Gold Nanocages as Saturable Absorbers for Passively Q-Switched Nd:YVO4 Lasers with Optimized Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
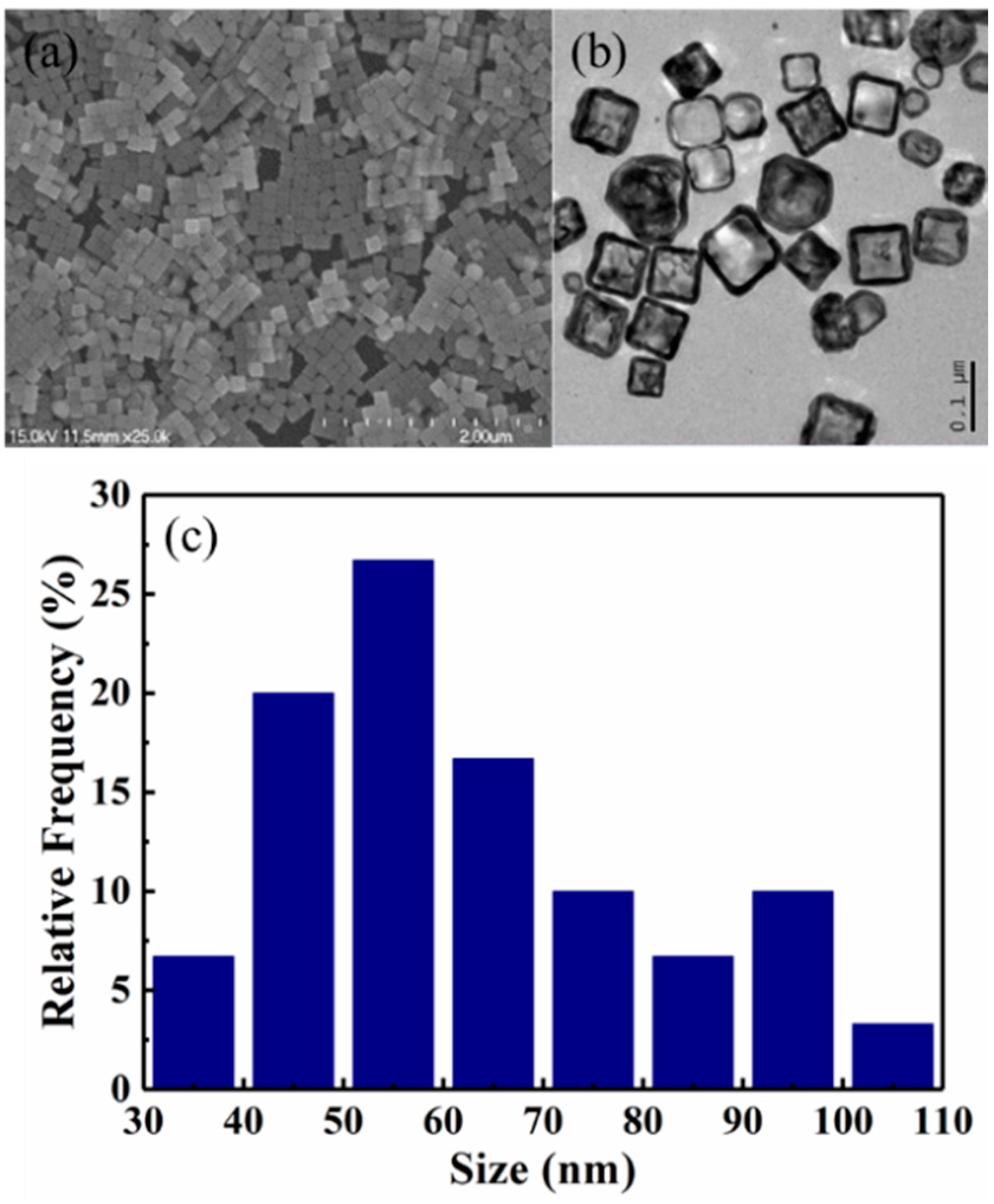
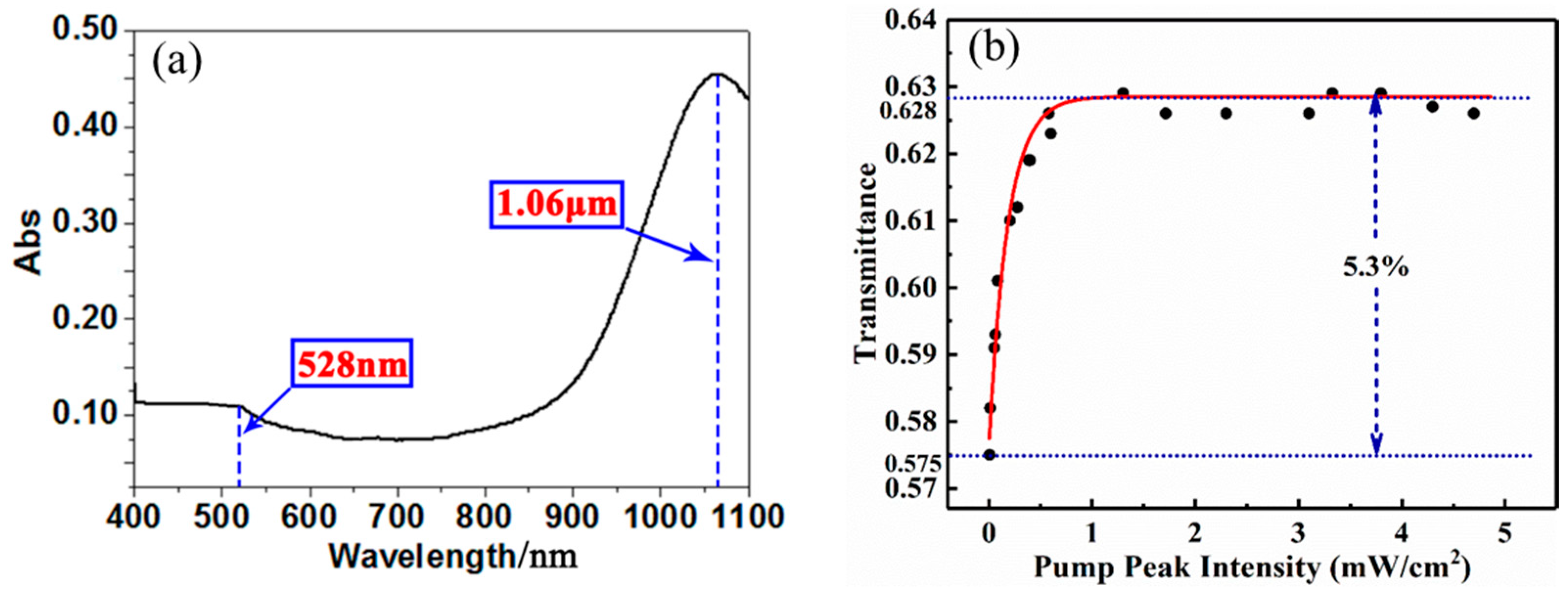
2. Preparation and the Characterization of the GNCs
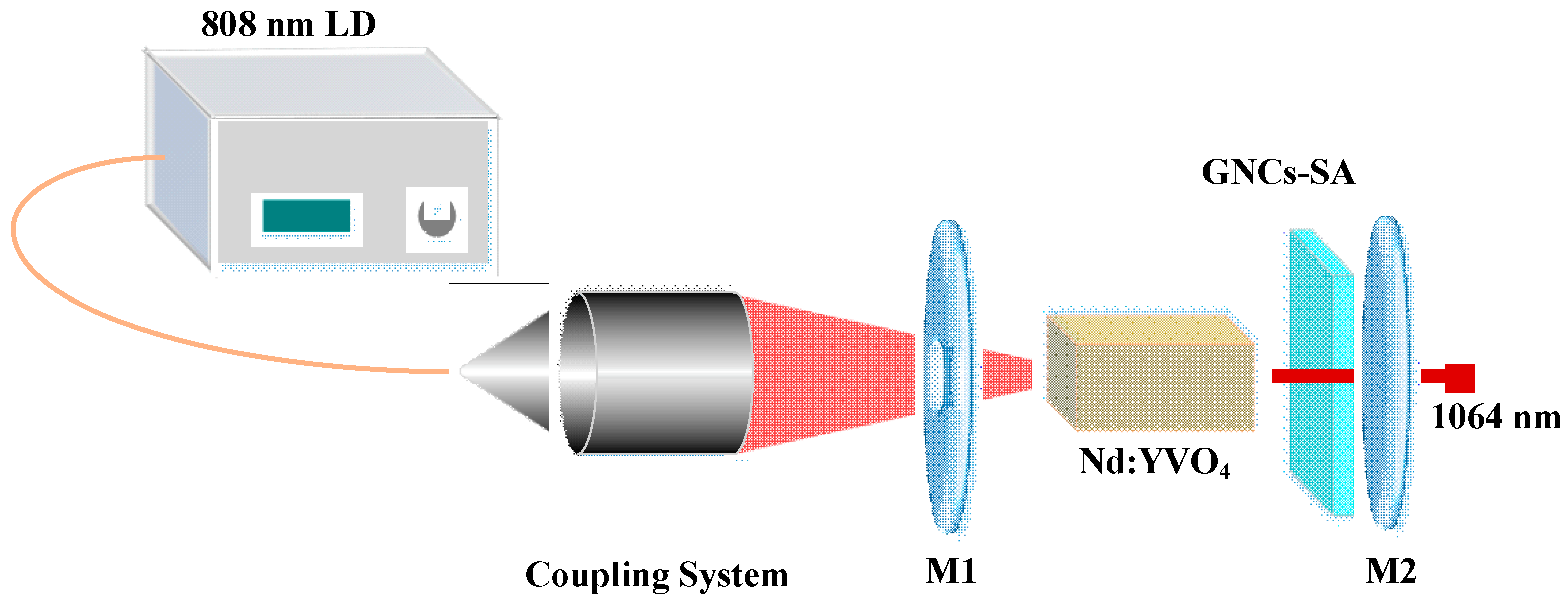
3. Experimental Setup
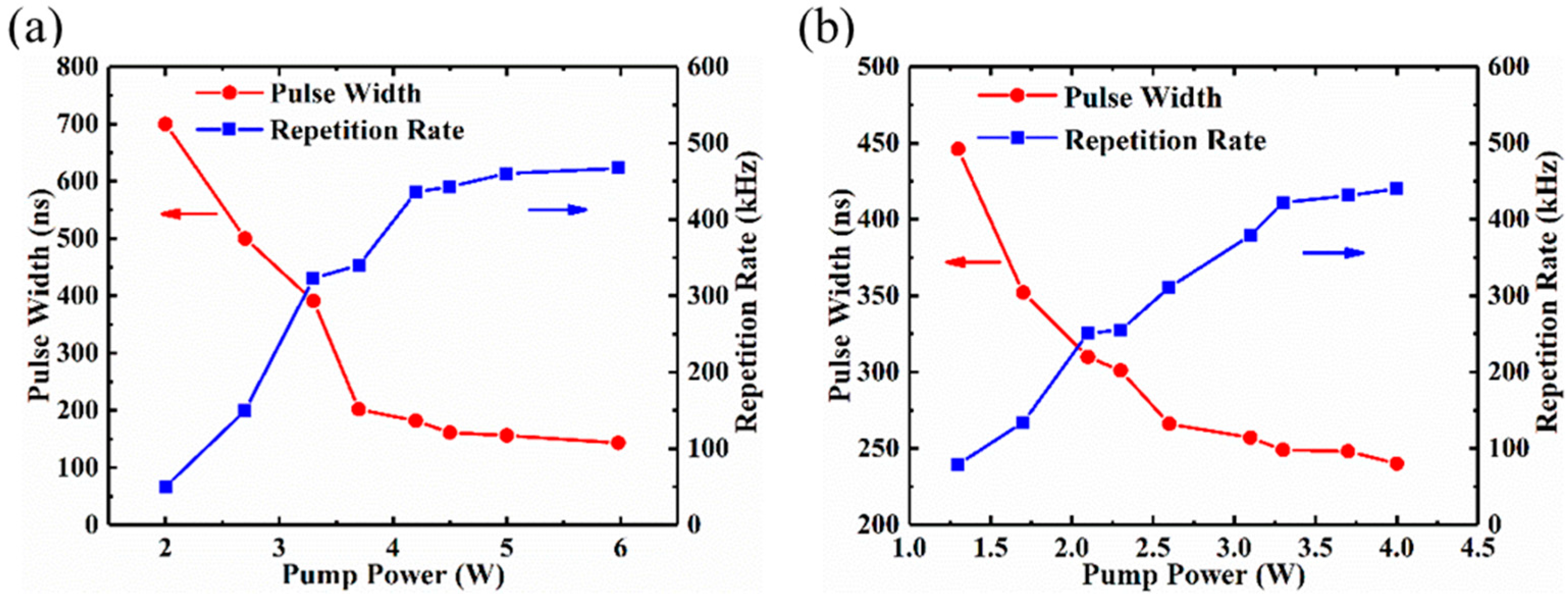
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kajava, T.T.; Gaeta, A.L. Q switching of a diode-pumped Nd:YAG laser with GaAs. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1244–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, U.; Miller, D.A.B.; Boyd, G.D.; Chiu, T.H.; Ferguson, J.F.; Asom, M.T. Solid-state low-loss intracavity saturable absorber for Nd:YLF lasers: An antiresonant semiconductor Fabry-Perot saturable absorber. Opt. Lett. 1992, 17, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, S.H.; Chen, Y.C. High-power monolithic unstable-resonator solid-state laser. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, S.; Lamikiz, A.; Ukar, E.; Calleja, A.; Arrizubieta, J.A.; Lopez de Lacalle, L.N. Analysis of the regimes in the scanner-based laser hardening process. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 90, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, A.; Tabernero, I.; Ealo, J.; Campa, F.; Lamikiz, A.; Lopez de Lacalle, L.N. Feed rate calculation algorithm for the homogeneous material deposition of blisk blades by 5-axis laser cladding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Liang, H.C.; Su, K.W.; Chen, Y.F. High power passively Q-switched ytterbium fiber laser with Cr4+:YAG as a saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.Z. InGaAs/GaAs saturable absorber for diode-pumped passively Q-switched dual-wavelength Tm:YAP lasers. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 13574–13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhotnikov, O.; Grudinin, A.; Pessa, M. Ultra-fast fibre laser systems based on SESAM technology: New horizons and applications. New J. Phys. 2004, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Lee, C.K.; Xu, J.L.; Zhu, Z.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Gao, S.F.; Xia, H.P.; You, Z.Y.; Tu, C.Y. Passively Q-switched tri-wavelength Yb3+:GdAl3(BO3)4 solid-state laser with topological insulator Bi2Te3 as saturable absorber. Photonics Res. 2015, 3, A97–A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.W.; Zhao, S.Z.; Li, T.; Yang, K.J.; Li, G.Q.; Li, D.C.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, W.C.; Xu, J.Q.; Hang, Y. Dual-Wavelength Passively Q-Switched Nd, Mg:LiTaO3 Laser With a Monolayer Graphene as Saturable Absorber. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2015, 21, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.P.; Hasan, T.; Torrisi, F.; Popa, D.; Privitera, G.; Wang, F.Q.; Bonaccorso, F.; Basko, D.M.; Ferrari, A.C. Graphene mode-locked ultrafast laser. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.X.; Yu, H.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, A.Z.; Zhao, M.W.; Chen, Y.X.; Mei, L.M.; Wang, J.Y. Broadband few-layer MoS2 saturable absorbers. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3538–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.T.; Lou, F.; Zhao, R.W.; He, J.L.; Li, J.; Su, X.C.; Ning, J.; Yang, K.J. Exfoliated layers of black phosphorus as saturable absorber for ultrafast solid-state laser. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3691–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.D.; Peng, J.; Cai, Z.P.; Weng, J.; Luo, Z.Q.; Chen, N.; Xu, H.Y. Gold nanoparticles as a saturable absorber for visible 635 nm Q-switched pulse generation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 24071–24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Griebner, U.; Herrmann, J. Theory of passive mode locking of solid-state lasers using metal nanocomposites as slow saturable absorbers. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.A. Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabelli, L.; Puchau, M.C.; Casares, J.G.; Langer, J.; Marzán, L.L. monodisperse gold nanotriangles: Size control, large-scale self assembly, and performance in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5833–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Genet, C. Light in tiny holes. Nature 2007, 445, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Husakou, A.; Herrmann, J. Linear and nonlinear optical characteristics of composites containing metal nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7488–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Guo, X.Y.; Jia, Z.X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, D.; Qin, G.S.; Qin, W.P. Gold nanorods as saturable absorbers for all-fiber passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.F.; Mou, C.B.; Bai, X.K.; Wang, S.F.; Chen, N.; Zeng, X.L. Passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser using evanescent field interaction with gold-nanosphere based saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 18537–18542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.N.; Liu, J. Gold nanobipyramids as saturable absorbers for passively Q-switched laser generation in the 1.1 μm region. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1150–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Feng, C.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, Q.P.; Qin, G.S.; Qin, W.P.; Gao, X.J.; Dun, Y.Y.; Li, P. Gold nanorods as a saturable absorber for passively Q-switching Nd:YAG lasers at 1064.3 and 1112 nm. Laser Phys. Lett. 2017, 14, 055808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.X.; Li, P.; Chen, X.H.; Lei, G.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, B.H. Diode-pumped passively Q-switched Nd:YAG ceramic laser with a gold nanotriangles saturable absorber at 1 µm. Appl. Phys. Express 2017, 10, 082701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Chen, X.H.; Bai, J.X.; Liu, B.H.; Hu, Q.Y.; Li, P. Au nanocages/SiO2 as saturable absorbers for passively Q-switched all-solid-state laser. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 045043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.X.; Li, P.; Guo, L.; Zhang, B.T.; Hu, Q.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, B.H.; Chen, X.H. Au nanocage/SiO2 saturable absorber for passive Q-switching Yb-doped fiber laser. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 055109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, B.T.; Liu, B.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chen, X.H. Passively Q-switched Yb-doped dual-wavelength fiber laser based on a gold-nanocage saturable absorber. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 8242–8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Petrova, H.; Chen, J.Y.; McLellan, J.M.; Siekkinen, A.R.; Marquez, M.; Li, X.D.; Xia, Y.N.; Hartland, G.V. Ultrafast laser studies of the photothermal properties of gold nanocages. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 1520–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wiley, B.; Li, Z.Y.; Campbell, D.; Saeki, F.; Cang, H.; Au, L.; Lee, J.; Li, X.D.; Xia, Y.N. Gold Nanocages: Engineering Their Structure for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Brandl, D.W.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Plasmonic nanostructures: Artificial molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.R.; Wei, C.; Chi, H.; Zhou, L.Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y. Au nanocages saturable absorber for 3-µm mid-infrared pulsed fiber laser with a wide wavelength tuning range. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 30350–30359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabalak, S.E.; Au, L.; Li, X.D.; Xia, Y.N. Facile synthesis of Ag nanocubes and Au nanocages. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabalak, S.E.; Chen, J.Y.; Sun, Y.G.; Lu, X.M.; Au, L.; Cobley, C.M.; Xia, Y.N. Gold nanocages: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Growth and galvanic replacement of silver nanocubes in organic media. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Merkoci, F.; Arenal, R.; Arbiol, J.; Esteve, J.; Bastus, N.G.; Puntes, V. Enhanced reactivity of high-index surface platinum hollow nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, B.M.; Said, A.A.; Stryland, E.W.V. High-sensitivity, single-beam n2 measurements. Opt. Lett. 1989, 14, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of GNPs | Wavelength /nm | Maximum Output Power /mW | Conversion Efficiency /% | Slope Efficiency /% | Narrowest Pulse Width | Repetition Frequency /kHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNRs | 1560 | 12.5 | ~4.5 | ~4.4 | 4.8 μs | 39.9 | [20] |
| GNS | 1562 | 7.7 | 3.5 | 1.78 μs | 58.1 | [21] | |
| GNBPs | 1064.1 | 151 | 1.26 | 2.82 | 396 ns | 90.6 | [22] |
| GNRs | 1064.3 | 101 | 1.24 | 223 ns | 300 | [23] | |
| GNTs | 1064.3 | 226 | 5.4 | 10.7 | 179 ns | 320 | [24] |
| GNCs/SiO2 | 1064.3 | 150.2 | 6.21 | 154.2 | 280 | [25] | |
| GNCs/SiO2 | 1060.5 | 10.6 | 2.41 | 4.0 | 1.4 μs | 136.9 | [26] |
| GNCs | 1059.9&1060.5 | 6.03 | 1.57 | 2.75 | 2.06 μs | 134.9 | [27] |
| GNCs | 1064.1 | 372 | 9.4 | 14.1 | 143 ns | 467 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Li, P. Gold Nanocages as Saturable Absorbers for Passively Q-Switched Nd:YVO4 Lasers with Optimized Performance. Crystals 2020, 10, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100903
Zhang B, Chen X, Li H, Xu L, Liu B, Li P. Gold Nanocages as Saturable Absorbers for Passively Q-Switched Nd:YVO4 Lasers with Optimized Performance. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100903
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bin, Xiaohan Chen, Haoyuan Li, Liwei Xu, Binghai Liu, and Ping Li. 2020. "Gold Nanocages as Saturable Absorbers for Passively Q-Switched Nd:YVO4 Lasers with Optimized Performance" Crystals 10, no. 10: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100903
APA StyleZhang, B., Chen, X., Li, H., Xu, L., Liu, B., & Li, P. (2020). Gold Nanocages as Saturable Absorbers for Passively Q-Switched Nd:YVO4 Lasers with Optimized Performance. Crystals, 10(10), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100903





