Effect of Doping of Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Nematic Liquid Crystal p-Methoxybenzylidene p-Decylaniline
Abstract
1. Introduction
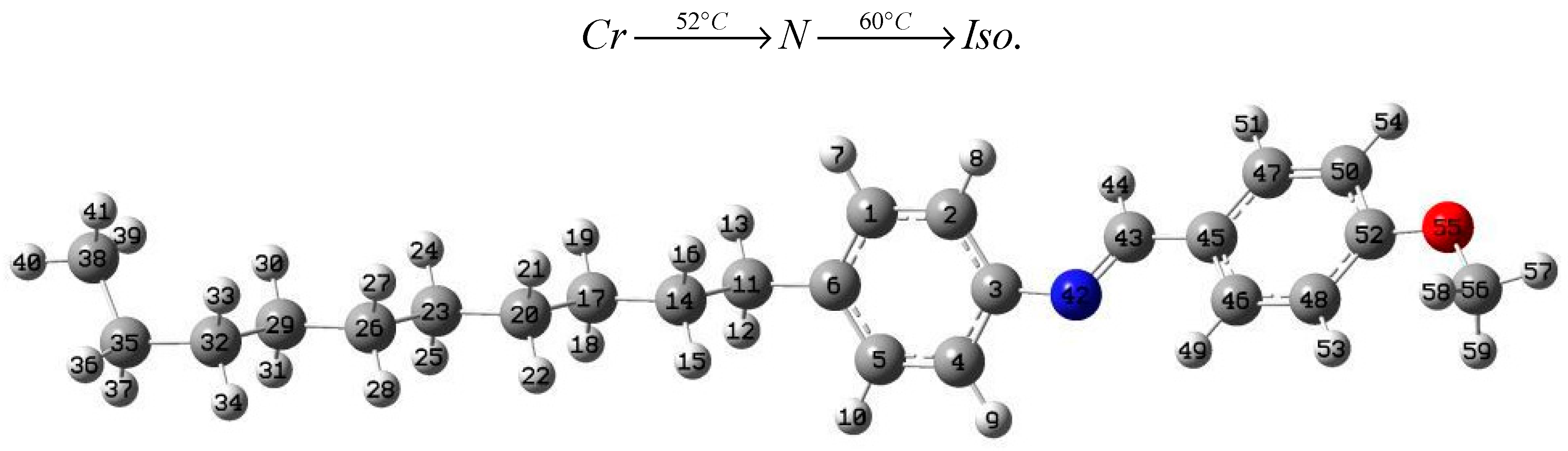
2. Experimental Details
Preparation of Homogenous Mixture of CSQDs and MBDA Composites
3. Results and Discussion
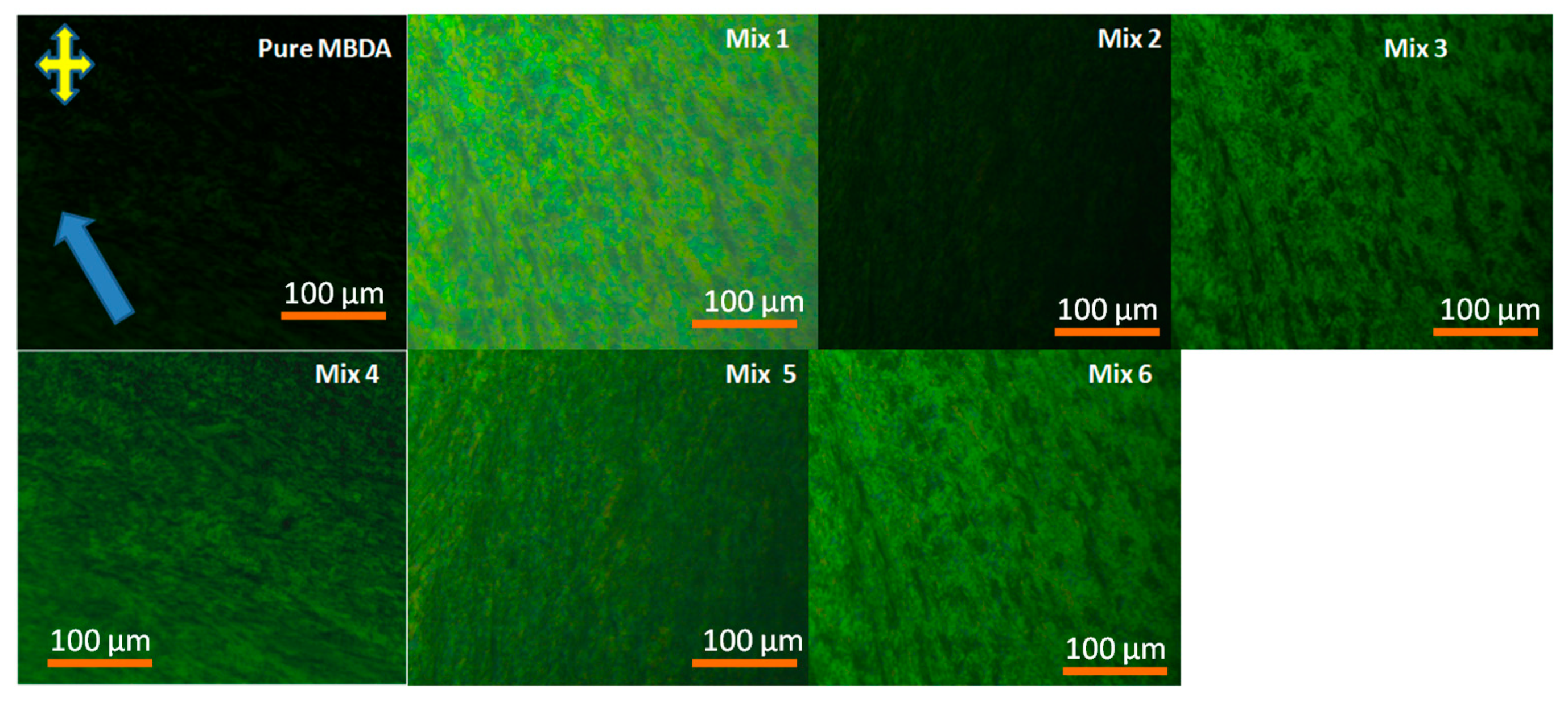
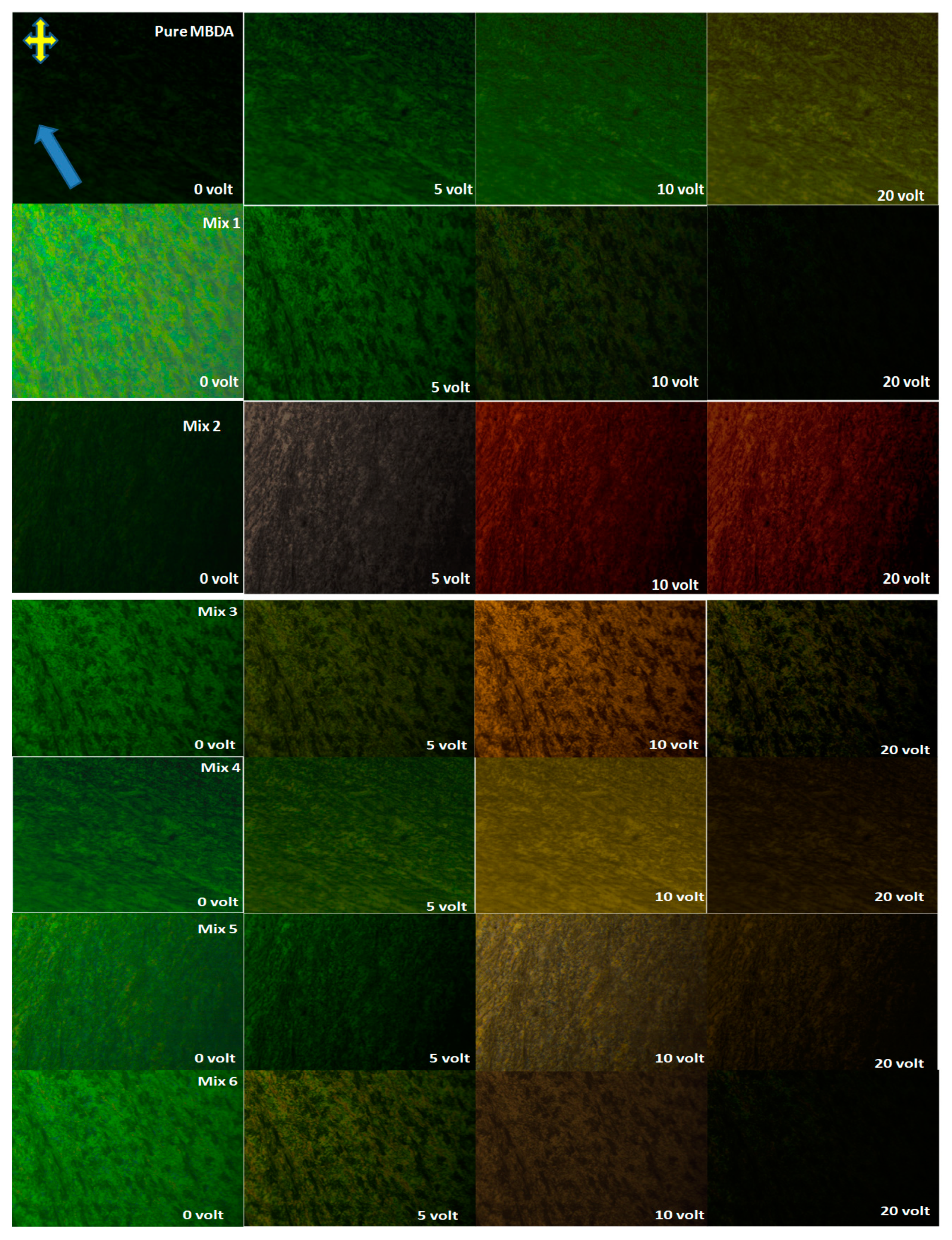
3.1. Polarizing Optical Micrographs
3.2. Dielectric Response and Dielectric Anisotropy
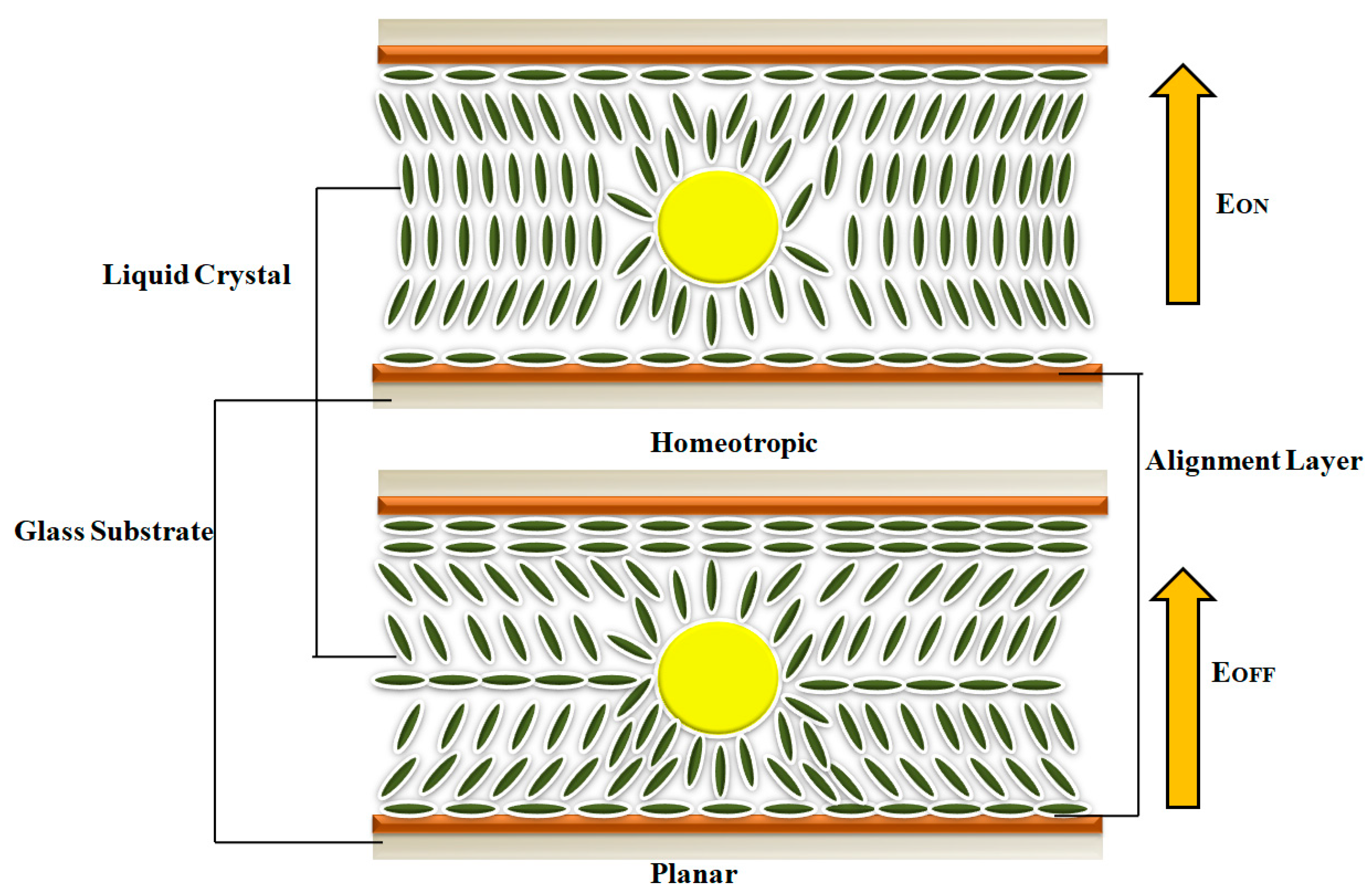
3.2.1. Field-Induced Reorientation of Liquid Crystal in QD Doped Sample
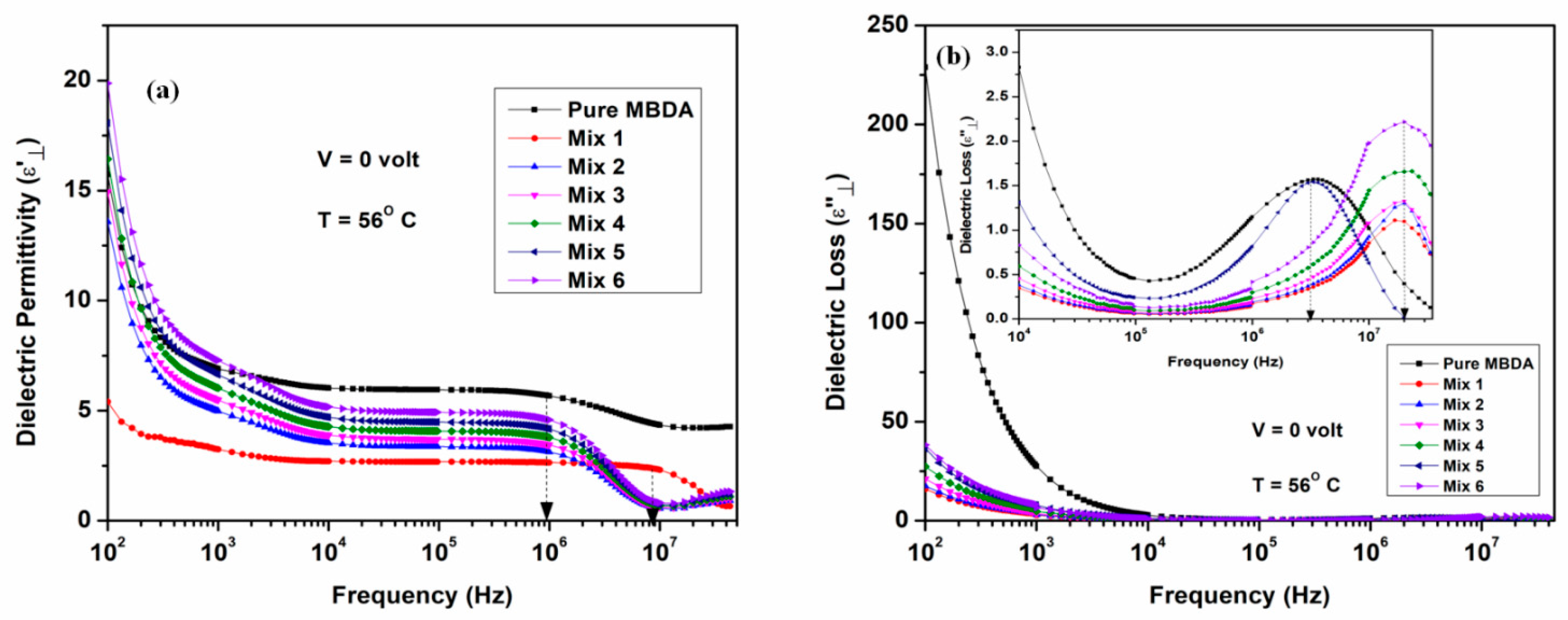
3.2.2. Dielectric Response at Planar Geometry
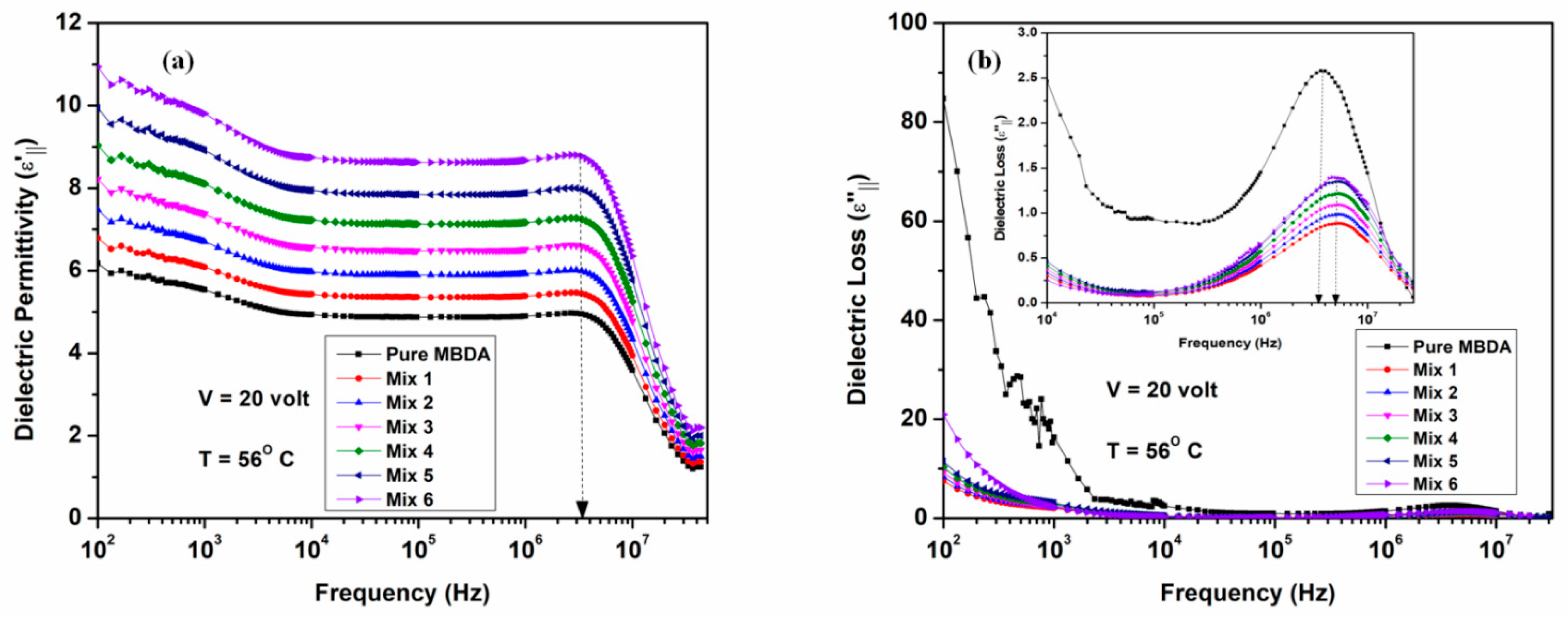
3.2.3. Dielectric Response at Homeotropic Geometry
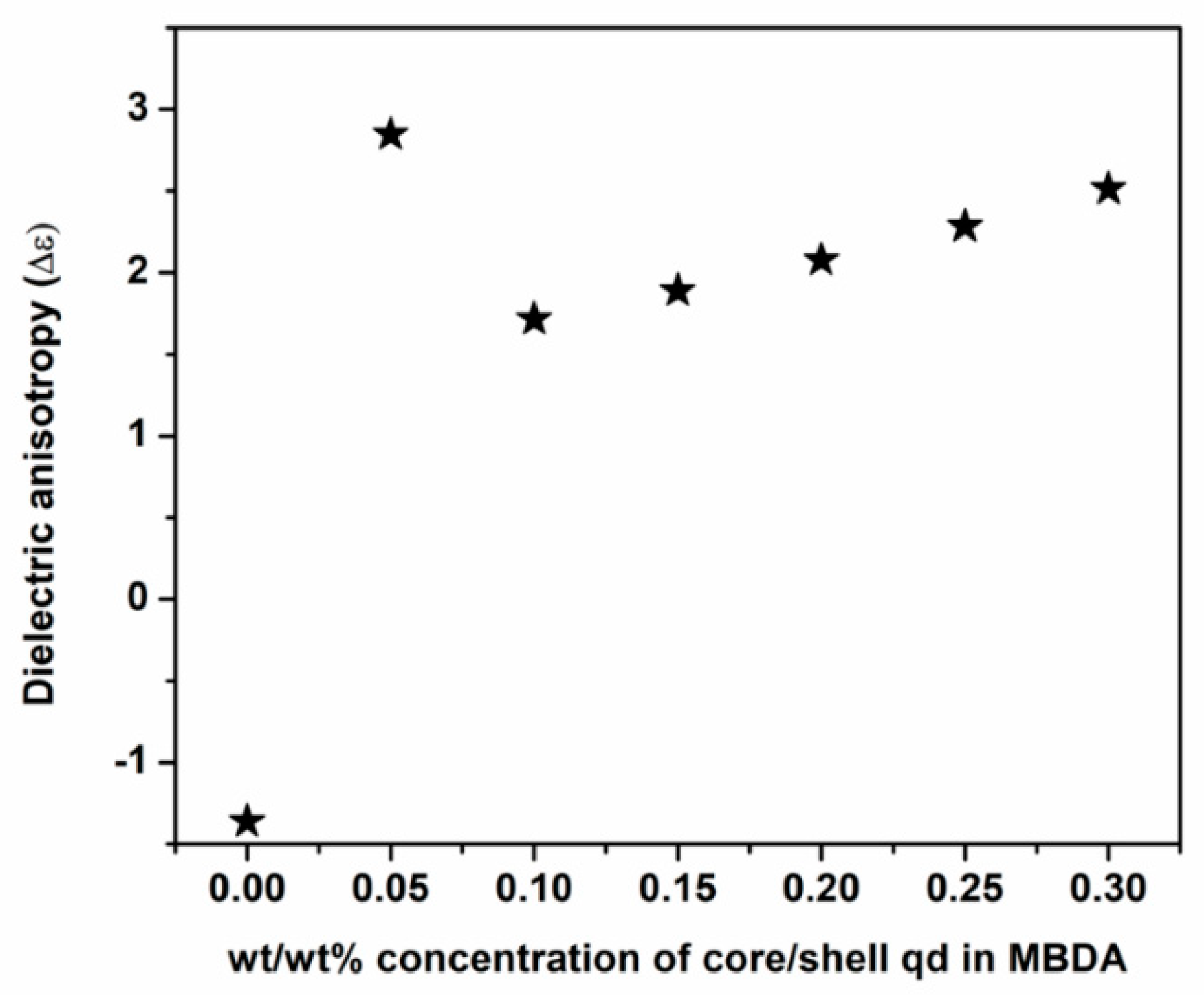
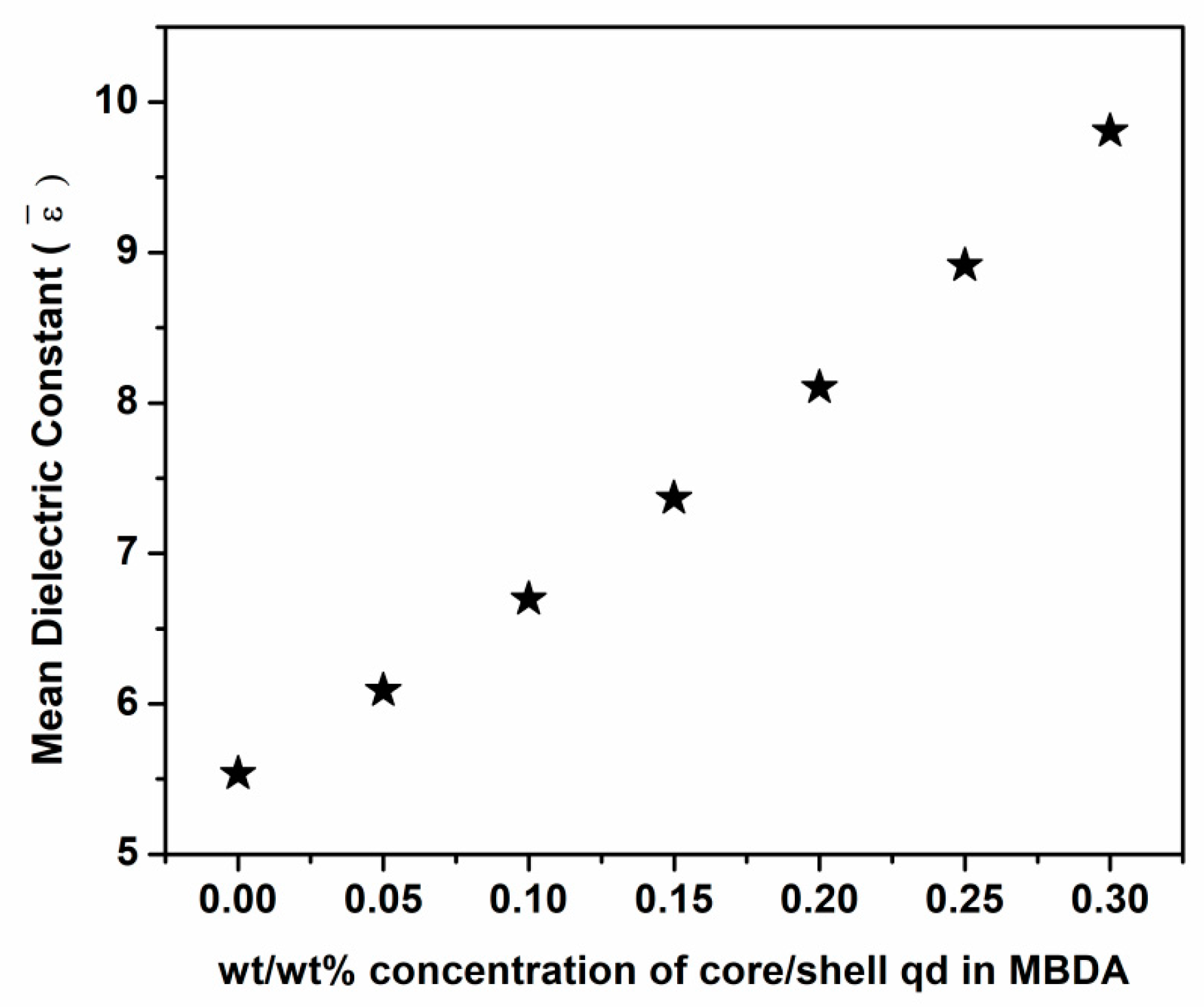
3.2.4. Dielectric Anisotropy and Mean Dielectric Constant
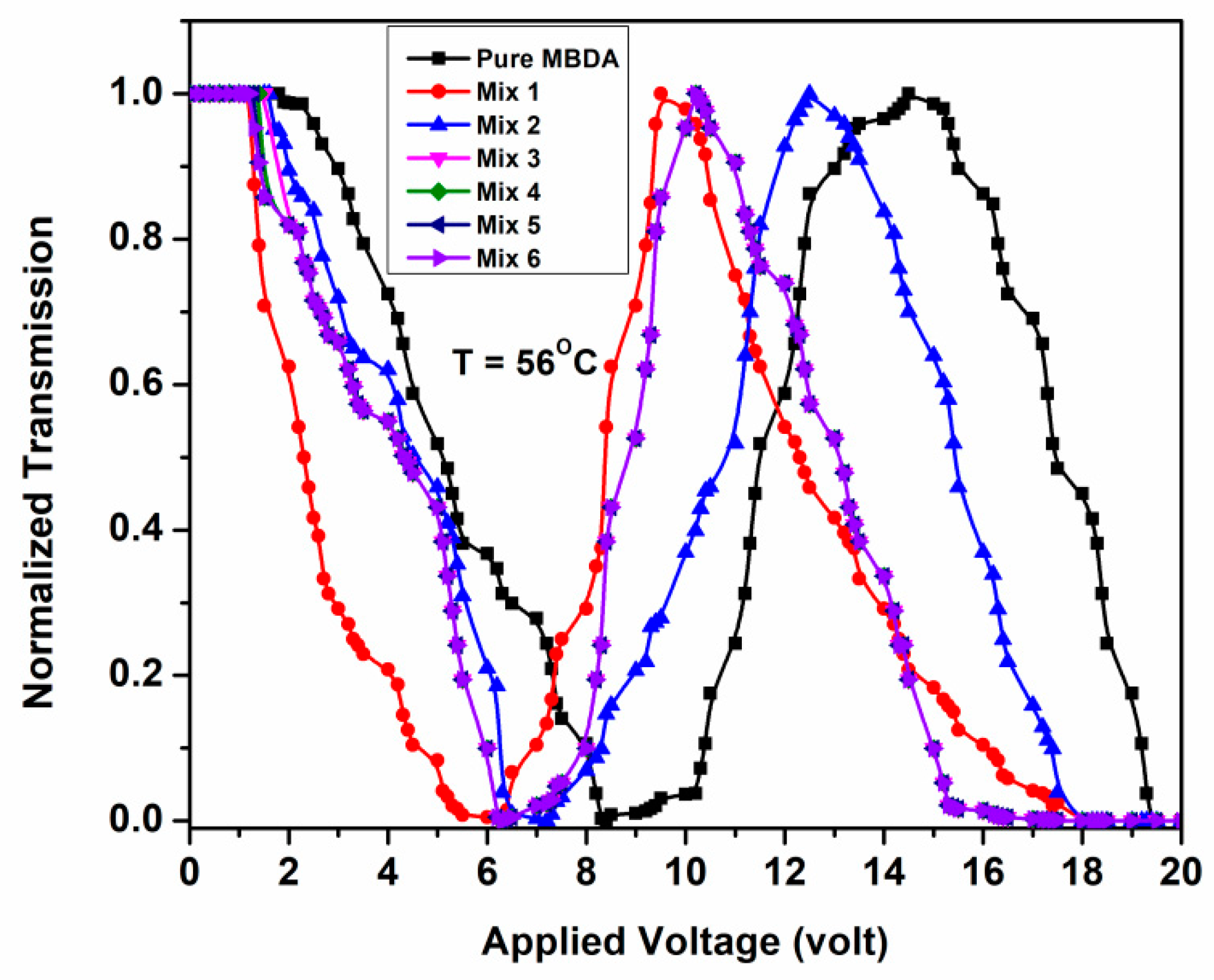
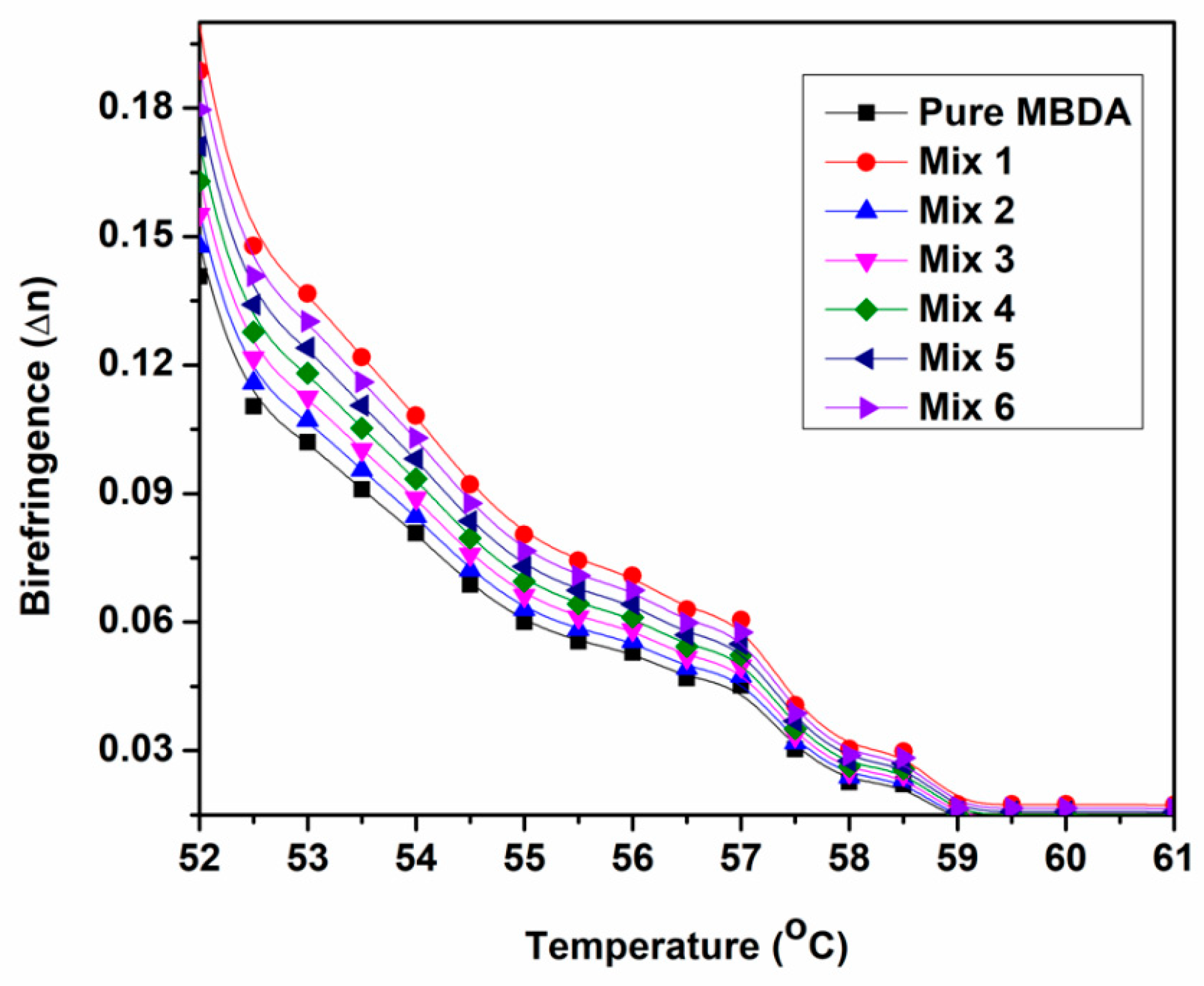
3.3. Electro-Optical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Peng, F.; Yamaguchi, T.; Song, X.; Wu, S.-T. High Performance Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Liquid Crystals for Display Applications. Crystals 2013, 3, 483–503. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, P.; Heckmeier, M.; Tarumi, K. Design and synthesis of nematic liquid crystals with negative dielectric anisotropy. Liq. Cryst. 1999, 26, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, P.; Reiffenrath, V.; Bremer, M. Nematic liquid crystals with negative dielectric anisotropy: Molecular design and synthesis. Synlett 1999, 1999, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, M.; Goodby, J.W.; Toyne, K.J. Nematic materials with negative dielectric anisotropy for display applications. Proc. SPIE 2000, 3955, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, T.X.; Wu, S.T. High transmittance in-plane switching liquid crystal displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2006, 2, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Peng, F.; Wu, S.T. Fringe-field switching with a negative dielectric anisotropy liquid crystal. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, F.J. Electric-field-induced orientational deformation of nematic liquid-crystals: Tunable birefringence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 20, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Kataoka, S.; Sasaki, T.; Chida, H.; Tsuda, H.; Ohmuro, K.; Sasabayashi, T.; Koike, Y.; Okamoto, K. A Super-High Image Quality Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment LCD by New Rubbing-Less Technology; SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1998; Volume 29, pp. 1077–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, H.J.; Jo, M.H.; Jang, I.W.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Hur, H.J. Achieving high light efficiency and fast response time in fringe field switching mode using a liquid crystal with negative dielectric anisotropy. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 39, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Iannacchione, G.S. Evidence for directed self-assembly of quantum dots in a nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 010701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, D.P.; Manohar, R.; Kumar, S. Tuning phase retardation behaviour of nematic liquid crystal using quantum dots. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidalilir, Z.; Soheyli, E.; Sabaeian, M.; Sahraei, R. Enhanced electrochemical and electro-optical properties of nematic liquid crystal doped with Ni:ZnCdS/ZnS core/shell quantum dots. J. Molliq. 2020, 320, 114373. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, A.K.; Tripathi, P.K.; Pandey, K.K.; Singh, B.P.; Manohar, R. Dielectric properties and activation energies of Cu:ZnO dispersed nematic mesogenN-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-4-butylaniline liquid crystal. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Impact of Dispersion of Nanoscale Particles on the Properties of Nematic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2019, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Manohar, R. Effect of graphene oxide dispersion in nematic mesogen and their characterization results. Appl. Phy. A 2019, 125, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Pathak, G.; Srivastava, A.; Herman, J.; Manohar, R. Cd1−XZnXS/ZnS core/shell quantum dots in nematic liquid crystals to improve material parameter for better performance of liquid crystal based devices. J. Molliq. 2018, 255, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Vimal, T.; Singh, D.P.; Gupta, S.K.; Tripathi, P.; Phadnis, C.; Mahamuni, S.; Srivastava, A.; Manohar, R. Cd1-xZnxS/ZnS core/shell quantum dot ferroelectric liquid crystal composite system: Analysis of faster optical response and lower operating voltage. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Manohar, R.; Daoudi, A.; Sahraoui, A.H.; Phadnis, C.; Mahamuni, S. Quenching of photoluminescence and enhanced contrast of ferroelectric liquid crystal dispersed with Cd1−XZnXS/ZnS nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2016, 173, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.K.; Joshi, B.; Singh, S. Pristine and quantum dots dispersed nematic liquid crystal. Impact of dispersion and applied voltage on dielectric and electro-optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2017, 69, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, E.; Cirtoaje, C.; Danila, O. Dynamic behavior of nematic liquid crystal mixtures with quantum dots in electric fields. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.K.; Nam, M.K.; Char, K.; Lee, S. Gram-scale one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent blue emitting Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5307–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, D.; Qian, L.; Kuan Tseng, T.; Holloway, P.H. Quantum dots and their multimodal applications: A review. Materials 2010, 3, 2260–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Pandey, F.P.; Parmar, A.S.; Singh, S.; Hegde, G.; Manohar, R. Effect of carbonaceous oil palm leaf quantum dot dispersion in nematic liquid crystal on zeta potential, optical texture and dielectric properties. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Hegde, G.; Manohar, T.; Manohar, R. Effect of oil palm leaf–based carbon quantum dot on nematic liquid crystal and its electro–optical effects. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 48, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rastogi, A.; Pandey, F.; Manohar, R.; Singh, S. Effect of Doping of Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Nematic Liquid Crystal p-Methoxybenzylidene p-Decylaniline. Crystals 2021, 11, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060605
Rastogi A, Pandey F, Manohar R, Singh S. Effect of Doping of Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Nematic Liquid Crystal p-Methoxybenzylidene p-Decylaniline. Crystals. 2021; 11(6):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060605
Chicago/Turabian StyleRastogi, Ayushi, Fanindra Pandey, Rajiv Manohar, and Shri Singh. 2021. "Effect of Doping of Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Nematic Liquid Crystal p-Methoxybenzylidene p-Decylaniline" Crystals 11, no. 6: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060605
APA StyleRastogi, A., Pandey, F., Manohar, R., & Singh, S. (2021). Effect of Doping of Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Nematic Liquid Crystal p-Methoxybenzylidene p-Decylaniline. Crystals, 11(6), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060605





