Effect of Nickel Oxide Doping to Ceria-Supported Gold Catalyst for CO Oxidation and Water-Gas Shift Reactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
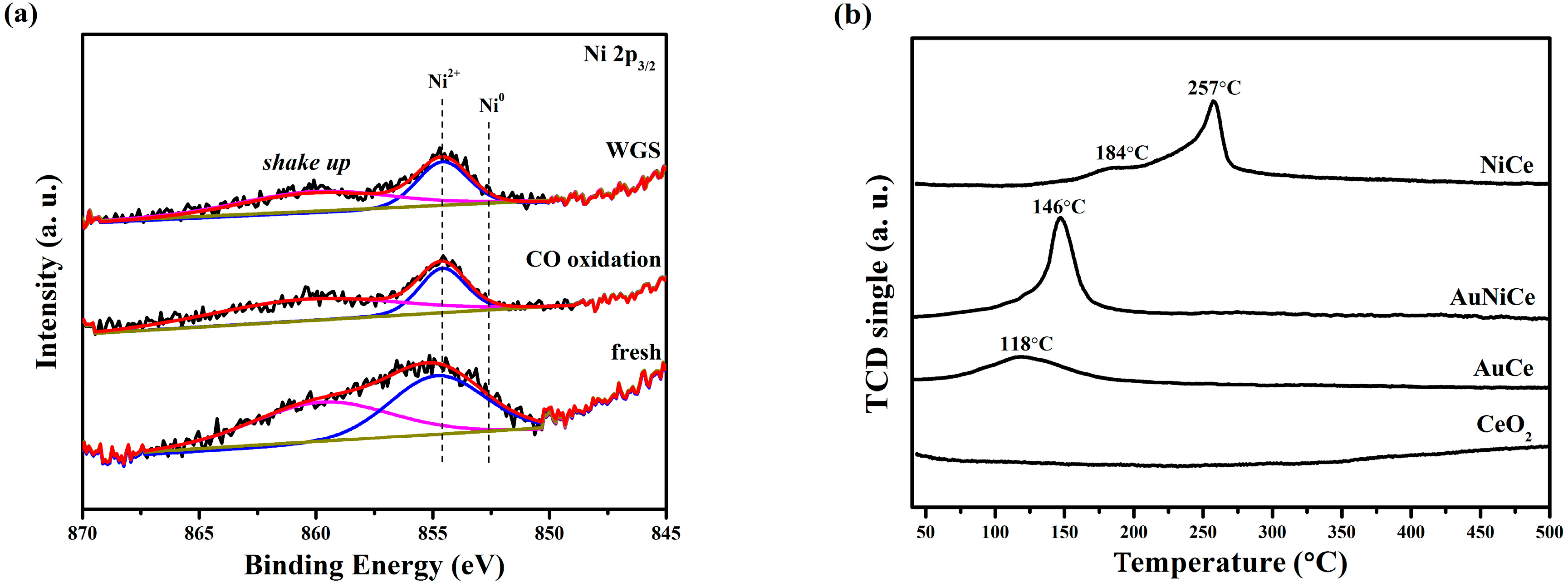
2.1. Effect of Nickel Oxide during Deposition of Gold
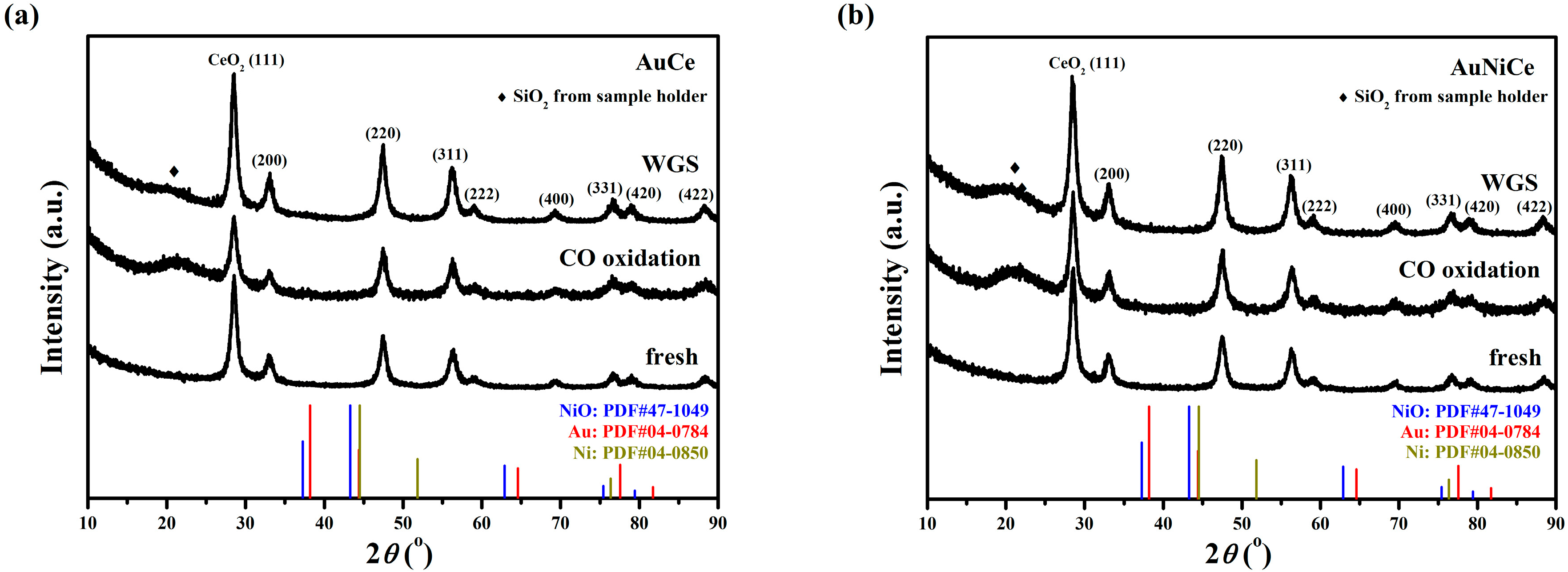
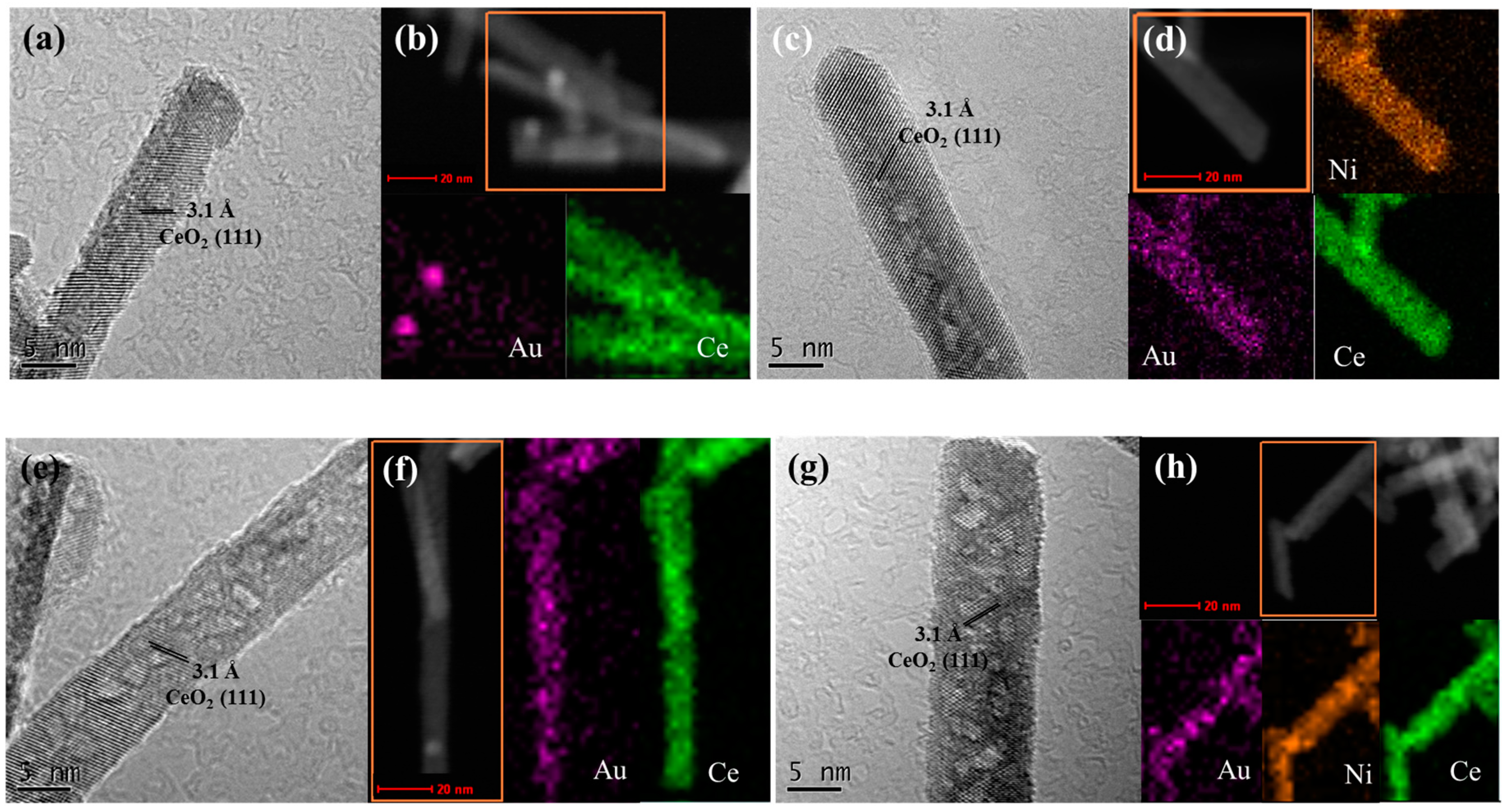
2.2. Structural and Textural Properties for Ceria-Supported Gold-Nickel Catalysts
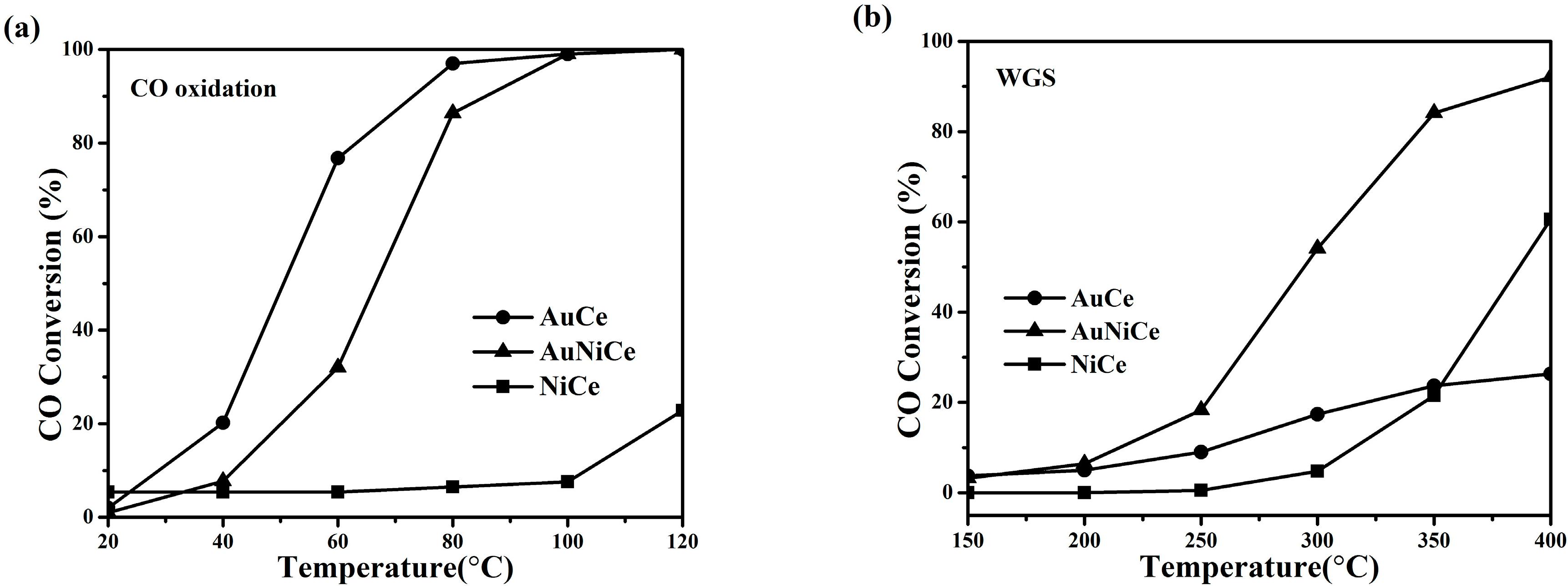
2.3. Catalytic Performance of Ceria-Supported Gold-Nickel Catalysts
2.4. Structural and Textural Properties for Used Ceria-Supported Gold-Nickel Catalysts
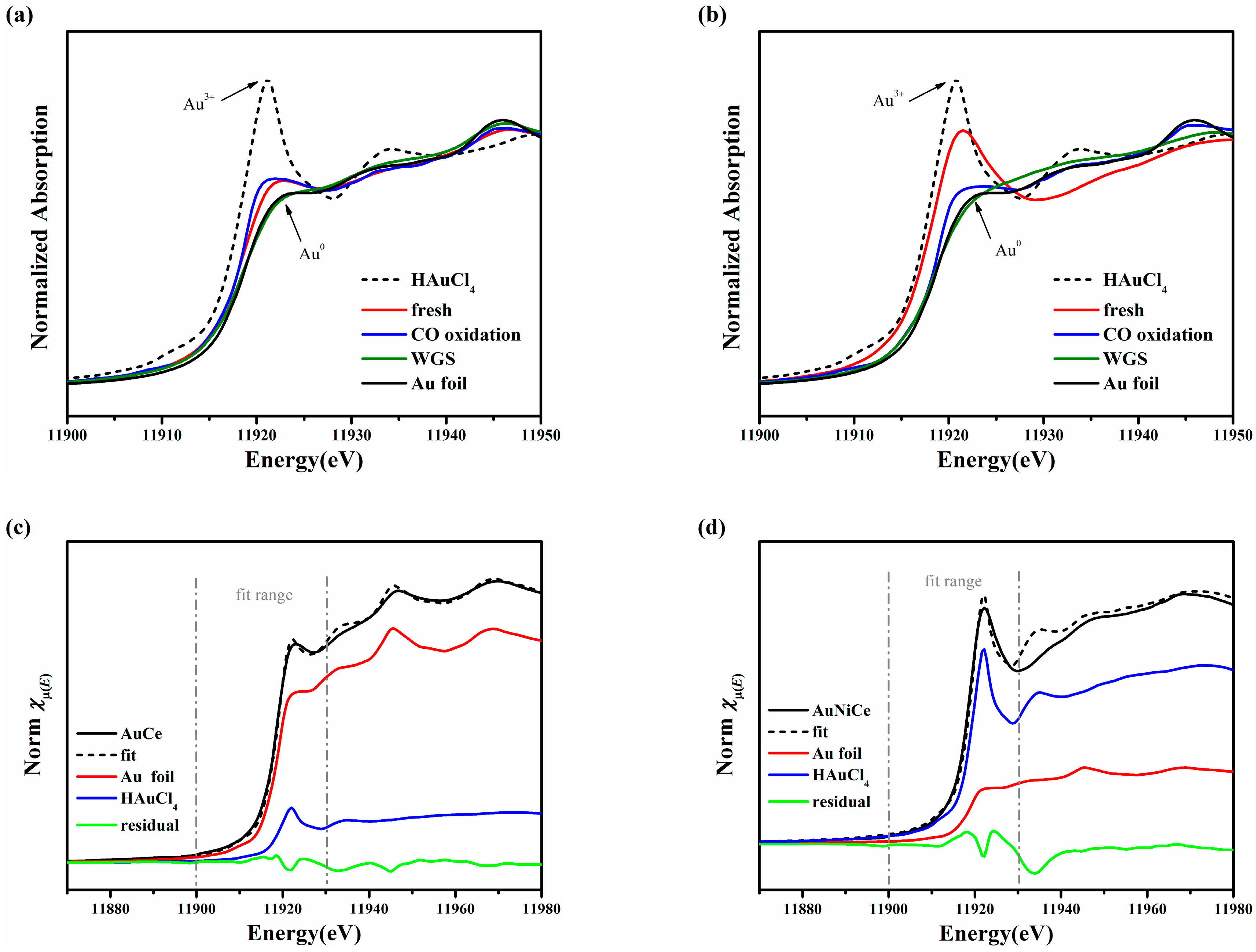
2.5. Electronic Structure of Gold and Nickel for Ceria-Supported Catalysts
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Nickel Oxide to Gold-Ceria Catalyst for CO Oxidation Reaction
3.2. Effect of Nickel Oxide to Gold-Ceria Catalyst for Water-Gas Shift Reaction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Raw Materials
4.2. Preparation of Ceria Nanorods
4.3. Preparation of Gold-Nickel Cluster on Ceria
4.4. Characterizations
4.5. X ray Absorption Fine Structure
4.6. Catalytic Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrettin, S.; Concepcion, P.; Corma, A.; Lopez Nieto, J.M.; Puntes, V.F. Nanocrystalline CeO2 increases the activity of Au for CO oxidation by two orders of magnitude. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2538–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Carley, A.F.; Landon, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Identification of active gold nanoclusters on iron oxide supports for CO oxidation. Science 2008, 321, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.N.; Yuan, Z.; He, S.G. CO oxidation promoted by gold atoms supported on titanium oxide cluster anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3617–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, X.N.; Zhao, Y.X.; He, S.G. CO oxidation catalyzed by single gold atoms supported on aluminum oxide clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14307–14313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gu, D.; Jin, Z.; Du, P.P.; Si, R.; Tao, J.; Xu, W.Q.; Huang, Y.Y.; Senanayake, S.; Song, Q.S.; et al. Uniform 2 nm gold nanoparticles supported on iron oxides as active catalysts for CO oxidation reaction: Structure-activity relationship. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4920–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeno, M.; Ramírez Reina, T.; Ivanova, S.; Laguna, O.; Odriozola, J. Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity. Catalysts 2016, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2884–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, K.T.; Eom, D.; Chan, S.W.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Flynn, G.W.; Wen, X.D.; Batista, E.R. Scanning tunneling microscopy and theoretical study of water adsorption on Fe3O4: Implications for catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18979–18985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Allard, L.F.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Atomically dispersed Au-(OH)x species bound on titania catalyze the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3768–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Herron, J.A.; Xu, Y.; Allard, L.F.; Lee, S.; Huang, J.; Mavrikakis, M.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Catalytically active Au-O(OH)x- species stabilized by alkali ions on zeolites and mesoporous oxides. Science 2014, 346, 1498–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Gao, R.; Xu, W.; Ye, Y.; Lin, L.; Wen, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.; et al. Atomic-layered Au clusters on α-MoC as catalysts for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Science 2017, 357, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Gold atoms stabilized on various supports catalyze the water-gas shift reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, H.X.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Si, R.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H.P.; Liu, H.C.; Yan, C.H. Shape-Selective Synthesis and Oxygen Storage Behavior of Ceria Nanopolyhedra, Nanorods, and Nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24380–24385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Carpenter, C.; Yi, N.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Comparison of the activity of Au/CeO2 and Au/Fe2O3 catalysts for the CO oxidation and the water-gas shift reactions. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.S.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, Y.M.; Fan, K.N.; Cao, Y. Morphology effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, S. Effects of the structure of ceria on the activity of gold/ceria catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and benzene. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, M.; Wang, J.; Lee, W.S.; Williams, W.D.; Kim, S.M.; Stach, E.A.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Size and support effects for the water-gas shift catalysis over gold nanoparticles supported on model Al2O3 and TiO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssensa, T.V.W.; Clausena, B.S.; Hvolbækb, B.; Falsigc, H.; Christensenc, C.H.; Bligaardb, T.; Nørskov, J.K. Insights into the reactivity of supported Au nanoparticles: Combining theory and experiments. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, L.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W. Size-Dependent Reaction Pathways of Low-Temperature CO Oxidation on Au/CeO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketoshi, A.; Haruta, M. Size- and Structure-specificity in Catalysis by Gold Clusters. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.W.; Du, P.P.; Fu, X.P.; Ma, C.; Zeng, J.; Si, R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jia, C.J.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yan, C.H. Contributions of distinct gold species to catalytic reactivity for carbon monoxide oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active Nonmetallic Au and Pt Species on Ceria-Based Water-Gas Shift Catalysts. Science 2003, 301, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, R.W.J.; Sivadinarayana, C.; Wilson, O.M.; Yan, Z.; Goodman, D.W.; Crooks, R.M. Titania-Supported PdAu Bimetallic Catalysts Prepared from Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticle Precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1380–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, A.I.; Machavariani, V.S.; Rubshtein, A.; Rosenberg, Y.; Voronel, A.; Stern, E.A. Local structure of disordered Au-Cu and Au-Ag alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 9364–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveline, B.; van, B.J.A. Electronic and Geometric Structures of Supported Platinum, Gold, and Platinum-Gold Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 9761–9768. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Su, D.-S.; Mou, C.-Y. Au–Cu alloy nanoparticles supported on silica gel as catalyst for CO oxidation: Effects of Au/Cu ratios. Catal. Today 2011, 160, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yi, L. Comparison of electrocatalytic activity of carbon-supported Au–M (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) bimetallic nanoparticles for direct borohydride fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11984–11993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Wang, A.; Yang, X.; Allard, L.F.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, B.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Miao, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. FeOx-supported platinum single-atom and pseudo-single-atom catalysts for chemoselective hydrogenation of functionalized nitroarenes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, G.; Duchesne, P.N.; Gu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Weng, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, P.; Pao, C.W.; et al. Interfacial effects in iron-nickel hydroxide-platinum nanoparticles enhance catalytic oxidation. Science 2014, 344, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-W.; Du, P.-P.; Zou, S.-H.; He, H.-Y.; Wang, R.-X.; Jin, Z.; Shi, S.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Si, R.; Song, Q.-S.; et al. Highly Dispersed Copper Oxide Clusters as Active Species in Copper-Ceria Catalyst for Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fu, X.-P.; Jia, C.-J.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Si, R.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yan, C.-H. Structural Determination of Catalytically Active Subnanometer Iron Oxide Clusters. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3072–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, S.; Osaki, M.; Nagai, Y.; Nishimura, Y.F.; Dohmae, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Hirata, H. XAFS study on promoting effect of Au via NiO reduction in Au-Ni bimetallic clusters. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, A.V.; Zharova, P.A.; Nikolaev, S.A.; Tsodikov, M.V. Direct Au-Ni/Al2O3 catalysed cross-condensation of ethanol with isopropanol into pentanol-2. Catal. Today 2017, 279, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhu, H. Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Stream Over Au/CeO2–NiO Catalysts: Effect of the Preparation Method. Catal. Lett. 2017, 148, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahammadunnisa, S.; Manoj Kumar Reddy, P.; Lingaiah, N.; Subrahmanyam, C. NiO/Ce1−xNixO2−δ as an alternative to noble metal catalysts for CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, A.; Leppelt, R.; Plzak, V.; Behm, R. The role of cationic Au3+ and nonionic Au0 species in the low-temperature water–gas shift reaction on Au/CeO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 252, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Fan, J.; Lan, H.; Yang, Y. Ultra-low-gold loading Au/CeO2 catalysts for ambient temperature CO oxidation: Effect of preparation conditions on surface composition and activity. J. Catal. 2010, 273, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Song, C. NiO nanosheets rooting into Ni-doped CeO2 microspheres for high performance of CO catalytic oxidation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 198, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Shi, W.; Wei, C.; Song, X.; Yang, S.; Sun, Z. Baize-like CeO2 and NiO/CeO2 nanorod catalysts prepared by dealloying for CO oxidation. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 045602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Frenkel, A.I.; Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Reaction-Relevant Gold Structures in the Low Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction on Au-CeO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12834–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I. Powder pattern programs. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1971, 4, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I. The accuracy of cell dimensions determined by Cohen’s method of least squares and the systematic indexing of powder data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1973, 6, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-S.; Wei, X.-J.; Li, J.; Gu, S.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.H.; Ma, J.-Y.; Li, L.-N.; Gao, Q.; Si, R. The XAFS beamline of SSRF. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2015, 26, 050102. [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel, A.I.; Wang, Q.; Marinkovic, N.; Chen, J.G.; Barrio, L.; Si, R.; Cámara, A.L.; Estrella, A.M.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Hanson, J.C. Combining X-ray Absorption and X-ray Diffraction Techniques for in Situ Studies of Chemical Transformations in Heterogeneous Catalysis: Advantages and Limitations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17884–17890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
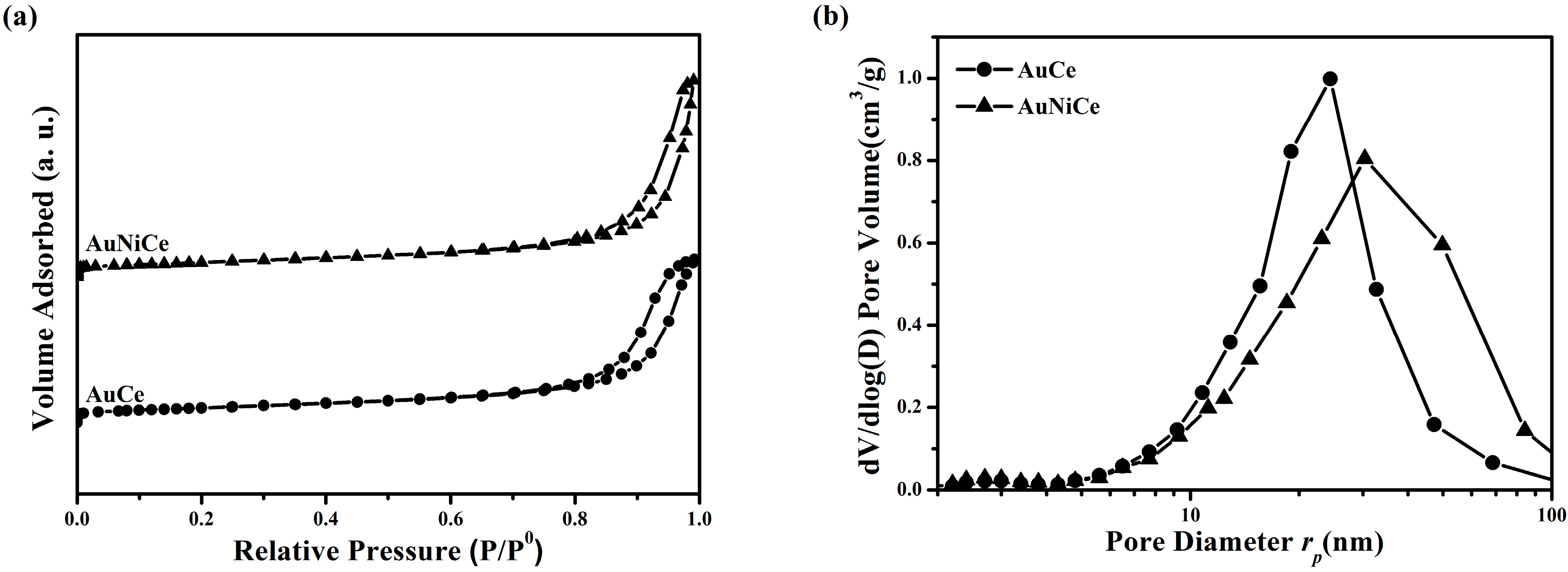
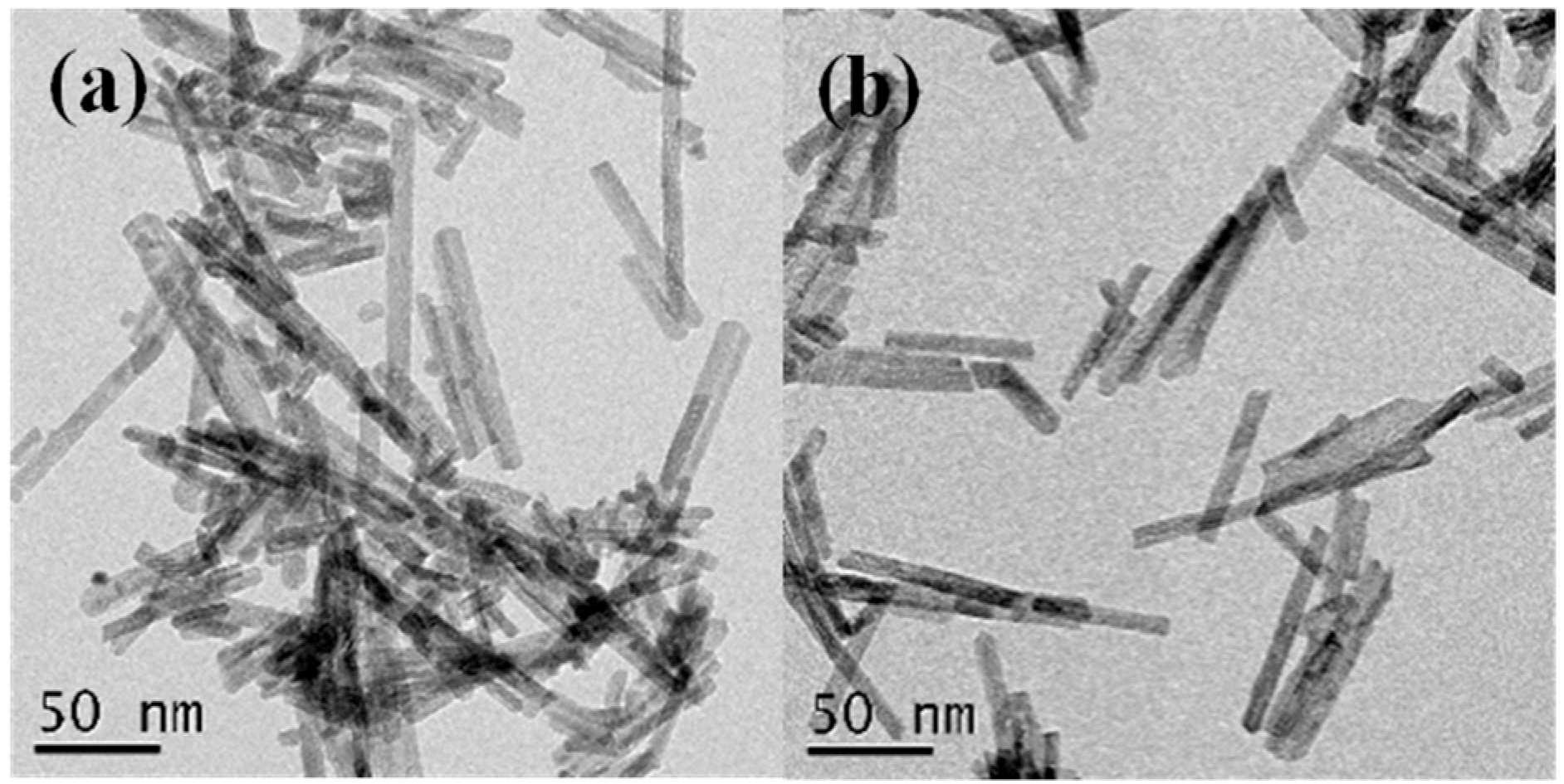
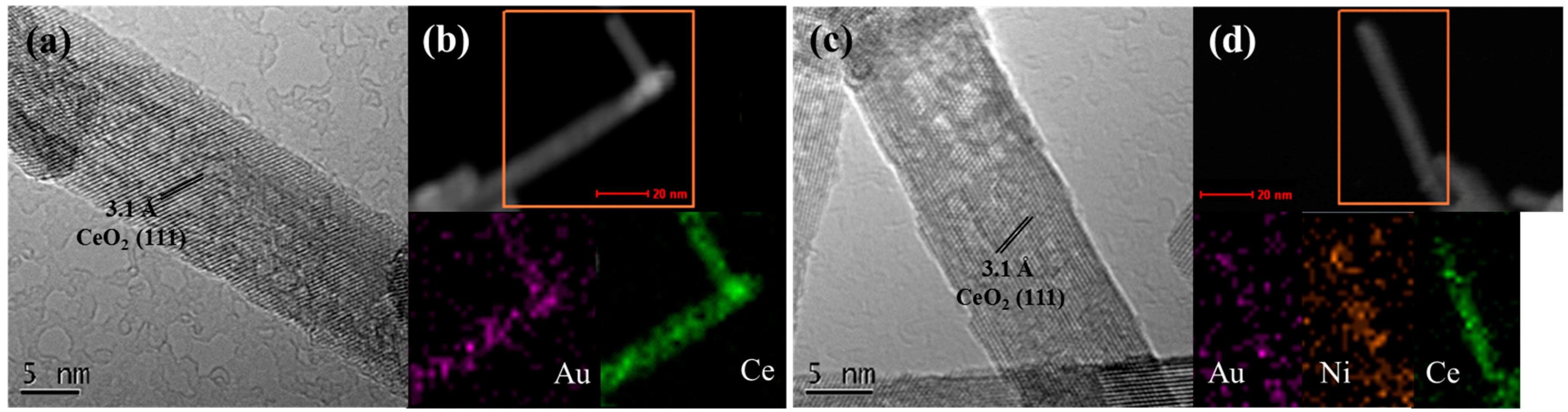
| Sample | Au (at%) a | Ni (at%) a | SBET (m2/g) c | Vp (cm3/g) c | a (Å) d | DXRD (nm) d | DTEM (nm) g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuCe | 0.21(0.04) | - | 99 | 0.44 | 5.4134(2) 5.4157(3) e 5.4100(1) f | 9.4 | 8.1(1.8) h 20–150 i |
| AuNiCe | 0.13(0.05) | 3.9(0.1) 4.5, 3.8, 4.3 b | 99 | 0.53 | 5.4088(1) 5.4108(1) e 5.4149(1) f | 9.7 | 8.7(1.9) h 20–150 i |
| Sample | TR (°C) a | H2 Consump. (μmol/gcat) | T50 (°C) CO Oxidation c | r (μmol gAu−1 s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO Oxidation c (40 °C) | WGS d (250 °C) | ||||
| AuCe | 118 | 341a (5) b | 50 | 1030 | 781 |
| AuNiCe | 146 | 1278 (525) | 66 | 631 | 2542 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, M.; Wei, S.; Jia, C.-J.; Wang, D.-L.; Si, R. Effect of Nickel Oxide Doping to Ceria-Supported Gold Catalyst for CO Oxidation and Water-Gas Shift Reactions. Catalysts 2018, 8, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120584
Shu M, Wei S, Jia C-J, Wang D-L, Si R. Effect of Nickel Oxide Doping to Ceria-Supported Gold Catalyst for CO Oxidation and Water-Gas Shift Reactions. Catalysts. 2018; 8(12):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120584
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Miao, Shuai Wei, Chun-Jiang Jia, Dao-Lei Wang, and Rui Si. 2018. "Effect of Nickel Oxide Doping to Ceria-Supported Gold Catalyst for CO Oxidation and Water-Gas Shift Reactions" Catalysts 8, no. 12: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120584
APA StyleShu, M., Wei, S., Jia, C.-J., Wang, D.-L., & Si, R. (2018). Effect of Nickel Oxide Doping to Ceria-Supported Gold Catalyst for CO Oxidation and Water-Gas Shift Reactions. Catalysts, 8(12), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120584




