Synthesis of a Novel Magnetically Retrievable Nanocomposite with Au Nanocatalysts for Hydration Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
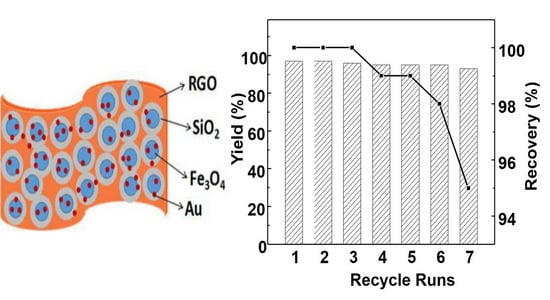
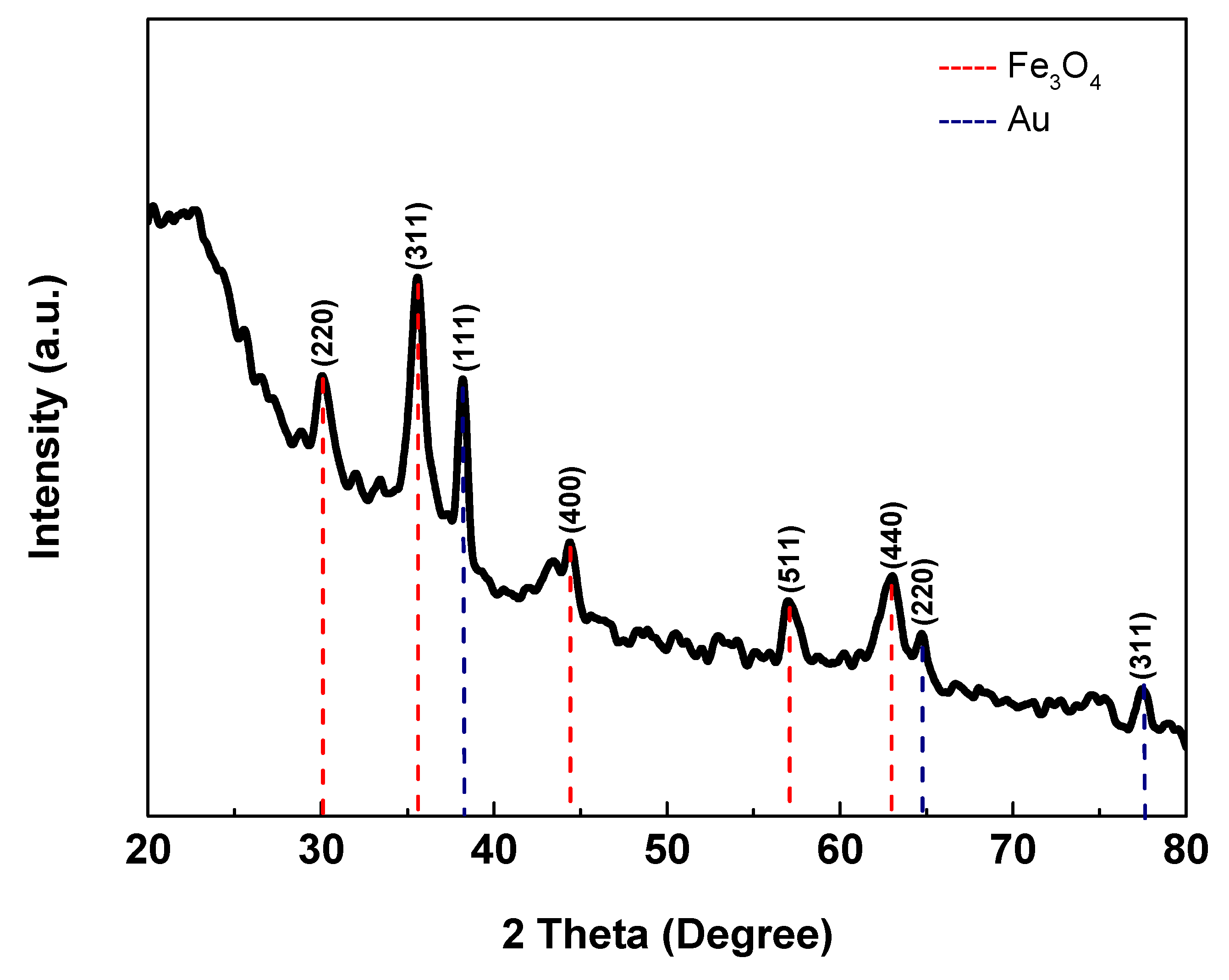
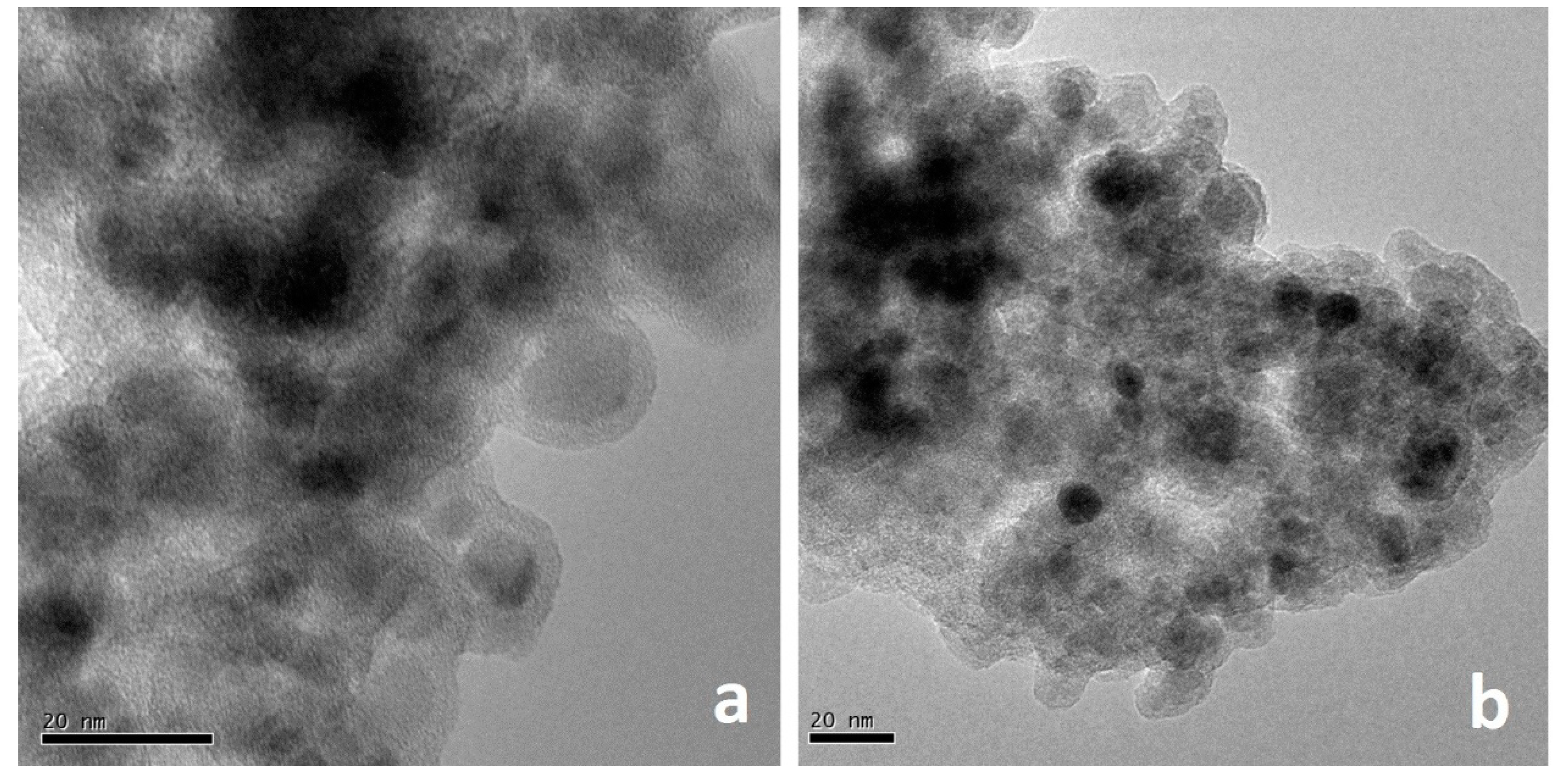
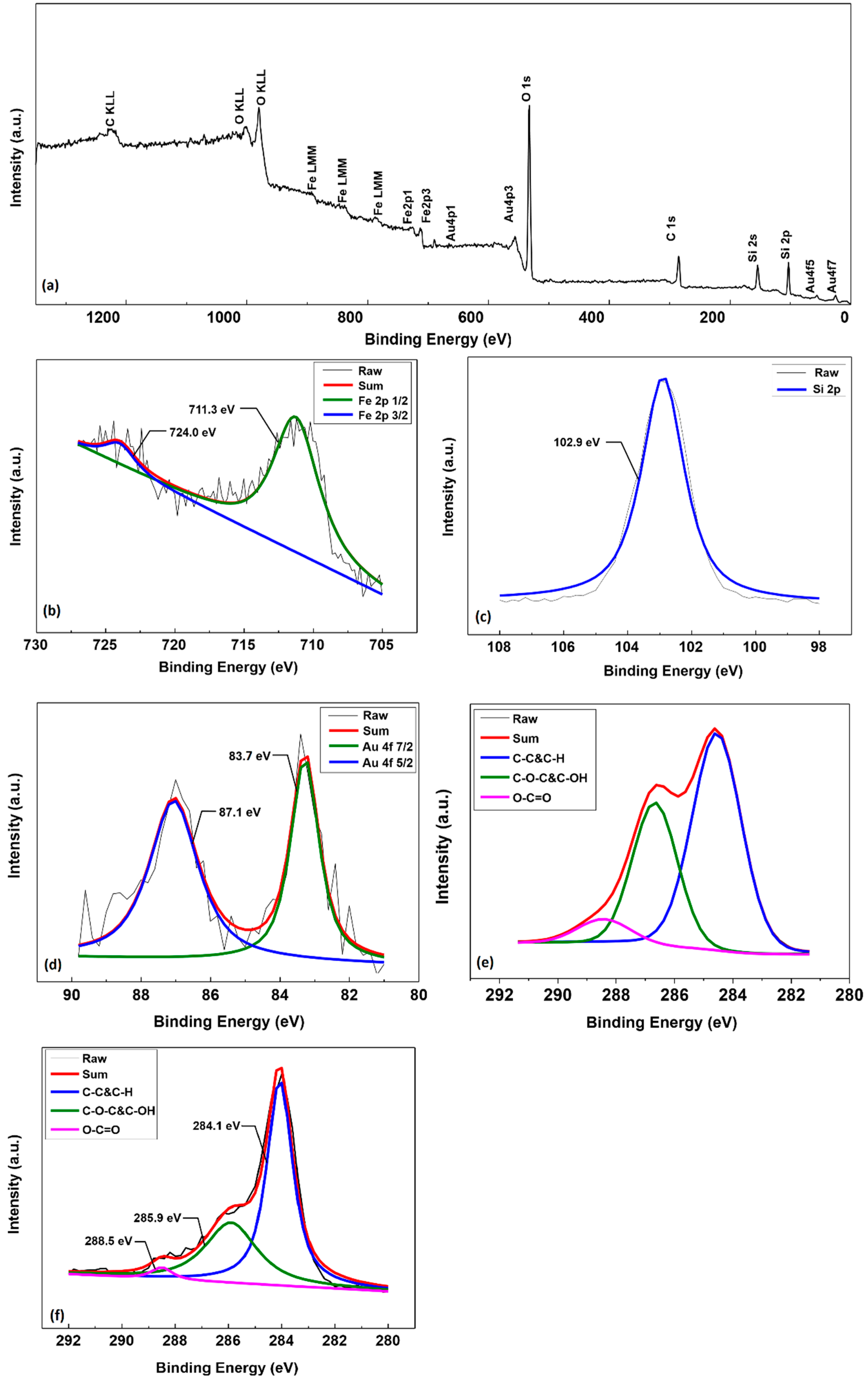
2.1. Characterization of Au-SiO2@Fe3O4-RGO
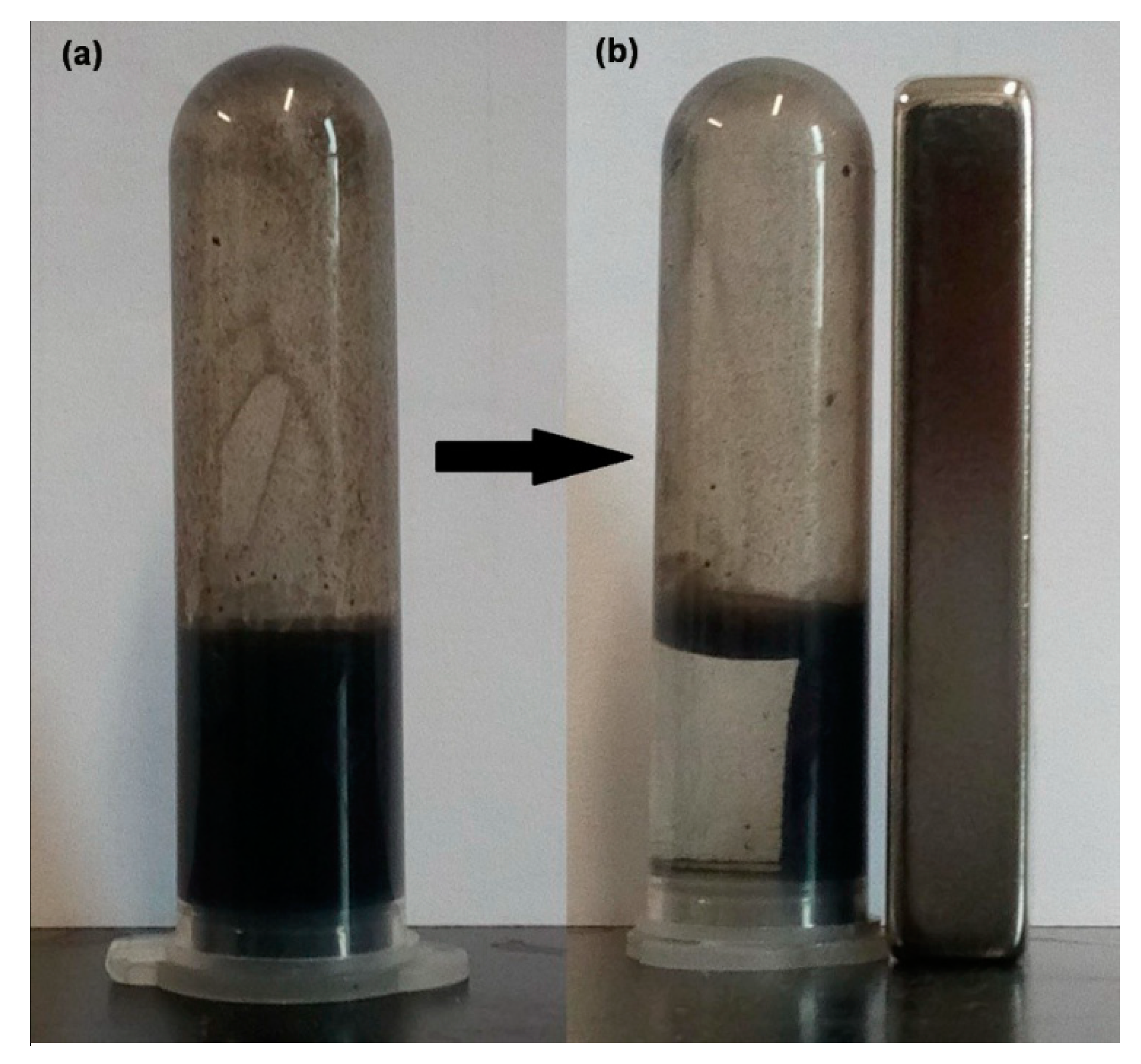
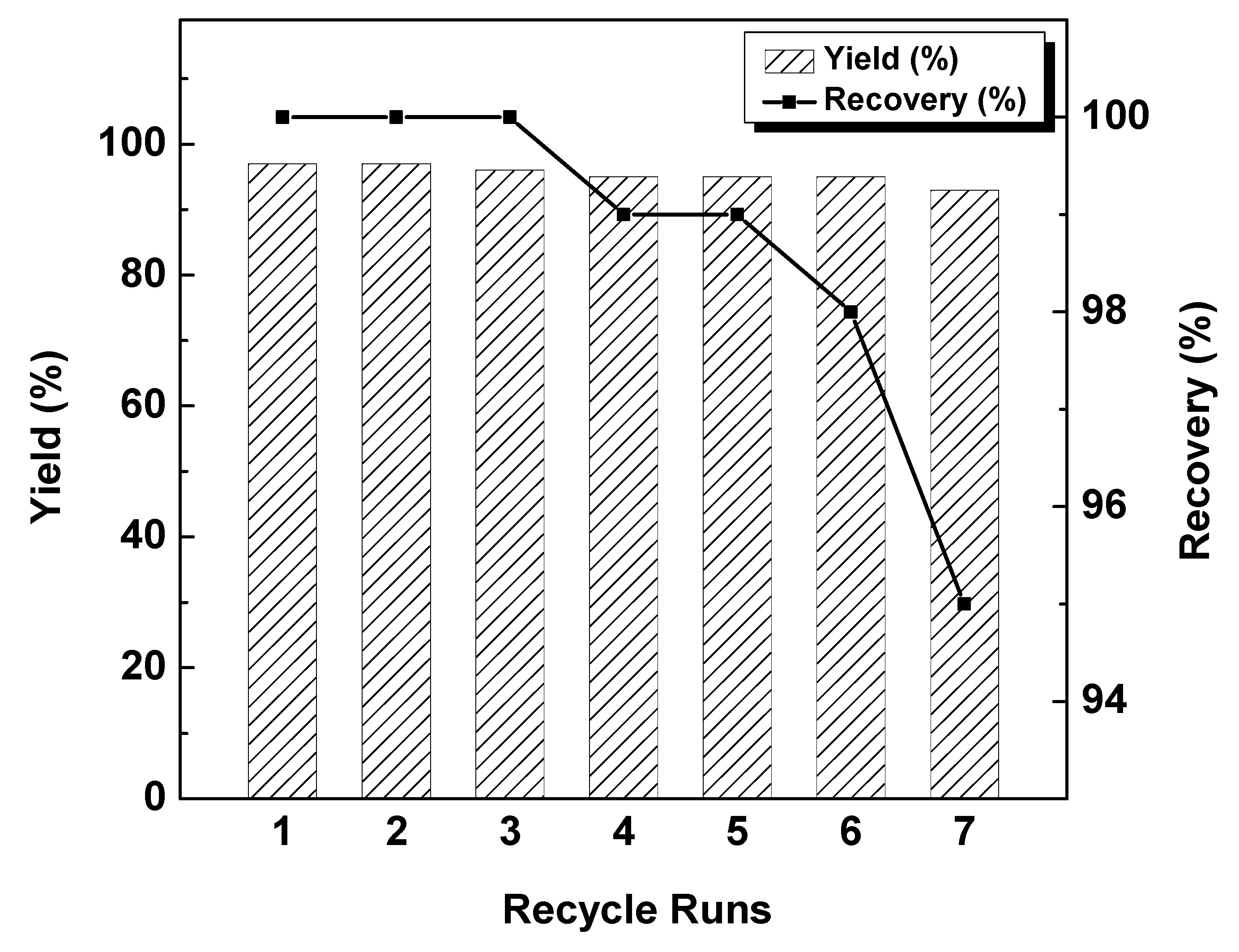
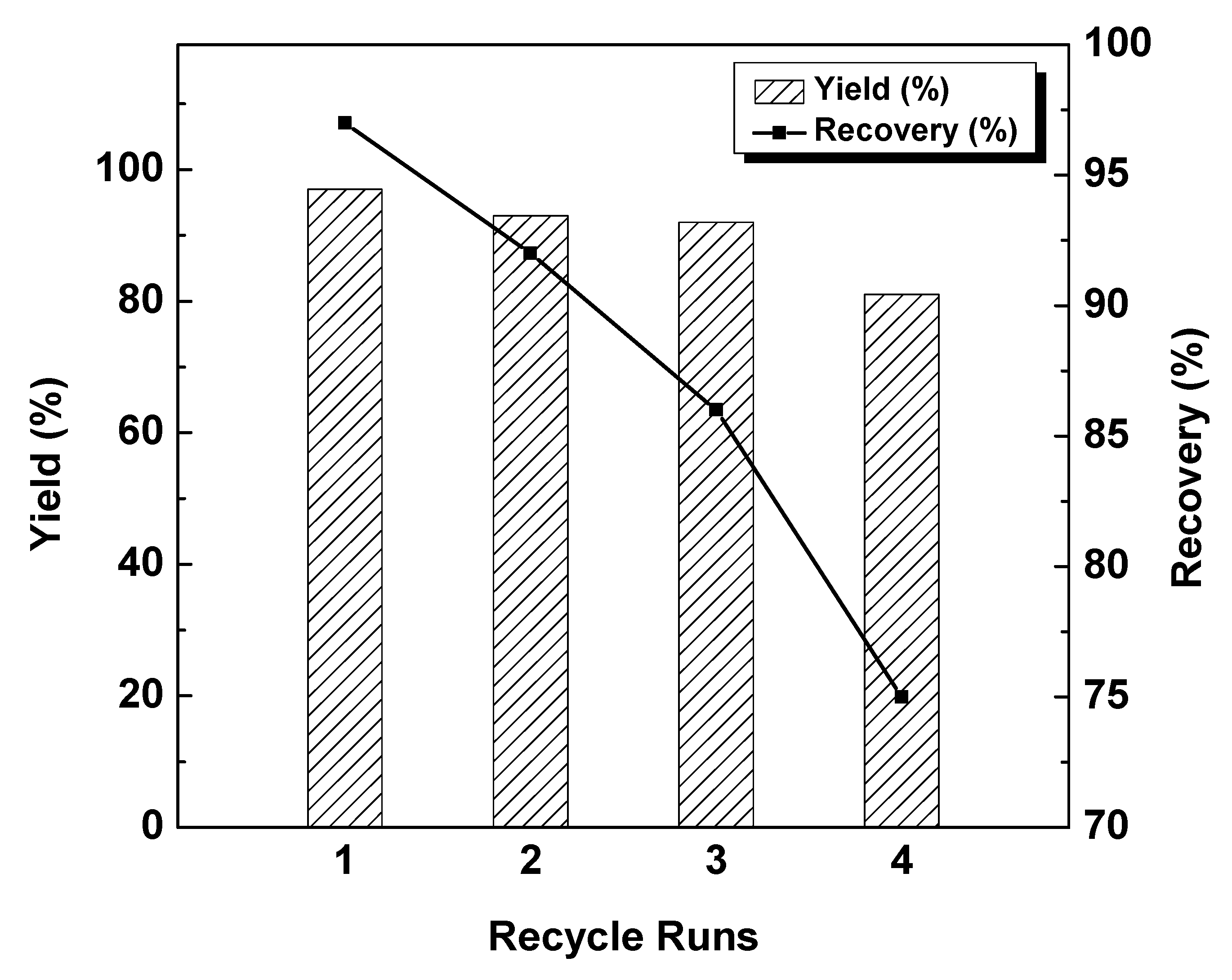
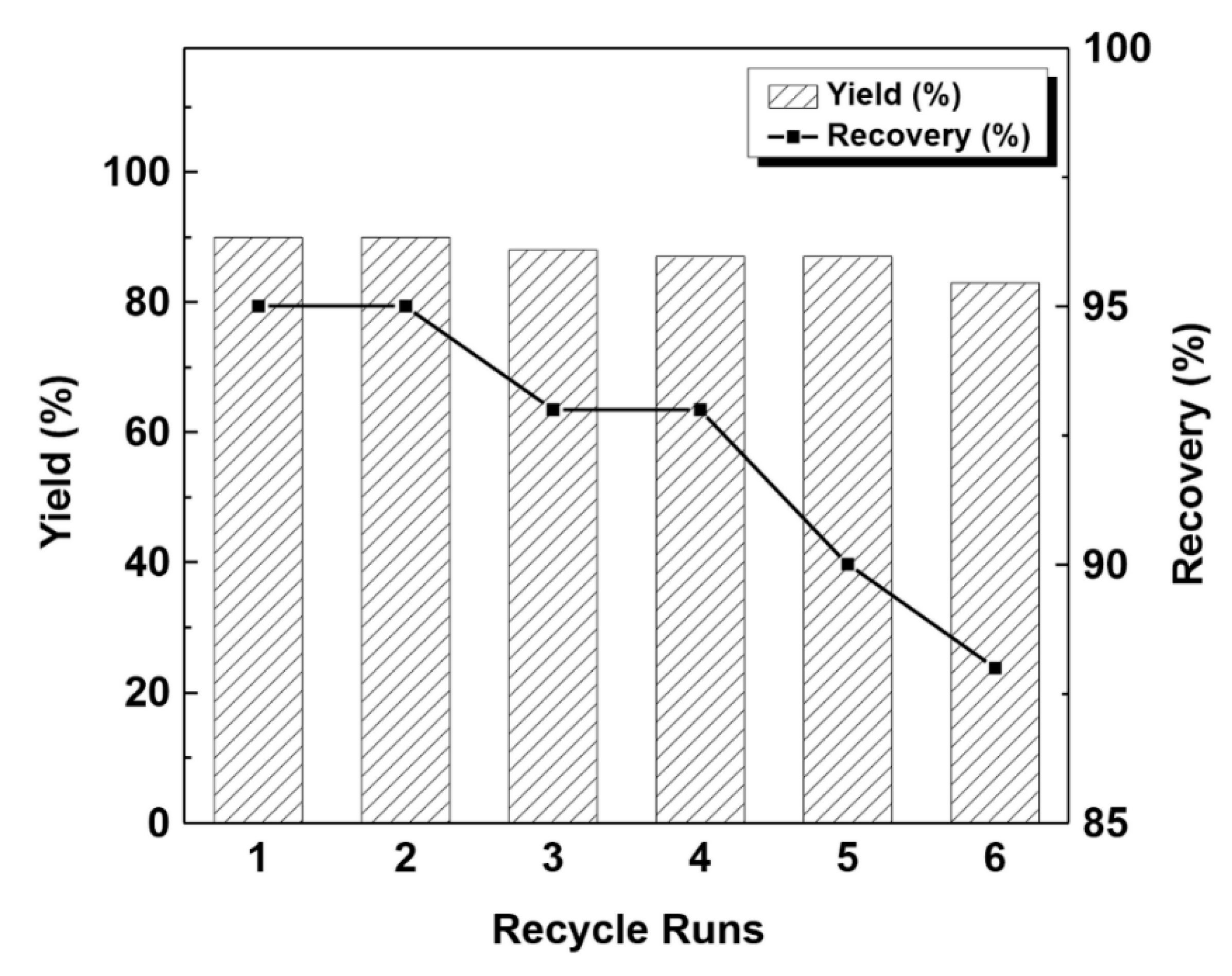
2.2. Catalytic Reaction
3. Materials and Methods
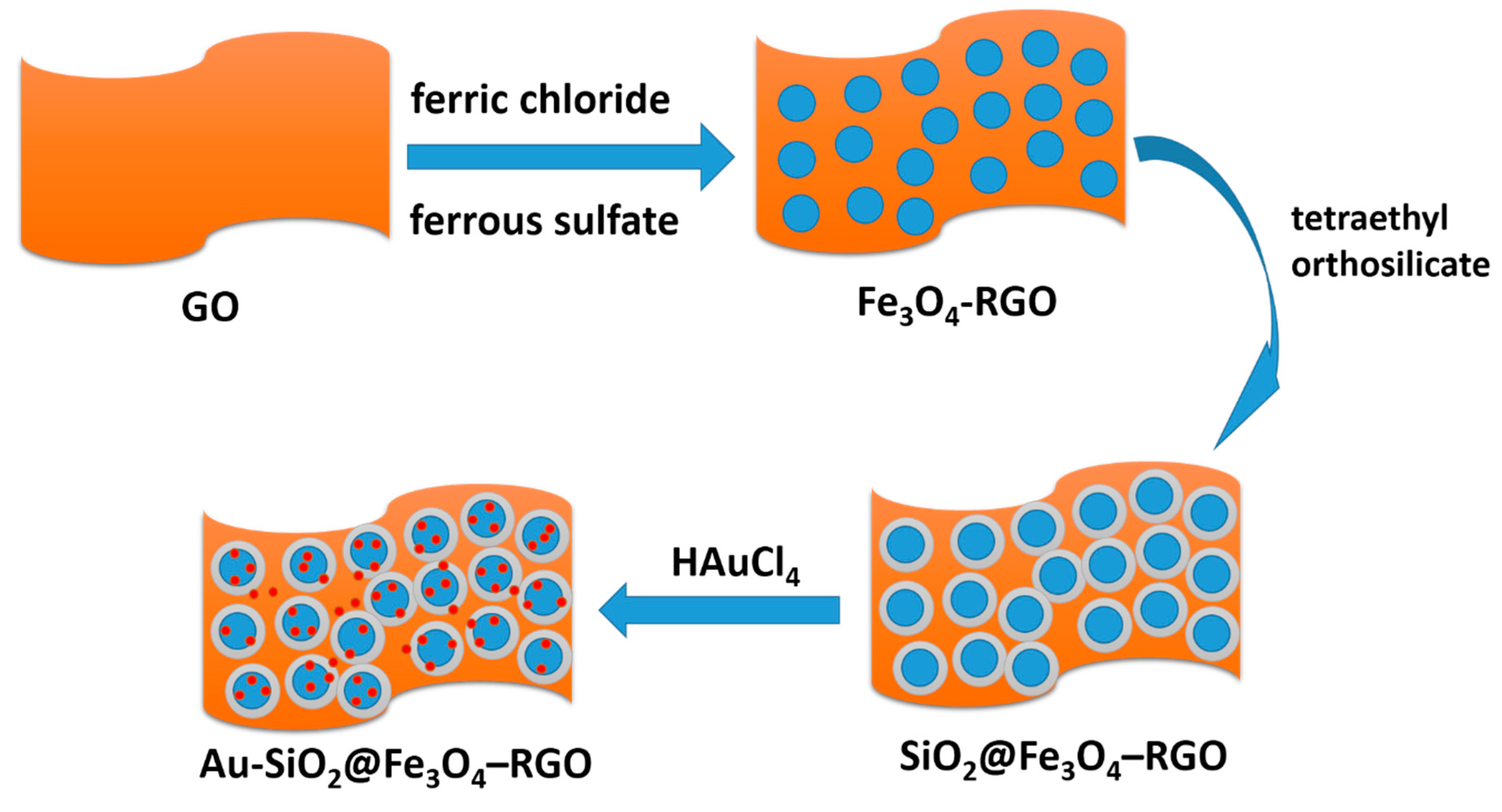
3.1. Preparation of Fe3O4-RGO
3.2. Synthesis of Au-SiO2@Fe3O4-RGO
3.3. Catalytic Hydration Reactions
3.4. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, D.; Jenkins, W. LXIX.—The interaction of acetylene and mercuric chloride. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1919, 115, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Miao, C.; Wang, W.; Lei, Z.; Sun, W. Hydration of terminal alkynes catalyzed by a water-soluble salen-Co(III) complex. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, N.; Lu, L.; Zhu, G. Regioselective hydration of terminal alkynes catalyzed by a neutral gold(I) complex [(IPr)AuCl] and one-pot synthesis of optically active secondary alcohols from terminal alkynes by the combination of [(IPr)AuCl] and Cp*RhCl[(R,R)-TsDPEN]. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Cai, C. Catalytic hydration of alkynes to ketones by a salen–gold (III) complex. Catal. Commun. 2015, 65, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, L.; Petrova, P.; Liotta, L.F.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; Kaszkur, Z.; Munteanu, G.; Tabakova, T. Gold catalysts on Y-doped ceria supports for complete benzene oxidation. Catalysts 2016, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Ilieva, L.; Ivanov, I.; Zanell, R.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; Kaszkur, Z.; Andreev, D. Influence of the preparation method and dopants nature on the WGS activity of gold catalysts supported on doped by transition metals ceria. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszak, R.; Ferraz, C.P.; Sha, J.; Houda, S.; Rossi, L.M.; Paul, S. Advances in base-free oxidation of bio-based compounds on supported gold catalysts. Catalysts 2017, 7, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Ivanov, I.; Karakirova, Y.; Karashanova, D.; Venezia, A.M.; Petrova, P.; Avdeev, G.; Kolentsova, E.; Ivanov, K. Promotional effect of gold on the WGS activity of alumina-supported copper-manganese mixed oxides. Catalysts 2018, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T. Recent Advances in Design of Gold-Based Catalysts for H-2 Clean-Up Reactions. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts for organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.; Parak, W. Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1333–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Dai, C.; Xu, Y.; Yue, T.; Zhao, M. Precisely tailoring bubble morphology in microchannel by nanoparticles self-assembly. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3707–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Laurent, S.; Fattahi, H.; Elst, L.; Muller, R. Superparamagnetic nanosystems based on iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical imaging. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W. Application of iron oxide nanoparticles in glioma imaging and therapy: from bench to bedside. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7808–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Le, X.; Dong, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Ma, J. Ni@Pd core–shell nanoparticles modified fibrous silica nanospheres as highly efficient and recoverable catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 162, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Hong, K.; Lee, T.; Moon, C.; Hong, S.; Zhang, K.; Suh, J.; Choi, K.; Varma, R.; Jang, H. Magnetically retrievable nanocomposite adorned with Pd nanocatalysts: efficient reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous media. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Park, Y.; Yeon, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, W.; Ko, S.; Cheon, J. Demonstration of a magnetic and catalytic Co@Pt nanoparticle as a dual-function nanoplatform. Chem. Commun. 2006, 15, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z. Multifunctional composite core–shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4474–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhao, G.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Removal of Cu(II) and Fulvic Acid by Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Decorated with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2012, 4, 4991–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. Fluorescence analysis of 6-mercaptopurine with the use of a nano-composite consisting of BSA-capped Au nano-clusters and core–shell Fe3O4–SiO2 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Wang, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles attached to graphene oxide and its use as an adsorbent. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2012, 379, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, F.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, P. Fabrication of hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4@SiO2@polyaniline quaternary composite and its improved electrochemical performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 634, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubir, N.; Yacou, C.; Motuzas, J.; Zhang, X.; Costa, J. Structural and functional investigation of graphene oxide–Fe3O4 nanocomposites for the heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xiao, W.; Li, Q. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of graphene based Au–TiO2 photocatalysts for efficient visible-light hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3847–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, A.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Enhanced hydrogenation of olefins and ketones with a ruthenium complex covalently anchored on graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 15039–15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.; Offeman, R. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Entry | Sample | Au (mmol/g) | Solvent | Yield (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blank | / | dioxane | 9 |
| 2 | SiO2@Fe3O4–RGO | / | dioxane | 10 |
| 3 | Au–SiO2@Fe3O4–RGO | 0.31 | dioxane | 97 |
| 4 | Au–RGO | 0.36 | dioxane | 95 |
| 5 | Au–SiO2@Fe3O4–RGO | 0.31 | H2O | 90 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Q. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetically Retrievable Nanocomposite with Au Nanocatalysts for Hydration Reaction. Catalysts 2019, 9, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100789
Yu X, Dai Y, Wu Y, Cheng Y, Zhao Q. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetically Retrievable Nanocomposite with Au Nanocatalysts for Hydration Reaction. Catalysts. 2019; 9(10):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100789
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaoxi, Yingjie Dai, Youran Wu, Yunfeng Cheng, and Qingshan Zhao. 2019. "Synthesis of a Novel Magnetically Retrievable Nanocomposite with Au Nanocatalysts for Hydration Reaction" Catalysts 9, no. 10: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100789
APA StyleYu, X., Dai, Y., Wu, Y., Cheng, Y., & Zhao, Q. (2019). Synthesis of a Novel Magnetically Retrievable Nanocomposite with Au Nanocatalysts for Hydration Reaction. Catalysts, 9(10), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100789