Synergy between Ionic Liquids and CuCl2 in Gas–Liquid Phase Reactions of Acetylene Hydrochlorination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
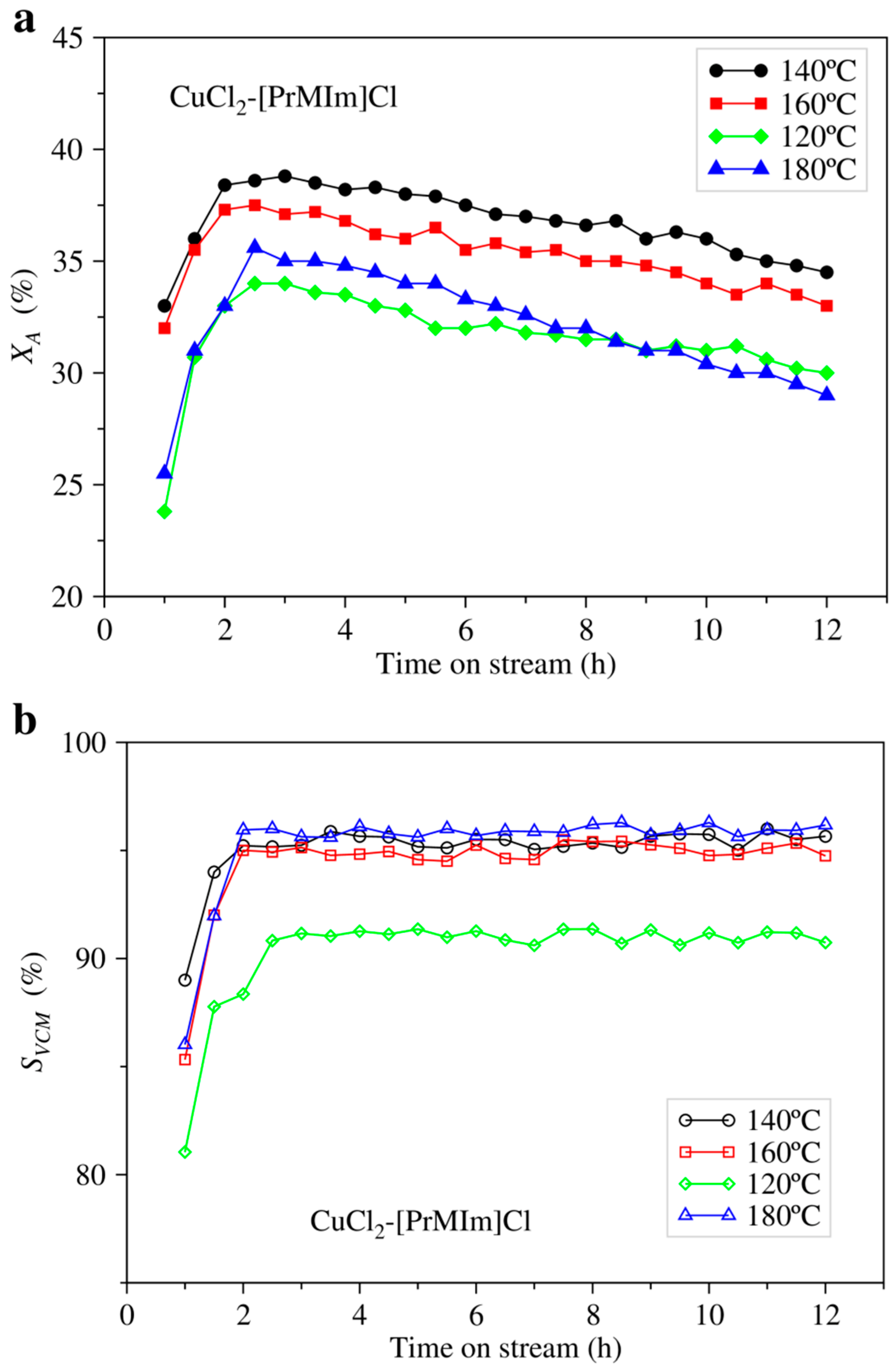
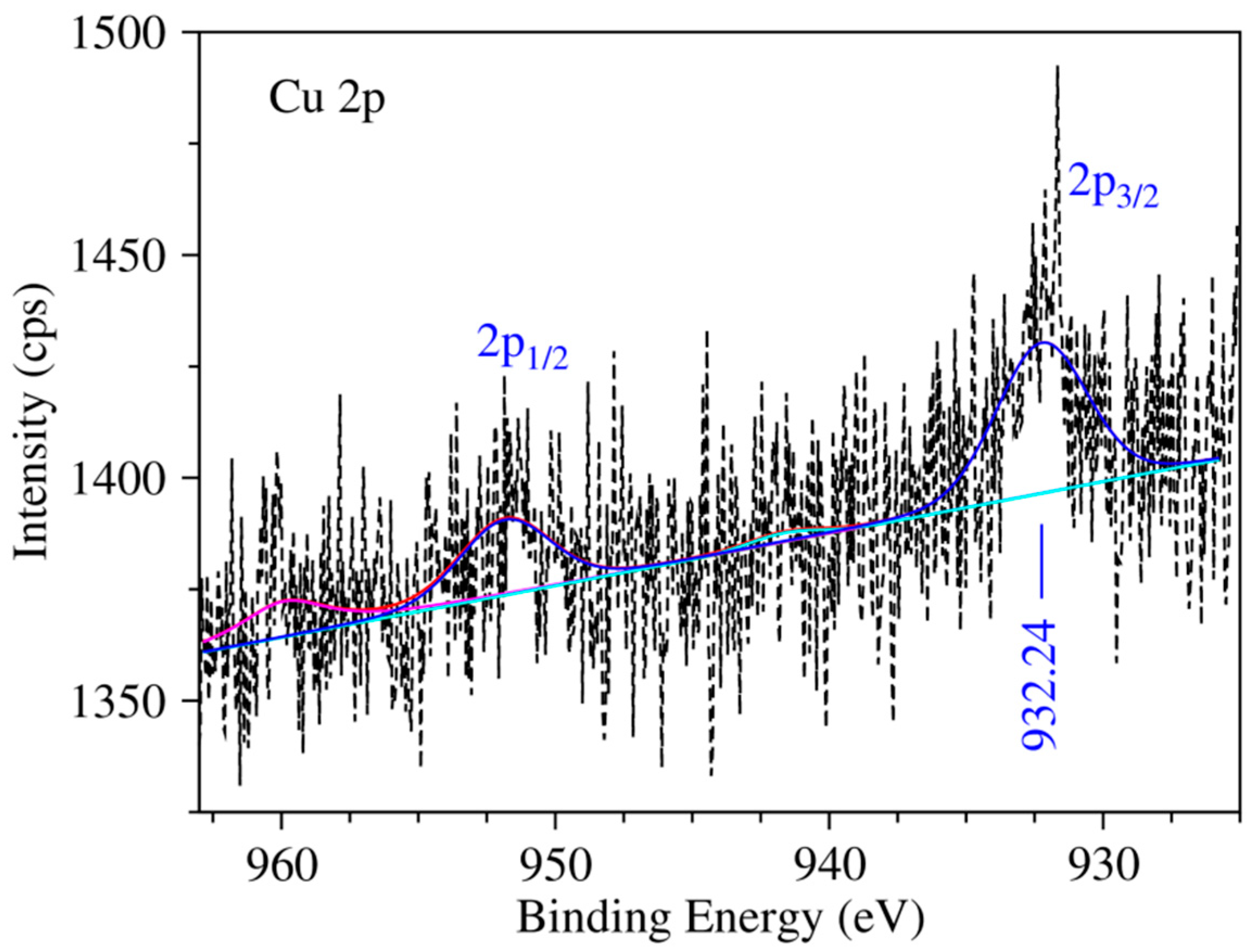
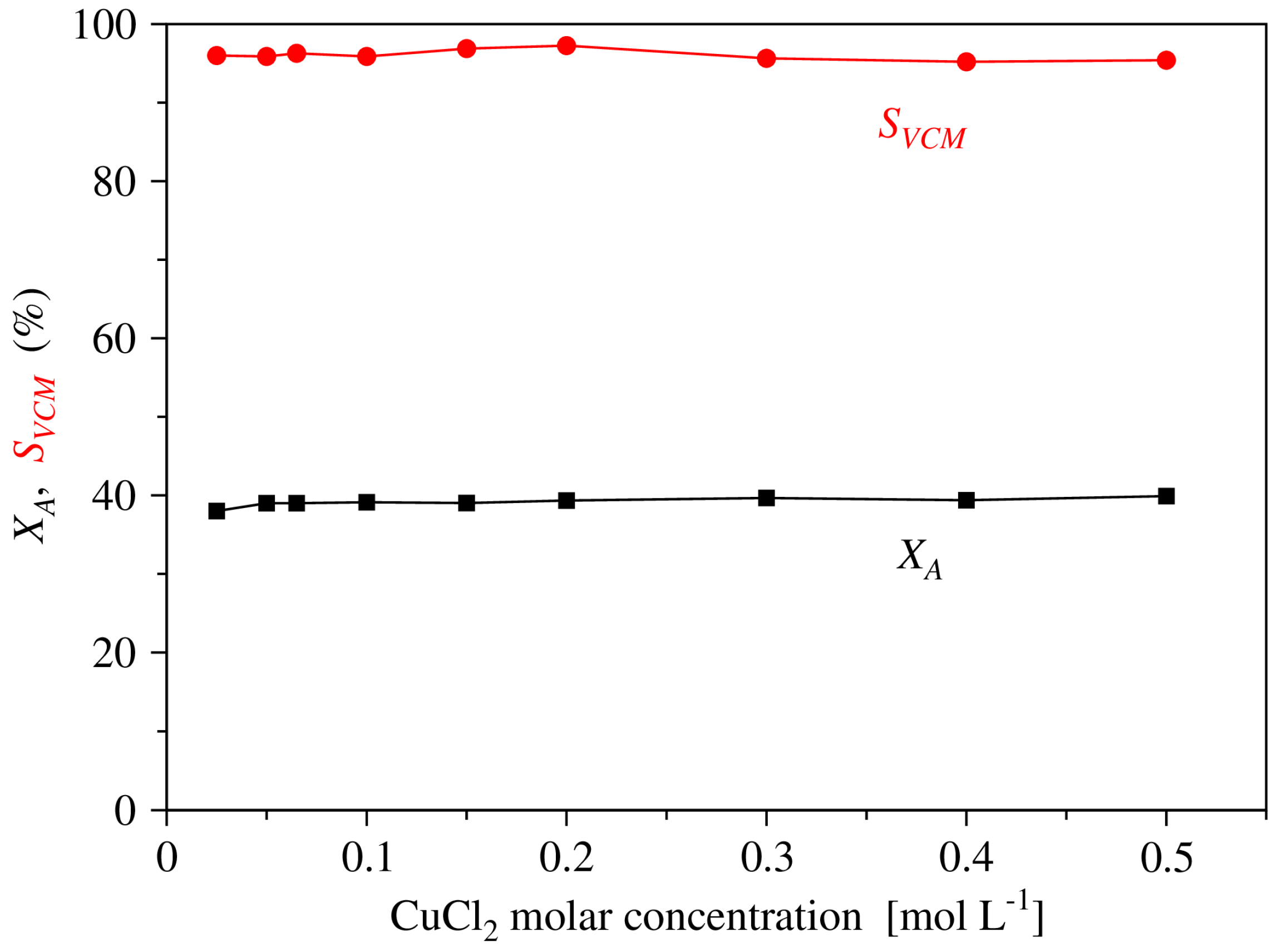
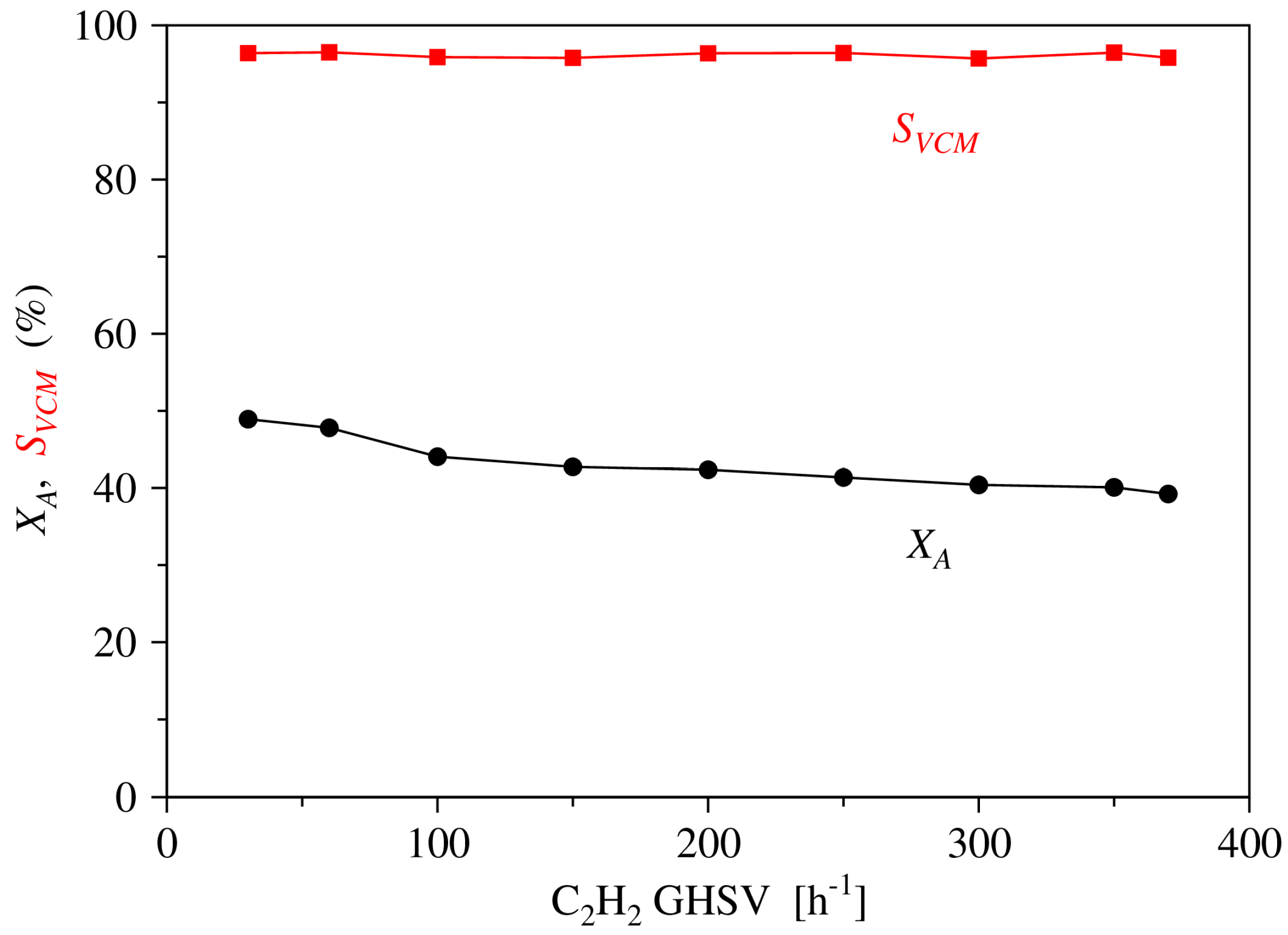
2.1. Experimental Results
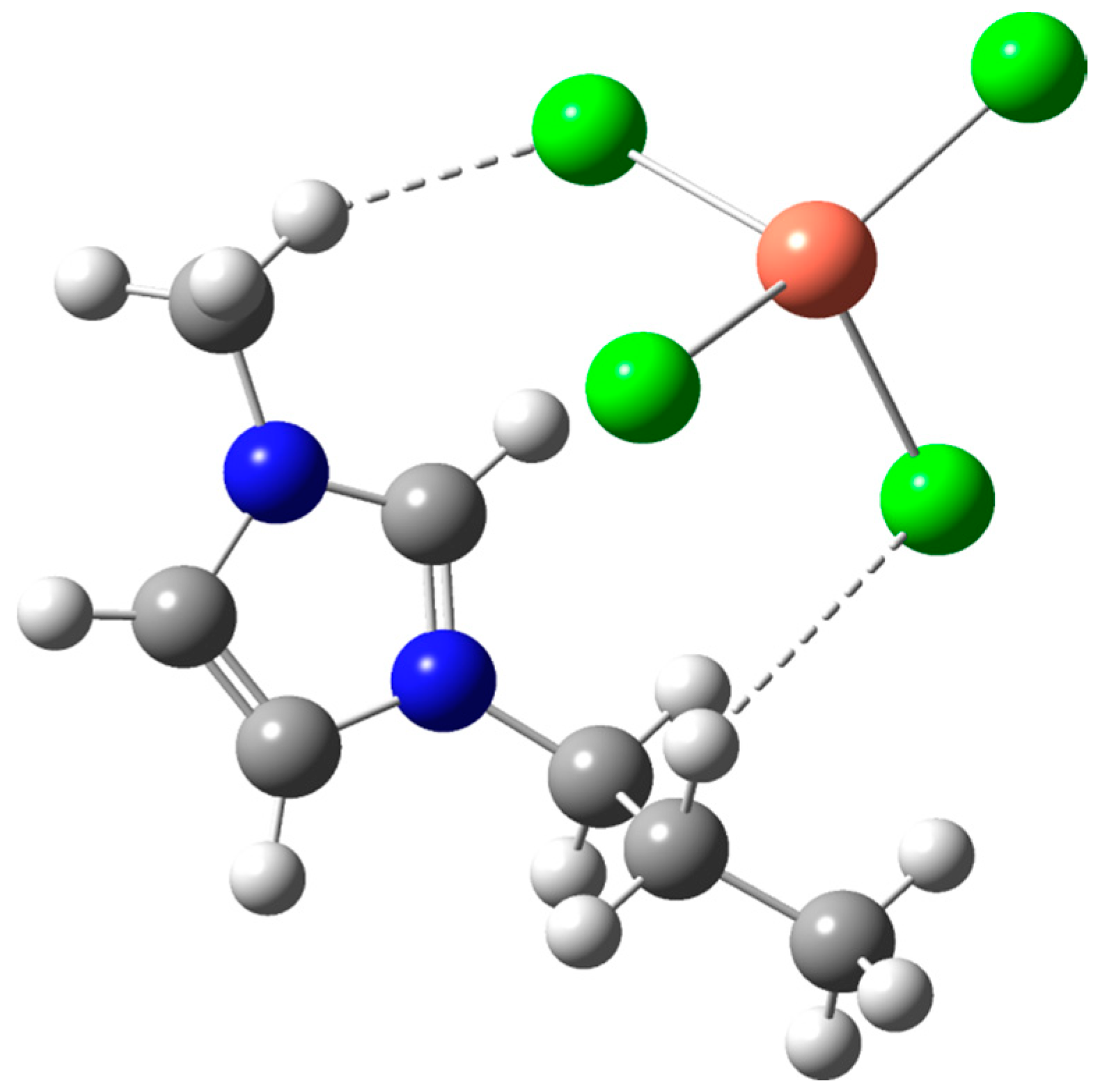
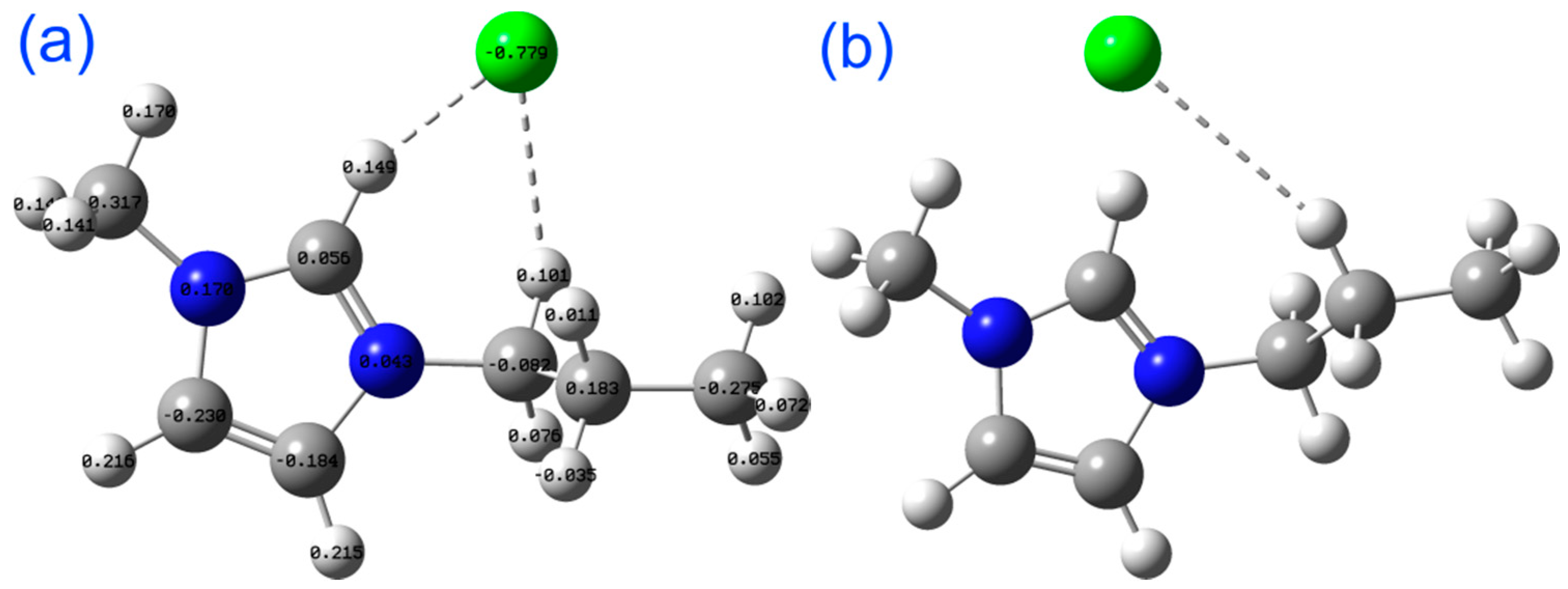
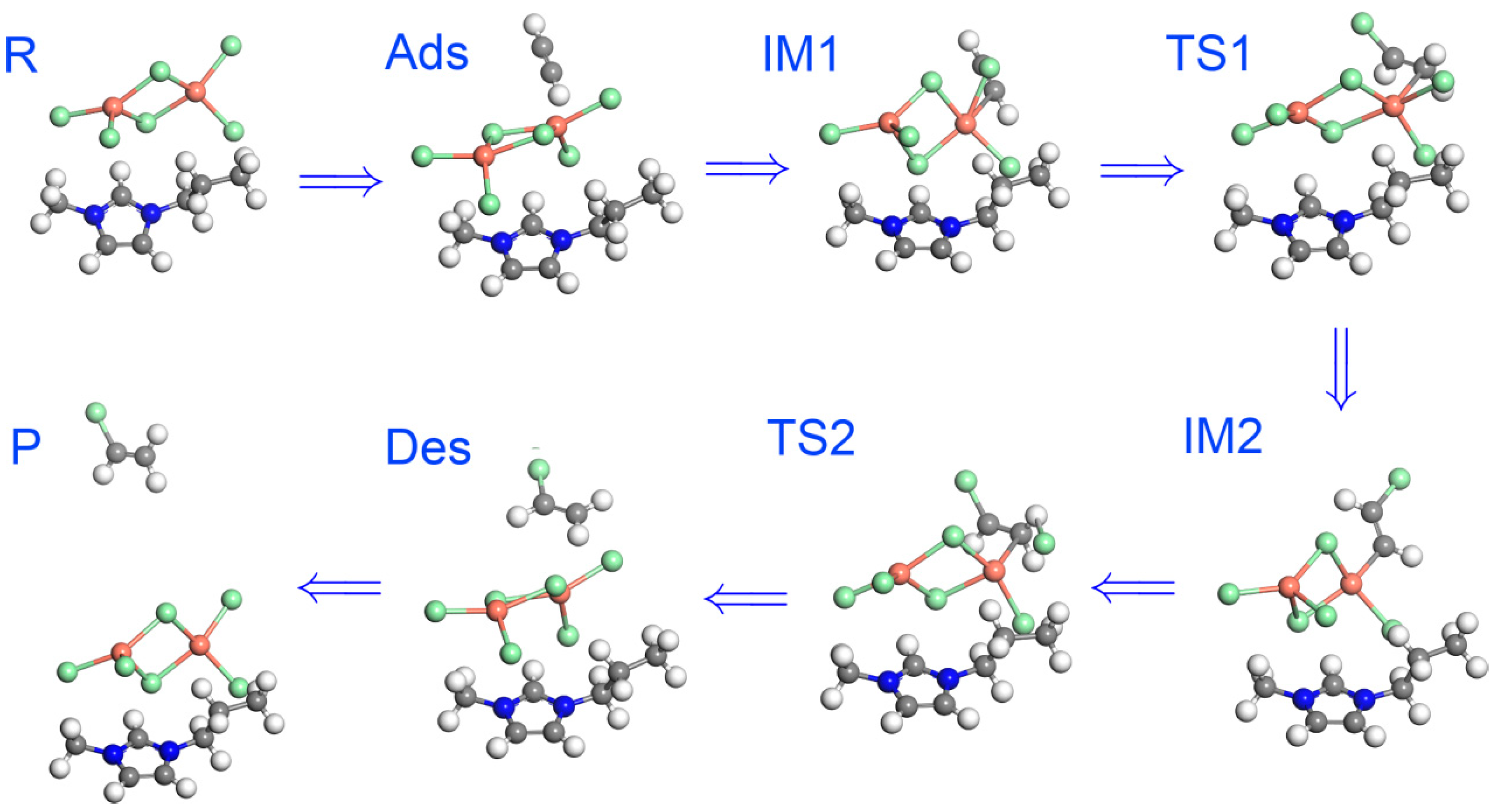
2.2. Mechanistic Study Using DFT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Methods of DFT Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchings, G.J. Vapor phase hydroehlorination of acetylene: Correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 96, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.; Carthey, N.; Hutchings, G.J. Discovery, Development, and Commercialization of Gold Catalysts for Acetylene Hydrochlorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14548–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malta, G.; Freakley, S.J.; Kondrata, S.A.; Hutchings, G.J. Acetylene hydrochlorination using Au/carbon: a journey towards single site catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11733–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Luo, G.H. Green production of PVC from laboratory to industrialization: State-of-the-art review of heterogeneous non-mercury catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 65, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, B.; Coville, N.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Vapour phase hydrochlorination of acetylene with group VIII and IB metal chloride catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1988, 43, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieiaut, J.P.; Vandalfsen, J. Undefined. Rec. Truv. Chim. 1932, 51, 636. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Shen, B.X.; Song, Q.L. Kinetics of acetylene hydrochlorination over bimetallic Au–Cu/C catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2010, 134, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, B.X.; Zhao, J.G.; Bi, X.T. Trimetallic Au-Cu-K/AC for acetylene hydrochlorination. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Dai, B.; Wang, X.G.; Xu, L.L.; Zhu, M.Y. Hydrochlorination of acetylene to vinyl chloride monomer over bimetallic Au–La/SAC catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Li, W.; Jin, Y.H.; Sheng, W.; Hu, M.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.L. Ru-Co(III)-Cu(II)/SAC catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 189, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, J.T.; Xu, J.H.; Ni, J.; Zhang, T.T; Xu, X.L.; Li, X.N. Activated-carbon-supported Gold–Cesium(I) as highly effective catalysts for hydrochlorination of acetylene to vinyl chloride. ChemPlusChem 2015, 80, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Di, X.X.; Xu, J.T.; Gu, S.C.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ni, J.; Li, X.N. Activated carbon supported ternary Gold–Cesium(I)–Indium(III) catalyst for the hydrochlorination of acetylene. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4973–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Di, X.X.; Di, S.X.; Wang, B.L.; Yue, Y.X.; Sheng, G.F; Lai, H.X.; Guo, L.L.; Wang, H.; et al. Carbon-supported perovskite-like CsCuCl3 nanoparticles: a highly active and cost-effective heterogeneous catalyst for the hydrochlorination of acetylene to vinyl chloride. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gu, S.C.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Di, X.X.; Pan, Z.Y.; Li, X.N. Promotional effect of copper(II) on an activated carbon supported low content bimetallic Gold–Cesium(I) catalyst in acetylene hydrochlorination. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101427–101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.L.; Lai, H.X.; Yue, Y.X.; Sheng, G.F; Deng, Y.Q.; He, H.H.; Guo, L.L.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.N. Zeolite supported ionic liquid catalysts for the hydrochlorination of acetylene. Catalysts 2018, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vekariya, R.L. A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Song, Y.H.; Jin, R.; Shi, J.; Yu, Z.Y.; Cao, S.K. Gas–liquid acetylene hydrochlorination under nonmercuric catalysis using ionic liquids as reaction media. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gu, S.C.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Yu, Y.; Di, X.X.; Ni, J.; Pan, Z.Y.; Li, X.N. Supported ionic-liquid-phase-stabilized Au(III) catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Di, S.X.; Wang, B.L.; Xu, H.; Ni, J.; Guo, L.L.; Pan, Z.Y.; Li, X.N. Stabilizing Au(III) in supported-ionic-liquid-phase (SILP) catalyst using CuCl2 via a redox mechanism. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 206, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y.Z.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J.L. Improvement of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on the activity of ruthenium catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. Mol. Catal. 2017, 443, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.F.; Xu, S.G.; Liu, Y.L.; Cao, S.K. Mechanistic study on metal-free acetylene hydrochlorination catalyzed by imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Mol. Catal. 2018, 461, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yue, Y.X.; Sheng, G.F.; Wang, B.L.; Lai, H.X.; Di, S.X.; Zhai, Y.Y.; Guo, L.L.; Li, X.N. Supported ionic liquid-palladium catalyst for the highly effective hydrochlorination of acetylene. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.T.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, X.N.; Di, X.X.; Ni, J.; Wang, J.G.; Cen, J. Influence of surface chemistry of activated carbon on the activity of gold/activated carbon catalyst in acetylene hydrochlorination. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14272–14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Di, X.X.; Xu, J.T.; Xu, J.H.; Feng, F.; Ni, J.; Li, X.N. Nitrogen-modified activated carbon supported bimetallic Gold–Cesium(I) as highly active and stable catalyst for the hydrochlorination of acetylene. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6925–6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, J.T.; Xu, J.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Di, X.X.; Ni, J.; Li, X.N. Enhancement of Au/AC acetylene hydrochlorination catalyst activity and stability via nitrogen-modified activated carbon support. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, B.L.; Yue, Y.X.; Sheng, G.F.; Wang, Q.T.; Yu, L.; Hu, Z.-T.; Li, X.N. Highly active AuCu-based catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination prepared using organic aqua regia. Materials 2019, 12, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Gu, S.C.; He, H.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, X.N. One-pot synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped activated carbon supported AuCl3 as efficient catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.L.; Yue, Y.X.; Sheng, G.F.; Lai, H.X.; Wang, S.S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Feng, F.; Hu, Z.T.; et al. Nitrogen- and phosphorus-codoped carbon-based catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. J. Catal. 2019, 373, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.L.; Xu, X.L.; Yu, Y.; Di, S.X; Xu, H.; Zhai, Y.Y.; He, H.H.; Guo, L.L.; Pan, Z.Y.; et al. Alternative solvent to aqua regia to activate Au/AC catalysts for the hydrochlorination of acetylene. J. Catal. 2017, 350, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.L.; Yue, Y.X.; Di, S.X; Zhai, Y.Y.; He, H.H.; Sheng, G.F.; Lai, H.X.; Zhu, Y.H.; Guo, L.L.; et al. Towards a greener approach for the preparation of highly active Gold/Carbon catalyst for the hydrochlorination of ethyne. J. Catal. 2018, 365, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Part B: Applications in Coordination, Organometallic, and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Hangbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Chastain, J., King, R.C., Jr., Eds.; Physical Electronics Inc.: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Malta, G.; Kondrat, S.A.; Freakley, S.J.; Davies, C.J.; Dawson, S.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Dymkowski, K.; Fernandez-Alonso, F.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; et al. Deactivation of a single-site Gold-on-Carbon acetylene hydrochlorination catalyst: An X-ray absorption and inelastic neutron scattering study. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8493–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Davies, C.J.; Morgan, D.J.; Carley, A.F.; Johnston, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Characterization of Au3+ species in Au/C catalysts for the hydrochlorination reaction of acetylene. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakitin, Y.V.; Kalinnikova, V.T.; Khodasevichb, S.G.; Novotortsev, V.M. Structures of the complex ions [CuCl4]2− and [CuCl5]3−. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2007, 33, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, A.; Nalla, S.; Bond, M.R. The square-planar to flattened-tetrahedral CuX42−(X = Cl, Br) structural phase transition in 1,2,6-trimethylpyridinium salts. Acta Cryst. 2015, B71, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xing, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Su, B.; Bao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q. Differential solubility of ethylene and acetylene in room-temperature ionic liquids: A theoretical study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 3944–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Lu, X.M.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, S.C. Ionic Liquids: Physicochemical Properties; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M.; Lide, D.R.; Bruno, T.J. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids completely UnCOILed–Critical expert overviews; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Delley, B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 7756–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delley, B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J. Gaussian 16, Revision A.03; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.T.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle–Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J. Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields: A comparison of local, nonlocal, and hybrid density functional. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jordan, K.D. Comparison of density functional and MP2 calculations on the water monomer and dimer. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 10089–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XII. Further extensions of Gaussian-type basis sets for use in molecular-orbital studies of organic-molecules. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. Accuracy of AH equilibrium geometries by single determinant molecular-orbital theory. Mol. Phys. 1974, 27, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresman, J.B.; Frisch, A. Exploring Chemistry with Electronic Structure Methods, 2nd ed.; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]

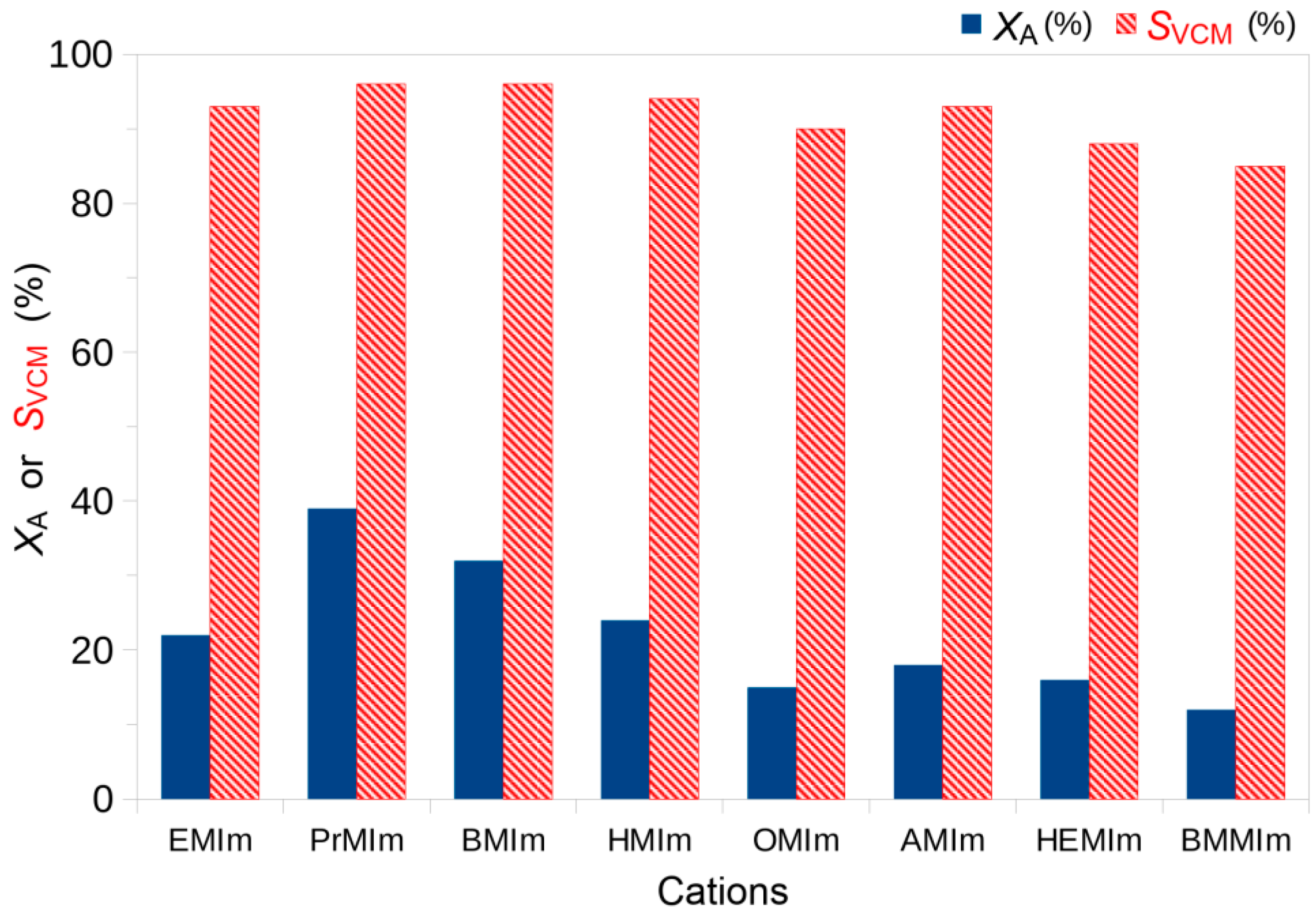
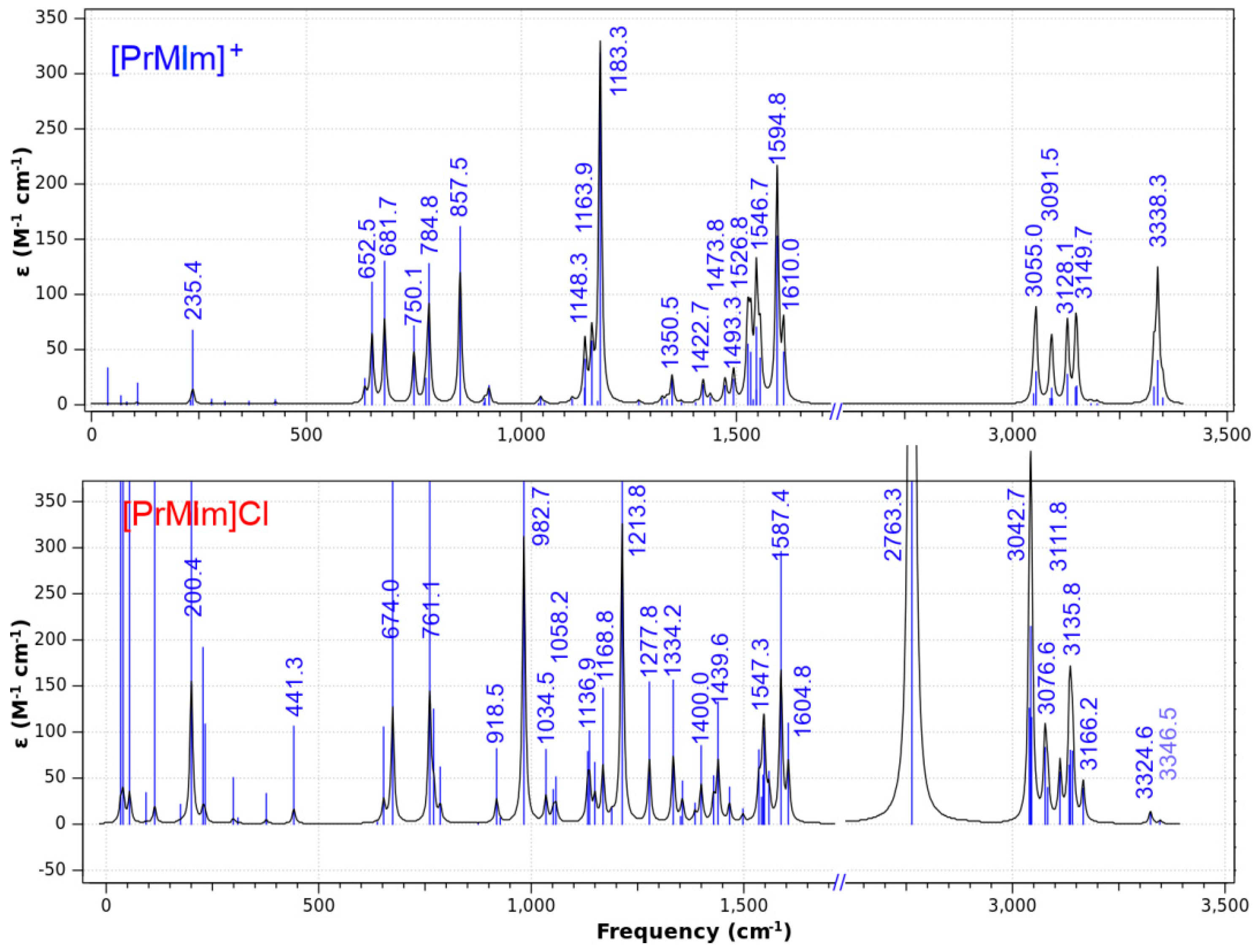



| M | EMIm | PrMIm | BMIm | HMIm | OMIm | AMIm | HEMIm | BMMIm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XA (%) | 22 | 39 | 32 | 24 | 15 | 18 | 16 | 12 |
| SVCM (%) | 93 | 96 | 96 | 94 | 90 | 93 | 88 | 85 |
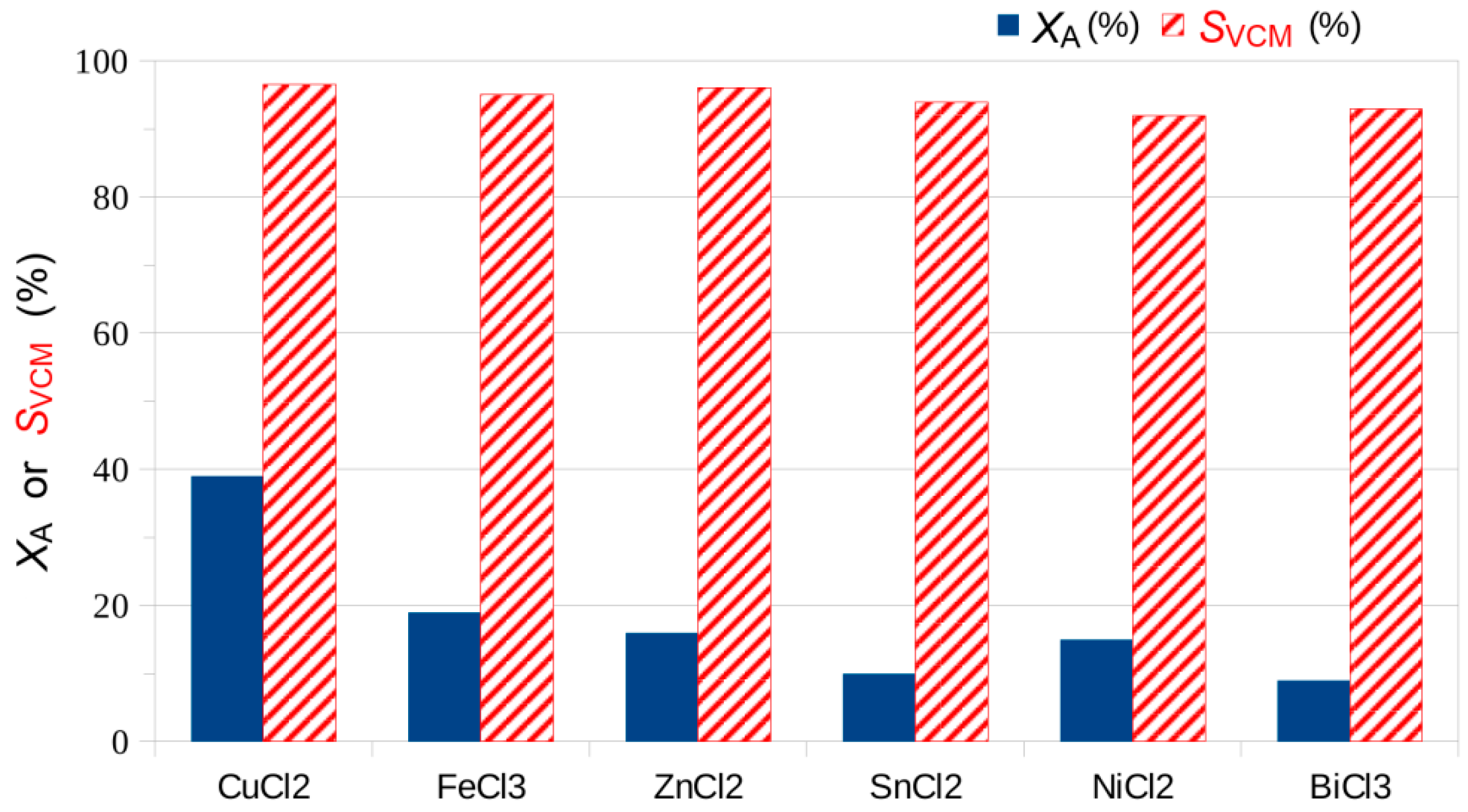
| MClx | CuCl2 | FeCl3 | ZnCl2 | SnCl2 | NiCl2 | BiCl3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XA (%) | 39 | 19 | 16 | 10 | 15 | 9 |
| SVCM (%) | 96.5 | 95 | 96 | 94 | 92 | 93 |
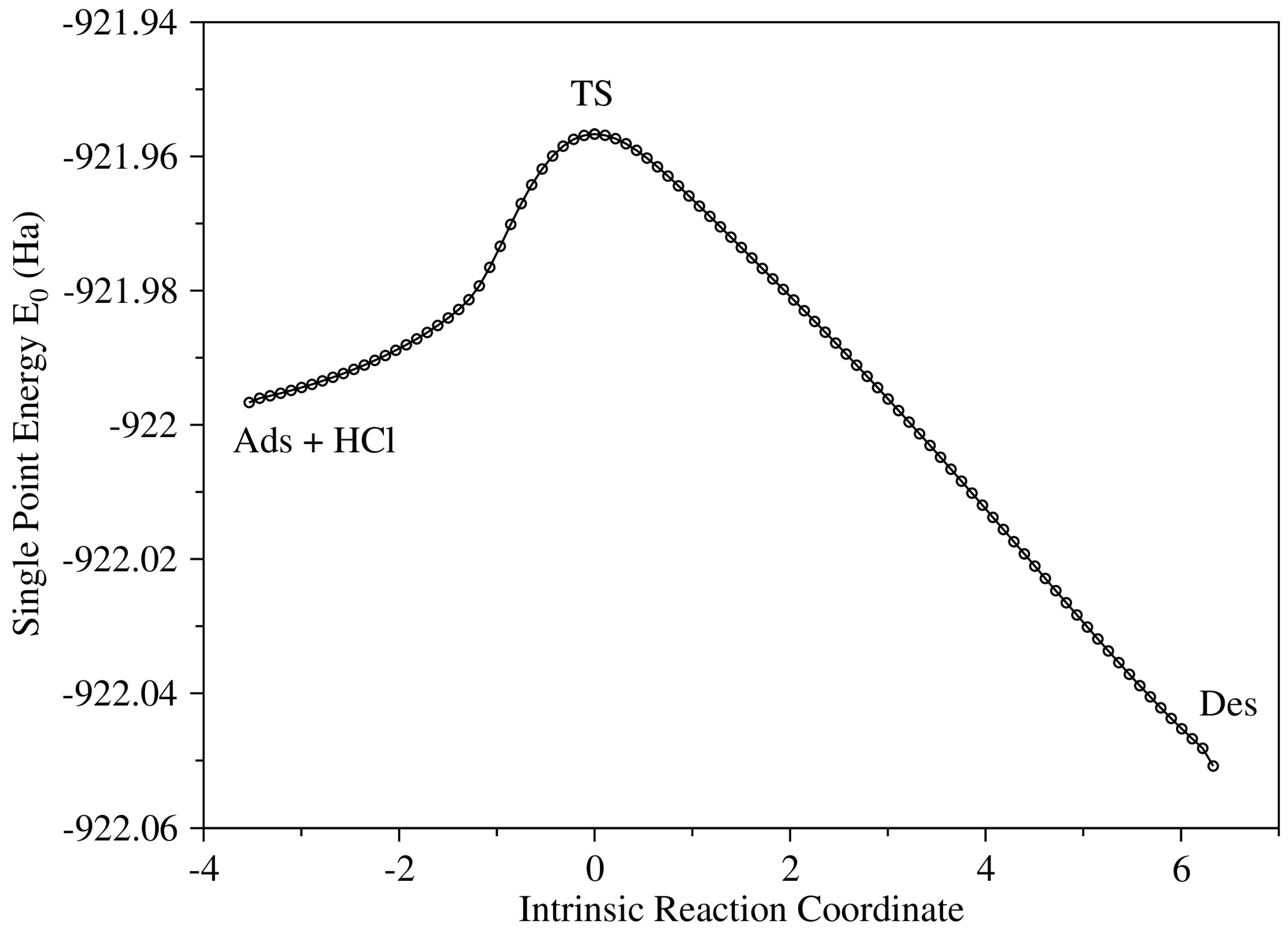
| Energy | R | Ads | TS | Des | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PrMIm]+: E | 0 | −4.54422 | 25.02324 | −43.40721 | −41.09202 |
| [PrMIm]+: G | 0 | −2.36146 | 24.91584 | −34.7227 | −33.65141 |
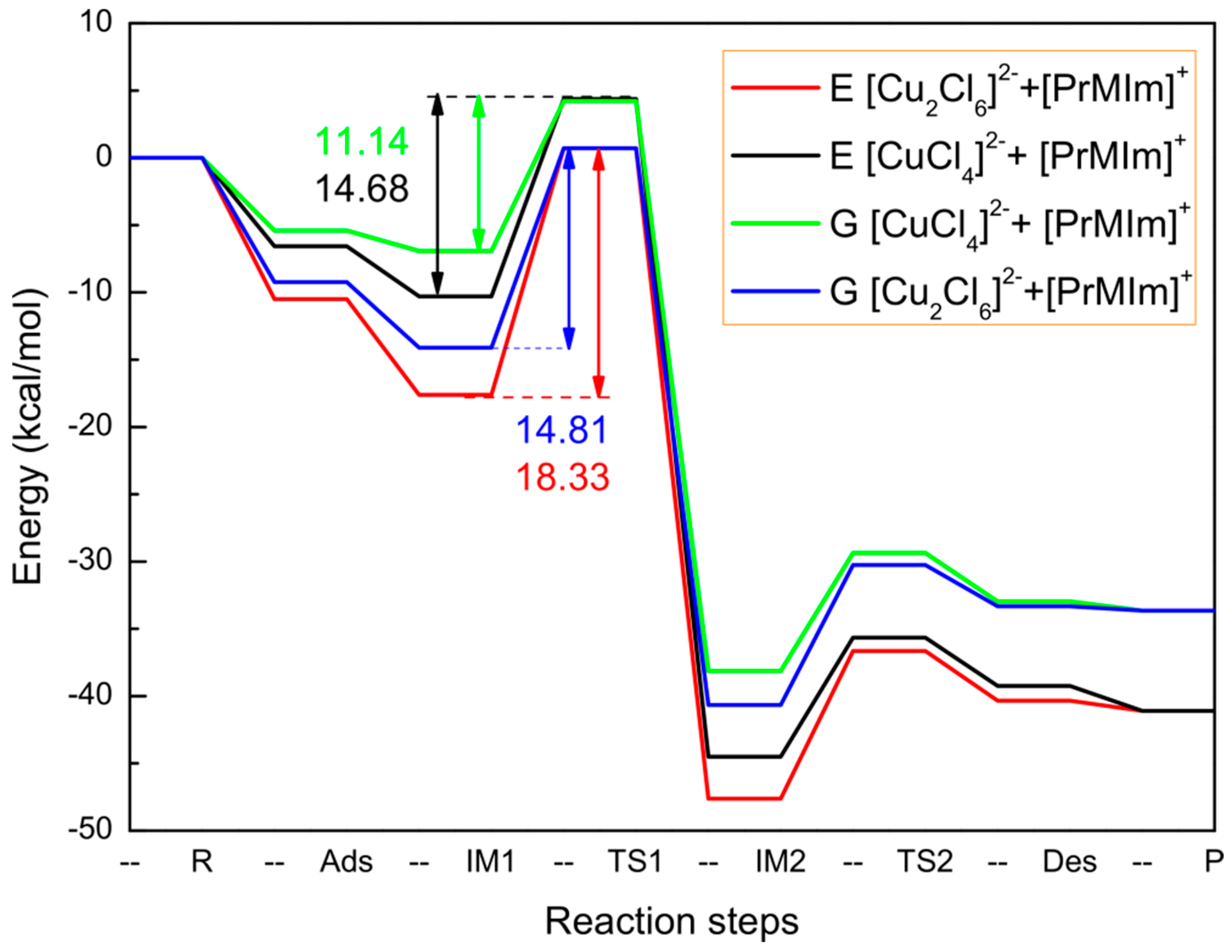
| Energy | R | Ads | IM1 | TS1 | IM2 | TS2 | Des | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Cu2Cl6]2−: E | 0 | −10.4962 | −17.6158 | −0.7144 | −47.6207 | −36.6548 | −40.3414 | −41.0920 |
| [Cu2Cl6]2−: G | 0 | −9.2365 | −14.1023 | −0.7096 | −40.6574 | −30.2568 | −33.3256 | −33.6514 |
| [CuCl4]2−: E | 0 | −6.5772 | −10.3016 | 4.3732 | −44.4982 | −35.6521 | −39.2439 | −41.0920 |
| [CuCl4]2−: G | 0 | −5.4169 | −46.9216 | 4.2157 | −38.1267 | −29.3651 | −32.9651 | −33.6514 |
| IL | Tm (°C) | Tf (°C) | Tg (°C) | Td (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIm]Cl | 41 ~ 70 | - | −76 ~ −69 | 254 |
| [PrMIm]Cl | 60, 62 | −140 | - | 281 ~ 282 |
| [EMIm]Cl | 77 ~ 90 | 73 | - | 281 ~ 285 |
| [HMIm]Cl | −85 , −75 | - | −75 | 253 |
| [OMIm]Cl | 12, 12.3 | - | −87 ~ −77 | 243 |
| [AMIm]Cl | 17, 49–51 | - | - | 273 |
| [HEMIm]Cl | 60.8 ± 2, 86 | −111 | - | - |
| [BMMIm]Cl | 79, 99,100 | - | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Wang, B.; He, H.; Hu, Z.-T.; Zhao, J.; Li, X. Synergy between Ionic Liquids and CuCl2 in Gas–Liquid Phase Reactions of Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts 2019, 9, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060504
Yu Y, Yue Y, Wang B, He H, Hu Z-T, Zhao J, Li X. Synergy between Ionic Liquids and CuCl2 in Gas–Liquid Phase Reactions of Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts. 2019; 9(6):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060504
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yi, Yuxue Yue, Bolin Wang, Haihua He, Zhong-Ting Hu, Jia Zhao, and Xiaonian Li. 2019. "Synergy between Ionic Liquids and CuCl2 in Gas–Liquid Phase Reactions of Acetylene Hydrochlorination" Catalysts 9, no. 6: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060504
APA StyleYu, Y., Yue, Y., Wang, B., He, H., Hu, Z.-T., Zhao, J., & Li, X. (2019). Synergy between Ionic Liquids and CuCl2 in Gas–Liquid Phase Reactions of Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts, 9(6), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060504





