A Review on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–Based Catalysts at Low Temperatures: Catalysts, Mechanisms, Kinetics and DFT Calculations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
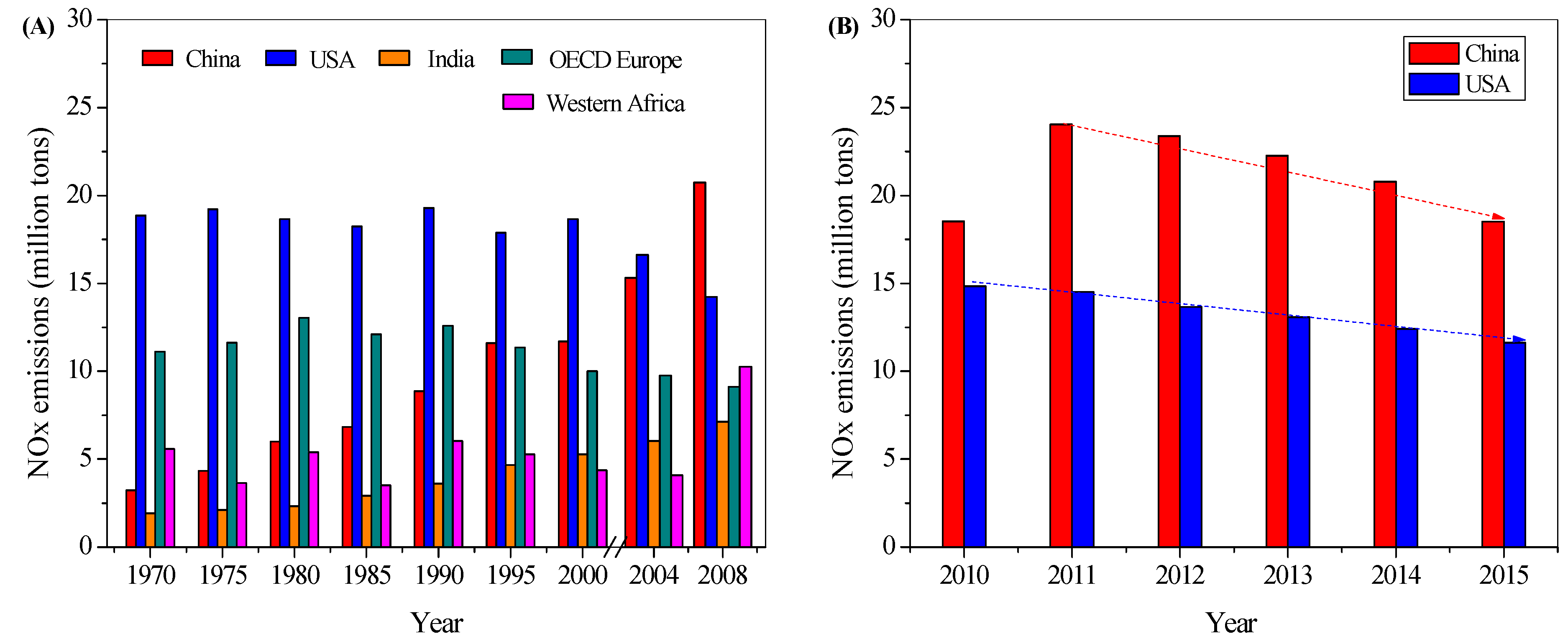
1.1. NOx Emissions and Legislations
1.2. NOx Abatement and Demand of LT–SCR Technique
1.3. Catalysts for LT–SCR
2. Mn-Based Catalysts
2.1. Multi–Metal Oxides
2.1.1. Composite Oxides
2.1.2. Spinel Crystal Catalysts
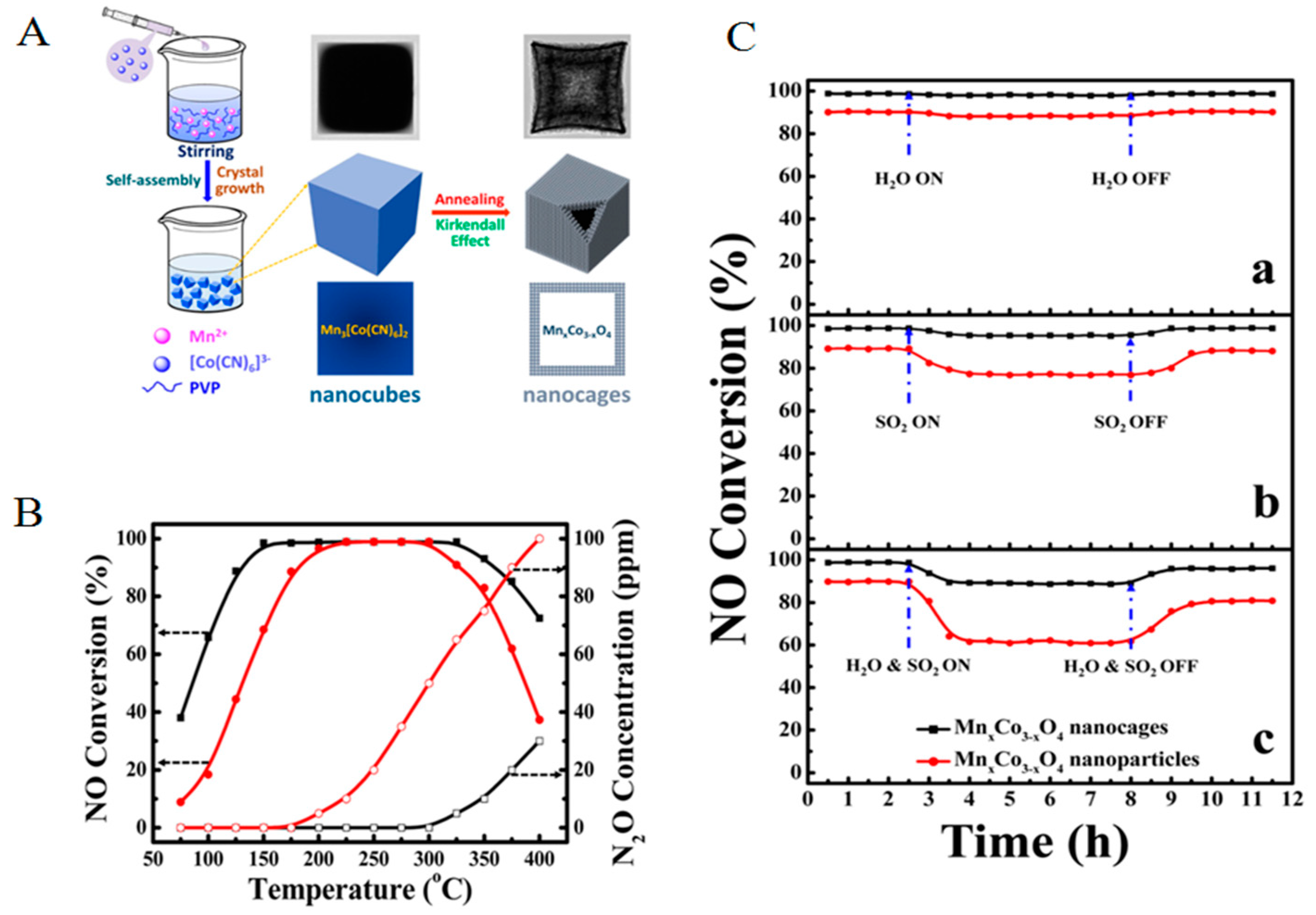
2.1.3. Specific Structure/Shape Catalysts
2.2. Metal Oxides as the Carrier
2.3. Molecular Sieves as the Carrier
2.4. Carbon Materials as the Carrier
2.4.1. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
2.4.2. Graphene (GE)
3. SCR Mechanisms
3.1. Adsorption Behavior of Reactants
3.2. Reaction Pathways
3.2.1. Langmuir–Hinshelwood Mechanism
3.2.2. Eley–Rideal Mechanism
3.2.3. Effects of H2O and SO2
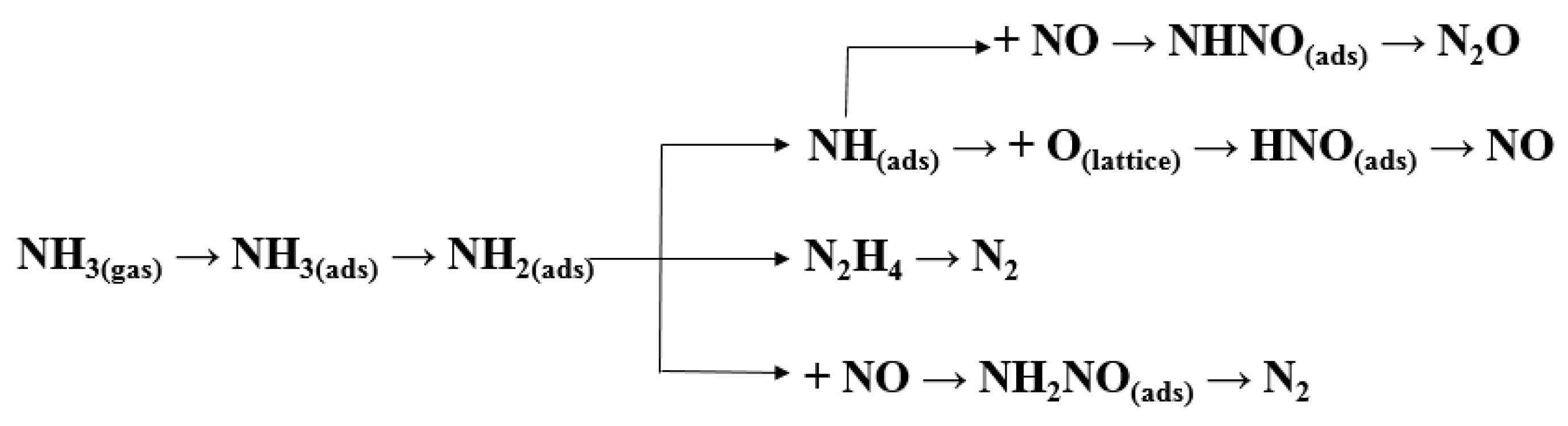
3.3. By–Product of N2O
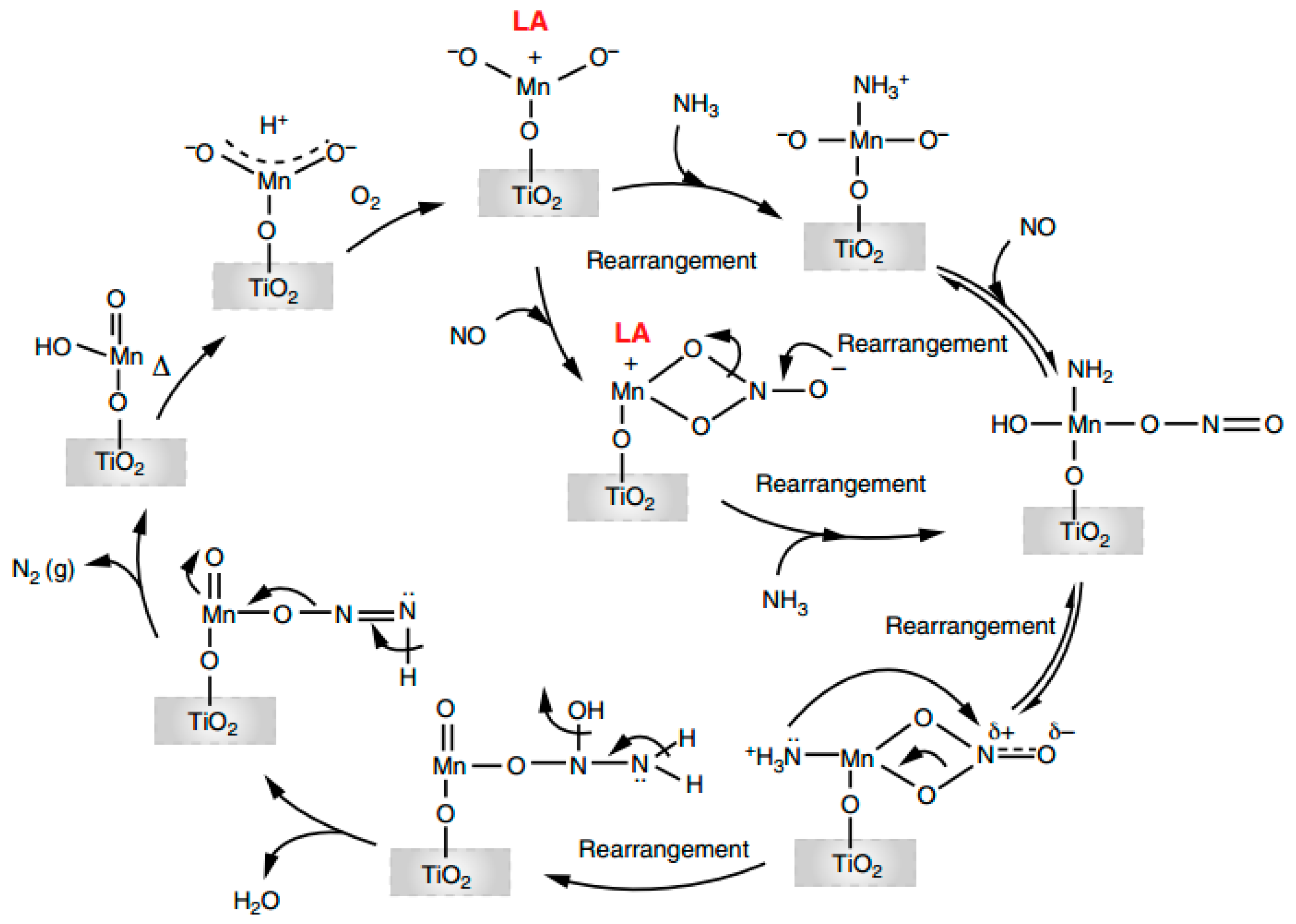
3.4. Promoting Effect of Redox Cycles
4. Reaction Kinetics
4.1. Macro–Kinetics
4.2. Micro–Kinetics
4.2.1. LH Mechanism
4.2.2. ER Mechanism
4.2.3. Total Reaction Kinetic Equations
5. New Insight from DFT Calculation
5.1. Analysis of Material Properties
5.2. Visualization of Reaction and Poisoning Mechanisms
5.3. Design of Functional Materials
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, S.; Hegde, M.S.; Madras, G. Catalysis for NOx abatement. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, P.; Parvulescu, V.I. Catalytic NOx Abatement Systems for Mobile Sources: From Three-Way to Lean Burn after-Treatment Technologies. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3155–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Li, C.; Lu, P.; Qu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, M.; Fang, Y. A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by supported catalysts at 100–300 °C–catalysts, mechanism, kinetics. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaca, C.; Costa, M. NOx control through reburning using biomass in a laboratory furnace: Effect of particle size. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Denison, M.; Adams, B.; Brown, D. Towards comprehensive computational fluid dynamics modeling of pyrolysis furnaces with next generation low-NOx burners using finite-rate chemistry. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.M. Catalytic abatement of nitrogen oxides–stationary applications. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, I.; Lietti, L.; Tronconi, E.; Forzatti, P. Dynamics of SCR reaction over a TiO2-supported vanadia-tungsta commercial catalyst. Catal. Today 2000, 60, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; He, H. Vanadium- Based Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Prog. Chem. 2012, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, A.M.; Gao, F.; Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Peden, C.H.F.; Szanyi, J. Recent advances in automotive catalysis for NOx emission control by small-pore microporous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7371–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Gao, P.-X. A review of NOx storage/reduction catalysts: mechanism, materials and degradation studies. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 552–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, X. High-efficiency removal of NOx using a combined adsorption-discharge plasma catalytic process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, J.; Yi, H.; Zhao, S. Nitric oxide decomposition using atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge reactor with different adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58417–58425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, R.; Wang, T.; Yang, C. Follow-up research for integrative process of pre-oxidation and post-absorption cleaning flue gas: Absorption of NO2, NO and SO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Han, Y.; Chen, C. Simultaneous Removal of SO2 and NO from Flue Gas Using Multicomposite Active Absorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Hu, G.; He, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Regeneration of full-scale commercial honeycomb monolith catalyst (V2O5–WO3/TiO2) used in coal-fired power plant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Bao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, W. Study of the V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalyst Synthesized from Waste Catalyst on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3. Catalysts 2017, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, C.; Chen, J.; Meng, X. Deactivation mechanism of de-NOx catalyst (V2O5-WO3/TiO2) used in coal fired power plant. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2012, 40, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, N.; Lambert, R.M. Lean NOx reduction with CO + H2 mixtures over Pt/Al2O3 and Pd/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 35, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, N.; Isaac, J.; Lambert, R.M. A comparison of sodium-modified Rh/γ-Al2O3 and Pd/γ-Al2O3 catalysts operated under simulated TWC conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 33, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Co-doping a metal (Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ce, and Zr) on Mn/TiO2 catalyst and its effect on the selective reduction of NO with NH3 at low-temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 110, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Performance and kinetics study for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over MnOx–CeO2 catalyst. J. Catal. 2003, 217, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Cai, S.; Hu, H.; Fang, C.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Rational design and in situ fabrication of MnO2@NiCo2O4 nanowire arrays on Ni foam as high-performance monolith de-NOx catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11543–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Gu, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. Ni-Mn bi-metal oxide catalysts for the low temperature SCR removal of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148–149, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Sun, K.; Shen, K. Influence of the addition of transition metals (Cr, Zr, Mo) on the properties of MnOx–FeOx catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by Ammonia. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 392, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Mn-Ce mixed oxide catalyst at low temperatures. Catal. Today 2013, 216, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Environmentally-benign catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx from diesel engines: structure-activity relationship and reaction mechanism aspects. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8445–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, M.; Palkovits, R. Nitrogen oxide removal over hydrotalcite-derived mixed metal oxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Zou, W.; Yu, S.; Shao, Y.; Dong, L. Promotional Effect of Ce on Iron-Based Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Catalysts 2016, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, D.A.; Uphade, B.S.; Smirniotis, P.G. TiO2-supported metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 I. Evaluation and characterization of first row transition metals. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, W.S.; Brands, D.S.; Smit, H.I.; Poels, E.K.; Bliek, A. Mechanism of the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3. J. Catal. 1997, 171, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, W.S.; Biervliet, M.; Poels, E.K.; Bliek, A. Deactivation by SO2 of MnOx/Al2O3 catalysts used for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 16, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Park, E.D.; Kim, J.M.; Yie, J.E. Manganese oxide catalysts for NOx reduction with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 327, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Tang, X. Effects of MnO2 Crystal Structure and Surface Property on the NH3-SCR Reaction at Low Temperature. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2012, 28, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Chang, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, J. Structural and Surface Effect of MnO2 for Low Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Cao, Q.; Hu, B.; Huang, Z.; Tang, X. Surface structure sensitivity of manganese oxides for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 101, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Yang, H.; Fan, X.; Zhang, X. Catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over different-shaped MnO2 at low temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.P.; Huang, Z.W.; Hua, W.M.; Gu, X.; Tang, X.F. Effect of H2O on catalytic performance of manganese oxides in NO reduction by NH3. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 437, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, S.; Deorsola, F.A.; Galletti, C.; Pirone, R. Nanostructured MnOx catalysts for low-temperature NOx SCR. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 278, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over amorphous MnOx catalysts prepared by three methods. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J. Nano-MnOx Catalyst for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3 in Low-temperature. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J. Novel MnOx Catalyst for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Chin. J. Catal. 2006, 27, 843–848. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Yeon, T.H.; Park, E.D.; Yie, J.E.; Kim, J.M. Novel MnOx Catalysts for NO Reduction at Low Temperature with Ammonia. Catal. Lett. 2006, 106, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Ke, R.; Luo, C.; Hao, J. Effects of precursors on the surface Mn species and the activities for NO reduction over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; He, K. Effects of calcination temperature on Mn species and catalytic activities of Mn/ZSM-5 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Structure–activity relationship of VOx/CeO2 nanorod for NO removal with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, L. Promoting effect of MoO3 on the NOx reduction by NH3 over CeO2/TiO2 catalyst studied with in situ DRIFTS. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Deng, S.; A. Rong, T. A Ce–Sn–Ox catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2013, 40, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Lv, G.; Wang, C.; Hao, Q.; Hui, K. Cerium doped copper/ZSM-5 catalysts used for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxide with ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhibo, X.; Chunmei, L.; Dongxu, G.; Xinli, Z.; Kuihua, H. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over iron-cerium mixed oxide catalyst: catalytic performance and characterization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, A.; Wang, Z.; Schwämmle, T.; Ke, J.; Li, X. Novel Fe-W-Ce Mixed Oxide for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 at Low Temperatures. Catalysts 2017, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts-A review. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Song, H. Catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4280–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Park, E.D.; Kim, J.M.; Yie, J.E. Cu–Mn mixed oxides for low temperature NO reduction with NH3. Catal. Today 2006, 111, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Xie, J.; Mei, D.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Effect of CuMn2O4 spinel in Cu–Mn oxide catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25540–25551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Wei, L.; Hao, J. MnOx-SnO2 Catalysts Synthesized by a Redox Coprecipitation Method for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3. Chin. J Catal. 2008, 29, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.Q.; Yang, R.T.; Chang, R. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 over Fe-Mn based catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2002, 5, 452–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Sun, K.; Zhou, C. Influence of chromium modification on the properties of MnOx-FeOx catalysts for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zha, K.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Scale-Activity Relationship of MnOx-FeOy Nanocage Catalysts Derived from Prussian Blue Analogues for Low-Temperature NO Reduction: Experimental and DFT Studies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2581–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Z.; Liu, F.; He, H.; Shi, X.; Mo, J.; Wu, Z. Manganese–niobium mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.-J.; Wang, C.; Ding, Z.-N.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhang, Z.-K. Li-modified MnO2 catalyst and LiMn2O4 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2014, 42, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Guo, R.-T.; Liu, S.-M.; Wang, S.-X.; Pan, W.-G.; Li, M.-Y. The enhanced performance of MnOx catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction by the modification with Eu. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 531, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Niu, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, Y. Promoting catalytic performances of Ni-Mn spinel for NH3-SCR by treatment with SO2 and H2O. Catal. Commun. 2016, 85, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T.; Chang, R. MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 51, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.S.; Yang, R.T. A superior catalyst for low-temperature NO reduction with NH3. Chem. Commun. 2003, 34, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Characterization and FTIR Studies of MnOx-CeO2 Catalyst for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15738–15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenmann, F.; Maciejewski, M.; Baiker, A. Selective reduction of NO by NH3 over manganese–cerium mixed oxides: Relation between adsorption, redox and catalytic behavior. Appl. Catal. B 2006, 62, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, S.; Deorsola, F.A.; Pirone, R. MnOx-CeO2 catalysts synthesized by solution combustion synthesis for the low-temperature NH3-SCR. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ma, K.; Zou, W.; He, S.; An, J.; Yang, F.; Dong, L. Influence of preparation methods on the physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperature. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, R.; Ye, F.; Jia, F.; Ji, L. MnOx-CeO2 catalysts supported by Ti-Bearing Blast Furnace Slag for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Schwank, J.W.; Hao, J. Effect of Sn on MnOx–CeO2 catalyst for SCR of NOx by ammonia: Enhancement of activity and remarkable resistance to SO2. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casapu, M.; Krocher, O.; Elsener, M. Screening of doped MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for low-templerature NO-SCR. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 88, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Schwank, J.W.; Hao, J. Improvement of activity and SO2 tolerance of Sn-modified MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5294–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y.; Si, Z.; Weng, D. Effects of WO3 doping on stability and N2O escape of MnOx–CeO2 mixed oxides as a low-temperature SCR catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2015, 69, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.W.; Sun, Y.; Su, W.; Liu, J. MnO2 doped CeO2 with tailored 3-D channels exhibits excellent performance for NH3-SCR of NO. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26231–26235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Chu, C.; Li, C. Promotional mechanisms of activity and SO2 tolerance of Co- or Ni-doped MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X. BiMnO3 Perovskite Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperature. Chin. J. Catal. 2012, 33, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Chi Tsang, S. Cr–MnOx mixed-oxide catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. J. Catal. 2010, 276, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, W.; Sun, K. Porous bimetallic Mn2Co1Ox catalysts prepared by a one-step combustion method for the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2015, 72, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zhan, S.; Yu, H.; Zhu, D. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over ordered mesoporous MnxCo3−xO4 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2015, 62, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zhan, S.; Yu, H.; Zhu, D.; Wang, S. Facile preparation of ordered mesoporous MnCo2O4 for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. In Situ DRIFTs Investigation of the Low-Temperature Reaction Mechanism over Mn-Doped Co3O4 for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 22924–22933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, R.; Zhang, D. Rational Design of High-Performance DeNOx Catalysts Based on MnxCo3–xO4 Nanocages Derived from Metal–Organic Frameworks. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Chi, G.; Si, M. A comparative study of manganese–cerium doped metal–organic frameworks prepared via impregnation and in situ methods in the selective catalytic reduction of NO. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5928–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X. Synthesis of Bimetallic MOFs MIL-100(Fe-Mn) as an Efficient Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M. MOF-74 as an Efficient Catalyst for the Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26817–26826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, B.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. Low-temperature synthesis of Mn-based mixed metal oxides with novel fluffy structures as efficient catalysts for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides by ammonia. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12396–12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Maitarad, P.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W. In situ synthesis of 3D flower-like NiMnFe mixed oxides as monolith catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10645–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 over Fe–Mn Mixed-Oxide Catalysts Containing Fe3Mn3O8 Phase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Qiu, M.; Yang, S.; Zhu, D.; Yu, H.; Li, Y. Facile preparation of MnO2 doped Fe2O3 hollow nanofibers for low temperature SCR of NO with NH3. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20486–20493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhan, S.; Guan, Q.; Tian, Y. Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn2O3-Doped Fe2O3 Hexagonal Microsheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 5224–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Park, H.J.; Choi, S.J.; Park, D.E.; Yie, E.J. Low-temperature catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia over supported manganese oxide catalysts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirniotis, P.G.; Sreekanth, P.M.; Peña, D.A.; Jenkins, R.G. Manganese Oxide Catalysts Supported on TiO2, Al2O3, and SiO2: A Comparison for Low-Temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 6436–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jin, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of ceria doping on SO2 resistance of Mn/TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO on MnOx/TiO2 prepared by different methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Nam, I.-S.; Choung, J.W.; Kil, J.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Cha, M.-S.; Yeo, G.K. High deNOx performance of Mn/TiO2 catalyst by NH3. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Shen, K.; Zhou, C.; Jin, B.; Sun, K. Novel ultrasonic–modified MnOx/TiO2 for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with ammonia. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhou, W.; Xie, A.; Wu, F.; Yao, C.; Li, X.; Zuo, S.; Liu, T. Effect of MnO2 polymorphs structure on the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over TiO2–Palygorskite. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.K.; Boningari, T.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Novel manganese oxide confined interweaved titania nanotubes for the low-temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NOx by NH3. J. Catal. 2016, 334, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron and manganese oxides supported on titania. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 44, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Liu, T.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Deng, L. Iron-doped Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhuang, K.; Xu, B.; Ding, Y.; Yu, L.; Fan, Y. Promotional effect of iron oxide on the catalytic properties of Fe-MnOx/TiO2 (anatase) catalysts for the SCR reaction at low temperatures. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putluru, S.S.R.; Schill, L.; Jensen, A.D.; Siret, B.; Tabaries, F.; Fehrmann, R. Mn/TiO2 and Mn–Fe/TiO2 catalysts synthesized by deposition precipitation—Promising for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 165, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Huang, T.; Shen, K. Novel holmium-modified Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts with a broad temperature window and high sulfur dioxide tolerance for low-temperature SCR. Catal. Commun. 2017, 88, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Pang, D.; Zhang, C.; Meng, J.; Zhu, R.; Ouyang, F. In situ IR studies of Co and Ce doped Mn/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Mechanistic Aspects of deNOx Processing over TiO2 Supported Co–Mn Oxide Catalysts: Structure–Activity Relationships and In Situ DRIFTs Analysis. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6069–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hu, X.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Yan, T.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Photocatalytic preparation of nanostructured MnO2-(Co3O4)/TiO2 hybrids: The formation mechanism and catalytic application in SCR deNOx reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 203, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cen, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Weng, X. The role of cerium in the improved SO2 tolerance for NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148–149, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Nickel-doped Mn/TiO2 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: Catalytic evaluation and characterizations. J. Catal. 2012, 288, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, W.; Tade, M.; Liu, S. Improved activity of W-modified MnOx–TiO2 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Deng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tang, X.; Yao, S.; Lu, H. Effect of Zr Addition on the Low-Temperature SCR Activity and SO2 Tolerance of Fe–Mn/Ti Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 14866–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qi, F.; Xiong, S.; Dang, H.; Liao, Y.; Wong, P.K.; Li, J. MnOx supported on Fe–Ti spinel: A novel Mn based low temperature SCR catalyst with a high N2 selectivity. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 181, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, K.H.; Hong, S.C. MnOx/CeO2–TiO2 mixed oxide catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195–196, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Lv, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, P. Promoted performance of a MnOx/PG catalyst for low-temperature SCR against SO2 poisoning by addition of cerium oxide. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82952–82959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tang, C.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Gao, F.; Dong, L. Effect of metal ions doping (M = Ti4+, Sn4+) on the catalytic performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 495, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, T. The effect of Ce–Zr on NH3-SCR activity over MnOx(0.6)/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-H.; Shin, B.; Shin, M.-C.; Van Tyne, C.J.; Lee, H. Dispersion and valence state of MnO2/Ce(1 − x)ZrxO2–TiO2 for low temperature NH3-SCR. Catal. Commun. 2014, 57, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-H.; Lee, I.; Park, H.; Lee, H. Experimental evidence and mechanism of the oxygen storage capacity in MnO2-Ce(1−x)ZrxO2/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature SCR. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5182–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Pang, D.; Ouyang, F.; Zhang, C. SO42−–Mn–Co–Ce supported on TiO2/SiO2 with high sulfur durability for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2016, 78, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirniotis, P.G.; Pena, D.A.; Uphade, B.S. Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Using Mn, Cr, and Cu Oxides Supported on Hombikat TiO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2479–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Pappas, D.K.; Ettireddy, P.R.; Kotrba, A.; Smirniotis, P.G. Influence of SiO2 on M/TiO2(M = Cu, Mn, and Ce) Formulations for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3: Surface Properties and Key Components in Relation to the Activity of NOx Reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Ettireddy, P.R.; Somogyvari, A.; Liu, Y.; Vorontsov, A.; McDonald, C.A.; Smirniotis, P.G. Influence of elevated surface texture hydrated titania on Ce-doped Mn/TiO2 catalysts for the low-temperature SCR of NOx under oxygen-rich conditions. J. Catal. 2015, 325, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettireddy, P.R.; Ettireddy, N.; Mamedov, S.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Surface characterization studies of TiO2 supported manganese oxide catalysts for low temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 76, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-L.; Guo, R.-T.; Wang, Q.-S.; Pan, W.-G.; Wang, W.-H.; Yang, N.-Z.; Lu, C.-Z.; Wang, S.-X. The catalytic performance of Mn/TiWOx catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Fuel 2016, 181, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Trunschke, A.; Bentrup, U.; Brzezinka, K.W.; Schreier, E.; Schneider, M.; Pohl, M.M.; Fricke, R. Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Ammonia over Egg-Shell MnOx/NaY Composite Catalysts. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T.; Chang, R. Low-Temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over USY-Supported Manganese Oxide-Based Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2003, 87, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Hao, J. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn–Fe/USY under lean burn conditions. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carja, G.; Kameshima, Y.; Okada, K.; Madhusoodana, C.D. Mn–Ce/ZSM-5 as a new superior catalyst for NO reduction with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 73, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhong, B.; Wang, W.; Guan, X.; Huang, B.; Ye, D.; Wu, H. In situ DRIFTS study of NO reduction by NH3 over Fe–Ce–Mn/ZSM-5 catalysts. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Huang, B.; Dong, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, X. In situ FT-IR study of highly dispersed MnOx/SAPO-34 catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Dong, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, B. Low-temperature SCR of NOx by NH3 over MnOx/SAPO-34 prepared by two different methods: a comparative study. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybek, T.; Rogóż, M.; Papp, H. The interaction of NO with active carbons promoted with transition metal oxides/hydroxides. Catal. Today 2004, 90, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzine, M.; Cifredo, G.A.; Gatica, J.M.; Harti, S.; Chafik, T.; Vidal, H. Original carbon-based honeycomb monoliths as support of Cu or Mn catalysts for low-temperature SCR of NO: Effects of preparation variables. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 342, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Niaei, A.; Salari, D.; Panahi, P.N.; Samandari, M. Modelling and optimization of Mn/activate carbon nanocatalysts for NO reduction: comparison of RSM and ANN techniques. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Yi, H.; Li, J. Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over AC/C supported manganese-based monolithic catalysts. Catal. Today 2007, 126, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, C.; Zhan, L.; Li, C.; Qiao, W.; Ling, L. MnOx–CeO2/Activated Carbon Honeycomb Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 at Low Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11667–11673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhan, L.; Li, C.; Qiao, W.; Ling, L. Effect of SO2 on Activated Carbon Honeycomb Supported CeO2–MnOx Catalyst for NO Removal at Low Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, P.; Zhai, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Qing, R.; Zhang, W. Low temperature SCR of NO with catalysts prepared by modified ACF loading Mn and Ce: effects of modification method. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Zou, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Tang, C.; Gao, F.; Dong, L. Construction of hybrid multi-shell hollow structured CeO2–MnOx materials for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5989–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Su, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wang, K.; Luo, H.; Ye, D. Manganese oxides supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Catalytic activity and characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 192, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkhalil, M.; Moghaddam, A.Z.; Rashidi, A.; Towfighi, J.; Mortazavi, Y. Preparation of highly active manganese oxides supported on functionalized MWNTs for low temperature NOx reduction with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, l.; Wang, L.; Pan, S.; Wei, Z.; Huang, B. Effects of cerium on the selective catalytic reduction activity and structural properties of manganese oxides supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Fabrication of Mn-CeOx/CNTs catalysts by a redox method and their performance in low-temperature NO reduction with NH3. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28385–28388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Fang, C.; Li, H.; Gao, R.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J. In situ supported MnO(x)-CeO(x) on carbon nanotubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Low-temperature NO reduction with NH3 over Mn–CeOx/CNT catalysts prepared by a liquid-phase method. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1738–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Preparation of Mn–FeOx/CNTs catalysts by redox co-precipitation and application in low-temperature NO reduction with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2015, 62, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, X. One-step synthesis of ternary MnO2–Fe2O3–CeO2–Ce2O3/CNT catalysts for use in low-temperature NO reduction with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2015, 71, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Qiu, F.; Yang, H.; Tian, W.; Hou, T.; Zhang, X. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia over Mn–Ce–OX/TiO2-carbon nanotube composites. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Cai, S.; Fang, C.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Gao, R.; Shi, L. Design of meso-TiO2@MnOx-CeOx/CNTs with a core-shell structure as DeNOx catalysts: promotion of activity, stability and SO2-tolerance. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9821–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, D.; Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Maitarad, P.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over nanoflaky MnOx on carbon nanotubes in situ prepared via a chemical bath deposition route. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9199–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Hu, H.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Design of multi-shell Fe2O3@MnO(x)@CNTs for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: improvement of catalytic activity and SO2 tolerance. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Sheng, Z.; Yang, L.; Dong, F. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over a manganese and cerium oxide/graphene composite prepared by a hydrothermal method. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Song, C.; Chang, C.-C.; Teng, Y.; Tong, Z.; Tang, X. Manganese Oxides Supported on TiO2–Graphene Nanocomposite Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 at Low Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 11601–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Song, C.; Jia, S.; Tong, Z.; Tang, X.; Teng, Y. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over cerium and manganese oxides supported on TiO2–graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Lu, X.; Jia, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Xing, Y. Catalytic Reduction of NOx Over TiO2–Graphene Oxide Supported with MnOx at Low Temperature. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zhan, S.; Zhu, D.; Yu, H.; Shi, Q. NH3-SCR performance improvement of mesoporous Sn modified Cr-MnOx catalysts at low temperatures. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.; He, H. Structure-Activity Relationship of Iron Titanate Catalysts in the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Phy. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16929–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T. Homogeneous MnOx–CeO2 pellets prepared by a one-step hydrolysis process for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, Y.; Arandiyan, H.; Xu, J.; Hao, J. Ge, Mn-doped CeO2–WO3 catalysts for NH3–SCR of NOx: Effects of SO2 and H2 regeneration. Catal. Today 2013, 201, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, C. Adsorption and Activation of NH3 during Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3. Chin. J. Catal. 2006, 27, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, W.S.; Brands, D.S.; Poels, E.K.; Bliek, A. Mechanism of the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3. J. Catal. 1997, 171, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramis, G.; Yi, L.; Busca, G.; Turco, M.; Kotur, E.; Willey, R.J. Adsorption, Activation, and Oxidation of Ammonia over SCR Catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 157, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, C.; Jing, G. Reactions and Mechanisms of Low- Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Manganese Oxide-Based Catalysts. Prog. Chem. 2010, 22, 1882–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Yan, N.; Ma, L.; Chang, H. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn–Fe spinel: Performance, mechanism and kinetic study. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 110, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Hao, J. Origination of N2O from NO reduction by NH3 over β-MnO2 and α-Mn2O3. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 99, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guan, B.; Lin, H.; Zhu, L. In situ DRIFTS study of the mechanism of low temperature selective catalytic reduction over manganese-iron oxides. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Bushev, V.; Kantcheva, M.; Klissurski, D. Infrared spectroscopy study of the species arising during nitrogen dioxide adsorption on titania (anatase). Langmuir 1994, 10, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, Z.; Lee, S.-C. Mechanism study of the promotional effect of O2 on low-temperature SCR reaction on Fe–Mn/TiO2 by DRIFT. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.Q.; Yang, R.T. FTIR and Kinetic Studies of the Mechanism of Fe3+-Exchanged TiO2-Pillared Clay Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, C.; Shan, W.; Shi, X. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over environmental-friendly iron titanate catalyst. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettireddy, P.R.; Ettireddy, N.; Boningari, T.; Pardemann, R.; Smirniotis, P.G. Investigation of the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia over Mn/TiO2 catalysts through transient isotopic labeling and in situ FT-IR studies. J. Catal. 2012, 292, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Liao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dang, H.; Yang, S. The mechanism of the effect of H2O on the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn–Fe spinel. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.S.; Jeong, S.K.; Hong, S.H.; Hong, S.C. Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with NH3 over Natural Manganese Ore at Low Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 4491–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.; He, H. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over manganese substituted iron titanate catalyst: Reaction mechanism and H2O/SO2 inhibition mechanism study. Catal. Today 2010, 153, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, S.; Martín, J.A.; Yates, M.; Avila, P.; Blanco, J. N2O formation in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature on CuO-supported monolithic catalysts. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singoredjo, L.; Korver, R.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J. Alumina supported manganese oxides for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 1992, 1, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, F.J.J.G.; Van den Kerkhof, F.M.G.; Bosch, H.; Ross, J.R.H. Mechanism of the reaction of nitric oxide, ammonia, and oxygen over vanadia catalysts. 2. Isotopic transient studies with oxygen-18 and nitrogen-15. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6633–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstrom, M.; Topsøe, N.-Y.; Dumesic, J.A. Density functional theory studies of mechanistic aspects of the SCR reaction on vanadium oxide catalysts. J. Catal. 2003, 213, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapteijn, F.; Singoredjo, L.; Andreini, A.; Moulijn, J.A. Activity and selectivity of pure manganese oxides in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 1994, 3, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Fang, D.; Mei, D.; Hu, H.; He, F. Research Progress on Application of CeO2 in SCR Denitration Catalyst at Low Temperature. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 33, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Woo, S.I. Novel Mn-Ce-Ti mixed-oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14500–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, D.; Shi, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Porous Ni-Mn oxide nanosheets in situ formed on nickel foam as 3D hierarchical monolith de-NOx catalysts. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7346–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Shan, W.; Lian, Z.; Xie, L.; Yang, W.; He, H. Novel MnWOx catalyst with remarkable performance for low temperature NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, R. DRIFT Study of Manganese/Titania-Based Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapteijn, F.; Singoredjo, L.; Dekker, N.J.J.; Moulijn, J.A. Kinetics of the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn2O3-WO3/γ-Al2O3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N.; Li, J. Competition of selective catalytic reduction and non selective catalytic reduction over MnOx/TiO2 for NO removal: the relationship between gaseous NO concentration and N2O selectivity. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, C. Ab initio Study of the First Electron Transfer of O2 on MnO2 Surface. Acta Chim. Sin. 2006, 64, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Diao, G.; Ye, F.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Q. Dimethyl ether catalytic combustion over manganese oxides with different structures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 146–147, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Sun, M.; Diao, G.; Lan, B.; Cheng, G. A Theoretical Investigation of the α-MnO2 (110) Surface. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2014, 1031, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yu, W.; Su, W.; Huang, X.; Li, J. An experimental and DFT study of the adsorption and oxidation of NH3 on a CeO2 catalyst modified by Fe, Mn, La and Y. Catal. Today 2015, 242, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jing, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Novel microwave dielectric response of Ni/Co-doped manganese dioxides and their microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18291–18299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitarad, P.; Zhang, D.; Gao, R.; Shi, L.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Zhang, J. Combination of Experimental and Theoretical Investigations of MnOx/Ce0.9Zr0.1O2 Nanorods for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Ammonia. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 9999–10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, J.; Zheng, H.; Ma, S.; Wei, Y.; Duan, A.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Hensen, E.J.M. A mechanistic DFT study of low temperature SCR of NO with NH3 on MnCe1−xO2(111). Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Xu, J.; Hao, J. Design Strategies for Development of SCR Catalyst: Improvement of Alkali Poisoning Resistance and Novel Regeneration Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12623–12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Si, W.; Luo, J.; Dai, Q.; Luo, X.; Liu, X.; Hao, J. Insight into deactivation of commercial SCR catalyst by arsenic: an experiment and DFT study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13895–13900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phil, H.H.; Reddy, M.P.; Kumar, P.A.; Ju, L.K.; Hyo, J.S. SO2 resistant antimony promoted V2O5/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 78, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Müller, C.; Yang, Z.; Hermansson, K.; Kullgren, J. SOx on ceria from adsorbed SO2. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 184703–184714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cen, W.; Wu, Z.; Weng, X.; Wang, H. SO2 Poisoning Structures and the Effects on Pure and Mn Doped CeO2: A First Principles Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22930–22937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Han, X.; Chen, J. Enhancing Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction on MnO2 with Vacancies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2474–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Catalysts | Preparation Method (Cal. Tem./°C) | Reaction Conditions | NOx Conversion/% (Tem./°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnOx | Precipitation (350 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 25,000 h−1 | 100% (75–175 °C) | [33,43] |
| MnOx | Rheological phase (350 °C); Solid phase (60 °C); co–precipitation (100 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 47,000 h−1 | ~100% (80–150 °C) | [40,41,42] |
| Mn–Ce–Ox | Citric acid method (650 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 2 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 42,000 h−1 | ~100% (120–150 °C) | [22] |
| Mn–FeOx | Co–precipitation (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 800 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 24,000 h−1 | ~100% (120–300 °C) | [25] |
| MnO2/TiO2 | Impregnating (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 24,000 h−1 | ~100% (150–200 °C) | [44] |
| Mn/ZSM–5 | Ion–exchange (300 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 4.5 vol %, N2 balanced, GHSV = 36,000 h−1 | ~100% (150–390 °C) | [45] |
| VOx/CeO2 | Hydrothermal (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 120,000 h−1 | 95–100% (250–350 °C) | [46] |
| Ce10Mo5/TiO2 | Impregnating (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 128,000 h−1 | ~90% (275–400 °C) | [47] |
| Ce–Sn–Ox | Co–precipitation (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 20,000 h–1 | 90–100% (200–400 °C) | [48] |
| CuCe–ZSM–5 | Ion–exchange (600 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 15,000 h−1 | ~90% (148–427 °C) | [49] |
| Fe0.95Ce0.05Ox | Co–precipitation (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balanced, GHSV = 30,000 h−1 | 79–100% (175–300 °C) | [50] |
| Fe0.5WCeOx | Sol-gel method | [NO] = [NH3] = 450 ppm, [O2] = 2.5 vol %, N2 balanced, GHSV = 20,000 h−1 | 80% at 160 °C; 95–100% (250–500 °C) | [51] |
| Parameters | Catalysts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial V2O5–WO3/TiO2 | Novel V2O5–WO3/TiO2 | MnxCo3−xO4 Nanocages | Mn–W–TiOx | Cu-SSZ or Cu-SAPO | |
| Operation Temperature | 300–400 °C | 200–400 °C | 150–300 °C | 125–275 °C | 225–400 °C |
| SCR activity | ≥90% | ≥90% | ~100% | ≥98% | ≥85% |
| Degradation | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Ammonia slippage | ≤3 ppm | ≤5 ppm | − | − | − |
| Hazardous | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Catalysts | Preparation Method | Reaction Conditions | Original/Deactivated/Recovered Activity (Loss of Activity) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | ||||
| MnOx | Low-temperature solid phase | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 47,000 h−1, 10% H2O, at 80 °C | 98%/87%/96% (11.2%) | [40] |
| MnO2 | Hydrothermal (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, 10% H2O, at 200 °C | 92%/70%/- (23.9%) | [38] |
| Mn–Ce–Ox | CTAB template (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 64,000 h−1, 5% H2O, at 100 °C | 100%/47%/- (53.0%) | [26] |
| Mn–Ni–Ox | Co-precipitation (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 64,000 h−1, 10% H2O, at 230 °C | 100%/94%/- (6.0%) | [24] |
| Mn–Co–Ox | Metal−organic frameworks template (450 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 38,000 h−1, 8% H2O, at 175 °C | 99%/98%/99% (slightly) | [83] |
| SO2 | ||||
| MnOx | Low-temperature solid phase | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 47,000 h−1, 100 ppm SO2, at 80 °C | 98%/25%/- (74.5%) | Our work |
| MnOx | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 3 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 30,000 h−1, 100 ppm SO2, at 120 °C | 80%/10%/50% (87.5%) | [19] | |
| Mn–Cr–Ox | Citric acid (650 °C) | 99%/84%/96% (15.2%) | [89] | |
| Mn–Ni–Ox | Co-precipitation (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 64,000 h−1, 100 ppm SO2, at 230 °C | 100%/82%/98% (18.0%) | [24] |
| Mn–Co–Ox | Metal−organic frameworks template (450 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 38,000 h−1, 100 ppm SO2, at 175 °C | decreases slightly | [83] |
| Mn–Ce–Sn–Ox | Co-precipitation (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 2 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 35,000 h−1, 100 ppm SO2, at 250 °C | 100%/96%/- | [71,159] |
| Mn–Ce–Ni–Ox | Co-precipitation (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 48,000 h−1, 150 ppm SO2, at 175 °C | 91%/78%/88% (14.3%) | Our work [76] |
| Mn–Ce–Co–Ox | 90%/76%/88% (15.6%) | |||
| H2O+SO2 | ||||
| Mn–Cu–Ox | Co-precipitation (350 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 30,000 h−1, 11% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 125 °C | 95%/64%/90% (32.6%) | [54] |
| Mn–Ce–Ox | Co-precipitation (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 2 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 42,000 h−1, 2.5% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 150 °C | 94%/83%/94% (11.7%) | [64] |
| Mn–Ce–Ox | CTAB template (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 64,000 h−1, 5% H2O + 50 ppm SO2, at 100 °C | 100%/35%/- (65.1%) | [26] |
| Mn–Ce–Sn–Ox | Co-precipitation (500 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 2 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 35,000 h−1, 12% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 100 °C | 100%/70%/90% (30.0%) | [71] |
| Mn–Co–Ox | Metal−organic frameworks template (450 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 38,000 h−1, 8% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 175 °C | 99%/89%96% (10.1%) | [83] |
| Mn–Co–Ox | KIT-6 template (450 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 500 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 50,000 h−1, 5% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 200 °C | 100%/86%/93% (14.1%) | [80] |
| Fe0.3Ho0.1Mn0.4 /TiO2 | Impregnation (450 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 800 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, N2 balance, GHSV = 50,000 h−1, 15% H2O + 200 ppm SO2, at 120 °C | 95%/80%/85% (15.8%) | [104] |
| Mn(0.25)–W(0.25)–TiO2(0.5) | One-pot co-precipitation (400 °C) | [NO] = [NH3] = 1000 ppm, [O2] = 5 vol %, He balance, GHSV = 100,000 h−1, 10% H2O + 100 ppm SO2, at 125–250 °C | 100%/98%/- (slightly) | [110] |
| Species | Split V3 (cm–1) | Corresponding V3 (cm−1) | Form | Desorption/Decomposition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrosyl | 1835 | 50 °C | ||
| Bridged nitrate | 1620 | 1220 | 150–300 °C | |
| Bidentate nitrate | 1290 | 1555 | 300–425 °C | |
| Linear nitrite | 1466 | 1075 (V1) | 50–200 °C | |
| Monodentate nitrite | 1415 | 1322 (V1) | 50–200 °C | |
| Bridged nitrite | 1230 | 50–250 °C |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Meng, X. A Review on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–Based Catalysts at Low Temperatures: Catalysts, Mechanisms, Kinetics and DFT Calculations. Catalysts 2017, 7, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070199
Gao F, Tang X, Yi H, Zhao S, Li C, Li J, Shi Y, Meng X. A Review on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–Based Catalysts at Low Temperatures: Catalysts, Mechanisms, Kinetics and DFT Calculations. Catalysts. 2017; 7(7):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070199
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fengyu, Xiaolong Tang, Honghong Yi, Shunzheng Zhao, Chenlu Li, Jingying Li, Yiran Shi, and Xiaomi Meng. 2017. "A Review on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–Based Catalysts at Low Temperatures: Catalysts, Mechanisms, Kinetics and DFT Calculations" Catalysts 7, no. 7: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070199
APA StyleGao, F., Tang, X., Yi, H., Zhao, S., Li, C., Li, J., Shi, Y., & Meng, X. (2017). A Review on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn–Based Catalysts at Low Temperatures: Catalysts, Mechanisms, Kinetics and DFT Calculations. Catalysts, 7(7), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070199






