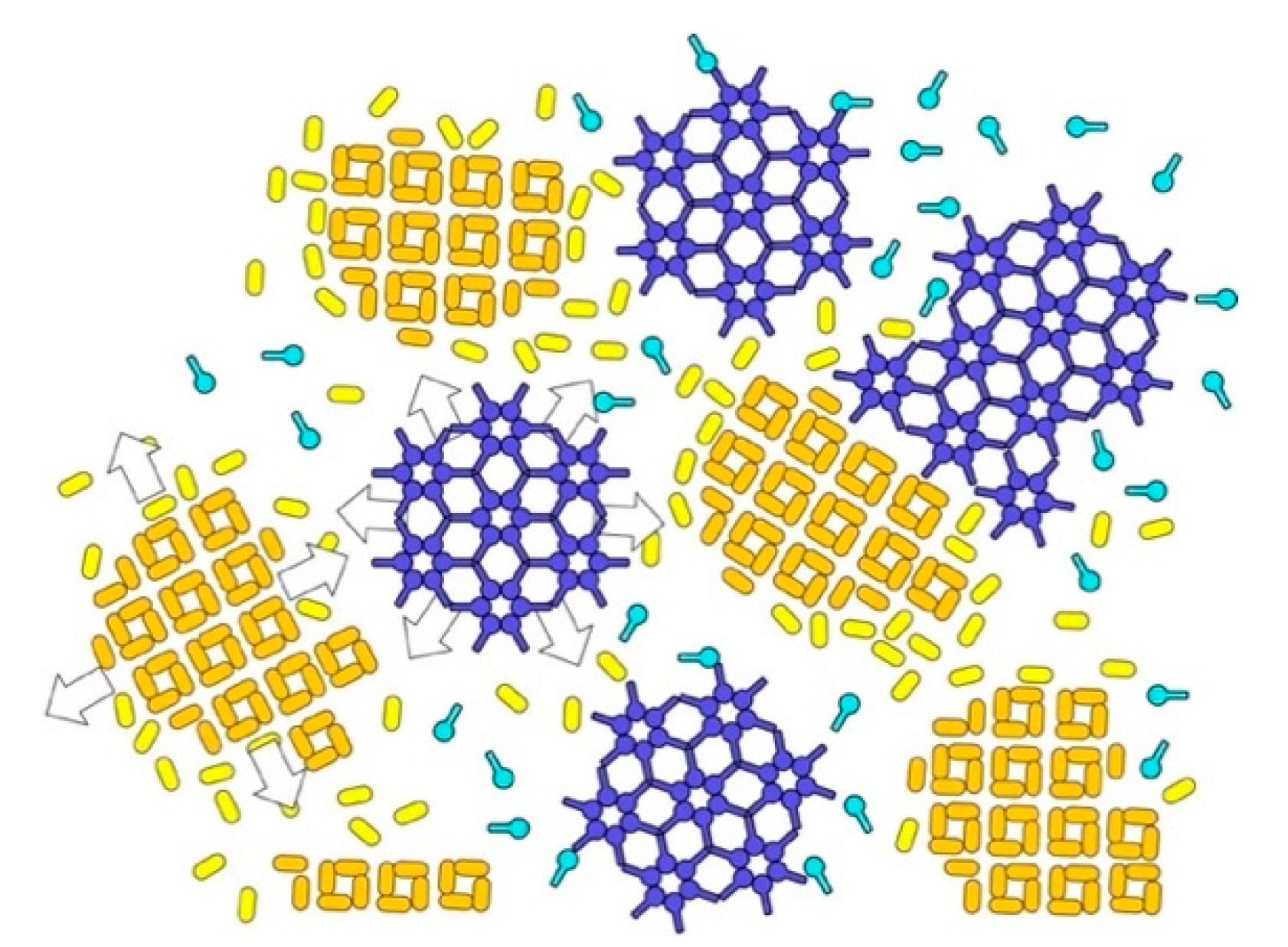
3. Reassembly of S-Layer Proteins
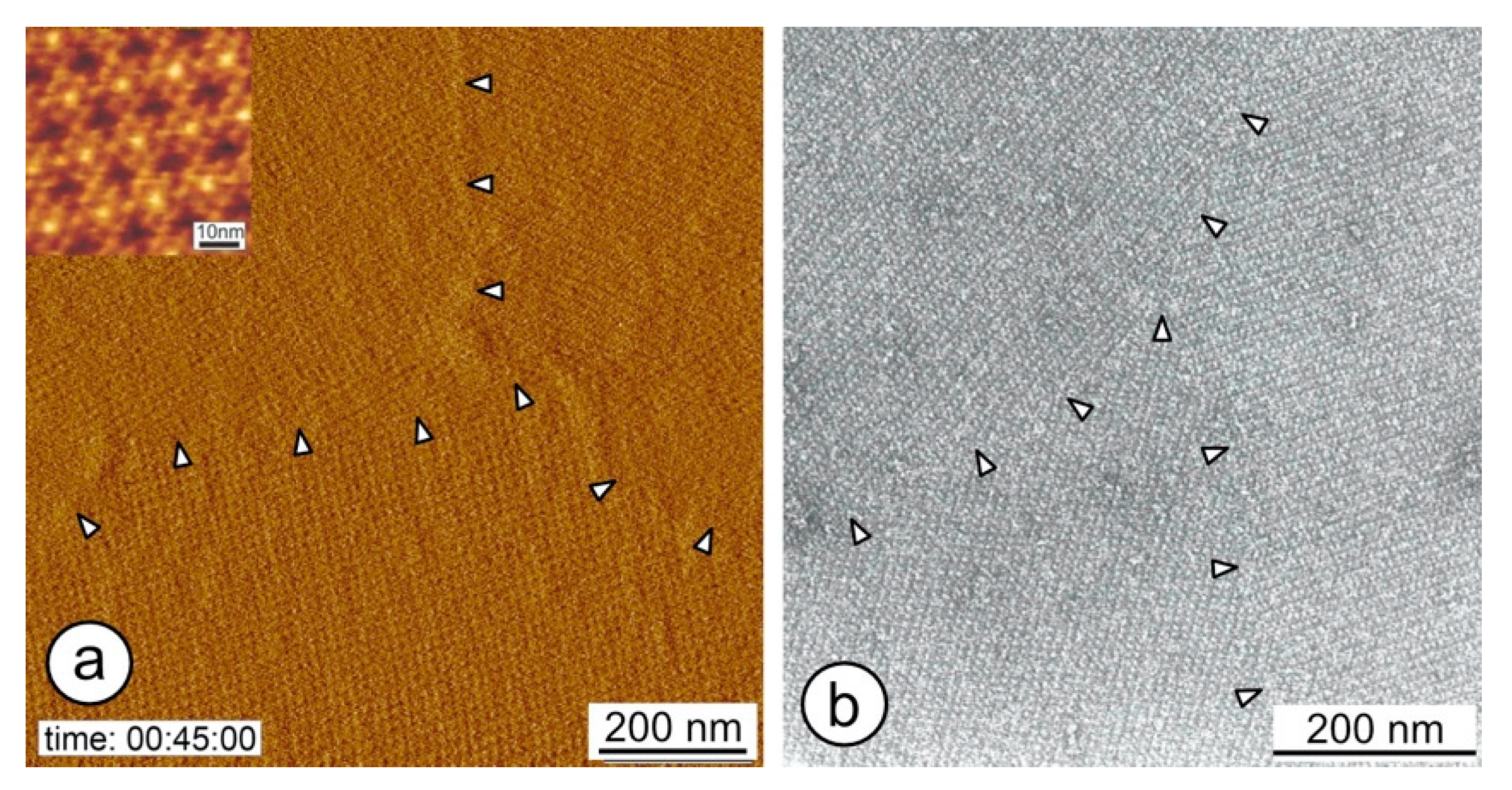
4. Reassembly in Solution
5. Reassembly at the Liquid–Solid Interface
6. Reassembly at the Air–Water Interface, at Lipid, and Polyelectrolyte Layers
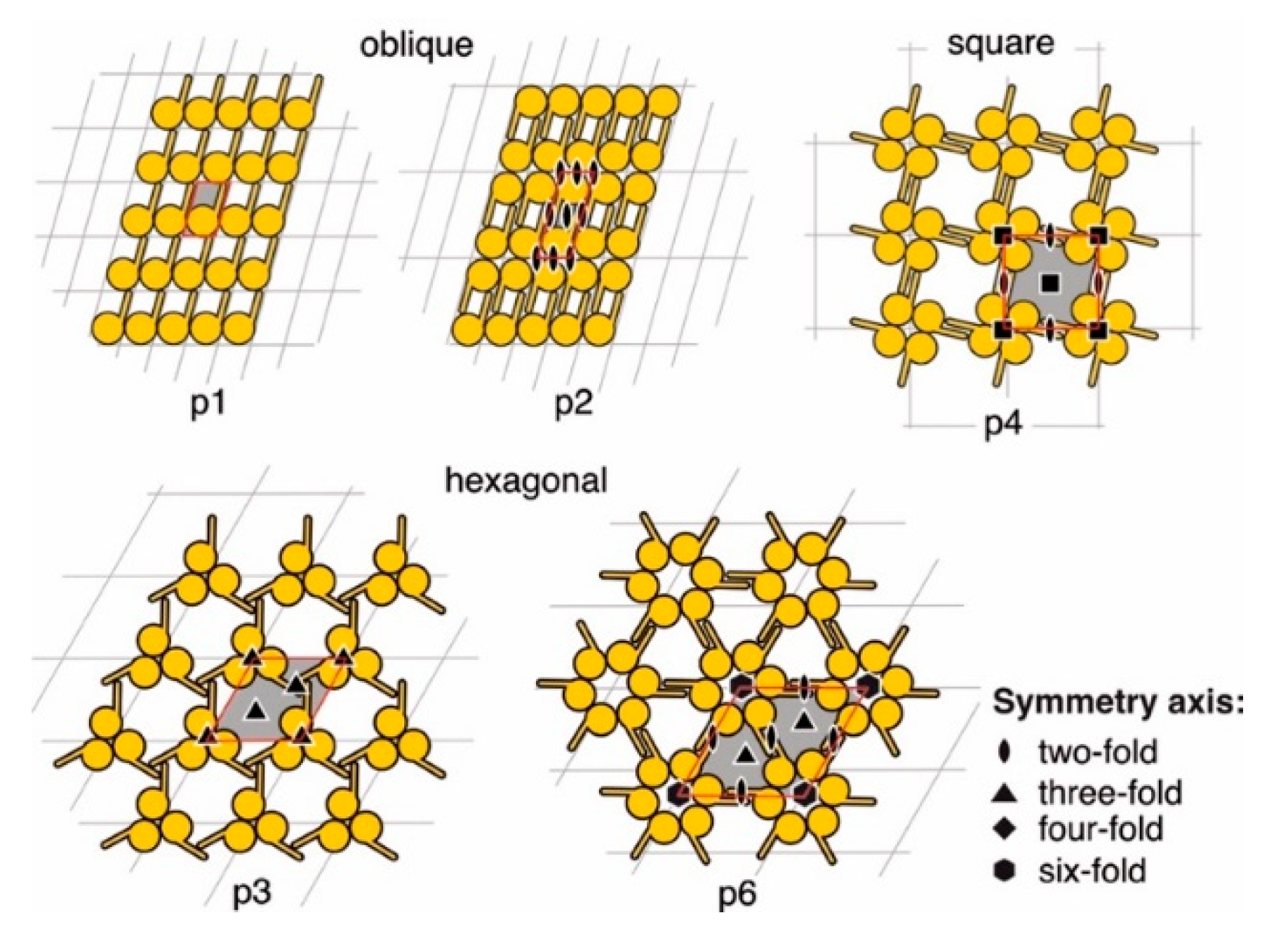
7. Two-Dimensional Crystal Terminology
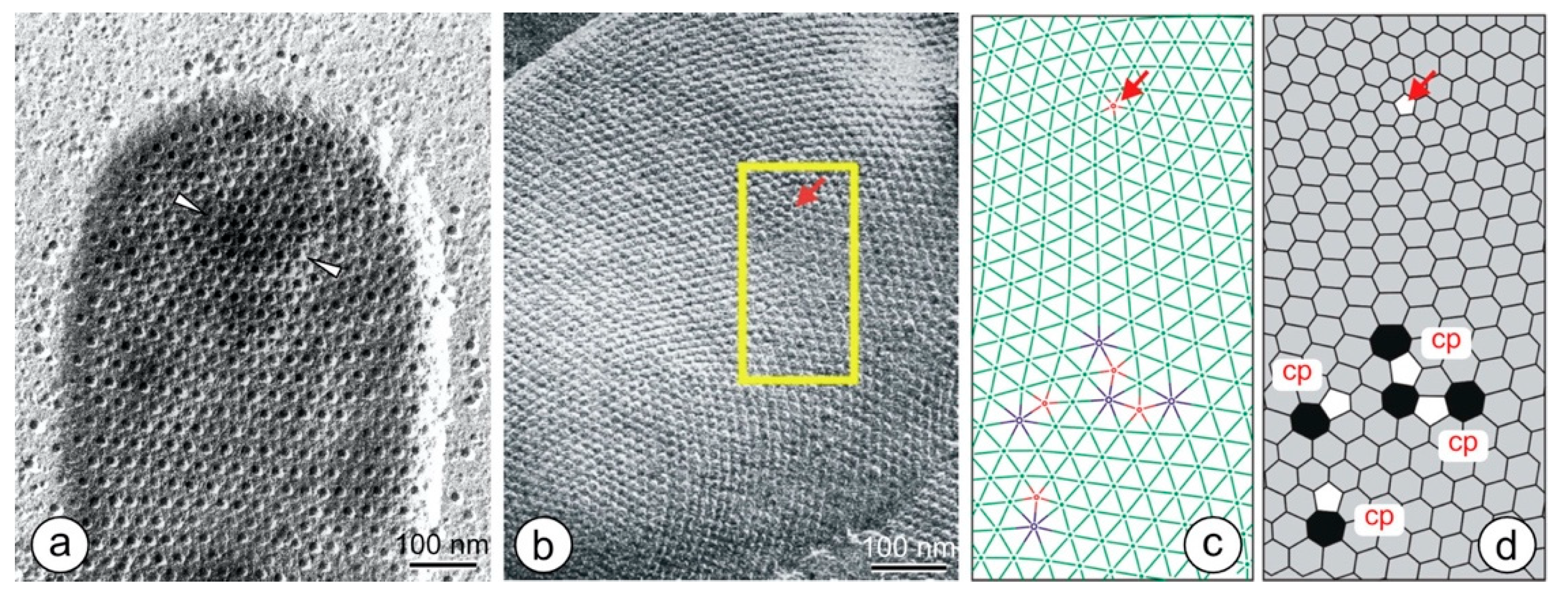
8. Lattice Imperfections
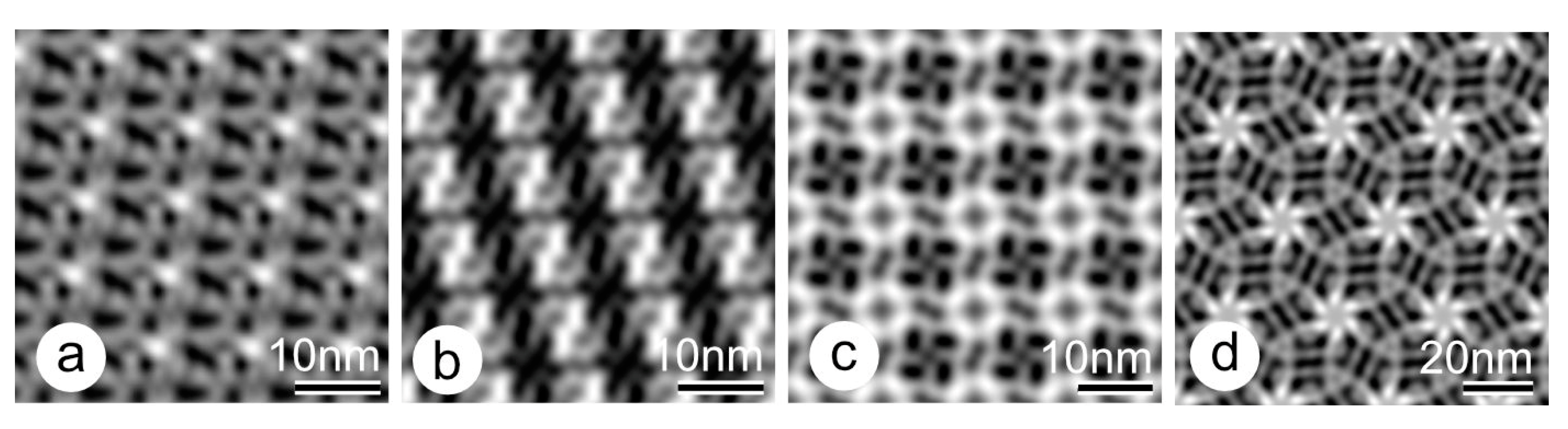
9. Changes in the Ultrastructure of the Same S-Layer Protein
10. Pores in the S-Layer Structure
11. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
The 80 Two-Sided Plane Groups (2D-Space Groups)
- Lattice type indicated by a small letter, p (primitive) or c (centered),
- Symmetry in a direction normal to the plane, arbitrarily taken as the z-axis,
- Symmetry in the plane, along an axis designated x, and
- Symmetry in another direction in the plane.
| Oblique | Rectangular | Square | Hexagonal | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| triclinic | monoclinic/rectangular | 27 | tetragonal | trigonal | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 8 | 28 | 49 | 65 | p3 | |||||||||||||
| 2 | 9 | 29 | 50 | 66 | ||||||||||||||
| 10 | 30 | 51 | 67 | |||||||||||||||
| monoclinic/oblique | 11 | 31 | 52 | 68 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | 12 | 32 | 53 | 69 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 13 | 33 | 54 | 70 | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | 14 | 34 | 55 | 71 | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 15 | 35 | 56 | 72 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 16 | 36 | 57 | |||||||||||||||
| 17 | 37 | 58 | hexagonal | |||||||||||||||
| 18 | 38 | 59 | 73 | |||||||||||||||
| 39 | 60 | 74 | ||||||||||||||||
| orthorhombic | 40 | 61 | 75 | |||||||||||||||
| 19 | 41 | 62 | 76 | |||||||||||||||
| 20 | 42 | 63 | 77 | |||||||||||||||
| 21 | 43 | 64 | 78 | |||||||||||||||
| 22 | 44 | 79 | ||||||||||||||||
| 23 | 45 | 80 | ||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 46 | Symmetry elements: m a, b n 2, 3, 4, 6 | mirror plane axial glide plane diagonal glide plane n-fold rotation axis inversion center rotoinversion axis 2-fold screw axis symmetry element x normal to symmetry element y (e.g., = two-fold rotation axis normal to mirror plane m) | |||||||||||||||
| 25 | 47 | |||||||||||||||||
| 26 | 48 | |||||||||||||||||
References
- Hahn, T. (Ed.) International Tables for Crystallography: Volume A: Space-Group Symmetry, 5th ed.; The International Union of Crystallography; John Wiley&Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S. The Origins of Life: Old Problems, New Chemistries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S. Life as a nanoscale phenomenon. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5306–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B.; Egelseer, E.M.; Pum, D. S-layers: Principles and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 823–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, S.V.; Meyer, B.H. The archaeal cell envelope. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egelseer, E.M.; Ilk, N.; Pum, D.; Messner, P.; Schäffer, C.; Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layers, microbial, biotechnological applications. In Encyclopedia of Industrial Biotechnology: Bioprocess, Bioseparation, and Cell Technology; Flickinger, M.C., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 7, pp. 4424–4448. [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B.; Egelseer, E.M.; Pum, D.; Horejs, C.M.; Tscheliessnig, R.; Ilk, N. Nanobiotechnology with S-Layer Proteins as Building Blocks. Mol. Assem. Nat. Eng. Syst. 2011, 103, 277–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, N.; Egelseer, E.M.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer fusion proteins—Construction principles and applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Glauert, A.M. Analysis of Regular Arrays of Subunits on Bacterial Surfaces—Evidence for a Dynamic Process of Assembly. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1975, 50, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B. Regular arrays of macromolecules on bacterial cell walls: Structure, chemistry, assembly, and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1978, 53, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sára, M. Crystalline bacterial cell surface layers (S layers): From supramolecular cell structure to biomimetics and nanotechnology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavkov-Keller, T.; Howorka, S.; Keller, W. The structure of bacterial S-layer proteins. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 103, 73–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursigara, C.M.; Koval, S.F.; Moyles, D.M.; Harris, R.J. Inroads through the bacterial cell envelope: Seeing is believing. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, P.; Schaffer, C.; Kosma, P. Bacterial Cell-Envelope Glycoconjugates. Adv. Carbohyd. Chem. Biochem. 2013, 69, 209–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. Relevance of glycosylation of S-layer proteins for cell surface properties. Acta Biomater. 2015, 19, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layer Ultrafiltration Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.W.; Remsen, C.C. Cell Envelope of Nitrosocystis-Oceanus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1970, 33, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.J.; Murray, R.G.E. Superficial Macromolecular Arrays on Cell-Wall of Spirillum-Putridiconchylium. J. Bacteriol. 1974, 119, 1019–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, M.; Lederer, F.L.; Gunther, T.J.; Raff, J.; Pollmann, K. Characterization of Three Different Unusual S-Layer Proteins from Viridibacillus arvi JG-B58 That Exhibits Two Super-Imposed S-Layer Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sára, M.; Pum, D.; Küpcü, S.; Messner, P.; Sleytr, U.B. Isolation of two physiologically induced variant strains of Bacillus stearothermophilus NRS 2004/3a and characterization of their S-layer lattices. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sára, M.; Kuen, B.; Mayer, H.F.; Mandl, F.; Schuster, K.C.; Sleytr, U.B. Dynamics in oxygen-induced changes in S-layer protein synthesis from Bacillus stearothermophilus PV72 and the S-layer-deficient variant T5 in continuous culture and studies of the cell wall composition. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelli, L.; Meyer, B.H.; McLaren, M.; Sanders, K.; Quax, T.E.F.; Gold, V.A.M.; Albers, S.V.; Daum, B. Architecture and modular assembly of Sulfolobus S-layers revealed by electron cryotomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25278–25286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Characterization of the ultrastructure and the self-assembly of the surface layer of Bacillus stearothermophilus strain NRS 2004/3a. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1986, 97, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Sára, M.; Küpcü, Z.; Messner, P. Structural and chemical characterization of S-layers of selected strains of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Desulfotomaculum nigrificans. Arch. Microbiol. 1986, 146, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sára, M.; Küpcü, S.; Sleytr, U.B. Localization of the carbohydrate residue of the S-layer glycoprotein from Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum L111-69. Arch. Microbiol. 1989, 151, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Beveridge, T.J. Bacterial S-layers. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sára, M. Conserved anchoring mechanisms between crystalline cell surface S-layer proteins and secondary cell wall polymers in Gram-positive bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, C.; Huber, C.; Moll, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Interaction of the crystalline bacterial cell surface layer protein SbsB and the secondary cell wall polymer of Geobacillus stearothermophilus PV72 assessed by real-time surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Charge distribution on the S layer of Bacillus stearothermophilus NRS 1536/3c and importance of charged groups for morphogenesis and function. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 2804–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorvary, E.; Schroedter, A.; Talapin, D.V.; Weller, H.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Formation of nanoparticle arrays on S-layer protein lattices. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothbauer, M.; Küpcü, S.; Sticker, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Ertl, P. Exploitation of S-layer Anisotropy: pH-dependent Nanolayer Orientation for Cellular Micropatterning. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8020–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B. Self-assembly of the hexagonally and tetragonally arranged subunits of bacterial surface layers and their reattachment to cell walls. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1976, 55, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B. Heterologous reattachment of regular arrays of glycoproteins on bacterial surfaces. Nature 1975, 257, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Reassembly of S-layer proteins. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 312001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucisik, M.H.; Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B. Emulsomes Meet S-layer Proteins: An Emerging Targeted Drug Delivery System. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pum, D.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layer Protein Self-Assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2484–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.; Gyorvary, E.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Nanotechnology with S-layer proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 300, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, R.P.; Fairweather, N.F. Biogenesis and functions of bacterial S-layers. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Messner, P. Self-assemblies of crystalline bacterial cell surface layers. In Electron Microscopy of Subcellular Dynamics; Plattner, H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke, R.; Welsch, R.; Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Stability and self-assembly of the S-layer protein of the cell wall of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1985, 366, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobeth, M.; Blecha, A.; Bluher, A.; Mertig, M.; Korkmaz, N.; Ostermann, K.; Rodel, G.; Pompe, W. Formation of tubes during self-assembly of bacterial surface layers. Langmuir 2011, 27, 15102–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Shin, S.H.; Bertozzi, C.R.; De Yoreo, J.J. Self-catalyzed growth of S layers via an amorphous-to-crystalline transition limited by folding kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16536–16541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Chung, S.; Sanii, B.; Comolli, L.R.; Bertozzi, C.R.; De Yoreo, J.J. Direct observation of kinetic traps associated with structural transformations leading to multiple pathways of S-layer assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12968–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, A.; Iturri, J.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D. In Vitro Characterization of the Two-Stage Non-Classical Reassembly Pathway of S-Layers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, B.; Cometto, F.; Rad, B.; De Yoreo, J.J.; Lingenfelder, M. Dynamically resolved self-assembly of S-layer proteins on solid surfaces. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10264–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Large-scale reconstruction of crystalline bacterial surface layer proteins at the air-water interface and on lipids. Thin Solid Films 1994, 244, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, E.; Fronzes, R.; Garcia-Pino, A.; Van Gerven, N.; Papapostolou, D.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Howorka, S.; Remaut, H. SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly. Nature 2012, 487, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, B.; Haxton, T.K.; Shon, A.; Shin, S.H.; Whitelam, S.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Ion-specific control of the self-assembly dynamics of a nanostructured protein lattice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comolli, L.R.; Siegerist, C.E.; Shin, S.H.; Bertozzi, C.; Regan, W.; Zettl, A.; De Yoreo, J. Conformational transitions at an S-Layer growing boundary resolved by Cryo-TEM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4829–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleutel, M.; Van Driessche, A.E.S. Role of clusters in nonclassical nucleation and growth of protein crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E546–E553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Györvary, E.S.; Stein, O.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Self-assembly and recrystallization of bacterial S-layer proteins at silicon supports imaged in real time by atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 2003, 212, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pum, D.; Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Structure, surface charge, and self-assembly of the S-layer lattice from Bacillus coagulans E38-66. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 5296–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Relevance of charged groups for the integrity of the S-layer from Bacillus coagulans E38-66 and for molecular interactions. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, A.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D. A New Method for Dispersing Pristine Carbon Nanotubes Using Regularly Arranged S-Layer Proteins. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitwieser, A.; Pum, D.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sleytr, U.B. Magnetic beads functionalized with recombinant S-layer protein exhibit high human IgG-binding and anti-fouling properties. Curr. Top. Pept. Protein Res. 2016, 17, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.E.; Moreno-Flores, S.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Surface dependence of protein nanocrystal formation. Small 2010, 6, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Flores, S.; Kasry, A.; Butt, H.J.; Vavilala, C.; Schmittel, M.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. From native to non-native two-dimensional protein lattices through underlying hydrophilic/hydrophobic nanoprotrusions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4707–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.E.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Influence of surface chemistry and protein concentration on the adsorption rate and S-layer crystal formation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11905–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpcü, S.; Sára, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Liposomes coated with crystalline bacterial cell surface protein (S-layers) as immobilization structures for macromolecules. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1235, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ücisik, M.H.; Küpcü, S.; Debreczeny, M.; Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer Coated Emulsomes as Potential Nanocarriers. Small 2013, 9, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucisik, M.H.; Küpcü, S.; Breitwieser, A.; Gelbmann, N.; Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer fusion protein as a tool functionalizing emulsomes and CurcuEmulsomes for antibody binding and targeting. Colloid Surf. B 2015, 128, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Krastev, R.; Bosio, V.; Kupcu, S.; Pum, D.; Fery, A.; Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Recrystallization of bacterial S-layers on flat polyelectrolyte surfaces and hollow polyelectrolyte capsules. Small 2005, 1, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, B.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer stabilized lipid membranes. Biointerphases 2008, 3, FA3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holser, W.T. Point Groups and Plane Groups in a Two-Sided Plane and their Subgroups. Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 1958, 110, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopský, V.; Litvin, D.B. (Eds.) International Tables for Crystallography: Volume E: Subperiodic Groups, 5th ed.; The International Union of Crystallography; John Wiley&Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, W.; Engelhardt, H. Three-dimensional structure of bacterial surface layers. In Electron Microscopy of Proteins; Harris, J.R., Horne, R.W., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: London, UK, 1987; Volume 6, pp. 109–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hovmoller, S.; Sjogren, A.; Wang, D.N. The structure of crystalline bacterial surface layers. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1988, 51, 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, L.A.; Henderson, R.; Unwin, P.N.T. Three-dimensional structure determination by electron microscopy of two-dimensional crystals. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1982, 39, 183–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sára, M.; Stetter, K.O.; Sleytr, U.B. Ultrastructure of the cell envelope of the archaebacteria Thermoproteus tenax and Thermoproteus neutrophilus. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 166, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, W.O.; Baumeister, W. Principles of organization in S layers. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 187, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, W.; Wildhaber, I.; Phipps, B.M. Principles of organization in eubacterial and archaebacterial surface proteins. Can. J. Microbiol. 1989, 35, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavkov, T.; Egelseer, E.M.; Tesarz, M.; Svergun, D.I.; Sleytr, U.B.; Keller, W. The structure and binding behavior of the bacterial cell surface layer protein SbsC. Structure 2008, 16, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagan, R.P.; Albesa-Jove, D.; Qazi, O.; Svergun, D.I.; Brown, K.A.; Fairweather, N.F. Structural insights into the molecular organization of the S-layer from Clostridium difficile. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 1308–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethordic, A.; Egelseer, E.M.; Tesarz, M.; Sleytr, U.B.; Keller, W.; Pavkov-Keller, T. Crystallization of domains involved in self-assembly of the S-layer protein SbsC. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2012, 68, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Chan, A.C.K.; Nomellini, J.F.; Murphy, M.E.P.; Smit, J. Surface-layer protein from Caulobacter crescentus: Expression, purification and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2016, 72, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Falke, S.; Drobot, B.; Oberthuer, D.; Kikhney, A.; Guenther, T.; Fahmy, K.; Svergun, D.; Betzel, C.; Raff, J. Analysis of self-assembly of S-layer protein slp-B53 from Lysinibacillus sphaericus. Eur. Biophys. J. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, T.A.M.; Kureisaite-Ciziene, D.; Hardy, G.G.; Yu, E.W.; Devant, J.M.; Hagen, W.J.H.; Brun, Y.V.; Briggs, J.A.G.; Lowe, J. Structure of the hexagonal surface layer on Caulobacter crescentus cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, W.J.; Roberts, A.K.; Shone, C.C.; Acharya, K.R. The structure of the S-layer of Clostridium difficile. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Kügelgen, A.; Tang, H.; Hardy, G.G.; Kureisaite-Ciziene, D.; Brun, Y.V.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Robinson, C.V.; Bharat, T.A.M. In Situ Structure of an Intact Lipopolysaccharide-Bound Bacterial Surface Layer. Cell 2020, 180, 348–358.e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schur, F.K.M. Toward high-resolution in situ structural biology with cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging. Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 2019, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Briggs, J.A.G. Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 579, 329–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, R.A.; Sleytr, U.B. An analysis of the fine structure of the surface layer from two strains of clostridia, including correction for distorted images. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1977, 58, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, W.O.; Baumeister, W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J. Microsc. 1982, 127, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pum, D.; Messner, P.; Sleytr, U.B. Role of the S layer in morphogenesis and cell division of the Archaebacterium Methanocorpusculum sinense. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 6865–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.F. Disclinations. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.F.; Scriven, L.E. Function of Dislocations in Cell Walls and Membranes. Nature 1970, 228, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.F. Negative wedge disclinations of rotation 2π radians and topological changes of membranous systems. Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1975, 32, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspar, D.L.D.; Klug, A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1962, 27, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.F.; Scriven, L.E. Intrinsic Disclinations as Dislocation Sources and Sinks in Surface Crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1971, 42, 3309–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWit, A.; Borckmans, P.; Dewel, G. Twist grain boundaries in three-dimensional lamellar Turing structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12765–12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, R.; El-Abed, A.; Angelova, A.; Goldmann, M.; Peretti, P. Asymmetrical ion-channel model inferred from two-dimensional crystallization of a peptide antibiotic. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 3026–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Anisotropic crystal growth of the S-layer of Bacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 at the air/water interface. Colloids Surf. A 1995, 102, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Ilk, N.; Rünzler, D.; Egelseer, E.M.; Weigert, S.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sára, M. The three S-layer-like homology motifs of the S-layer protein SbpA of Bacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 are not sufficient for binding to the pyruvylated secondary cell wall polymer. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, D.; Huber, C.; Schlegel, B.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. S-layer-streptavidin fusion proteins as template for nanopatterned molecular arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14646–14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sára, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Molecular sieving through S-layers of Bacillus stearothermophilus strains. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 4092–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Ultrafiltration Membranes with Uniform Pores from Crystalline Bacterial-Cell Envelope Layers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1986, 25, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, M.; Manigley, C.; Wolf, G.; Sleytr, U.B. Isoporous Ultrafiltration Membranes from Bacterial-Cell Envelope Layers. J. Membr. Sci. 1988, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupcu, S.; Sara, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Influence of Covalent Attachment of Low-Molecular-Weight Substances on the Rejection and Adsorption Properties of Crystalline Proteinaceous Ultrafiltration Membranes. Desalination 1993, 90, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sára, M.; Sleytr, U.B. Production and characteristics of ultrafiltration membranes with uniform pores from two-dimensional arrays of proteins. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 33, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, F.; Garda, V.G.; Rad, B.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Programmable assembly of 2D crystalline protein arrays into covalently stacked 3D bionanomaterials. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, M.; Li, D.; Mann, V.R.; Yun, L.; Jani, S.; Rad, B.; Cohen, B.E.; Ashby, P.D.; Ryan, K.R.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Engineering the S-Layer of Caulobacter crescentus as a Foundation for Stable, High-Density, 2D Living Materials. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, J.; Matys, S.; Suhr, M.; Vogel, M.; Günther, T.; Pollmann, K. S-Layer-Based Nanocomposites for Industrial Applications. In Protein-Based Engineered Nanostructure; Cortajarena, A.L., Grove, T.Z., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 245–279. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U. Biomimetic S-layer—Lipid self-assemblies as platform for membrane-active peptides and proteins. Eur. Biophys. J. 2015, 44, S98. [Google Scholar]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer proteins for assembling ordered nanoparticle arrays. In Nanobioelectronics—For Electronics, Biology, and Medicine; Offenhäuser, A., Rinaldi, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Völlenkle, C.; Weigert, S.; Ilk, N.; Egelseer, E.; Weber, V.; Loth, F.; Falkenhagen, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Construction of a functional S-layer fusion protein comprising an immunoglobulin G-binding domain for development of specific adsorbents for extracorporeal blood purification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B. S-Layer Protein-Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbauer, M.; Ertl, P.; Theiler, B.A.; Schlager, M.; Sleytr, U.B.; Kupcu, S. Anisotropic Crystalline Protein Nanolayers as Multi-Functional Biointerface for Patterned Co-Cultures of Adherent and Non-Adherent Cells in Microfluidic Devices. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley, P.; Kirk, J.A.; Ma, S.W.; Jones, S.; Fagan, R.P. Spatial organization of Clostridium difficile S-layer biogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
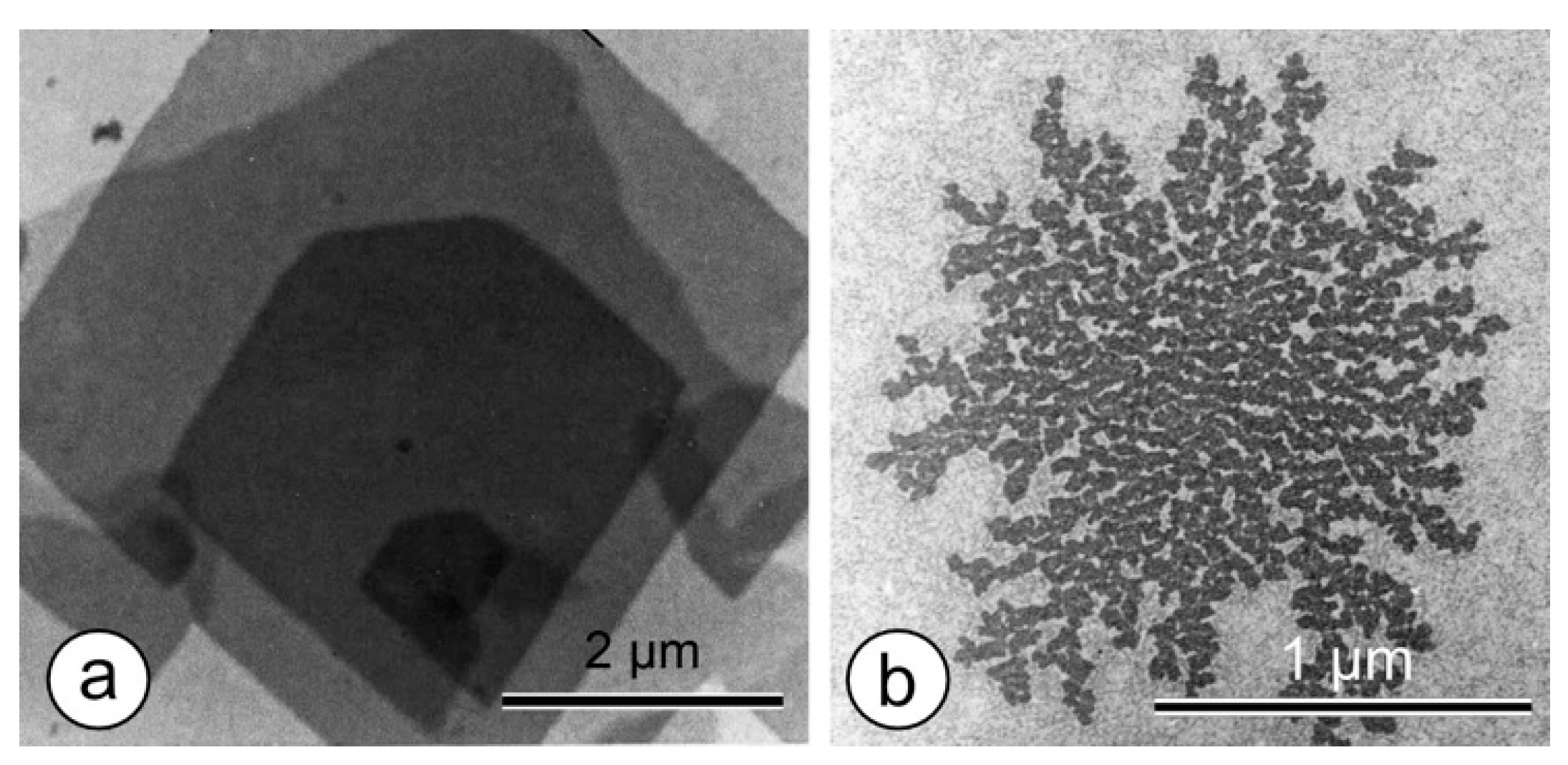
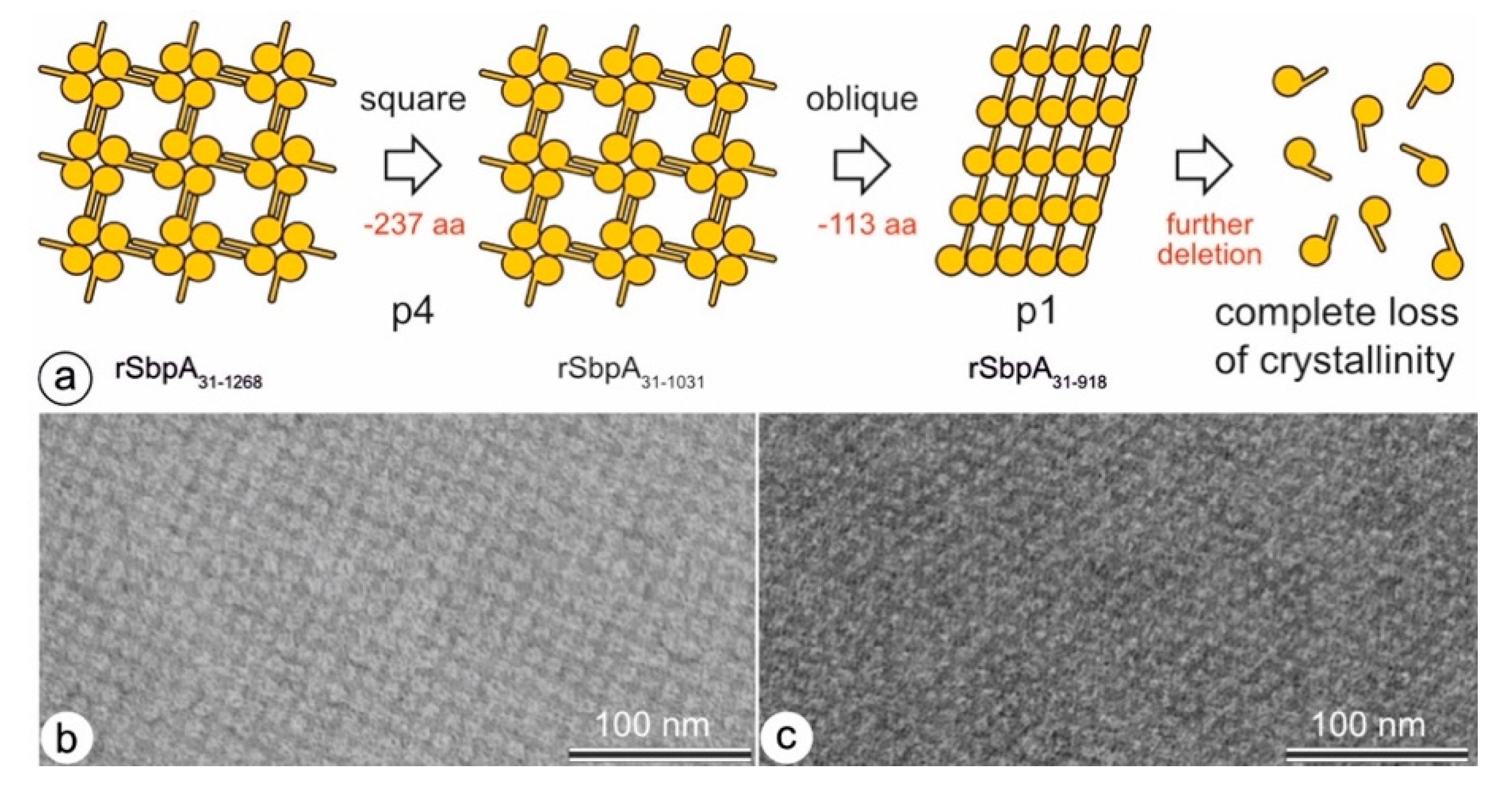
| No. | Two-Sided Plane Group (2D-Space Group) | One-Sided Plane Group (2D-Plane Group) (Projection Symmetry) | Lattice Type | S-Layer Lattice Symmetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | p1 | p1 | oblique | p1 |
| 2 | p21 | p2 | p2 | |
| 3 | p12 | pm | rectangular | - |
| 4 | p121 | pg | - | |
| 5 | c12 | cm | - | |
| 6 | p222 | pmm | - | |
| 7 | p2221 | pmg | - | |
| 8 | p22121 | pgg | - | |
| 9 | c222 | cmm | - | |
| 10 | p4 | p4 | square | p4 |
| 11 | p422 | p4m | - | |
| 12 | p4212 | p4g | - | |
| 13 | p3 | p3 | hexagonal | p3 |
| 14 | p312 | p3m1 | - | |
| 15 | p321 | p31m | - | |
| 16 | p6 | p6 | p6 | |
| 17 | p622 | p6m | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pum, D.; Breitwieser, A.; Sleytr, U.B. Patterns in Nature—S-Layer Lattices of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells. Crystals 2021, 11, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080869
Pum D, Breitwieser A, Sleytr UB. Patterns in Nature—S-Layer Lattices of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells. Crystals. 2021; 11(8):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080869
Chicago/Turabian StylePum, Dietmar, Andreas Breitwieser, and Uwe B. Sleytr. 2021. "Patterns in Nature—S-Layer Lattices of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells" Crystals 11, no. 8: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080869
APA StylePum, D., Breitwieser, A., & Sleytr, U. B. (2021). Patterns in Nature—S-Layer Lattices of Bacterial and Archaeal Cells. Crystals, 11(8), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080869







