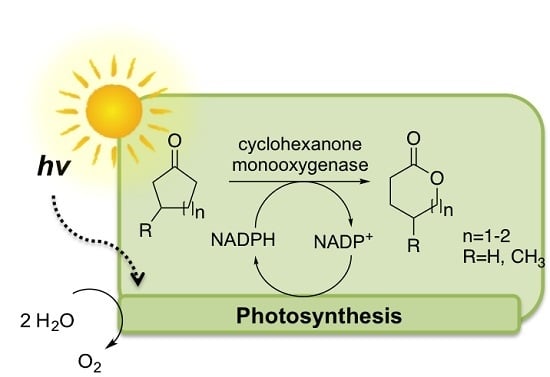
Enzymatic Oxyfunctionalization Driven by Photosynthetic Water-Splitting in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
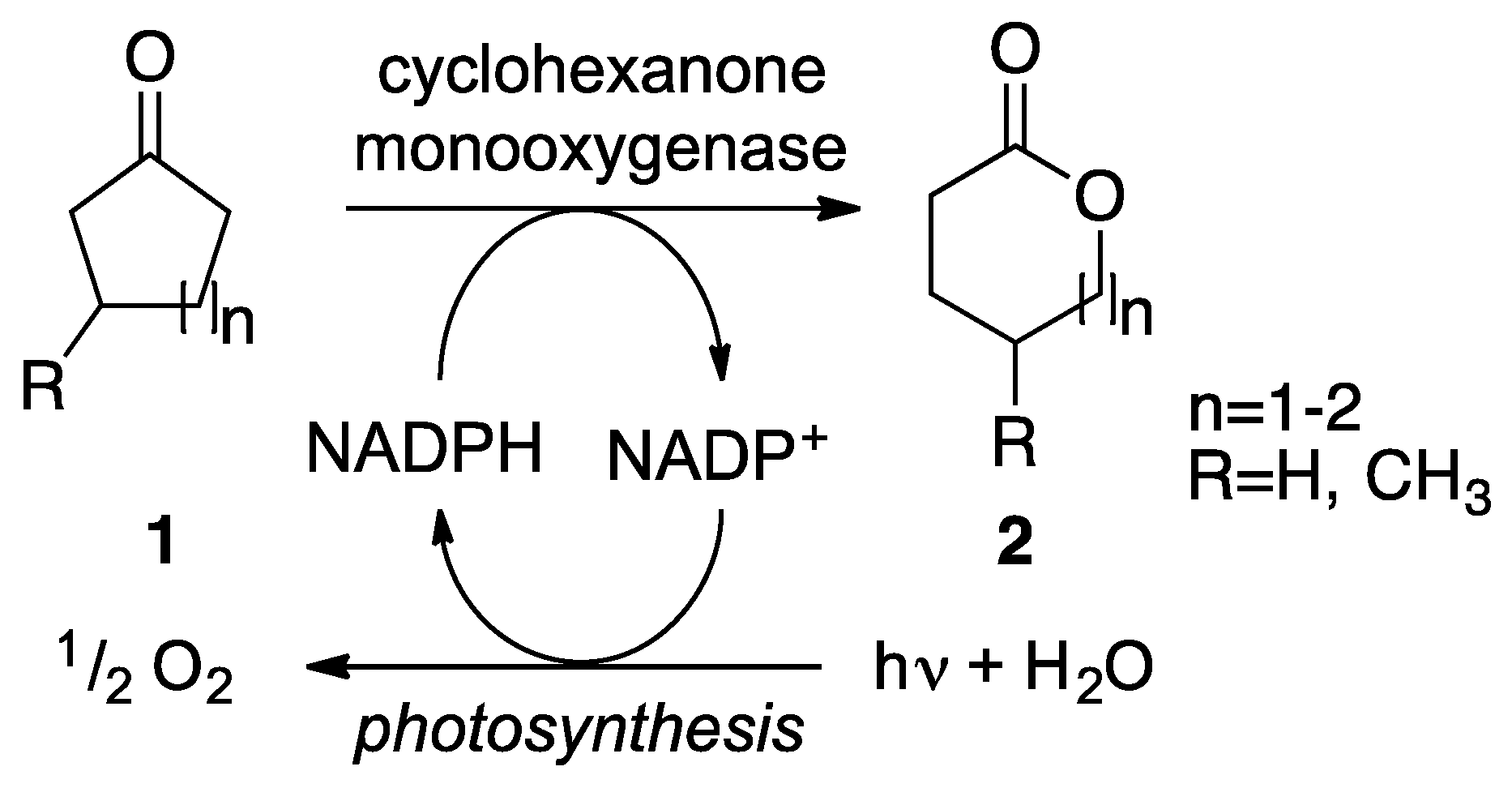
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Expression of CHMO in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
2.2. Substrate Spectrum and Side-Reactions
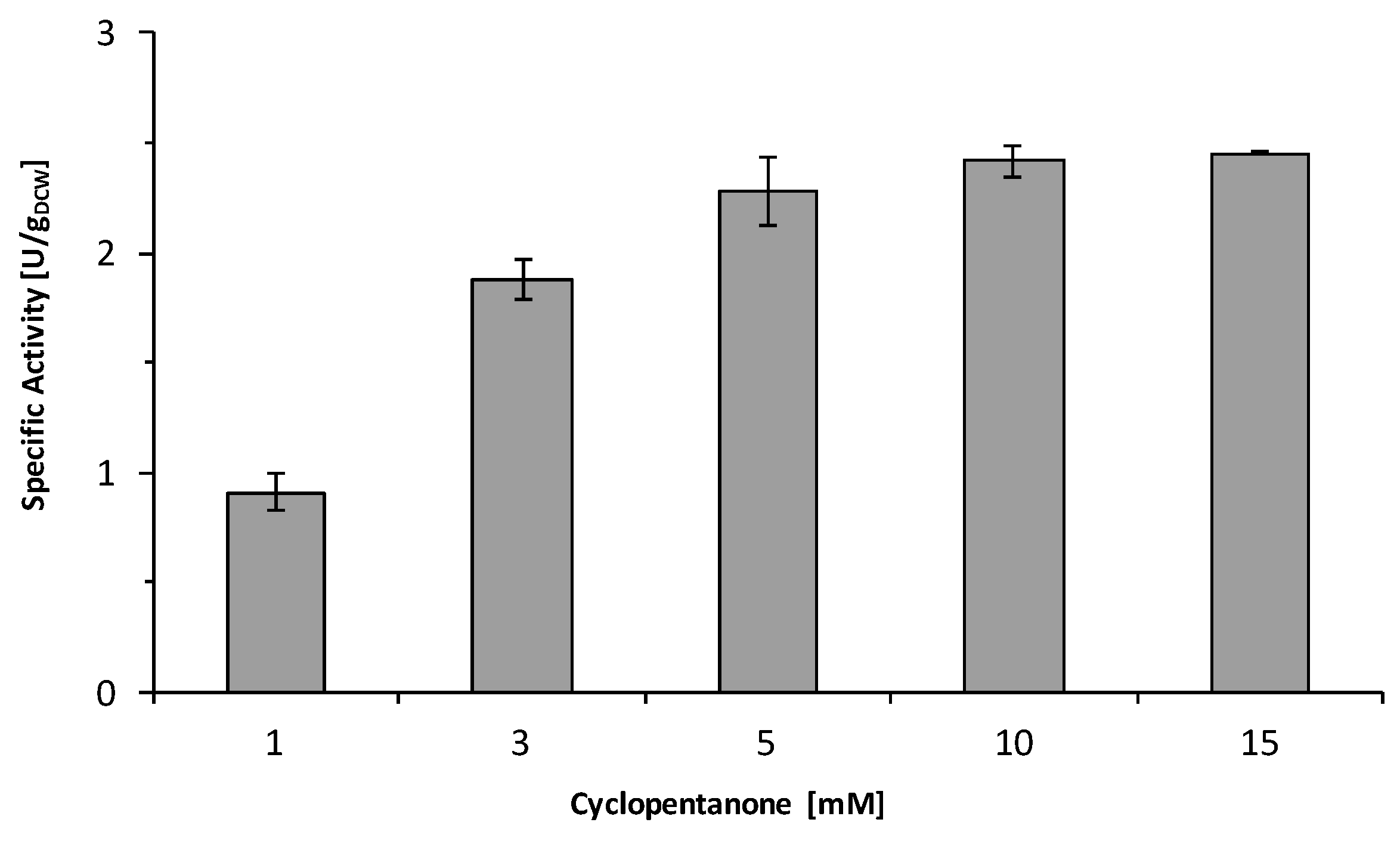
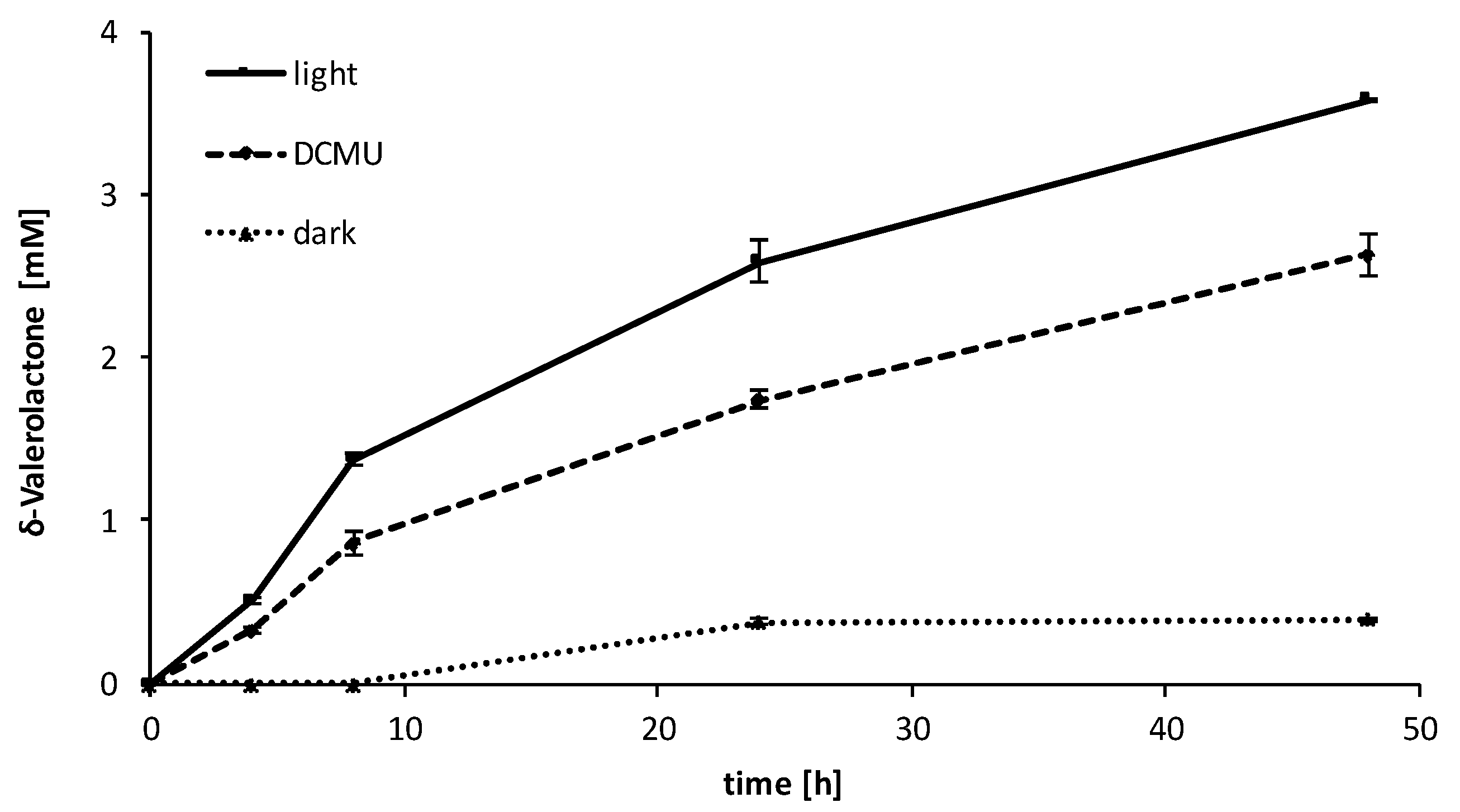
2.3. Influence of the Light Availability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Cloning and Transformation of Synechocystis
4.3. Biotransformation Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Buehler, K.; Schallmey, A.; Bühler, B. Enzyme-mediated oxidations for the chemist. Green Chem. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Scherkus, C.; Muschiol, J.; Menyes, U.; Winkler, T.; Hummel, W.; Gröger, H.; Liese, A.; Herz, H.G.; Bornscheuer, U.T. An enzyme cascade synthesis of ε-caprolactone and its oligomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2784–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, S.; Spickermann, D.; Schrittwieser, J.H.; Leggewie, C.; van Berkel, W.J.; Arends, I.W.; Hollmann, F. More efficient redox biocatalysis by utilising 1, 4-butanediol as a ‘smart cosubstrate’. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, R.M.; Dobretsov, S.; Sudesh, K. Applications of cyanobacteria in biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.K.; Atsumi, S. Metabolic design for cyanobacterial chemical synthesis. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 120, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formighieri, C.; Melis, A. A phycocyanin phellandrene synthase fusion enhances recombinant protein expression and β-phellandrene (monoterpene) hydrocarbons production in synechocystis (cyanobacteria). Metab. Eng. 2015, 32, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowaczyk, M.; Rexroth, S.; Rögner, M. Biotechnology; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh, R.; Muraki, N.; Shinmura, K.; Kubota-Kawai, H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Nowaczyk, M.M.; Rögner, M.; Hase, T.; Ikegami, T.; Kurisu, G. X-ray structure and nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the interaction sites of the ga-substituted cyanobacterial ferredoxin. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 6052–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamanaka, R. Light-mediated regulation of asymmetric reduction of ketones by a cyanobacterium. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2002, 13, 2529–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamanaka, R. Light mediated cofactor recycling system in biocatalytic asymmetric reduction of ketone. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1782–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Nakamura, K.; Murakami, M.; Murakami, A. Selective synthesis of cinnamyl alcohol by cyanobacterial photobiocatalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górak, M.; Żymańczyk-Duda, E. Application of cyanobacteria for chiral phosphonate synthesis. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köninger, K.; Gómez Baraibar, Á.; Mügge, C.; Paul, C.E.; Hollmann, F.; Nowaczyk, M.M.; Kourist, R. Recombinant cyanobacteria for the asymmetric reduction of C=C bonds fueled by the biocatalytic oxidation of water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5582–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, A.; Bordewick, S.; Genz, M.; Schmidt, S.; van den Bergh, T.; Peters, C.; Joosten, H.J.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Switch in cofactor specificity of a baeyer–villiger monooxygenase. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 2312–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gründel, M.; Scheunemann, R.; Lockau, W.; Zilliges, Y. Impaired glycogen synthesis causes metabolic overflow reactions and affects stress responses in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiology 2012, 158, 3032–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölsch, K.; Havel, J.; Haslbeck, M.; Weuster-Botz, D. Identification, cloning, and characterization of a novel ketoreductase from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6697–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
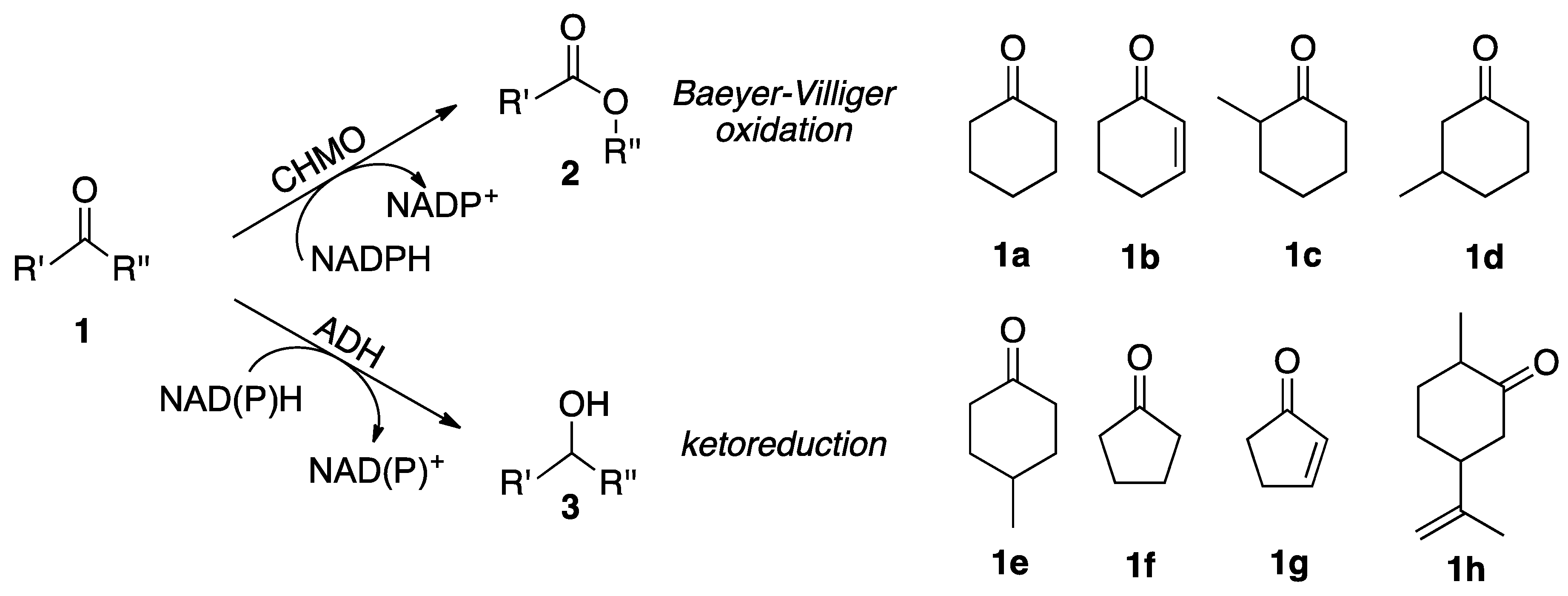

| Entry | Substrate | Side-Product Product | Synechocystis WT (%) 1 | Synechocystis Cyclohexanone Monooxygenase (CHMO) (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1c | 2c | 0 | 48 |
| 3c | 35 | 23 | ||
| 2 | 1d | 2d | 0 | 72 |
| 3d | 16 | 8 | ||
| 3 | 1e | 2e | 0 | 82 |
| 3e | 47 | 8 |
| Entry | Substrate | Specific Activity 1 (U/gDCW 2) | Ketoreduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1a | 2.3 ± 0.05 | 50% |
| 2 | 1b | n.c. 3 | - |
| 3 | 1c | 2.0 ± 0.09 | 30% |
| 4 | 1d | 2.94 ± 0.05 | 25% |
| 5 | 1e | 5.73 ± 0.02 | <5% |
| 6 | 1f | 2.3 ± 0.06 | 0% |
| 7 | 1g | n.c. | - |
| 8 | 1h | n.c. | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Böhmer, S.; Köninger, K.; Gómez-Baraibar, Á.; Bojarra, S.; Mügge, C.; Schmidt, S.; Nowaczyk, M.M.; Kourist, R. Enzymatic Oxyfunctionalization Driven by Photosynthetic Water-Splitting in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Catalysts 2017, 7, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080240
Böhmer S, Köninger K, Gómez-Baraibar Á, Bojarra S, Mügge C, Schmidt S, Nowaczyk MM, Kourist R. Enzymatic Oxyfunctionalization Driven by Photosynthetic Water-Splitting in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Catalysts. 2017; 7(8):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080240
Chicago/Turabian StyleBöhmer, Stefanie, Katharina Köninger, Álvaro Gómez-Baraibar, Samiro Bojarra, Carolin Mügge, Sandy Schmidt, Marc M. Nowaczyk, and Robert Kourist. 2017. "Enzymatic Oxyfunctionalization Driven by Photosynthetic Water-Splitting in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803" Catalysts 7, no. 8: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080240
APA StyleBöhmer, S., Köninger, K., Gómez-Baraibar, Á., Bojarra, S., Mügge, C., Schmidt, S., Nowaczyk, M. M., & Kourist, R. (2017). Enzymatic Oxyfunctionalization Driven by Photosynthetic Water-Splitting in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Catalysts, 7(8), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080240