Adsorption Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Supported Gold Catalyst under Self-Generated Alkaline Conditions for Efficient Elimination of Carbon Monoxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
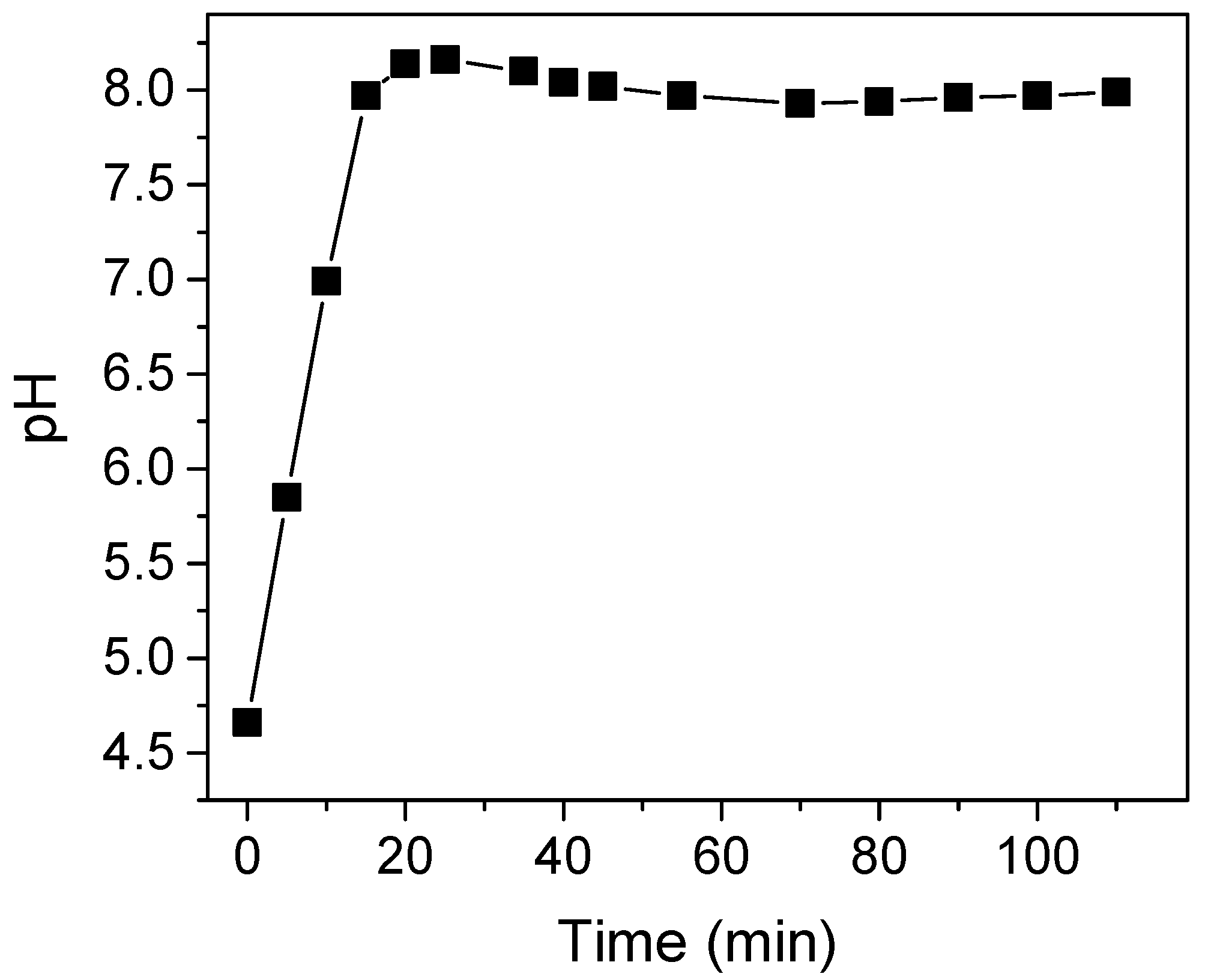
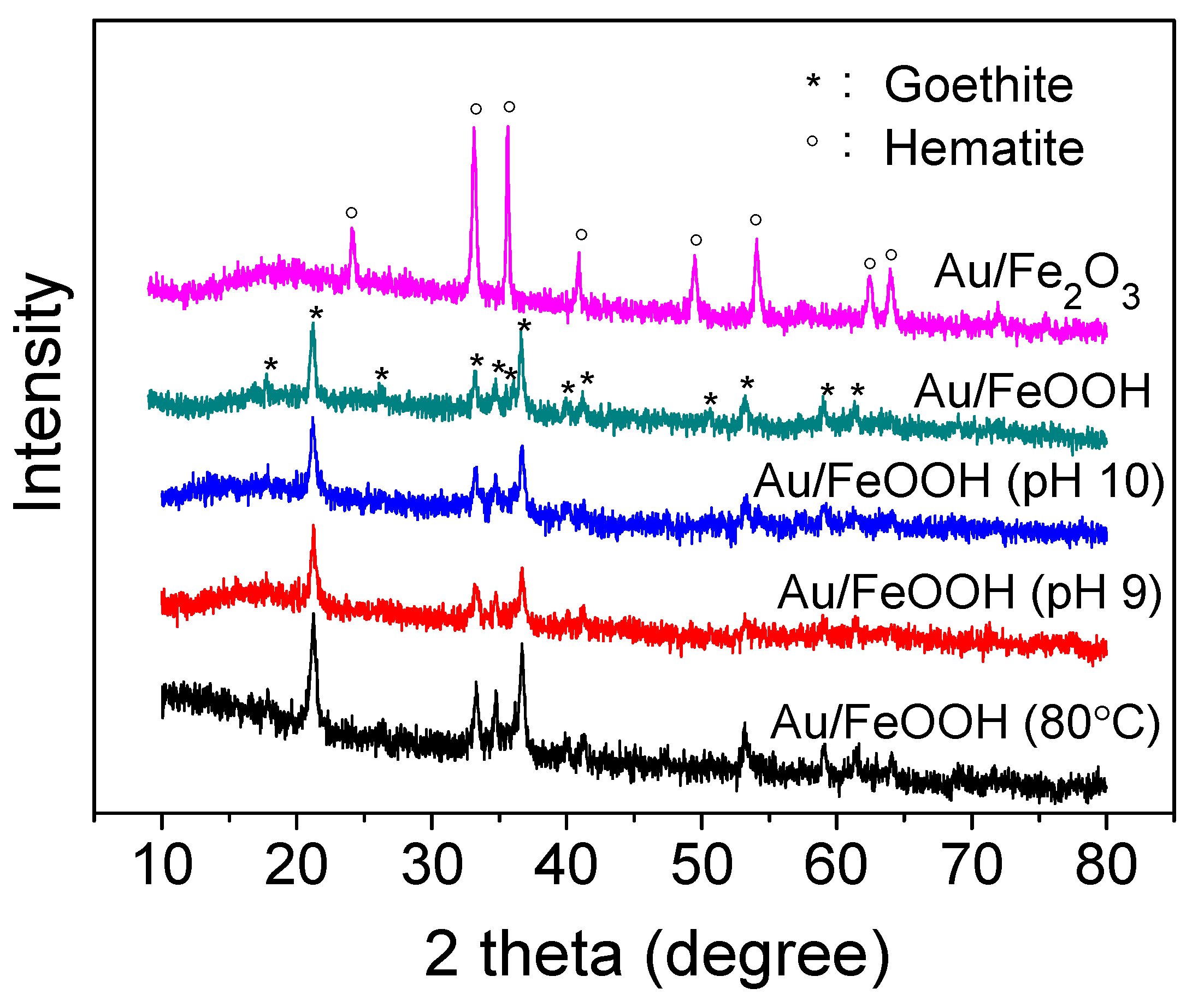
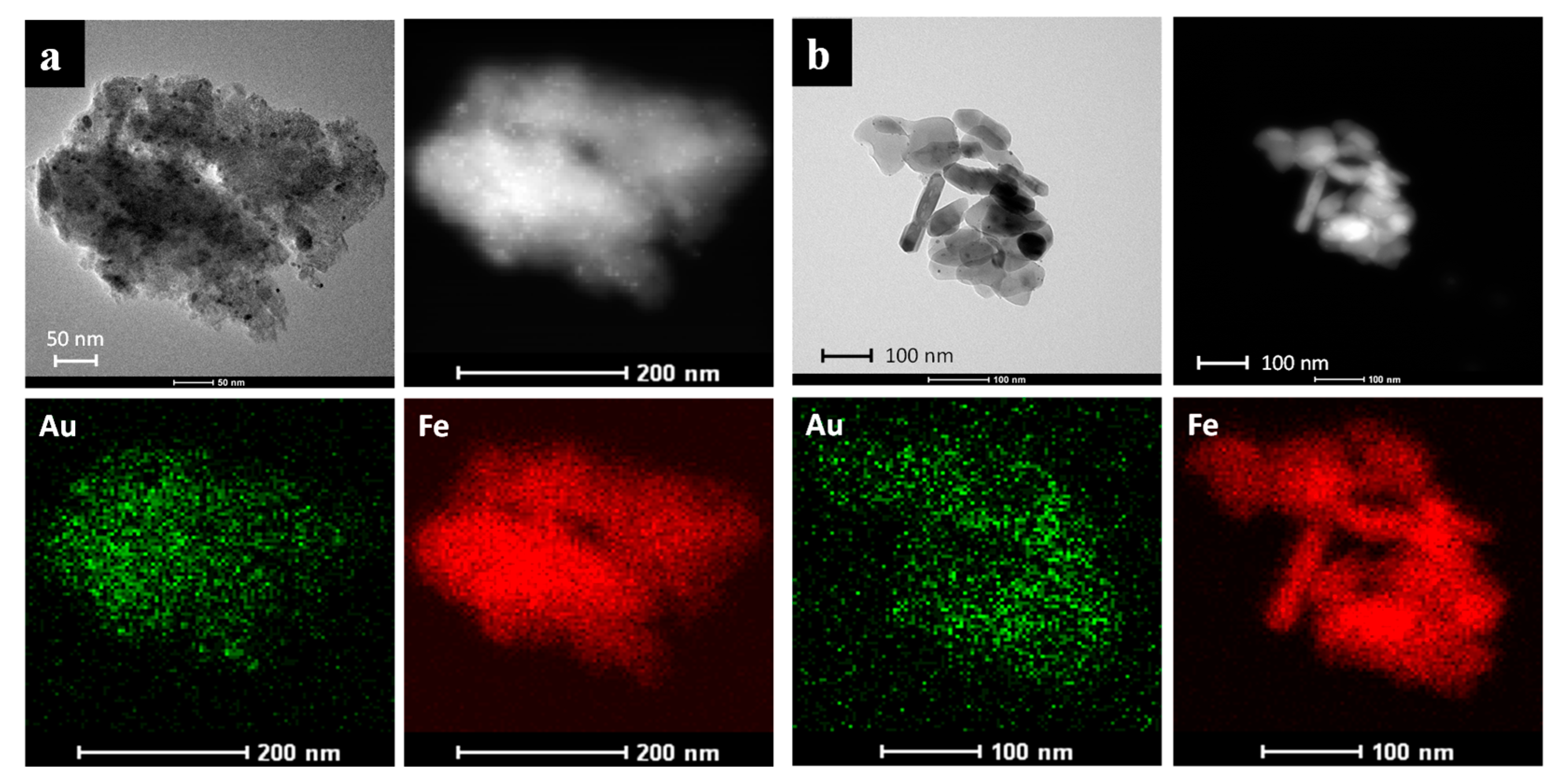
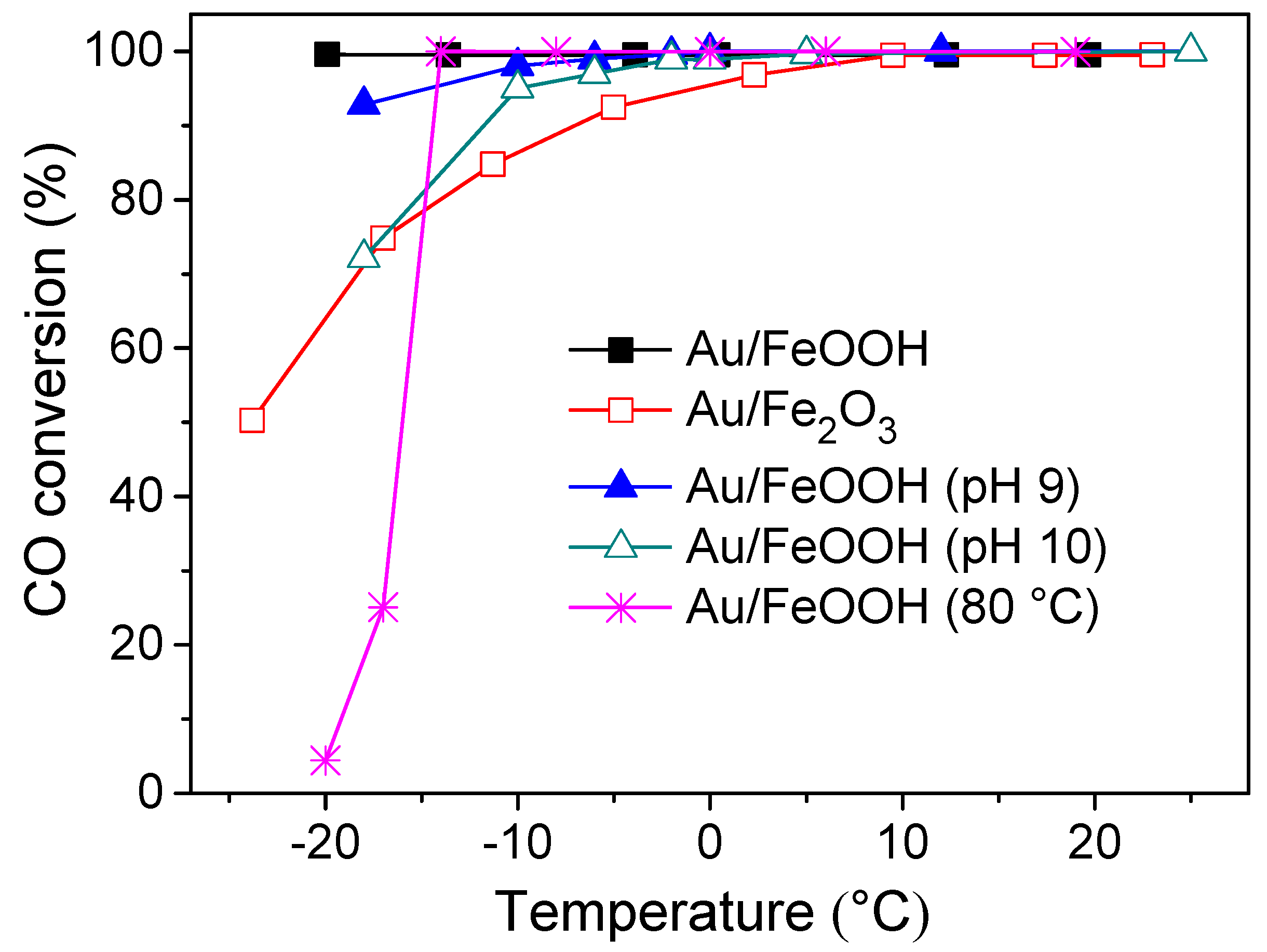
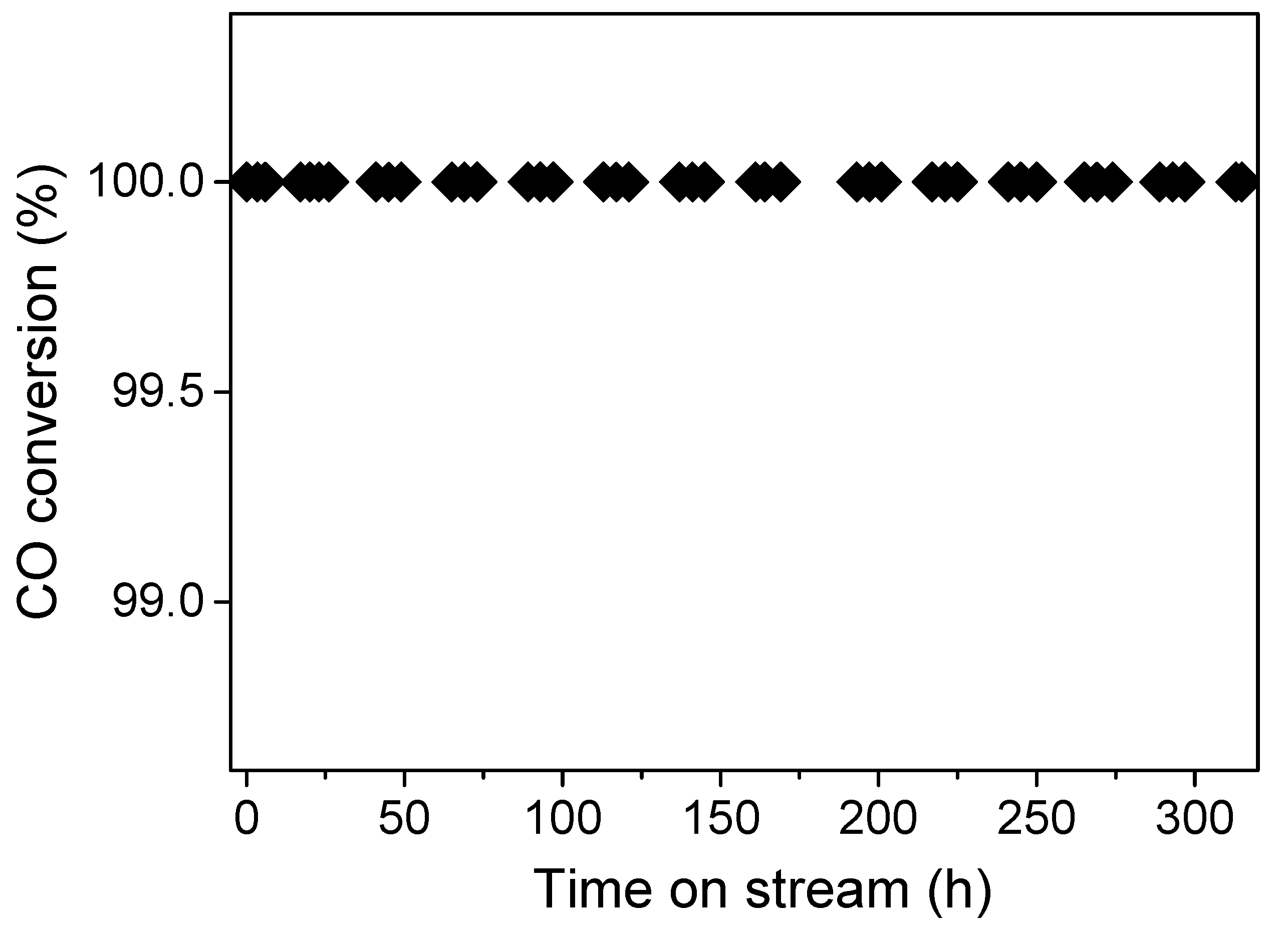
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M.; Ramírez Reina, T.; Ivanova, S.; Laguna, O.; Odriozola, J. Au/CeO2 catalysts: Structure and CO oxidation activity. Catalysts 2016, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.T.; Hao, Z.P.; Ma, C.Y. Morphology effects of Co3O4 on the catalytic activity of Au/Co3O4 catalysts for complete oxidation of trace ethylene. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Duan, X.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. Au nanoparticles deposited on the external surfaces of TS-1: Enhanced stability and activity for direct propylene epoxidation with H2 and O2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 150–151, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshipour, S.; Mirmasoudi, S.S. Cross-linked chitosan aerogel modified with Au: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wan, Y. Thermally reduced gold nanocatalysts prepared by the carbonization of ordered mesoporous carbon as a heterogeneous catalyst for the selective reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. J. Catal. 2016, 344, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.; Rooke, J.C.; Genty, E.; Cousin, R.; Siffert, S.; Su, B.L. Gold catalysts in environmental remediation and water-gas shift technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Liotta, L.F. Supported gold catalysts for the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolentseva, E.; Simakov, A.; Beloshapkin, S.; Estrada, M.; Vargas, E.; Sobolev, V.; Kenzhin, R.; Fuentes, S. Gold catalysts supported on nanostructured Ce-Al-O mixed oxides prepared by organic sol-gel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115–116, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoranová, T.; Mori, T.; Yan, P.; Ševčíková, K.; Václavů, M.; Matolín, V.; Nehasil, V. Study of the character of gold nanoparticles deposited onto sputtered cerium oxide layers by deposition-precipitation method: Influence of the preparation parameters. Vacuum 2015, 114, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Haruta, M. Preparation of gold nanoparticles supported on Nb2O5 by deposition precipitation and deposition reduction methods and their catalytic activity for CO oxidation. Cuihua Xuebao/Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, A.; Louis, C.; Zanella, R. Improved activity and stability in CO oxidation of bimetallic Au-Cu/TiO2 catalysts prepared by deposition-precipitation with urea. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sun, Q.; Feng, X.; He, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, H.; Cao, H. Catalytic oxidation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene over CaCO3/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 450, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Wang, S. Magnetic Fe3O4/carbon sphere/cobalt composites for catalytic oxidation of phenol solutions with sulfate radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.D.; Besson, M.; Descorme, C. TiO2-supported gold catalysts in the catalytic wet air oxidation of succinic acid: Influence of the preparation, the storage and the pre-treatment conditions. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Gold catalysts supported on nanosized iron oxide for low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide and formaldehyde. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zuo, S. Promoting effects of Ce and Pt addition on the destructive performances of V2O5/γ-Al2O3 for catalytic combustion of benzene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 542, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Schüth, F. A systematic study of the synthesis conditions for the preparation of highly active gold catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 226, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Keane, M.A. The development of gold catalysts for use in hydrogenation reactions. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiya-Djowe, A.; Laminsi, S.; Noupeyi, G.L.; Gaigneaux, E.M. Non-thermal plasma synthesis of sea-urchin like α-FeOOH for the catalytic oxidation of Orange II in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176–177, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, I.V.; Afanas’eva, V.A. Gold(III) amine complexes in aqueous alkali solutions. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 55, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y. Ions removal by iron nanoparticles: A study on solid-water interface with zeta potential. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Mesoporous iron oxide-silica supported gold catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4008–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotolevich, Y.; Kolobova, E.; Mamontov, G.; Khramov, E.; Cabrera Ortega, J.E.; Tiznado, H.; Farías, M.H.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Zubavichus, Y.; Mota-Morales, J.D.; et al. Au/TiO2 catalysts promoted with Fe and Mg for n-octanol oxidation under mild conditions. Catal. Today 2016, 278, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meire, M.; Tack, P.; De Keukeleere, K.; Balcaen, L.; Pollefeyt, G.; Vanhaecke, F.; Vincze, L.; Van Der Voort, P.; Van Driessche, I.; Lommens, P. Gold/titania composites: An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study on the influence of the reduction method. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2015, 110, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan Cuenya, B.; Behafarid, F. Nanocatalysis: Size- and shape-dependent chemisorption and catalytic reactivity. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2015, 70, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Wang, S. Gold-supported tin dioxide nanocatalysts for low temperature CO oxidation: Preparation, characterization and DRIFTS study. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2013, 108, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, S.X.; Wang, C. Size-dependent dynamic structures of supported gold nanoparticles in CO oxidation reaction condition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7700–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvesh, K.S.; Ryosuke, Y.; Ogino, C.; Akihiko, K. Biogenic synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles by Escherichia coli K12 and its heterogeneous catalysis in degradation of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, F.; Akbarzadeh, H.; Rezania, H. Chemical ordering effect on melting temperature, surface energy of copper-gold bimetallic nanocluster. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 617, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Mallesham, B.; Reddy, P.S.; Großmann, D.; Grünert, W.; Reddy, B.M. Nano-Au/CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation: Influence of dopants (Fe, La and Zr) on the physicochemical properties and catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Kohyama, M.; Tanaka, S.; Takeda, S. Theoretical study of atomic oxygen on gold surface by Hückel theory and DFT calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 9568–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, I.X.; Tang, W.; Neurock, M.; Yates, J.T. Spectroscopic observation of dual catalytic sites during oxidation of CO on a Au/TiO2 catalyst. Science 2011, 333, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H. Catalytic removal of volatile organic compounds using ordered porous transition metal oxide and supported noble metal catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Mou, C.Y. Catalysis by gold: New insights into the support effect. Nano Today 2013, 8, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tan, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Pei, Y.; Zeng, X.C. CO self-promoting oxidation on nanosized gold clusters: Triangular Au3 active site and CO induced O–O scission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2583–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
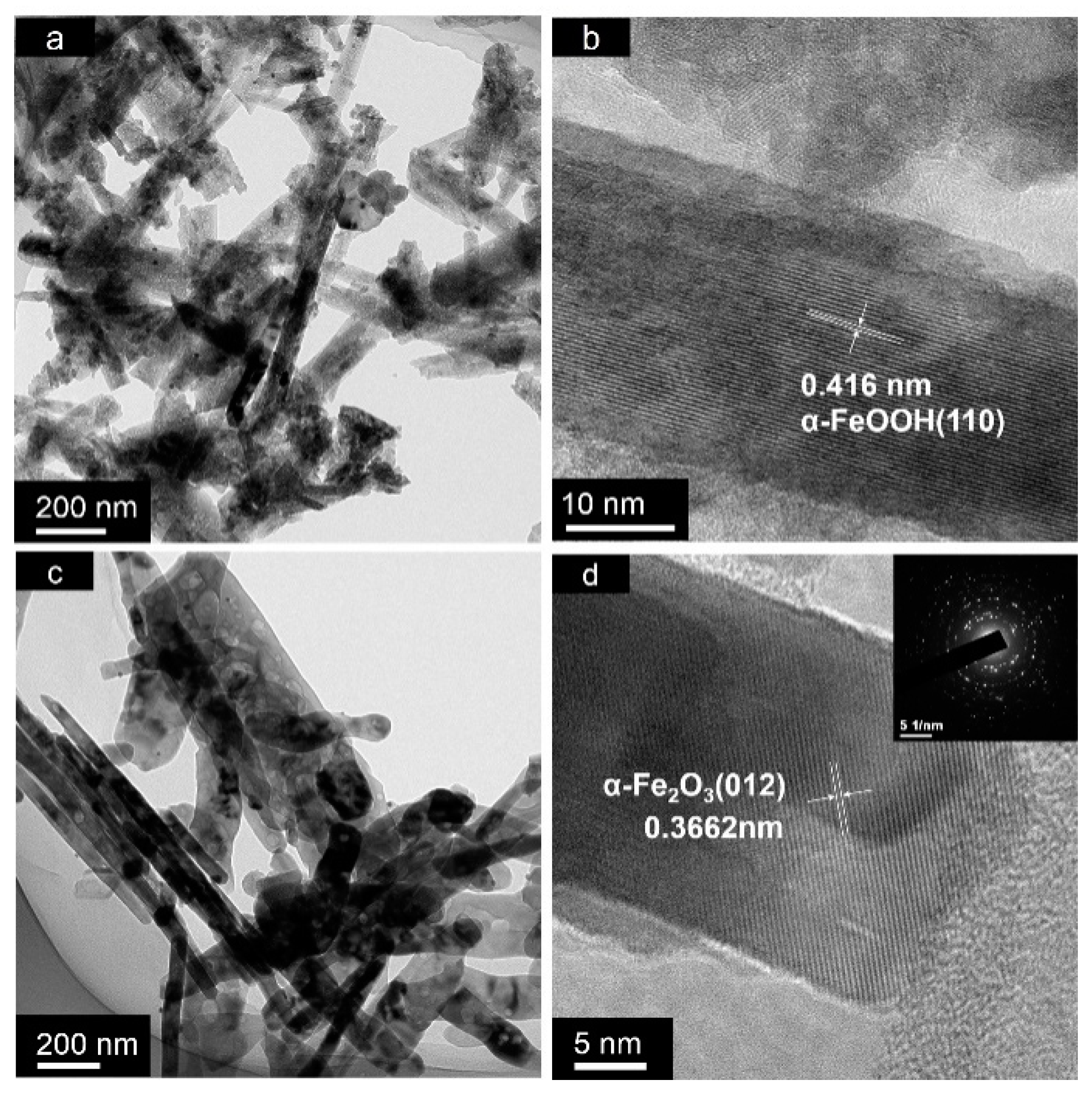
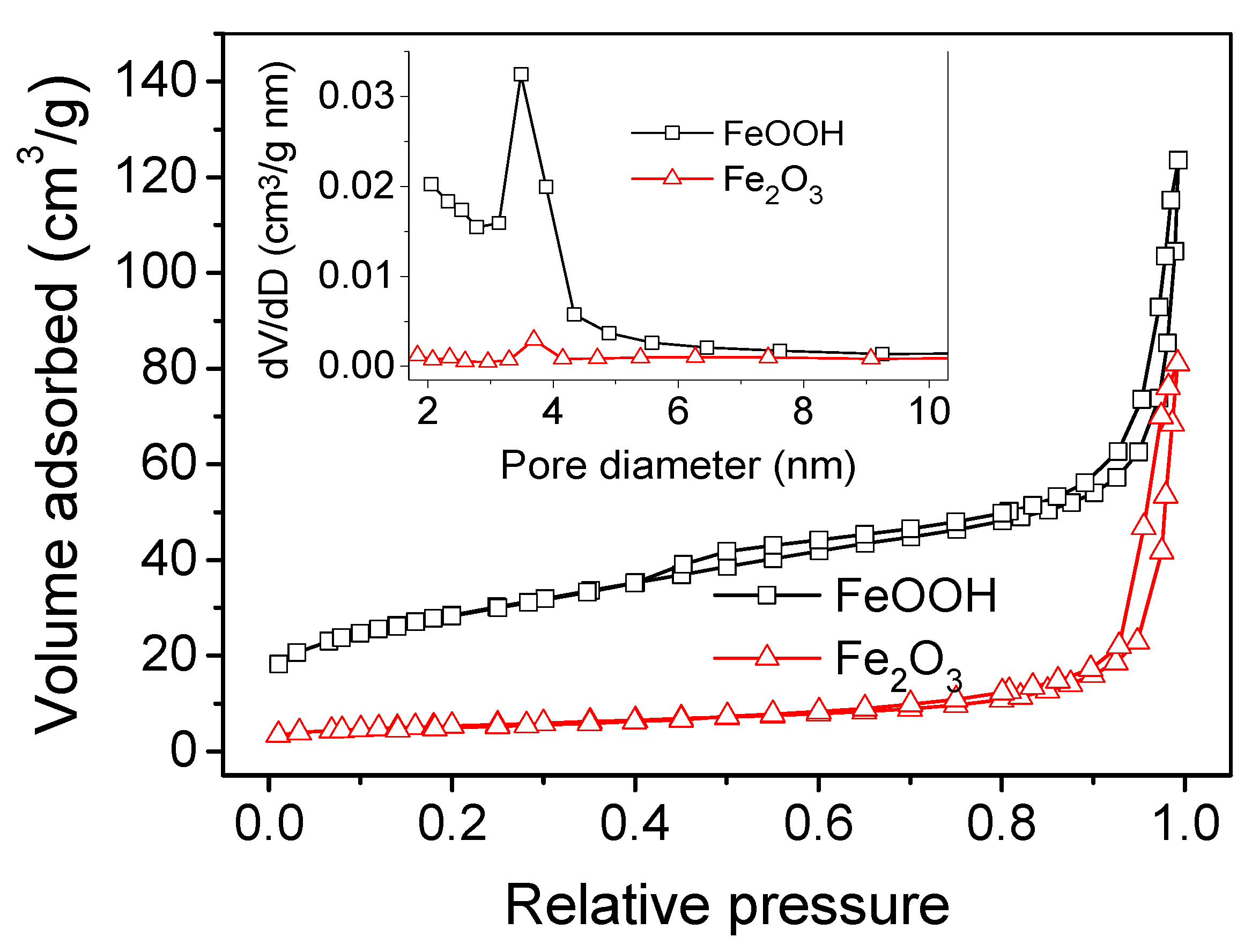

| Catalysts | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Micropore Area (m2/g) | External Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (m3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeOOH | 102 | 16.7 | 85.2 | 0.19 |
| Fe2O3 | 19 | 3.5 | 15.4 | 0.13 |
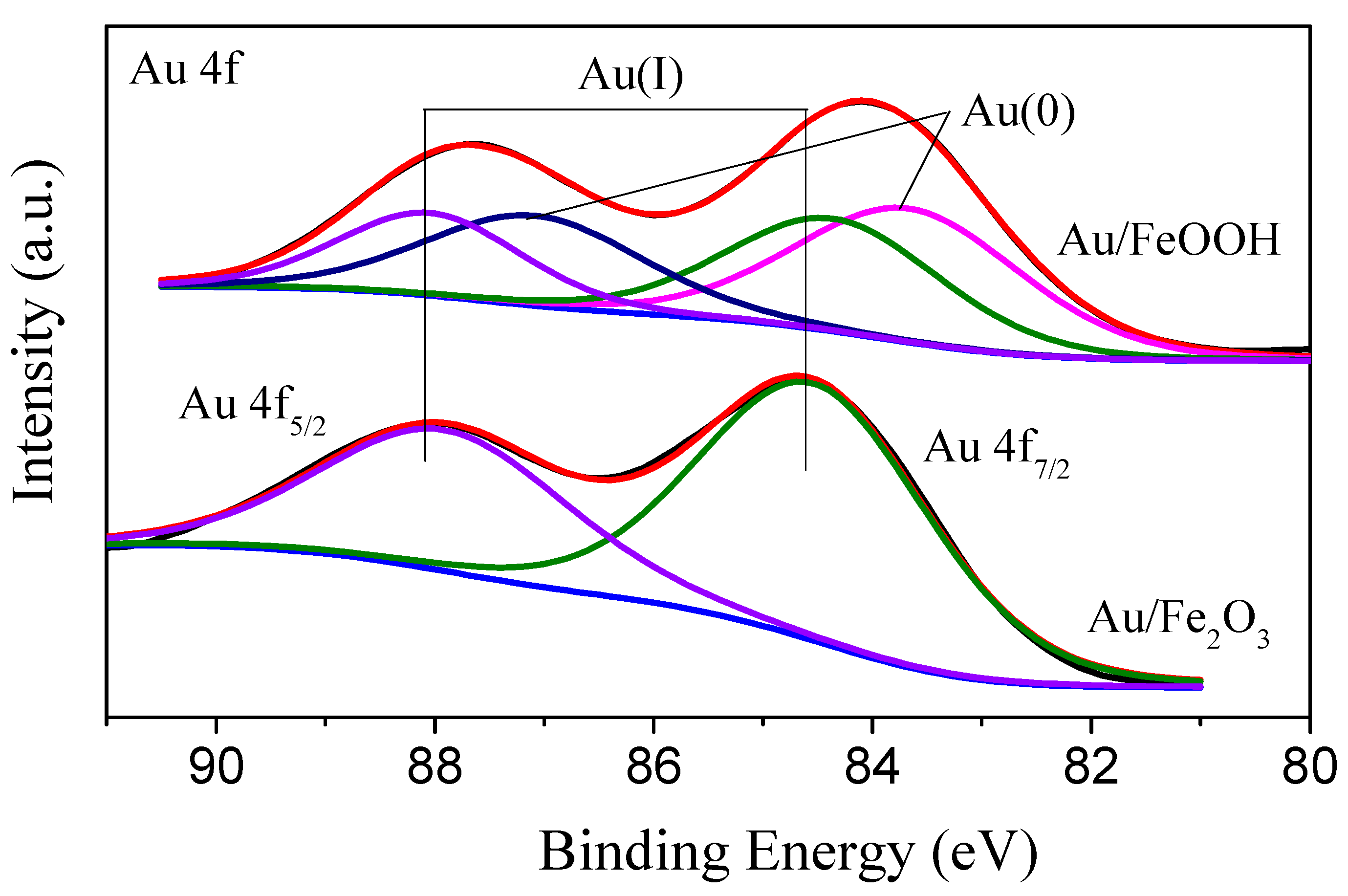
| Catalysts | Au Loading (%) | Percentage of Au(0) (%) | Percentage of Au(I) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au/FeOOH | 2.3 | 55.7 | 44.3 |
| Au/Fe2O3 | 1.4 | 0 | 100 |
| Au/FeOOH (80 °C) | 1.9 | 66.4% | 33.6% |
| Au/FeOOH (pH 9) | 2.1 | 41.5 | 58.5 |
| Au/FeOOH (pH 10) | 1.5 | 42.0 | 58.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, F.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Adsorption Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Supported Gold Catalyst under Self-Generated Alkaline Conditions for Efficient Elimination of Carbon Monoxide. Catalysts 2018, 8, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090357
Pan F, Zhang W, Ye Y, Huang Y, Xu Y, Yuan Y, Wu F, Li J. Adsorption Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Supported Gold Catalyst under Self-Generated Alkaline Conditions for Efficient Elimination of Carbon Monoxide. Catalysts. 2018; 8(9):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090357
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Feng, Weidong Zhang, Yuxiao Ye, Yixuan Huang, Yanzhe Xu, Yufeng Yuan, Feng Wu, and Jinjun Li. 2018. "Adsorption Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Supported Gold Catalyst under Self-Generated Alkaline Conditions for Efficient Elimination of Carbon Monoxide" Catalysts 8, no. 9: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090357
APA StylePan, F., Zhang, W., Ye, Y., Huang, Y., Xu, Y., Yuan, Y., Wu, F., & Li, J. (2018). Adsorption Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Supported Gold Catalyst under Self-Generated Alkaline Conditions for Efficient Elimination of Carbon Monoxide. Catalysts, 8(9), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090357





