An Efficient Support-Free Nanoporous Co Catalyst for Reverse Water–Gas Shift Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
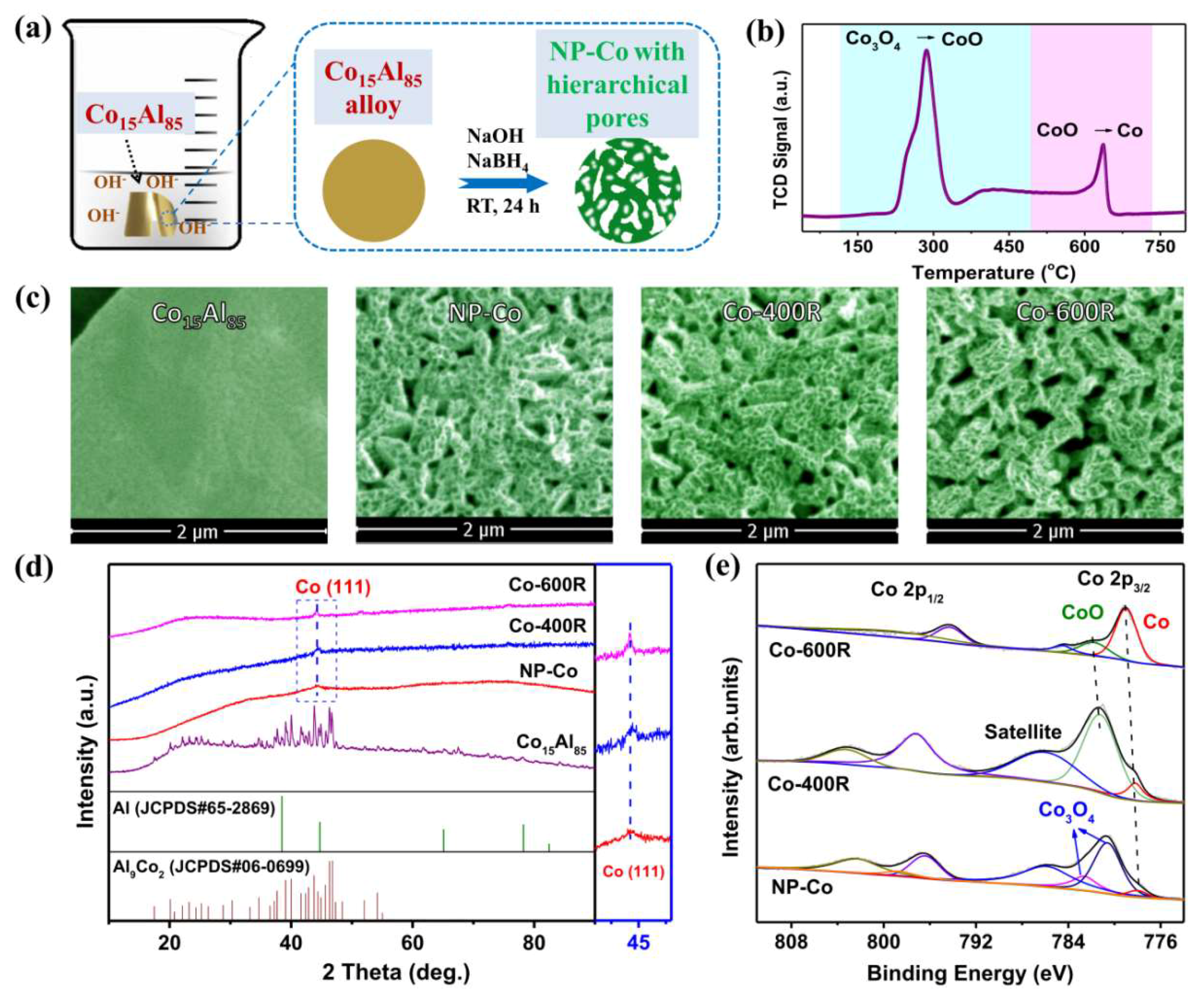
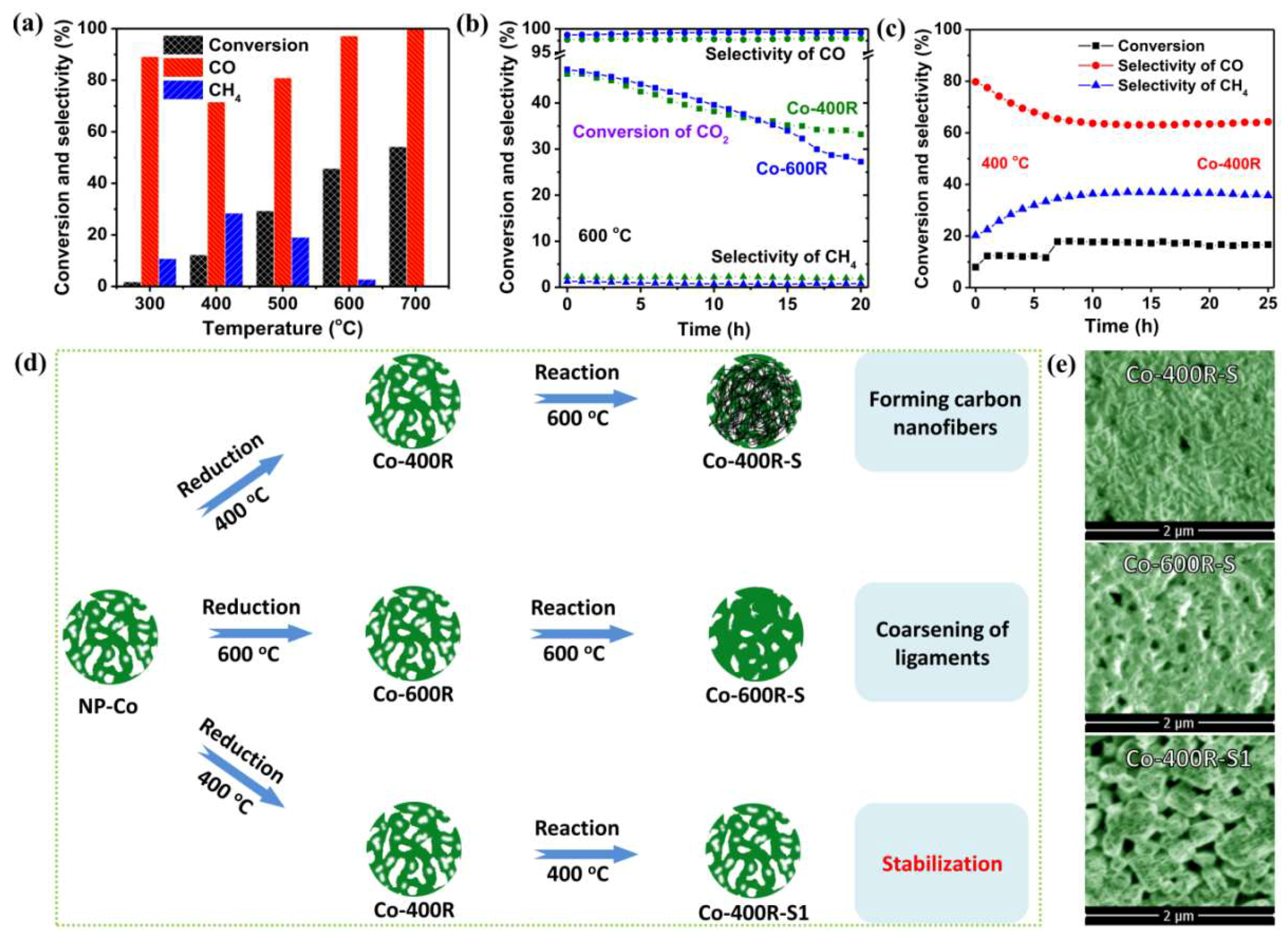
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Activity Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Porosoff, M.D.; Yan, B.; Chen, J.G. Catalytic reduction of CO2 by H2 for synthesis of CO, methanol and hydrocarbons: Challenges and opportunities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, Y.A.; Kuhn, J.N. CO2 conversion by reverse water gas shift catalysis: Comparison of catalysts, mechanisms and their consequences for CO2 conversion to liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 49675–49691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, S.; Amin, N.A.S.; Rahimpour, M.R. Hydrogenation of CO2 to value-added products—A review and potential future developments. J. CO2 Util. 2014, 5, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Su, X.; Chen, X.; Duan, H.; Liang, B.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Promotion effects of potassium on the activity and selectivity of Pt/zeolite catalysts for reverse water gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 216, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Kovarik, L.; Szanyi, J. Heterogeneous catalysis on atomically dispersed supported metals: CO2 reduction on multifunctional Pd catalysts. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2094–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Xu, Z.; Ge, J. Monodispersed gold nanoparticles supported on a zirconium-based porous metal-organic framework and their high catalytic ability for the reverse water-gas shift reaction. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7953–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronda-Lloret, M.; Rico-Francés, S.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Ramos-Fernandez, E.V. CuOx/CeO2 catalyst derived from metal organic framework for reverse water-gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 562, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.V.; Vono, L.L.R.; Wojcieszak, R.; Dias, C.S.B.; Wender, H.; Teixeira-Neto, E.; Rossi, L.M. Selective hydrogenation of CO2 into CO on a highly dispersed nickel catalyst obtained by magnetron sputtering deposition: A step towards liquid fuels. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Reverse water-gas shift reaction over co-precipitated Co-CeO2 catalysts: Effect of Co content on selectivity and carbon formation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 3682–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, Z.S.; He, Y.; Yang, K.R.; Lounsbury, A.W.; Zhu, J.; Tran, T.M.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Batista, V.S.; Pfefferle, L.D. Hard templating ultrathin polycrystalline hematite nanosheets: Effect of nano-dimension on CO2 to CO conversion: Via the reverse water-gas shift reaction. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12984–12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kunkel, C.; Ramírez De La Piscina, P.; Homs, N.; Viñes, F.; Illas, F. Effective and Highly Selective CO Generation from CO2 Using a Polycrystalline α-Mo2C Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4323–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, J.L.; Park, E.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Uhm, S. Dopant Effect of Barium Zirconate-Based Perovskite-Type Catalysts for the Intermediate-Temperature Reverse Water Gas Shift Reaction. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Zhou, G.; Ge, S.; Xie, H.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, K. CO2 reverse water-gas shift reaction on mesoporous M-CeO2 catalysts. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, T.; Xie, H.; Zheng, X. Effects of structure on the carbon dioxide methanation performance of Co-based catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 10012–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Ramírez, J.; Sánchez, P.; Kyriakou, V.; Zafeiratos, S.; Marnellos, G.E.; Konsolakis, M.; Dorado, F. Effect of support nature on the cobalt-catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H. Mesoporous Co-CeO2 catalyst prepared by colloidal solution combustion method for reverse water-gas shift reaction. Catal. Today 2018, 316, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M. Nanoporous metal by dealloying for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. MRS Bull. 2018, 43, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Martínez, A.; Concepción, P.; Moreno-Tost, R. Cobalt particle size effects in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Structural and in situ spectroscopic characterisation on reverse micelle-synthesised Co/ITQ-2 model catalysts. J. Catal. 2009, 266, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Deng, Z.; Shi, W. Low temperature CO oxidation and CH4 combustion over Co3O4 nanosheets. Fuel 2017, 203, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Marcelot-Garcia, C.; Aït Atmane, K.; Berrichi, E.; Lacroix, L.M.; Zwick, A.; Warot-Fonrose, B.; Lachaize, S.; Decorse, P.; Piquemal, J.Y.; et al. Carbon coating, carburization, and high-temperature stability improvement of cobalt nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15808–15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B.; Duan, H.; Hou, B.; Huang, Y. Catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methane: A review of recent studies. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaritis, C.; Edake, M.; Couillard, M.; Einakchi, R.; Baranova, E.A. Insight towards the role of ceria-based supports for reverse water gas shift reaction over RuFe nanoparticles. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 26, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Duan, H.; Su, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Delgado, J.J.; Zhang, T. Promoting role of potassium in the reverse water gas shift reaction on Pt/mullite catalyst. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ge, Q.; Liu, C.J. Effect of PdIn bimetallic particle formation on CO2 reduction over the Pd-In/SiO2 catalyst. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, B.; Shi, C. Selective reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide over Au/CeO2 catalyst and identification of reaction intermediate. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Cheng, W.H.; Lin, S.S. Study of iron-promoted Cu/SiO2 catalyst on high temperature reverse water gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 257, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.W.; Shi, C.; Ma, D. Highly Dispersed Copper over β-Mo2C as an Efficient and Stable Catalyst for the Reverse Water Gas Shift (RWGS) Reaction. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugic, B.; Wang, L.; Heine, C.; Zakharov, D.N.; Lechner, B.A.J.; Stach, E.A.; Biener, J.; Salmeron, M.; Madix, R.J.; Friend, C.M. Dynamic restructuring drives catalytic activity on nanoporous gold-silver alloy catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2016, 16, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biener, M.M.; Biener, J.; Wichmann, A.; Wittstock, A.; Baumann, T.F.; Bäumer, M.; Hamza, A.V. ALD Functionalized Nanoporous Gold: Thermal Stability, Mechanical Properties, and Catalytic Activity. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Patterson, P.M.; Das, T.K.; Luo, M.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of water on Co/Al2O3 catalysts and XAFS characterization of reoxidation phenomena. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 270, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Yuan, X.; Du, X.; Zhao, W.; Bi, Q.; Huang, F. Efficient Reduction of CO2 to CO Using Cobalt–Cobalt Oxide Core–Shell Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Catalysts | H2:CO2 | Temp. (°C) | WHSV (mL/g/h) | Conv. (%) (μmolCO2/g/s) | Sel. of CO (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PtK/Mullite | 1:1 | 550 | 30,000 | 30.9 (52) | 99.2 | [23] |
| Pd–In/SiO2 | 1:1 | 600 | 60,000 | 29.4 (44) | 100 | [24] |
| K80-Pt/L | 1:1 | 400 | 30,000 | 13 (21.9) | 100 | [4] |
| Au/CeO2 | 1:1 | 400 | 6000 | 21 (15.7) | 100 | [25] |
| Mn–CeO2 | 4:1 | 400 | 60,000 | 8.1 (6.1) | 100 | [13] |
| BaZr0.8Y0.16Zn0.04O3 | 1:1 | 600 | 2400 | 37.5 (5.6) | 97 | [12] |
| Cu–Fe/SiO2 | 1:1 | 600 | 120,000 | 15 (112) | N/A | [26] |
| Ni/nSiO2 | 4:1 | 400 | 400,000 | 25 (13) | 96 | [8] |
| Co–CeO2 | 1:1 | 600 | 300,000 | 38 (711) | 100 | [9] |
| Co–CeO2 | 4:1 | 400 | 60,000 | 35 (26.2) | 62 | [13] |
| Mesoporous Co–CeO2 | 1:1 | 600 | 600,000 | 34.5 (1749) | 99.8 | [16] |
| Fe2O3 | 1:1 | 510 | 120,000 | 28 (84) | 100 | [10] |
| Cu/β-Mo2C | 2:1 | 600 | 300,000 | −(477) | 99.2 | [27] |
| Co-400R | 1:1 | 400 | 300,000 | 12.3 (184) | 71.6 | This work |
| Co-400R | 1:1 | 500 | 300,000 | 29.4 (440) | 80.9 | This work |
| Co-400R | 1:1 | 600 | 300,000 | 45.8 (686) | 97.2 | This work |
| Co-400R | 1:1 | 700 | 300,000 | 54.2 (812) | 99.9 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xiao, Z. An Efficient Support-Free Nanoporous Co Catalyst for Reverse Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts 2019, 9, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050423
Shen Y, Cao Z, Xiao Z. An Efficient Support-Free Nanoporous Co Catalyst for Reverse Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts. 2019; 9(5):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050423
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yongli, Zhen Cao, and Zihui Xiao. 2019. "An Efficient Support-Free Nanoporous Co Catalyst for Reverse Water–Gas Shift Reaction" Catalysts 9, no. 5: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050423
APA StyleShen, Y., Cao, Z., & Xiao, Z. (2019). An Efficient Support-Free Nanoporous Co Catalyst for Reverse Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts, 9(5), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050423





