High-Entropy FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Changes
3.2. Structural Changes
Thermodynamic Considerations
3.3. Thermal Analysis
3.3.1. Annealing Treatment
3.3.2. Consolidation of Powders
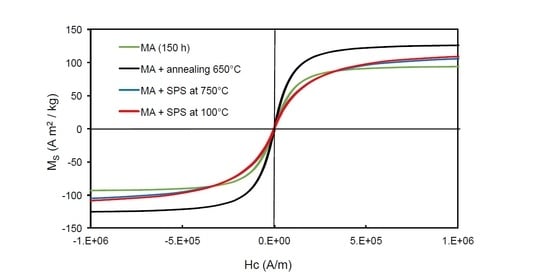
3.4. Magnetic Behavior
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senkov, O.; Wilks, G.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Chapman and Hall/CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Raanaei, H.; Eskandari, H.; Mohammad-Hosseini, V. Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe–Co–Ni alloy processed by mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 398, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Takahashi, S. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe–Co–Ni nanoparticles by hydrogen plasma–metal reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 214, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianlong, Q.I.; Yanhui, L.I.; Takeuchi, A.; Guoqiang, X.; Miao, H.; Zhang, W. Soft magnetic Fe25Co25Ni25(B,Si)25 high entropy bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, T. New soft magnetic Fe25Co25Ni25(P, C, B)25 high entropy bulk metallic glasses with large supercooled liquid region. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Sun, H.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Li, F. Effect of cooling rate on the phase structure and magnetic properties of Fe 26.7 Co 28.5 Ni 28.5 Si 4.6 B 8.7 P 3 high entropy alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 435, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Jiang, Z.; Macdonald, B.E.; Lin, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Lavernia, E.J. Influence of Cr removal on the microstructure and mechanical behaviour of a high-entropy Al0.8Ti0.2CoNiFeCr alloy fabricated by powder metallurgy. Powder Met. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lavernia, E.J. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an FCC structured single-phase nanocrystalline Co25Ni25Fe25Al7.5Cu17.5 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 107, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wen, H.; Chen, Z.; Lavernia, E.J. Effects of Co and sintering method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of a high-entropy Al0.6NiFeCrCo alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 646, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of superfine-grained high entropy alloy by spark plasma sintering gas atomized powder. Intermetallics 2016, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y. Ultra-High Strength TiC/Refractory High-Entropy-Alloy Composite Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. JOM 2017, 69, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Murty, B.; Kottada, R.S. Alloying behavior in multi-component AlCoCrCuFe and NiCoCrCuFe high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 534, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, D.; Yang, S. Fabrication and properties of nanocrystalline Co0.5FeNiCrTi0.5 high entropy alloy by MA–SPS technique. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Fang, S.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, H.; Zhu, D. Alloying behavior and deformation twinning in a CoNiFeCrAl0.6Ti0.4 high entropy alloy processed by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fu, Z.; Fang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhu, D. Processing, microstructure and properties of Al0.6CoNiFeTi0.4 high entropy alloy with nanoscale twins. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L. Maud: A Rietveld analysis program designed for the internet and experiment integration. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2000, 56, S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Bhushan, B. A review of nanoindentation continuous stiffness measurement technique and its applications. Mater. Charact. 2002, 48, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.; Pharr, G. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louidi, S.; Bentayeb, F.-Z.; Suñol, J.-J.; Escoda, L. Formation study of the ball-milled Cr20Co80 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerniz, N.; Azzaza, S.; Chater, R.; Abbas, H.; Bououdina, M.; Bouchelaghem, W. Magnetic and structural properties of nanostructured Fe–20Al–2Cr powder mixtures. Mater. Charact. 2015, 100, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ye, H.; Lu, K. Allotropic transformation of cobalt induced by ball milling. Nanostruct. Mater. 1995, 6, 723–726. [Google Scholar]
- Cardellini, F.; Mazzone, G. Thermal and structural study of the h.c.p.-to-f.c.c. transformation in cobalt. Philos. Mag. A 1993, 67, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleg, S.; Azzaza, S.; Bensalem, R.; Suñol, J.-J.; Khene, S.; Fillion, G. Magnetic and structural studies of mechanically alloyed (Fe50Co50)62Nb8B30 powder mixtures. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 482, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chang, S.-Y.; Hong, Y.-D.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J. Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of Cu–Ni–Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Si alloy systems with multi-principal elements. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloshkin, S.; Tcherdyntsev, V.; Tomilin, I.; Baldokhin, Y.; Shelekhov, E. Phase transformations in Fe–Ni system at mechanical alloying and consequent annealing of elemental powder mixtures. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2001, 299, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Lee, S.; Niihara, K. Characterization of nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiTiAl high-entropy solid solution processed by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Hu, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-A.; Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K. Competition between elements during mechanical alloying in an octonary multi-principal-element alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 481, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Wen, H.; Lavernia, E.J. Influence of Ti addition and sintering method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of a medium-entropy Al 0.6 CoNiFe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 619, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, S.; Janghorban, K.; Akbari, G.; Ghafari, M.; Salahinejad, E. Effects of boron addition on mechanical alloying and ordering behaviors of Fe–Al–(B) alloy powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallah, H.I.; Azabou, M.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.-J.; López, I.; Llorca-Isern, N.; Khitouni, M. The magnetic and structural properties of nanostructured (Fe75Al25) 100-xBx alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifati, A.; Sharafi, S. Structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured (Fe70Co30)100−xCux alloy prepared by high energy ball milling. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Zhu, M.; Qi, M.; Li, G.B.; Yang, D.Z. The enhancement of solid solubility limits of AlCo intermetallic compound by high-energy ball milling. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 2945–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, A.R.; Desré, P.J.; Benameur, T. Mechanically driven alloying of immiscible elements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.-T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Shiu, M.-H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater. Charact. 2012, 70, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.-T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Shiu, M.-H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiTix alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 103–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E. Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Tan, X.H.; Hou, X.L.; Wu, S.W.; Tan, G.S.; Yu, L.Y. The effects of phase constitution on magnetic and mechanical properties of FeCoNi(CuAl)x (x = 0–1.2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Schönecker, S.; Bergqvist, L.; Holmström, E.; Varga, L.K.; Vitos, L. Mechanism of magnetic transition in FeCrCoNi-based high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 103, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Shahi, R.R. Phase evolution and magnetic characteristics of TiFeNiCr and TiFeNiCrM (M = Mn, Co) high entropy alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 442, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, A.; Liu, C. Composition dependence of structure, physical and mechanical properties of FeCoNi(MnAl) x high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 87, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowroozi, M.; Shokrollahi, H. The effects of milling time and heat treatment on the micro-structural and magnetic behavior of Fe42Ni28Zr8Ta2B10C10 synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 335, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Esparza, C.; Baldenebro-López, F.; Santillán-Rodríguez, C.; Guel, I.E.; Matutes-Aquino, J.; Herrera-Ramirez, J.; Martínez-Sánchez, R. Microstructural and magnetic behavior of an equiatomic NiCoAlFe alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S317–S323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y. Microstructure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed FeSiBAlNi (Nb) high entropy alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 355, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avar, B.; Ozcan, S. Characterization and amorphous phase formation of mechanically alloyed Co60Fe5Ni5Ti25B5 powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, S.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharafi, S.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Atar, N. Structural, magnetic and electron transfer effect of Cr additive on Fe65Co35 nanopowder fabricated mechanical alloying. Powder Technol. 2015, 279, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shang, C.; Ge, W.; Jia, H.; Liaw, P.K.; Wang, Y. Effects of elemental addition on the microstructure, thermal stability, and magnetic properties of the mechanically alloyed FeSiBAlNi high entropy alloys. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Axinte, E.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y. Effect of C and Ce addition on the microstructure and magnetic property of the mechanically alloyed FeSiBAlNi high entropy alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 414, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Eslamizadeh, H.; Raanaei, H. Study of synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured (Fe67 Ni33)70 Ti10 B20 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 451, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekta, E.B.; Taghvaei, A.H.; Sharafi, S. Glass formation and magnetic study of new Fe70Ta5Si10C15 powders prepared by mechanical alloying with high thermal stability. Powder Technol. 2017, 322, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, V.; Leonov, A.; Szewczak, E.; Matyja, H. Structural defects and thermal stability of Ti(Al) solid solution obtained by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 242, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, G.L. Novel microstructure and properties of multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.-C.; Yeh, J.-W.; Shun, T.-T.; Chen, S.-K.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-C. On the elemental effect of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, Q. Effect of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of multiprincipal elements high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Davies, H.A. Tensile and compressive mechanical behavior of a CoCrCuFeNiAl0.5 high entropy alloy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2009, 23, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Argatov, I.I.; Sabina, F.J. A two-phase self-consistent model for the grid indentation testing of composite materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 121, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberle, T.L. Properties influencing wear of metals. J. Met. 1951, 3, 438–439. [Google Scholar]
- Tromas, C.; Arnoux, M.; Milhet, X. Hardness cartography to increase the nanoindentation resolution in heterogeneous materials: Application to a Ni-based single-crystal superalloy. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Samples | Phases | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Goodness of Fit | Fit Parameters (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | BCC–Fe | 2.866(7) | 1.16 | Rb: 3.12 Rexp: 3.46 Rwp: 4.019 |
| FCC–Ni | 3.523(0) | |||
| HCP–Co | 2.507(1) | |||
| c = 4.068(5) | ||||
| FCC–Co | 3.544(2) | |||
| FCC–Si | 5.430(3) | |||
| 1 h | BCC–Fe(B) | 2.867(1) | 1.14 | Rb: 2.41 Rexp: 2.95 Rwp: 3.39 |
| FCC–Ni | 3.523(6) | |||
| HCP–Co | 2.508(5) | |||
| c = 4.065(6) | ||||
| FCC–Co | 3.538(2) | |||
| FCC–Si | 5.430(4) | |||
| 5 h | BCC–Fe(Co,B,Si) | 2.868(1) | 1.06 | Rb: 1.70 Rexp: 2.10 Rwp: 2.23 |
| FCC–Ni | 3.525(3) | |||
| HCP–Co | 2.512(6) | |||
| c = 4.079(6) | ||||
| 10 h | BCC–Fe(Co,B,Si) | 2.868(6) | 1.12 | Rb: 1.53 Rexp: 1.91 Rwp: 2.15 |
| FCC–Ni | 3.526(0) | |||
| HCP–Co | 2.502(6) | |||
| c = 4.119(3) | ||||
| 25 h | BCC Fe–Co–Ni(B,Si) | 2.869(2) | 1.08 | Rb: 1.59 Rexp: 1.96 Rwp: 2.13 |
| FCC Fe–Co–Ni(B,Si) | 3.541(5) | |||
| 50 h | FCC Fe–Co–Ni(B,Si) | 3.601(2) | 1.08 | Rb: 1.39 Rexp: 1.84 Rwp: 2.00 |
| 100 h | FCC Fe–Co–Ni(B,Si) | 3.626(0) | 1.13 | Rb: 1.18 Rexp: 1.34 Rwp: 1.52 |
| 150 h | FCC Fe–Co–Ni(B,Si) | 3.630(8) | 1.07 | Rb: 1.55 Rexp: 1.94 Rwp: 2.09 |
| Element (Atomic Radius, Å) | Fe | Co | Ni | B | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe (1.24) | - | −1 | −2 | −26 | −35 |
| Co (1.25) | −1 | - | 0 | −24 | −38 |
| Ni (1.24) | −2 | 0 | - | −24 | −40 |
| B (0.82) | −26 | −24 | −24 | _- | −14 |
| Si (1.15) | −35 | −38 | −40 | −14 | - |
| Alloy | ΔHmix (kJ mol−1) | ΔSmix (JK−1 mol−1) | Tm (K) | δ (%) | Ω | VEC * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCoNi(B0.5Si0.5) | −24.12 | 12.96 | 1831.50 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 7.625 |
| Element | Zone | Fe | Co | Ni | Si | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS at 1000 °C | Black Grey | 8.38 25.58 | 5.17 25.46 | 5.10 25.11 | 32.07 23.85 | 48.65 - |
| SPS at 750 °C | Black Grey | 13.47 25.39 | 10.55 25.38 | 10.41 25.23 | 21.28 24.00 | 44.29 - |
| Samples | Ms (A m2/kg) | Hc (A/m) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-milled | 94.31 | 3905 | 0.034 |
| Annealed at 650 °C | 127.30 | 2353 | 0.025 |
| MA + SPS at 750 °C | 110.91 | 1994 | 0.012 |
| MA + SPS at 1000 °C | 115.84 | 2220 | 0.012 |
| Alloy | Phase | Ms (Am2/kg) | Hc (A/m) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe42Ni28Zr8Ta2B10C10 (198 h MA) | Amorphous + BCC | 93.91 | 2654 | [50] |
| NiCoAlFe (MA) | FCC + BCC | 89.50 | 1732 | [51] |
| FeSiBAlNi (260 h MA) | Amorphous | 1 | 23,077 | [52] |
| FeSiBAlNiNb HEA (100 h MA) | BCC + FCC + Amorphous | ~10 | ~27,852 | [52] |
| Co60Fe5Ni5Ti25B5 (7 h MA) | Amorphous | 53.4 | 605 | [53] |
| (Fe65Co35)95Cr5 (100 h MA) | BCC | ~205 | ~5570 | [54] |
| FeSiBAlNiCo HEA (140 h MA) | Amorphous | ~2 | ~18,303 | [55] |
| FeSiBAlNiCe HEA (MA) | Amorphous | 1 | 18,303 | [56] |
| TiFeNiCrCo HEA (MA) | FCC | 24.44 | 11,900 | [48] |
| (Fe67Ni33)70Ti10B20 HEA (120 h MA) | Amorphous + nanocrystalline phase | 105.38 | 2925 | [57] |
| Fe70Ta5Si10C15 (150 h MA) | Amorphous/nanocrystalline | - | 2720 | [58] |
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 (150 h MA) | FCC | 94.31 | 3905 | This work |
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 (150 h MA + 1 h 650 °C annealing) | FCC + BCC phases | 127.30 | 2353 | This work |
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 (150 h MA + SPS at 750 °C) | FCC + (Fe,Ni)23B6 | 110.91 | 1994 | This work |
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 (150 h MA + SPS at 1000 °C) | FCC + FeCo2B | 115.84 | 2220 | This work |
| Alloy | Process | σy (MPa) | σmax (MPa) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 | MA (powder) MA + SPS at 1000 °C | - 722 | - 926 | 626 176 |
| FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 | MA + SPS at 750 °C | 913 | 1062 | 518 |
| Hardness (GPa) | Indentation Elastic Modulus (GPa) | H/E | H3/E2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA + SPS at 750 °C | 6.3 ± 0.3 | 111 ± 4 | 0.057 | 0.02 |
| MA + SPS at 1000 °C | 3.6 ± 0.08 | 102 ± 4 | 0.035 | 0.0045 |
| Surface Fraction | Hardness (GPa) | Indentation Modulus (GPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPS 750 (FeNi)23B6 phase | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 65 ± 13 |
| SPS 750 FCC phase | balance | 8.2 ± 2 | 192 ± 59 |
| SPS 1000 FeCo2B phase | 0.30 ± 0.07 | 7.4 ± 1.4 | 38 ± 11 |
| SPS 1000 FCC phase | balance | 2.3 ± 1.2 | 177 ± 72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaara, K.; Chemingui, M.; Le Gallet, S.; Gaillard, Y.; Escoda, L.; Saurina, J.; Suñol, J.J.; Bernard, F.; Khitouni, M.; Optasanu, V. High-Entropy FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Crystals 2020, 10, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100929
Zaara K, Chemingui M, Le Gallet S, Gaillard Y, Escoda L, Saurina J, Suñol JJ, Bernard F, Khitouni M, Optasanu V. High-Entropy FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100929
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaara, Kaouther, Mahmoud Chemingui, Sophie Le Gallet, Yves Gaillard, Lluisa Escoda, Joan Saurina, Joan Josep Suñol, Frédéric Bernard, Mohamed Khitouni, and Virgil Optasanu. 2020. "High-Entropy FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering" Crystals 10, no. 10: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100929
APA StyleZaara, K., Chemingui, M., Le Gallet, S., Gaillard, Y., Escoda, L., Saurina, J., Suñol, J. J., Bernard, F., Khitouni, M., & Optasanu, V. (2020). High-Entropy FeCoNiB0.5Si0.5 Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Crystals, 10(10), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100929