Influences of Central Units and Terminal Chains on the Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bent-Core Liquid Crystals (BCLCs)
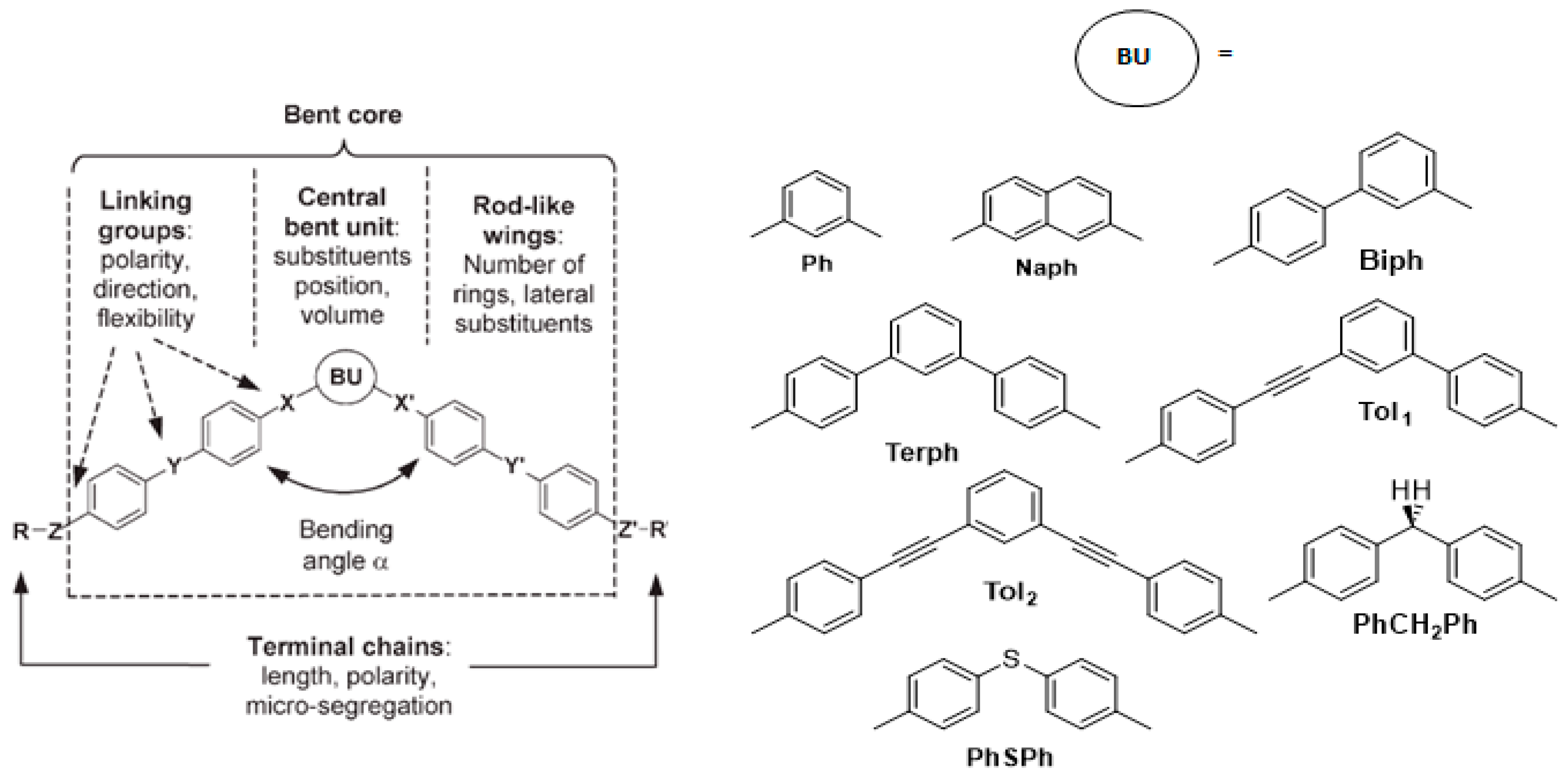
2.1. Molecular Structure of Bent-Core Liquid Crystals
2.1.1. 1,3-Dihydroxybenzene/Resorcinol
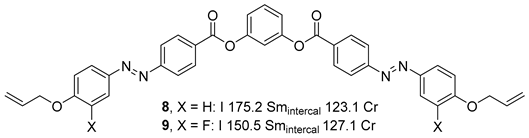
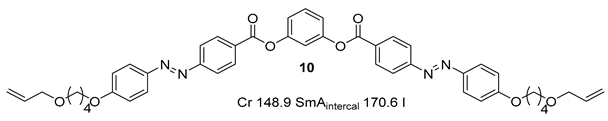
Substituted 1,3-Dihydroxybenzene/Resorcinol
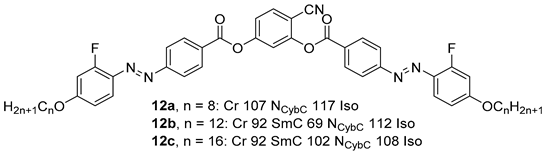
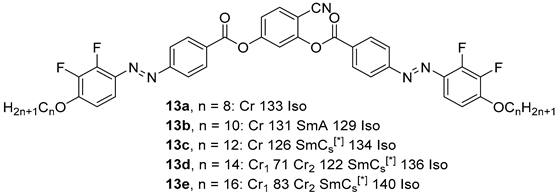
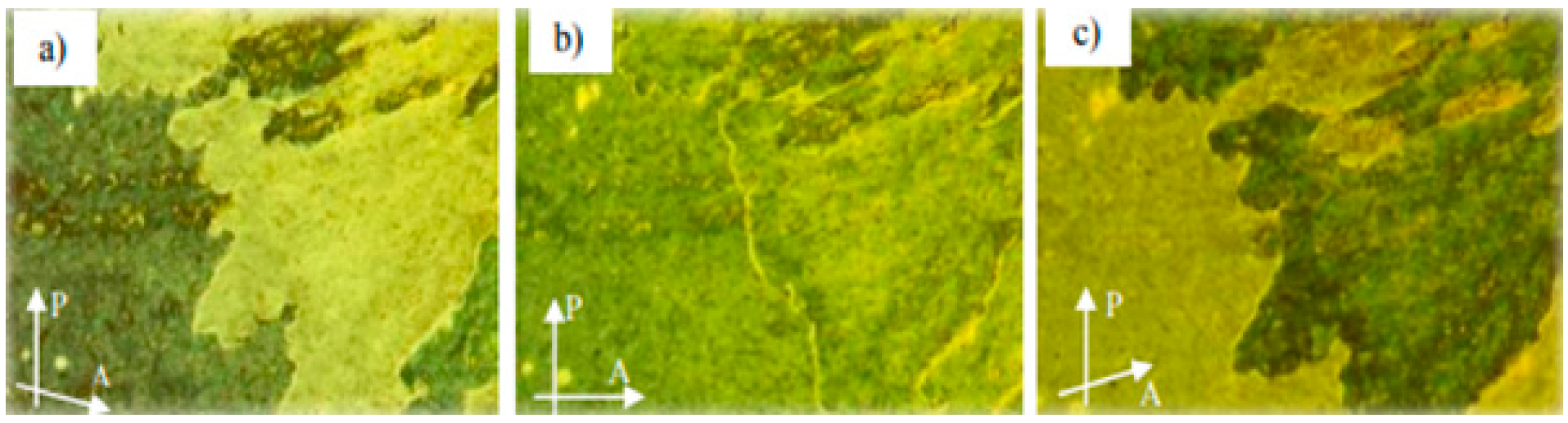
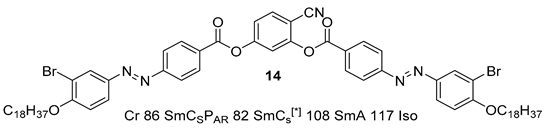
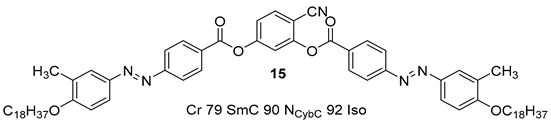
2.1.2. 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde

Substituted 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
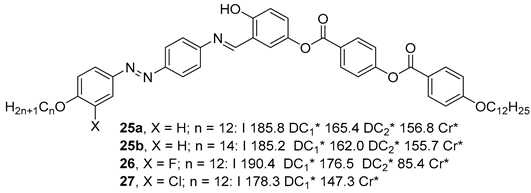
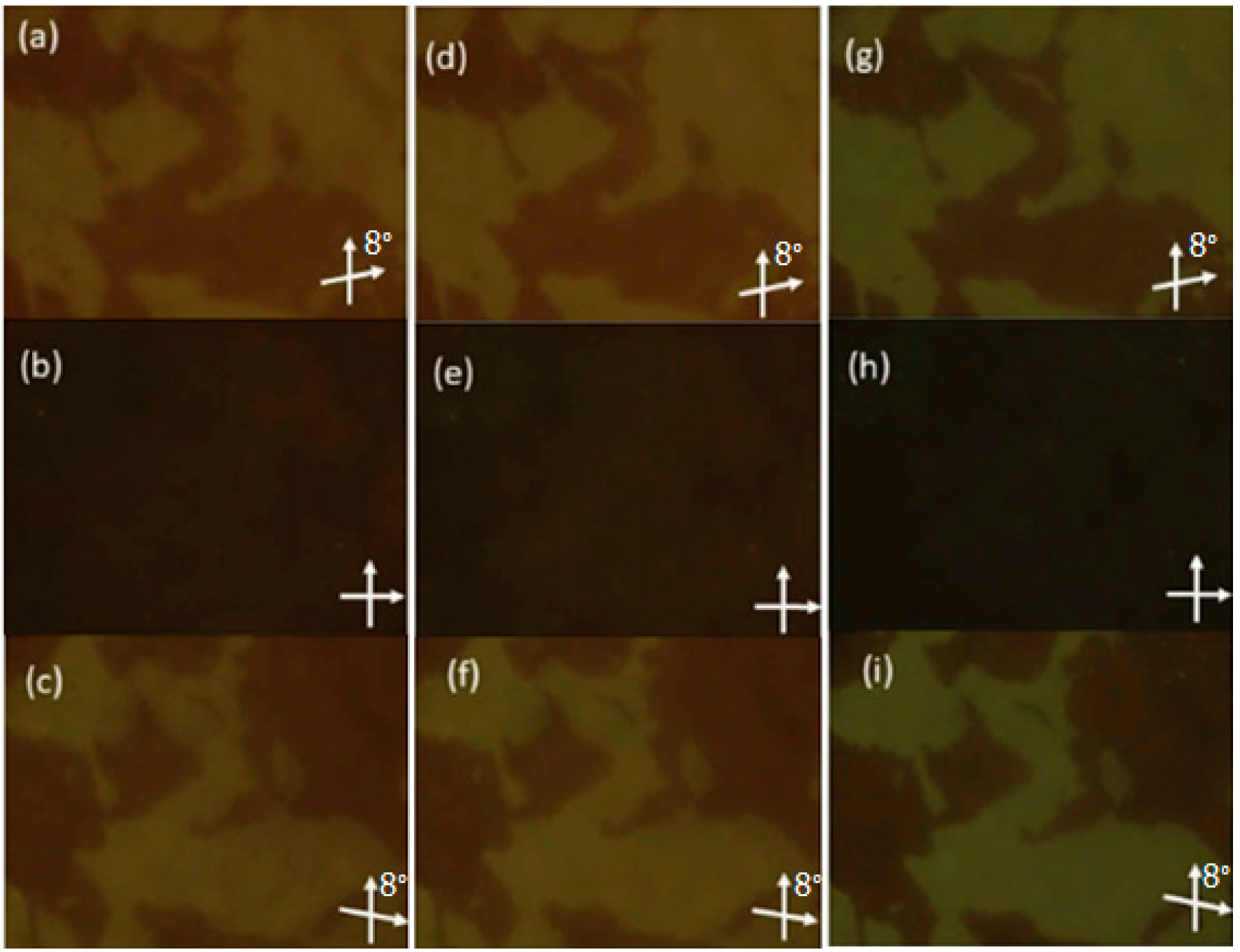
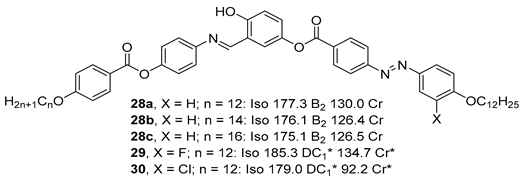
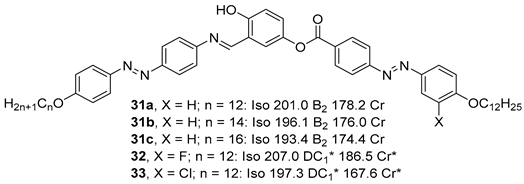
2.1.3. 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
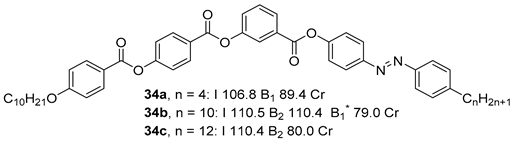

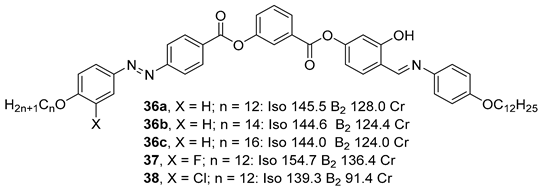
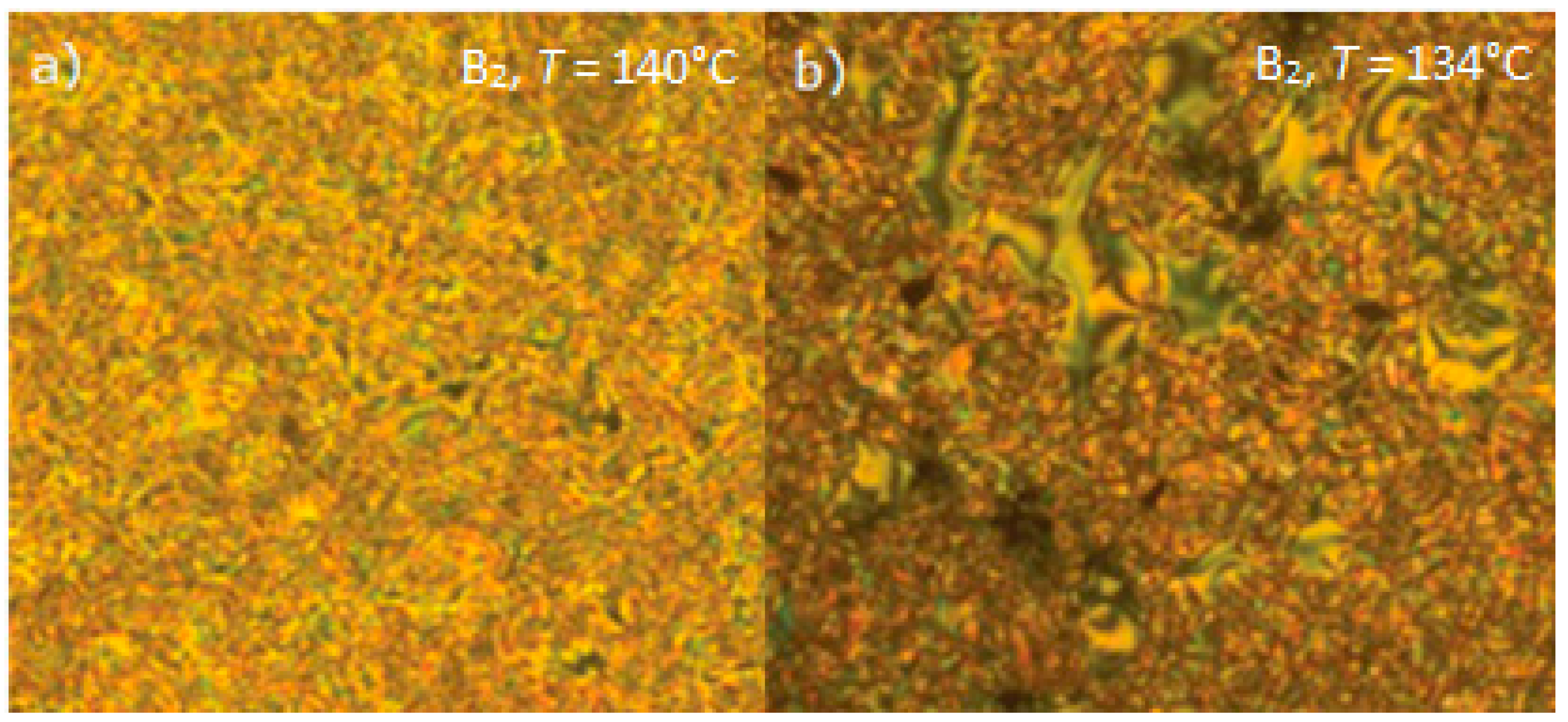
Substituted 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid

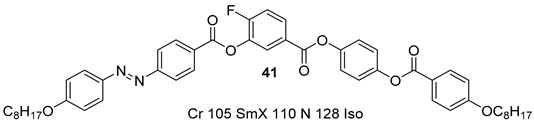
2.1.4. Substituted 3-Nitrobenzoic Acid
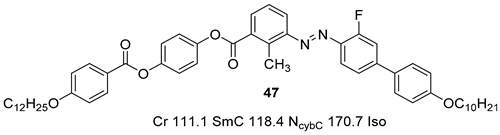
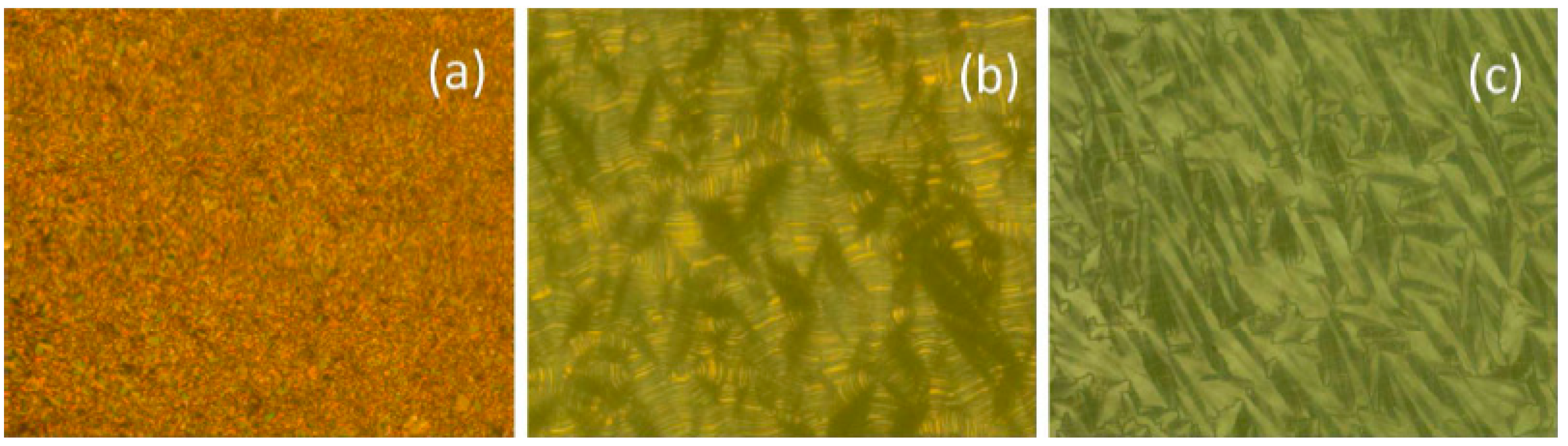
2.1.5. Other Aromatic Bent-Core Units
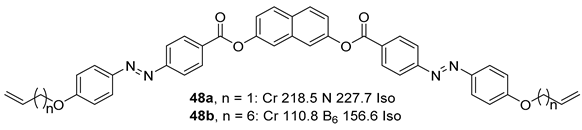

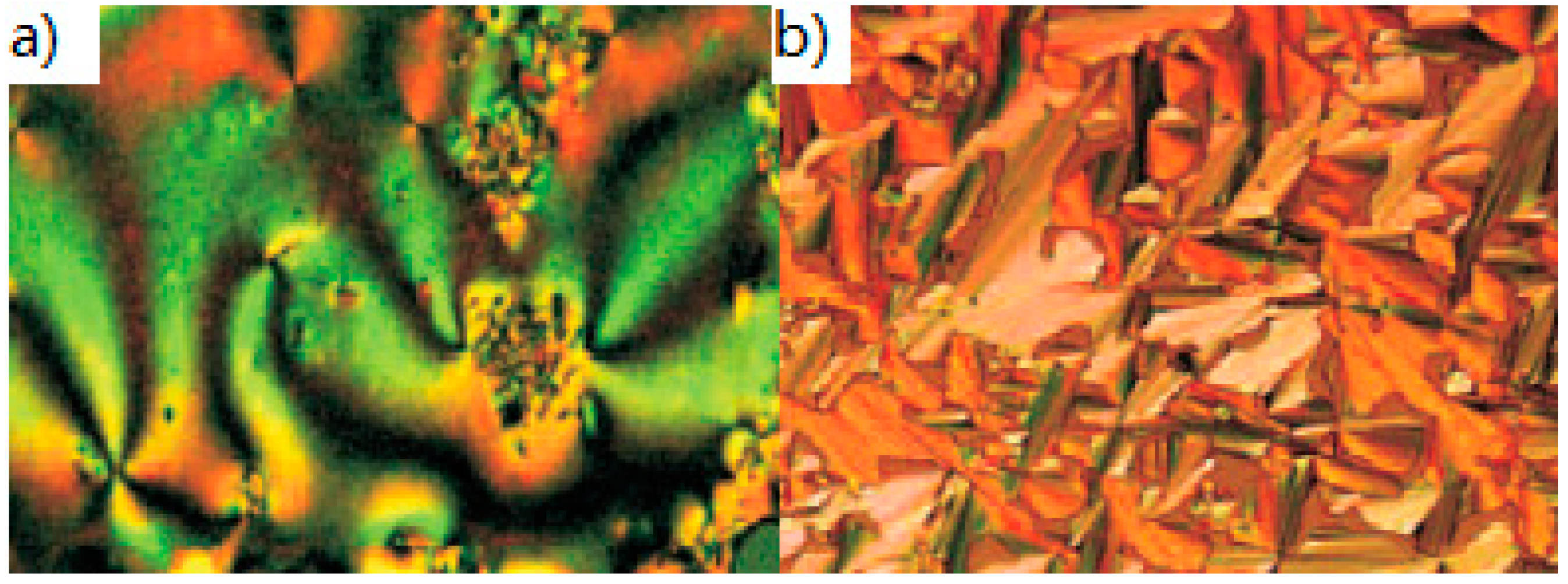
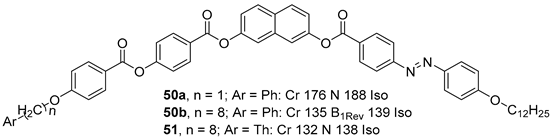
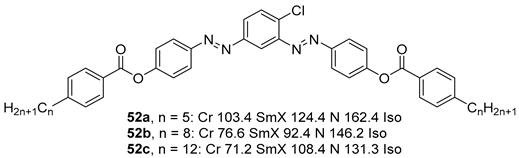
2.1.6. Heterocyclic Core Unit
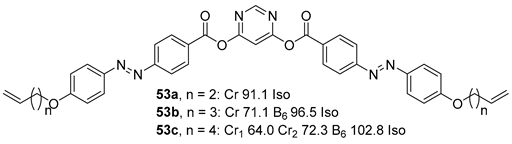
2.2. V-Shaped BCLCs
2.3. Hockey-Sick Molecules

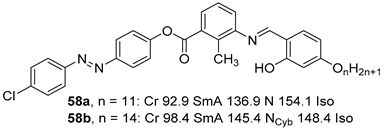

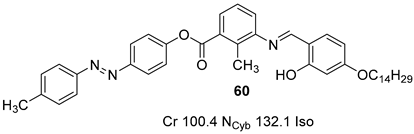
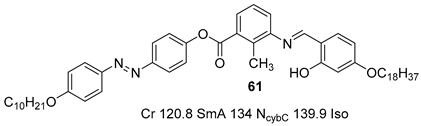
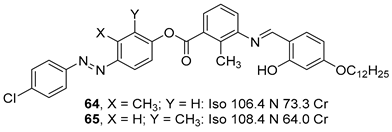
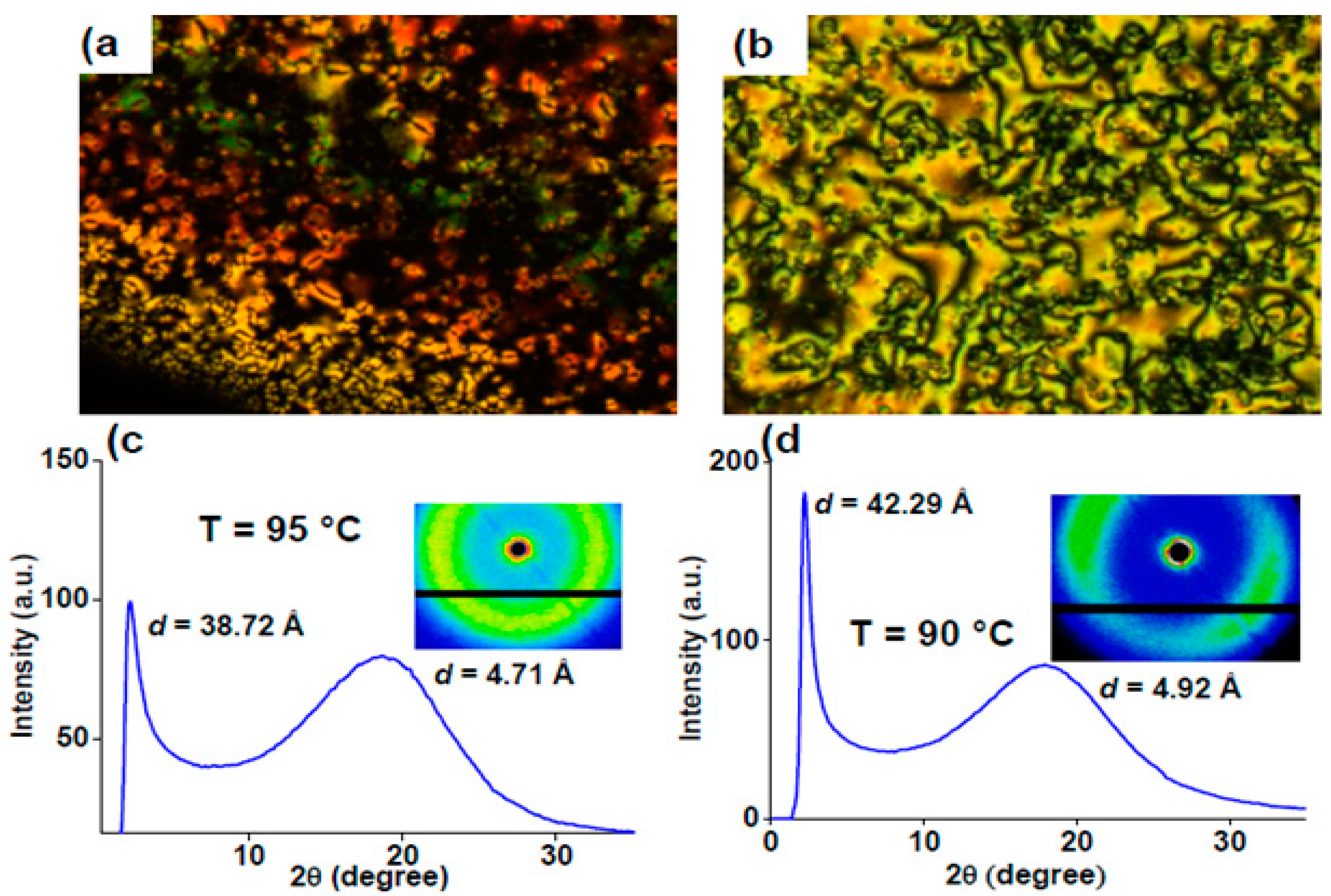
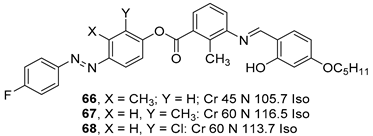
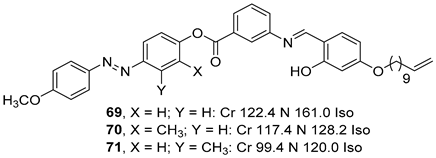
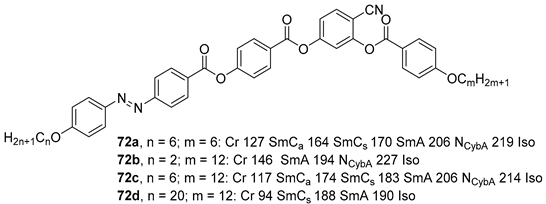
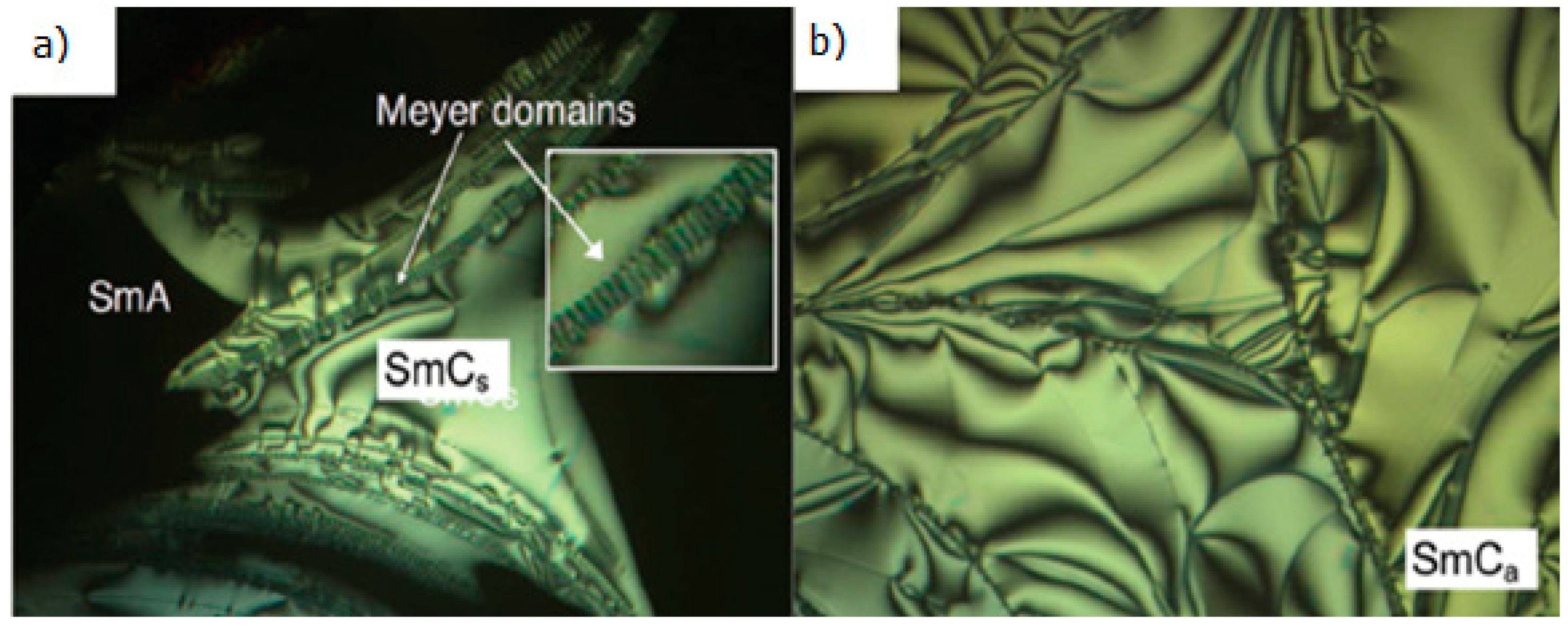
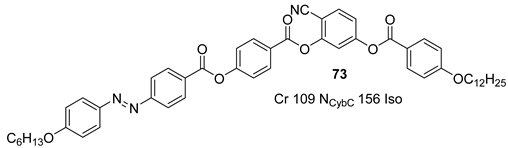
2.4. Heterocyclic Aromatic Core
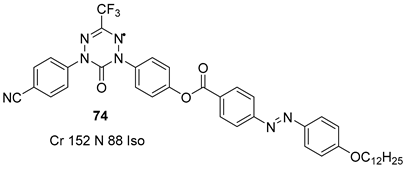
3. Photoisomerization
4. Potential Applications and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niori, T.; Sekine, T.; Watanabe, J.; Furukawa, T.; Takezoe, H. Distinct ferroelectric smectic liquid crystals consisting of banana shaped achiral molecules. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 6, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, D.R.; Natale, G.; Shao, R.; Maclennan, J.E.; Clark, N.A.; Körblova, E.; Walba, D.M. Spontaneous Formation of Macroscopic Chiral Domains in a Fluid Smectic Phase of Achiral Molecules. Science 1997, 278, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorländer, D. Die Richtung der Kohlenstoff-Valenzen in Benzol-Abkömmlingen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1929, 62, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorländer, D.; Apel, A. Die Richtung der Kohlenstoff-Valenzen in Benzolabkömmlingen (II.). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1932, 65, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, W.; Jákli, A. Applications of Bent-Core Mesogens. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jákli, A. Liquid crystals of the twenty-first century—nematic phase of bent-core molecules. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Liebert, L.; Strzelecki, L.; Keller, P. Ferroelectric liquid crystals. J. Phys. Lett. 1975, 36, L69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, J.; Iglesias, R.; Serrano, J.; Sierra, T.; De La Fuente, M.; Palacios, B.; Perez-Jubindo, M.; Vazquez, J. Switchable columnar metallomesogens. New helical self-assembling systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherowsky, G.; Chen, X.H. New switchable columnar liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 1994, 17, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.; Helfrich, W.J.L.C. Ferroelectrically switchable columnar liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 1992, 12, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Lee, M.A.; Petschek, R.G. Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals: Realizability and Molecular Constraints. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 60, 2303–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petschek, R.G.; Wiefling, K.M. Novel ferroelectric fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredgold, R. Ferroelectric liquid crystals do not have to be chiral. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1990, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.-D. Ferroelectric liquid crystalline ordering of rigid rods with dipolar interactions. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1994, 254, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladis, P.; Brand, H.R. Electrooptic response of smectic O and smectic O. Liq. Cryst. 1993, 14, 1327–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournilhac, F.; Blinov, L.; Simon, J.; Yablonsky, S. Ferroelectric liquid crystals from achiral molecules. Nature 1992, 359, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Nakata, Y.; Simizu, K. Frustrated bilayer smectic phase in main-chain polymers with two different spacers. J. Phys. II 1994, 4, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akutagawa, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Yasuhara, K. Mesomorphic behaviour of 1, 3-phenylene bis [4-(4-alkoxyphenyliminomethyl) benzoates] and related compounds. Liq. Cryst. 1994, 17, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Miyamoto, S. Mesomorphic behavior of 2, 4-bis-(4-alkoxybenzylidene) cyclopentanones and related compounds. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1993, 237, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezoe, H.; Watanabe, J. Ferroelectricity in liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1999, 328, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Hirose, Y.; Tokita, M.; Watanabe, T.; Miyata, S. Polar structure in polypeptide cholesteric liquid crystals evidenced from observation of second-harmonic generation due to the helicoidal cavity effect. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5937–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Kinoshita, Y.; Takezoe, H.; Watanabe, J. Ferroelectricity in the lyotropic cholesteric phase of poly L-glutamate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, L136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentjev, E.; Osipov, M.; Sluckin, T. General, Ferroelectric instability in semiflexible liquid crystalline polymers of directed dipolar chains. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1994, 27, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezoe, H.; Takanishi, Y. Bent-Core Liquid Crystals: Their Mysterious and Attractive World. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 597–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C.; Dantlgraber, G. From antiferroelectricity to ferroelectricity in smectic mesophases formed by bent-core molecules. J. Phys. 2003, 61, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.B.; Serrano, J.L.; de La Fuente, M.R.; Folcia, C.L. Banana-shaped liquid crystals: A new field to explore. J. Mater. Chem 2005, 15, 5093–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxebarria, J.; Blanca Ros, M. Bent-core liquid crystals in the route to functional materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2919–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, A.; Jákli, A. Polar bent-shape liquid crystals – from molecular bend to layer splay and chirality. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 615–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C.; Photinos, D. Biaxial nematic phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4263–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, H.F.; Kaur, S.; Görtz, V.; Belaissaoui, A.; Cowling, S.; Goodby, J. The nematic phases of bent-core liquid crystals. Chemphyschem 2014, 15, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Görtz, V. Chiral resolution in bent-core nematic liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Today 2010, 19, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelamaggad, C.V.; Shashikala, I.S.; Hiremath, U.S.; Liao, G.; Jakli, A.; Rao, D.S.S.; Prasad, S.K.; Li, Q. Fluorine containing nonsymmetrical five-ring achiral banana-shaped compounds with columnar and synclinic antiferroelectric layered phases. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, M.; Alaasar, M.; Poryvai, A.; Novotná, V.; Poppe, S.; Tschierske, C.; Svoboda, J. Photosensitive bent-core liquid crystals based on methyl substituted 3-hydroxybenzoic acid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35805–35813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podruczna, M.; Hofmańska, A.; Niezgoda, I.; Pociecha, D.; Galewski, Z. Influence of terminal groups on liquid-crystalline polymorphism of selected azobenzene derivatives. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogojawlensky, A.; Winogradow, N. Über das Verhalten von Schmelz- und Klärungskurven der flüssigen Kristalle und ihrer Mischungen. J. Z. für Phys. Chemie. 1907, 60U, 433. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, V.; Rao, D.S.S.; Prasad, S.K. A novel class of banana-shaped azo compounds exhibiting antiferroelectric switching behaviour. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 28, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Kang, S.-W.; Kumar, S. Novel examples of achiral bent-core azo compounds exhibiting B1 and anticlinic–antiferroelectric B2 mesophases. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Jákli, A. Achiral bent-core azo compounds: Observation of photoinduced effects in an antiferroelectric tilted smectic mesophase. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.K.; Nair, G.G.; Hegde, G. Dynamic Self-Assembly of the Liquid-Crystalline Smectic A Phase. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Tsutsumi, O. Optical Switching and Image Storage by Means of Azobenzene Liquid-Crystal Films. Science 1995, 268, 1873–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T. Photomodulation of liquid crystal orientations for photonic applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2037–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.; Kumar, S.; Tschierske, C.; Israel, G.; Ster, D.; Hegde, G. Synthesis and photoswitching properties of bent-shaped liquid crystals containing azobenzene monomers. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 36, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, H.M.D.; Burdette, S.C. Photoisomerization in different classes of azobenzene. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1809–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Tripathy, S.K.; Li, L.; Kumar, J. Laser-induced holographic surface relief gratings on nonlinear optical polymer films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochon, P.; Batalla, E.; Natansohn, A. Optically induced surface gratings on azoaromatic polymer films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K. Photoalignment of Liquid-Crystal Systems. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1847–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, H.A. Linearity of optical amplifiers and the Tomonaga approximation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2001, 18, 1777–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natansohn, A.; Rochon, P. Photoinduced Motions in Azo-Containing Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4139–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickasundaram, S.; Kannan, P.; Hassan, Q.M.A.; Palanisamy, P.K. Azo dye based poly(alkyloxymethacrylate)s and their spacer effect on optical data storage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 19, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, C.; Senthil, S.; Kannan, P. Click chemistry-assisted triazole-substituted azobenzene and fulgimide units in the pendant-based copoly(decyloxymethacrylate)s for dual-mode optical switches. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 7843–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.M.; Yuvaraj, A.R.; Lutfor, M.R.; Mashitah, M.Y.; Gurumurthy, H. Synthesis, liquid crystal characterization and photo-switching studies on fluorine substituted azobenzene based esters. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6279–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. New azobenzene containing bent-core liquid crystals based on disubstituted resorcinol. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Abadía, M.; Robles-Hernández, B.; de la Fuente, M.R.; Giménez, R.; Ros, M.B. Photoresponsive Cyanostilbene Bent-Core Liquid Crystals as New Materials with Light-Driven Modulated Polarization. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6586–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jákli, A.; Prasad, V.; Shankar Rao, D.S.; Liao, G.; Jánossy, I. Light-induced changes of optical and electrical properties in bent-core azo compounds. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 021709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaveni, N.G.; Prasad, V.; Roy, A. Azo functionalised achiral bent-core liquid crystals: Observation of photo-induced effects in B7 and B2 mesophases. J. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.G.; Prasad, S.K.; Hiremath, U.S.; Yelamaggad, C. Effect of light on the polarization of a banana-shaped achiral compound doped with a photoactive azobenzene material. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M. Azobenzene-containing bent-core liquid crystals: An overview. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 2208–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zep, A.; Sitkowska, K.; Pociecha, D.; Gorecka, E. Photoresponsive helical nanofilaments of B4 phase. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Masuko, S.; Araoka, F.; Ishikawa, K.; Takezoe, H. A General Method for the Enantioselective Formation of Helical Nanofilaments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6863–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaveni, N.G.; Roy, A.; Prasad, V. Achiral bent-core azo compounds: Effect of different types of linkage groups and their direction of linking on liquid crystalline properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8948–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horčic, M.; Kozmík, V.; Svoboda, J.; Novotná, V.; Pociecha, D. Transformation from a rod-like to a hockey-stick-like and bent-shaped molecule in 3, 4′-disubstituted azobenzene-based mesogens. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 7560–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iamsaard, S.; Anger, E.; Aßhoff, S.J.; Depauw, A.; Fletcher, S.P.; Katsonis, N. Fluorinated azobenzenes for shape-persistent liquid crystal polymer networks. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 10062–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanishi, Y.; Izumi, T.; Watanabe, J.; Ishikawa, K.; Takezoe, H.; Iida, A. Field-induced molecular reorientation keeping a frustrated structure in an achiral bent-shaped liquid crystal. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 2771–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, T.J.; Murthy, N.S.; Samulski, E.T. Javelin-, Hockey Stick- and Boomerang-Shaped Liquid Crystals. Structural Variations on p-Quinquephenyl. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 8845–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannarius, R.; Li, J.; Weissflog, W. Ferroelectric Smectic Phase Formed by Achiral Straight Core Mesogens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Grande, S.; Weissflog, W.; Eremin, A.; Schröder, M.W.; Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Kresse, H. Structural and conformational investigations in SmA and different SmC phases of new hockey stick-shaped compounds. Liq. Cryst. 2003, 30, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.A.; Tschierske, C. Bent-core liquid crystals: Polar order, superstructural chirality and spontaneous desymmetrisation in soft matter systems. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 907–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaveni, N.G.; Prasad, V.; Roy, A. Azo-functionalised liquid crystalline dimers composed of bent-core and rod-like moieties: Synthesis and mesomorphic properties. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monika, M.; Prasad, V.; Nagaveni, N.G. Hockey stick-shaped azo compounds: Effect of linkage groups and their direction of linking on mesomorphic properties. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 1490–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, H.T. New symmetric azobenzene molecules of varied central cores: Synthesis and characterisation for liquid crystalline properties. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V. Liquid crystalline compounds with V-shaped molecular structures: Synthesis and characterization of new azo compounds. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 28, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V. Bent—Shaped Achiral Azo Compounds Exhibiting Banana Mesophases. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 363, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzl, G.; Wirth, I.; Weissflog, W. The first ‘banana phase’ found in an original Vorländer substance. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 28, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, I.; Diele, S.; Eremin, A.; Pelzl, G.; Grande, S.; Kovalenko, L.; Pancenko, N.; Weissflog, W. New variants of polymorphism in banana-shaped mesogens with cyano-substituted central core. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesekus, G.; Dierking, I.; Gerber, S.; Wulf, M.; Vill, V. Chiral banana liquid crystals derived from sugars. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 31, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgova, S.; Geivandova, T.; Francescangeli, O.; Strigazzi, A. Banana-shaped 1, 2, 4-oxadiazoles. J. Phys. 2003, 61, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, T.J.; Samulski, E.T. Non-linear boomerang-shaped liquid crystals derived from 2,5-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 27, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Weissflog, W. Banana-Shaped Compounds—A New Field of Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Tschierske, C.; Diele, S.; Wirt, I. A novel class of non-chiral banana-shaped liquid crystals with ferroelectric properties. Chem. Commun. 1998, 23, 2573–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadashiva, B.; Raghunathan, V.; Pratibha, R.J.F. Evidence of columnar structure in compounds composed of banana-shaped molecules. Ferroelectrics 2000, 243, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, H.N.S.; Sadashiva, B.K. Banana-shaped mesogens: Effect of lateral substituents on seven-ring esters containing a biphenyl moiety. Liq. Cryst. 2002, 29, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissflog, W.; Nádasi, H.; Dunemann, U.; Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Eremin, A.; Kresse, H. Influence of lateral substituents on the mesophase behaviour of banana-shaped mesogens. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2748–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walba, D.M.; Körblova, E.; Shao, R.; Maclennan, J.E.; Link, D.R.; Glaser, M.A.; Clark, N.A. A ferroelectric liquid crystal conglomerate composed of racemic molecules. Science 2000, 288, 2181–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillon, J.; Marcerou, J.; Laguerre, M.; Nguyen, H.; Achard, M. New banana-shaped thiobenzoate liquid crystals with B6, B1 and B2 phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Pegenau, A.; Diele, S.; Wirth, I.; Tschierske, C. Molecular design of nonchiral bent-core liquid crystals with antiferroelectric properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfor, M.R.; Hegde, G.; Kumar, S.; Tschierske, C.; Chigrinov, V.G. Synthesis and characterization of bent-shaped azobenzene monomers: Guest–host effects in liquid crystals with azo dyes for optical image storage devices. Opt. Mater. 2009, 32, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, C.; Lehmann, A.; Baumeister, U.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Nematic phases of bent-core mesogens. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1704–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, A.; Floegel, M.; Kornek, U.; Stern, S.; Stannarius, R.; Nádasi, H.; Weissflog, W.; Zhu, C.; Shen, Y.; Park, C.S.; et al. Transitions between paraelectric and ferroelectric phases of bent-core smectic liquid crystals in the bulk and in thin freely suspended films. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 051701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Poppe, M.; Nagaraj, M.; Vij, J.K.; Tschierske, C. Development of polar order and tilt in lamellar liquid crystalline phases of a bent-core mesogen. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5003–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Poppe, S.; Tschierske, C. Development of Polar Order by Liquid-Crystal Self-Assembly of Weakly Bent Molecules. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5541–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
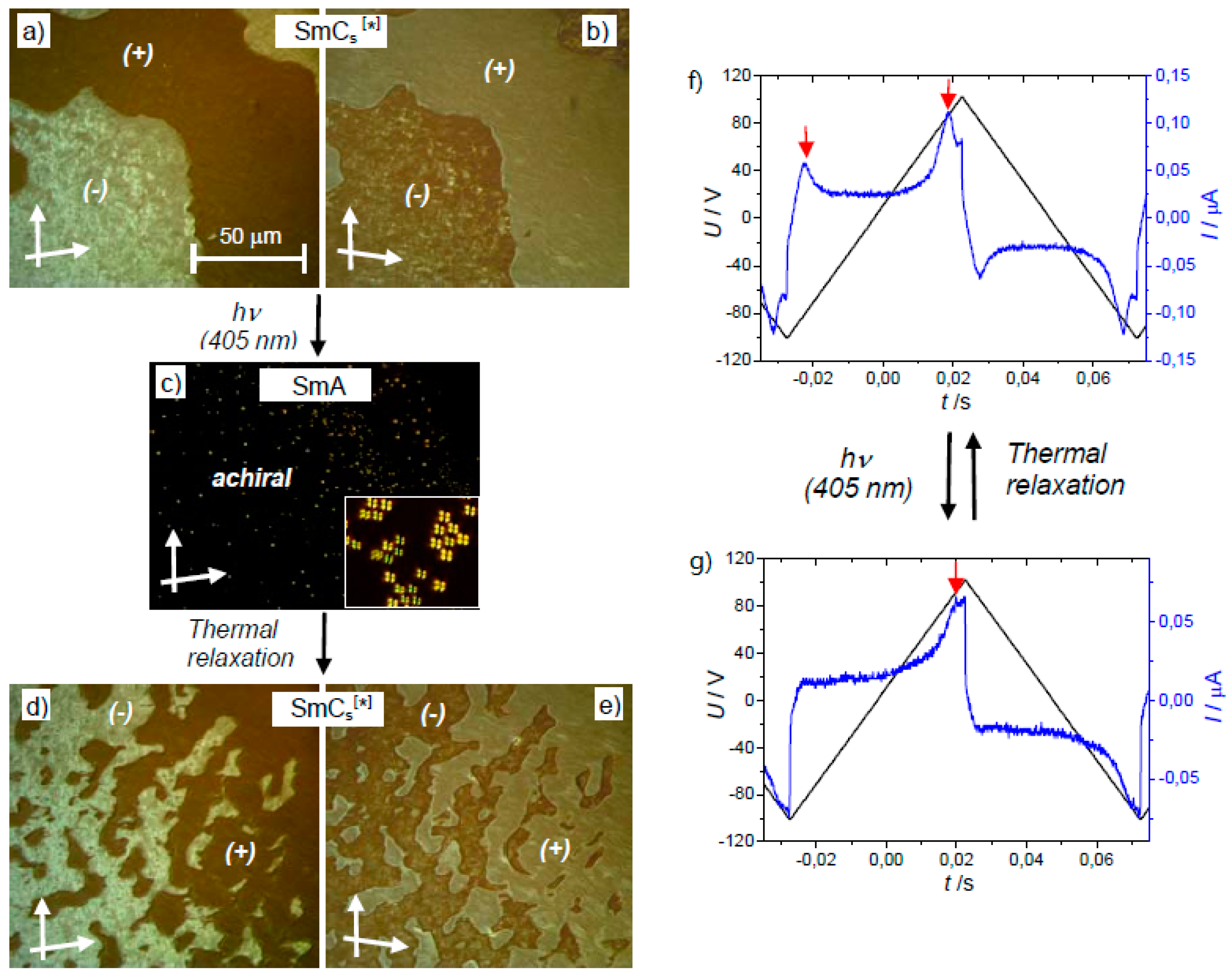
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Belau, S.; Sebastián, N.; Kurachkina, M.; Eremin, A.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Tschierske, C. Polar Order, Mirror Symmetry Breaking, and Photoswitching of Chirality and Polarity in Functional Bent-Core Mesogens. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 6362–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Mirror symmetry breaking in liquids and liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 2221–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Poppe, S.; Kerzig, C.; Klopp, C.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. Cluster phases of 4-cyanoresorcinol derived hockey-stick liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8454–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Schmidt, J.-C.; Darweesh, A.F.; Tschierske, C. Azobenzene-based supramolecular liquid crystals: The role of core fluorination. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Tamba, M.-G.; Sebastián, N.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. Development of Polar Order in the Liquid Crystal Phases of a 4-Cyanoresorcinol-Based Bent-Core Mesogen with Fluorinated Azobenzene Wings. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Ferrero, C.; Dingemans, T.; Samulski, E.T. Cybotaxis dominates the nematic phase of bent-core mesogens: A small-angle diffuse X-ray diffraction study. J. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galerne, Y. Comment on “Thermotropic Biaxial Nematic Liquid Crystals”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 219803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lim, T.-K.; Kim, W.-T.; Jin, J.-I. Dynamics of electro-optical switching processes in surface stabilized biaxial nematic phase found in bent-core liquid crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Kang, S.-W.; Suresh, K.A.; Joshi, L.; Wang, Q.; Kumar, S. Thermotropic Uniaxial and Biaxial Nematic and Smectic Phases in Bent-Core Mesogens. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17224–17227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, J.; Mbanga, B.; Éber, N.; Fodor-Csorba, K.; Sprunt, S.; Gleeson, J.T.; Jakli, A. Giant flexoelectricity of bent-core nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 157802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescangeli, O.; Stanic, V.; Torgova, S.I.; Strigazzi, A.; Scaramuzza, N.; Ferrero, C.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Weiss, T.M.; Berardi, R.; Muccioli, L.; et al. Ferroelectric Response and Induced Biaxiality in the Nematic Phase of Bent-Core Mesogens. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Microsegregation: From Basic Concepts to Complexity in Liquid Crystal Self-Assembly. Isr. J. Chem. 2012, 52, 935–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, M. Fluorinated liquid crystals—properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 2070–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guittard, F.; Taffin de Givenchy, E.; Geribaldi, S.; Cambon, A. Highly fluorinated thermotropic liquid crystals: An update. J. Fluor. Chem. 1999, 100, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodby, J.W.; Saez, I.M.; Cowling, S.J.; Gasowska, J.S.; MacDonald, R.A.; Sia, S.; Watson, P.; Toyne, K.J.; Hird, M.; Lewis, R.A.; et al. Molecular complexity and the control of self-organising processes. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 36, 567–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomola, K.; Guo, L.; Pociecha, D.; Araoka, F.; Ishikawa, K.; Takezoe, H. An optically uniaxial antiferroelectric smectic phase in asymmetrical bent-core compounds containing a 3-aminophenol central unit. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7944–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Mirror symmetry breaking in fluorinated bent-core mesogens. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82890–82899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunemann, U.; Schröder, M.W.; Reddy, R.A.; Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Weissflog, W. The influence of lateral substituents on the mesophase behaviour of banana-shaped mesogens. Part II. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4051–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissflog, W.; Murthy, H.N.S.; Diele, S.; Pelzl, G. Relationships between molecular structure and physical properties in bent-core mesogens. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 2657–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmahel, M.; Poryvai, A.; Xiang, Y.; Pociecha, D.; Troha, T.; Novotná, V.; Svoboda, J.; Kohout, M. Photosensitive bent-core nematic liquid crystals with various linking units in the side arms: Structure-properties relationships. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.S.; Kumar, J.; Prasad, V.; Monika, M. The first examples of V-shaped compounds exhibiting a B5 mesophase and a direct transition from the isotropic to a polar biaxial smectic A mesophase. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, L.E.; Jung, H.T.; Krüerke, D.; Heberling, M.S.; Nakata, M.; Jones, C.D.; Chen, D.; Link, D.R.; Zasadzinski, J.; Heppke, G.; et al. Helical Nanofilament Phases. Science 2009, 325, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Helical Nano-crystallite (HNC) Phases: Chirality Synchronization of Achiral Bent-Core Mesogens in a New Type of Dark Conglomerates. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6583–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintuvuori, J.S.; Yu, G.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.R. Emergent chirality in achiral liquid crystals: Insights from molecular simulation models of the behaviour of bent-core mesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.S.; Kumar, J.; Prasad, V. Achiral bent-core salicylaldimine compounds exhibiting dark conglomerate and B2 mesophases: Effect of linkage groups and lateral substituents. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Kang, S.-W.; Qi, X.; Kumar, S. Photo-responsive and electrically switchable mesophases in a novel class of achiral bent-core azo compounds. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.S.; Sunil, B.N.; Hegde, G.; Prasad, V. Influence of alkyl and alkoxy groups on photoresponsive behaviour of bent-core azo mesogens: Synthesis, mesomorphic and photoswitching properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; Brautzsch, M.; Tschierske, C. 4-Methylresorcinol based bent-core liquid crystals with azobenzene wings—A new class of compounds with dark conglomerate phases. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5487–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, H.; Xu, M.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, E.; Liu, D.; Poryvai, A.; Kohout, M.; Éber, N.; Buka, Á. Light Tunable Gratings Based on Flexoelectric Effect in Photoresponsive Bent-Core Nematics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Nagendrappa Gowdru, N.; Manjunath, M. Thermally stable azo-substituted bent-core nematogens: Observation of chiral domains in the nematic mesophases composed of smectic nano clusters. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Prasad, V. Ferroelectric Nematic and Ferrielectric Smectic Mesophases in an Achiral Bent-Core Azo Compound. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Yusoff, M.M.; Hegde, G.; Malek, M.N.F.A.; Samah, N.A.; Srinivasa, H.T.; Kumar, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Naphthalene-Based Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals for Photoswitching Properties. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2014, 61, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.L.; Asik, J.; Kumar, S.; Tschierske, C. Liquid crystalline banana-shaped monomers derived from 2,7-naphthalene: Synthesis and properties. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 35, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfor, M.R.; Yusoff, M.M.; Hegde, G.; Fazli, M.N.; Malek, A.; Samah, N.A.; Srinivasa, H.T. Synthesis of Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals for Photoswitching Properties. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 587, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajzíková, K.; Svoboda, J.; Novotná, V.; Pociecha, D.; Gorecka, E. Bent-core mesogens with an aromatic unit at the terminal position. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4672–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, H.; Skouta, R.; Schneebeli, S.; Kamenetska, M.; Breslow, R.; Venkataraman, L.; Hybertsen, M.S. Probing the conductance superposition law in single-molecule circuits with parallel paths. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khobragade, D.; Stensrud, E.S.; Mucha, M.; Smith, J.R.; Pohl, R.; Stibor, I.; Michl, J. Preparation of Covalent Long-Chain Trialkylstannyl and Trialkylsilyl Salts and an Examination of their Adsorption on Gold. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8483–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaletová, E.; Kohutová, A.; Hajduch, J.; Kaleta, J.; Bastl, Z.; Pospíšil, L.; Stibor, I.; Magnera, T.F.; Michl, J. The Scope of Direct Alkylation of Gold Surface with Solutions of C1–C4 n-Alkylstannanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12086–12099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
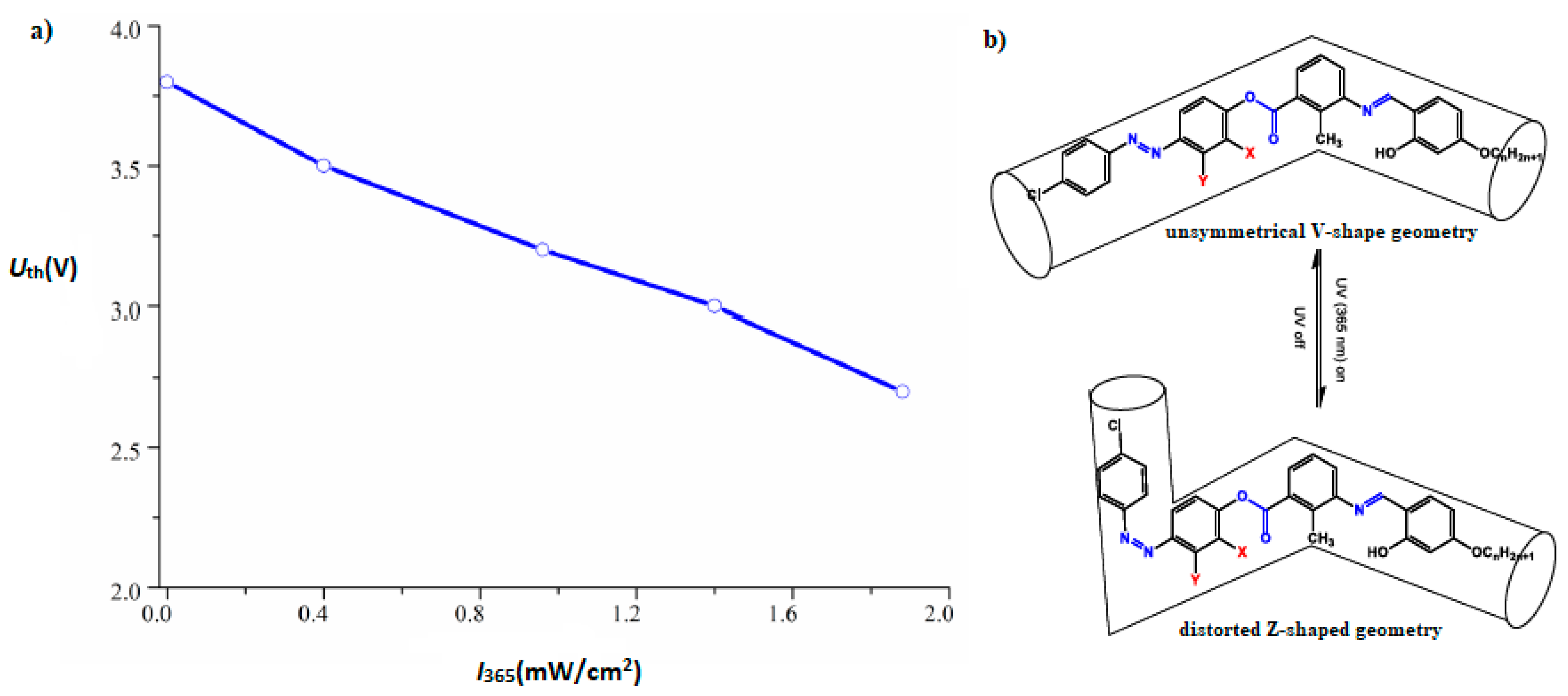
- Jinying, L.; Zelong, Z.; Daoren, Y.; Zhiyong, Z.; Jintao, G.; Junfei, Q. Synthesis of 4-Chloro-1,3-Diazobenzene Bent-Cores Liquid Crystals and Characterizations of Their Mesogenic Behaviors and Photoisomerization Phenomena. ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaveni, N.G.; Raghuvanshi, P.; Roy, A.; Prasad, V. Azo-functionalised achiral bent-core liquid crystalline materials: Effect of presence of –N=N– linkage at different locations in the molecular architecture. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1238–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Hegde, G.; Yusoff, M.M.; Malek, M.N.F.A.; Srinivasa, H.T.; Kumar, S. New pyrimidine-based photo-switchable bent-core liquid crystals. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Li, X.; Kang, S.; Tokita, M.; Watanabe, J. Formation of banana phases in bent-shaped molecules with unusual bent angles as low as 60°. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4517–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhan, M.S.; Wang, K. A hexagonal columnar phase formed in lateral fluorinated bent-shaped molecules based on a 1,7-naphthalene central core. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-W.; Hattori, M.; Uehara, F.; Tokita, M.; Kawauchi, S.; Watanabe, J.; Kang, S. Smectic A–hexagonal columnar–B7 phase transition of acute-angle bent-core molecules. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.-W.; Takimoto, K.; Tokita, M.; Watanabe, J.; Kang, S. Bent Molecules with a 60° Central Core Angle that Form B7 and B2 Phases. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 8216–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Harada, M.; Li, X.; Tokita, M.; Watanabe, J. Notable formation of a cubic phase from small bent-angle molecules based on the 1,7-naphthalene central core and alkylthio tails. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Prehm, M.; May, K.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. 4-Cyanoresorcinol-Based Bent-Core Mesogens with Azobenzene Wings: Emergence of Sterically Stabilized Polar Order in Liquid Crystalline Phases. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1703–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, E.; Gallardo, H.; Caramori, G.F.; Sebastián, N.; Tamba, M.-G.; Eremin, A.; Kawauchi, S.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Polar Order and Symmetry Breaking at the Boundary between Bent-Core and Rodlike Molecular Forms: When 4-Cyanoresorcinol Meets the Carbosilane End Group. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8181–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, H.; Poppe, M.; Bilgin-Eran, B.; Karanlık, G.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Effects of molecular chirality on self-assembly and switching in liquid crystals at the cross-over between rod-like and bent shapes. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 7405–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Saito, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Tokita, M.; Takanishi, Y.; Takezoe, H.; Watanabe, J. Low-Birefringent, Chiral Banana Phase below Calamitic Nematic and/or Smectic C Phases in Oxadiazole Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5205–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.C.; Yu, L.J. Mesophases of Achiral Bent Molecules. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5410–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, A.S.; Grover, C.; Komitov, L.; Andersson, G. Ferro-, ferri- and antiferro-electric behaviour in a bent-shaped mesogen. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissflog, W.; Dunemann, U.; Findeisen-Tandel, S.; Tamba, M.G.; Kresse, H.; Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Baumeister, U.; Eremin, A.; Stern, S.; et al. At the boundary to banana-shaped liquid crystals: Polar properties of phases formed by new asymmetric achiral four-ring bent-core mesogens. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, R.; Nath, R.K.; Paul, M.K.; Rao, N.V.S.; Tuluri, F.; Shen, Y.; Shao, R.; Chen, D.; Zhu, C.; Smalyukh, I.I.; et al. Four-ring achiral unsymmetrical bent core molecules forming strongly fluorescent smectic liquid crystals with spontaneous polar and chiral ordered B7 and B1 phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7332–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki Yoon, D.; Deb, R.; Chen, D.; Körblova, E.; Shao, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Rao, N.V.S.; Walba, D.M.; Smalyukh, I.I.; Clark, N.A. Organization of the polarization splay modulated smectic liquid crystal phase by topographic confinement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21311–21315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, R.K.; Sarkar, D.D.; Shankar Rao, D.S.; Nandiraju, V.S.R. Influence of polar substituents on the mesomorphism of non-symmetrical achiral four-ring bent-core compounds: Synthesis and characterisation. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 39, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.K.; Turlapati, S.; Begum, N.; Mohiuddin, G.; Rao, N.V.S.; Ghosh, S. Impact of terminal polar substitution on elastic, electro-optic and dielectric properties of four-ring bent-core nematic liquid crystals. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11509–11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patranabish, S.; Mohiuddin, G.; Begum, N.; Laskar, A.R.; Pal, S.K.; Rao, N.V.S.; Sinha, A. Cybotactic nematic phase of achiral unsymmetrical bent-core liquid crystals—Quelling of polar ordering and the influence of terminal substituent moiety. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 257, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Turlapati, S.; Rao, N.; Ghosh, S. Elastic and dielectric properties of ferroelectric nanoparticles/bent-core nematic liquid crystal blend. Eur. Phys. J. E 2017, 40, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, G.; Prehm, M.; Nagaraj, M.; Vij, J.K.; Weyland, M.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. 1,2,4-Oxadiazole-Based Bent-Core Liquid Crystals with Cybotactic Nematic Phases. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Begum, N.; Turlapati, S.; Roy, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Rao, N.V.S. Ferroelectric-like switching in the nematic phase of four-ring bent-core liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, H.; Tandon, P.; Chakraborty, N.; Rao, N.V.S.; Ayala, A.P. Study of Cr→SmA phase transition and hydrogen bonding in four-ring bent-core liquid crystal. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 178, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.; Kaur, S.; Mohiuddin, G.; Nandi, R.; Gupta, S.P.; Rao, N.V.S.; Pal, S.K. Structural Understanding, Photoswitchability, and Supergelation of a New Class of Four Ring-Based Bent-Shaped Liquid Crystal. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.; Kaur, S.; Xiang, Y.; Yin, H.; Mohiuddin, G.; Rao, N.V.S.; Pal, S.K. Photoswitchable Bent-Core Nematic Liquid Crystals with Methylated Azobenzene Wing Exhibiting Optic-Field-Enhanced Fréedericksz Transition Effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlapati, S.; Sunil, B.N.; Vishwakarma, V.K.; Achalkumar, A.S.; Hegde, G. Influence of lateral methyl/chloro substituents on the liquid crystalline and photoswitching behaviour of bent-core mesogens bearing azobenzene wings: Synthesis and characterization. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5731–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.K.; Saha, S.K.; Kalita, G.; Bhattacharya, B.; Sarkar, U. Low-temperature nematic phase in azo functionalised reactive hockey stick mesogens possessing lateral methyl group. Dyes Pigment. 2020, 173, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.C.; Yu, L.J. Mesophases of hockey stick mesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 35, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, E.; Findeisen-Tandel, S.; Dabrowski, R.; Giesselmann, F.; Weissflog, W.; Baumeister, U.; Lagerwall, J. On the balance between syn- and anticlinicity in smectic phases formed by achiral hockey-stick mesogens with and without chiral dopants. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2950–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novotná, V.; Žurek, J.; Kozmík, V.; Svoboda, J.; Glogarová, M.; Kroupa, J.; Pociecha, D. Novel hockey-stick mesogens with the nematic, synclinic and anticlinic smectic C phase sequence. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 35, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuściński, S.; Wojciechowska, A.; Urbaniak, K.; Kaszyński, P.; Jasiński, M. Hockey-stick liquid crystalline 6-oxoverdazyl. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahimwalla, Z.; Yager, K.G.; Mamiya, J.-I.; Shishido, A.; Priimagi, A.; Barrett, C. Azobenzene photomechanics: Prospects and potential applications. Polym. Bull. 2012, 69, 967–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Broer, D. Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers. J. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haan, L.T.; Schenning, A.P.; Broer, D. Programmed morphing of liquid crystal networks. Polymer 2014, 55, 5885–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iamsaard, S.; Villemin, E.; Lancia, F.; Aβhoff, S.-J.; Fletcher, S.P.; Katsonis, N. Preparation of biomimetic photoresponsive polymer springs. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, S.; Simeth, N.A.; König, B. Heteroaryl azo dyes as molecular photoswitches. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjoudis, E.; Mavridis, I.M. Photochromism and thermochromism of Schiff bases in the solid state: Structural aspects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Gaur, A.K.; Gupta, D.; Saraswat, M.; Venkataramani, S. Tripodal N-Functionalized Arylazo-3, 5-dimethylpyrazole Derivatives of Trimesic Acid: Photochromic Materials for Rewritable Imaging Applications. ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; Volume 83. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Jing, H.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Ye, W.-J.; Xu, M.-Y.; Wang, E.; Salamon, P.; Éber, N.; Buka, Á. Tunable optical grating based on the flexoelectric effect in a bent-core nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 7, 064032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Tan, G.; Wu, S.-T. Large-angle and high-efficiency tunable phase grating using fringe field switching liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 12274–12285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Tan, G.; Huang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Choi, T.-H.; Yoon, T.-H.; Wu, S.-T. A Low Voltage Liquid Crystal Phase Grating with Switchable Diffraction Angles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
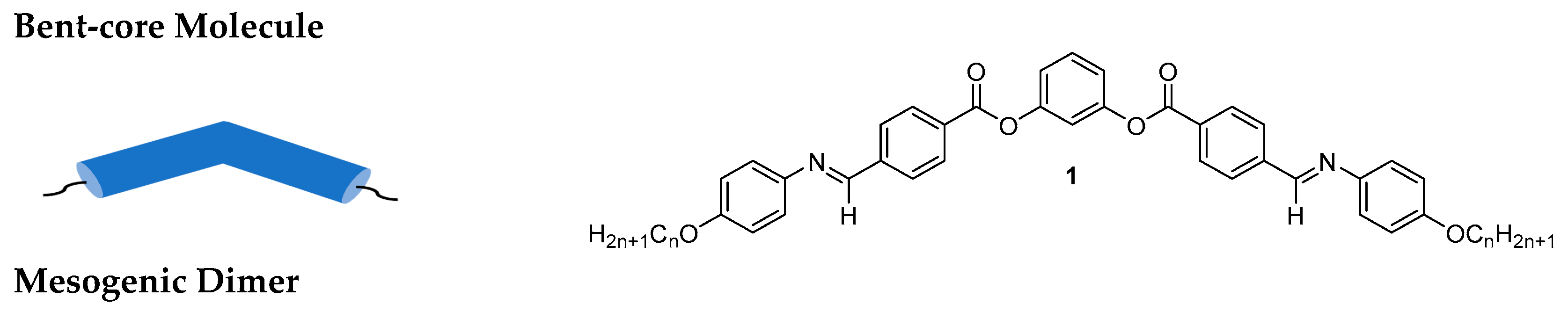

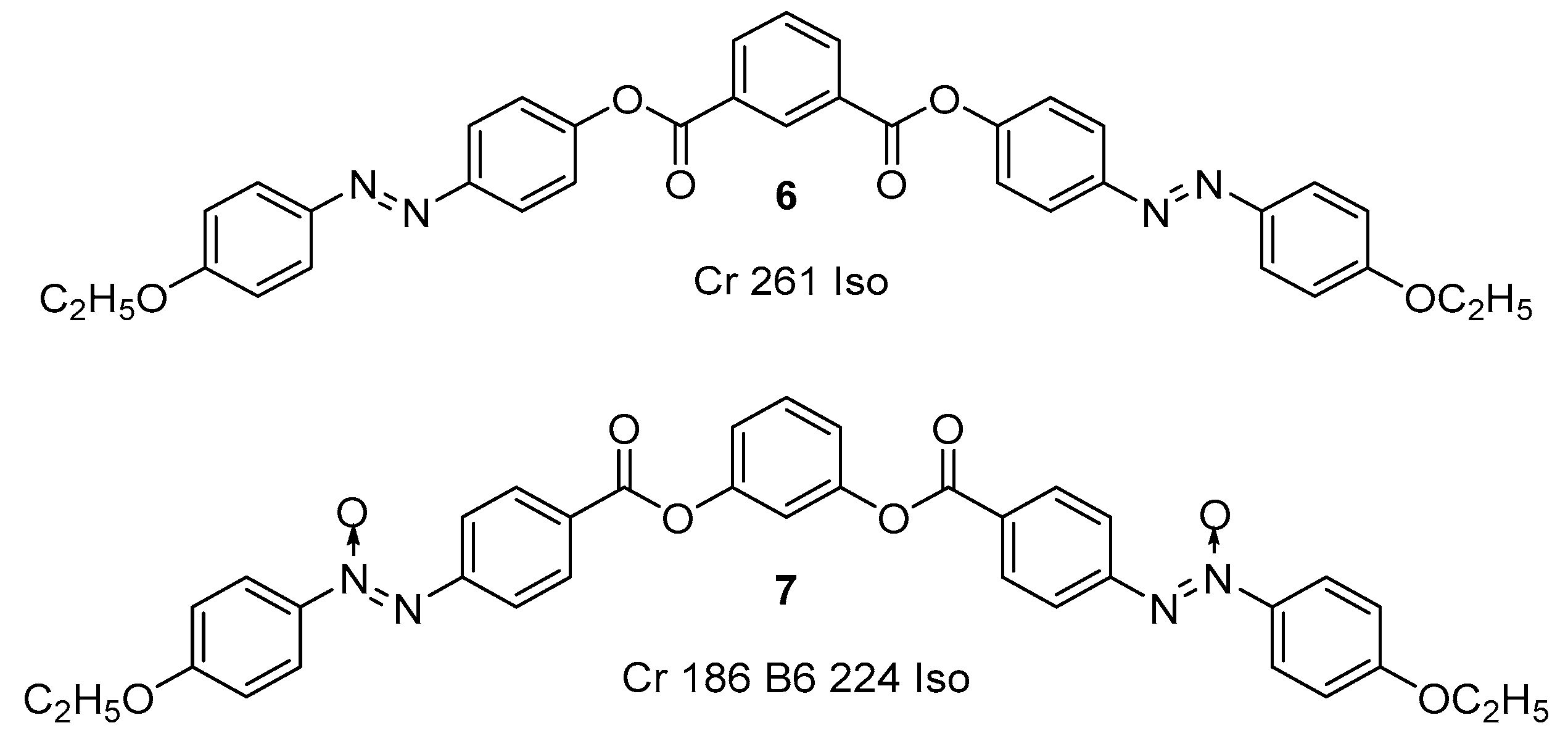
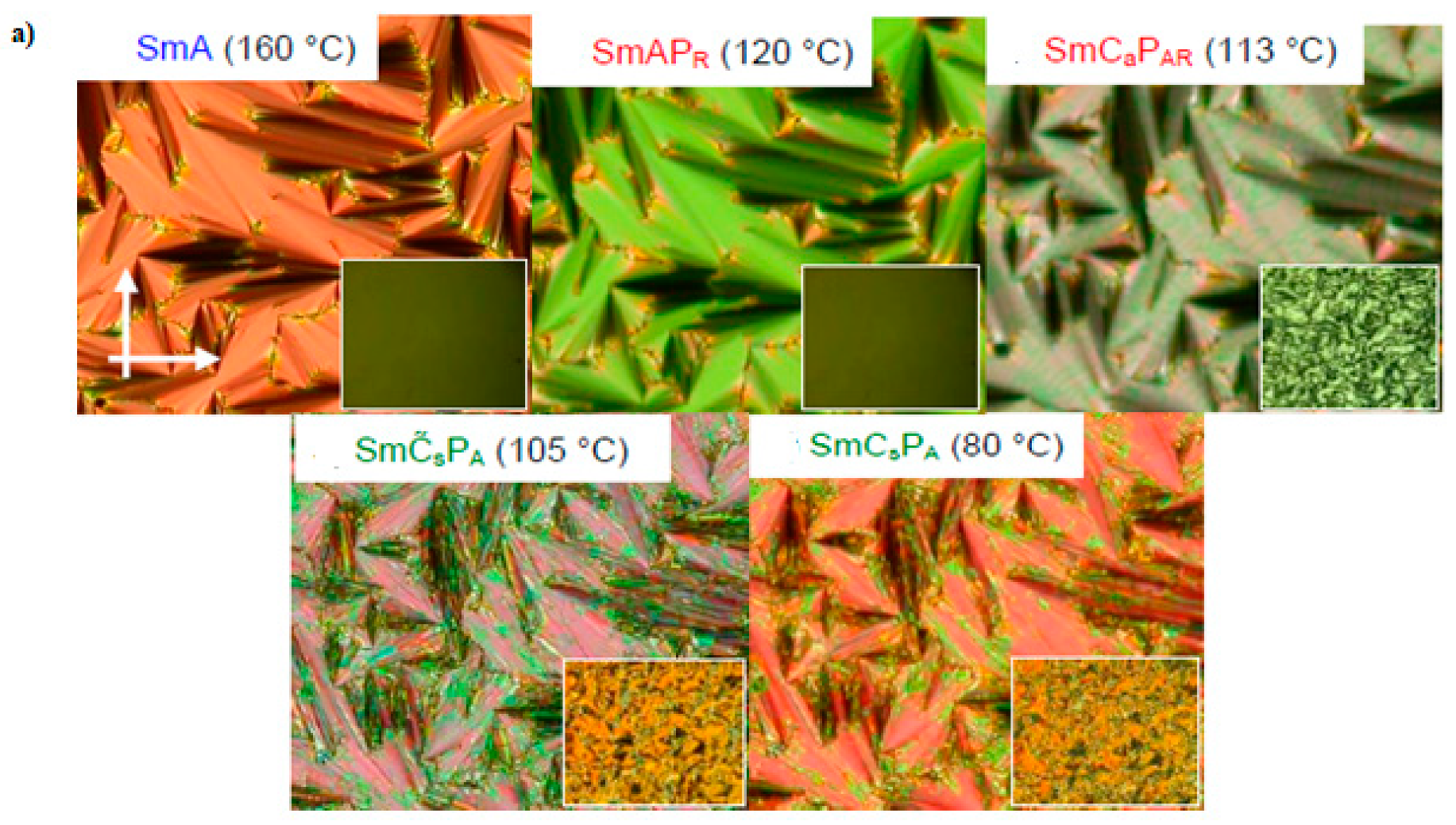
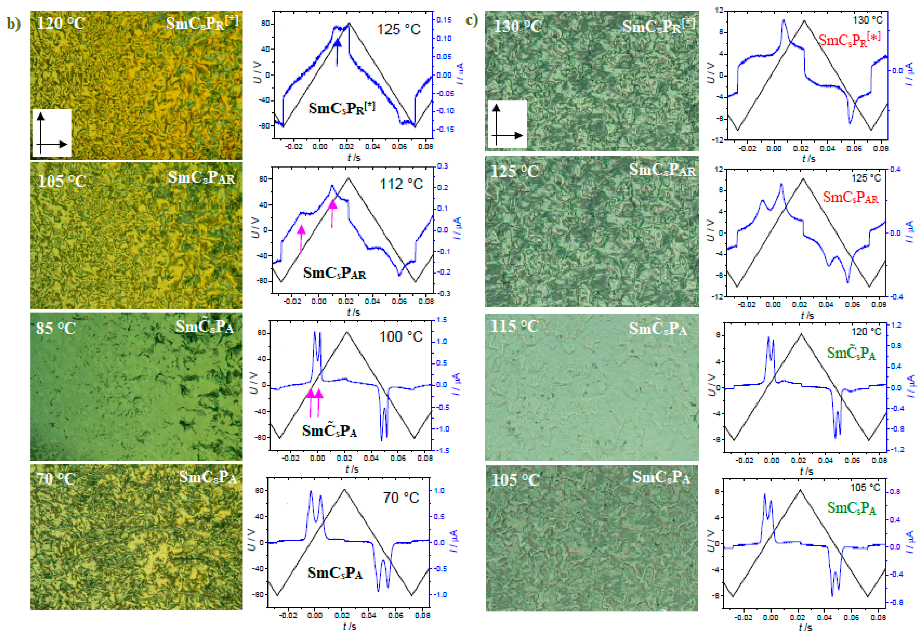
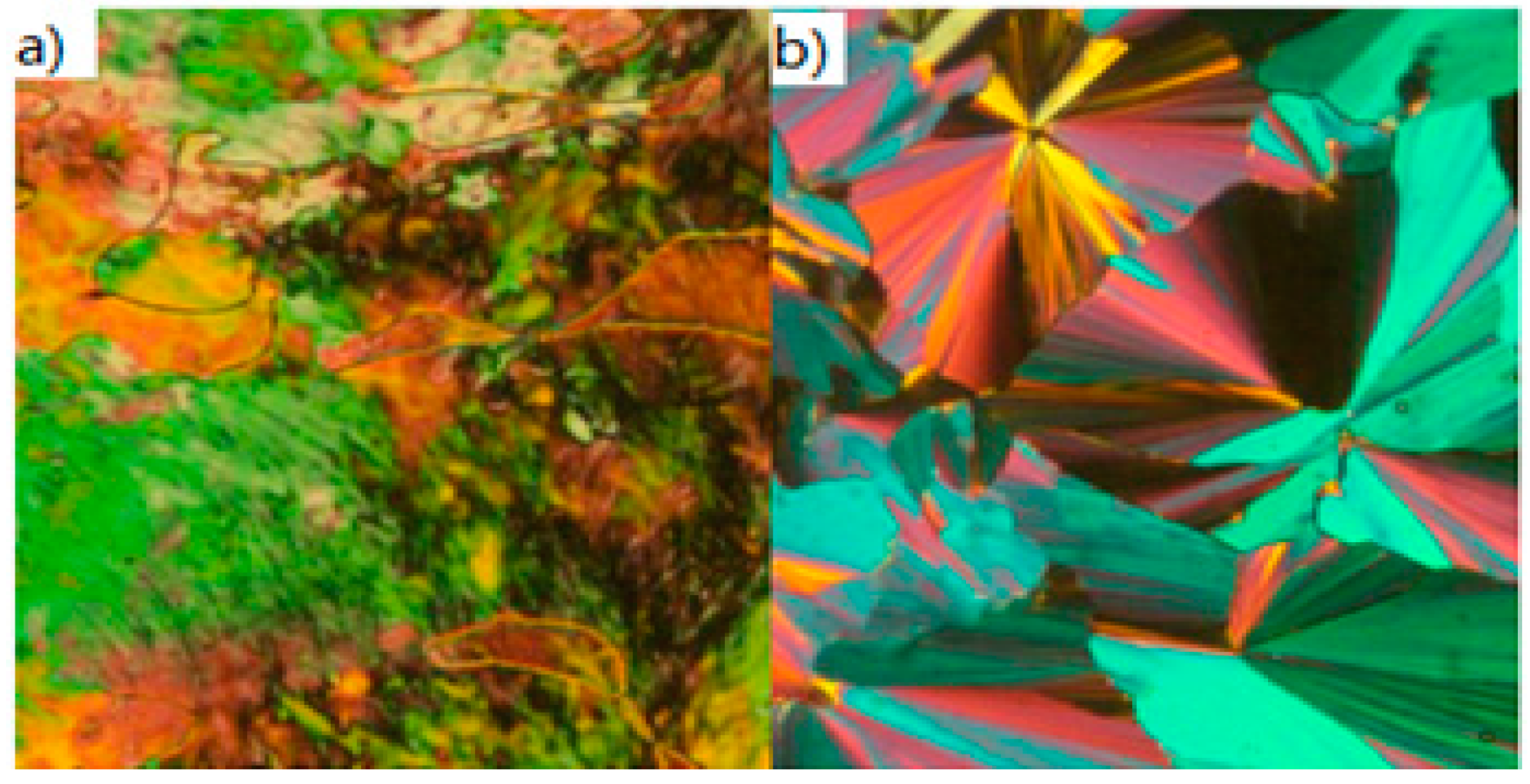
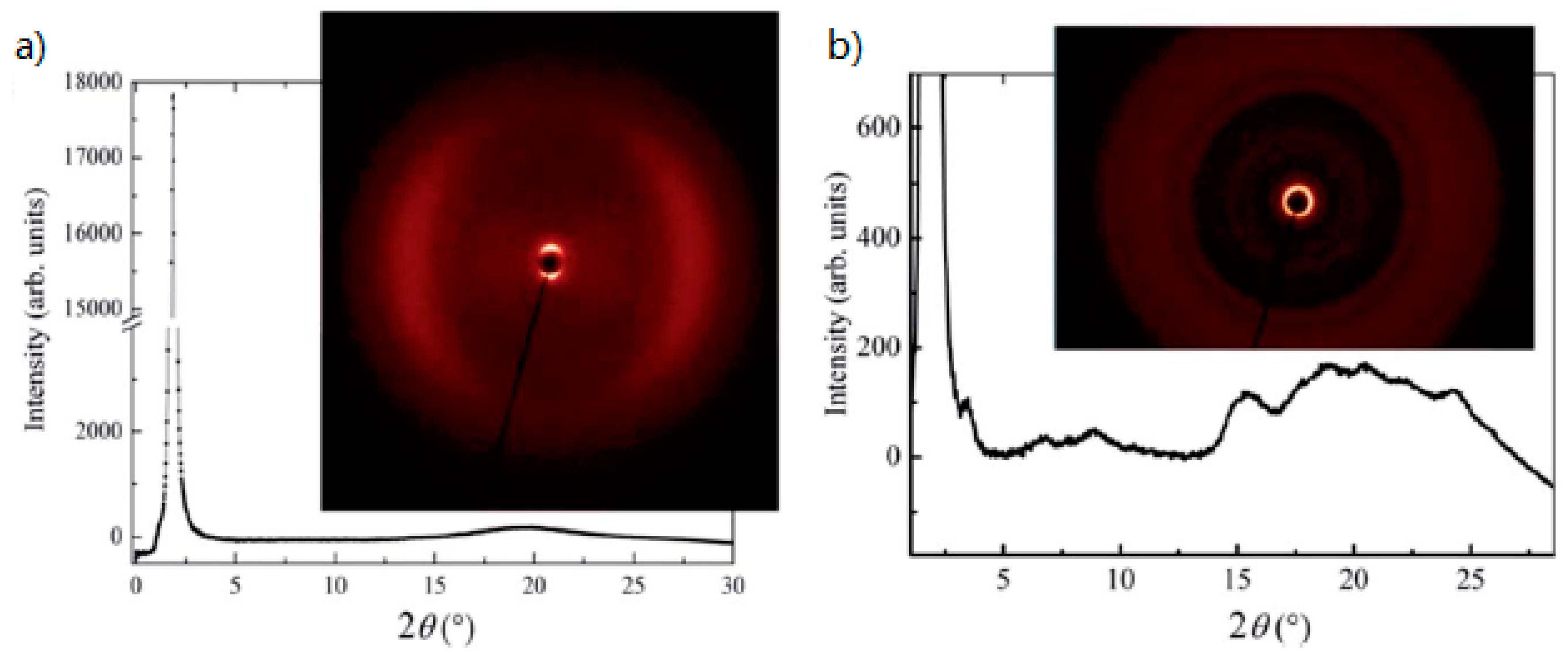

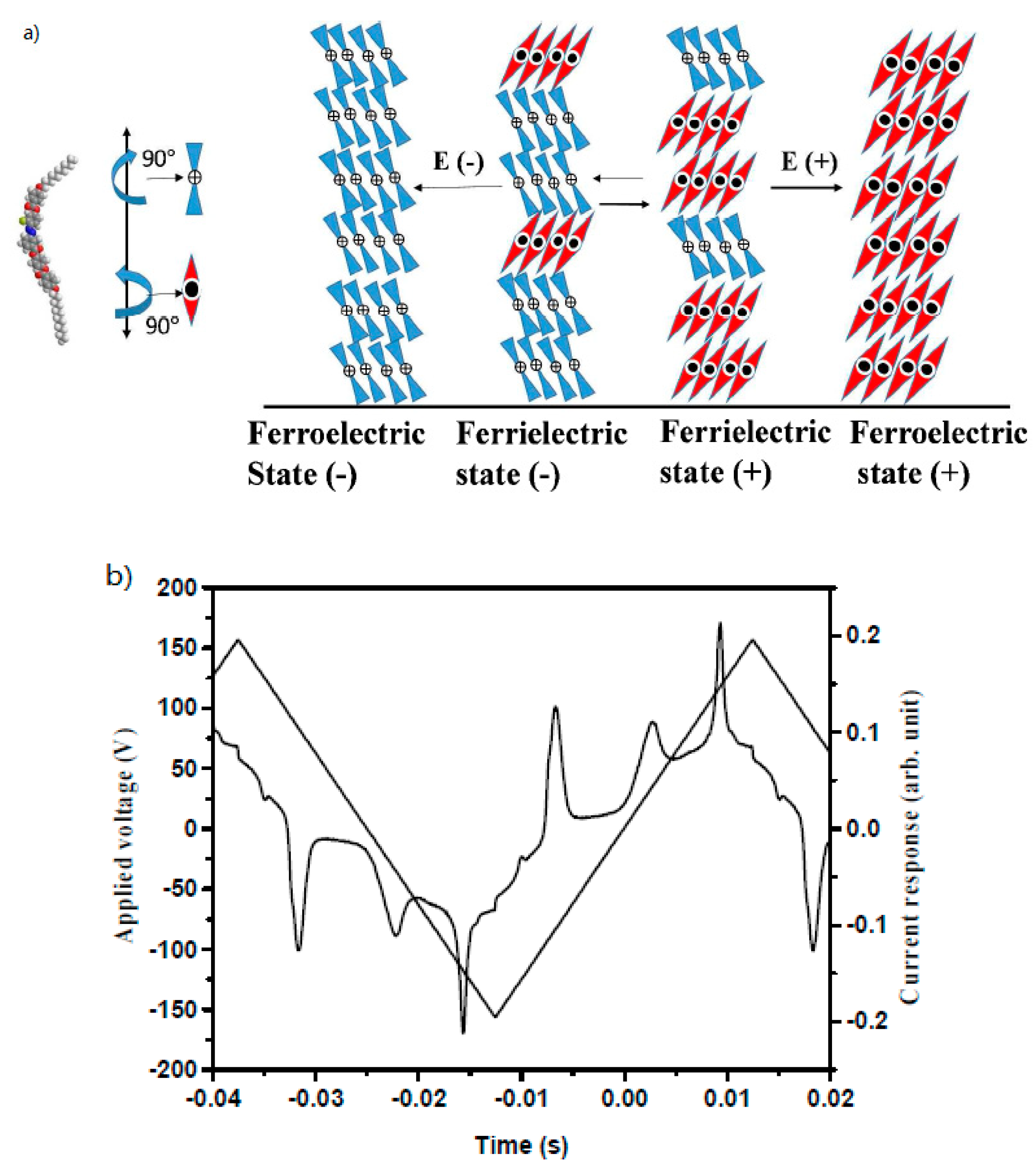

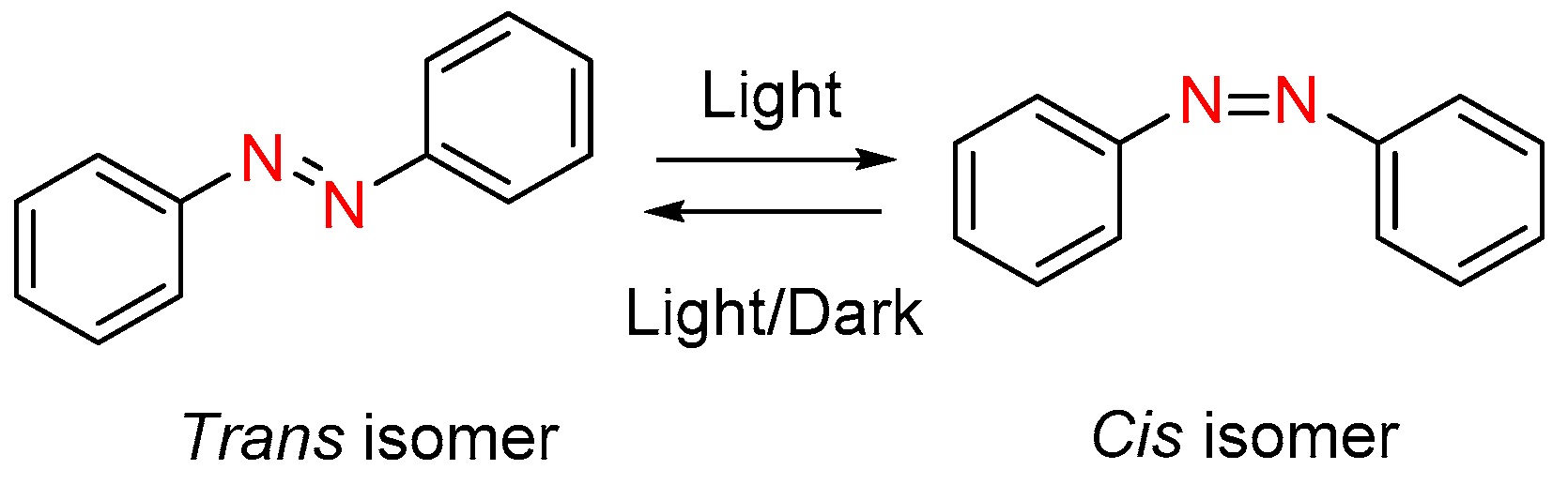
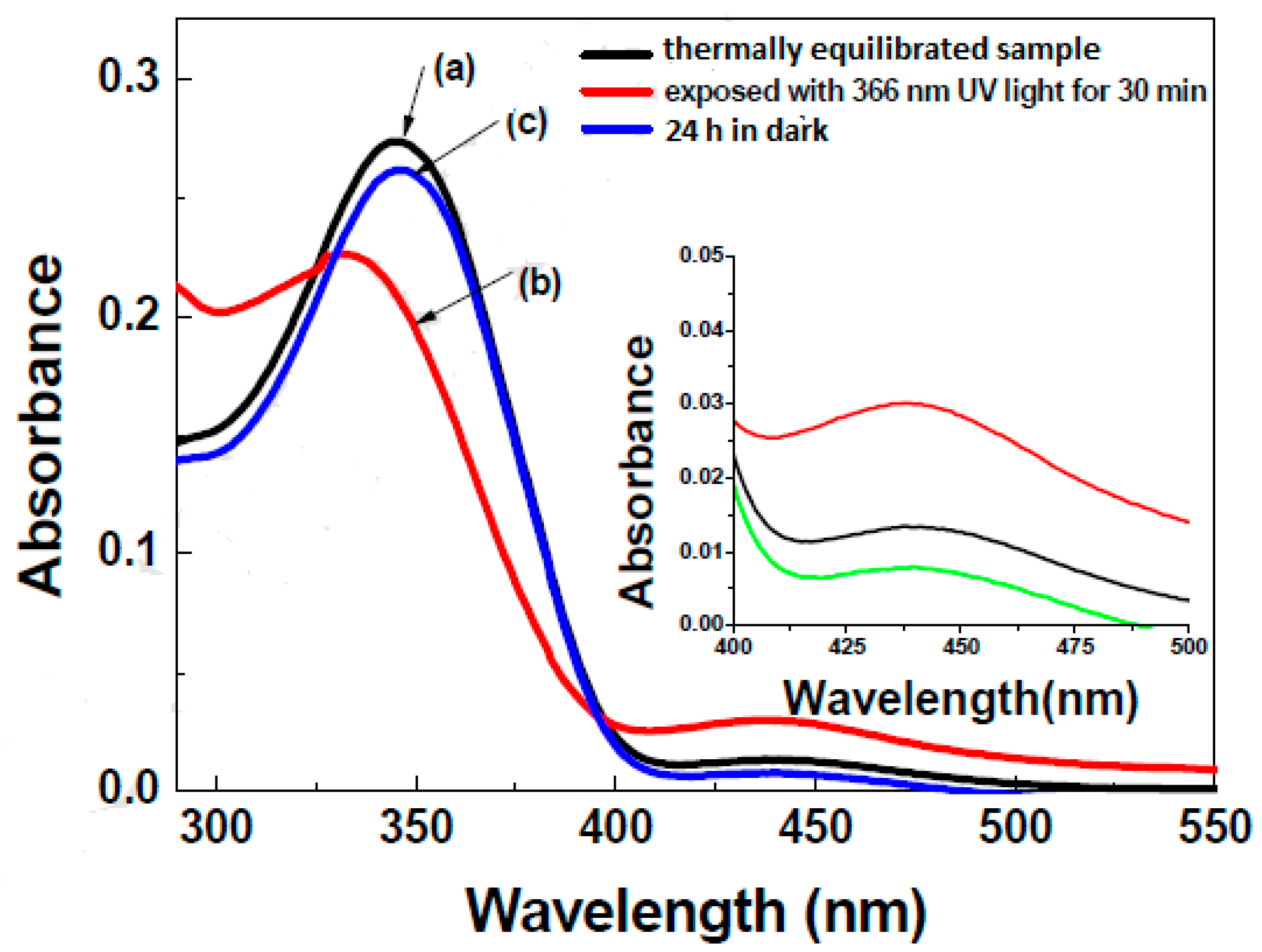
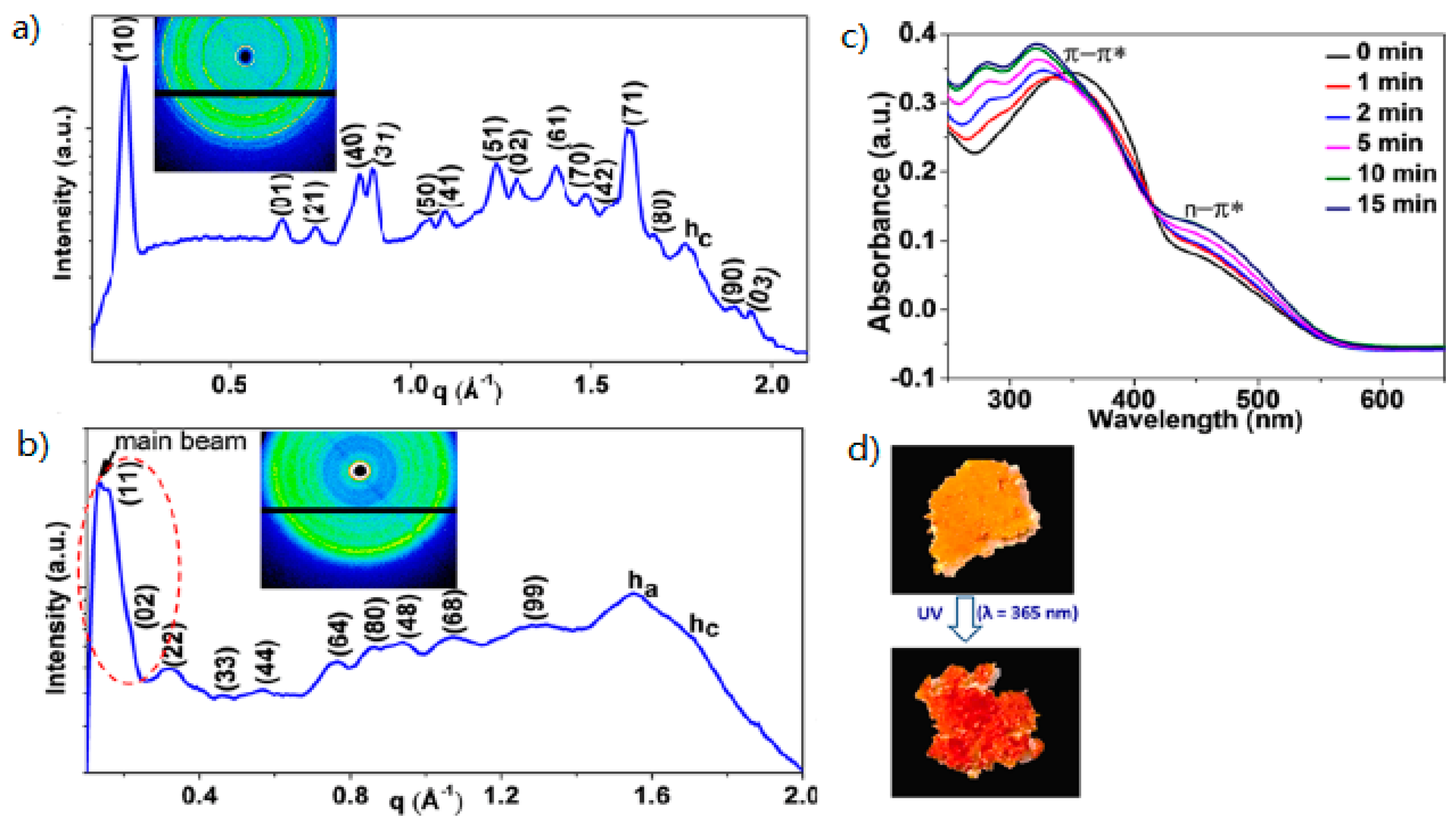
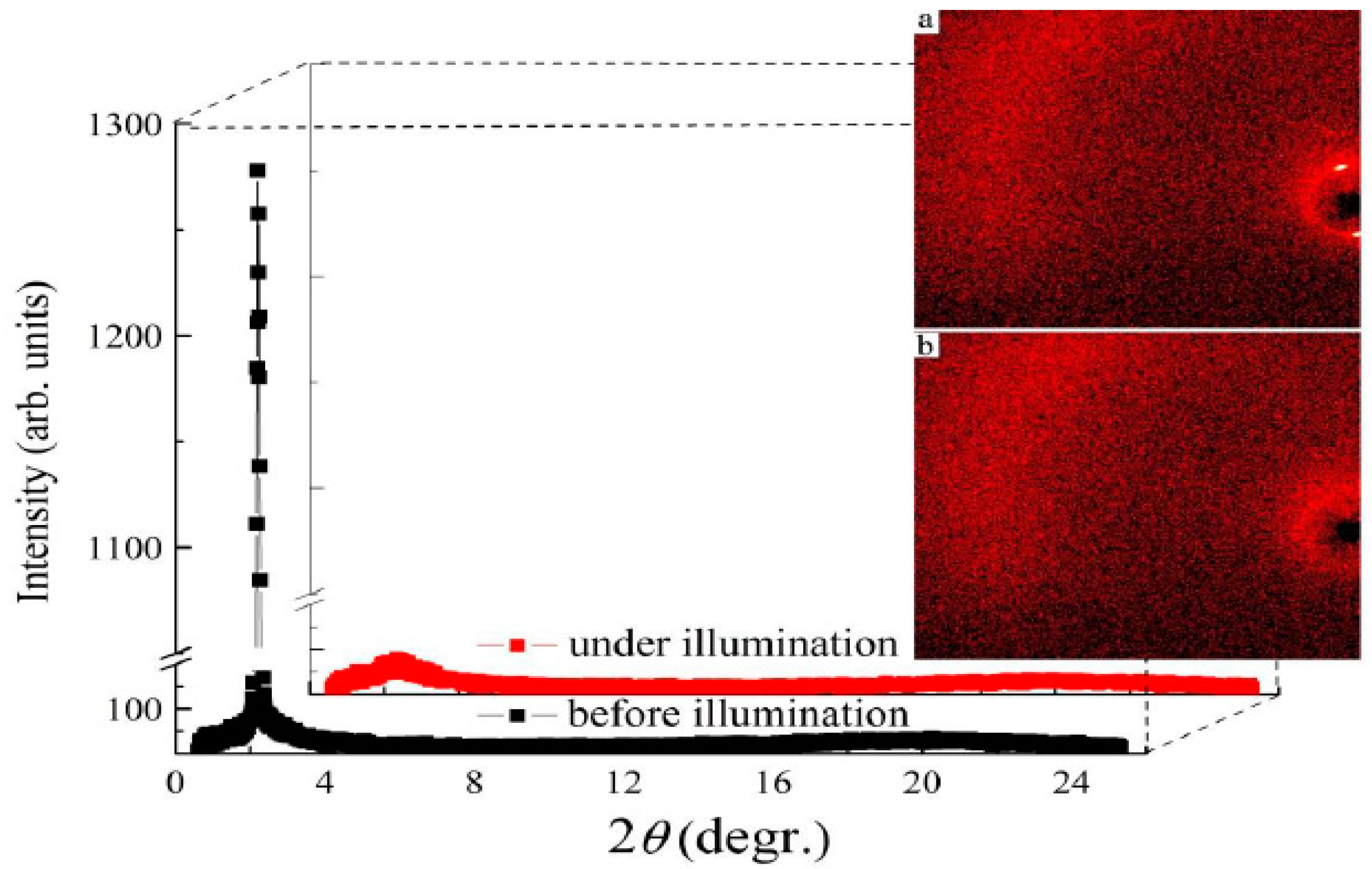
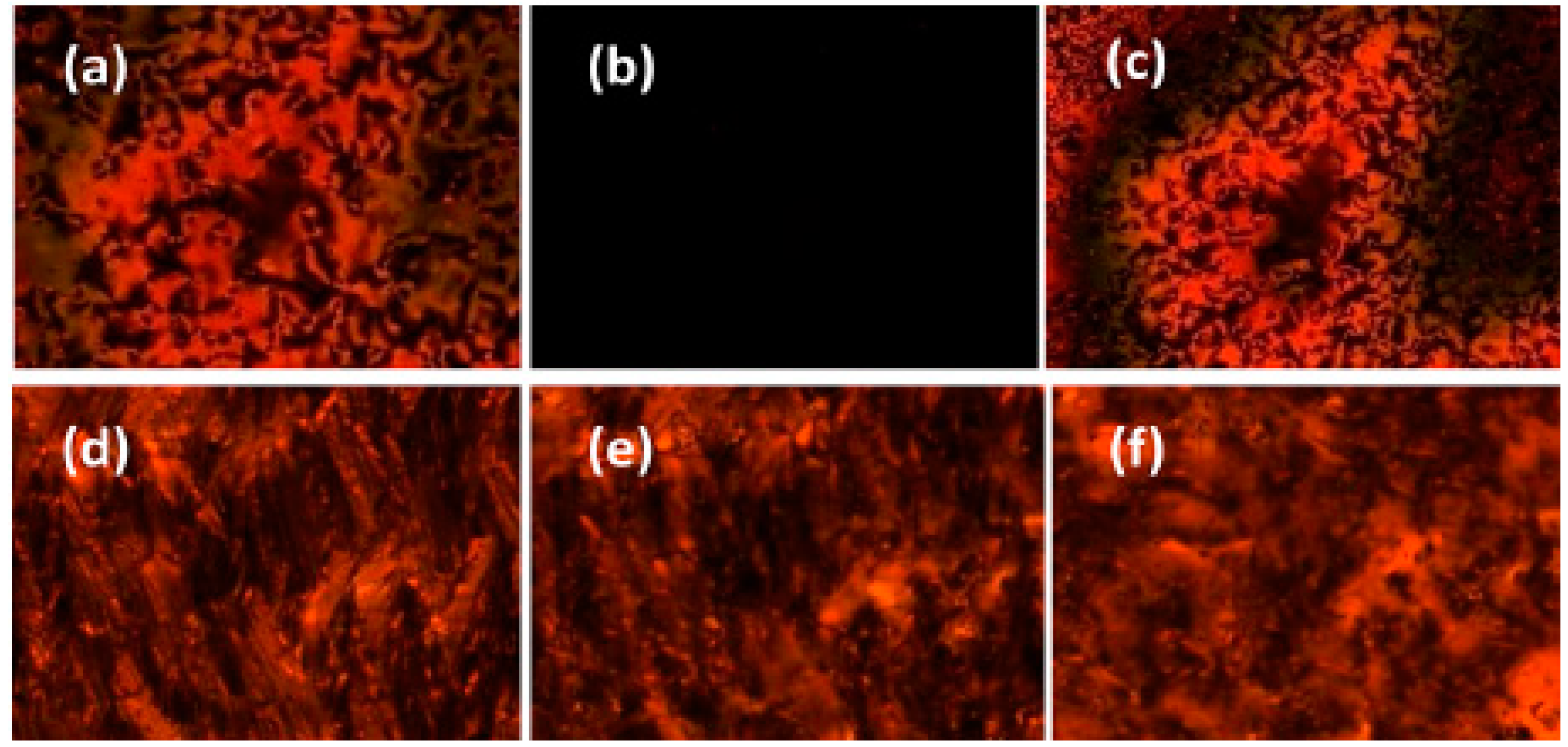
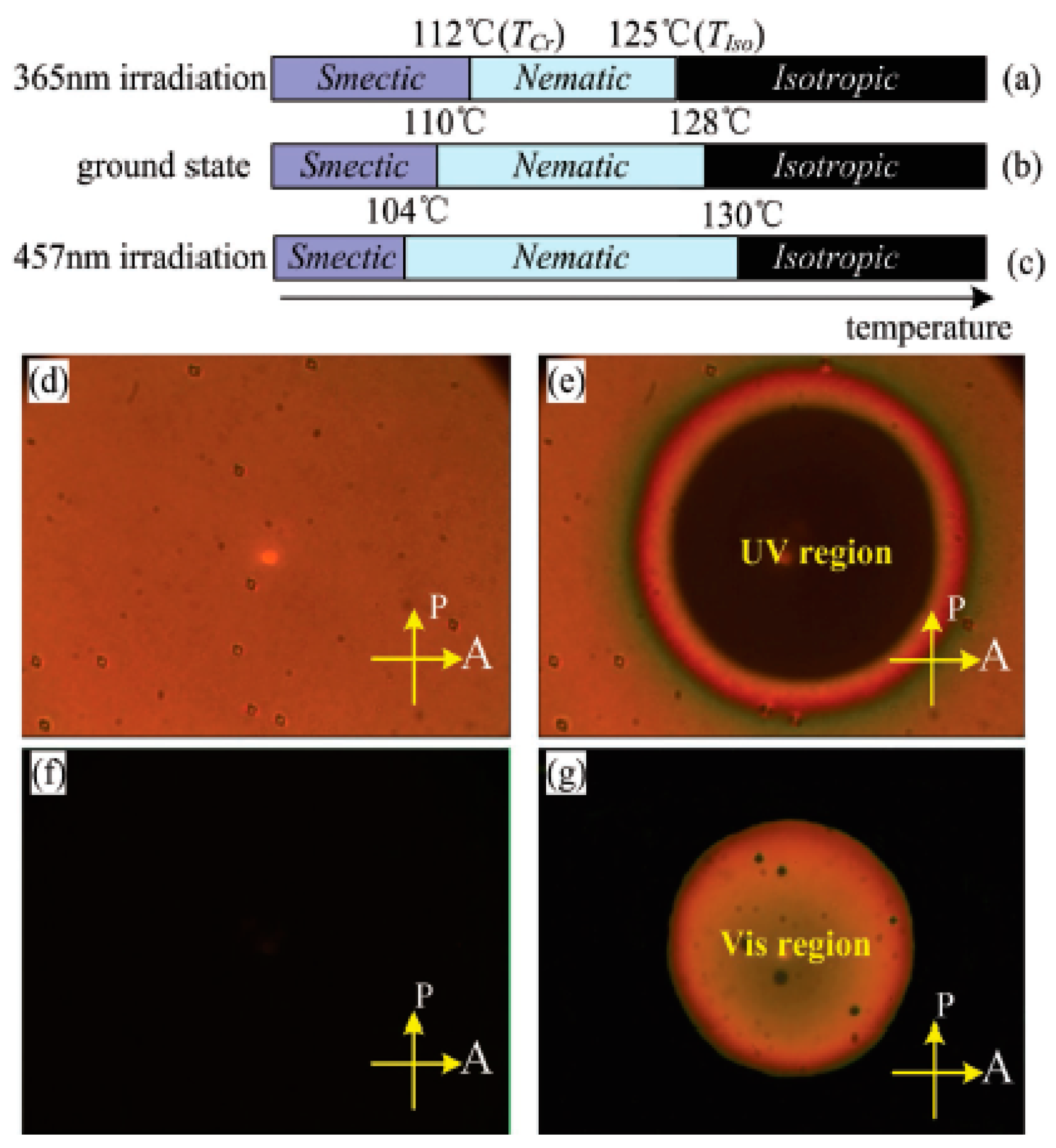
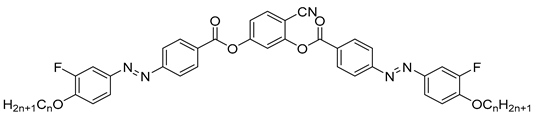
| Compound | n | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|
| 11a | 4 | Cr 164 NcybA 136 Iso |
| 11b | 6 | Cr 112 SmAPAR 101 SmAPR 117 NcybA 128 Iso |
| 11c | 8 | Cr 112 SmCaPA 104 SmAPAR 110 SmAPR 137 Iso |
| 11d | 10 | Cr 108 SmCaPA 108 SmCsPAR 112 SmAPR 143 Iso |
| 11e | 12 | Cr 104 SmCaPA 98 SmCsPA 108 SmCsPAR ≈ 111 SmCsPR[*] 135 SmA 147 Iso |
| 11f | 14 | Cr 101 SmCaPA 98 SmCsPA 107 SmCsPAR ≈ 112 SmCsPR[*] 134 SmCs[*] 142 SmA 147 Iso |
| 11g | 16 | Cr 101 SmCaPA 93 SmCsPA 105 SmCsPAR ≈ 112 SmCsPR[*] 126 SmCs[*] 145 SmA 149 Iso |
| 11h | 18 | Cr 102 SmCaPA 94 SmCsPA 101 SmCsPAR ≈ 108 SmCsPR[*] 121 SmCs[*] 143 SmA 148 Iso |
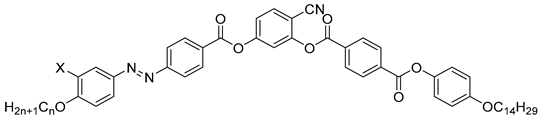
| Compound | X | n | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16a | H | 8 | Iso 164 SmA ~ 154 SmAPR 114 SmCaPAR 109 SmsPA 82 SmCsPA 58 Cr |
| 16b | H | 16 | Iso 163 SmA 156 SmCs[*] ~ 126 SmCsPR[*] 111 SmCsPAR 109 SmsPA 78 SmCsPA 62 Cr |
| 17 | F | 16 | Iso 165 SmA 152 SmCsPR[*] 127 SmCsPAR 120 SmsPA 107 SmCsPA 100 Cr |
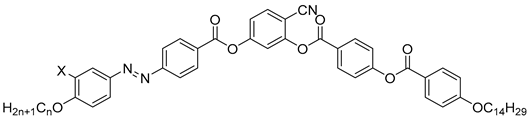
| Compound | X | n | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18a | H | 16 | Iso 123 NCybC 121 SmCsPR[*] 96 SmCsPAR 80 SmsPA 73 SmCs’PA 66 SmCsPA 48 B5 36 M |
| 18b | H | 20 | Iso 130 SmCsPR[*] 98 SmCsPAR 75 SmsPA 36 Cr |
| 19 | F | 16 | Iso 131 SmCsPR[*] 104 SmCsPAR 87 SmsPA 84 SmCs’PA 60 Cr |

| Compound | X | L | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20a | H | OOC | Iso 92 N 64 SmCAPA 46 Cr |
| 20b | H | – * | Iso 98 N 79 SmCX 71 Cr |
| 20c | H | OOC–CH=CH | Iso 107 N 70 Cr |
| 20d | OH | N=CH | Iso 105 SmCAPA 64 Cr |
| 20e | H | CH=CH | Iso 113 N 95 SmCAPA 88 Cr |
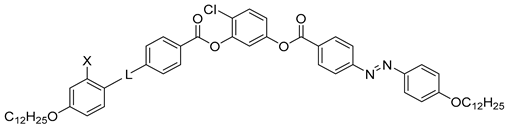
| Compound | X | L | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21a | H | OOC | Iso 97 Cr |
| 21b | H | – * | Iso 94 N 78 Cr |
| 21c | H | OOC–CH=CH | Iso 110 N 83 Cr |
| 21d | OH | N=CH | Iso 113 N 110 SmCAPA 99 Cr |
| 21e | H | CH=CH | Iso 123 Cr |
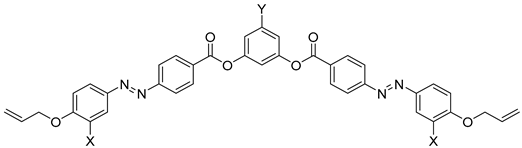
| Compound | X | Y | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22a | H | Cl | Iso 144.3 Smintercal 126.0 Cr |
| 22b | H | COOH | Iso 168.9 Cr |
| 23a | F | Cl | Iso 142.9 Smintercal 126.3 C |
| 23b | F | COOH | Iso 165.0 Cr |
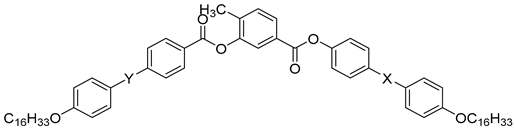
| Compound | X | Y | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 39a | N=N | COO | Iso 106 N 105 SmCs1 92 SmCs2 82 SmCs3 80 DC |
| 39b | OOC | N=N | Iso 108 Cr |
| 39c | N=N | N=N | Iso 117 N 116 SmCs 107 Cr |
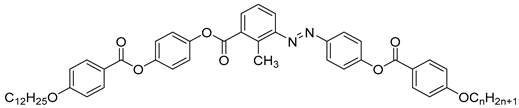
| Compound | n | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|
| 42a | 10 | Cr 101.0 SmA 124.5 N 185.1 Iso |
| 42b | 12 | Cr 98.4 SmX2 126.1 SmX1 130.8 SmA 132.2 N 180.7 Iso |
| 42c | 18 | Cr 99.1 SmX2 117.0 SmX1 1135.5 SmA 145.0 N 167.8 Iso |

| Compound | n | X | Y | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43a | 12 | CH3 | H | Cr 131.4 N 156.7 Iso |
| 43b | 18 | CH3 | H | Cr 129.5 N 145.0 Iso |
| 44a | 12 | H | CH3 | Cr 111.7 N 158.3 Iso |
| 44b | 18 | H | CH3 | Cr 96.3 SmX1 106.0 SmA 107.5 N 148.0 Iso |
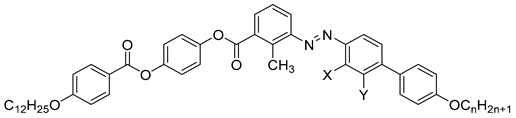
| Compound | n | X | Y | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45a | 12 | Cl | H | Iso 149.0 N 114.4 Cr |
| 45b | 18 | Cl | H | Iso 139.0 N 115.4 SmA 112.3 Cr |
| 46a | 12 | H | Cl | Iso 160.4 N 106.7 SmA 101.0 SmX2 93.0 Cr |
| 46b | 18 | H | Cl | Iso 149.0 N 119.3 SmA 111.8 SmX1 96.4 SmX2 91.0 Cr |
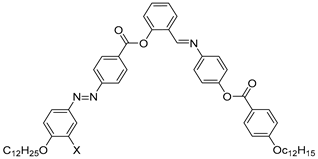
| Compound | X | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|
| 54 | H | Cr 112.7 SmAPA 116.6 Iso |
| 55 | Cl | Cr 104.2 Iso |
| 56 | F | Cr 102.5 B5 108.1 Iso |

| Compound | n | X | Y | Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62a | 4 | Cl | H | Iso 147.9 N 79.7 Cr |
| 62b | 12 | Cl | H | Iso 110.6 N 86.0 Cr |
| 63a | 4 | H | Cl | Iso 140.3 N 97.0 Cr |
| 63b | 12 | H | Cl | Iso 113.6 N 95.4 SmA 83.4 Cr |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ting, T.X.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Influences of Central Units and Terminal Chains on the Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2020, 10, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100857
Ting TX, Sarjadi MS, Rahman ML. Influences of Central Units and Terminal Chains on the Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals. Crystals. 2020; 10(10):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100857
Chicago/Turabian StyleTing, Tang Xin, Mohd Sani Sarjadi, and Md Lutfor Rahman. 2020. "Influences of Central Units and Terminal Chains on the Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals" Crystals 10, no. 10: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100857
APA StyleTing, T. X., Sarjadi, M. S., & Rahman, M. L. (2020). Influences of Central Units and Terminal Chains on the Banana-Shaped Liquid Crystals. Crystals, 10(10), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100857





