Iron-Doped Lithium Tantalate Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering: A Study of the Iron Role in the Structure and the Derived Magnetic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
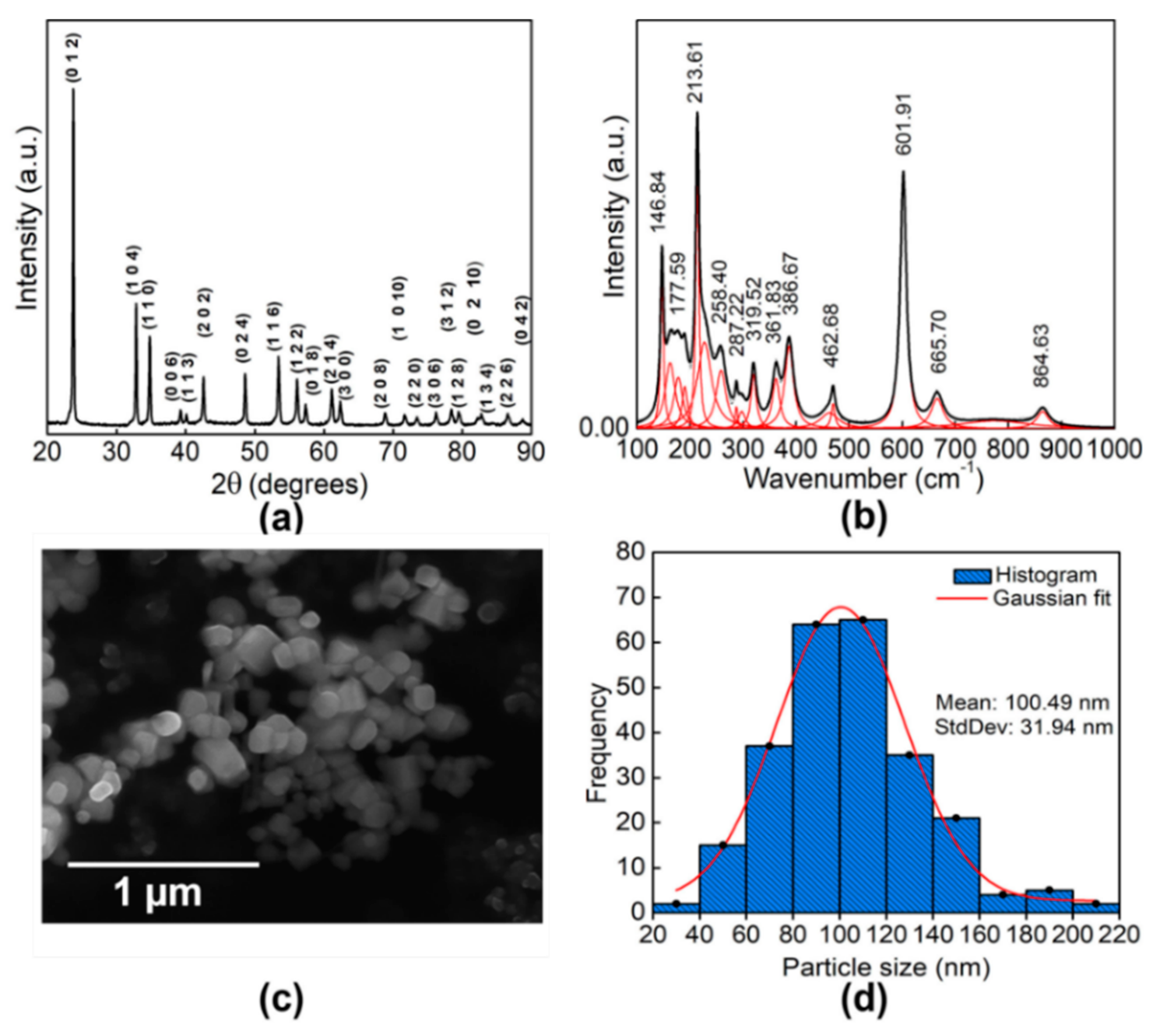
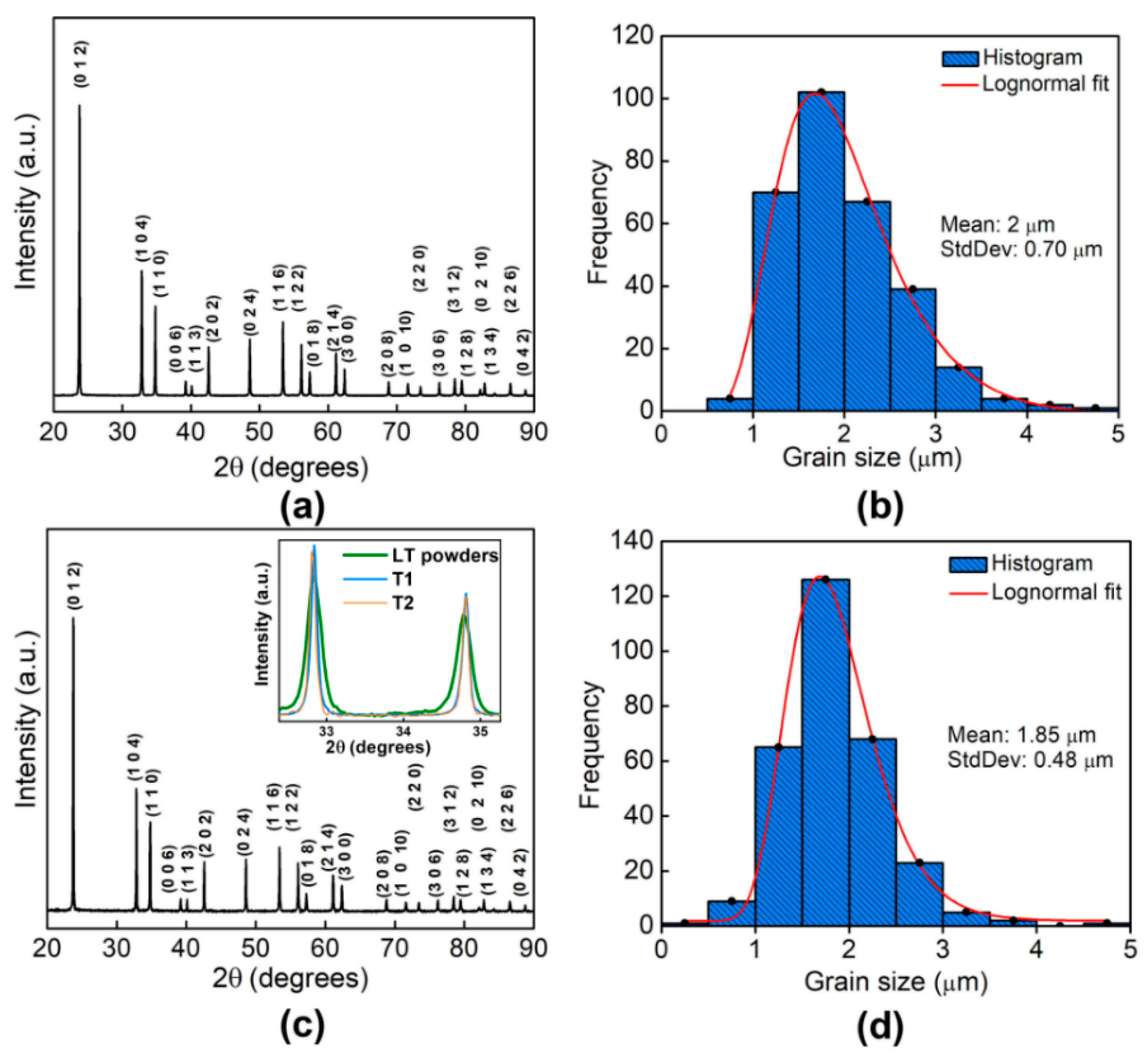
3.1. Structural and Morphological Properties of the LT NPs, T1, and T2
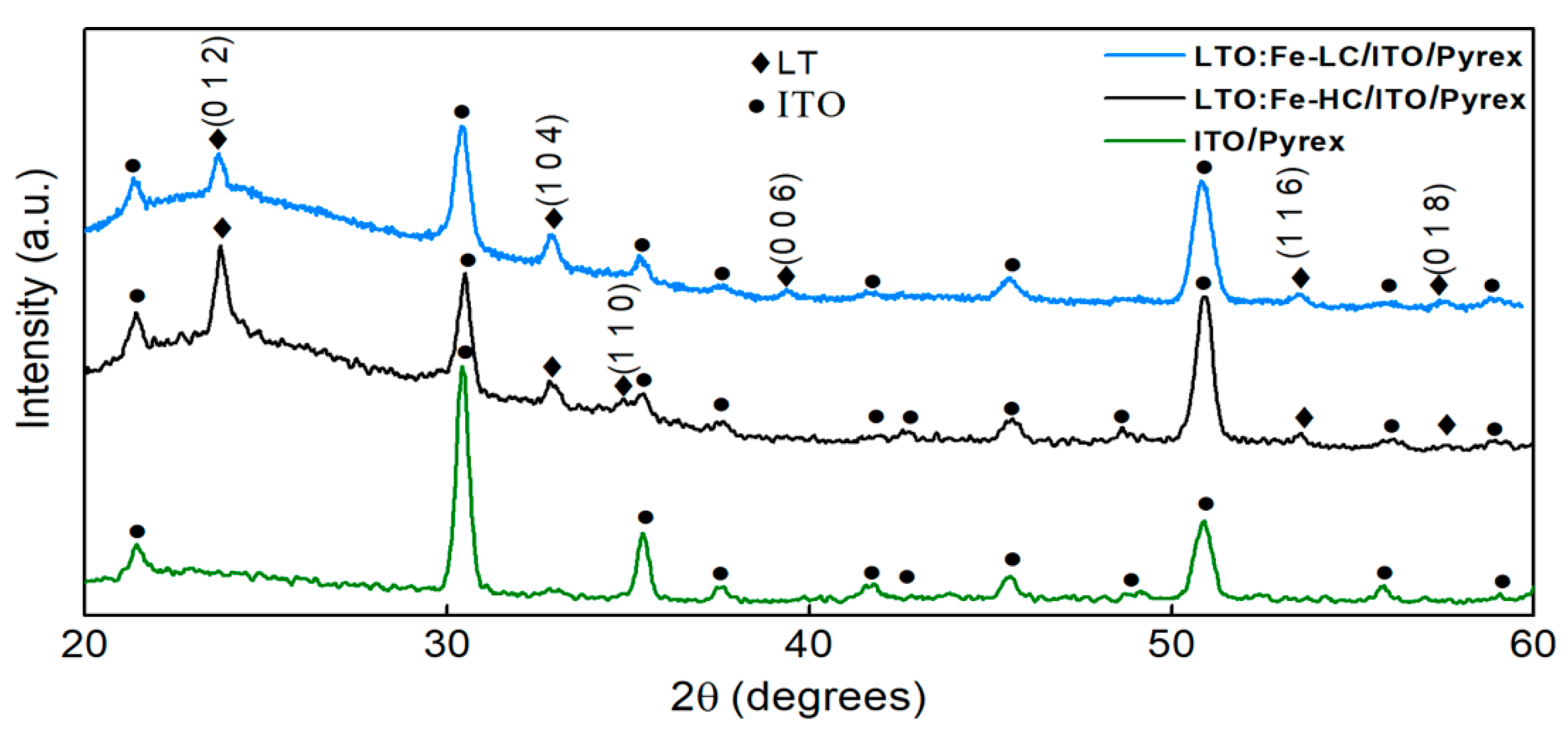
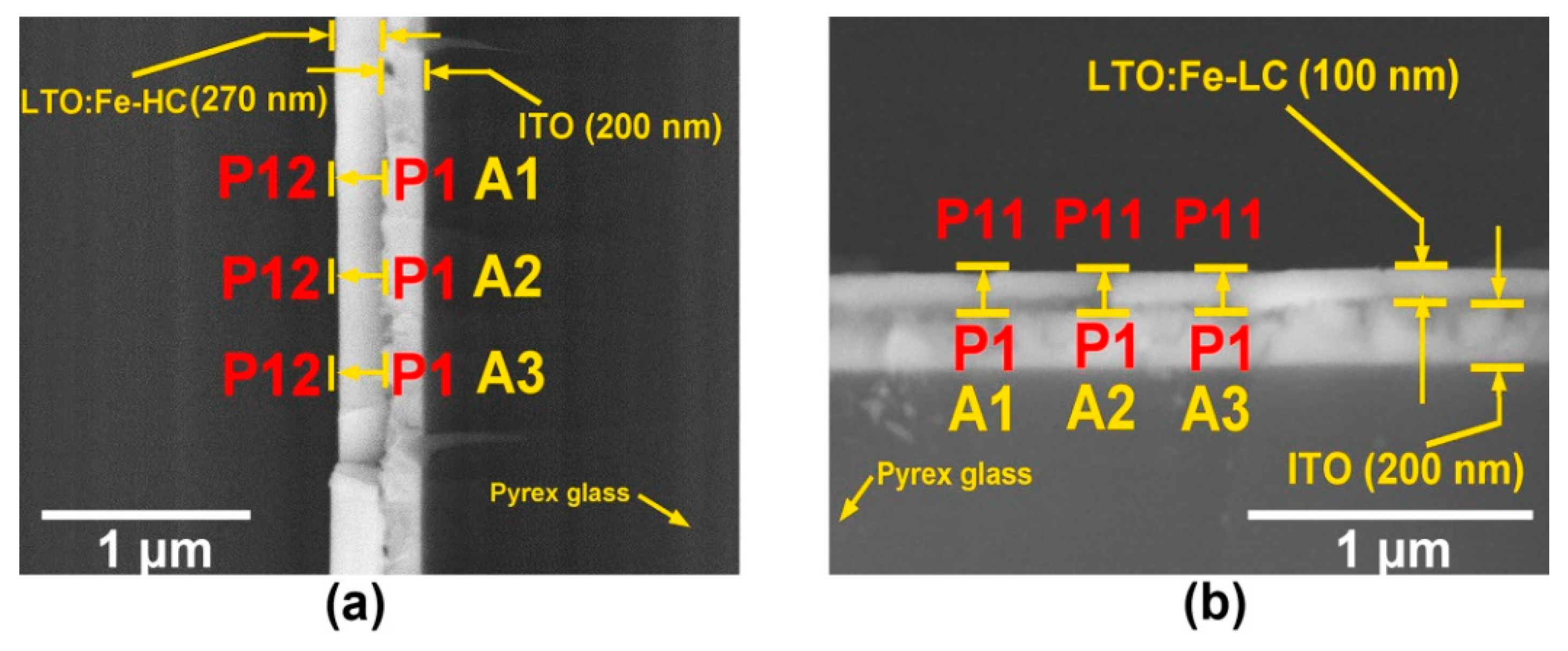
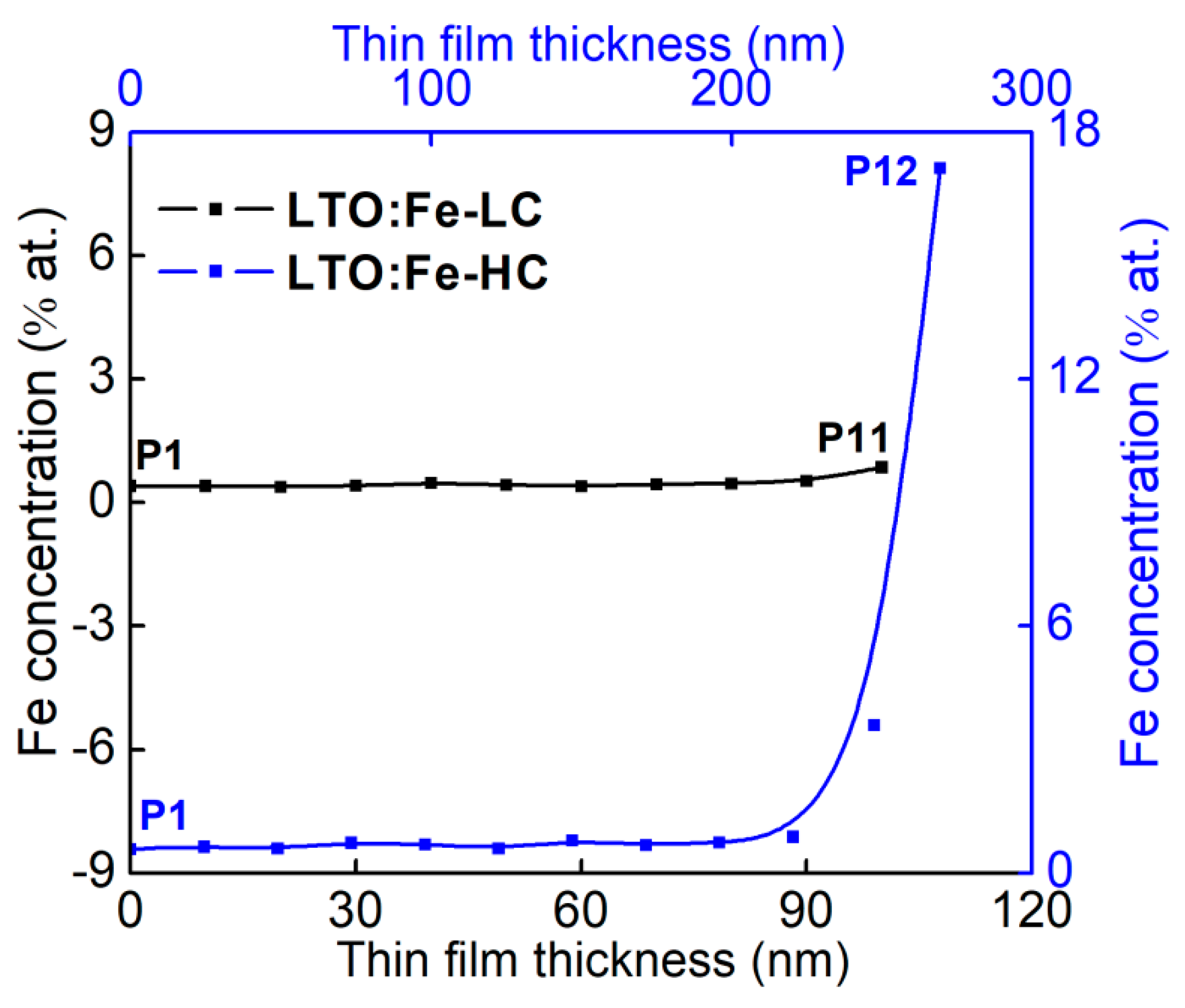
3.2. Structural and Morphological Properties of the LTO:Fe-LC and LTO:Fe-HC Thin Films
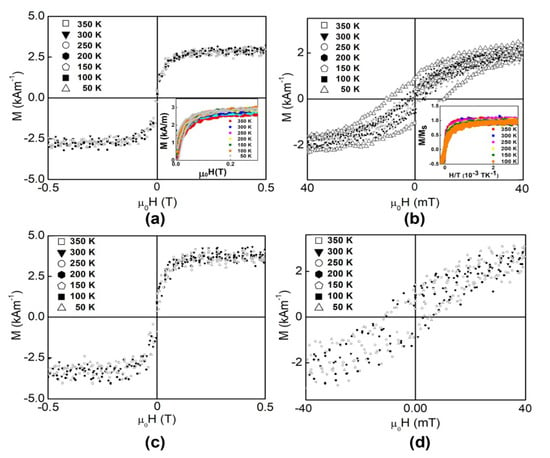
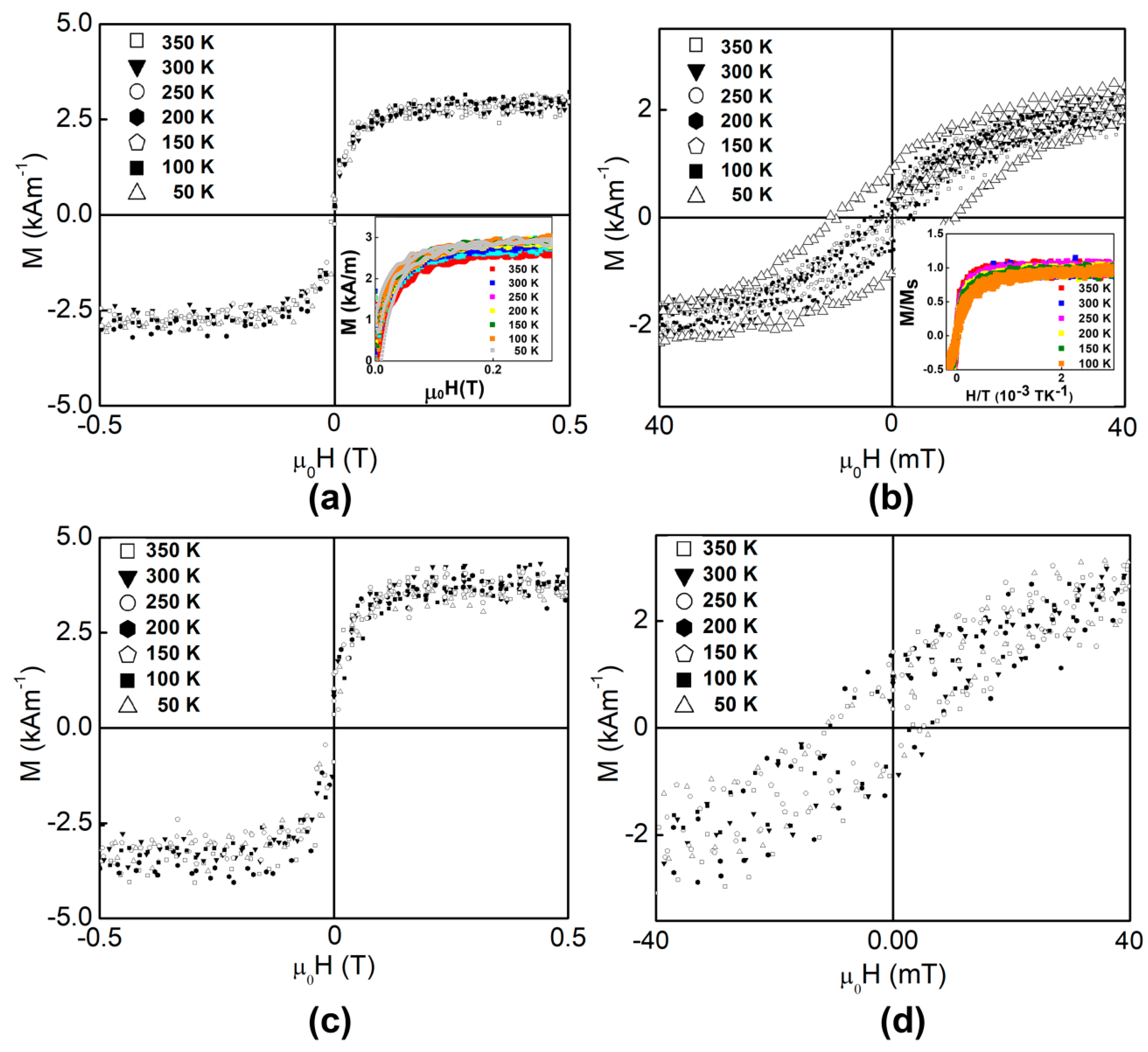
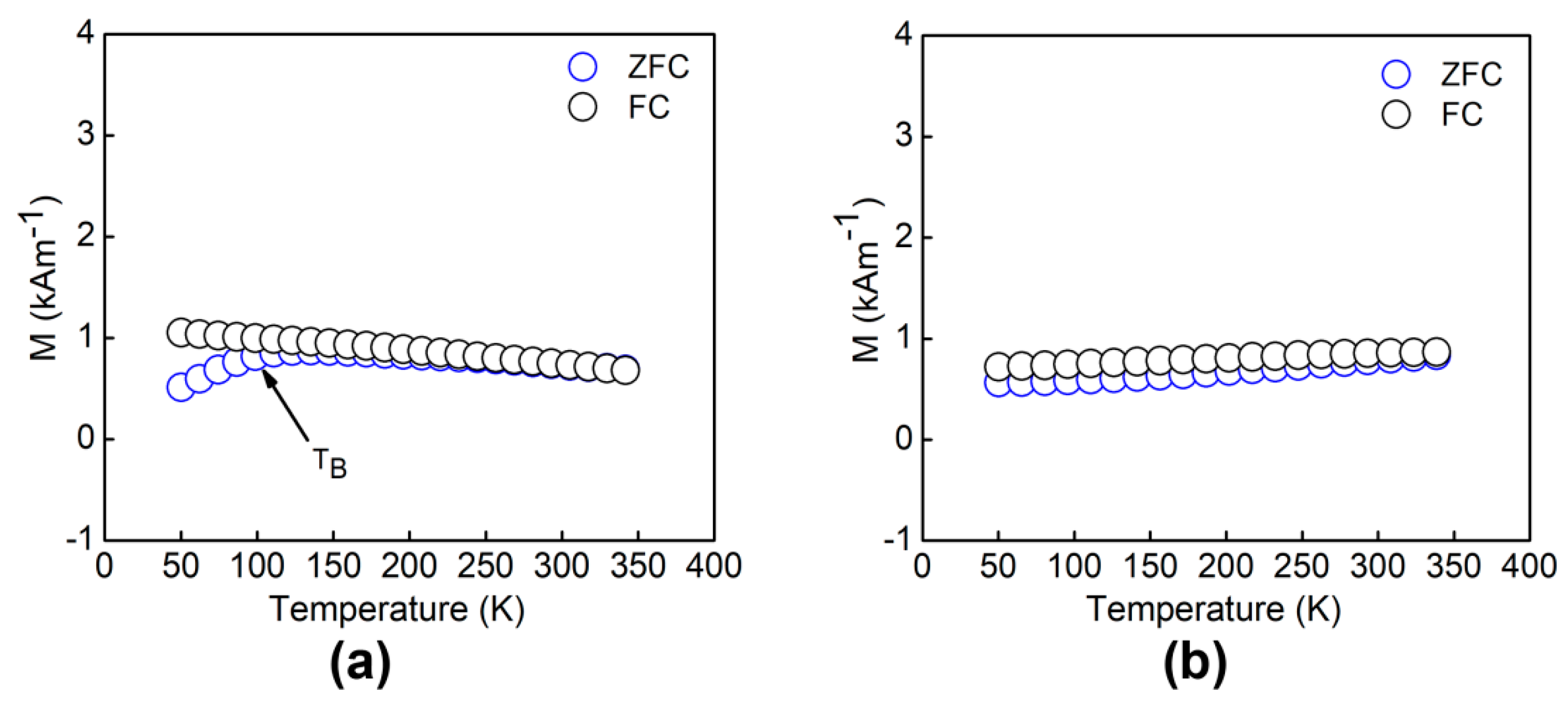
3.3. Magnetic Properties of the LTO:Fe-HC and LTO:Fe-LC Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ishihara, T. Inorganic Perovskite Oxides. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Kasap, S., Peter, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.H.; Sheng, P.; Luo, J.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Pan, F.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Z. Strong d–d electron interaction inducing ferromagnetism in Mn-doped LiNbO3. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Zhou, X.; Ge, S. Raman scattering and room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped SrTiO3 particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 9233–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.C.; Gupta, V.; Kaur, J.; Kotnala, R.K. Raman spectra, photoluminescence, magnetism and magnetoelectric coupling in pure and Fe doped BaTiO3 nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 578, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.H.; Shen, X.; Ni, X.D.; Yao, Y.; Yu, R.C. Room-Temperature Magnetism Realized by Doping Fe into Ferroelectric LiTaO3. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2014, 31, 017501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Sheng, P.; Tang, G.S.; Pan, F.; Yan, W.S.; Hu, F.C.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, D. Electronic structure and magnetism of Fe-doped LiNbO3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.; Wöhlecke, M. Lithium Niobate: Defects, Photorefraction and Ferroelectric Switching, 1st ed.; Hull, R., Osgood, R.M., Parisi, J., Warlimont, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3540707662. [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi, S.; Tomita, K.; Iwaoka, M.; Kato, H.; Kakihana, M. The hydrothermal and solvothermal synthesis of LiTaO3 photocatalyst: Suppressing the deterioration of the water splitting activity without using a cocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 5638–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, M.; Yang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Fang, M. Powder synthesis and properties of LiTaO3 ceramics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, E.; Benke, A.; Gerth, K.; Böttcher, H.; Mehner, E.; Klein, C.; Krause-Buchholz, U.; Bergmann, U.; Pompe, W.; Meyer, D.C. Pyroelectrocatalytic Disinfection Using the Pyroelectric Effect of Nano- and Microcrystalline LiNbO3 and LiTaO3 Particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, N.; Takaoka, J.; Chino, T.; Fukami, T.; Elouadi, B. Improved Piezoelectric Properties of LiTaO3 Family Solid Solution Ceramics with Modified Composition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 7426–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Gou, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y. Influence of thermal annealing on structural and optical properties of RF-sputtered LiTaO3 thin films. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 026405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.; Gou, J. Study of the crystalline and optical properties of lithium tantalate thin films deposited by high power RF magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 026402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combette, P.; Nougaret, L.; Giani, A.; Pascal-delannoy, F. RF magnetron-sputtering deposition of pyroelectric lithium tantalate thin films on ruthenium dioxide. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 304, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougaret, L.; Combette, P.; Pascal-Delannoy, F. Growth of lithium tantalate thin films by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering with lithium enriched target. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Qian, W.; Li, K.; Xie, J.S. Ferroelectric Property of Ion Beam Enhanced Deposited Lithium Tantalate Thin Film. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 335, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riefer, A.; Sanna, S.; Schmidt, W.G. LiNb1-xTaxO3 Electronic Structure and Optical Response from First-Principles Calculations. Ferroelectrics 2013, 447, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, K.; Liu, M.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, D. An optical spectroscopy study of defects in lithium tantalate single crystals. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 2531–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; Bhaumik, I.; Ganesamoorthy, S.; Bright, R.; Soharab, M.; Karnal, A.; Gupta, P. Control of Intrinsic Defects in Lithium Niobate Single Crystal for Optoelectronic Applications. Crystals 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.G.; Chiu, M. Substitution site of the Fe3+ impurity in crystalline LiNbO3. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 12556–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gog, T.; Schotters, P.; Falta, J.; Materlik, G.; Grodzicki, M. The lattice position of Fe in Fe-doped LiNbO 3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 7, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignoni, S.; Fontana, M.D.; Bazzan, M.; Ciampolillo, M.V.; Zaltron, A.M.; Argiolas, N.; Sada, C. Micro-Raman analysis of Fe-diffused lithium niobate waveguides. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 101, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, G.J.; Kuo, C.L.; Hsieh, P.H.; Hwang, W.S. Investigation of the Defect Structure of Congruent and Fe-Doped LiNbO3 Powders Synthesized by the Combustion Method. Materials 2017, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitova, T.; Hormes, J.; Falk, M.; Buse, K. Site-selective investigation of site symmetry and site occupation of iron in Fe-doped lithium niobate crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olimov, K.; Falk, M.; Buse, K.; Woike, T.; Hormes, J.; Modrow, H. X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy investigations of valency and lattice occupation site of Fe in highly iron-doped lithium niobate crystals. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 5135–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T.S.; Catlow, C.R.A.; Chadwick, A.V.; Cole, M.; Geatches, R.M.; Greaves, G.N.; Tomlinson, S.M. Studies of cation dopant sites in metal oxides by EXAFS and computer-simulation techniques. J. Mater. Chem. 1992, 2, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, E.; Olaya, J.; Cubillos, G. Thin Film Growth Through Sputtering Technique and Its Applications. In Crystallization—Science and Technology; Barsi Andreeta, M.R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 398–432. [Google Scholar]
- Crystallography Open Database. Available online: http://www.crystallography.net/cod/2101846.html (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Sanna, S.; Neufeld, S.; Rüsing, M.; Berth, G.; Zrenner, A.; Schmidt, W.G. Raman scattering efficiency in LiTaO3 and LiNbO3 crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 224302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repelin, Y.; Husson, E.; Bennani, F.; Proust, C. Raman spectroscopy of lithium niobate and lithium tantalate. Force field calculations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1999, 60, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, H.P.; Harold, P.; Alexander, L.E.; Leroy, E. X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1974; ISBN 9780471493693. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.N. Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd ed.; Dekker, M., Ed.; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780824709884. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Kong, Y.; Yan, W.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; et al. Determination of the composition of lithium tantalate by means of Raman and OH− absorption measurements. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 95, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro-Ruiz, C.; Sánchez-Dena, O.; Cabral-Larquier, E.; Elizalde-Galindo, J.; Farías, R. Structural and Magnetic Behavior of Oxidized and Reduced Fe Doped LiNbO3 Powders. Crystals 2018, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Kuo, C.L.; Hsieh, P.H.; Hwang, W.S. Raman spectra and ferromagnetism of nanocrystalline Fe-doped Li0.43Nb0.57O3+δ. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 10764–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.D.; Bourson, P. Microstructure and defects probed by Raman spectroscopy in lithium niobate crystals and devices. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 40602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Singh, P. A review of the structures of oxide glasses by Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67583–67609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengue, O.M.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Lanfredi, A.J.C.; Leite, E.R.; Chiquito, A.J. Structural characterization of indium oxide nanostructures: A Raman analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 45401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachiri, E.; El Bachiri, A.; El Hasnaoui, M.; Bennani, F.; Bousselamti, M. Effect of Ni-doping Charge on Structure and Properties of LiNbO3. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 3353–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials, 2nd ed.; Hanzo, L., Ed.; IEEE/Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780471477419. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Hsu, Y.J.; Lin, Y.F.; Lu, S.Y. Superparamagnetism Found in Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Nanowires: Mn-Doped CdSe. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 17964–17968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.C.; Goya, G.F.; Jardim, R.F.; Muccillo, R.; Carreño, N.L.V.; Longo, E.; Leite, E.R. Superparamagnetism and magnetic properties of Ni nanoparticles embedded in SiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.P.; da Silva, R.C.; Cruz, M.M.; Godinho, M. Influence of structural transitions of BaTiO3 on the magnetic properties of Fe nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 200, 072014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yao, T.; Pan, Z.; Mai, C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Z.; Hu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, W. Role of Co clusters in wurtzite Co:ZnO dilute magnetic semiconductor thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 043903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, M.G.; Jang, H.M.; Ryu, S.; Kim, Y.M. Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1338–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.R.; Ogale, S.B.; Higgins, J.S.; Zheng, H.; Millis, A.J.; Kulkarni, V.N.; Ramesh, R.; Greene, R.L.; Venkatesan, T. Co-occurrence of Superparamagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Highly Reduced Cobalt-Doped Rutile TiO2−δ Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 166601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Zhou, H.M.; Beyermann, W.P.; Liu, J.L. Epitaxial Mn-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor thin films grown by plasma-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 314, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Mlack, J.T.; Venkatesan, M.; Stamenov, P. Magnetization Process in Dilute Magnetic Oxides. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2501–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Venkatesan, M.; Fitzgerald, C.B. Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackland, K.; Monzon, L.M.A.; Venkatesan, M.; Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism of Nanostructured CeO2. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosivand, S.; Monzon, L.M.A.; Ackland, K.; Kazeminezhad, I.; Coey, J.M.D. Structural and magnetic properties of sonoelectrocrystallized magnetite nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Dilute magnetic oxides. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2006, 10, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Haque, S.M.; Shukla, D.; Choudhary, R.J.; Jha, S.N.; Bhattacharyya, D. X-ray absorption spectroscopy of Mn doped ZnO thin films prepared by rf sputtering technique. AIP Adv. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhu, L.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Ye, Z. Acceptor defect-participating magnetic exchange in ZnO:Cu nanocrystalline film: Defect structure evolution, Cu-N synergetic role and magnetic control. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1330–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.K.; Dhawan, M.S.; Gaur, S.K.; Dolia, S.N.; Kumar, S.; Shripathi, T.; Deshpande, U.P.; Xing, Y.T.; Saitovitch, E.; Garg, K.B. Study of ferromagnetism in Mn doped ZnO dilute semiconductor system. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, N.; Susila, V.M.; Ramachandran, K. On the possibility of ferromagnetism in CdO:Mn at room temperature. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2011, 6, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depla, D.; Mahieu, S.; Greene, J.E. Sputter Deposition Processes. In Handbook of Deposition Technologies for Films and Coatings; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 253–296. ISBN 9780815520313. [Google Scholar]
- Khalaf, M.K.; Al-Taay, H.F.; Ali, D.S. Effect of radio frequency magnetron sputtering power on structural and optical properties of Ti6Al4V thin films. Photonic Sens. 2017, 7, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Sun, Y.; Hing, P. The influence of deposition conditions on structure and morphology of aluminum nitride films deposited by radio frequency reactive sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2003, 434, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Nénert, G. The HighScore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.J.B.; Redfern, S.A.T. Unit cell refinement from powder diffraction data: The use of regression diagnostics. Mineral. Mag. 1997, 61, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| LTO:Fe-LC | LTO:Fe-HC | |
|---|---|---|
| Target | T1 (LT-0.5%wt. Fe) | T2 (LT-1.8%wt. Fe) |
| Atmosphere | Argon | Argon |
| Handling pressure | 0.4 Pa | 0.4 Pa |
| R.F. gun power | 30 W | 50 W |
| Substrate temperature | 450 °C | 450 °C |
| Substrate-target distance | 16 cm | 16 cm |
| Deposition time | 1.5 h | 2.5 h |
| Lattice Parameters (Å) | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | Weighted R Profile | Goodness of Fit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b | c | ||||
| LT powders | 5.155 | 13.766 | 316.79 | 8.21 | 4.08 |
| T1 | 5.154 | 13.780 | 316.99 | 9.26 | 5.03 |
| T2 | 5.152 | 13.783 | 316.82 | 10.38 | 2.05 |
| LTO:Fe-HC | 5.140 | 13.753 | 314.66 | 5.73 | 1.25 |
| LTO:Fe-LC | 5.149 | 13.700 | 314.59 | Sigmafit = 4.96 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villalobos Mendoza, S.D.; Holguín Momaca, J.T.; Elizalde Galindo, J.T.; Carrillo Flores, D.M.; Olive Méndez, S.F.; Farías Mancilla, J.R. Iron-Doped Lithium Tantalate Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering: A Study of the Iron Role in the Structure and the Derived Magnetic Properties. Crystals 2020, 10, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10010050
Villalobos Mendoza SD, Holguín Momaca JT, Elizalde Galindo JT, Carrillo Flores DM, Olive Méndez SF, Farías Mancilla JR. Iron-Doped Lithium Tantalate Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering: A Study of the Iron Role in the Structure and the Derived Magnetic Properties. Crystals. 2020; 10(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillalobos Mendoza, Sergio David, José Trinidad Holguín Momaca, José Trinidad Elizalde Galindo, Diana María Carrillo Flores, Sion Federico Olive Méndez, and José Rurik Farías Mancilla. 2020. "Iron-Doped Lithium Tantalate Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering: A Study of the Iron Role in the Structure and the Derived Magnetic Properties" Crystals 10, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10010050
APA StyleVillalobos Mendoza, S. D., Holguín Momaca, J. T., Elizalde Galindo, J. T., Carrillo Flores, D. M., Olive Méndez, S. F., & Farías Mancilla, J. R. (2020). Iron-Doped Lithium Tantalate Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering: A Study of the Iron Role in the Structure and the Derived Magnetic Properties. Crystals, 10(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10010050