Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
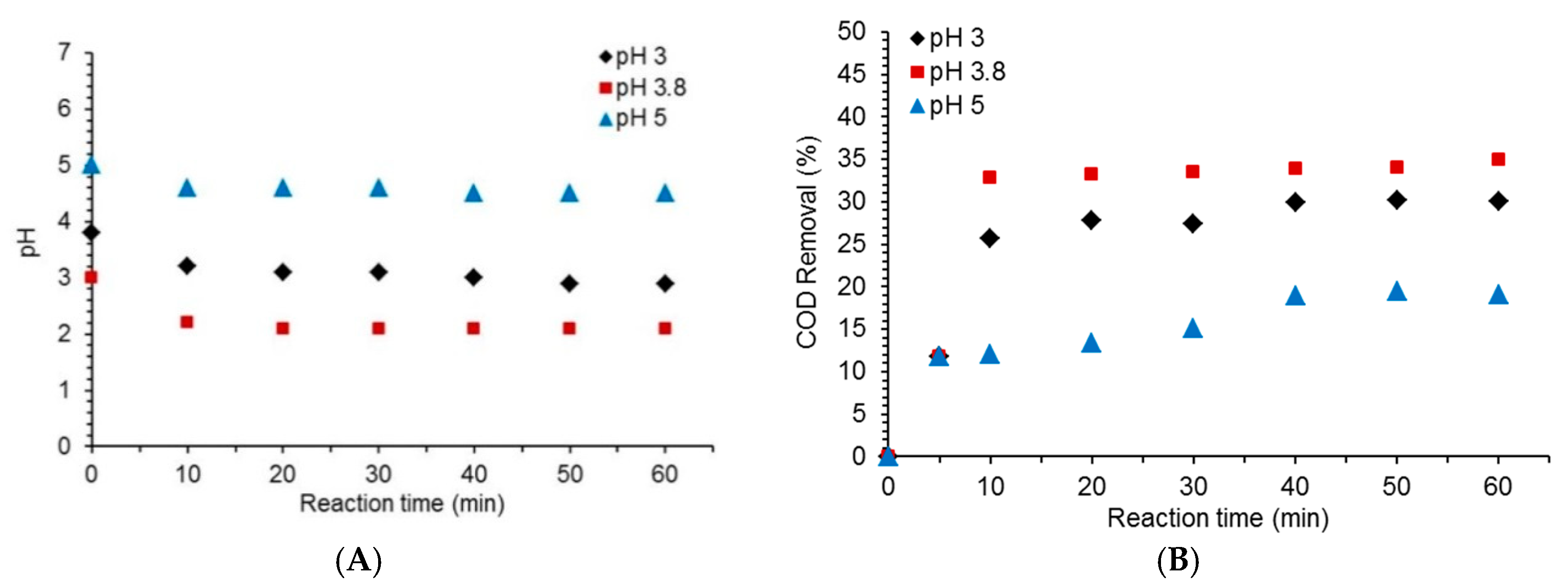
2.1. Effect of Initial pH
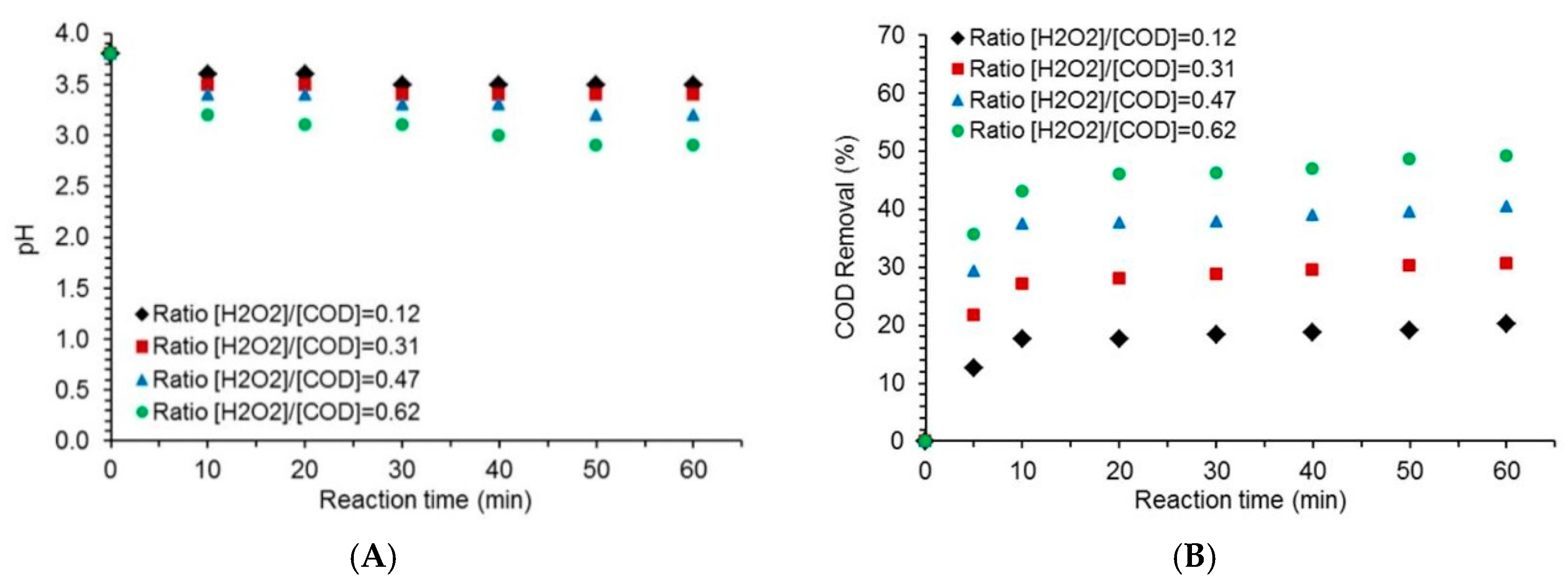
2.2. Effect of the [H2O2] to [COD] Ratio
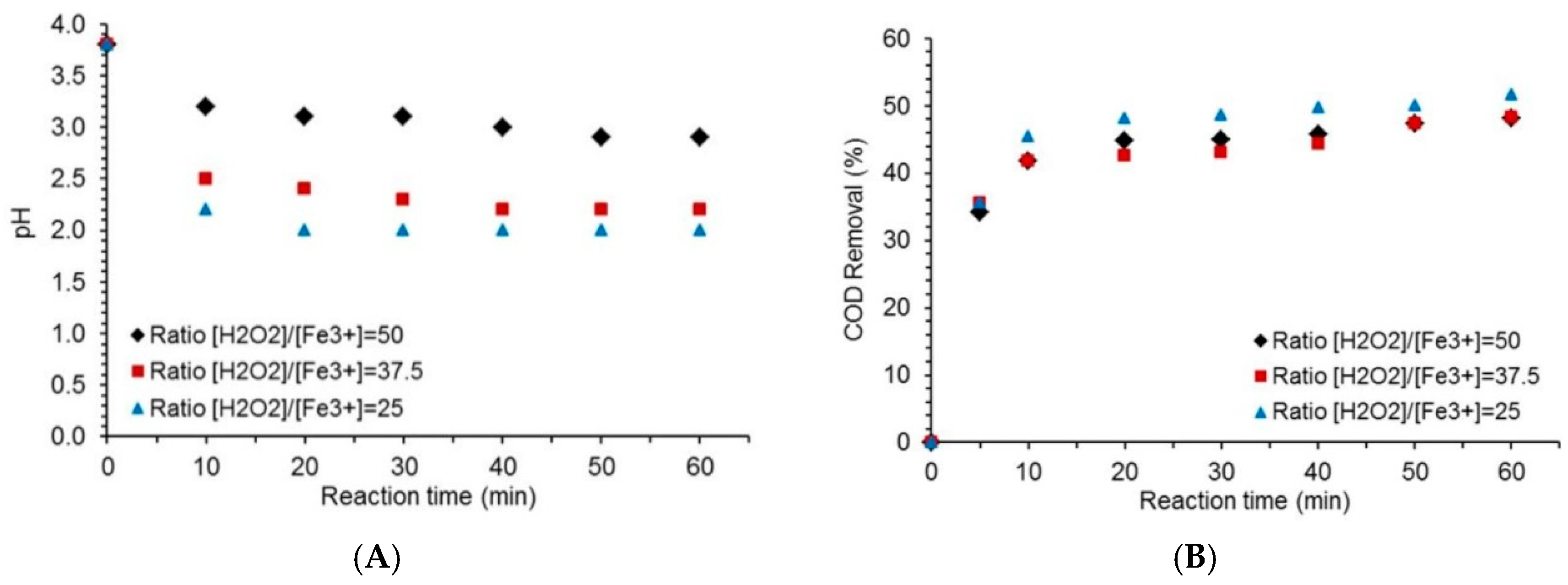
2.3. Effect of the [H2O2 to [Fe3+] Ratio
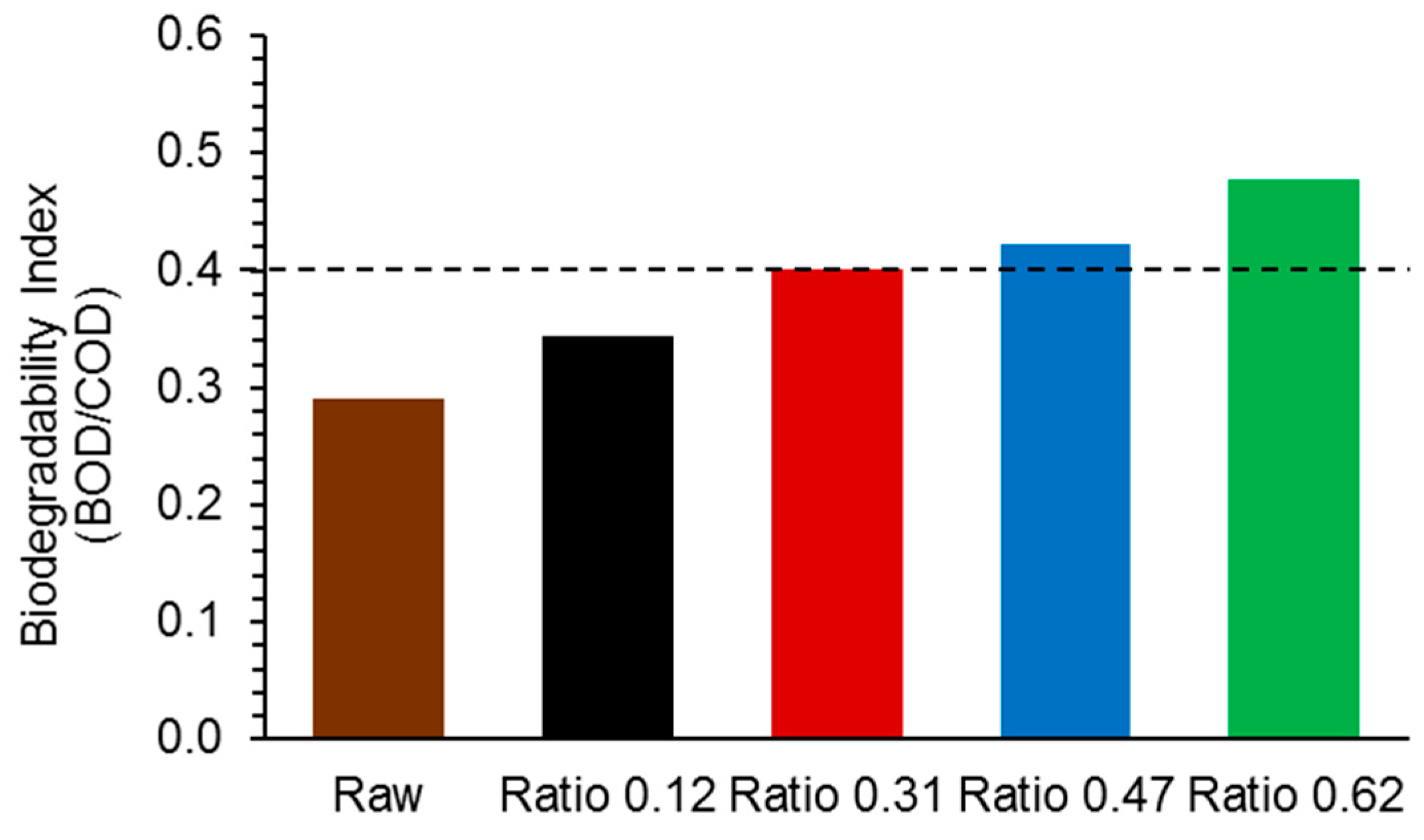
2.4. Biodegradability Enhancement
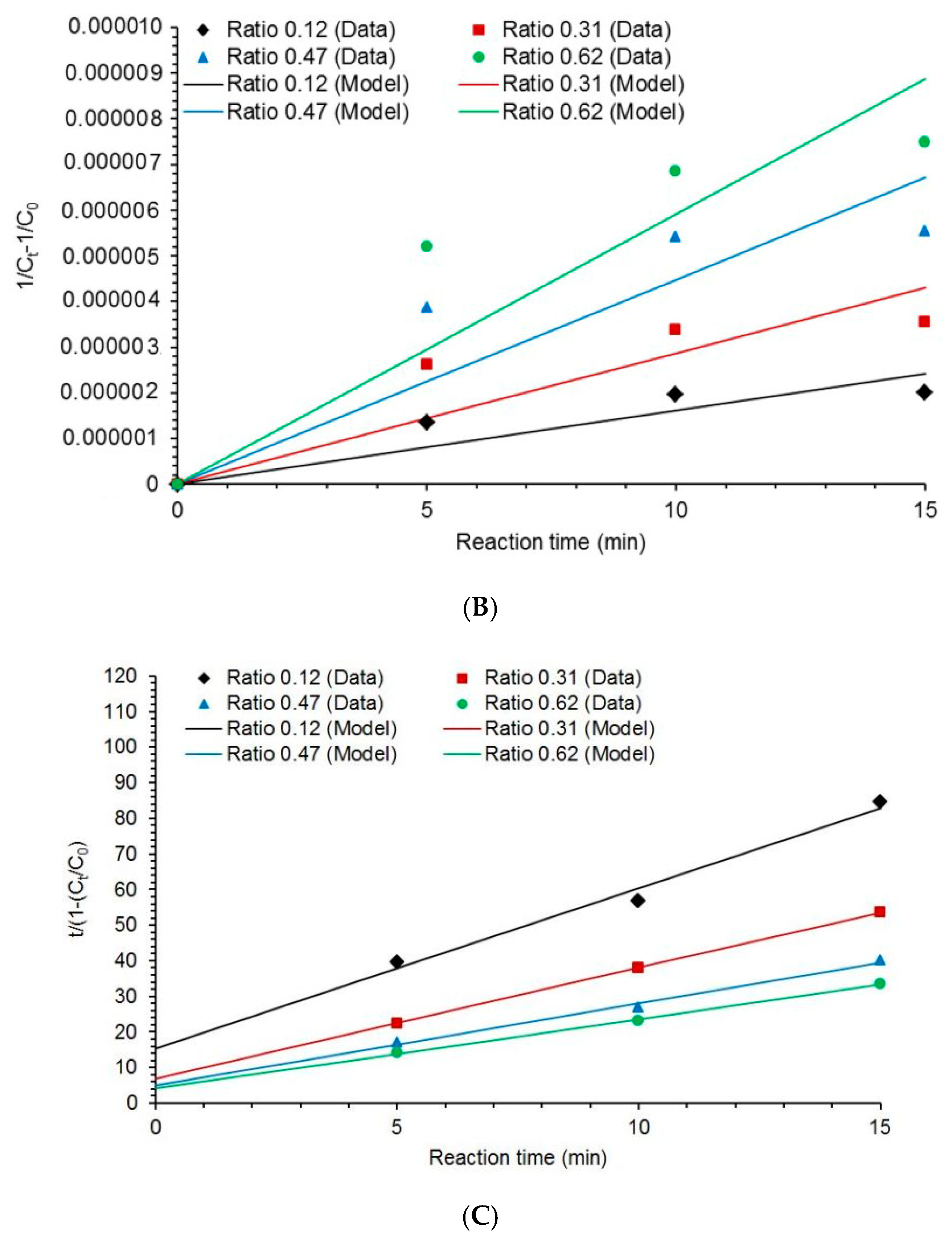
2.5. Kinetic of COD Degradation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Kinetic Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- España-Gamboa, E.; Mijangos-Cortes, J.; Barahona-Perez, L.; Dominguez-Maldonado, J.; Hernández-Zarate, G.; Alzate-Gaviria, L. Vinasses: Characterization and treatments. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 1235–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran de Heredia, J.; Torregrosa, J.; Dominguez, J.R.; Partido, E. Degradation of wine distillery wastewaters by the combination of aerobic biological treatment with chemical oxidation by fenton’ s reagent. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, A.C.; Riedesel, K.J.; Owens, J.M. Stillage characterization and anaerobic treatment of ethanol stillage from conventional and cellulosic feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 63–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharayat, Y. Distillery wastewater: Bioremediation approaches. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2012, 9, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Reis, C.E.; Hu, B. Vinasse from Sugarcane Ethanol Production: Better treatment or better utilization? Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, R.F.F.; Moraes, J.E.F.; Machulek, A.; Pinto, J.M. A mechanistic kinetic model for phenol degradation by the Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, M.A. Chemical degradation methods for wastes and pollutants: Environmental and industrial applications. In Environmental Science & Pollution; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780824756475. [Google Scholar]
- Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: Oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv. Environ. Res. 2004, 8, 501–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, G.R. Assessment of Solar Photo-Fenton in Raceway Pond Reactors for Micropollutant Removal in Secondary Effluents From Agro-Food Industry and Municipal WWWTPs; Tesis Doctorales; Editorial Universidad de Almería: Almería, Spain, 2017; ISBN 9788416642793. [Google Scholar]
- Davarnejad, R.; Hosseinitabar, P. Application of iron electrode in textile industry wastewater treatment using electro-fenton technique: Experimental and statistical study. Int. J. Eng. Trans. A Basics 2016, 29, 887–897. [Google Scholar]
- De Laat, J.; Gallard, H. Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by Fe (III) in homogeneous aqueous solution: Mechanism and kinetic modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2726–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, R.; Chohadia, A.K.; Jain, A.; Punjabi, P.B. Fenton and photo-fenton process. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Emerging Green Chemical Technology; Ameta, S., Ameta, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 49–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Decolorization of the azo dye Reactive Black 5 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation. Dyes Pigment. 2006, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, P.; Mohedano, A.F.; Casas, J.A.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. An overview of the application of Fenton oxidation to industrial wastewaters treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Quina, M.J.; Quinta-ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Detoxification of olive mill wastewaters by fenton’ s process. Catalysts 2018, 8, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarto, S.; Paesal, P.; Tanyong, I.B.; Laksmana, W.T.; Prasetya, A.; Ariyanto, T. Catalytic degradation of textile wastewater effluent by peroxide oxidation assisted by uv light irradiation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, L.F.; Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Duda, R.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Madeira, L.M. Treatment of sugarcane vinasse by combination of coagulation/fl occulation and Fenton ’ s oxidation. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.K. Removal of COD & Colour from Distillery Wastewater Using Fenton Oxidation; Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee: Roorkee, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, M.; Hassan, A.; Noor, Z.; Aris, A. Performance of fenton oxidation towards sulfide removal for spent caustic remediation. In Proceedings of the 2011 National Postgraduate Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–20 September 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Lei, Y. Fenton’s oxidation kinetics, pathway, and toxicity evaluation of diethyl phthalate in aqueous solution. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2016, 19, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosofi, Y.; Almasi, A.; Mousavi, S.A.; Mizzouri, N.S. Decolorization of Methylene blue from aqueous solution using ultrasonic/fenton like process. Int. J. Eng. Trans. B Appl. 2016, 29, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Duesterberg, C.K.; Mylon, S.E.; Waite, T.D. pH Effects on iron-catalyzed oxidation using fenton’ s reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8522–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.; Chen, Y.; Chang, C.; Chang, C.; Shie, J.; Li, Y. Photochemical mineralization of di-n-butyl phthalate with H2O2/Fe3+. J. Hazard. Matter 2006, 135, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, S.; Gürkan, T.; Duman, O. On-line spectrophotometric method for the determination of optimum operation parameters on the decolorization of Acid Red 66 and Direct Blue 71 from aqueous solution by Fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovo, A.G.; Hassan, A.K.; Sillanpaa, M.; Tang, W.Z. Degradation of Acid Blue 161 by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heredia, J.B.; Dominguez, J.R.; Partido, E. Physico-chemical treatment for the depuration of wine distillery wastewaters (vinasses). Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadavifar, M.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Younesi, H.; Galehdar, M. Fenton and photo-Fenton treatment of distillery effluent and optimization of treatment conditions with response surface methodology. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 5, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Neto, A.R.; Duda, R.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Madeira, L.M. Combination of chemical coagulation, photo-Fenton oxidation and biodegradation for the treatment of vinasse from sugar cane ethanol distillery. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Removal of COD from olive mill wastewater by Fenton’ s reagent: Kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mate. 2009, 168, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L. Metcalf & Eddy Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 9780070416901. [Google Scholar]
- Al-momani, F.; Touraud, E.; Degorce-dumas, J.R.; Roussy, J.; Thomas, O. Biodegradability enhancement of textile dyes and textile wastewater by VUV photolysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2002, 153, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.R.; Duarte, E.T.F.M.; de Souza Girardi, G.; Velani, V.; da Hora Machado, A.E.; Sattler, C.; de Oliveira, L.; de Miranda, J.A. Study of kinetic parameters related to the degradation of an industrial effluent using Fenton-like reactions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 179, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouran, S.R.; Aziz, A.R.A.; Mohd, W.; Wan, A. Review on the main advances in photo—Fenton oxidation system for recalcitrant wastewaters. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Online monitoring of Fenton-mediated reactive red 6B oxidation kinetics. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.S.; Ramos, M.D.N.; Velloso, C.C.V.; Aguiar, A. Kinetic evaluation of dye decolorization by fenton processes in the presence of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palas, B.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S. Green catalysts for Fenton-like oxidation of Procion Red MX-5B: Influence of the activation method and the reaction parameters on dye removal. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Shi, T.N.; Wu, L.C.; Qi, S.Y. Discoloration of methyl orange in the presence of schorl and H2O2: Kinetics and mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.; Modirshahla, N.; Ghanbary, F. A kinetic model for the decolorization of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, Z.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M. Photocatalytic Decomposition of Organic Dyes. Organic Pollutants in Wastewater I: Methods of Analysis, Removal and Treatment; Materials Research Forum LLC: Millersville, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
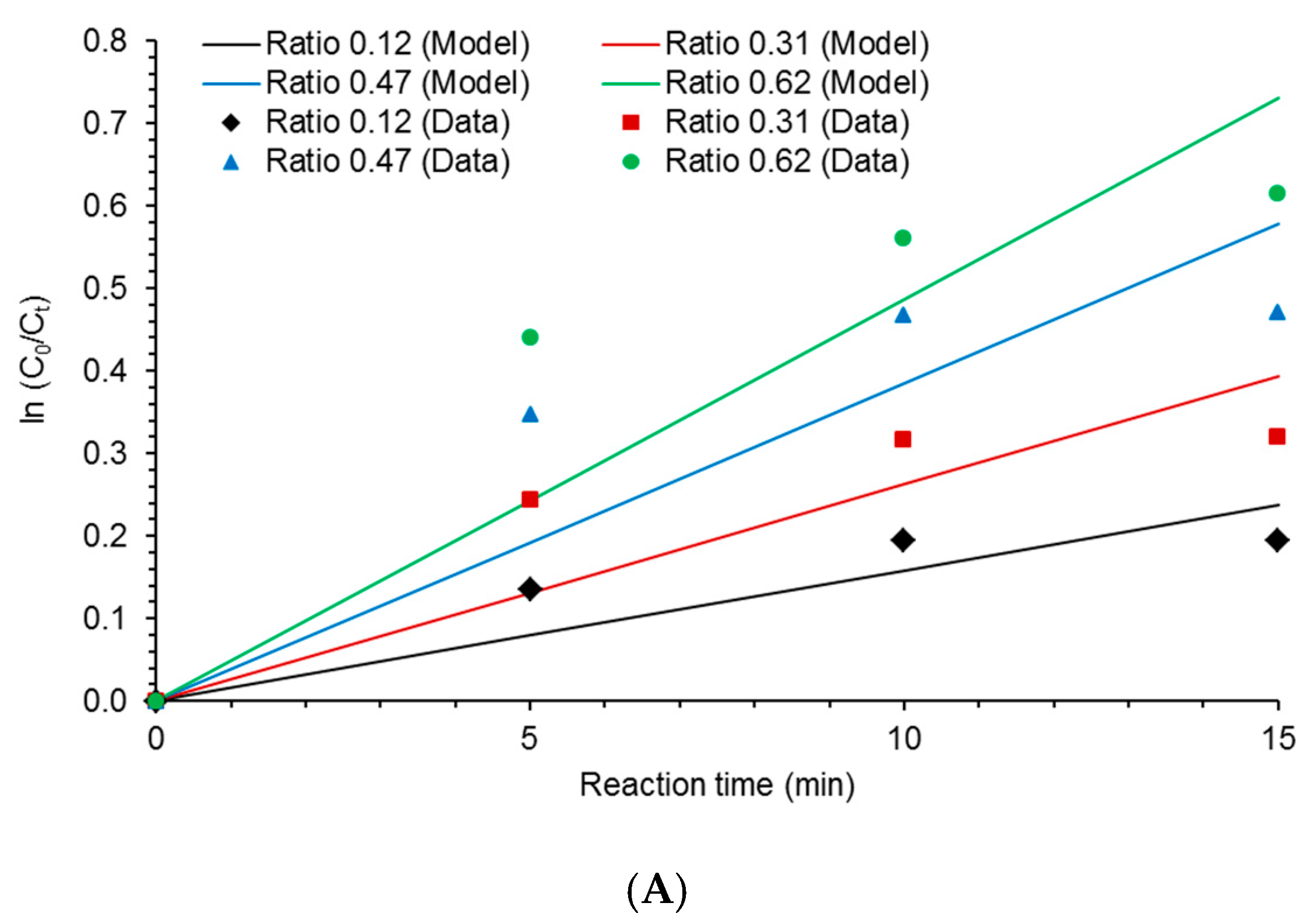
| Kinetic Model | Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| First order | (10) | |
| Second order | (11) | |
| BMG model | (12) | |
| Kinetic Model | Ratio of [H2O2] to [COD] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.62 | |
| First order kinetic | ||||
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0158 | 0.0262 | 0.0385 | 0.0487 |
| R2 | 0.8221 | 0.7804 | 0.7964 | 0.8272 |
| Second order kinetic | ||||
| k2 (L·mg−1·min−1) × 10−6 | 0.160 | 0.286 | 0.448 | 0.591 |
| R2 | 0.8390 | 0.8058 | 0.8230 | 0.8403 |
| BMG kinetic model | ||||
| 1/m (min−1) | 0.0650 | 0.1428 | 0.2015 | 0.3511 |
| 1/b | 0.2225 | 0.3224 | 0.4345 | 0.5129 |
| R2 | 0.9809 | 0.9957 | 0.9919 | 0.9912 |
| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 132,250 |
| BOD5 | mg/L | 31,250 |
| pH | - | 3.80 |
| Iron | mg/L | 128.10 |
| Sulfate | mg/L | 3275.53 |
| Phenol | mg/L | 4.64 |
| Appearance | - | Dark brown |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakika, D.C.; Sarto, S.; Mindaryani, A.; Hidayat, M. Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters. Catalysts 2019, 9, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110881
Hakika DC, Sarto S, Mindaryani A, Hidayat M. Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters. Catalysts. 2019; 9(11):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110881
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakika, Dhias Cahya, Sarto Sarto, Aswati Mindaryani, and Muslikhin Hidayat. 2019. "Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters" Catalysts 9, no. 11: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110881
APA StyleHakika, D. C., Sarto, S., Mindaryani, A., & Hidayat, M. (2019). Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters. Catalysts, 9(11), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110881




