Direct Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes Promoted by Sodium tri(sec-butyl)borohydride
Abstract
1. Introduction
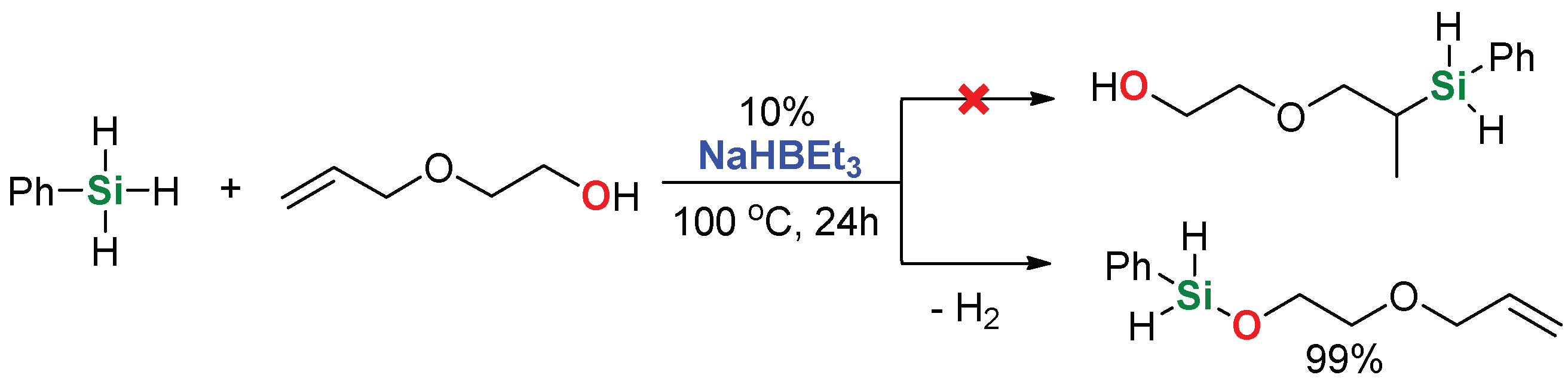
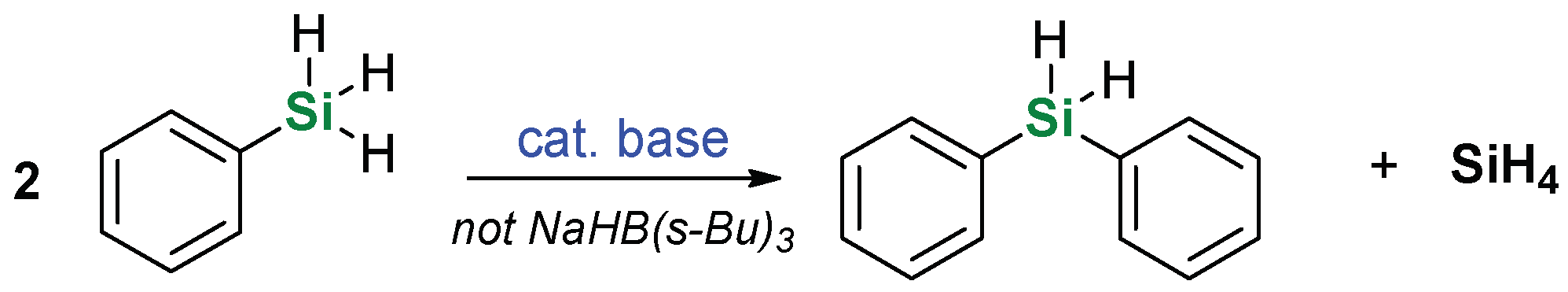
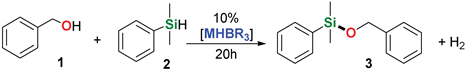
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Silanes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pouget, E.; Tonnar, J.; Lucas, P.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Ganachaud, F.; Boutevin, B. Well-Architectured Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Containing Copolymers Obtained by Radical Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1233–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.; Fröba, M. Vitalising porous inorganic silica networks with organic functions—PMOs and related hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Mesoporöse organisch-anorganische Hybridmaterialien auf Silicabasis. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 3290–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoshita, N.; Tani, T.; Inagaki, S. Syntheses, properties and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilicas prepared from bridged organosilane precursors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Kanematsu, H.; Tanaka, T. Overview of silane-based polymer coatings and their applications. In Industrial Applications for Intelligent Polymers and Coatings; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 493–509. ISBN 9783319268934. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W.; Lu, K.T. Organic–inorganic hybrid linseed oil-based urethane oil wood coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvornic, P.R.; Owen, M.J. Silicone Surface Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nihei, T. Dental applications for silane coupling agents. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 58, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, M.; Chan, T.H. Use of Organosilicon Reagents as Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis. Synthesis (Stuttg) 1985, 1985, 817–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C. The Triisopropylsilyl Group in Organic Chemistry: Just a Protective Group, or More? Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1009–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekelburger, H.B.; Wilcox, C.S. 2.06 Formation of Enolates. In Comprehensive Organic Synthesis II; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 243–272. ISBN 9780080977430. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.K.; Hernandez, O. 4-Dimethylaminopyridine: An efficient and selective catalyst for the silylation of alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chang, H. 1,1,3,3-Tetramethylguanidine: An Effective catalyst for the t-butyldimethylsilylation of alcohols. Synth. Commun. 1984, 14, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Thompson, R.R.; Ellern, A.; Sadow, A.D. Coordinatively Saturated Tris(oxazolinyl)borato Zinc Hydride-Catalyzed Cross Dehydrocoupling of Silanes and Alcohols. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Espinosa, D.; Sabater, S.; Carretero-Cerdán, A.; Baya, M.; Mata, J.A. High Production of Hydrogen on Demand from Silanes Catalyzed by Iridium Complexes as a Versatile Hydrogen Storage System. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2558–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijjamarri, S.; Chidara, V.K.; Rousova, J.; Du, G. Dehydrogenative coupling of alcohols and carboxylic acids with hydrosilanes catalyzed by a salen–Mn(v) complex. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3886–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, B.T.; Cutler, A.R. Mn(CO)5C(O)-p-C6H5CH3-catalyzed hydrosilane SiH/SiD exchange: Evidence from a kinetics study implicating coordinatively unsaturated manganese silyl intermediates. Organometallics 1993, 12, 2006–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Lopes, R.; Royo, B. Dehydrogenative silylation of alcohols catalysed by half-sandwich iron N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 775, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, R.A.; Ison, E.A.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Catalysis by cationic oxorhenium(v): Hydrolysis and alcoholysis of organic silanes. Dalton Trans. 2009, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.-K.; Ferguson, G.; Robertson, V.; Schlaf, M. Nature of the active silane alcoholysis catalyst in the Ru w Cl x (CO) y (PMe 3) z (w, x, y, z = 1 or 2) system; Ru 2 (µ-Cl) 2 Cl 2 (CO) 4 (PMe 3) 2 as a new catalyst for silane alcoholysis in a polar solvent. Can. J. Chem. 2001, 79, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maifeld, S.V.; Miller, R.L.; Lee, D. Activation of silanes by Grubbs carbene complex Cl2(PCy3)2Ru CHPh: Dehydrogenative condensation of alcohols and hydrosilylation of carbonyls. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6363–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, K.; Fernández-Alvarez, F.J.; Polo, V.; Lalrempuia, R.; Pérez-Torrente, J.J.; Oro, L.A. Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogen Production from Hydrosilanes and Water. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, L.D.; Messerle, B.A.; Rehr, M.; Soler, L.P.; Hambley, T.W. Cationic Iridium(I) Complexes as Catalysts for the Alcoholysis of Silanes. Organometallics 2003, 22, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.E.; Lu, Z.; Richardson, T.; Crabtree, R.H. Silane alcoholysis by a nickel(II) complex in a N, O, S ligand environment. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 4709–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshita, J.; Taketsugu, R.; Nakahara, Y.; Kunai, A. Convenient synthesis of alkoxyhalosilanes from hydrosilanes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 3258–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Watanabe, A.; Sawamura, M. Versatile dehydrogenative alcohol silylation catalyzed by Cu(I)-phosphine complex. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendler, S.; Auer, G.; Oestreich, M. Kinetic Resolution of Chiral Secondary Alcohols by Dehydrogenative Coupling with Recyclable Silicon-Stereogenic Silanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7620–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caseri, W.; Pregosin, P.S. Hydrosilylation chemistry and catalysis with cis-PtCl2(PhCH:CH2)2. Organometallics 1988, 7, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Takagi, K.; Miyahara, T.; Sawamura, M. Gold(I)−Phosphine Catalyst for the Highly Chemoselective Dehydrogenative Silylation of Alcohols. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, A.; Oestreich, M. Potassium tert -Butoxide-Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Si–O Coupling: Reactivity Pattern and Mechanism of an Underappreciated Alcohol Protection. Chem. Asian J. 2009, 4, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinath, A.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Anga, S.; Panda, T.K. Dehydrogenative Coupling of Hydrosilanes and Alcohols by Alkali Metal Catalysts for Facile Synthesis of Silyl Ethers. Aust. J. Chem. 2017, 70, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Cui, C. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Organocatalysts for Dehydrogenative Coupling of Silanes and Hydroxyl Compounds. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11143–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, J.M.; Foster, K.L.; Beck, V.H.; Piers, W.E. B(C 6 F 5) 3-Catalyzed Silation of Alcohols: A Mild, General Method for Synthesis of Silyl Ethers. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 4887–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toutov, A.A.; Betz, K.N.; Haibach, M.C.; Romine, A.M.; Grubbs, R.H. Sodium Hydroxide Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5776–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.-S.; Kim, T.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Nam, S.-W.; Kang, S.O. Silane-based hydrogen storage materials for fuel cell application: Hydrogen release via methanolysis and regeneration by hydride reduction from organosilanes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 12305–12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaranek, M.; Witomska, S.; Patroniak, V.; Pawluć, P. Unexpected catalytic activity of simple triethylborohydrides in the hydrosilylation of alkenes. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5404–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrodzki, M.; Witomska, S.; Pawluć, P. Sodium triethylborohydride as a catalyst for the dehydrogenative silylation of terminal alkynes with hydrosilanes. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5948–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Inoue, K.; Ishikawa, J.I.; Iwata, K. Disproportionation reactions of organohydrosilanes in the presence of base catalysts. J. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 629, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Woo, H.-G. Dehydrocoupling, Redistributive Coupling, and Addition of Main Group 4 Hydrides. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 52, ISBN 9780120311521. [Google Scholar]
- Howie, C.R.; Lee, J.K.; Schowen, R.L. Catalysis in organosilicon chemistry. IV. Proton inventory of the transition state for hydride expulsion from silicon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 5286–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
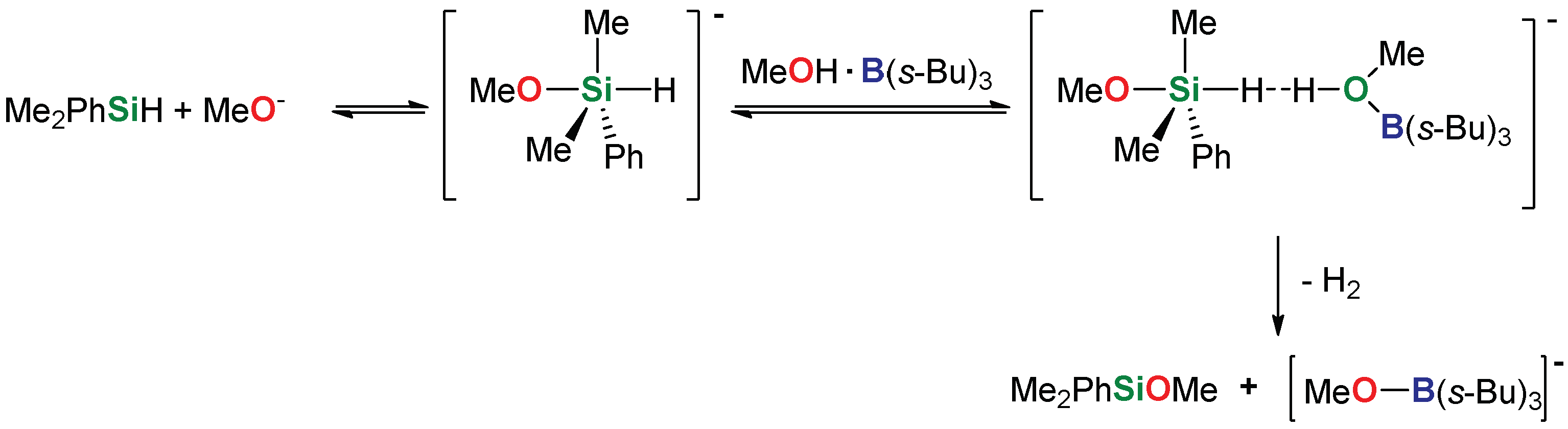
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | [MHBR3] | Solvent, c of 2 | T [°C] | Conv. of 2 2 |
| 1 | NaHBEt3 | Neat | RT | 17 |
| 2 | LiHBEt3 | Neat | RT | 26 |
| 3 | KHBEt3 | Neat | RT | 31 |
| 4 | Neat | 40 | 66 | |
| 5 | NaHB(s-Bu)3 | Neat | RT | 57 |
| 6 | Neat | 40 | 100 | |
| 7 | THF, 1M | RT | 11 | |
| 8 | Toluene, 1M | RT | 55 | |
| 9 | Neat | RT | 693 | |
| 10 | Neat | 40 | 1004 | |
| # | Silane | Alcohol | Product | t/h 2 | Isol. Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Me2PhSiH | Benzyl alcohol | 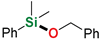 | 1 h | 98% |
| 2 | Ethanol | 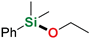 | 3 min | 93% | |
| 3 | Methanol | 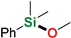 | 10 min | 86% | |
| 4 | 2-Allyloxyethanol | 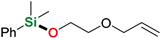 | 48 h | 86% | |
| 5 3 | 4-Bromobenzyl alcohol | 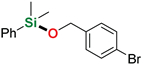 | 24 h | 46% | |
| 6 3 | 4-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 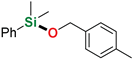 | 6 h | 94% | |
| 7 3 | 4-Fluorobenzyl alcohol | 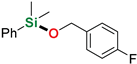 | 6 h | 86% | |
| 8 3 | 1-Cyclopropylethanol | 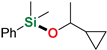 | 4 h | 98% | |
| 9 3 | 3-Butyn-1-ol | 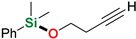 | 24 h | 99% | |
| 10 4,5 | Ph2SiH2 | Ethanol | 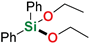 | 3 min | 93% |
| 11 4,6 | Benzyl alcohol | 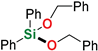 | 24 h | 97% | |
| 12 4,6 | Hexan-1-ol | 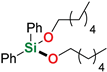 | 24 h | 99% | |
| 13 4 | Cyclohexanol | 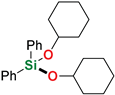 | 1 h | 88% | |
| 14 | MePh2SiH | Ethanol | 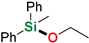 | 48 h | 96% |
| 15 | Benzyl alcohol | 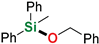 | 48 h | 93% | |
| 16 | 2-Allyloxyethanol | 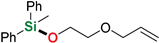 | 48 h | 98% | |
| 17 4 | PhSiH3 | Cyclohexanol | 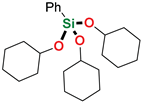 | 1 h | 89% |
| 18 4 | 2-Allyloxyethanol |  | 1 h | 99% | |
| 19 3 | i-Pr3SiH | Methanol | 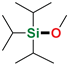 | 72 h, 67% conv. | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skrodzki, M.; Zaranek, M.; Witomska, S.; Pawluc, P. Direct Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes Promoted by Sodium tri(sec-butyl)borohydride. Catalysts 2018, 8, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120618
Skrodzki M, Zaranek M, Witomska S, Pawluc P. Direct Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes Promoted by Sodium tri(sec-butyl)borohydride. Catalysts. 2018; 8(12):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120618
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkrodzki, Maciej, Maciej Zaranek, Samanta Witomska, and Piotr Pawluc. 2018. "Direct Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes Promoted by Sodium tri(sec-butyl)borohydride" Catalysts 8, no. 12: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120618
APA StyleSkrodzki, M., Zaranek, M., Witomska, S., & Pawluc, P. (2018). Direct Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols with Hydrosilanes Promoted by Sodium tri(sec-butyl)borohydride. Catalysts, 8(12), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120618





