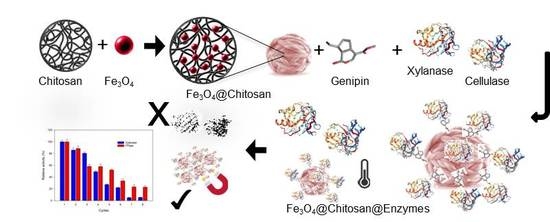
Enhanced Performance of Immobilized Xylanase/Filter Paper-ase on a Magnetic Chitosan Support
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Immobilization Yield and Efficiency
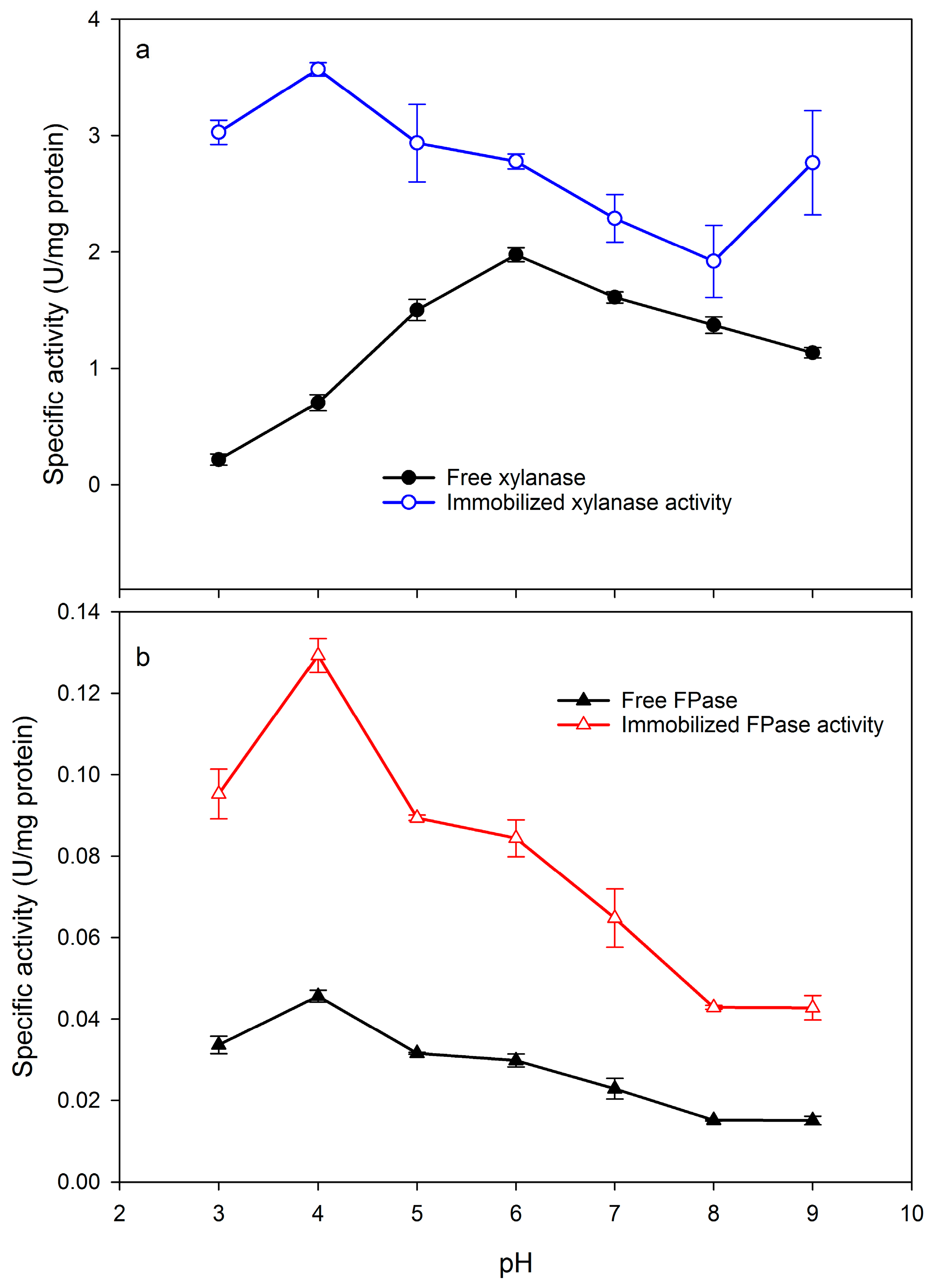
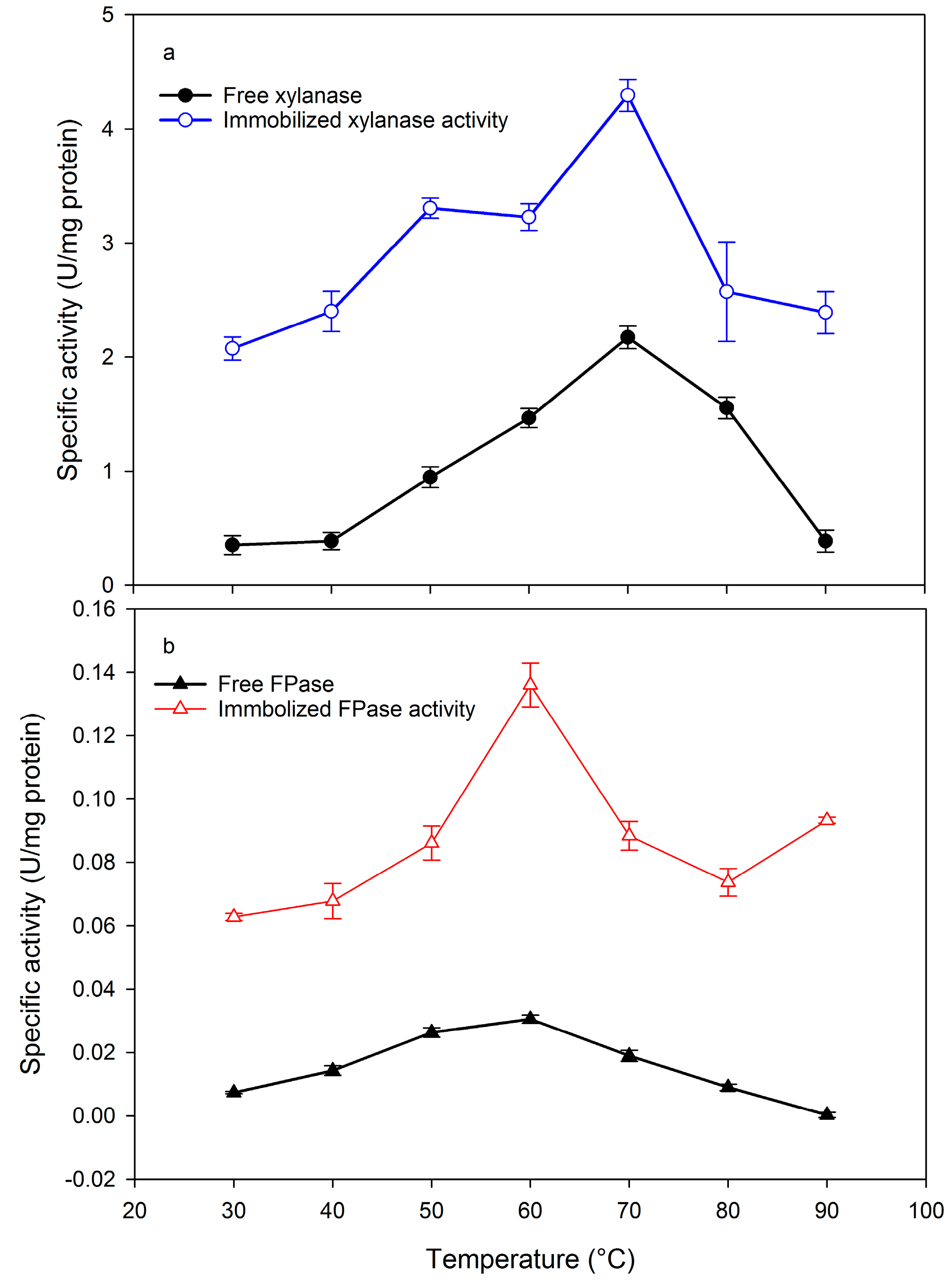
2.2. Effect of pH and Temperature on Xylanase and Filter paper-ase Activity
2.3. Kinetic Parameters of Xylanase and FPase
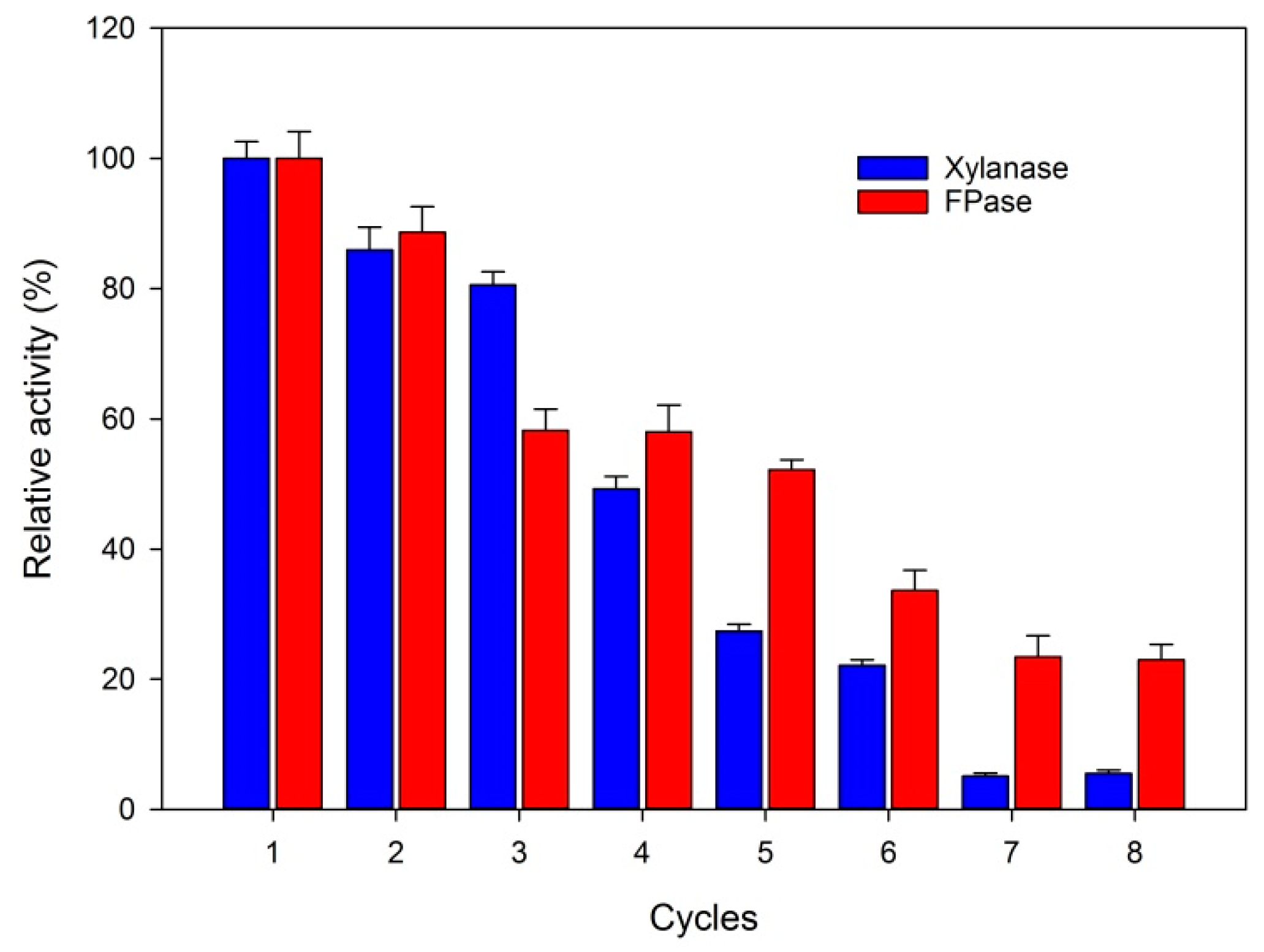
2.4. Reuse Capacity of Fe3O4@Chitosan@Enzymes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Chitosan-Coated Magnetite Particles (Fe3O4@Chitosan) and Enzyme Immobilization (Fe3O4@Chitosan@Enzymes)
3.3. Enzyme Activity Assay
3.4. Effect of Temperature and pH on Xylanase and FPase Activity
3.5. Kinetic Parameters of Xylanase and FPase
3.6. Reuse Capacity of Fe3O4@Chitosan@Enzymes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naskar, S.; Koutsu, K.; Sharma, S. Chitosan-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems: A review on two decades of research. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pessoa, M.G.; Paulino, B.N.; Pastore, G.M. Genipin: A natural blue pigment for food and health purposes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokareva, M.I.; Ivantsova, M.N.; Mironov, M.A. Heterocycles of natural origin as non-toxic reagents for cross-linking of proteins and polysaccharides. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2017, 53, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.E.E.; Cardoso, F.D.; Siqueira, L.B.; Ricardi, N.C.; Costa, T.H.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Klein, M.P.; Hertz, P.F. Influence of reaction parameters in the polymerization between genipin and chitosan for enzyme immobilization. Process Biochem. 2019, 84, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracida, J.; Arredondo-Ochoa, T.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Escamilla-García, M.; Shirai, K.; Regalado, C.; Amaro-Reyes, A. Improved thermal and reusability properties of xylanase by genipin cross-linking to magnetic chitosan particles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, S.D.; İdil, N.; Aksöz, N. Optimization of enzyme co-immobilization with sodium alginate and glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan beads. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmakçi, E.; Yuce-Dursun, B.; Demir, S. Maleic anhydride functionalization of OSTE based coatings via thiol-ene “Click” reaction for the covalent immobilization of xylanase. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 111, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolatti, E.P.; Valério, A.; Henriques, R.O.; Moritz, D.E.; Ninow, J.L.; Freire, D.M.G.; Manoel, E.A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; de Oliveira, D. Nanomaterials for biocatalyst immobilization—State of the art and future trends. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104675–104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, C.; Jiao, X.; Jia, S.; Jiang, Y.; Bilal, M.; Cui, J. Recent progress in multienzymes co-immobilization and multienzyme system applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 1254–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Q.; Dai, X.-Y.; Wei, X.-Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, T. Co-immobilization of pectinase and glucoamylase onto sodium aliginate/graphene oxide composite beads and its application in the preparation of pumpkin-hawthorn juice. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muley, A.B.; Thorat, A.S.; Singhal, R.S.; Babu, K.H. A tri-enzyme co-immobilized magnetic complex: Process details, kinetics, thermodynamics and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima Damásio, A.R.; Pessela, B.C.; da Silva, T.M.; Guimarães, L.H.S.; Jorge, J.A.; Guisán, J.M.; Polizeli, M.D.L.T.M. Co-immobilization of fungal endo-xylanase and α-L-arabinofuranosidase in glyoxyl agarose for improved hydrolysis of arabinoxylan. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.; Batista-Viera, F. Production of d-tagatose and d-fructose from whey by co-immobilized enzymatic system. Mol. Catal. 2019, 463, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Alcantara, A.R.; Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports: Immobilization mechanism, advantages, problems, and solutions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 746–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.M.; Souza, P.M.P.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Rodrigues, S. Co-immobilization of dextransucrase and dextranase in epoxy-agarose-tailoring oligosaccharides synthesis. Process Biochem. 2019, 78, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. A co-immobilization of pectinase and cellulase onto magnetic nanoparticles for antioxidant extraction from waste fruit peels. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, K.; Santhalembi, L.; Mortha, G.; Aurousseau, M.; Subramanian, S. Carrier-free co-immobilization of xylanase, cellulase and β-1, 3-glucanase as combined cross-linked enzyme aggregates (combi-CLEAs) for one-pot saccharification of sugarcane bagasse. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32849–32857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Zhao, Y.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers for enzymes immobilization: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2530–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa, F.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.; Ajamein, H.; Anarjan, N.; Vaghari, H.; Sayyar, Z.; Berenjian, A. A biotechnological perspective on the application of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2203–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, G.B.; Filho, E.X.F. Fungal co-cultures in the lignocellulosic biorefinery context: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 142, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Hernández, A.; Gracida, J.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Regalado, C.; Núñez, R.; Amaro-Reyes, A. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with chitosan: A potential approach for enzyme immobilization. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 9468574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.-F.; Meng, G.; Cui, B.-K.; Si, J.; Dai, Y.-C. Chitosan crosslinked with genipin as supporting matrix for biodegradation of synthetic dyes: Laccase immobilization and characterization. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 132, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, Y.W.; Leung, W.W.-F. Crosslinking of genipin and autoclaving in chitosan-based nanofibrous scaffolds: Structural and physiochemical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 10941–10962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ramírez, J.; Martínez-Hernández, J.L.; Segura-Ceniceros, P.; López, G.; Saade, H.; Medina-Morales, M.A.; Ramos-González, R.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ilyina, A. Cellulases immobilization on chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles: Application for Agave atrovirens lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgaonkar, M.; Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. Combi-metal organic framework (Combi-MOF) of α-amylase and glucoamylase for one pot starch hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, S.; Carneiro, L.A.B.D.C.; Ward, R.J.; Meleiro, L.P. Immobilization of a β-glucosidase and an endoglucanase in ferromagnetic nanoparticles: A study of synergistic effects. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 160, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. Magnetic macromolecular cross linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of glucoamylase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 83, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrestani, H.; Taheri-Kafrani, A.; Soozanipour, A.; Tavakoli, O. Enzymatic clarification of fruit juices using xylanase immobilized on 1,3,5-triazine-functionalized silica-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 109, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, A.C.O.; Ulrich, L.G.; Kornecki, J.F.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Tardioli, P.W.; Ribeiro, M.P.D.A. Combi-CLEAs of glucose oxidase and catalase for conversion of glucose to gluconic acid eliminating the hydrogen peroxide to maintain enzyme activity in a bubble column reactor. Catalysts 2019, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojitra, U.V.; Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. A magnetic tri-enzyme nanobiocatalyst for fruit juice clarification. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Reyes, A.; Gracida, J.; Huizache-Peña, N.; Elizondo-García, N.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Regalado, C. On-site hydrolytic enzymes production from fungal co-cultivation of Bermuda grass and corn cob. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 212, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goluguri, B.R.; Thulluri, C.; Addepally, U.; Shetty, P.R. Novel alkali-thermostable xylanase from Thielaviopsis basicola (MTCC 1467): Purification and kinetic characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Enzyme | Form | Km (mg/mL) | Vmax (U/mL) | Kcat (1/s) | Kcat/Km (mL/mg s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylanase | Free | 1.89 ± 0.46 | 6.31 ± 0.63 | 7.01 ± 0.70 | 3.71 ± 0.57 |
| Immobilized | 3.15 ± 0.16 | 11.6 ± 0.26 | 20.4 ± 0.90 | 6.50 ± 0.04 | |
| FPase | Free | 157 ± 87 | 2.06 ± 0.88 | 1.04 ± 0.44 | 0.007 ± 0.00 |
| Immobilized | 16.7 ± 1.6 | 2.82 ± 0.07 | 3.92 ± 0.19 | 0.235 ± 0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaro-Reyes, A.; Díaz-Hernández, A.; Gracida, J.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Escamilla-García, M.; Arredondo-Ochoa, T.; Regalado, C. Enhanced Performance of Immobilized Xylanase/Filter Paper-ase on a Magnetic Chitosan Support. Catalysts 2019, 9, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110966
Amaro-Reyes A, Díaz-Hernández A, Gracida J, García-Almendárez BE, Escamilla-García M, Arredondo-Ochoa T, Regalado C. Enhanced Performance of Immobilized Xylanase/Filter Paper-ase on a Magnetic Chitosan Support. Catalysts. 2019; 9(11):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110966
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaro-Reyes, Aldo, Azariel Díaz-Hernández, Jorge Gracida, Blanca E. García-Almendárez, Monserrat Escamilla-García, Teresita Arredondo-Ochoa, and Carlos Regalado. 2019. "Enhanced Performance of Immobilized Xylanase/Filter Paper-ase on a Magnetic Chitosan Support" Catalysts 9, no. 11: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110966
APA StyleAmaro-Reyes, A., Díaz-Hernández, A., Gracida, J., García-Almendárez, B. E., Escamilla-García, M., Arredondo-Ochoa, T., & Regalado, C. (2019). Enhanced Performance of Immobilized Xylanase/Filter Paper-ase on a Magnetic Chitosan Support. Catalysts, 9(11), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110966