Effect of Nano-Si3N4 on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
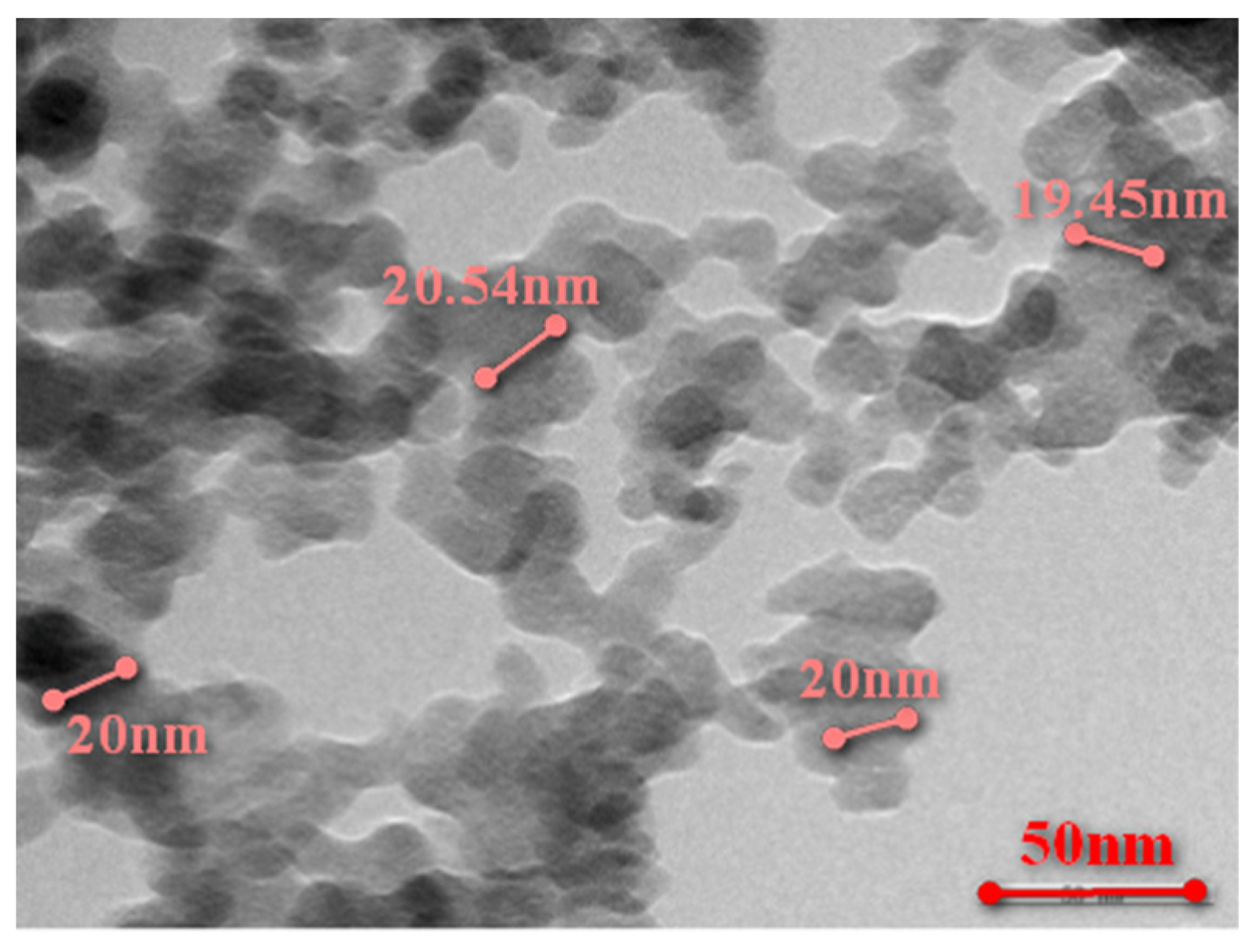
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportion and the Sample Casting
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Compressive Strength
2.3.2. Wear Resistance
2.3.3. Hydration Heat
2.3.4. XRD Test
2.3.5. Differential Thermal Analysis Test
2.3.6. Nanoindentation
2.3.7. Nitrogen Isotherm Adsorption Analysis
2.3.8. Microstructural Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties Results
3.1.1. Influence of the NSN on the Compressive Strength
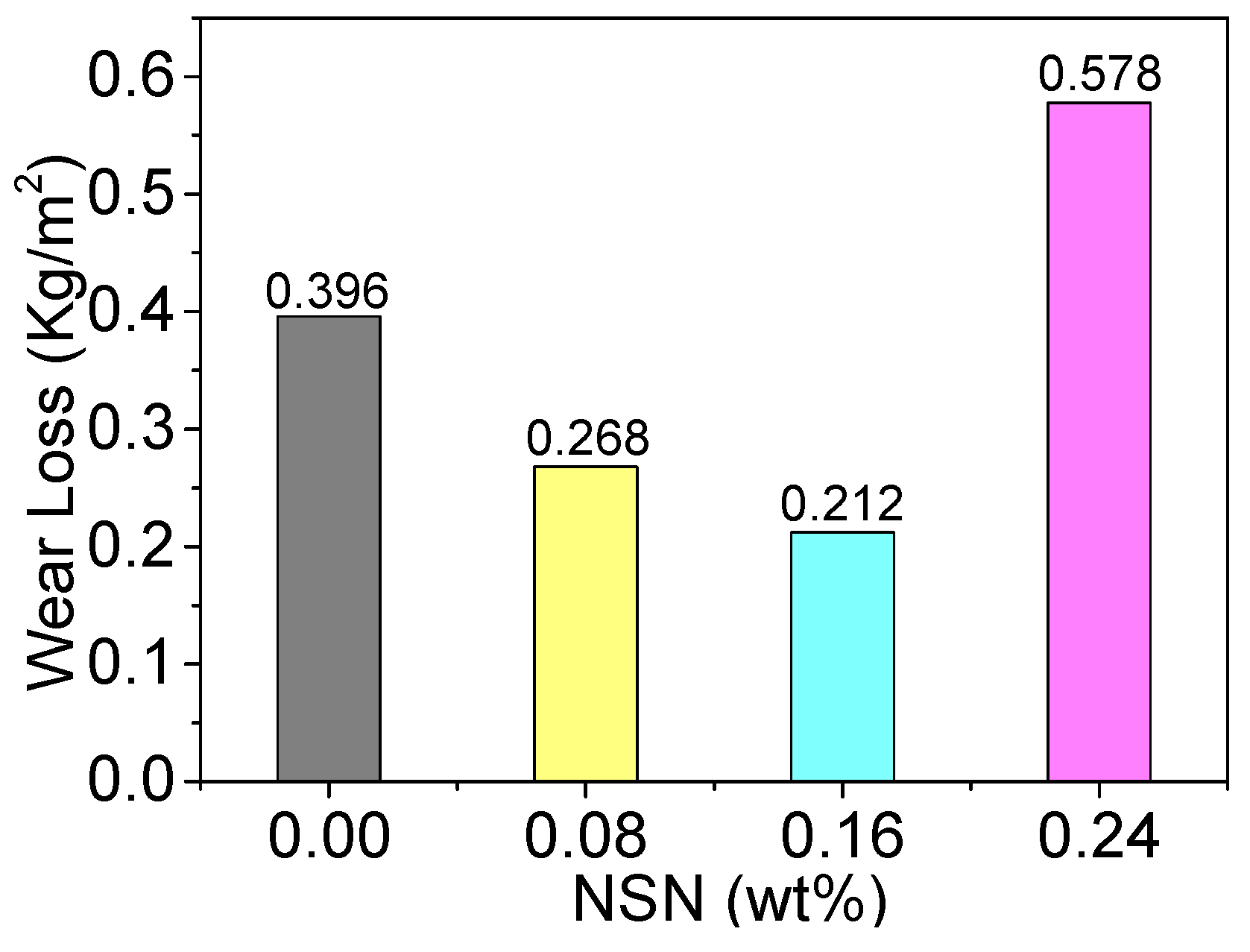
3.1.2. Influence of NSN on the Wear Resistance
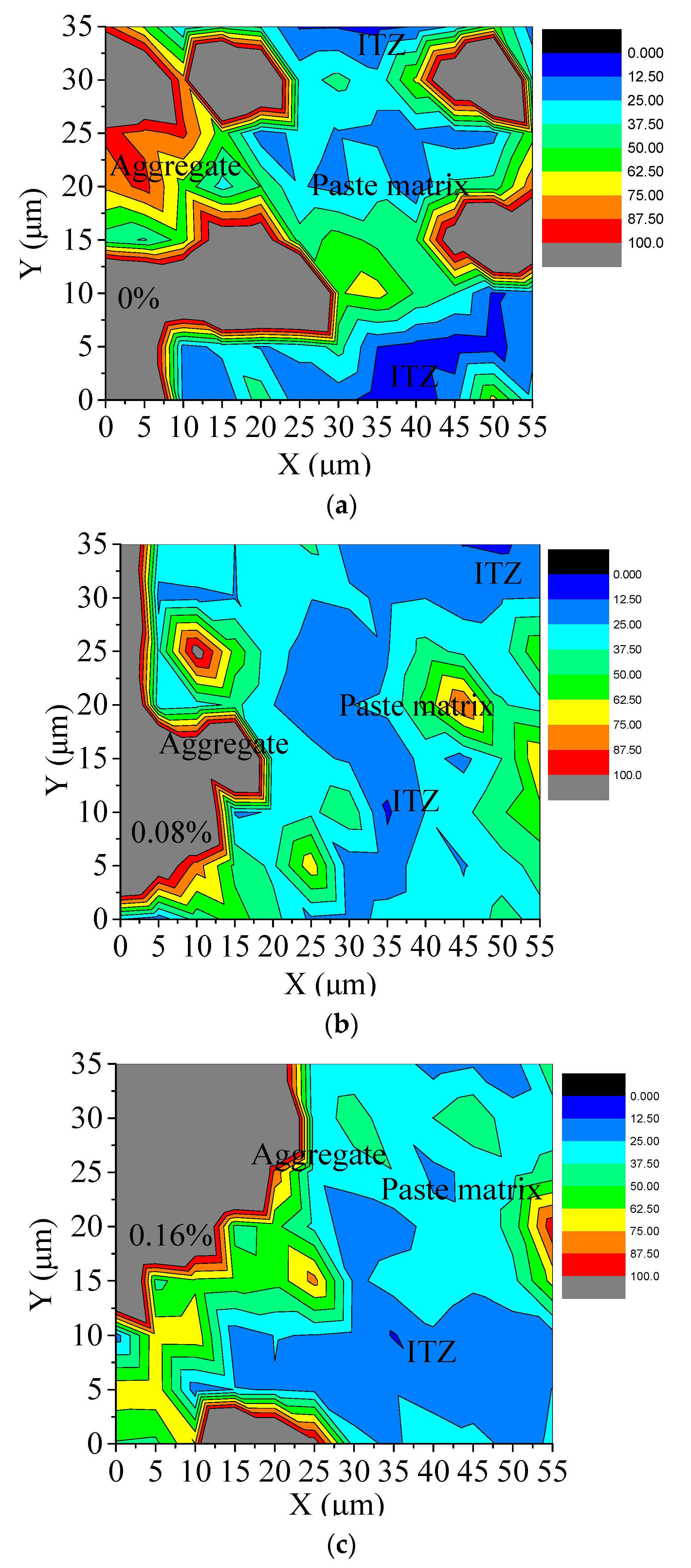
3.2. Micromechanical Properties Measured by Nanoindentation
3.3. Influence of NSN on the Hydration Process and Hydration Products
3.3.1. Hydration Heat Measurement Result
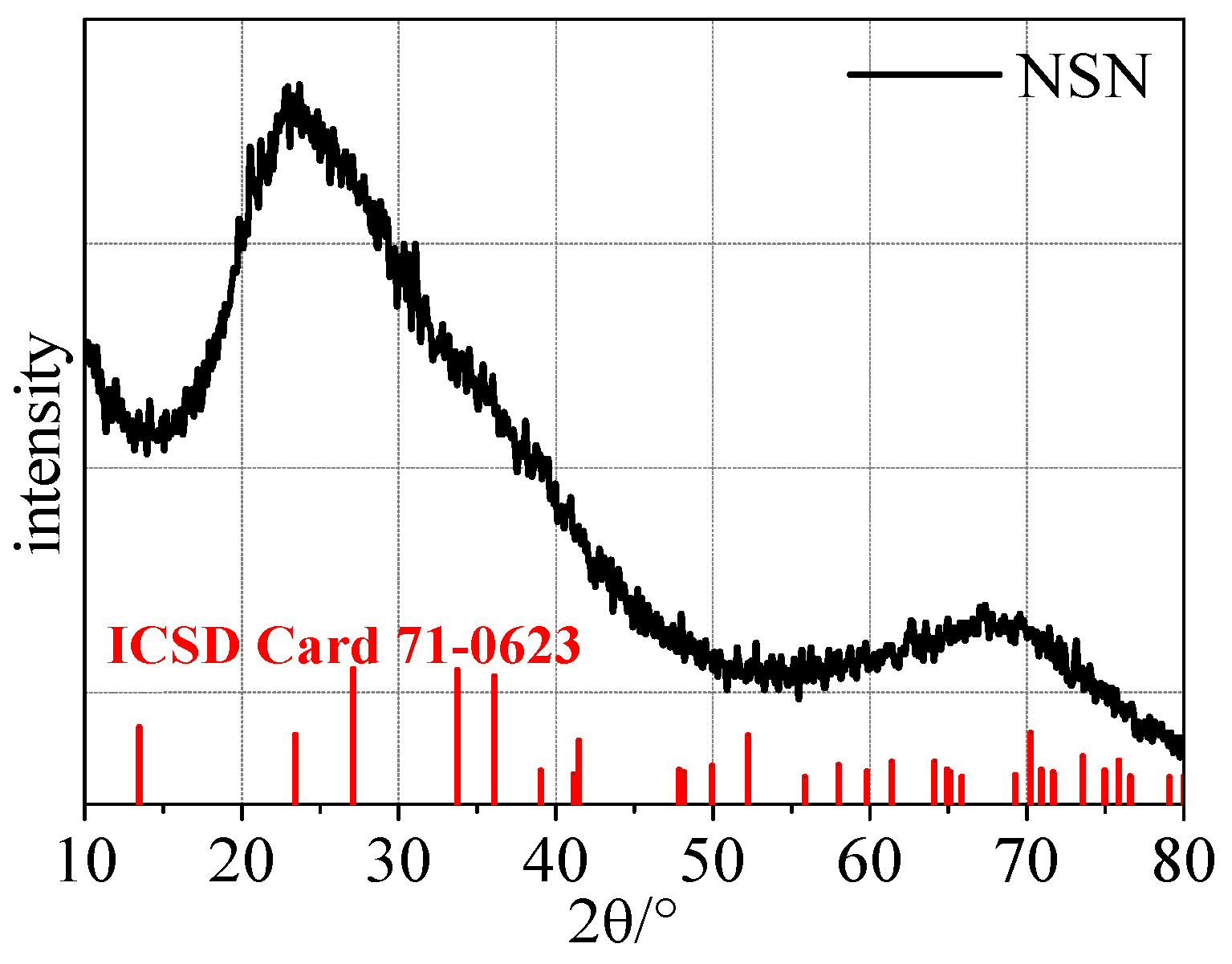
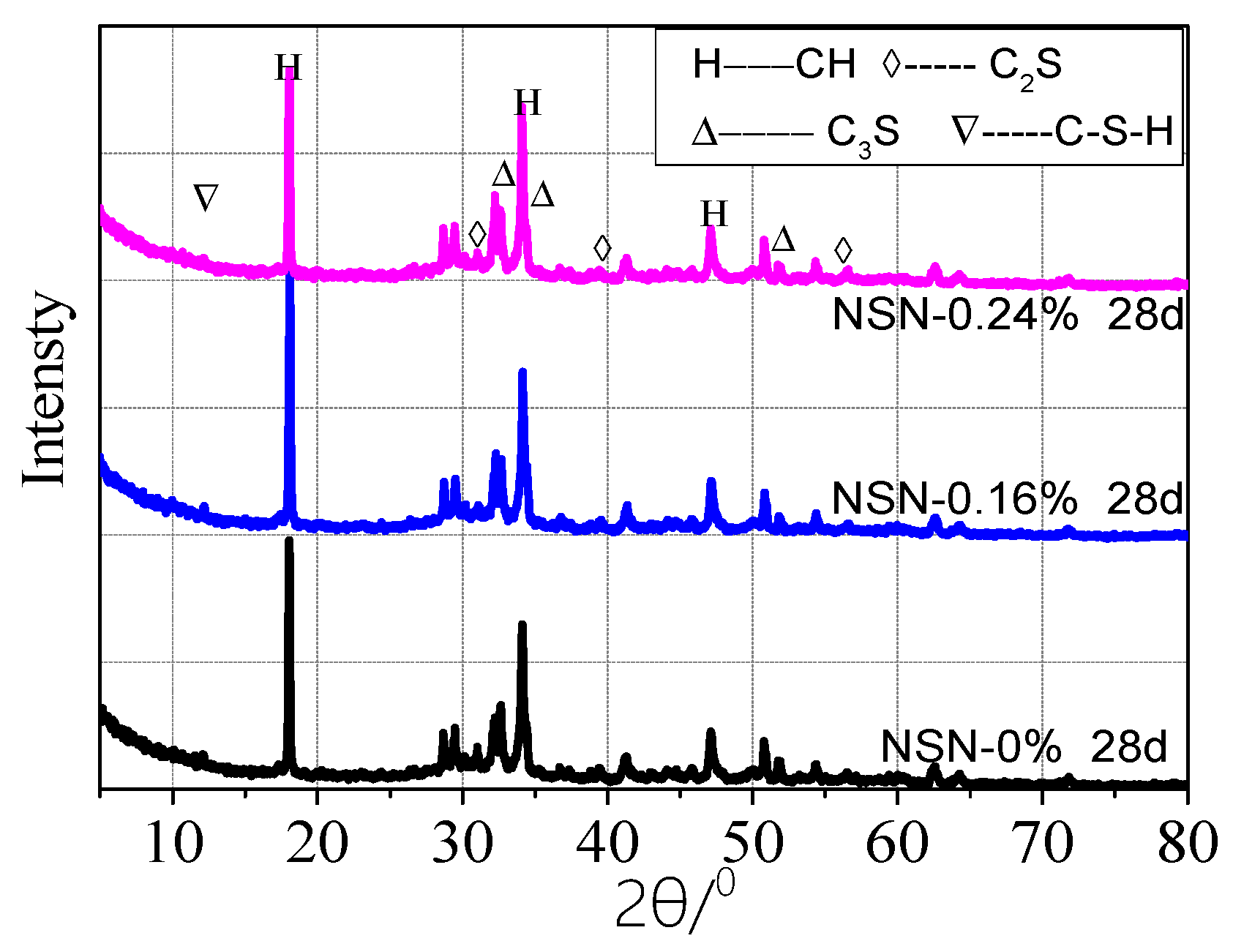
3.3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Patterns of Samples
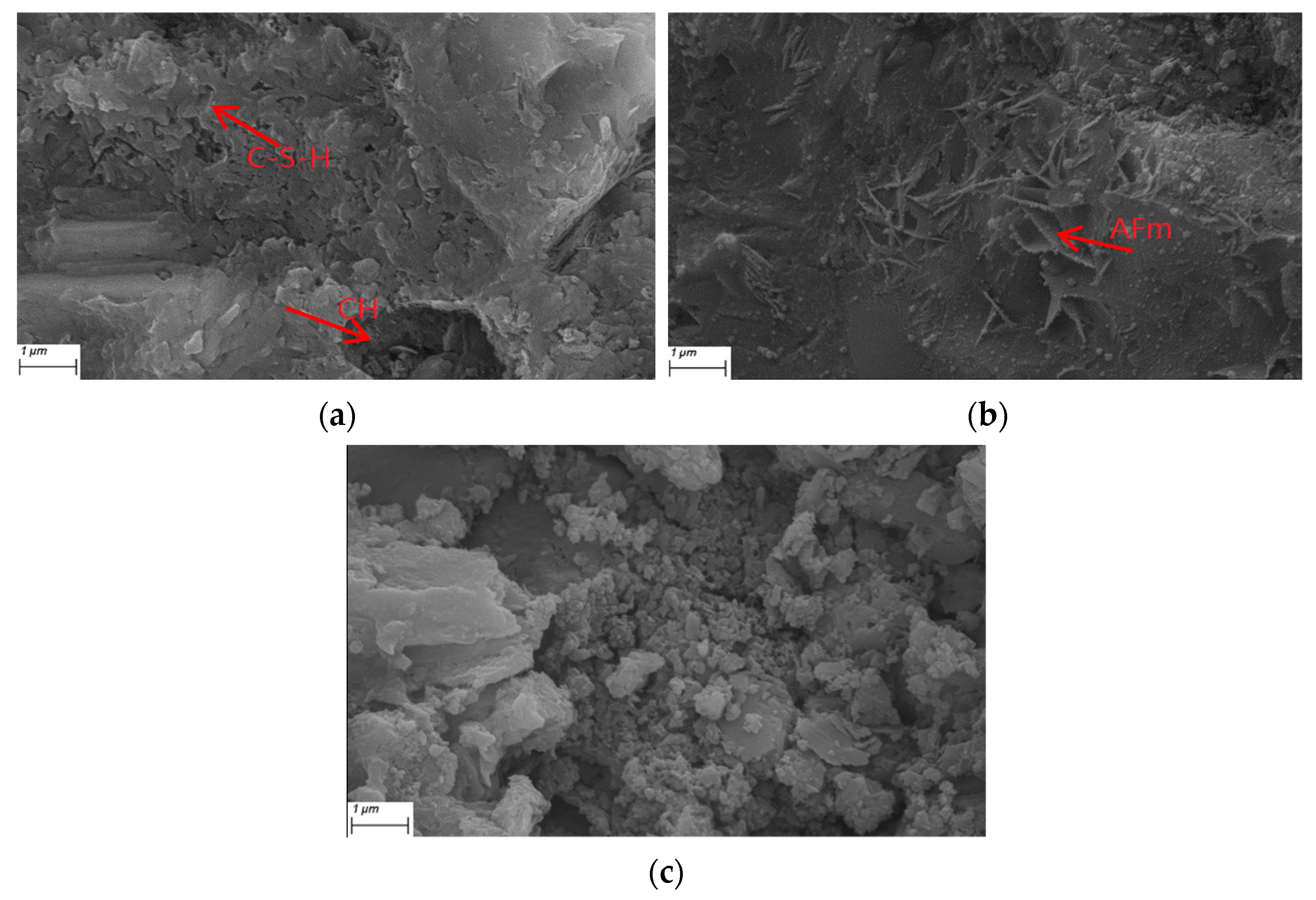
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Samples
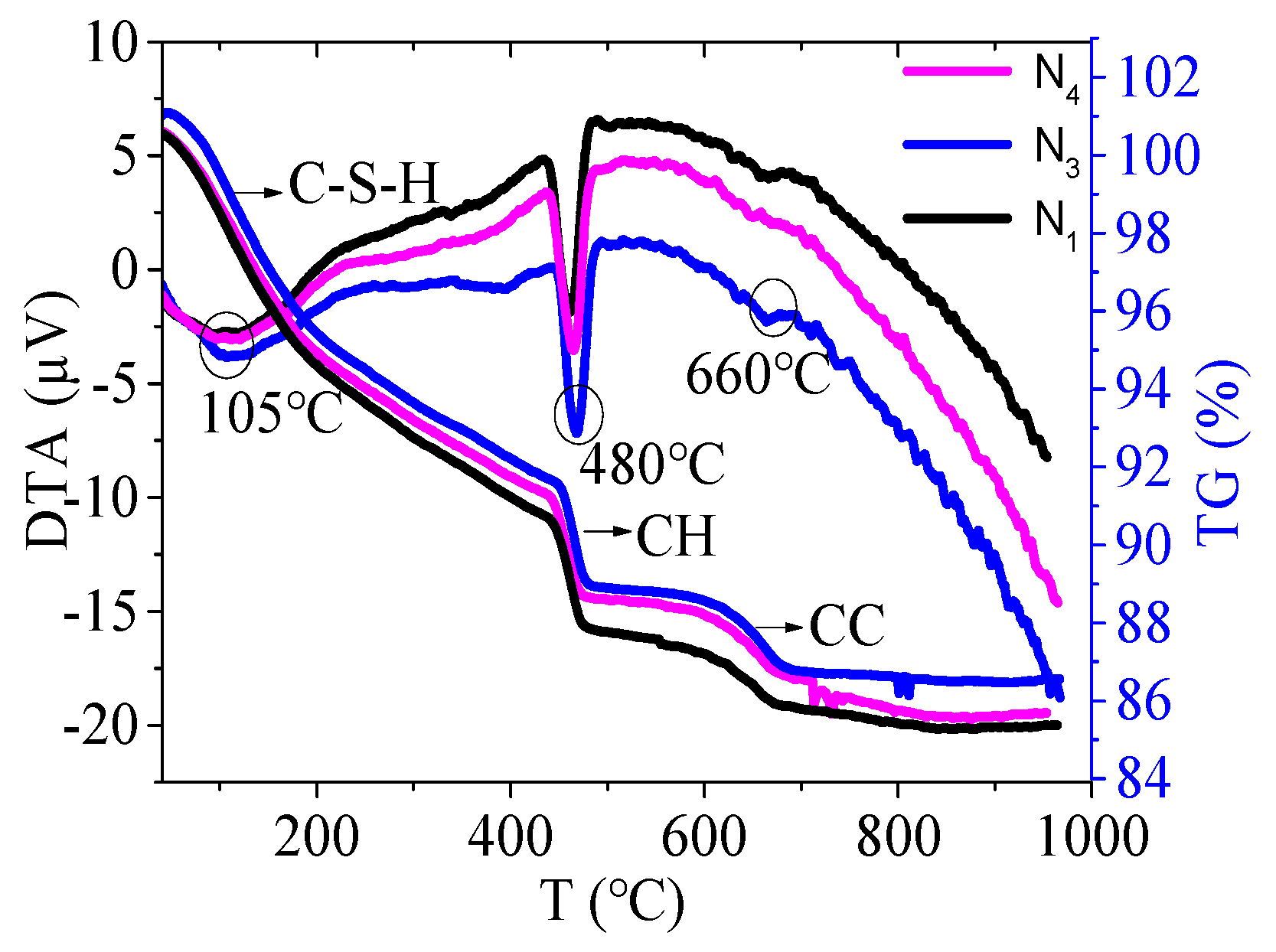
3.5. Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA-TG) Result
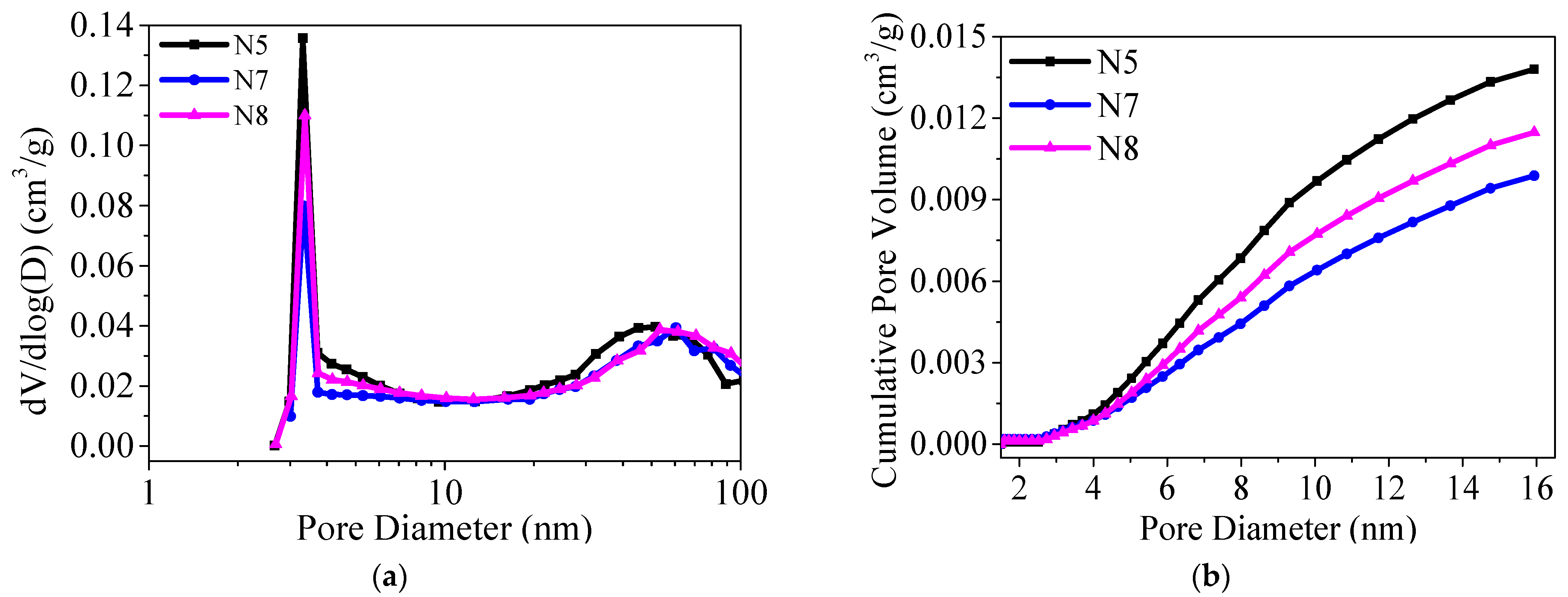
3.6. Microstructural Change in the Sample Incorporating NSN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Li, G.; Feng, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Effect of Delaminated MXene (Ti3C2) on the Performance of Cement Paste. J. Nanomater. 2019, 10, 3074206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Guan, X.; Zhao, R. Revealing the substitution preference of zinc in ordinary Portland cement clinker phases: A study from experiments and DFT calculations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C. Study on Design, Performance and Mechanism of Nano Modified Concrete Pavement Materials. Master’s Thesis, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha, China, 1 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Li, X.; Cai, X. The applicability of alkaline-resistant glass fiber in cement mortar of road pavement: Corrosion mechanism and performance analysis. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, R.C.; Shrivastava, S. Strength, abrasion and permeability studies on cement concrete containing quartz sandstone coarse aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; He, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, X. Abrasion erosion characteristics of concrete made with moderate heat Portland cement, fly ash and silica fume using sandblasting test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popek, M.; Sadowski, Ł.; Szymanowski, J. Abrasion Resistance of Concrete Containing Selected Mineral Powders. Procedia Eng. 2016, 153, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, Z.; Chen, X.; Cai, X. Influence and mechanism of micro/nano-mineral admixtures on the abrasion resistance of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, A. Mechanical properties of sandy soils reinforced with cement and randomly distributed glass fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 96, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.; Lameie, T.; Maleki, M.; Yazdani, R. Simultaneous effects of fiber and glass on the mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Qu, L. Effects of nano-particles on improvement in wear resistance and drying shrinkage of road fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, Y.; Yu, X.; Han, B. Enhancements and mechanisms of nanoparticles on wear resistance and chloride penetration resistance of reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Hou, P.; Ye, Z. Influences of nano-TiO2 on the properties of cement-based materials: Hydration and drying shrinkage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, B.; Zou, C. Effect and Mechanism of Nano-particles on Wear Resistance of Road Fly Ash Concrete. Bull. Chin. Ceramic. Soc. 2018, 37, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J.; Li, H.D.; Zeng, Q.; Chang, Q.F.; Wang, X.S. Effects of nanoclay addition on the permeability and mechanical properties of ultra high toughness cementitious composites. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2021, 21, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fan, C. Comparative Study on Dispersion of Carbon Nanofibers and Enhancement on Mechanical Property and Microstructure in Cement Composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.Y. Wear Resistance and Chloride Penetration Resistance of Nano Cement-Base Composites. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.X.; Gao, X.J. Effect of nano Al2O3 and MgO on abrasion resistance and mechanism of ultra-high performance concrete. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.W. Improving the abrasion resistance of hydraulic-concrete containing surface crack by adding silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 21, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gintautas, S.; Ekaterina, K.; Rostislav, D.; Jakub, H. Hydration and Microstructure of Nano Modified Cement Paste. Solid State Phenom. 2021, 6104, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, K.; Yang, S.; Meng, T.; Li, Y. Effect of Nano Compound Addition on the Properties and Microstructure of Cement Mortar with Mixed Fine Recycled Aggregate. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 719, 022074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Z. The Preparation and Microstructure Analysis of Nanoscale Silicon Nitride Podwer. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.B. Study on the Graphene/Silicon Nitride Based Composite Ceramic Tools and Their Friction and Wear Properties. Master’s Thesis, Qilu University of Technology, Jinan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H. Study on cutting performance and its extended application of coated silicon nitride cutting tool. Guangdong Univ. Technol. 2014, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes and Si3N4 Whiskers on Microstructure and Properities of Mo2FeB2-Based Cermets. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.G.; He, S.L.; Liu, R.A.; Jin, H.; Yang, W.L.; Zhang, Y.H. Preparation and Application of Silicon Nitride Ceramics. China Ceram. Ind. 2016, 23, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Zhu, J.; Guan, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, X.; Feng, C.; et al. Effect of MXene (Nano-Ti3C2) on Early-Age Hydration of Cement Paste. J. Nanomater. 2015, 16, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Effect of graphene oxide nanosheets of microstructure and mechanical properties of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, D.; Yu, X.; Cui, X.; Ou, J. Properties and modification mechanisms of nano-zirconia filled reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V.; Nardinocchi, A. Influence of type of fibers on the properties of high performance cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Kero, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Engström, F.; Samuelsson, C.; Qi, C. Mechanical Activation of Granulated Copper Slag and Its Influence on Hydration Heat and Compressive Strength of Blended Cement. Materials 2019, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.L. Effect of Nanoparticle on Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials and Its Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Chen, Y.; Fan, G.; Jin, Z.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J. Unveiling substitution preference of chromium ions in sulphoaluminate cement clinker phases. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 222, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X. Analysis of properties of cement-based materials by nanoindentation technique. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Highway Science, Ministry of Communications, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.Z. Effect of nano-silica modification on interfacial transition zone in concrete and its multiscale modelling. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 46, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, Y. Microfracture Characterization of Cement Paste at Early Age by Indentation Test. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Shu, X.; Liu, J. Hydration kinetics, pore structure, 3D network calcium silicate hydrate, and mechanical behavior of graphene oxide reinforced cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Liu, F.; Xiao, M. Effect of Nano-TiO2 Dispersibility on the Mechanics, Hydration Degree and Microscopic Properties of Cement Paste. J. Build. Mater. 2021, 1–11. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1764.TU.20210827.0842.002.html (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Chen, X.; Hou, D.; Han, Y.; Ding, X.; Hua, P. Clustering analysis of grid nanoindentation data for cementitious materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 12238–12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y. On Phase Identification of Hardened Cement Pastes by Combined Nanoindentation and Mercury Intrusion Method. Materials 2021, 14, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Zuo, J. Modification effects of nanosilica on the interfacial transition zone in concrete: A multiscale approach. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, R.; Tan, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, D. Air pore structure, strength and frost resistance of air-entrained mortar with different dosage of nano-SiO2 hydrosol. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, E.; Skripkiūnas, G.; Barauskas, I.; Barauskienė, I.; Hodul, J. Influence of carbon nanotubes and polycarboxylate superplasticiser on the Portland cement hydration process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.M. Correlations of the dispersing capability of NSF and PCE types of superplasticizer and their impacts on cement hydration with the adsorption in fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, X. Enhancement of nano-alumina on long-term strength of Portland cement and the relation to its influences on compositional and microstructural aspects. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 98, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.S.; Feng, C.H.; Zhu, L.F.; He, G.Y.; Hou, H.H.; Xia, R.J.; Gao, G.; Guan, X.M.; Zhu, J.P. Effect of nano-TiN on the performance of fly ash cement. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 37, 4072–4076. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, S.; Ouyang, X.; Fu, J.; Niu, Y.; Ma, Y. The role of graphene/graphene oxide in cement hydration. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; Khayat, K.H.; Wan, S. Effects of different nanomaterials on hardening and performance of ultra-high strength concrete (UHSC). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 70, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.G.; Reis, R.M.; Tobar, R.R.; Zanotto, E.D.; Ferreira, E.B. Simulation and experimental study of the particle size distribution and pore effect on the crystallization of glass powders. Acta Mater. 2019, 175, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
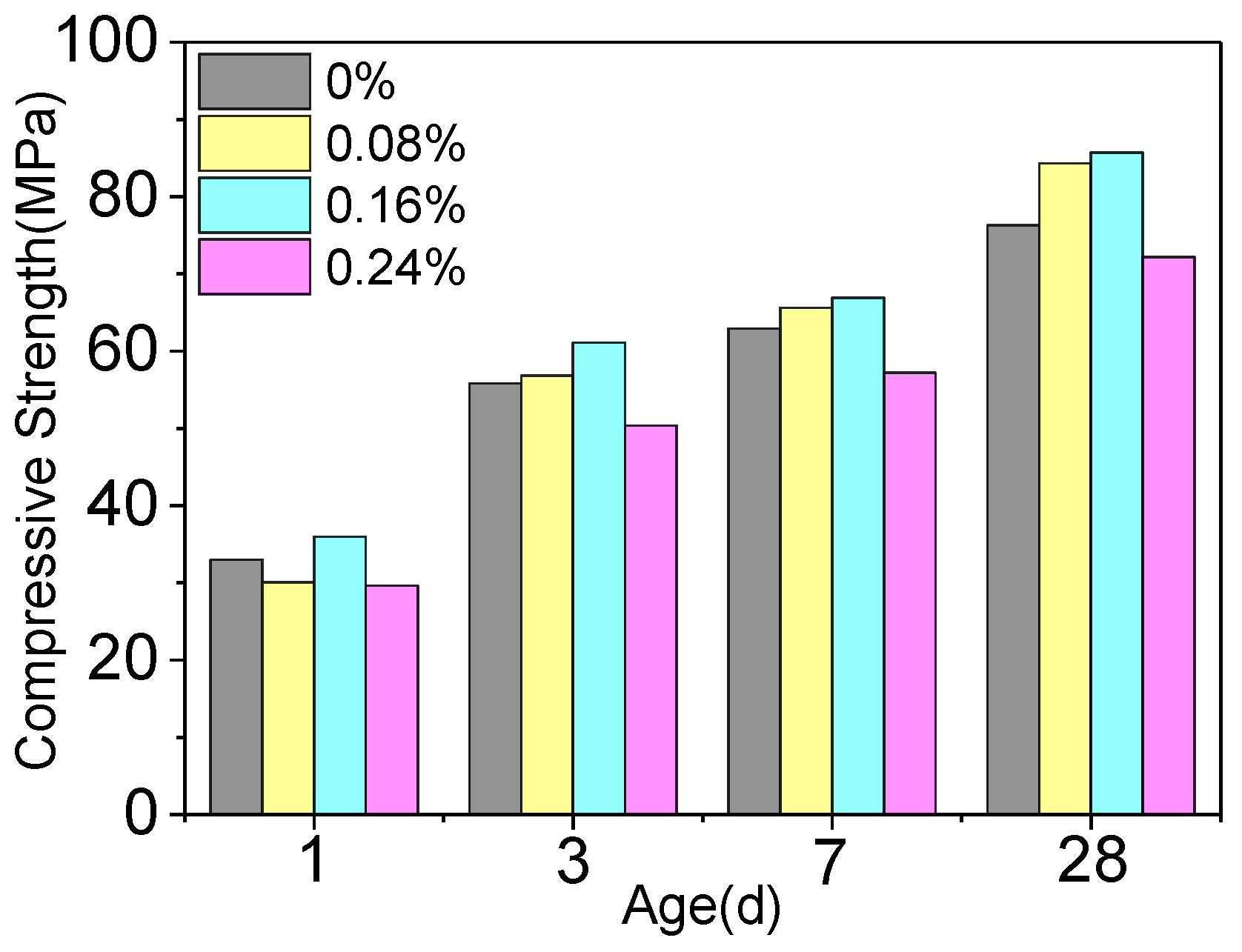

| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | Na2O | f-CaO | Loss | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21.66 | 4.60 | 3.30 | 62.79 | 2.93 | 2.40 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 1.36 | 0.01 |
| Number | Cement (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | Water Reducing Agent (%) | Nano-Si3N4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 240 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| N2 | 240 | 0 | 0.08 | |
| N3 | 240 | 0 | 0.16 | |
| N4 | 240 | 0 | 0.24 | |
| N5 | 540 | 1350 | 0.00 | |
| N6 | 540 | 1350 | 0.08 | |
| N7 | 540 | 1350 | 0.16 | |
| N8 | 540 | 1350 | 0.24 |
| Content/% | Modulus/GPa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore | LD C-S-H | HD C-S-H | All | Pore | LD C-S-H | HD C-S-H | |
| 0.00% | 27.97 | 38.98 | 33.05 | 100 | 5.94 | 19.93 | 32.33 |
| 0.08% | 25.64 | 38.46 | 35.90 | 100 | 8.71 | 18.84 | 32.94 |
| 0.16% | 12.12 | 36.36 | 51.52 | 100 | 9.45 | 19.44 | 32.66 |
| Sample | Ending Time of the Induction Period (h) | Peak Value (mW/g) | Total Heat Emission (J/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The First Peak | The Second Peak | |||
| 0.00% | 2.7 | 26.11 | 7.54 | 129.97 |
| 0.08% | 3.1 | 31.63 | 7.75 | 136.17 |
| 0.16% | 3.2 | 34.94 | 7.98 | 156.90 |
| 0.24% | 3.3 | 29.81 | 7.63 | 156.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.; Feng, C.; Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of Nano-Si3N4 on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials. Crystals 2021, 11, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121556
Zhu J, Zhu L, Feng C, Guan X, Sun Y, Zhang W. Effect of Nano-Si3N4 on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials. Crystals. 2021; 11(12):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121556
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jianping, Lifei Zhu, Chunhua Feng, Xuemao Guan, Yujiang Sun, and Wenyan Zhang. 2021. "Effect of Nano-Si3N4 on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials" Crystals 11, no. 12: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121556
APA StyleZhu, J., Zhu, L., Feng, C., Guan, X., Sun, Y., & Zhang, W. (2021). Effect of Nano-Si3N4 on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Materials. Crystals, 11(12), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121556








