The Role of Pulse Voltage Amplitude on Chemical Processes Induced by Streamer Discharge at Water Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
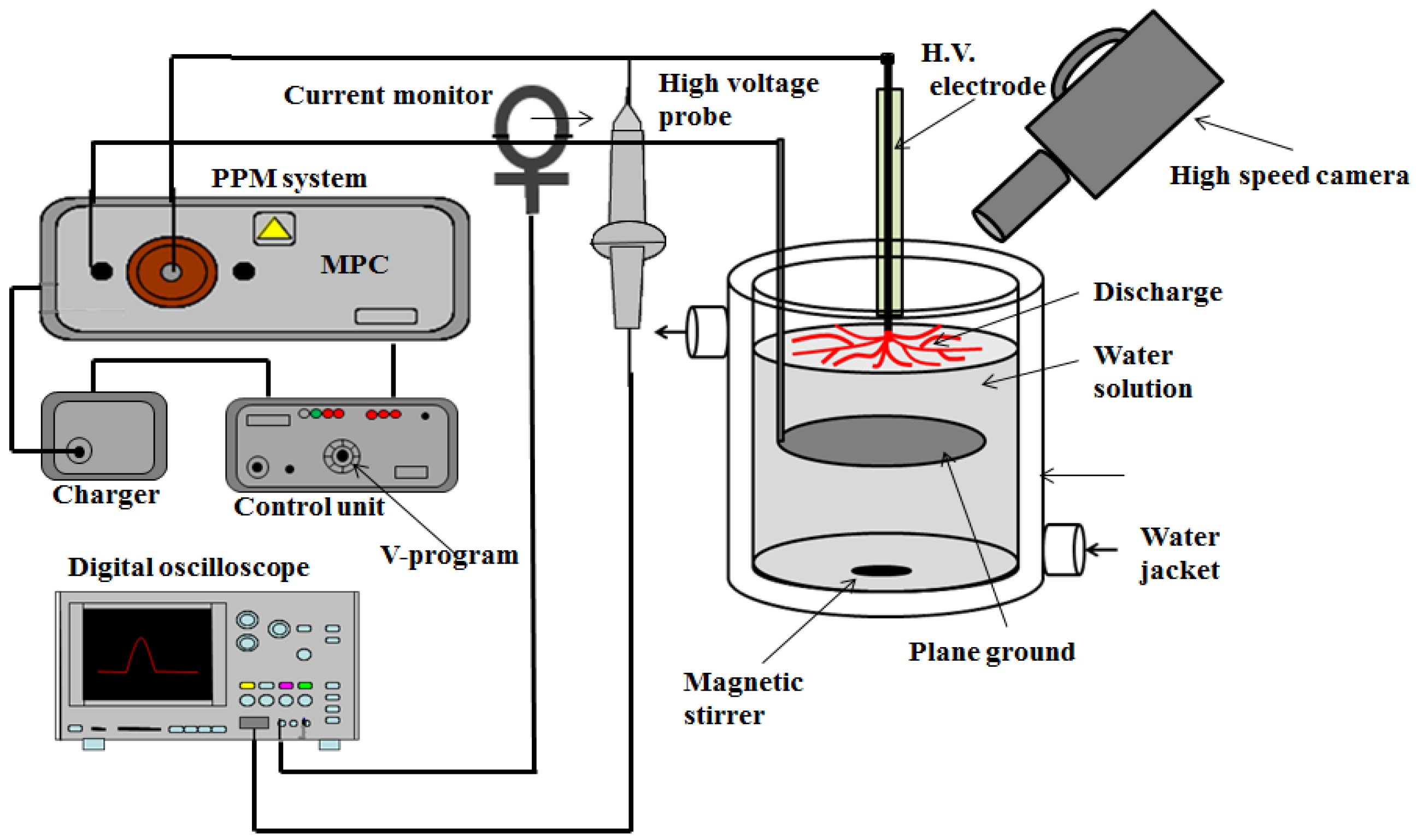
2. Experimental Methods
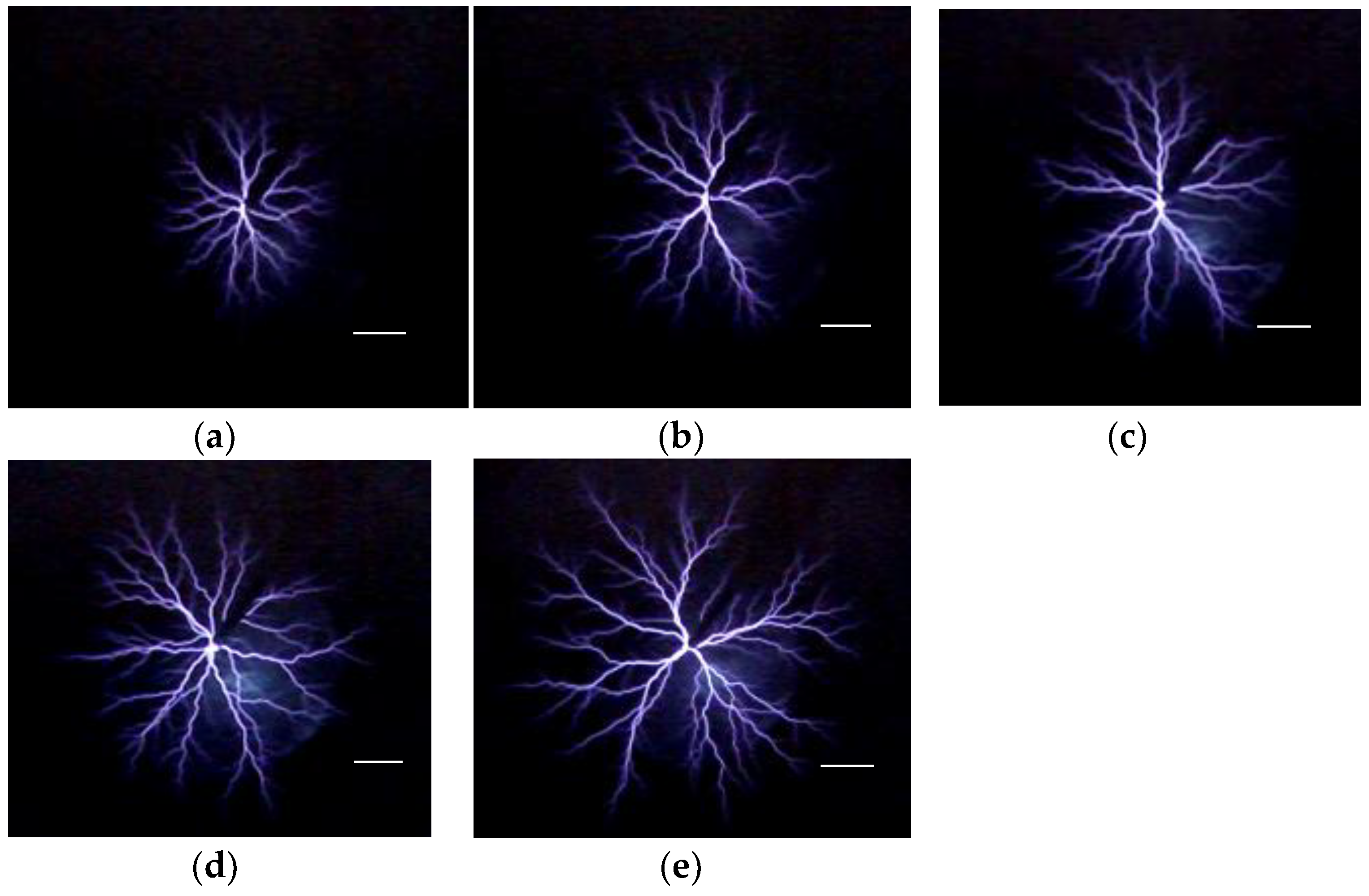
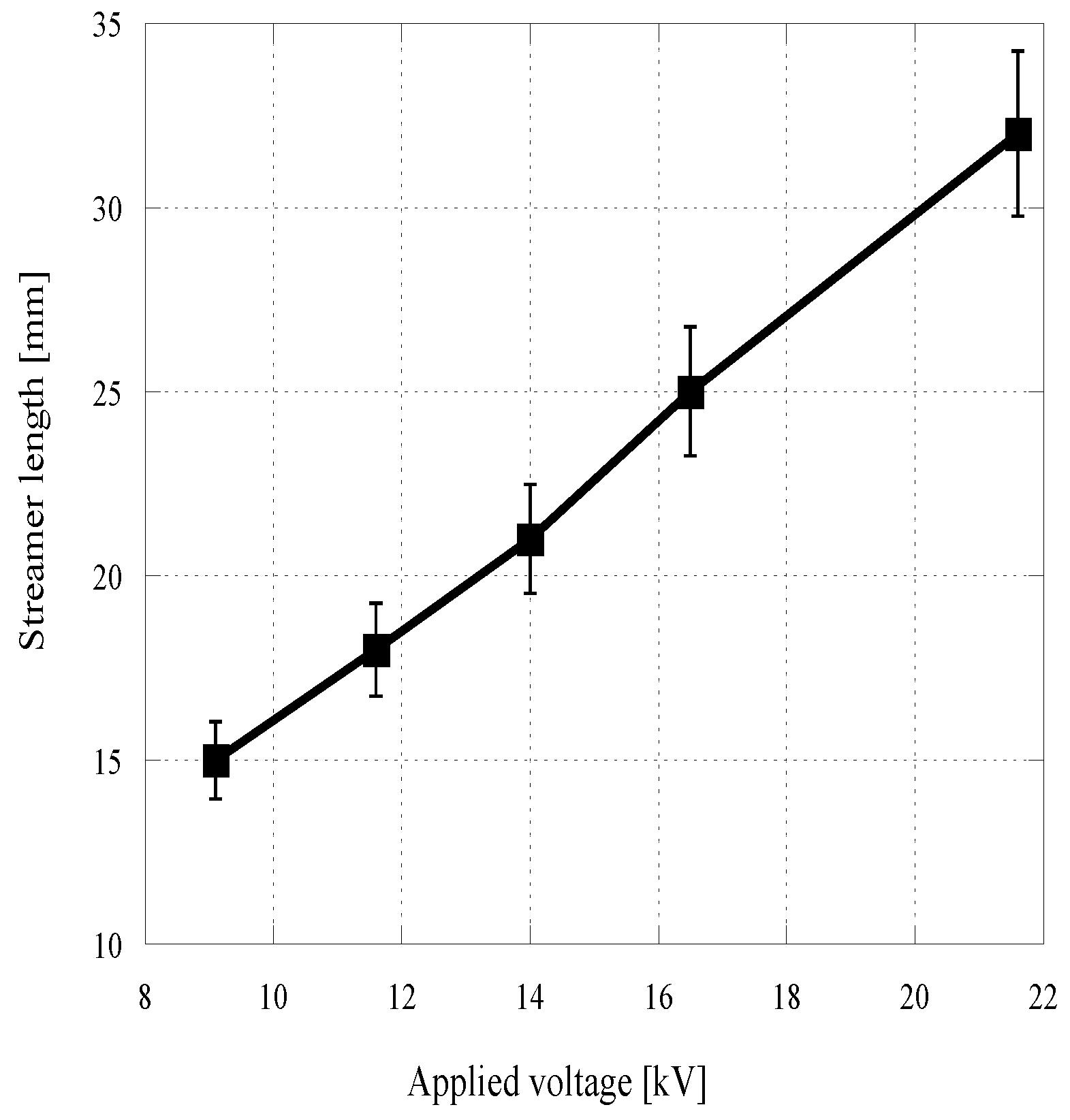
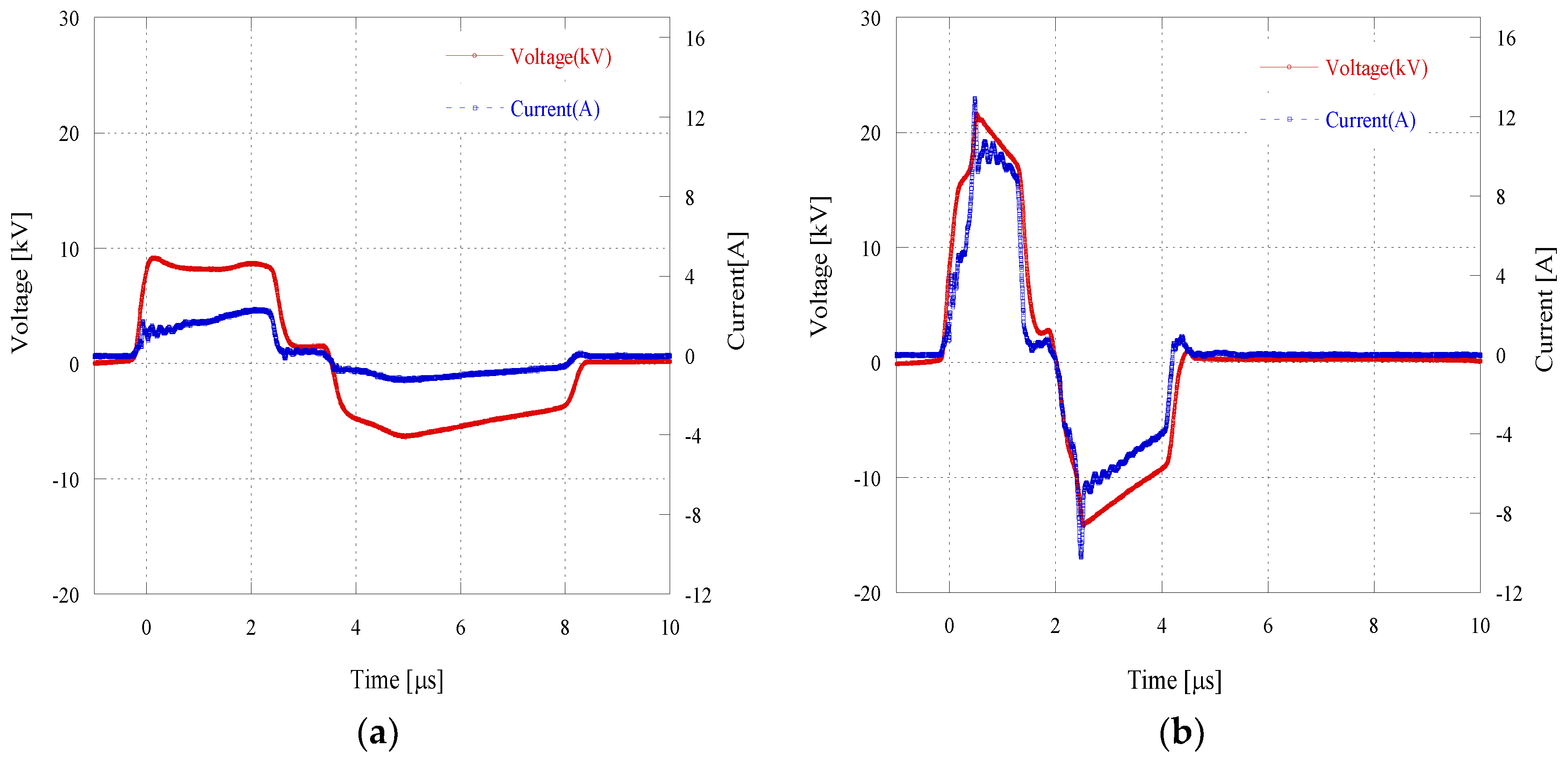
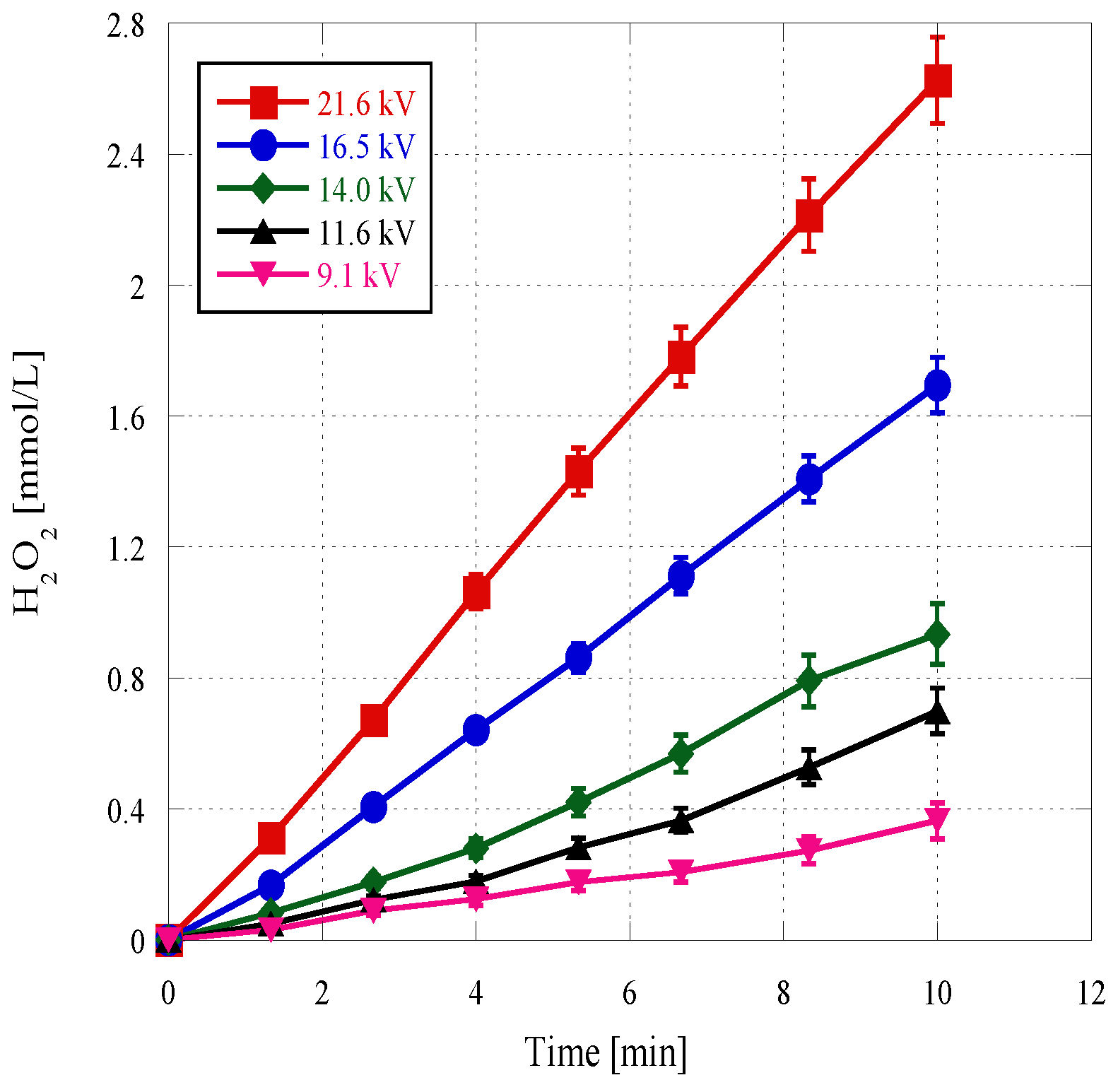
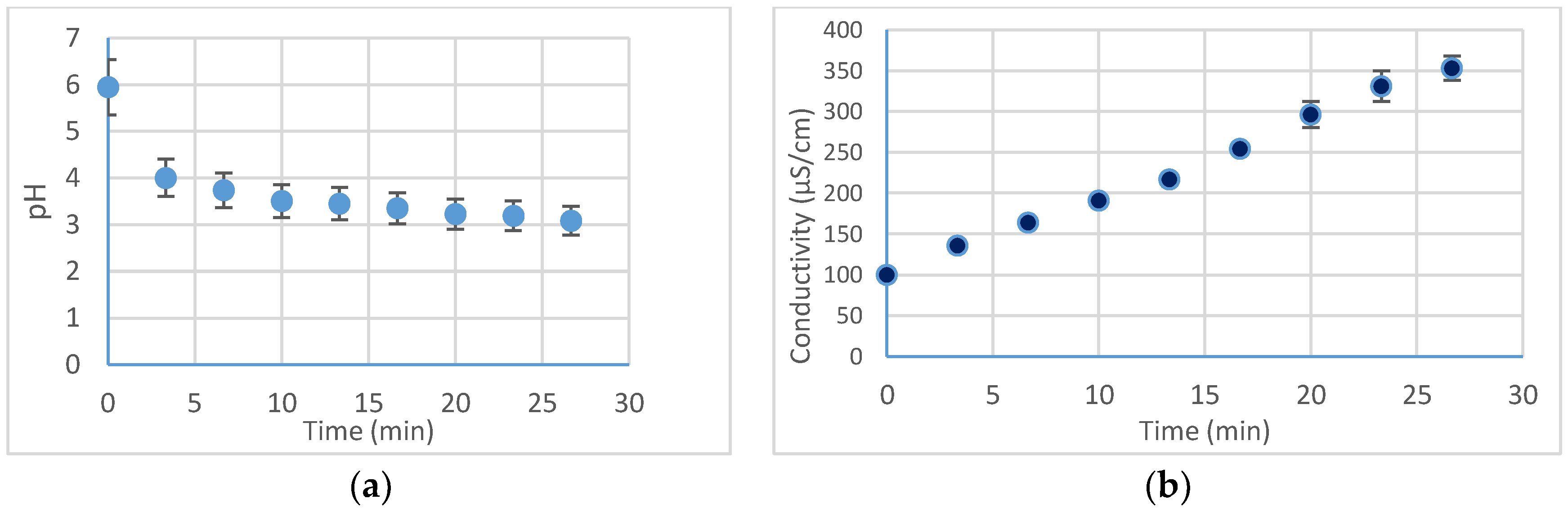
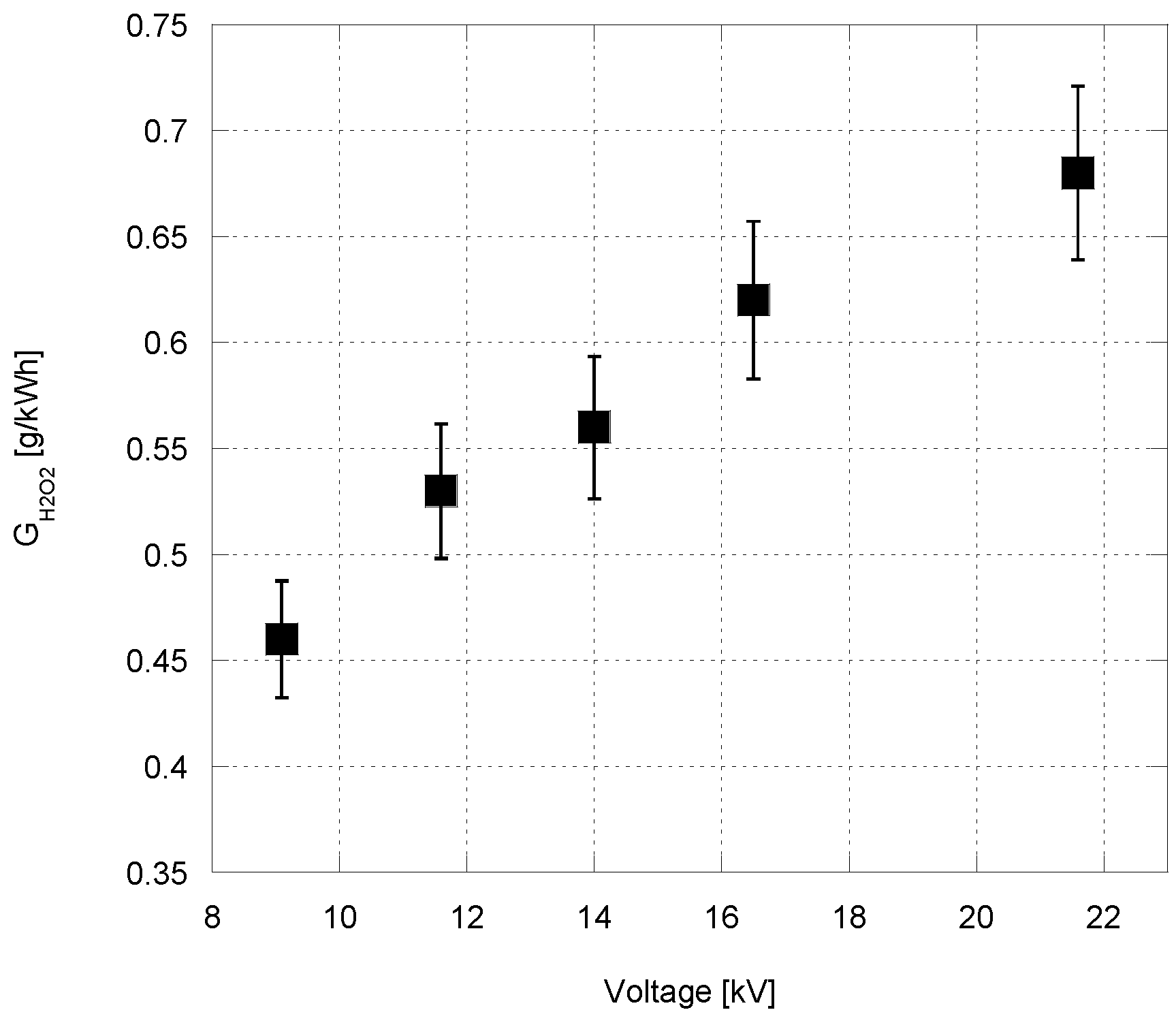
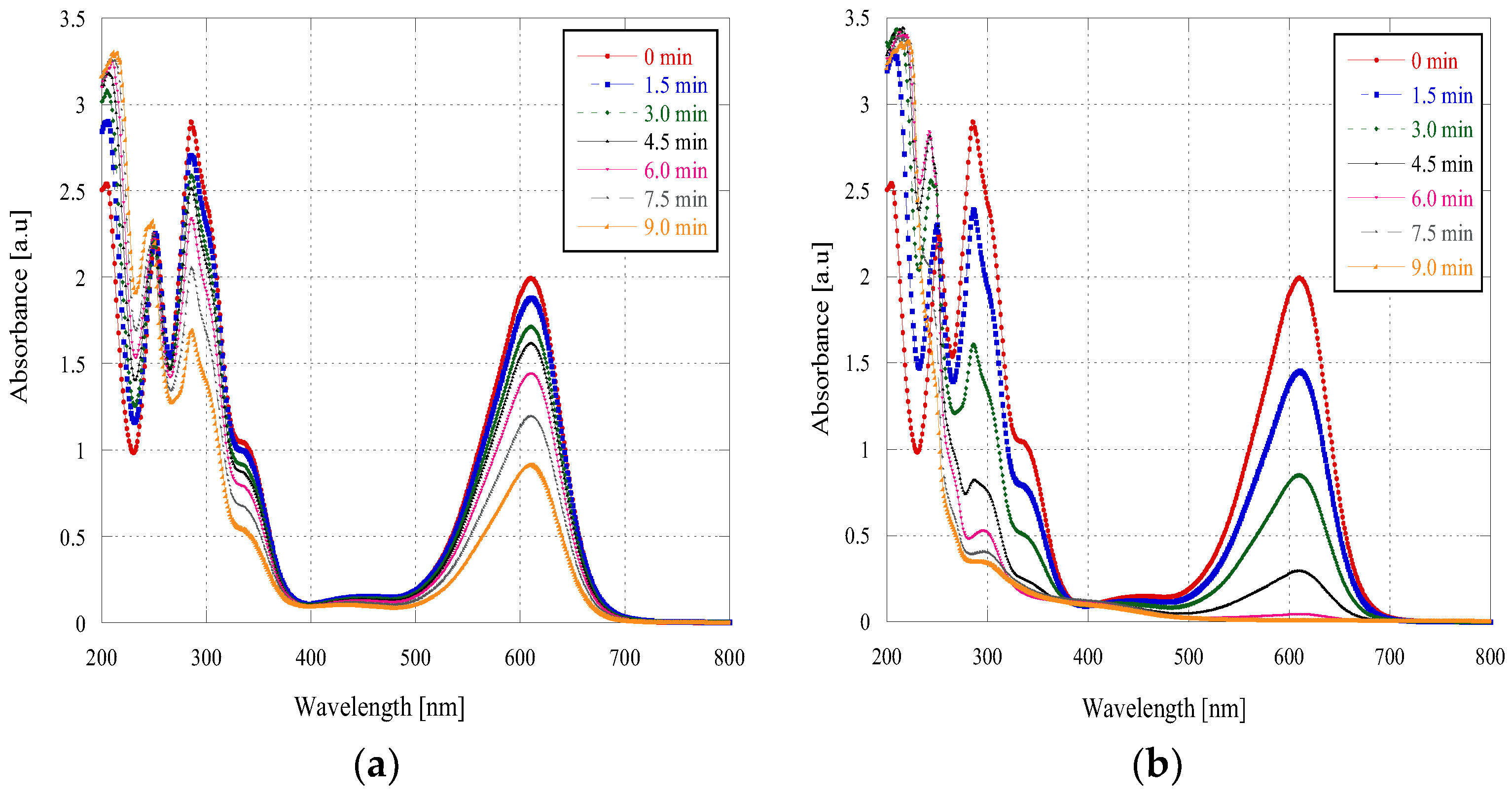
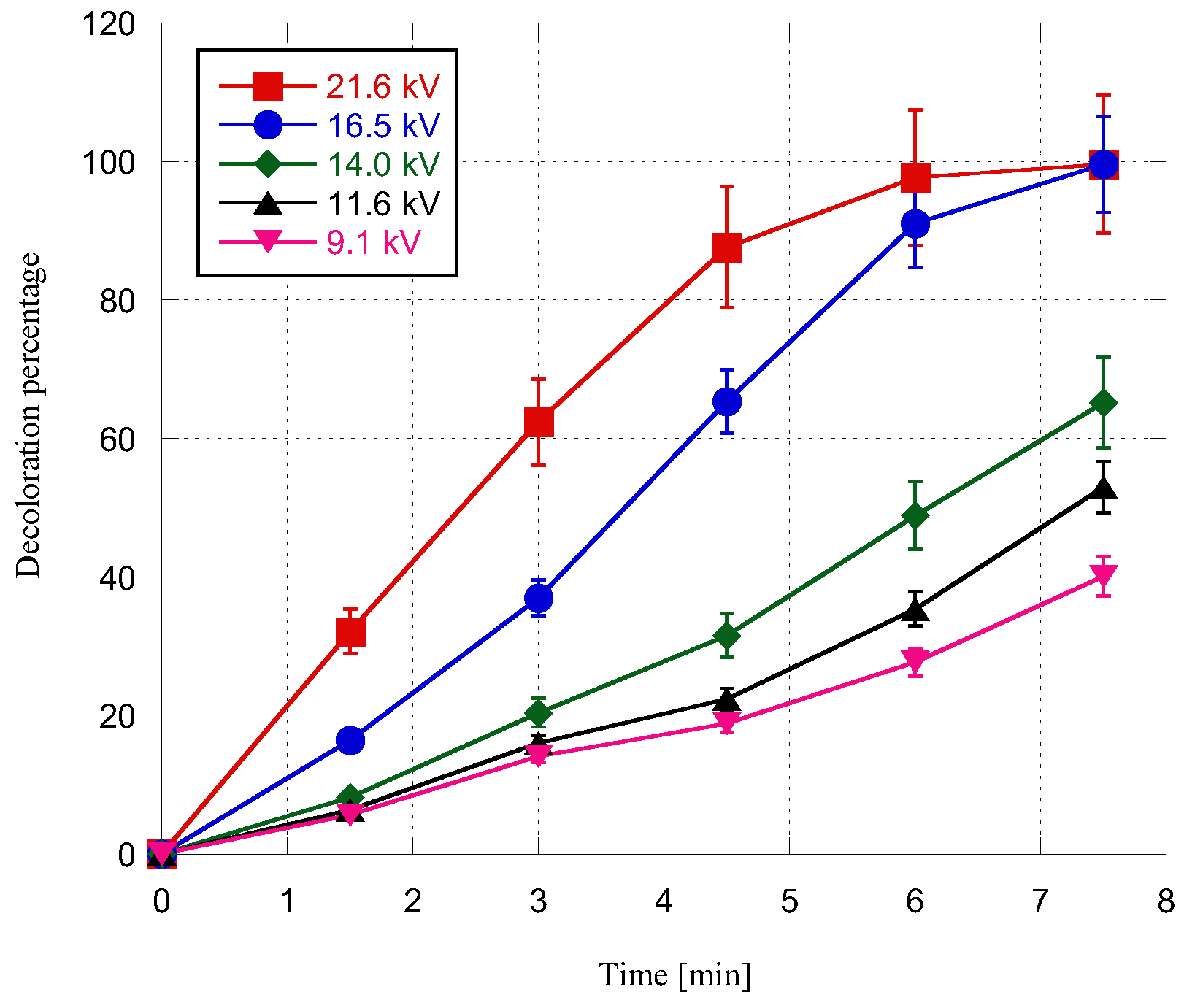
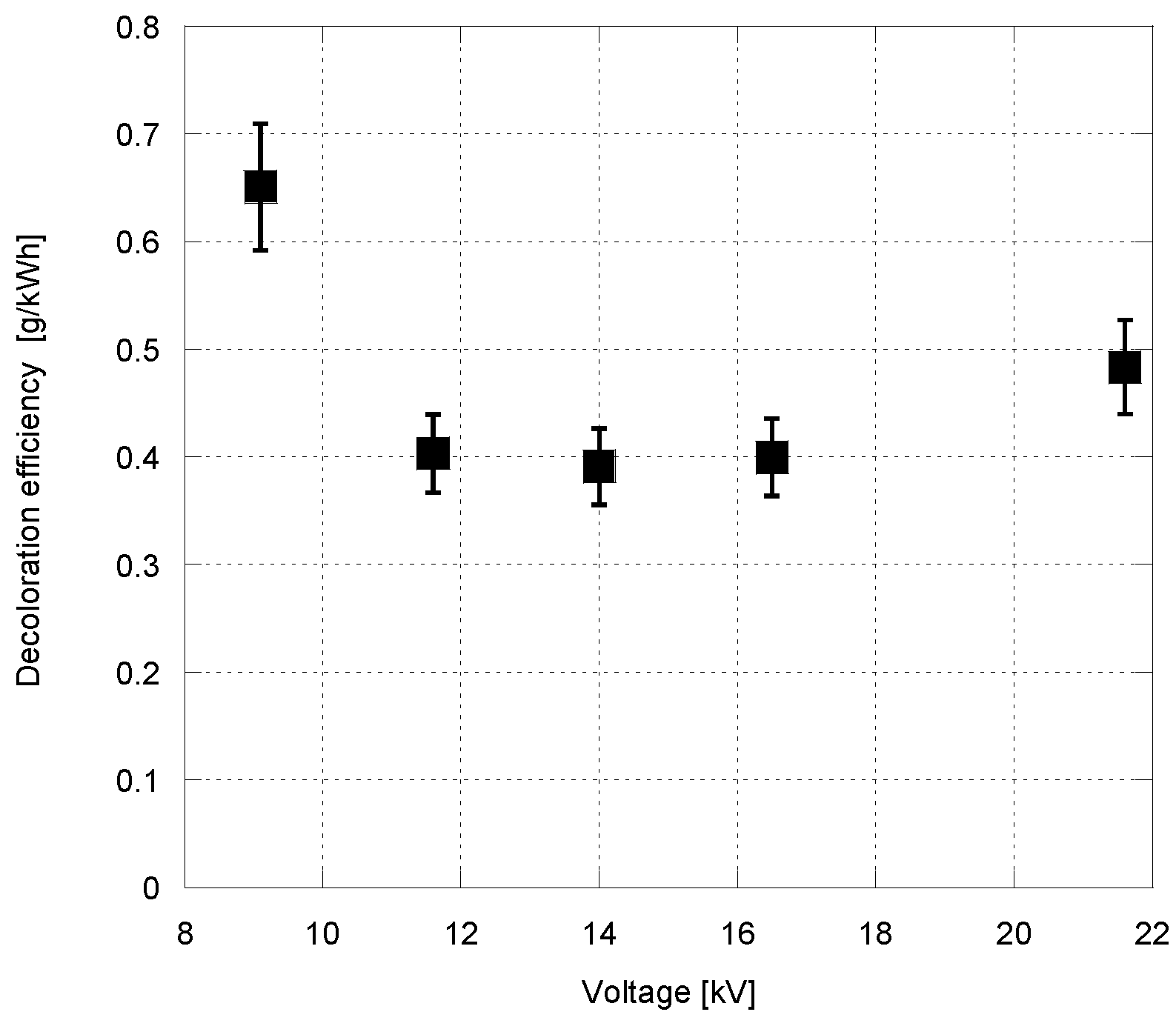
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akiyama, H.; Sakai, S.; Sakugawa, T.; Nakihira, T. Environmental applications of repetitive pulsed power. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2007, 14, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H. Streamer discharges in liquids and their applications. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2000, 7, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Locke, B.R. Plasmachemical oxidation processes in a hybrid gas-liquid electrical discharge reactor. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Tokutake, T.; Ohshima, T.; Sugirato, A.T. Aqueous phenol decomposition by pulsed discharge on the water surface. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, B.R.; Sato, M.; Sunka, P.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Chang, J.-S. Electrohydraulic discharge and nonthermal plasma for water treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 882–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, M.; Locke, B.R. Degradation of chemical warfare agent simulants using gas-liquid pulsed streamer discharges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukes, P.; Appleton, A.T.; Locke, B.R. Hydrogen peroxide and ozone formation in hybrid gas-liquid electrical discharge reactors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Sato, M.; Clements, J.S. Optical study of active species produced by a pulsed streamer corona discharges in water. J. Electrostat. 1997, 39, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z. Formation of active species by bipolar pulsed discharge in water. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 2360–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H. Formation of hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide by a novel nanosecond pulsed plasma power in water. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namihira, T.; Sakai, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamada, C.; Kiyan, T.; Sakugawa, T.; Katsuki, S.; Akiyama, H. Electron temperature and electron density of underwater pulsed discharge plasma produced by solid-state pulsed power generator. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2007, 35, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.A.; Locke, B.R.; Arce, P.; Finney, W.C. Formation of hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide and aqueous electrons by pulsed streamer corona discharge in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 41, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Oda, T. OH radical measurement in a pulsed arc discharge plasma observed by a LIF metho. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, N.; Yamamoto, D.; Kanki, T. Decomposition of phenol in water by a cylindrical wetted-wall reactor using direct contact of gas corona discharge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 5423–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, S.; Wada, K.; Kakuta, T.; Takaki, T.; Satta, N.; Takahashi, K. Influence of pulse width on decolorization efficiency of organic dye by discharge inside bubble in water. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 441, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Shimomura, N.; Uchiyama, I.; Fukawa, F.; Teranishi, K.; Akiyama, H. Decolorization of indigo carmine solution using nanosecond pulsed power. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2009, 16, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.H.; Liu, Y.N.; Bo, Z.; Li, X.D.; Cen, K.F. Degradation of gas-liquid glidding arc discharge on acid orange II. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willberg, D.M.; Lang, P.S.; Hochemer, R.H.; Kratel, A.; Hoffmann, M.R. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol, 3,4-dichloroaniline, and 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in an electrohydraulic discharge reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Lei, L. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol in different gas-liquid electrical discharge reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, A.T.; Ito, S.; Oshima, T.; Sato, M.; Skalny, J.D. Oxidative decoloration of dyes by pulsed discharge plasma in water. J. Electrostat. 2003, 58, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magureanu, M.; Piroi, D.; Gherendi, F.; Mandache, N.B.; Parvulescu, V. Decomposition of methylene blue in water by corona discharges. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2008, 28, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahni, M.; Locke, B.R. Quantification of hydroxyl radicals produced in aqueous phase pulsed electrical discharge reactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5819–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautier, M.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes in water: Case study of indigo and indigo carmine. J. Catal. 2001, 201, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Muramatsu, S.; Sonoda, T.; Blajan, M. Water treatment by low voltage discharge in water. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake, W.J.M.; Miyahara, Y.; Namihira, T.; Katsuki, S.; Sakugawa, T.; Hackam, R.; Akiyama, H. Pulsed streamer discharge characteristics of ozone production. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2000, 7, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackam, R.; Akiyama, H. Air pollution control by electrical discharges. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2000, 7, 654–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Degradation mechanism of Alizarin red in hybrid gas-liquid phase dielectric barrier discharge plasmas: Experimental and theoretical examination. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 138, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N.; Sakugawa, T.; Akiyama, H.; Akiyama, M. Hydrogen peroxide generation by pulsed discharge in bubbling water. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2013, 133, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Akishev, Y.; Aponin, G.; Balakirev, A.; Grushin, M.; Petryakov, A.; Karal’nik, V.; Trushkin, N. Stepwise expansion of a surface dielectric barrier discharge as a result of alternation in formation of streamers and leaders. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 135204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, T.; Oizumi, M.; Nakatani, T.; Sato, T. Effect of voltage polarity on oxidation-reduction potential by plasma in water. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 047115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Zahn, M.; Badent, A.; Kist, K.; Schwabe, A.J.; Yamashita, H.; Yamazawa, K.; Danikas, M.; Chadband, W.G.; Torshin, Y. Propagation and structure of streamers in liquid dielectrics. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2009, 14, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, S.; Akiyama, H.; Abou-Ghazala, A.; Schoenbach, K.H. Paraller streamer discharges between wire and plane electrode in water. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2002, 9, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmazio, I.; Urzedo, A.P.F.M.; Alves, T.M.A.; Catharino, R.R.; Eberlin, M.N.; Nascentes, C.C.; Augusti, R. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry monitoring of indigo carmine degradation by advanced oxidation processes. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruo-bing, Z.; Yan, W.; Ning-hui, W.; Jie, L. Plasma induced degradation of indigo carmine by bipolar pulsed dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) in the water-air mixture. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 808–812. [Google Scholar]
- Selma, M.; Takashima, K. Decolorization of indigo carmine dye by spark discharge in water. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Machmudah, S.; Goto, M. Pulsed Discharge Plasma over a Water Surface Induces Decoloration of Dyes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 441, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartode, A.P.; Parwate, D.V. UV photocatalytic decolorization study of synthetic waste water containing indigo carmine dye in presence of H2O2. Int. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 3, 22–31. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruma; Hosano, H.; Sakugawa, T.; Akiyama, H. The Role of Pulse Voltage Amplitude on Chemical Processes Induced by Streamer Discharge at Water Surface. Catalysts 2018, 8, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050213
Ruma, Hosano H, Sakugawa T, Akiyama H. The Role of Pulse Voltage Amplitude on Chemical Processes Induced by Streamer Discharge at Water Surface. Catalysts. 2018; 8(5):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050213
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuma, Hamid Hosano, Takashi Sakugawa, and Hidenori Akiyama. 2018. "The Role of Pulse Voltage Amplitude on Chemical Processes Induced by Streamer Discharge at Water Surface" Catalysts 8, no. 5: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050213
APA StyleRuma, Hosano, H., Sakugawa, T., & Akiyama, H. (2018). The Role of Pulse Voltage Amplitude on Chemical Processes Induced by Streamer Discharge at Water Surface. Catalysts, 8(5), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050213




