The ZSM-5-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with N2O: Effect of Lewis Acid Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
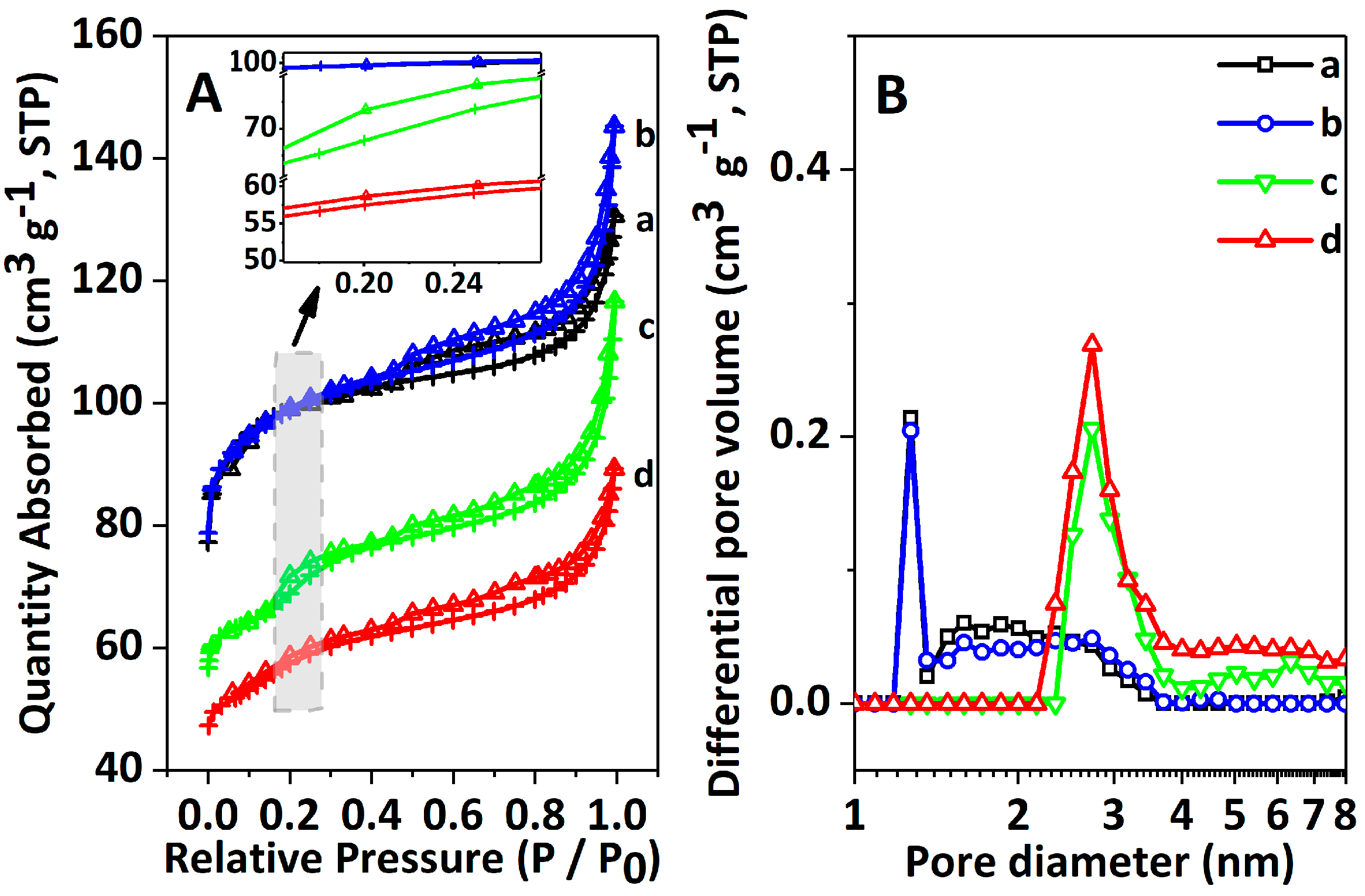
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of Catalysts
2.2. Catalysts Acidity
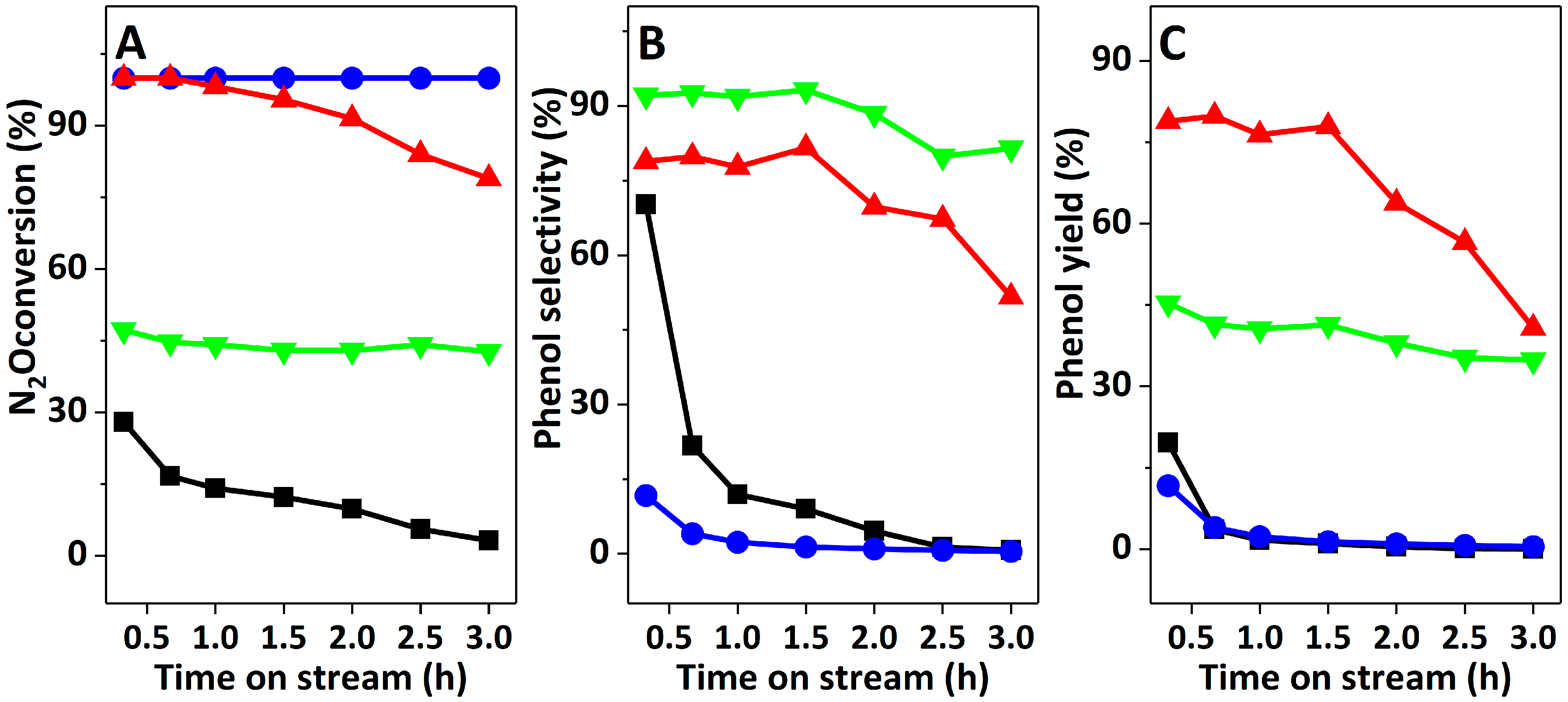
2.3. Catalyst Performance in Benzene Hydroxylation Reaction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Fe/ZSM-5
3.2. Water Steam Treatment
3.3. Different Temperature Calcinated Treatment
3.4. Catalyst Performance in BTOP Reaction
3.5. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, W. Direct Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol by N2O over Meso-Fe-ZSM-5 Catalysts Obtained via Alkaline Post-Treatment. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Hirata, J.; Matsukami, K.; Kagawa, S. Catalytic Oxidation by Oxide Radical Ions. 1. One-Step Hydroxylation of Benzene to Phenol over Group 5 and 6 Oxides Supported on Silica Gel. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Nakashiro, K.; Ono, Y. Hydroxylation of Benzene with Dinitrogen Monoxide over H-ZSM-5 Zeolite. Chem. Lett. 1988, 63, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, G.I.; Sheveleva, G.A.; Kharitonov, A.S.; Romannikov, V.N.; Vostrikova, L.A. Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol by Nitrous Oxide over Fe-ZSM-5 Zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1992, 82, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Howitt, C. Investigation of Zeolite Catalysts for the Direct Partial Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1993, 103, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; Monaci, R.; Solinas, V.; Berlier, G.; Bordiga, S.; Rossetti, I.; Oliva, C.; Forni, L. Activity and Deactivation of Fe-MFI Catalysts for Benzene Hydroxylation to Phenol by N2O. J. Catal. 2003, 214, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuranov, I.; Bulushev, D.A.; Renken, A.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Benzene Hydroxylation over FeZSM-5 Catalysts: Which Fe Sites Are Active? J. Catal. 2004, 227, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Pillai, K.S.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Effect of Steaming on One-Step Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with Nitrous Oxide over Fe/MFI Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 264, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekkoek, A.J.J.; Kim, W.; Degirmenci, V.; Xin, H.; Ryoo, R.; Hensen, E.J.M. Catalytic Performance of Sheet-like Fe/ZSM-5 Zeolites for the Selective Oxidation of Benzene with Nitrous Oxide. J. Catal. 2013, 299, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Gallardo-Llamas, A. Framework Composition Effects on the Performance of Steam-Activated FeMFI Zeolites in the N2O-Mediated Propane Oxidative Dehydrogenation to Propylene. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20529–20538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshizawa, K. Mechanism for the Direct Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol by FeO+. Organometallics 2005, 24, 3532–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, J. Direct Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol Catalyzed by a Vanadium-Substituted Heteropolymolybdic Acid Catalyst. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2006, 71, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensen, E.J.M.; Zhu, Q.; Van Santen, R.A. Selective Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with Nitrous Oxide over MFI Zeolites: 2. on the Effect of the Iron and Aluminum Content and the Preparation Route. J. Catal. 2005, 233, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanza, R.; Rossetti, I.; Mazzola, I.; Forni, L. Study of Fe-Silicalite Catalyst for the N2O Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 205, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyman, P.J.; van der Waal, P.; van Bekkum, H. Acid Dealumination of ZSM-5. Zeolites 1997, 18, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Koekkoek, A.; Yang, Q.; van Santen, R.; Li, C.; Hensen, E.J.M. A Hierarchical Fe/ZSM-5 Zeolite with Superior Catalytic Performance for Benzene Hydroxylation to Phenol. Chem. Commun. 2009, 7590–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.M.; Bibby, D.M.; Coddington, J.M.; Howe, R.F.; Meinhold, R.H. Dealumination of HZSM-5 Zeolites. J. Catal. 1996, 161, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, M.; Kesore, K.; Mönnig, R.; Schwieger, W.; Tißler, A.; Turek, T. Preparation of a Highly Active Fe-ZSM-5 Catalyst through Solid-State Ion Exchange for the Catalytic Decomposition of N2O. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 184, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Banno, K.; Shinjoh, H. Characterization of Fe/ZSM-5 DeNOx Catalysts Prepared by Different Methods: Relationships between Active Fe Sites and NH3-SCR Performance. J. Catal. 2008, 260, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, M.; Epelde, E.; Aguayo, A.T.; Gayubo, A.G.; Bilbao, J.; Castaño, P. Selective Dealumination of HZSM-5 Zeolite Boosts Propylene by Modifying 1-Butene Cracking Pathway. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kawi, S. A New MFI-Type Zeolite Containing Uniform Supermicropores: Synthesis by Structural Transformation of CTA+-MCM-41 and Application in SCR of NOx. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1354–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.X.; Xia, Y.D.; Mokaya, R. Zeolite ZSM-5 with Unique Supermicropores Synthesized Using Mesoporous Carbon as a Template. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zied, B.M.; Schwieger, W.; Unger, A. Nitrous Oxide Decomposition over Transition Metal Exchanged ZSM-5 Zeolites Prepared by the Solid-State Ion-Exchange Method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Yamashita, N.; Iwami, Y.; Takeda, K.; Kawakami, Y. Estimation of Dealumination Rate of ZSM-5 Zeolite by Adsorption of Water Vapor. Zeolites 1996, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Wu, W.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D. Direct Synthesis of Hierarchical ZSM-5 Zeolite and Its Performance in Catalyzing Methanol to Gasoline Conversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 141208145007001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Sun, K.; Sun, K.; Feng, Z.; Li, W.X.; Li, C. Direct Spectroscopic Observation of Fe(III)−Phenolate Complex Formed From the Reaction of Benzene With Peroxide Species on Fe/ZSM-5 At Room Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 9001–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Shishido, T.; Wang, Y. Iron-Catalyzed Propylene Epoxidation by Nitrous Oxide: Toward Understanding the Nature of Active Iron Sites with Modified Fe-MFI and Fe-MCM-41 Catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 239, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiga, S.; Buzzoni, R.; Geobaldo, F.; Lamberti, C.; Giamello, E.; Zecchina, A.; Leofanti, G.; Petrini, G.; Tozzola, G.; Vlaic, G. Structure and Reactivity of Framework and Extraframework Iron in Fe-Silicalite as Investigated by Spectroscopic and Physicochemical Methods. J. Catal. 1996, 158, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarin, J.; Tuilier; Durr, J.; Kessler, H. Optical and X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Studies of Iron MFI-Type Zeolite Prepared in Fluoride Medium. Zeolites 1992, 12, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xia, H.; Hensen, E.; Vansanten, R.; Li, C. Chemistry of N2O Decomposition on Active Sites with Different Nature: Effect of High-Temperature Treatment of Fe/ZSM-5. J. Catal. 2006, 238, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wen, D.; Yang, Y.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Cui, M.; Qiao, X. Enhanced Catalytic Performance for Light-Olefins Production from Chloromethane over Hierarchical Porous ZSM-5 Zeolite Synthesized by a Growth-Inhibition Strategy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, G.; Liu, H.; Bao, X. A Novel Method for Enhancing On-Stream Stability of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Gasoline Hydro-Upgrading Catalyst: Post-Treatment of HZSM-5 Zeolite by Combined Steaming and Citric Acid Leaching. Catal. Today 2007, 125, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.; Seijger, G.B.F.; van den Bleek, C.M.; Makkee, M.; Mul, G.; Calis, H.P.A. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 over Fe-ZSM-5 Catalysts Prepared by Sublimation of FeCl3 at Different Temperatures. Catal. Lett. 2003, 86, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, S.M.T.; Mezari, B.; Pidko, E.A.; Magusin, P.C.M.M.; Hensen, E.J.M. Influence of Steaming on the Acidity and the Methanol Conversion Reaction of HZSM-5 Zeolite. J. Catal. 2013, 307, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, B.; Hoffmann, J. Temperature-Programmed Desorption (TPD) of Various Bases from HY Zeolites. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1985, 27, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobree, L.J.; Hwang, I.-C.; Reimer, J.A.; Bell, A.T. Investigations of the State of Fe in H–ZSM-5. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophal, C. Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrous Oxide over Fe-MFI in the Presence of Propene as Reductant. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 16, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, K.; Nobukawa, T.; Yoshida, M.; Sato, Y.; Okumura, K.; Tomishige, K.; Kunimori, K. The Importance of Fe Loading on the N2O Reduction with NH3 over Fe-MFI: Effect of Acid Site Formation on Fe Species. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 69, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Dou, T.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, H. Synthesis and Application of a Novel Mesoporous Zeolite L in the Catalyst for the HDS of FCC Gasoline. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 381, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xin, W.; Xie, S.; Xu, L. Transformation of Isobutyl Alcohol to Aromatics over Zeolite-Based Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.H.; Dömök, M.; Olindo, R.; van Veen, A.C.; Lercher, J.A. Dealumination of HZSM-5 via Steam-Treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 164, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, L.; Tarasov, A.; Bogdan, V.; Tyrlov, A.; Fulmer, J. Selective Oxidation of Aromatic Compounds on Zeolites Using N2O as a Mild Oxidant. Catal. Today 2000, 61, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motz, J.L.; Heinichen, H.; Hölderich, W.F. Influence of Extra-Framework Alumina in H-[Al]ZSM-5 Zeolite on the Direct Hydroxylation of Benzene to Phenol. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 105, pp. 1053–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Dou, T.; Xu, J.; Deng, F. Hydrothermal Treatment on ZSM-5 Extrudates Catalyst for Methanol to Propylene Reaction: Finely Tuning the Acidic Property. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Van Teeffelen, R.M.; Van Santen, R.A.; Hensen, E.J.M. Effect of High-Temperature Treatment on Fe/ZSM-5 Prepared by Chemical Vapor Deposition of FeCl3: II. Nitrous Oxide Decomposition, Selective Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol, and Selective Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Isobutane. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.P.; Sobolev, V.I.; Panov, G.I. Deactivation by Coking and Regeneration of Zeolite Catalysts for Benzene-to-Phenol Oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 241, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhu, X.; Hensen, E.J.M. Stable Fe/ZSM-5 Nanosheet Zeolite Catalysts for the Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, P.M.; Grunwaldt, J.-D.; Jensen, P.A.; Knudsen, K.G.; Jensen, A.D. A Review of Catalytic Upgrading of Bio-Oil to Engine Fuels. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 407, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodart, P.; Nagy, J.B.; Debras, G.; Gabelica, Z.; Jacobs, P.A. Aluminum Siting in Mordenite and Dealumination Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 5183–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Viswanadham, N.; Ray, N.; Gupta, J.K.; Singh, I.D. Studies on Acidity, Activity and Coke Deactivation of ZSM-5 during n-Heptane Aromatization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 205, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckhuysen, B.M.; Wang, D.; Rosynek, M.P.; Lunsford, J.H. Conversion of Methane to Benzene over Transition Metal Ion ZSM-5 Zeolites I. Catalytic Characterization. J. Catal. 1998, 175, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piryutko, L.V.; Parenago, O.O.; Lunina, E.V.; Kharitonov, A.S.; Okkel, L.G.; Panov, G.I. Silylation Effect on the Catalytic Properties of FeZSM-11 in Benzene Oxidation to Phenol. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1994, 52, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, A.S.; Fenelonov, V.B.; Voskresenskaya, T.P.; Rudina, N.A.; Molchanov, V.V.; Plyasova, L.M.; Panov, G.I. Mechanism of FeZSM-5 Milling and Its Effect on the Catalytic Performance in Benzene to Phenol Oxidation. Zeolites 1995, 15, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





 ) refer to different temperature calcinated samples.
) refer to different temperature calcinated samples.
 ) refer to different temperature calcinated samples.
) refer to different temperature calcinated samples.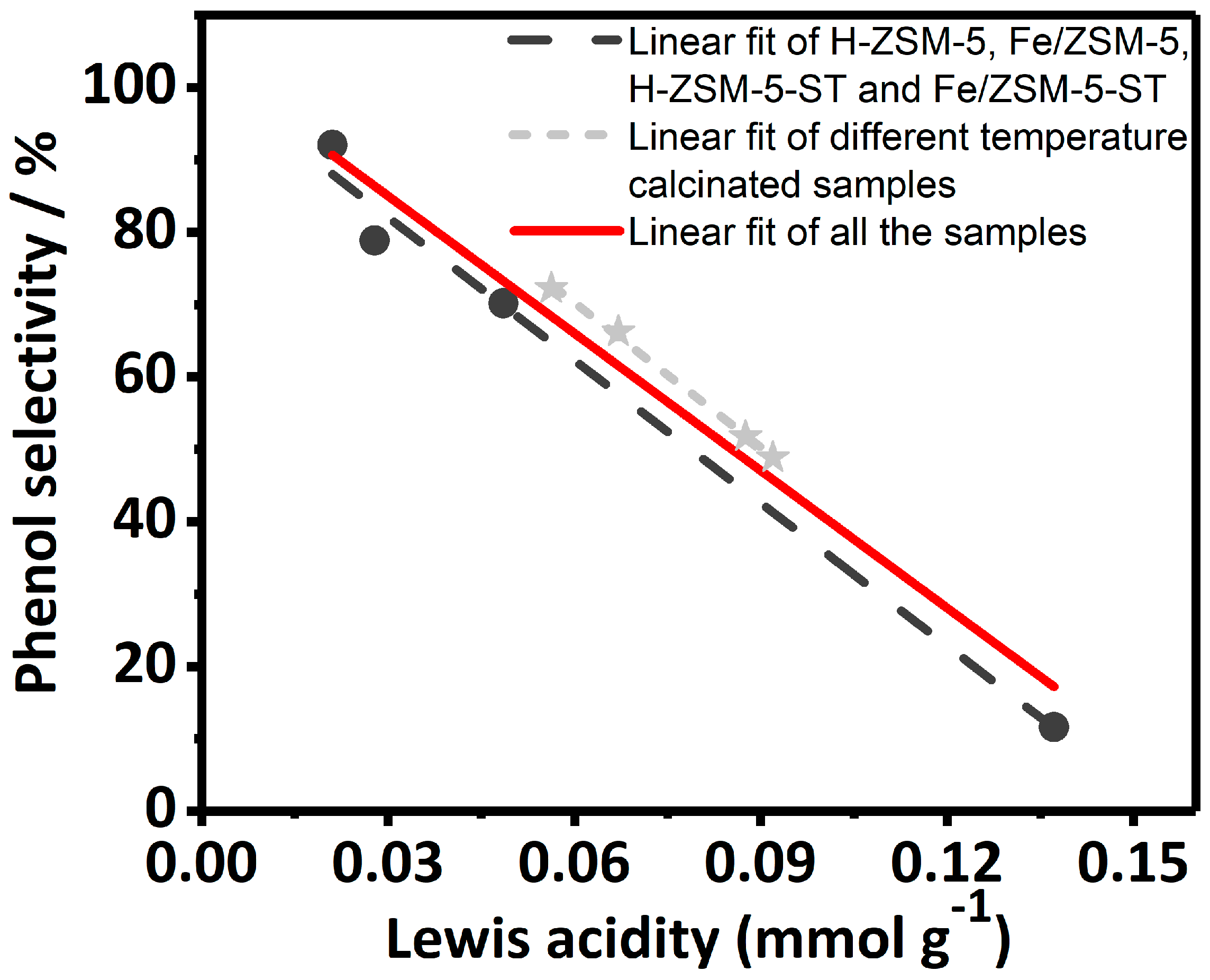
| Samples | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Smeso b/Smicro c | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso e/Vmicro f | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET a | Smeso b | Smicro c | Vtot d | Vmeso e | Vmicro f | |||
| H-ZSM-5 | 337 | 87 | 250 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 1.27 |
| Fe/ZSM-5 | 336 | 92 | 244 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 1.27 |
| H-ZSM-5-ST | 240 | 116 | 124 | 0.93 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 1.89 |
| Fe/ZSM-5-ST | 196 | 92 | 104 | 0.88 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 1.80 |
| Samples | A1 a [%] | A2 b [%] | A3 c [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/ZSM-5 | 20 | 52 | 28 |
| Fe/ZSM-5-ST | 35 | 54 | 11 |
| Samples | Total Acidity (mmol gcatal−1) | Weak Acidity (mmol gcatal−1) | Strong Acidity (mmol gcatal−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-ZSM-5 | 2.83 | 1.70 | 1.13 |
| Fe/ZSM-5 | 2.38 | 1.33 | 1.05 |
| H-ZSM-5-ST | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Fe/ZSM-5-ST | 0.89 | 0.52 | 0.37 |
| Samples | 423 K (Total) (mmol g−1) | B/L | 573 K (Strong) (mmol g−1) | B/L | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brønsted a | Lewis a | Brønsted | Lewis | |||
| H-ZSM-5 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 9.20 | 0.16 | 0 | -- |
| Fe/ZSM-5 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 4.50 |
| H-ZSM-5-ST | 0.04 | 0.02 | 2.00 | 0 | 0 | -- |
| Fe/ZSM-5-ST | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 0 | 0 | -- |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J. The ZSM-5-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with N2O: Effect of Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts 2019, 9, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010044
Ouyang C, Li Y, Li J. The ZSM-5-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with N2O: Effect of Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts. 2019; 9(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Cui, Yingxia Li, and Jianwei Li. 2019. "The ZSM-5-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with N2O: Effect of Lewis Acid Sites" Catalysts 9, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010044
APA StyleOuyang, C., Li, Y., & Li, J. (2019). The ZSM-5-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol with N2O: Effect of Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts, 9(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010044