Hyaluronic Acid-Coated MTX-PEI Nanoparticles for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Cells and Animals
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Cells
2.1.3. Animals
2.2. Methods
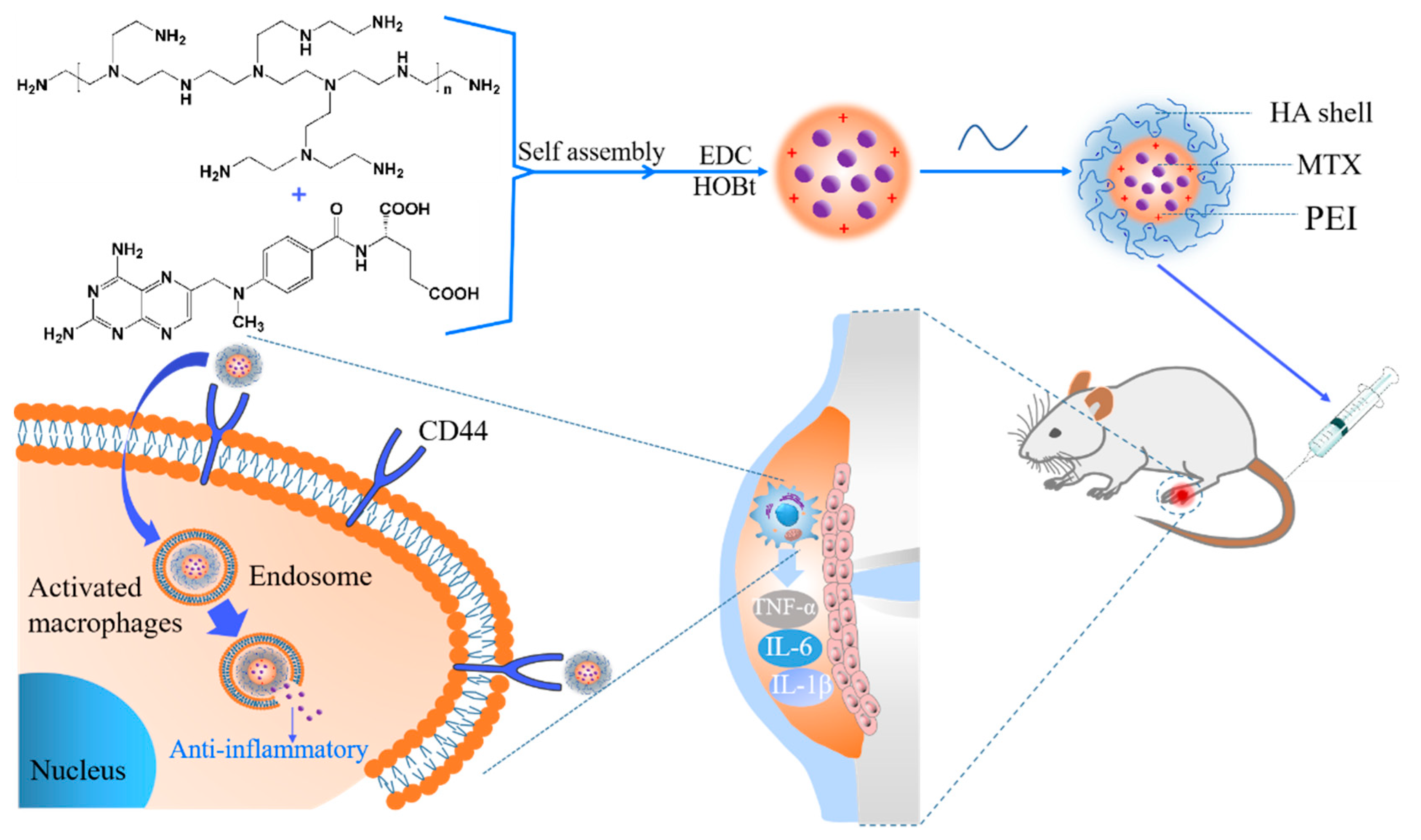
2.2.1. Preparation of Hyaluronic Acid Methotrexate-Linked Branched Polyethyleneimine (MTX-PEI@HA) Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.2.2. Characterization of MTX-PEI@HA
2.2.3. In Vitro Drug Release Profile
2.2.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Detection
2.2.5. Cellular Uptake Study
2.2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
2.2.7. Mice Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis
2.2.8. Therapeutic Efficacy In Vivo
2.2.9. Histological Analysis
2.2.10. Safety Evaluation In Vivo
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
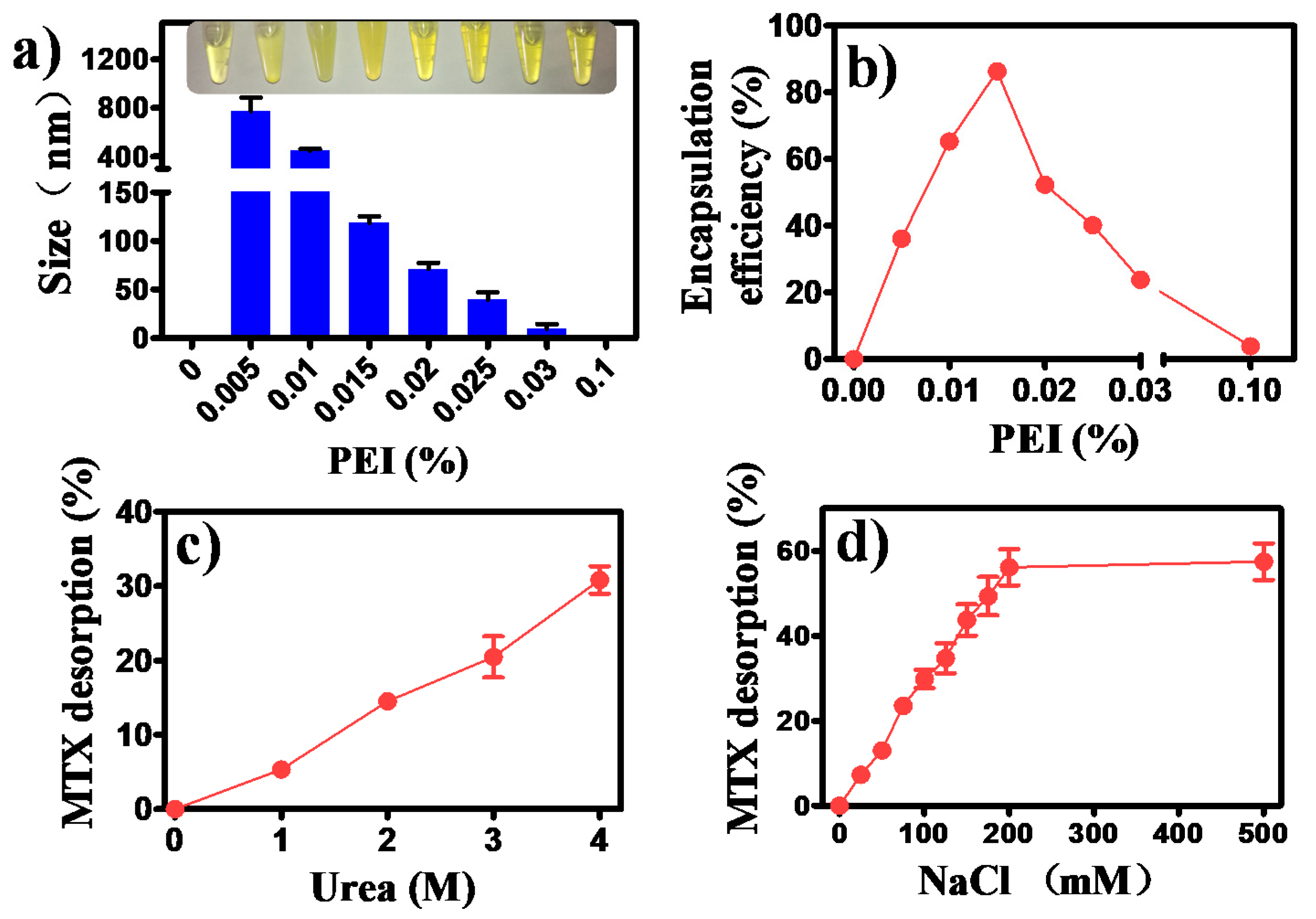
3.1. Formation of MTX/PEI NPs and Mechanism Understanding of the Interaction between MTX and PEI
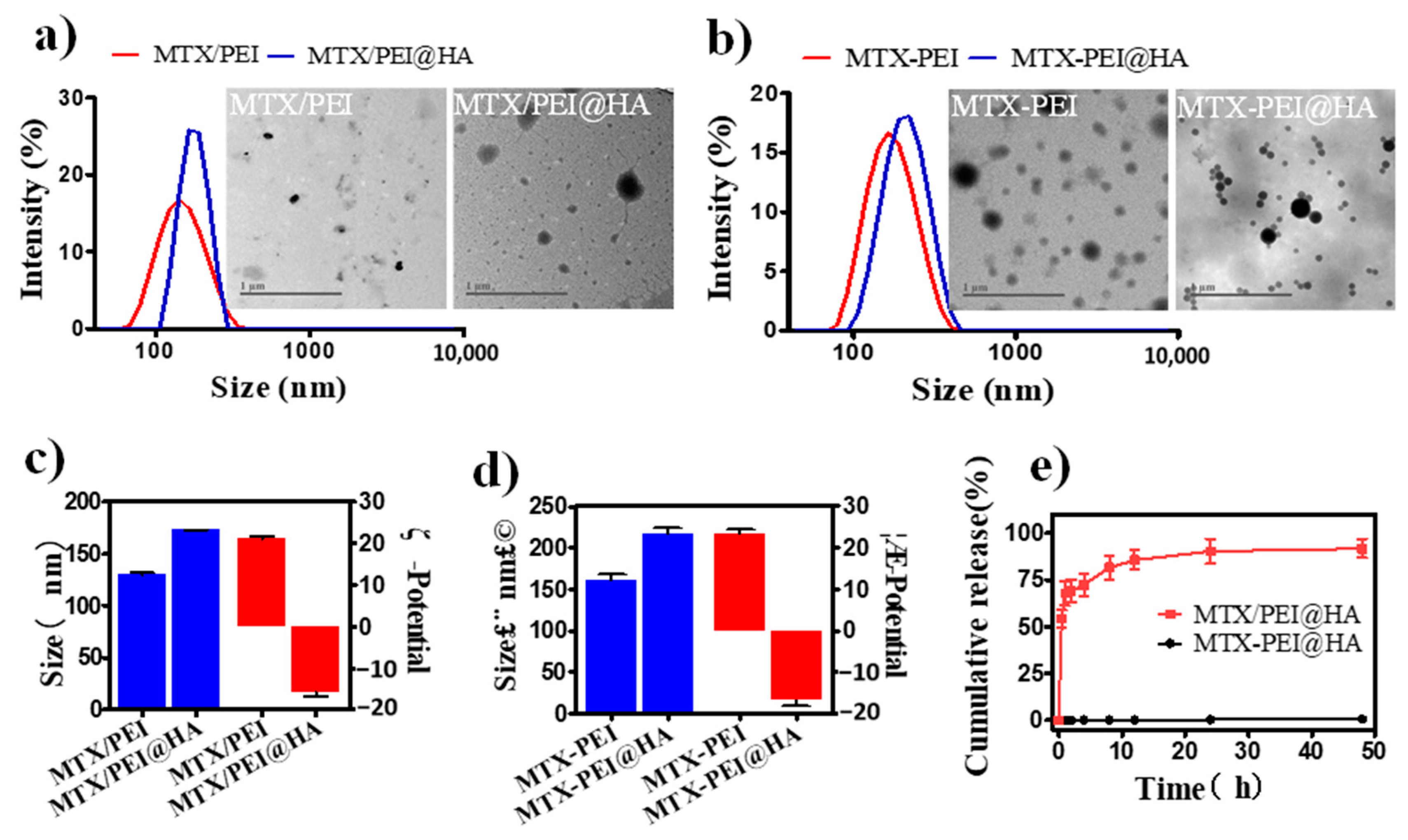
3.2. Systematical Characterization of MTX-PEI@HA NPs
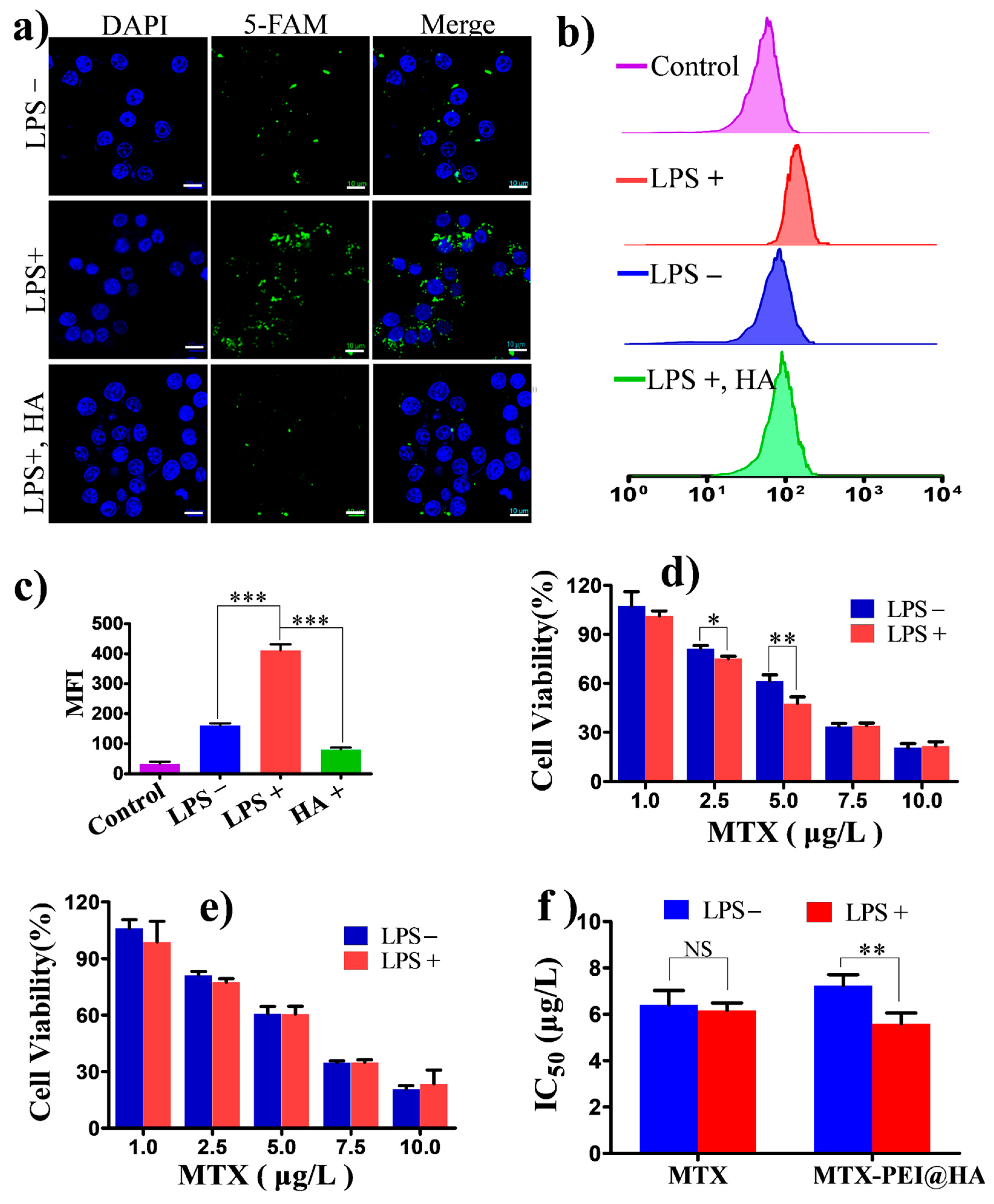
3.3. In Vitro Cellular Uptake and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the MTX-PEI@HA NPs
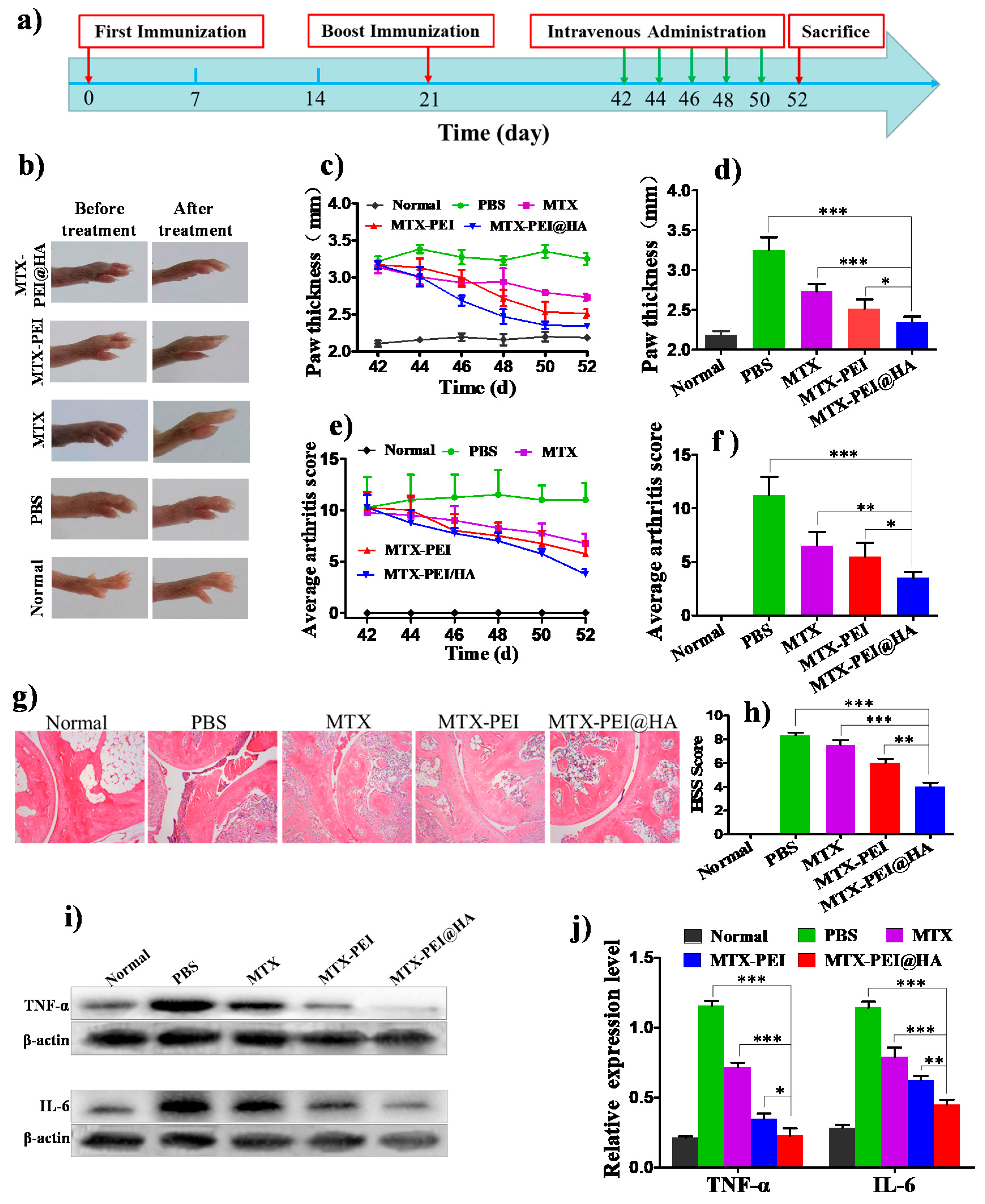
3.4. Therapeutic Effect of MTX-PEI@HA NPs on Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
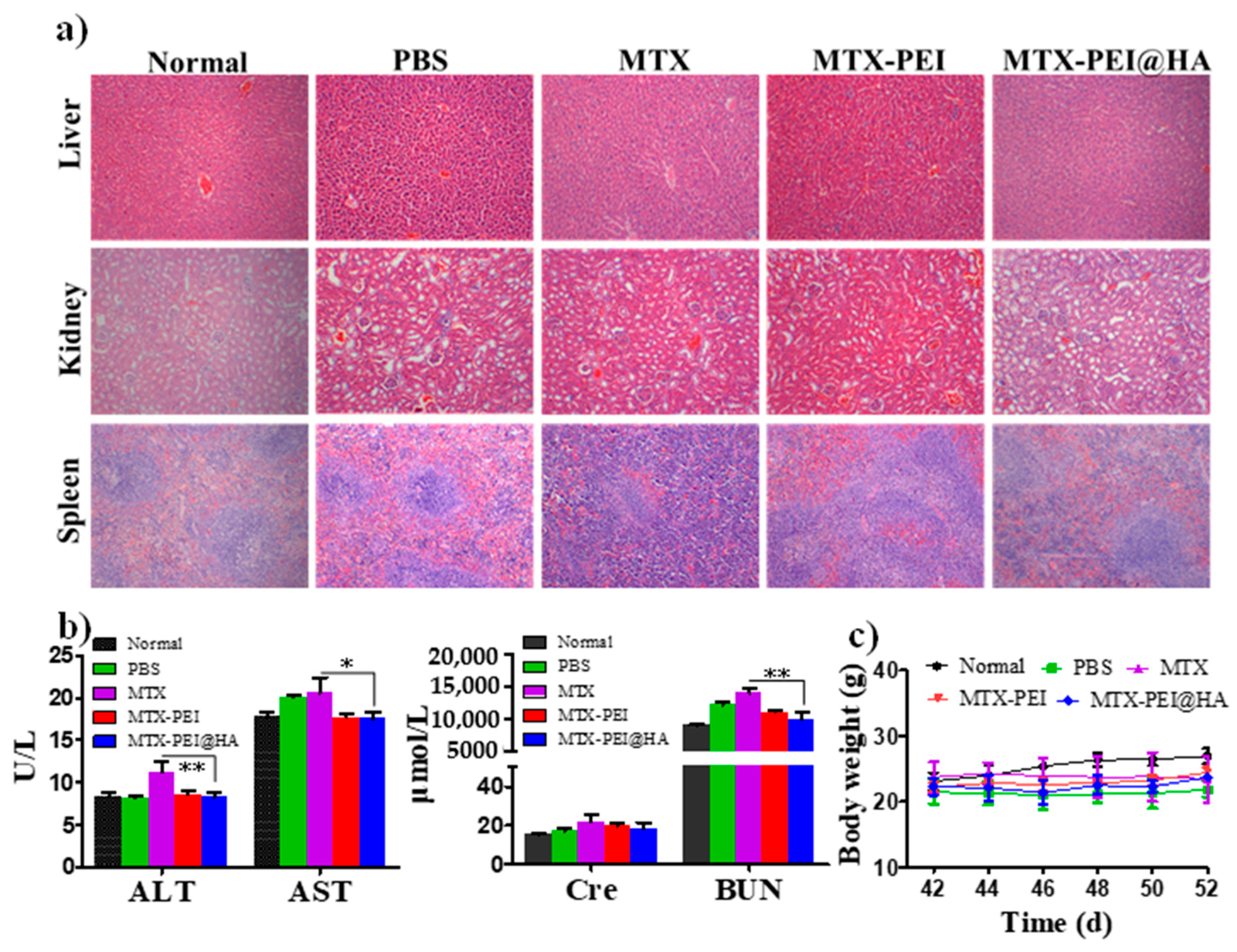
3.5. Systemic Toxicity of MTX-PEI@HA NPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, V.; Catrina, A.I.; Klareskog, L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: From triggering to targeting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Pope, J.E. Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouti, E.; Andreakos, E. The many facets of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 165, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Ma, C.; Ruan, J.; Long, H.W.Y. Sinomenine Inhibits the Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating the Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines and Monocyte/Macrophage Subsets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledingham, J.; Gullick, N.; Irving, K.; Gorodkin, R.; Aris, M.; Burke, J.; Gordon, P.; Christidis, D.; Galloway, S.; Hayes, E.; et al. BSR and BHPR guideline for the prescription and monitoring of non-biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.G.; Bae, S.C.; Lee, Y.H. Association of the MTHFR C677T and A1298C polymorphisms with methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Huang, J.; Shu, X.; Fan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, C. Polymorphisms and Pharmacogenomics for the Clinical Efficacy of Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.C.; Song, G.G. Association of the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism with responsiveness to and toxicity of DMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol. 2016, 75, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijde, D.; Breedveld, F.C.; Kavanaugh, A.; Keystone, E.C.; Landewe, R.; Patra, K.; Pangan, A.L. Disease activity, physical function, and radiographic progression after longterm therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate: 5-year results of PREMIER. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wluka, A.; Buchbinder, R.; Mylvaganam, A.; Hall, S.; Harkness, A.; Lewis, D.; Littlejohn, G.O.; Miller, M.H. Ryan, P.F.J. Long-term methotrexate use in rheumatoid arthritis: 12 years followup of 460 patients treated in community practice. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heijden, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Scheper, R.J.; Jansen, G. Drug Insight: Resistance to methotrexate and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs-from bench to bedside. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolmaali, S.S.; Tamaddon, A.M.; Dinarvand, R. A review of therapeutic challenges and achievements of methotrexate delivery systems for treatment of cancer and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Luo, X.L.; Hu, S.; Ding, J.S.; Zhou, W.H. Rational design of metal-organic frameworks to deliver methotrexate for targeted rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J. Control Release 2021, 330, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.P.; Cruz, M.A.E.; Tovani, C.B.; Ciancaglini, P. Biomedical applications of nanotechnology. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Tang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L. Nanomedicine-advantages for their use in rheumatoid arthritis theranostics. J. Control Release 2019, 316, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.K.; O’Mary, H.; Cui, Z. Nanomedicine delivers promising treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Sharma, G.; Thakur, K.; Anwar, F.; Katare, O.P.; Goni, V.G.; Kumar, V.; Zamzami, M.A.; Akhter, S. Emerging Advances in Nanomedicine as a Nanoscale Pharmacotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis: State of the Art. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, H.; Loddenkemper, C.; Miossec, P. Rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis-pathology of acute inflammation. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, S15–S19. [Google Scholar]
- Oore-ofe, O.; Soma, P.; Buys, A.V.; Debusho, L.K.; Pretorius, E. Characterizing pathology in erythrocytes using morphological and biophysical membrane properties: Relation to impaired hemorheology and cardiovascular function in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Goncalves, C.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Engineering nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis: Past, present, and future trends. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4489–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangirian, H.; Lemraski, E.G.; Webster, T.J.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Abdollahi, Y. A review of drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology and green chemistry: Green nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2957–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Yung, B.; Huang, P. Chen, X. Nanotechnology for Multimodal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13566–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivisatos, A.P. Less is more in medicine-Sophisticated forms of nanotechnology will find some of their first real-world applications in biomedical research, disease diagnosis and, possibly, therapy. Sci. Am. 2001, 285, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; Saravanakumar, G.; Park, J.H.; Park, K. Hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers for intracellular targeting: Interfacial interactions with proteins in cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 99, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadete, A.; Alonso, M.J. Targeting cancer with hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers: Recent advances and translational perspectives. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Han, H.S.; Sung, S.; Kang, J.H.; Sa, K.H.; Al Faruque, H.; Hong, J.; Nam, E.J.; Kim, I.S.; Park, J.H.; et al. Endogenous inspired biomineral-installed hyaluronan nanoparticles as pH-responsive carrier of methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis. J. Control Release 2017, 252, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, V.M.; Lopes-de-Araujo, J.; Lima, S.A.C.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Hyaluronic acid-conjugated pH-sensitive liposomes for targeted delivery of prednisolone on rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.L.; Hou, J.R.; Zhong, Z.R.; Hao, N.; Lin, Y. Li, C.H. Targeted delivery of hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Luria, A.; Rhodes, C.; Raghu, H.; Lingampalli, N.; Sharpe, O.; Rada, B.; Sohn, D.H.; Robinson, W.H.; Sokolove, J. Nicotine drives neutrophil extracellular traps formation and accelerates collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, F.; Chen, X. Remission of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through Combination Therapy of Microfracture and Transplantation of Thermogel-Encapsulated Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, J.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Yang, M.D.; Jia, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Chang, F.; Li, R.; et al. Intra-Articular Transplantation of Allogeneic BMMSCs Rehabilitates Cartilage Injury of Antigen-Induced Arthritis. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleagrahara, N.; Miranda-Hernandez, S.; Alim, M.A.; Hayes, L.; Bird, G.; Ketheesan, N. Therapeutic effect of quercetin in collagen-induced arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, B. Cationic lipids and polymers mediated vectors for delivery of siRNA. J. Control Release 2007, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Meng, H.; Kabehie, S.; George, S.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Polyethyleneimine coating enhances the cellular uptake of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and allows safe delivery of siRNA and DNA constructs. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.K.; Rosgen, J.; Englander, S.W. Urea, but not guanidinium, destabilizes proteins by forming hydrogen bonds to the peptide group. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Satoh, M. Effects of NaCl, NaOH, and HCl concentration on the cloud point of poly (vinyl methyl ether) in water-electrostatic interactions are inevitably involved in the hydrophobic interaction. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh-Huyen, T.; Rastogi, R.; Shelke, J.; Amiji, M.M. Modulation of Macrophage Functional Polarity towards Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype with Plasmid DNA Delivery in CD44 Targeting Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. UK 2015, 5, 16632. [Google Scholar]
- Farajzadeh, R.; Zarghami, N.; Serati-Nouri, H.; Momeni-Javid, Z.; Farajzadeh, T.; Jalilzadeh-Tabrizi, S.; Sadeghi-Soureh, S.; Naseri, N.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y. Macrophage repolarization using CD44-targeting hyaluronic acid-polylactide nanoparticles containing curcumin. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | ATGAAGGGCTGCTTCCAAAC | TCTCCACAGCCACAATGAGT |
| IL-6 | GGAGCCCACCAAGAACGATA | ACCAGCATCAGTCCCAAGAA |
| TNF-α | CTCATGCACCACCATCAAGG | ACCTGACCACTCTCCCTTTG |
| iNOS | CAGCTGGGCTGTACAAACCTT | CATTGGAAGTGAAGCGTTTCG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, S.; Liu, P.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W. Hyaluronic Acid-Coated MTX-PEI Nanoparticles for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Crystals 2021, 11, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040321
Zhong S, Liu P, Ding J, Zhou W. Hyaluronic Acid-Coated MTX-PEI Nanoparticles for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Crystals. 2021; 11(4):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040321
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Shenghui, Peng Liu, Jinsong Ding, and Wenhu Zhou. 2021. "Hyaluronic Acid-Coated MTX-PEI Nanoparticles for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy" Crystals 11, no. 4: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040321
APA StyleZhong, S., Liu, P., Ding, J., & Zhou, W. (2021). Hyaluronic Acid-Coated MTX-PEI Nanoparticles for Targeted Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Crystals, 11(4), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040321







