Abstract
CO2 methanation is a well-known reaction that is of interest as a capture and storage (CCS) process and as a renewable energy storage system based on a power-to-gas conversion process by substitute or synthetic natural gas (SNG) production. Integrating water electrolysis and CO2 methanation is a highly effective way to store energy produced by renewables sources. The conversion of electricity into methane takes place via two steps: hydrogen is produced by electrolysis and converted to methane by CO2 methanation. The effectiveness and efficiency of power-to-gas plants strongly depend on the CO2 methanation process. For this reason, research on CO2 methanation has intensified over the last 10 years. The rise of active, selective, and stable catalysts is the core of the CO2 methanation process. Novel, heterogeneous catalysts have been tested and tuned such that the CO2 methanation process increases their productivity. The present work aims to give a critical overview of CO2 methanation catalyst production and research carried out in the last 50 years. The fundamentals of reaction mechanism, catalyst deactivation, and catalyst promoters, as well as a discussion of current and future developments in CO2 methanation, are also included.
1. Introduction
Several studies [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] and recent reviews [10,11,12,13,14] have focused on the methanation reaction, mainly due to its important implications for energy and the environment. Methanation processes produce methane (Substitute or Synthetic Natural Gas, SNG) from hydrogen and COx. CO and CO2 methanation processes, discovered in 1902 by Paul Sabatier and Jean-Baptiste Senderens, represent a promising solution for reducing anthropogenic gas emissions [11].
The increasing use of renewable sources, due to their fluctuating character, makes mandatory the development of adequate storage systems in order to overcome the mismatch between power production and instantaneous demand (Figure 1). Water electrolysis is a mature technology to produce hydrogen and CO2 can be conveniently recovered from several industrial processes, such as biomass combustion and gasification, biogas facilities, power plants, oil refineries, and cement kilns.

Figure 1.
CO2 methanation as an alternative to H2 storage.
The reaction is also considered a key technology able to facilitate future manned space missions by the recycling of CO2 from breathing or wasted H2 from water electrolysis on the International Space Station [15,16,17].
The methanation of CO2 is an exothermic reaction (Equation (1)), typically operating between 200 °C and 450 °C, depending on the catalyst and experimental conditions [8,10]. Although several papers have been published on the subject in the recent past, no general consensus exists on the reaction’s operating mechanism, mainly due to the uncertainty in determining the intermediate compound involved in the rate determining step [10,11].
The first and most popular path considers the conversion of CO2 to CO, which, in turn, is hydrogenated to CH4 by the same mechanism involved in CO methanation. The second path includes the direct hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4, without formation of any CO intermediate (Figure 2). As said above, numerous reviews exist on this argument (i.e., mechanistic aspects, reactor type modeling, simulation); therefore, it is outside the scope of the present paper [10,11].
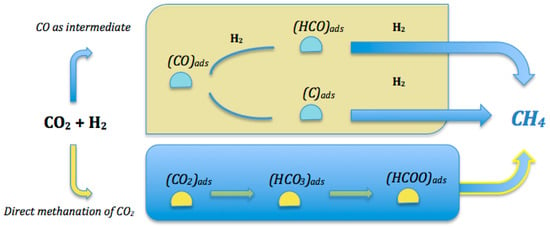
Figure 2.
Simplified reaction mechanisms of CO2 methanation.
The first part of the paper is dedicated to noble metal catalysts. These have so far demonstrated a high performance in the reaction, so are of relative interest from an industrial point of view on account of their high cost. Therefore, most of the discussion on the subject is devoted to Ni-based materials that couple a high catalytic activity and affordable cost.
Transition metals were deeply investigated as active catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation [18,19,20], and affect the CO2 activation and reduction steps. Iron, cobalt, nickel, and copper show high catalytic properties for CO2 activation. Chemisorption of carbon dioxide on transition metals is spontaneous, while the surface structure of the metal strongly affects the thermodynamic of the catalytic process [18]. For example, the binding energy of carbon dioxide on the iron surface is stronger than that of platinum, while the CO2 dissociation proceeds more easily on platinum than on iron [19]. All these works demonstrate that metal plays a pivotal role in CO2 hydrogenation (both in the activation and reduction steps).
In order to preserve and improve metal activity, reduction technology focused on the metal-supported catalyst development [21]. The physico-chemical characteristics (structure, chemical composition, defect groups, and thermal stability) of supports are fundamental aspects to consider in metal-supported catalyst tuning because they affect the activity, productivity, and lifetime of the final heterogeneous catalyst. The interactions between support and metal were studied by different researchers in many reactions of environmental interest, such as dry reforming, steam reforming, partial oxidation, and autothermal reforming [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
2. Catalytic Materials for CO2 Methanation Reaction
This section provides a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, and the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
2.1. Noble Metal Catalysts
2.1.1. Rhodium
Rh is one of the most investigated metals for the CO2 methanation reaction. Particular emphasis has so far been placed on the hypotheses of a mechanism that allows methane to be formed on the surface of the catalyst, especially in the presence of alumina as a support. The steps leading to methane could be: (i) chemisorption of carbon dioxide; (ii) dissociation of carbon dioxide into CO and O adsorbed on the surface; (iii) reaction of dissociated species with hydrogen [30]. The oxidation state of the metal may also play an important role in the evolution of the reaction, since CO2 oxidizes the catalyst. Moreover, the production of methane depends upon the temperature, pressure, presence, and absence of promoters. Obviously, when varying the Rh content different metal particle sizes are formed, and at low temperatures (130–150 °C) the activity of larger particle sizes of Rh was found to be higher than that of smaller ones. Furthermore, the addition of Ba and K on the Al2O3 support allows significant differences in the catalytic behavior in the temperature range 300–700 °C. CH4 was preferentially formed below 500 °C on Ba-containing and pure Rh/Al2O3 while, at higher temperatures, significant amounts of CO were formed. Only CO was observed with the K-containing catalyst [30,31,32,33].
The presence of O2 could have a positive effect on the methanation of CO2 and CO. Belus et al. highlighted that oxygen, in low proportion, improves the catalytic performance of the Rh/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, but if the amount of O2 is too high, a negative effect is observed [31]. In Figure 3 the methane production, over Rh(1%)/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, at 125 °C, as a function of CO/O2 and CO2/O2 is reported. DRIFTS experiments explain that the positive effect of oxygen is due to the formation of more active species, such as gem-dicarbonyl. On the contrary, the negative effect could be attributed to the inevitable oxidation of the catalyst [31].
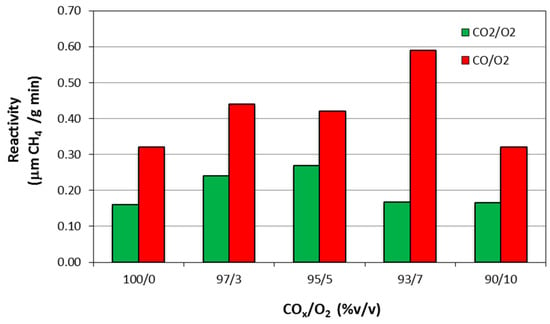
Figure 3.
CH4 production (μmol of methane by gram of catalyst/minute) as a function of CO2/O2 and CO/O2 ratios, over Rh(1%)/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, at 125 °C. Adapted from Beuls et al. [31].
A synergistic effect was recently observed by mechanically mixing Rh/γ–Al2O3 and Ni/activated carbon (Ni/AC). It appears that higher production of CH4, with respect to the single catalysts, is not due to a chemical interaction since no formation of new structures occurs when the catalysts are mixed. Authors hypothesize that Rh/γ-Al2O3 is able to efficiently adsorb CO2, whereas Ni/AC adsorbs a high amount of H2 but a small amount of CO2, resulting in high CO2 conversion and methane formation [34].
TiO2 has been also extensively investigated as a support for Rh in the CO2 methanation reaction, especially at low temperatures. Rh/TiO2 is one of the most active catalysts for the reaction, but the high cost of the metal prevents its widespread utilization at industrial scale. Such a high activity is thought to be attributed to a metal–support interaction that facilitates the breaking of the C=O bond, resulting in an increase of the catalytic activity [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Recently, the Density Functional Theory method (DFT) has been employed to study the CO2 methanation reaction on an Rh1/TiO2 (101) model [43]. The results show the co-adsorption properties of the Rh1/TiO2 catalyst surface. By the proposed mechanism, CO2 and H2 are co-adsorbed on the Rh atom and, subsequently, can react with each other to form CO. Further adsorption of H2 is inhibited on the CO adsorbed on Rh; therefore, the consecutive CO hydrogenation does not occur. The proposed mechanism explains why, experimentally, a high selectivity of Rh1/TiO2 to CO is observed, as a consequence of the frontier orbital charge density symmetry matching principle [44].
2.1.2. Ruthenium
Ru is one of the most active methanation catalysts. Its catalytic activity and selectivity to CH4 are, however, largely dependent on the dispersion of the metallic phase (at high dispersion the apparent activation energy reaches a minimum), on the type of the support, and an addition of modifiers/promoters that can more or less chemically interact with the metal [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Ru catalysts have been supported on a number of oxide materials, such as Al2O3, TiO2, SiO2, MgO, MgAl2O4, C, and Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 [55,56]. The activity of pre-reduced 3%Ru/Al2O3 catalyst (CO2 conversion, CH4 and CO yields), as a function of the reaction temperature, is reported in Figure 4 [53]. The best catalytic performance occurs at 673 K, with the highest CO2 conversion, CH4 yield, and limited CO yield.
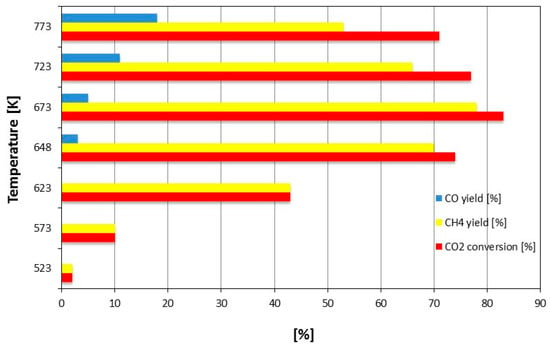
Figure 4.
CO2 conversion, CH4 and CO yields on pre-reduced 3%Ru/Al2O3 catalyst and GHSV = 55000 h−1, at different temperature reactions. Adapted from Garbarino et al. [53].
In particular, in order to lower the reaction temperature in CO2 methanation reaction, Ru/TiO2 catalysts have been used since the 1980s. Akamaru et al. [57] reported that they failed to reproduce the results of Gratzel et al. [58,59] using Ru/TiO2 catalysts prepared under the same experimental conditions. The main reason was the difficulty of controlling the preparation conditions in a wet process. Therefore, a dry technique, called polyhedral barrel sputtering, was developed; this technique, according to [60], is able to disperse metal nanoparticles on the support in clean conditions and control their size and deposition density. Using a Ru/TiO2 catalyst prepared with this technique, an onset temperature of 60 °C for CH4 generation was observed that increases upon increasing the size of metal particles. Recently, Xu et al. have demonstrated that the Ru particle size is not the main reason for the different behavior of Ru/rutile(TiO2)catalyst [61]. They reported that the increasing of hydroxyl groups on the TiO2 layer strongly increases the CO2 dissociation. The suggested mechanism assumes that the adsorbed CO2 reacts with the hydroxyl groups, producing CO via formate species intermediates. So, the pre-treatment temperature of the support should not be higher than 800 °C, because over this temperature value condensation of the hydroxyl groups occurs and the support does not play its important role.
Results of DFT analysis attribute the high activity of the catalyst to the difference between the Ru structure and the Ru surface, and to the weak charge transfer from adsorbed species to Ru atoms [57].
It is recognized that CeO2 plays an important role in promoting CO2 methanation and enhancing CH4 formation. On account of its basicity, CO2 is adsorbed on CeO2 and reduced due to the oxygen vacancies on CeO2, resulting in high CO2 conversion at T ≤ 350 °C. The addition of 30% CeO2 to 2 wt % Ru/Al2O3 leads to an enlarged specific surface area of the catalyst. Furthermore, the reaction intermediates (formates, carbonates) react with H2 faster on this catalyst than over Ru/Al2O3 [62]. Ceria is also a very good methanation catalyst when doped with 0.05 wt % Ru. Electron microscopy and XRD analyses suggest that Ru is incorporated into the ceria lattice. At T = 450 °C, this catalyst converts 55% CO2 with 99% selectivity to CH4. The reaction takes place on the reduced Ce0.95Ru0.05O2; the role of Ru is to lower the reduction temperature with respect to pure ceria [63].
Ru supported on TiO2–Al2O3 exhibits a much higher (3.1 times) activity than that on supported Al2O3. This result was attributed to the smaller averaged particle size of Ru supported on TiO2–Al2O3 (2.8 nm) versus the 4.3 nm measured on Al2O3, resulting from the interaction between the metal and the rutile TiO2, which hinders the aggregation of Ru particles [64].
Very recently, trimetallic catalysts drew attention to the reaction of the Baker group [65,66,67], which highlights how the adsorption strength of CO2 is controlled by the Lewis basicity of the catalyst, the d-band center of the metal surface, and the charge transfer from the metal surface to the chemisorbed CO2. Pd, Rh, and Ru supported on Mn/Cu–Ce–Al2O3 catalysts were also investigated and Ru/Mn/Cu–Al2O3 was found to be the most promising catalyst (10.9 wt % Ru loading, calcination temperature 1035 °C). Baker et al. claim the suitability of their catalysts for industrial application.
2.1.3. Palladium
A good catalytic performance has also been observed with Pd-based catalysts. Pd is able to dissociate molecular hydrogen [68,69] and makes available hydrogen atoms for the subsequent transfer and reaction with activated surface carbonate species formed by the reaction of CO2 on a Mg-containing oxide [70,71,72],with the aim of providing a pathway to minimize CO formation by using metal oxides that inhibit CO desorption. Intermixed Pd and Mg sites are obtained by using the reverse microemulsion synthesis route; 95% selectivity to CH4 and 59% CO2 conversion have been measured at 450 °C [73].
More recently, shape-controlled Pd nanoparticles embedded in mesoporous silica have been tested in the reaction; their performance has been compared with a Pd/SiO2 catalyst prepared by wet impregnation. The encapsulation was demonstrated to have a better stability towards sintering. Moreover, different activities and selectivities for the CO2 methanation were demonstrated by the different exposed facets (100, 111) of the metal [74].
2.2. Nickel-Based Catalysts
Supported Ni catalysts are the most widely investigated materials for CO2 methanation due to their high efficiency in CH4 production and low cost [75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89]. A lot of supports have been investigated for Ni catalysts since, as is well known, the catalytic performance strongly depends upon the nature and properties of the support. Its influence can be generally linked to physico-chemical peculiarities: (i) varying the dispersion of the active phase; (ii) modifying the reducibility of the oxide precursors by tuning the interaction between the active phase and the support.
In this part of the review, we will examine the role of the most investigated supports for the hydrogen reaction with CO2 to CH4 (Al2O3, zeolites, SiO2, CeO2, ZrO2, and Ce–ZrO2) with particular emphasis on the role of promoters/modifiers in their catalytic performance in the reaction. Other materials were recently investigated as nickel supports, such as hydrotalcite, carbon nanotubes, and W–Mg oxides. Section 2.2.4 and Section 2.2.5 will be dedicated to the main outcomes reached using these unconventional supports.
2.2.1. Alumina-Supported Nickel
The Ni/Al2O3 catalyst shows a high catalytic activity, although it suffers from severe carbon deposition or poor stability due to the high reaction temperature used [88,90]. Therefore, the aim throughout the years was to develop catalysts able to show both high activity and resistance to carbonaceous deposits in the reaction. So, since the pioneering work of Trimm et al. [91], a lot of papers have been published on the argument. We will examine here only the most recent ones, since the number of studies covering the topic is huge, and other previous reviews can easily be found in the literature. Rahamani et al. [92] have prepared, by impregnation, a series of Ni catalysts supported on mesoporous nanocrystalline γ-Al2O3, having high surface area and different Ni contents. The influence of calcination temperature was also investigated on CO2 conversion and CH4 selectivity. The catalyst with 20 wt % Ni shows higher activity and stability between 200 °C and 350 °C. According to He et al. [89], the combination of highly dispersed Ni particles with a strong basic support is thought to be responsible for the high performance of the Ni–Al hydrotalcite-derived catalyst. Such basic sites are originated from the formation of the Ni–O–Al structure; 100% CH4 selectivity and 82% CO2 conversion are reached at 350 °C.
In [93] a study on the methane yield as a function of different Ni-based compositions and reaction temperatures (250–500 °C) is reported. The data suggest that good performance is obtained at the expense of a CO intermediate on the corners of nanoparticles interacting with alumina, likely via an oxygenate mechanism.
In the light of a fluctuating supply of renewable hydrogen, various IR studies, under both stationary and transient conditions, have been done in order to get insight into the reaction mechanism. Since Ni is very prone to oxidation, studies have been carried out under “operando” conditions [94,95,96,97,98].
The results reported in [94] (81% CO2 conversion, 80% CH4 yield at 400 °C with a 23 wt % of Ni/CaO/Al2O3 catalyst), however, strongly suggest the importance of conducting experiments under realistic (i.e., transient) conditions. To ameliorate the performance of Ni/Al2O3 catalysts via substantial modifications of some specific (structural, electronic) properties, the addition of several promoters has been also attempted. Among these, CeO2 has often been employed on account of some positive effects, such as: (i) improvement of the thermal stability of Al2O3; (ii) promotion of the dispersion of the metal onto the support; (iii) change of the properties of the metal due to strong metal–support interaction (SMSI) [41,89,99,100,101].
Moreover, CeO2 is a well-known oxygen storage material, able to store and release in a reversible manner large amounts of oxygen depending on the experimental conditions adopted [102]. The results show that the presence of CeO2 has significant influence on CO2 conversion (for Ni/Al2O3, from 350 °C to 400 °C, 45% vs. 71% with a CeO2 content of 2 wt %). CH4 selectivity, independently from the CeO2 content, is higher than 99%. Stability was measured for a reaction time up to 120 h [103]. In [104], the effect of different promoters (CeO2, MnO2, IrO2, La2O3) on the catalytic performance of Ni supported on Al2O3 mesoporous nanoparticles was investigated. Both CO2 conversion and CH4 selectivity were demonstrated to be affected by the different promoters. The catalyst promoted by ceria exhibits the highest activity; also in this case, the catalyst with 2 wt % ceria was the most active and selective to CH4. The best results were obtained at 350 °C.
Few works have been published on Ni supported on zeolites for CO2 methanation [49,105,106,107]. Recently, Graca et al. [108] prepared, by ion exchange and impregnation, Ni–Ce catalysts supported on a partially exchanged HNaUSY zeolite.
Since temperatures >800 °C are necessary to reduce the exchanged Ni species, those present on the catalyst prepared by Graca et al. [108] are not in the metal form during the reaction; the activity observed was attributed to the zeolite support. Moreover, addition of ceria causes an improvement in both CO2 conversion and CH4 selectivity [41,108,109,110]. Thus, the catalyst properties result from the synergistic effect between the metal active sites and the promoters. The “operando” IR spectroscopy technique was also used to get a better insight into the mechanism of the reaction. According to [111], dissociated hydrogen reacts with carbonates and/or physisorbed CO2, giving rise firstly to formation of monodentate formates, then carbonyls, and finally to CH4.
Recently, Rivero-Mendoza et al. reported La–Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalytic activity relative to the Sabatier reaction [112], where catalytic studies coupled with in situ DRIFTS analyses provide insights on the CO2 methanation mechanism. The activation process of the catalyst promotes formation of oxidized Ni particles (Ni2+) decorated with LaOx moieties. During the reaction, in situ reduction of Ni occurs and LaOx species return to their initial oxidation state (La2O3). Since the in situ DRIFTS analyses results show the presence of adsorbed formates and CO species, it is reasonable to think that the Sabatier reaction, catalyzed by the La–Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, advances by the CO-based mechanism.
2.2.2. Silica-Supported Nickel
Metal–support interactions are generally present, although at a variable extent in t heterogeneous catalytic systems, implying that different combinations result in different performances in terms of activity and selectivity for a given process [113,114,115]. Among the numerous SiO2-based materials used as supports for metal catalysts, mesostructured silica nanoparticles (MSN) have recently found wide application in several processes and reactions, such as in drug delivery [116,117], biomedical imaging [118,119], and catalysis [120,121]. Their unique features include (i) nanosized dimension; (ii) ordered structures; (iii) very high surface area; (iv) large pore volume; (v) tunable pore size from 1.5 to 10 nm; (vi) tailorable pore diameters to host particles of different dimensions [122].
Recently, Aziz et al. have studied such materials, promoted by Ni, for CO2 methanation [123,124,125]. In [126] MSN (mesostructured silica nanoparticles) and Ni/MSN were prepared by sol-gel and impregnation methods. The reaction was carried out at temperatures between 150 °C and 450 °C. Ni/MSN was compared with other types of support; the activity of the reaction follows the order Ni/MSN > Ni/MCM-41 > Ni/HY > Ni/SiO2 > Ni/γ-Al2O3. IR characterization supports the hypothesis that the high activity of Ni/MSN is due to the high concentration of basic sites on account of the presence of both intra- and inter-particle porosity. The carbon species detected on the surface was attributed to the presence of defect sites and/or oxygen vacancies in MSN. The role of Ni sites is that of dissociating H2 to form atomic hydrogen, which, by reacting with the surface carbon species, forms CH4. A 200-h endurance test shows no deactivation for the Ni/MSN catalyst.
In [124], various metals were loaded on MSNs (Rh, Ru, Ni, Fe, Ir, Cu, Zn, V, Cr, Mn, Al, and Zr). The catalytic performance measurements clearly indicate that surface centers containing metallic and associated basic and/or oxygen vacancy sites are responsible for the catalytic activity. This latter, at 350 °C, follows the order Rh/MSN > Ru/MSN > Ni/MSN > Ir/MSN > Fe/MSN > Cu/MSN. However, on an areal basis, Ni/MSN exhibits the best performance. In the light of the catalytic activity tests and physico-chemical characterization results, a new, plausible pathway in the mechanism of CO2 methanation on metal based MSNs is formulated [12,124]. Firstly, CO2 and H2 are adsorbed on metal sites, and subsequently dissociate to form CO, O, and H atoms and migrate on the MSN surface. CO interacts with the oxides of MSN and forms bridged and linear carbonyls. Bidentate formate is also formed by interaction with atomic hydrogen. At the same time, the O atom splits onto the MSN surface and is stabilized in the oxygen vacancy near the metal site. Hydroxyls are formed on the MSN surface by interaction of adsorbed oxygen with atomic hydrogen, and, by reaction with another hydrogen atom, water is formed [12,124]. Then, the carbon species is hydrogenated to CH4. According to the Aziz et al., linear and bridged carbonyl, as well as bidentate formate, could be intermediates during the reaction course, as previously suggested [127,128,129,130,131].
In short, the role of MSN is the seat of sites for carbonyl species that are precursors for methane formation. In [125] the effect of Ni loading and water vapor on the performance and properties of Ni/MSN for CO2 methanation was investigated. It is well known that metal loading on a supported catalyst significantly affects its dispersion and interaction with the support, in turn affecting the catalytic behavior. In general, the lower the metal loading, the higher its dispersion, and vice versa. In this study, results show that after increasing Ni loading from 1 to 10 wt %, a decrease in crystallinity, surface area, and basicity of the catalysts is observed. On the other hand, the catalytic activity follows the order 10%Ni/MSN ≈ 5Ni/MSN > 3Ni/MSN > 1Ni/MSN at 400 °C with 100% CO2 conversion. It is then necessary to find a proper balance between Ni loading and basic sites concentration to achieve a high catalytic activity. As for the influence of water vapor on the feed stream, its presence was found to decrease the carbonyl species concentration on the surface of Ni/MSN, thus negatively affecting the catalytic activity of the reaction. It was suggested that such a negative effect could be attributed to the formation of CO2 through the water gas shift (WGS) reaction between intermediate CO and excess water. Moreover, Ni sintering is favored by the presence of water vapor [132]. Finally, the optimal conditions for the reaction over Ni/MSN were singled out by response surface methodology (RSM). Accordingly, 85% CO2 conversion could be achieved at 341 °C, 69.105 mLcat·g−1·h−1 gas hourly space velocity (GHSV), and 3.68 H2/CO2 ratio.
Amorphous pure silica materials, well known as mesoporous materials, such as highly ordered hexagonal structure MCM-41, or large pore size and high specific surface area SBA-15 material, are typical supports largely studied by the scientific community for different catalytic applications.
However, few scientific papers have been published on the performance of Ni-incorporated MCM-41 catalysts in the methanation reaction.
In 2007, Du et al. employed C16Ni/MCM-41 catalysts (with C16 indicating a 16 carbon alkyl template producing MCM-41 pores with 2.9 nm diameter) with different amounts of incorporated Ni to be tested for CO2 methanation [126]. A 3 wt % Ni catalyst at T = 300 °C shows 100% methane selectivity, although a very low CO2 conversion (about 10% max) is observed. In our opinion, the main drawback of this type of support is due to its limited stability in the presence of steam. Since water is one of the products of methanation reactions, these supports should be useful only for catalyst activity at very low temperatures.
Very recently, Xin et al., from the Chemical Engineering School of Shanghai, studied mesoporous materials as a support for nickel catalysts and their application in CO methanation [7,133]. Both catalysts tested by Xin and co-workers—Ni-SBA-15, prepared by a traditional impregnation method [7], and Ni-MCM-41, synthesized by a hydrothermal synthesis method [133]—show promising behavior in CO methanation.
Methanation of producer gas (CO, H2, CO2, and other trace species [134,135] was also recently investigated on NiO/SBA-15 [136,137,138,139]. Firstly, CO2 conversion increases on increasing the H2/CO2 ratio, up to a value of 6, and the maximum CO2 conversion increases on increasing the NiO loading regardless of the preparation method (heat treatment (HT) or solvent impregnation (SI)) [140]. However, on using the HT method the NiO particles are preferentially dispersed outside the SBA-15 pores, whereas by the SI method they are included into the SBA-15 pores. As expected, the maximum CO2 conversion and CH4 yield, regardless of the preparation method, are obtained on increasing the NiO loading.
2.2.3. Zirconia- and Ceria-Supported Catalysts
The interest in ZrO2 as a support for catalysts to be used in CO2 methanation is mainly due to its acidic/basic characteristics and CO/CO2 adsorption capability [141,142,143]. ZrO2 exists in three polymorphic structures (monoclinic (m), tetragonal (t), and cubic (c)). The monoclinic phase is thermodynamically the most stable below 1000 °C; the other phases are stabilized at such lower temperatures by doping the solid phase with low valent cations. Polymorphs of ZrO2 greatly influence their catalytic properties. For CO2 methanation, Ni/t-ZrO2 prepared from amorphous Ni–Zr alloys exhibits very high activity and almost 100% selectivity to methane at 200–300 °C [144,145]. It has been demonstrated that the catalytic activity increases with the amount of t-ZrO2 [144,146], achieving the maximum methanation rate at 300 °C with a catalyst prepared from amorphous alloy precursors. The catalytic activity can be significantly enhanced on Ni/ZrO2 catalysts prepared by Ni/Zr/earth elements alloys [147,148,149,150]. In the Ni/Zr/5at%Sm, samarium stabilizes tetragonal zirconia and increases the number of surface nickel atoms [146].
More recently, a highly efficient Ni/ZrO2 catalyst doped with Yb2O3 for co-methanation of CO and CO2 was developed. Over Ni6Zr2Yb at 300 °C, total conversion of CO and CO2 was observed. More interestingly, a heat resistance test shows that, after 24 h of reaction at 800 °C, followed by going down to 300 °C, the conversion does not change the 89% value. Characterization results demonstrate that both activity and thermal stability are due to the formation of a (Zr-Yb) oxide having the cubic ZrO2 structure. The promoting action of Yb2O3 was associated with the high solubility of Yb2O3 in the ZrO2 lattice (the ionic radius of Yb+3, 0.087 nm, is close to that of Zr+4, 0.079 nm) [149].
Moreover, a 50% at%Ni–50%at(Zr-Sm oxide) with Zr/Sm = 5 calcined at 650 °C or 800 °C shows high activity for CO2 methanation. The increase in Sm+3 ion content in the ZrO2 lattice on increasing the calcination temperature leads to an increase in oxygen vacancies. According to the study of CO and CO2 adsorption on tetragonal and monoclinic ZrO2, the CO2 adsorption capacity of m-ZrO2 is more than one order of magnitude higher than that of t-ZrO2, and the CO adsorption capacity of m-ZrO2 is from 5 to 10 times higher than of t-ZrO2 depending on the adsorption temperature [142]. As a consequence, the rate-determining step for the reaction cannot be the adsorption of CO2 and CO. In this study, the high activity of Ni/t-ZrO2 derives from the presence of oxygen vacancies, which allow a strong interaction with oxygen and weaken the C–O bond strength, leading to the enhancement of hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4 [150].
The most investigated rare-earth oxide as promoter of Ni–ZrO2 catalysts for CO2 methanation was ceria. Ceria was also studied as a single support for efficient Ni catalysts in CO2 methanation [81,151,152,153,154], although its synergic effect with zirconia seems to increase the nickel performance.
The main role of ceria is attributed to its high oxygen storage capacity and ability to highly disperse nickel [155,156,157,158,159]. The Ce/Zr composition is a factor that has a strong influence on the catalytic performance of ceria-zirconia (CZ) in several types of reactions such as the reduction in three-way catalysts [160], the methane partial oxidation, and ethanol/methane reforming [161,162,163].
In [159] the C/Z composition of the mixed oxides fixes the ratio between the Ni2+ incorporated into the CZ fluorite structure and the surface Ni0. Ni2+ enhances the catalyst specific activity; thus, a compromise between the two nickel species has to be found in order to optimize the catalytic system. Accordingly, a C/Z mass ratio of 60/40 leads to the best Ni2+/Ni0 ratio, resulting in the best catalytic activity. The mechanism of the reaction was also studied by Ocampo et al. on Ni/CZ under stoichiometric conditions [155,164]. The CO2 conversion was observed to increase from 250 °C to 400 °C towards the thermodynamic value. Mono- and bidentate carbonates are present already at 150 °C, as detected by FTIR analysis. Thus, from the evidence shown in the work, the main reaction pathway does not involve CO as an intermediate. CO2 adsorbs on the sites of mild basicity to form covalent carbonates, hydrogen carbonates, and then bidentate carbonates. These species are reduced and hydrogenated by H atoms formed by the dissociation of hydrogen on the surface of Ni0 particles to form formates and finally release CH4. However, a parallel pathway is hypothesized involving CO formed by a redox cycle on reduced ceria.
Pan et al. hold the presence of medium basic sites responsible for the high activity of Ni/CZ with respect to Ni/SiO2 [165]. The equilibrium CO2 conversion is reached at 340 °C. CO2–TPD profiles of Ni/CZ show weak and medium sites, different from Ni/Al2O3, which shows weak and strong basic sites; CO2 adsorbed on strong basic sites cannot desorb from Ni/Al2O3 surface until 700 °C. Consequently, the strongly adsorbed CO2 on the surface does not participate in the reaction carried out from 220 °C to 400 °C. According to [166], CO2 reacts with surface hydroxyls and surface oxygen to form hydrogen and monodentate carbonate, respectively [164,166,167,168,169,170,171,172]. Formate species could be also important intermediates during the reaction [63,173,174]. Combining CO2–TPD and FTIR results, medium basic sites promote formation of monodentate formate and its hydrogenation during the CO2 methanation, in accordance with [165,175]. The tetragonal phases, thought to be responsible for the activity in CZ-supported Ni catalysts, are distinguished into t, t’, and t”, according to the type of tetragonal distortion and its nature. The t phase is a stable one and is formed through a diffusional phase decomposition; t’ is obtained through a diffusionless transition and is metastable. The t” form is intermediate between t’ and cubic [176,177,178,179].
The H2–TPR profiles reported in [180] show peaks in the temperature range from 400 °C to 600 °C for CZ, attributed to a reduction of surface oxygen and bulk oxygen in Ce0.5Zr0.5O2, respectively [42,181,182], while the peaks around 360 °C are assigned to the reduction of surface oxygen in CZ and of the bulk NiO, having weak interaction with the support. Peaks at 400–600 °C are related to bulk oxygen in CZ and NiO having strong interaction with the support, or Ni ions incorporated into CZ [183]. In Figure 5 the qualitative behavior of TPR profiles (the data from our research are not yet published) of nickel catalysts supported on doped ceria with increasing nickel content is reported.
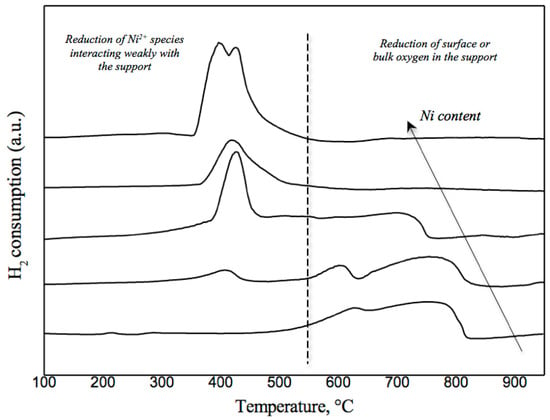
Figure 5.
Qualitative TPR-H2 profiles for impregnated Ni- supported on doped ceria.
Takano et al. recently investigated a 50 wt % Ni/(Zr + Ca) catalyst (molar ratios 0.125–0.333) affording 100% CH4 selectivity with a CO2 conversion of 90% at T = 400 °C. The comparison with 50 wt % Ni/(Zr + Sm) catalyst highlighted the higher conversion under the same flow rate conditions. The Ca content dependence of the catalytic activity has been related, according to [184], to the number of oxygen vacancies in t-ZrO2 since calcium is a more effective additive than samarium. Hydrogen is atomically absorbed on Ni, and is able to reduce carbonates to formate, formaldehyde, methoxy species, and methane.
Other relevant papers on supported ZrO2 and ceria Ni catalysts that must be cited for their significant results are [185,186,187]; moreover, an interesting paper regarding unconventional supports for nickel catalysts has been published recently by Abate et al. [188]. This is a pioneering research work in which quaternary system catalysts have been prepared. In particular, the authors prepared a Ni-based catalyst by wet impregnation technique applied to γ-Al2O3 powder as a host for ZrO2, TiO2, and CeO2 oxides. The best catalyst, named Ni/C15, is composed of a quaternary system with 55% γ-Al2O3 and 15% of each of the other oxides. The catalytic performance of the Ni/C15 catalyst in CO2 methanation is superior to that of similar catalysts prepared with lower amounts of quaternary oxides (Ni/C5 and Ni/C10) and to that of nickel supported on commercial γ-Al2O3. A larger amount of all four oxides seems to favor the formation of large-sized nickel particles that are more active at lower temperatures. At 300 °C the CO2 conversion to CH4 is higher than 80%.
2.2.4. Hydrotalcite-Supported Nickel
With respect to the aforementioned conventional supports, other materials are emerging as potential, and sometime promising, supports for nickel catalyst in CO2 methanation. Among these, the hydrotalcite-like compounds are noteworthy.
Hydrotalcite-like compounds, also known as layered double hydroxides, are layered structure materials composed of a mixed hydroxide of divalent/trivalent metals. The general representative chemical formula is [M1−x2+Mx3+(OH)2](An−)x/n•y H2O, where M2+ and M3+ are any divalent and trivalent cations, An− is an exchangeable interlayer anion (organic or inorganic), and the water molecules are either crystalline in the lattice or physisorbed on the surface [189].
Several authors have studied these materials as supports for Ni catalysts (Ni–Al/hydrotalcite), comparing their catalytic activity in CO2 methanation with commercial Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Taking together the Abate et al. [190] and He et al. [191] results, it is possible to display the activity of Ni–Al/hydrotalcite catalysts prepared at three different pH values (12, 10, and 8.7). Both works report a high Ni dispersion on the hydrotalcite support with respect to the conventional catalyst (Ni/γ-Al2O3), indicating that this new support is a promising material for preparing stable and well-dispersed Ni catalysts. Even if the amount of loaded nickel on the support ranges between 75 and 80 wt %, the authors demonstrated that the catalysts possess a narrow nickel particle size distribution in the range of 3–9 nm. This means that more reducible nickel species can be obtained. The catalytic performance of Ni–Al–Hydrotalcite catalysts shows a maximum activity at 300 °C, with similar CO2 conversion and CH4 yield (85% for catalysts prepared by Abate et al. and 80%–82% for the catalyst prepared by He et al.).
Aluminum is the main metal present in this type of material; therefore, many works on the argument report the effect of the Ni/Al ratio on the catalyst performance. Gabrovska et al. [192] studied the variation of Ni2+/Al3+ molar ratio effect on the catalytic activity of Ni-Al-Hydrotalcite. The effect on the catalyst performance cannot be defined directly but has to be correlated to other fundamental parameters of the CO2 methanation process, such as reaction temperature, space velocity, and reduction temperature. The catalyst with the highest amount of Ni (Ni2+/Al3+ = 3) shows a talovite-like phase and higher conversion after reduction at 400–450 °C, under all reaction temperatures and space velocities tested.
The catalyst with the highest amount of Al (Ni2+/Al3+ = 0.5), and, of course, the lowest amount of nickel, shows high methanation activity, at 260 °C only after reduction at a high temperature (higher than 500 °C), in order to reduce the NiAl2O4 species.
The hydrotalcite material seems to be a promising support for Ni catalysts due to the possibility of hosting a large amount of catalyst (metal) without losing the important peculiarity of high particle size dispersion. The great quantity of aluminum present in these materials must be taken into account because it affects the reducibility of species that are formed with nickel, retarding the nickel metal sintering.
Finally, Wierzbicki et al. modified the redox properties of a hydrotalcite-based catalyst by lanthanum incorporation [193]. The presence of La increases the basicity of the support and, simultaneously weakens the interactions between Ni and the Al–Mg/Hydrotalcite matrix, producing more reducible nickel species.
2.2.5. Other Supported-Nickel Catalysts
Carbon nanotubes were also investigated as nickel supports for CO2 methanation [194]. However, they do not show innovative properties as supports for Ni catalyst because the catalytic performance of Ni–CNT is high only in the initial stage of reaction but decreases over time. As occurs for other supports, on introducing ceria on the CNTs surface the catalyst activity and stability increase, due to the promoting effect of ceria on nickel species dispersion and their reduction [195].
Recently, a synergic effect between Ni and a W–Mg mixed oxide has been reported by Yan et al. [195]. The researchers studied a series of W-doped Ni–Mg mixed oxide catalysts in CO2 methanation, demonstrating their excellent activity, CH4 selectivity, and stability up to 450 °C. Particularly, the maximum CO2 conversion is attained when the W:Ni molar ratio in the final catalyst is 1:1.
W, in fact, plays an important role in the catalyst performance: its presence promotes the formation of CO2 adsorption sites, enhancing the catalyst activity and simultaneously favoring the Ni–Mg interactions, producing very sintering-resistant Ni species, and leading to a very stable NiWMgOx catalyst.
2.2.6. Nickel–Iron-Based Catalysts
The last part of this review is entirely dedicated to catalysts active in the CO2 methanation reaction based on Ni–Fe systems, either as alloys or ferrites. The first papers on the application of these classes of catalysts in the reaction date back to the early 1990s, and recently they have found renewed interest due to the possible ways of exploiting CO2 for obtaining methane as a promising energy source for methane production and/or in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis (FTS).
Recently, Merkache et al. published a scientific work in which the activity of iron catalyst in the CO2 hydrogenation was reported [196]. They tested a mesoporous-supported iron catalyst, Fe–KIT-6, synthesized for the first time with high iron loading. The high density of the iron sites strongly improves the CO2 methanation selectivity of the catalyst at high temperatures [196]. However, it is well known that the activity and selectivity of iron catalysts are a function not only of the iron loading but also of the oxidation state of iron atoms.
Magnetite and M(II)-bearing ferrites form a family of oxygen-deficient spinel ferrites represented by the general formula MxFe3−xO4−δ, where δ represents the reduction degree of the ferrite. The oxygen deficient ferrite (ODF) is formed by hydrogen reduction at 300 °C [197]:
MxFe3−xO4 + δH2 = MxFe3−xO4−δ + δH2O.
ODF decomposes CO2 to carbon and oxygen. Carbon deposits on the ferrite surface, while oxygen penetrates the lattice of the ODF; therefore, carbon reacts with H2 to form CH4 at 200–300 °C [198,199,200,201,202]. Several ferrites (MxFe3−xO4 where M = Fe, Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, Mg, Mn) have been investigated The most active results are for the NixFe3−xO4, with over 86% CH4 yield at 200–300 °C [199,202,203].
In [197] ultrafine Ni(II) ferrite (UNF) with 36% Ni2+ substitution is synthesized and tested at 300 °C in CO2 methanation. The yield of CH4 obtained on the UNF catalyst was 1.5–6.0 times (depending of GHSV) larger than that of the nickel ferrite (NF) catalyst. Furthermore, investigations on UNFs have mainly regarded methanation by using waste heat in stationary sources such as power plants and carbon recycling systems in flue gas in LNG power plants [204,205].
From 2004 to 2007 an interesting series of papers appeared in the literature [206,207,208,209] that, starting from fundamental concepts of heterogeneous catalysis, were applied by the authors to the methanation reaction. According to [210], one of the fundamental results is the well-known volcano curve. This is obtained when the activity of catalysts, for a given reaction, is plotted as a function of a parameter related to the ability of the surface to form chemical bonds with reactants, intermediates, or products [211,212].
Starting from the point of view that several elementary reactions at metal surfaces show a linear Bronsted–Evans–Polanyi (BEP) relation [213] between the activation energy and the reaction energy, and reactions belonging to the same class follow the same relation, Bligaard et al. [206] investigated the implications of this finding on the kinetics of surface catalyzed chemical processes.
For the scope of the present review, the analysis presented in [206] can be used to understand the volcano curve for the methanation reaction, although related only to the CO methanation (Figure 6). Secondly, such analysis deals only with the catalytic activity; for reactions where selectivity plays a role, it cannot be used.
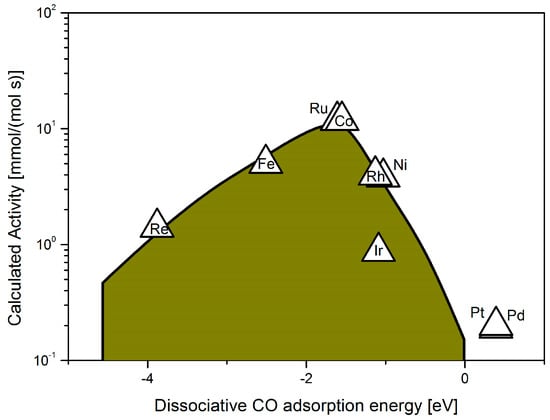
Figure 6.
Activities of different supported transition metals as a function of the reaction energy for dissociative CO chemisorption at 550 K. Adapted from Bligaard et al. [206].
DFT (Density Functional Theory) is used to describe semi-quantitatively the kinetics of catalytic reactions on the basis of thermochemistry and activation energies [214,215,216].
Following the previous study [206], in [207] a screening of several intermetallic alloys to be used for CO methanation has been reported including experimental results. According to the authors, the two important characteristics of a catalyst surface in determining the rate of the reaction are the barrier for CO dissociation and the stability of the atomic C and O intermediates. The BEP relation reported in [207] shows the volcano dependence on the rate of Ediss [206]. For weak adsorption at the right in the volcano curve the barrier for dissociation is high, thus limiting the reaction rate; on the other branch (left) a strong adsorption leads to a low rate of removal of adsorbed C and O to from the reaction products. The interpolation model used in the study suggests a potential candidate for improving the methanation reaction use of alloy catalysts formed by combining the elements on the left and right branches of the curve. Moreover, a multi-objective optimization target is included in the investigation; in the economics literature, a typical solution is represented by the Pareto-optimal set [217,218].
In [207] it is clearly shown that, taking into consideration all the above reported considerations, Ni–Fe alloys have to be considered the best candidates for an “all-inclusive” material of choice for the reaction. The experimental results fully confirm the predictions from the computational screening. On the other hand, Ni–Fe alloys, also tested for CO2 methanation, have not shown results concordant with those here discussed [219,220]. This, in our opinion, could be due to the different operational conditions adopted in the investigations.
The same approach (computational screening/experimental verifications) was followed in [208] for both CO2 hydrogenation and simultaneous CO and CO2 hydrogenation. The former reaction was carried out at 250 °C with a gas mixture containing 9% CO2 in 91% H2. The latter was conducted with a gas containing 2% CO, 2% CO2, and 96% H2 at 220–230 °C. It has been shown that the conversion of CO2 to methane is significantly higher over the Ni–Fe alloy catalyst in comparison to pure Ni. For the simultaneous CO–CO2 hydrogenation, the best catalysts have a Ni/Fe ratio >1. However, the pure Fe catalyst shows a lower activity than pure Ni.
In the last study of the series [209], some mono- and bi-metallic Ni–Fe catalysts supported on MgAl2O4 and Al2O3 were tested in CO methanation (reaction conditions: 2% vol. CO in H2, 25,000 h−1 GHSV, reduction at 500 °C in CO/H2 mixture for 4 h, reaction temperature in the range 200–300 °C).
Bimetallic catalysts with compositions 25Fe75Ni and 50Fe50Ni show better activity compared with monometallic Ni and Fe catalysts. The selectivity to CH4 was found to increase at higher CO conversions and higher Ni loading in the catalysts. The maximum catalytic activity and the highest selectivity to methane are observed for a 20 wt % total metal loading on MgAl2O4.
DFT was recently applied to investigate the three different mechanisms of CO2 methanation on Ni(111) surfaces with and without formation of CO as an intermediate [221]. The three mechanisms fall into two categories [222,223,224]: conversion of CO2 to CO prior to methanation involving a CO intermediate [225,226], and direct hydrogenation of CO2 to methane without the formation of CO as an intermediate [63,127,227,228].
On the basis of the calculated energy barrier values for each of the three paths and the correlated determination of the rate determining step (r.d.s.), path 2 (the decomposition of CO2 into CO and O, further decomposition of CO into C and O (r.d.s), and hydrogenation of C to CH4)) appears to be the most accredited mechanism.
Other recent relevant studies devoted to Ni–Fe-based catalysts for methanation reactions regarded the effect of the Fe content on Al2O3-supported catalysts in the co-methanation of CO and CO2 [229]; the influence of the second metal for CO hydrogenation [230]; the effect of the preparation method [231]; and the effect of the addition of a noble metal (Ru) [232] on the activity and selectivity of the reactions investigated.
In [229] the maximum carbon conversion and CH4 selectivity on NixFe1−x/Al2O3 (20 wt % metal content on the support) was observed for the Ni0.7Fe0.3/Al2O3 catalyst. Higher Fe content causes a decrease in C conversion and CH4 productivity because of the occurrence of WGS reaction and C2–C5 hydrocarbon formation.
Alumina xerogel (AX)—used as a support of Ni catalysts with the addition of a second metal M (M = Fe, Ni, Co, Ce, La)—was tested in CO hydrogenation (feed composition CO:H2:N2 = 1:3:1.7) at 230 °C and 10 bar. Both CO conversion and CH4 yield decrease in the order 30Ni10FeAX > 30Ni10NiAX > 30Ni10CoAX > 30Ni10CeAX > 30Ni10LaAX. The low performance exhibited by both Ce and La as a second metal appears to denote that transition metals (Fe, Co, Ni) are more effective in promoting the reaction than lanthanides (Ce, La). Moreover, on the basis of temperature-programmed surface reaction (TPSR) experiments, the higher performance of 30Ni10FeAX was attributed to the optimal CO dissociation energy and the largest H2 adsorption [230]. Following the latter two studies discussed above, Hwang et al. investigated, on the same catalytic system (AX-supported Ni-Fe), the effect of the precipitation agent, on the catalysts prepared by coprecipitation, on methane production from CO2 and H2. The precipitation agent used ((NH4)2CO3, Na2CO3, NH4OH, or NaOH) has a decisive role on the catalytic performance since it influences the extent of the active surface area. Therefore, among the catalysts tested, NiFeAl-(NH4)2CO3, affording the smallest particle size, shows the best results in terms of CO2 conversion and CH4 yield [231].
The alumina xerogel support was again used to investigate the effect of the addition of different ruthenium contents (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0) on the activity of the same reaction; in operative conditions the feed composition is CO2:H2:N2 = 1:4:1.7, P = 10 bar, T = 220 °C. A close correlation between the metal surface area and the amount of desorbed CO2 (measured by CO2–TPD) was found. Both CO2 conversion and CH4 yield show a well-defined volcano-shaped trend with respect to Ru content. Furthermore, the CH4 yield increases on increasing the metal surface area and the amount of desorbed CO2 [232].
Bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts were tested in the CO methanation reaction for the production of substitute natural gas (SNG) under industrial (0.1–0.3 MPa) total methanation conditions to be adopted in processes related to the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis [232,233,234,235,236]. Thus, in [5] the activity of bimetallic Ni3Fe/γ-Al2O3 was first compared with that of a reference Ni/γ-Al2O3 under conditions of 3.0 MPa and H2/CO = 3.1. Ni3Fe/γ-Al2O3 achieves the 100% CO conversion at 225 °C, whereas Ni/γ-Al2O3 reaches total CO conversion at 275 °C. Also, in the high temperature range of 500–600 °C, the CO conversion of the bimetallic catalyst is higher than that of the monometallic catalyst, with 99% selectivity to CH4 from 300 °C to 450 °C. The influence of the Ni/Fe ratio on the catalytic activity of a number of bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts in CO methanation at 0.1 MPa was also investigated. Ni3Fe1.8/γ-Al2O3 shows the lowest CO conversion and CH4 selectivity, even lower than that of Ni/γ-Al2O3. Clearly, the higher Fe content is responsible for the poor catalyst performance. Comparing all the results obtained in high-pressure methanation test with the low-pressure experiments reported in [5], Tian et al. conclude that the performance of Ni–Fe catalysts is not determined by the content of individual Ni or Fe, but by the synergistic effect of the two metals in the catalyst. Another process able to produce CH4 has been reported to be the decomposition of CO2 to carbon and oxygen [237,238,239,240]. In this regard, ferrite catalysts have been previously used for this reaction and being non-stoichiometric or oxygen-deficient materials are able to decompose water to hydrogen and CO2 to carbon [241,242,243,244,245].
In [246] the decomposition of CO2 was carried out on the nanophase NiFe2O4 (NFN, NixFe3−xO4−δ, 0 < δ < 1) at 300 °C to obtain CO, CO2, or CH4. After the CO2 decomposition, the reactor was flushed with hydrogen to carry out the methanation process. The two reaction routes for decomposing CO2 by oxygen-deficient ferrites are: (i) decomposition to carbon and oxygen; (ii) decomposition into carbon monoxide and oxygen [247,248,249,250,251].
The experimental results reported in [246] clearly show that the prepared NFNs were effective at decomposing CO2 into carbon and oxygen after reduction by hydrogen. In conclusion, the overall mechanism of CO2 decomposition over NiFe2O4 nanoparticles can be summarized as follows: (i) H2 gas decomposes and produces the water molecule, making the NiFe2O4 oxygen-deficient; (ii) the oxygen-deficient NiFe2O4 adsorbs oxygen atoms from CO2 and produces carbon on the surface or CO when NiFe2O4 is less active; (iii) the produced carbon reacts with H2 and produces CH4 by methanation.
A new interesting iron source for supported bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts preparation has recently been proposed by Wang et al. [252], and consists of using calcined olivine as a promising Ni support for CO2 methanation. Before this study, the activity of calcined olivine supported nickel has been demonstrated in gasification [253] and steam reforming [254] of biomass. Olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the general formula (MgxFe1−x)2SiO4 and is a common Earth mineral. The peculiarity of the support consists in the possibility of allowing interaction between NiO and olivine structure to lead to a better dispersion of Ni species. This effect is promoted by the simultaneous presence of iron and MgO. First of all, Wang et al. describe the effect of the support calcination on iron species. They observed that iron was extracted by the olivine structure during the calcination process so that more reducible iron species can be formed (analyzed by usual TPR experiments). The amount of reducible iron species increases on increasing the temperature to 800 °C. Form 800 °C to 1200 °C a reversal trend was registered, probably due to the reintegration of extracted iron into the olivine structure. Over 1200 °C the reducible iron amount increases again and MgSiO3 species are formed, as confirmed by the XRD spectrum. TPR profiles of Ni/olivine catalysts obtained by calcining the support at different temperatures show that for the catalyst calcined at lower temperature nickel is just deposited on the olivine structure with a weak interaction as highly dispersed particles. On the contrary, for catalysts calcined at temperatures >900 °C, a NiO–MgO solid solution phase and grafted NiO species were formed. The best catalyst, obtained by calcination of the support at 350 °C and reduction at 500 °C, is able to reach, under tested conditions, a CO2 conversion of 98.4% and a CH4 selectivity of 99.9%.
Important and very recent results that confirm the role of iron on the dispersion of NiO nanoparticles, increasing the quantity of the reduced active nickel species, were reported by Lu et al. regarding zirconia-supported doped nickel catalysts [255] and Pandey et al., regarding five series of Ni–Fe bimetallic supported catalysts [256]. The morphology of Ni–ZrO2 and Ni–Fe/ZrO2 catalysts has been compared. Using TEM images, it is possible to notice that the average size of NiO particles on the Ni–ZrO2 catalyst is higher than the average size of the NiO particles dispersed on Ni–Fe/ZrO2 catalyst [255].
3. Industrial Applications and Concluding Remarks
The use of carbon dioxide as a feedstock for fuels, and for energy in general, is a promising route that permits adherence to main international protocols on environmental protection. Hydrogenation is an appropriate way to reduce CO2 and provide a range of substances compatible with existent technologies. The methane produced in this way could be directly injected into already existent pipeline networks or storage infrastructures. Obviously, the main challenge that ensures an environmentally friendly process is obtaining hydrogen from renewable sources and energy. Water electrolysis promoted by renewable energy (wind, solar, etc.) is an economic and clean method of H2 production. Hydrogen can be directly injected into a natural gas grid or combined with CO2 by a methanation process.
Energy production by these ways is the basis of the Power-to-Gas concept (P2G). However, currently, this is only a model: there are demo-plants and industrial-scale plants that demonstrate the possibility of producing energy by gas. Germany seems to be at the cutting edge in the P2G technology that provides SNG (Substitute or Synthetic Natural Gas) as a product, since 2009.
In Stuttgard there is a demonstration Power-to-methane plant (250 kW power input as capacity) founded by ZSW (the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research) by ETOGAS GmbH. ETOGAS, in Wertle, Germany, is an industrial-scale Power-to-methane plant (6300 kW power input as capacity) that produces methane for Audi. The produced methane, named Audi-e-gas, comes from the CO2 obtained by a waste-biogas plant.
More recently, the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) coordinated the innovative HELMETH project (Integrated High-Temperature Electrolysis and Methanation for Effective Power to Gas Conversion) [257]. The project, co-financed by the EU’s Seventh Framework Program, has the objective of proving the highly efficient Power-to-Gas (P2G) technology by thermally integrating high-temperature electrolysis (SOEC Technology) with methanation. The expected efficiency should be higher than 85%, superior to the efficiency for hydrogen generation via conventional water electrolysis. In practice, high-temperature electrolysis (endothermic) and methanation (exothermic) can be coupled and thermally integrated with increasing globally conversion efficiency.
At the same time, the Electrochaea Company has developed a commercial power-to gas system solution using a microorganism (methanogenic archaea) as biocatalyst, patented as BioCat, for a methanation technology to operate at lower costs and with higher flexibility than conventional thermochemical methanation processes [258]. Archaea BioCat exhibits several properties including high mass conversion efficiency and high tolerance to many contaminants typically present in industrial CO2 sources, such as O2, H2S and particulates that can poison common catalysts. Moreover, archaea are highly selective towards methane formation, so minimal post-reaction gas treatment is needed before injecting the produced gas into the gas grid. The power-to-gas technology of the Electrochaea system uses an electrolyzer to produce hydrogen, which is fed into a bioreactor containing the archaea along with carbon dioxide from a biogenic (anaerobic digesters, fermentation plants) or industrial source (fuel gas from combustion processes). In February 2014, Electrochaea began its first commercial-scale demonstration project BioCat: a 1 MW power-to-gas plant based on biological methanation.
High flexibility, reduced technological cost, and high process efficiency make biomethanation technology an attractive source of renewable energy. The global evaluation of biomethanation assets should also include the Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment (LSCA) methodology. Kristjanpoller et al. have published an interesting work on the biomethanation plant assessment [259]. The work pinpoints two important concepts that will guide research and generate proposals for industrial plant improvement: effectiveness and efficiency. The first is related to the extent to which the objectives of the process are met; the second is the measure of the economy in which the resources of the company are used, including the cost of the catalyst.
In any case, even if the mechanism that currently promotes methanation on nanosized metal catalysts, as well as the best-performing catalyst system and the effectiveness of industrial power-to-gas plants are under scientific debate, we can say without a doubt that the commercialization of CO2 methanation processes plays a pivotal role in the future of environmentally friendly energy systems.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to write the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Iglesias, G.M.; de Vries, C.; Claeys, M.; Schaub, G. Chemical energy storage in gaseous hydrocarbons via iron Fischer–Tropsch synthesis from H2/CO2-Kinetics, selectivity and process considerations. Catal. Today 2015, 242, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, C.; Duyar, M.S.; Hoskins, M.; Farrauto, R. Catalytic and adsorption studies for the hydrogenation of CO2 to methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 152–153, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschany, F.; Schelereth, D.; Hinrichsen, O. On the kinetics of the methanation of carbon dioxide on coprecipitated NiAl(O)x. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, J.; Ang, M.L.; Kawi, S. Enhanced activity of CO2 methanation over Ni/CeO2–ZrO2 catalysts: Influence of preparation method. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Shi, H.; Pan, W.; Cheng, Y. Bimetallic Ni-Fe total-methanation catalyst for the production of substitute natural gas under high pressure. Fuel 2013, 104, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelló, S.; Berrueco, C.; Montané, D. High-loaded nickel–alumina catalyst for direct CO2 hydrogenation into synthetic natural gas (SNG). Fuel 2013, 113, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xin, Z.; Meng, X.; Bian, Z.; Lv, Y. Highly dispersed nickel within mesochannels of SBA-15 for CO methanation with enhanced activity and excellent thermostability. Fuel 2017, 188, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, T.; Grünig, J.; Roman Schuster, M.; Rothenfluh, T.; Orth, A. Methanation of CO2—Storage of renewable energy in a gas distribution system. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2014, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebdelfar, S.; Ravanchi, M.T. Carbon dioxide utilization for methane production: A thermodynamic analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 134, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B.; Duan, H.; Hou, B.; Huang, Y. Catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methane: A review of recent studies. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsch, S.; Schneider, J.; Matthischke, S.; Schluter, M.; Gotz, M.; Lefebre, J.; Prabhakaran, P.; Bajohr, S. Review on methanation—From fundamentals to current projects. Fuel 2016, 166, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Ahmad, A. CO2 methanation over heterogeneous catalysts: Recent progress and future prospects. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2647–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.V. Light-Promoted Hydrogenation of Carbon dioxide—An overview. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, J. Methanation of carbon dioxide: An overview. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.X.; Hou, W.H. Study on Ru-based catalyst used in reductive reaction of CO2. Space Med. Med. Eng. 2004, 17, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Shang, C.X. A study on CO2 methanization reduction technology. Space Med. Med. Eng. 1994, 7, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.H.; Wu, B.Z.; Ren, C.B. Comparative analysis of Sabatier CO2 reduction system for space station. Space Med. Med. Eng. 2011, 24, 384–390. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Cundari, T.R.; Wilson, A.K. CO2 reduction on transition metal (Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu) surface: In comparison with homogeneous catalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012, 116, 5681–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.J.; Park, D.H.; Huh, D.S. Adsorption and dissociation reaction of carbon dioxide on Pt(111) and Fe(111) surface: MO-study. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2000, 21, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Solymosi, F. The bonding, structure and reaction of CO2 adsorbed on clean and promoted metal surface. J. Mol. Catal. 1991, 65, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechete, I.; Vedrine, J.V. Nanoporous materials as new engineered catalysts for the synthesis of green fuels. Molecules 2015, 20, 5638–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italiano, G.; Espro, C.; Arena, F.; Frusteri, F.; Parmaliana, A. Catalytic features of Mg modified Ni/SiO2/Silica cloth systems in the decomposition of methane for making COx-Free Hydrogen. Catal. Lett. 2008, 124, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, P.; Aloise, A.; Macario, A.; Crea, F.; Antonucci, P.L.; Giordano, G.; Nagy, J.B. Zeolite-supported Ni catalyst for methane reforming with carbon dioxide. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2011, 37, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, F.; Vinci, A.; Espro, C.; Gumina, B.; Musolino, M.G.; Pietropalo, R. Hydrogenolysis vs. aqueous phase reforming (APR) of glycerol promoted by a heterogeneous Pd/Fe catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4466–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, P.; Macario, A.; Aloise, A.; Antonucci, P.L.; Giordano, G.; Nagy, J.B. Effect of support surface on methane dry-reforming catalyst preparation. Catal. Today 2013, 218–219, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candamano, S.; Frontera, P.; Macario, A.; Crea, F.; Nagy, J.B. Preparation and characterization of active Ni-supported catalyst for syngas production. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 96, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, J.P.; Burch, R.; Coleman, H.M. Metal-catalyzed steam reforming of ethanol in the production of hydrogen for fuel cell application. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeo, F.; Nichio, N.N.; Feretti, O.A.; Resasco, D. Study of Ni catalysts on different supports to obtain synthesis gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Faro, M.; Frontera, P.; Antonucci, P.L.; Aricò, A.S. Ni-Cu based catalysts prepared by two different methods and their catalytic activity toward the ATR of methane. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, M.; Beuls, A.; Ruiz, P. Catalytic production of methane from CO2 and H2 at low temperature: Insight on the reaction mechanism. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuls, A.; Swalus, C.; Jacquemin, M.; Heyen, G.; Karelovic, A.; Ruiz, P. Methanation of CO2: Further insight into the mechanism over Rh/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 113–114, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelovic, A.; Ruiz, P. CO2 hydrogenation at low temperature over Rh/γ-Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of the metal particle size on catalytic performances and reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 113–114, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayapalaa, R.; Yu, F.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mlsna, T.T. K-promoted Mo/Co- and Mo/Ni-catalyzed Fischer–Tropsch synthesis of aromatic hydrocarbons with and without a Cu water gas shift catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 480, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swalus, C.; Jacquemin, M.; Poleunis, C.; Bertrand, P.; Ruiz, P. CO2 methanation on Rh/γ-Al2O3 catalyst at low temperature: “In situ” supply of hydrogen by Ni/activated carbon catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelovic, A.; Ruiz, P. Mechanistic study of low temperature CO2 methanation over Rh/TiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solymosi, F.; Erdöhelyi, A.; Bánsági, T. Methanation of CO2 on supported rhodium catalyst. J. Catal. 1981, 68, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Kladi, A.; Verykios, X.E. Effects of Carrier Doping on Kinetic Parameters of CO2 Hydrogenation on Supported Rhodium Catalysts. J. Catal. 1994, 148, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solymosi, F.; Tombácz, I.; Koszta, J. Effects of variation of electric properties of TiO2 support on hydrogenation of CO and CO2 over Rh catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 95, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.T. The influence of metal oxides on the activity and selectivity of transition metal catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 1995, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, K.J.; Boffa, A.B.; Salmeron, M.; Bell, A.T.; Somorjai, G.A. The kinetics of CO2 hydrogenation on a Rh foil promoted by Titania overlayers. Catal. Lett. 1991, 9, 415426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A.; Deleitenburg, C.; Dolcetti, G.; Lorca, J.L. CO2 Methanation under Transient and Steady-State Conditions over Rh/CeO2 and CeO2-Promoted Rh/SiO2: The Role of Surface and Bulk Ceria. J. Catal. 1995, 151, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleitenburg, C.; Trovarelli, A. Metal-Support Interactions in Rh/CeO2, Rh/TiO2, and Rh/Nb2O5 Catalysts as Inferred from CO2 Methanation Activity. J. Catal. 1995, 156, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Song, W.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Deng, J.; Zhong, W.; Liu, J.; Gong, X.Q.; Zhao, Z. Elucidation of the high CO2 reduction selectivity of isolated Rh supported on TiO2: A DFT study. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 6128–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Shingu, H. A molecular Orbital Theory of Reactivity in Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmierz, M. Kinetic study on carbon dioxide hydrogenation over Ru/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2008, 137, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.A.; Steffgen, F.W. Catalytic Methanation. Catal. Rev. 1974, 8, 159–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherbee, G.D.; Bartholomew, C.H. Hydrogenation of CO2 on group VIII metals: IV. Specific activities and selectivities of silica-supported Co, Fe, and Ru. J. Catal. 1984, 87, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawa, S.; Sayama, K.; Okabe, K.; Arakawa, H. Methanol synthesis from CO2 and H2 over silver catalyst. Energy Convers. Manag. 1995, 36, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Maggiore, R.; Minicò, S.; Galvagno, S. Influence of the support on CO2 methanation over Ru catalysts: An FT-IR study. Catal. Lett. 1998, 51, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ichikuni, N.; Shimazu, S.; Uematsu, T. Catalytic properties of sprayed Ru/Al2O3 and promoter effects of alkali metals in CO2 hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1998, 172, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ichikuni, N.; Shimazu, S.; Uematsu, T. Hydrogenation of CO2 over sprayed Ru/TiO2 fine particles and strong metal-support interaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 180, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toemen, S.; Bakar, W.A.W.A.; Ali, R. Effect of ceria and strontian over Ru/Mn/Al2O3 catalyst: Catalytic methanation, physicochemical and mechanistic studies. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 13, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, G.; Bellotti, D.; Riani, P.; Magistri, L.; Busca, G. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ru/Al2O3 and Ni/Al2O3 catalysts at atmospheric pressure: Catalysts activation, behaviour and stability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 9171–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, G.; Bellotti, D.; Finocchio, E.; Magistri, L.; Busca, G. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ru/Al2O3: Catalytic activity and infrared study. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, Z.; Stołecki, K.; Raròg-Pilecka, W.; Miskiewicz, E.; Wilczkowska, E.; Karpinski, Z. Supported ruthenium catalysts for selective methanation of carbon oxides at very low COx/H2 ratios. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 342, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, S.; Gao, D.; Wang, S. Effect of support calcination temperature on the catalytic properties of Ru/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 for methanation of carbon dioxide. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2014, 42, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamarua, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Kuboc, M.; Abe, T. Density functional theory analysis of methanation reaction of CO2 on Ru nanoparticle supported on TiO2 (101). Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 470, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranathan Thampi, K.; Kiwi, J.; Grätzel, M. Methanation and photo-methanation of carbon dioxide at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Nature 1987, 327, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.M.; Kamble, V.S.; Kartha, V.B.; Iyer, R.M.; Ravindranathan Thampi, K.; Gratzel, M. FTIR spectroscopic study of the interaction of CO2 and CO2 + H2 over partially oxidized RuTiO2 catalyst. J. Catal. 1994, 146, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Tanizawa, M.; Watanabe, K.; Taguchi, A. CO2 methanation property of Ru nanoparticle-loaded TiO2 prepared by a polygonal barrel-sputtering method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Su, X.; Duan, H.; Hou, B.; Lin, Q.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Pei, G.; Geng, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Influence of pretreatment temperature on catalytic performance of rutile TiO2-supported ruthenium catalysts in CO2 methanation. J. Catal. 2016, 333, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Ochienga, O.J.; Kikuchi, R.; Haneda, T.; Kameyama, H. Promotion of CO2 methanation activity and CH4 selectivity at low temperatures over Ru/CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 10090–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, P.; McFarland, E.W.; Metiu, H. CO2 methanation on Ru-doped ceria. J. Catal. 2011, 278, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lin, Q.; Su, X.; Duan, H.; Geng, H.; Huang, Y. CO2 Methanation over TiO2-Al2O3 Binary Oxides Supported Ru Catalysts. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.H.; Ali, R.; Bakar, W.A.W.A. Optimization of CO2 methanation reaction over M*/Mn/Cu–Al2O3 (M*: Pd, Rh and Ru) catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.H.; Ali, R.; Bakar, W.A.W.A. The investigation of Ru/Mn/Cu–Al2O3 oxide catalysts for CO2/H2 methanation in natural gas. J. Tawain Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toemen, S.; Bakar, W.A.W.A.; Ali, R. Investigation of Ru/Mn/Ce/Al2O3 catalyst for carbon dioxide methanation: Catalytic optimization, physicochemical studies and RSM. J. Tawain Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodziński, A.; Bond, G.C. Selective Hydrogenation of Ethyne in Ethene-Rich Streams on Palladium Catalysts. Part 1. Effect of Changes to the Catalyst During Reaction. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2006, 48, 91–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, P.; Pietsch, J.; Parker, S.F. Poisoning and deactivation of palladium catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2001, 173, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurman, Y.; Mirodatos, C.; Ferreira-Aparicio, P.; Rodriguez-Ramos, I.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A. Bifunctional pathways in the carbon dioxide reforming of methane over MgO-promoted Ru/C catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2000, 66, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuszka, J. Carbon dioxide chemistry during oxidative coupling of methane on a Li/MgO catalyst. Catal. Today 1994, 21, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tomishige, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Fujimoto, K. Promoting effect of Pt, Pd and Rh noble metals to the Ni0.03Mg0.97O solid solution catalysts for the reforming of CH4 with CO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 165, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, G.M.; Lupini, A.R.; Rashkeev, S.; Pennycook, S.J.; Mullins, D.R.; Schwartz, V.; Bridges, C.A.; Dudney, N.J. Thermal stability and catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles supported on silica. J. Catal. 2009, 262, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Batail, N.; Silva, S.; Rafik-Clement, S.; Karelovic, A.; Debecker, D.P.; Chaumonnot, A.; Uzio, D. CO2 hydrogenation with shape-controlled Pd nanoparticles embedded in mesoporous silica: Elucidating stability and selectivity issues. Catal. Commun. 2015, 58, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmelle, R.; Duarte, R.B.; Franken, T.; Burnat, D.; Holzer, L.; Borgschulte, A. Development of improved nickel catalysts for sorption enhanced CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 41, 20185–20191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudagna, S.R.; Comelli, R.A.; Figoli, N.S. Influence of the tungsten oxide precursor on WOx-ZrO2 and Pt/WOx-ZrO2 properties. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 164, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.W.; Kuo, M.S.; Tsay, M.T.; Hsieh, M.C. Hydrogenation of CO2 over nickel catalysts on rice husk ash-alumina prepared by incipient wetness impregnation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 247, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jia, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Gua, F.; Xua, G.; Zhong, Z.; Sua, F. Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for CO methanation: Effect of Al2O3 supports calcined at different temperatures. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, S.; Shimizu, T.; Otsuka, K. Complete removal of carbon monoxide in hydrogen-rich gas stream through methanation over supported metal catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaci, S.; Protasova, L.; Lefevere, J.; Bedel, L.; Guilet, R.; Marty, P. Efficient CO2 methanation over Ni/Al2O3 coated structured catalysys. Catal. Today 2016, 273, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Shimizu, T.; Kameyama, H.; Haneda, T.; Kikuchi, R. Ni/CeO2 catalysts with high CO2 methanation activity and high CH4 selectivity at low temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 5527–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Chou, L. Methanation of carbon dioxide over a highly dispersed Ni/La2O3 catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2010, 31, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Nickel catalysts supported on MgO with different specific surface area for carbon dioxide reforming of methane. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, C.; Hayakawa, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawasaki, W.; Watanabe, R. A novel nickel-based structured catalyst for CO2 methanation: A honeycomb-type Ni/CeO2 catalyst to transform greenhouse gas into useful resource. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 532, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoylu, A.E.; Önsan, Z.I. Hydrogenation of carbon oxides using coprecipitated and impregnated Ni/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 164, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Rui, N.; Fan, Z.; Liu, C. Effect of the structure of Ni/TiO2 catalyst on CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2016, 41, 22017–22025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, D.C.D.; Letichevsky, S.; Borges, L.E.P.; Appel, L.G. The Ni/ZrO2 catalyst and the methanation of CO and CO2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 8923–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroyama, H.; Tsuda, Y.; Asakoshi, T.; Masitah, H.; Okanishi, T.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. Carbon dioxide methanation over Ni catalysts supported on various metal oxides. J. Catal. 2016, 343, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Kirihata, Y.; Izumiya, K.; Kumagai, N.; Habazaki, H.; Hashimoto, K. Higly active Ni/Y doped Zr2O catalyst for CO2 methanation. App. Surf. Sci. 2016, 358, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, G.Q.M. Role of CeO2 in Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts for carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 19, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoylu, A.E.; Akin, A.N.; Önsan, Z.I.; Trimm, D.L. Structure/activity relationships in coprecipitated nickel-alumina catalysts using CO2 adsorption and methanation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 145, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkania, F. Preparation of highly active nickel catalysts supported on mesoporous nanocrystalline γ-Al2O3 for CO2 methanation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, G.; Riani, P.; Magistri, L.; Busca, G. A study of the methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts at atmospheric pressure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 11557–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, B.; Carvalho, H.W.P.; Mangold, S.; Kleist, W.; Grunwaldt, J.D. Methanation of CO2: Structural response of a Ni-based catalyst under fluctuating reaction conditions unraveled by operando spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2015, 327, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckhuysen, B.M. Determining the active site in a catalytic process: Operando spectroscopy is more than a buzzword. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 4351–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsøe, H. Developments in operando studies and in situ characterization of heterogeneous catalysts. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwaldt, J.D.; Clausen, B.S. Combining XRD and EXAFS with on-line catalytic studies for in situ characterization of catalysts. Top. Catal. 2002, 18, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banares, M.A. Operando methodology: Combination of in situ spectroscopy and simultaneous activity measurements under catalytic reaction conditions. Catal. Today 2005, 100, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.S.; Shivakumara, C.; Hegde, M.S. Single step preparation of CeO2/CeAlO3/-Al2O3 by solution combustion method: Phase evolution, thermal stability and surface modification. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Ceria modified three-dimensionally ordered macro-porous Pt/TiO2 catalysts for water-gas shift reaction. J. Rare Earth 2009, 27, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laosiripojana, N.; Assabumrungrat, S. Catalytic steam reforming of ethanol over high surface area CeO2: The role of CeO2 as an internal pre-reforming catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 66, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.C.; Yu Yao, Y.F. Ceria in automotive exhaust catalysts: I. Oxygen storage. J. Catal. 1984, 86, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zou, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Ding, W. Effect of CeO2 addition on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for methanation of carbon dioxide with hydrogen. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2012, 21, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkani, F. Preparation of promoted nickel catalysts supported on mesoporous nanocrystalline gamma alumina for carbon dioxide methanation reaction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 4176–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.C.; Wolf, E.E. Co methanation activity and XPS studies of Pd supported on ZSM5 and Y-zeolites. Appl. Catal. 1984, 13, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckle, S.; Anfang, H.G.; Behm, R.J. Reaction Intermediates and side products in the methanation of CO and CO2 over supported Ru catalysts in H2-rich reformate gases. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 115, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelová, V.; Zukal, A.; Tvarůžková, Z.; Malíček, O. Hydrogenation of CO and CO2 Over Stabilized NiY Catalysts. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1984, 18, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Graca, I.; González, L.V.; Bacariza, M.C.; Fernandes, A.; Henriques, C.; Lopes, J.M.; Ribeiro, M.F. CO2 hydrogenation into CH4 on NiHNaUSY zeolites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.O.; Sreekala, R.; Rashid, K.K.A.; Yusuff, K.K.M.; Sen, B. Doping effects of cerium oxide on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for methanation. Catal. Today 1999, 49, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkowski, J.M.; Paryjczak, T. Characterization of Ru/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts and their Performance in CO2 Methanation. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2000, 71, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, A.; Azambre, B.; Bacariza, M.C.; Graca, I.; Ribeiroa, M.F.; Lopes, J.M.; Henriquesapp, C. Insight into CO2 methanation mechanism over NiUSY zeolites: An operando IR study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Mendoza, D.E.; Stanley, J.N.G.; Scott, J.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. An alumina-supported Ni-La-based catalyst for producing synthetic natural gas. Catalysts 2016, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, S.; Kondratenko, E.V.; Pohl, M.M.; Barkschat, A.; Rodemerck, U. Stable low-temperature dry reforming of methane over mesoporous La2O3-ZrO2 supported Ni catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 113–114, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, I.; Biffi, C.; Bianchi, C.L.; Nichele, V.; Signoretto, M.; Menegazzo, F.; Finocchio, E.; Ramis, G.; Di Michele, A. Ni/SiO2 and Ni/ZrO2 catalysts for the steam reforming of ethanol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 117–118, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichele, V.; Signoretto, M.; Menegazzo, F.; Gallo, A.; Dal Santo, V.; Cruciani, G.; Cerrato, G. Glycerol steam reforming for hydrogen production: Design of Ni supported catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111–112, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Gao, C.; Peng, B.; Shu, M.; Che, S. pH-Responsive Drug Delivery System Based on Coordination Bonding in a Mesostructured Surfactant/Silica Hybrid. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7230–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Haynes, C.L. Impacts of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Size, Pore Ordering, and Pore Integrity on Hemolytic Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, M.; Angelos, S.; Choi, E.; Patel, K.; Fraser Stoddart, J.; Zink, J.I. Mesostructured multifunctional nanoparticles for imaging and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6251–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Kaneda, M.; Terasaki, O.; Zhao, D.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Stucky, G.; Shin, H.J.; Ryoo, R. Direct imaging of the pores and cages of three-dimensional mesoporous materials. Nature 2000, 408, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Zeng, H.C. Targeted Synthesis of Silicomolybdic Acid (Keggin Acid) inside Mesoporous Silica Hollow Spheres for Friedel–Crafts Alkylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16235–16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, F.; Frei, H. Nanostructured Cobalt Oxide Clusters in Mesoporous Silica as Efficient Oxygen-Evolving Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1841–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulea, V.; Brunel, D.; Galarneau, A.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B.; Kooyman, P.J.; Fajula, F. Synthesis of well-dispersed ruthenium nanoparticles inside mesostructured porous silica under mild conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 79, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Mukti, R.R.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Sazegar, M.R. Highly active Ni-promoted mesostructured silica nanoparticles for CO2 methanation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Sidik, S.M. Methanation of carbon dioxide on metal-promoted mesostructured silica nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 486, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Saad, M.W.A. CO2 methanation over Ni-promoted mesostructured silica nanoparticles: Influence of Ni loading and water vapor on activity and response surface methodology studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Lim, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.L. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni-incorporated MCM-41 catalysts: The influence of catalyst pretreatment and study of steady-state reaction. J. Catal. 2007, 249, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. In situ FTIR spectroscopic study of the CO2 methanation mechanism on Ni/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.I.; Nakamura, M.; Doi, T.; Takezawa, N. Mechanisms of methanation of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide over nickel/alumina catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1993, 104, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Kovarik, L.; Szanyi, J. CO2 Reduction on Supported Ru/Al2O3 Catalysts: Cluster Size Dependence of Product Selectivity. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, J.J.; Alvero, R.; Capitán, M.J.; Carrizosa, I.; Odriozola, J.A. DRIFTS study of adsorbed formate species in the carbon dioxide and hydrogen reaction over rhodium catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1991, 71, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Betta, R.A.; Shelef, M. Heterogeneous methanation: In situ infrared spectroscopic study of RuAl2O3 during the hydrogenation of CO. J. Catal. 1977, 48, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, C.H.; Pannell, R.B.; Fowler, R.W. Sintering of alumina-supported nickel and nickel bimetallic methanation catalysts in H2H2O atmospheres. J. Catal. 1983, 79, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, Z.; Meng, X.; Tao, M. Synthesis, characterization and properties of anti-sintering nickel incorporated MCM-41 methanation catalysts. Fuel 2013, 109, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of Transportation Fuels from Biomass: Chemistry, Catalysts and Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, M.M.; Jablonski, W.S.; Magrini-Bair, K.A. Review of Catalytic Conditioning of Biomass-Derived Syngas. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic Triblock and Star Diblock Copolymer and Oligomeric Surfactant Syntheses of Highly Ordered, Hydrothermally Stable, Mesoporous Silica Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Pan, C.J.; Hwang, B.J. Highly-dispersed and thermally-stable NiO nanoparticles exclusively confined in SBA-15: Blockage-free nanochannels. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5193–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vradman, L.; Landau, M.V.; Kantorovich, D.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. Evaluation of metal oxide phase assembling mode inside the nanotubular pores of mesostructured silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 79, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Kawamoto, K. Preparation of the highly loaded and well-dispersed NiO/SBA-15 for methanation of producer gas. Fuel 2013, 103, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, E.M.; Kogler, M.; Bielz, T.; Klötzer, B.; Penner, S. In Situ FT-IR Spectroscopic Study of CO2 and CO Adsorption on Y2O3, ZrO2, and Yttria-Stabilized ZrO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 17666–17673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrovski, K.; Jung, K.T.; Bell, A.T. Investigation of CO and CO2 adsorption on tetragonal and monoclinic zirconia. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4297–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, B.B.; Ramos, I.R.; Ruiz, A.G. Interaction of Carbon Dioxide with the Surface of Zirconia Polymorphs. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3556–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Habazaki, H.; Yoshida, T.; Akiyama, E.; Kawashima, A.; Asami, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Komori, M.; Shimamura, K. Compositional dependence of the CO2 methanation activity of Ni/ZrO2 catalysts prepared from amorphous Ni-Zr alloy precursors. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 163, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habazaki, H.; Tada, T.; Wakuda, K.; Kawashima, A.; Asami, K.; Hashimoto, K. Corrosion, Electrochemistry and Catalysis of Metastable Metals and Intermetallics; Clayton, C.R., Hashimoto, K., Eds.; The Electrochemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 393. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, M.; Habazaki, H.; Asami, K.; Izumiya, K.; Hashimoto, K. Effect of tetragonal ZrO2 on the catalytic activity of Ni/ZrO2 catalyst prepared from amorphous Ni-Zr alloys. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Komori, M.; Akiyama, E.; Habazaki, H.; Kawashima, A.; Asami, K.; Hashimoto, K. CO2 methanation catalysts prepared from amorphous Ni-Zr-Sm and Ni-Zr-misch metal alloy precursors. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 267, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habazaki, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawashima, A.; Hashimoto, K. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni/(Zr-Sm)Ox catalysts. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 14, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, Z.M.; Lin, G.D.; Zhang, H.B. Highly efficient Ni-ZrO2 catalyst doped with Yb2O3 for co-methanation of CO and CO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 466, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Izumiyaa, K.; Kumagai, N.; Hashimoto, K. The effect of heat treatment on the performance of the Ni/(Zr-Sm oxide) catalysts for carbon dioxide methanation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8171–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Ren, J.; Miao, M.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, K. The catalytic methanation of coke oven gas over Ni-Ce/Al2O3 catalyst prepared by microwave heating: Effect of amorphous NiO formation. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 164, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, H.; Cui, K.; Jia, A.; Hu, G.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Role of surface Ni and Ce species of Ni/CeO2 catalyst in CO2 methanation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishcheva, M.V.; Potemkin, D.I.; Badmaev, S.D.; Snytnikov, P.V.; Paukshtis, E.A.; Sobyanin, V.A.; Parmon, V.N. On the mechanism of CO and CO2 methanation over Ni/CeO2 catalysts. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, B.; Rezaei, M.; Nemati Lay, E. Selective methanation of carbon monoxide in hydrogen rich stream over Ni/CeO2 nanocatalysts. J. Rare Earth 2015, 33, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, F.; Louis, B.; Roger, A.C. Methanation of carbon dioxide over nickel-based Ce0.72Zr0.28O2 mixed oxide catalysts prepared by sol–gel method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 369, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laosiripojana, N.; Assabumrungrat, S. Methane steam reforming over Ni/Ce–ZrO2 catalyst: Influences of Ce-ZrO2 support on reactivity, resistance toward carbon formation and intrinsic reaction kinetics. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 290, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Monte, R.; Fornasiero, P.; Kašpar, J.; Rumori, P.; Gubitosa, G.; Graziani, M. Pd/Ce0.6Zr0.4O2/Al2O3 as advanced materials for three-way catalysts Part 1. Catalyst characterisation, thermal stability and catalytic activity in the reduction of NO by CO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 24, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, R.; Krumeich, F.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Baiker, A. Flame-derived Pt/Ba/CexZr1−xO2: Influence of support on thermal deterioration and behavior as NOx storage-reduction catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, F.; Louis, B.; Kiwi-Minsker, L.; Roger, A.C. Effect of Ce/Zr composition and noble metal promotion on nickel based CexZr1−xO2 catalysts for carbon dioxide methanation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 392, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneda, M.; Shinoda, K.; Nagane, A.; Houshito, O.; Takagi, H.; Nakahara, Y.; Hiroe, K.; Fujitani, T.; Hamada, H. Catalytic performance of rhodium supported on ceria–zirconia mixed oxides for reduction of NO by propene. J. Catal. 2008, 259, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.P.; Silva, F.A.; Portela, L.S.; Mattos, L.V.; Noronha, F.B.; Hori, C.E. Effect of Ce/Zr ratio on the performance of Pt/CeZrO2/Al2O3 catalysts for methane partial oxidation. Catal. Today 2005, 107–108, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubaissy, B.; Pietraszek, A.; Roger, A.C.; Kiennemann, A. CO2 reforming of methane over Ce-Zr-Ni-Me mixed catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, M.H.; Gil Seo, J.; Min Cho, K.; Park, S.; Park, D.R.; Jung, J.C.; Song, I.K. Hydrogen production by auto-thermal reforming of ethanol over nickel catalysts supported on Ce-modified mesoporous zirconia: Effect of Ce/Zr molar ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 5052–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussa Aldana, P.A.; Ocampo, F.; Kobl, K.; Louis, B.; Thibault-Starzyka, F.; Daturi, M.; Bazina, P.; Thomas, S.; Roger, A.C. Catalytic CO2 valorization into CH4 on Ni-based ceria-zirconia. Reaction mechanism by operando IR spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2013, 215, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Insight into the reaction route of CO2 methanation: Promotion effect of medium basic sites. Catal. Commun. 2014, 45, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, S.T.; Calatayud, M.; Krause, A.O.I. Structure and Stability of Formates and Carbonates on Monoclinic Zirconia: A Combined Study by Density Functional Theory and Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16096–16102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizio, M.; Albarazi, A.; Cavadias, S.; Amouroux, J.; Galvez, M.E.; Da Costa, P. Hybrid plasma-catalytic methanation of CO2 at low temperature over ceria zirconia supported Ni catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11584–11592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sakata, Y.; Arai, T.; Domen, K.; Maruya, K.; Onishi, T. Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide adsorption on cerium oxide studied by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Part 1.Formation of carbonate species on dehydroxylated CeO2, at room temperature. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1989, 85, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mains, G.J.; White, J.M. Infrared and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study of CO and CO2 on Pt/CeO2. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 5931–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwood, M.; Doepper, R.; Renken, A. In-situ surface and gas phase analysis for kinetic studies under transient conditions the catalytic hydrogenation of CO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 151, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prairie, M.R.; Highfield, J.G.; Renken, A. Diffuse-reflectance FTIR spectroscopy for kinetic and mechanistic studies of CO2 hydrogenation in a continuous recycle reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prairie, M.R.; Renken, A.; Highfield, J.G.; Ravindranathan Thampi, K.; Grätzel, M. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of CO2 methanation on supported ruthenium. J. Catal. 1991, 129, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, C.; Wokaun, A. CO2 hydrogenation over Nickel/Zirconia catalysts from amorphous precursors: On the mechanism of methane formation. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 6341–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, C.; Wokaun, A.; Baiker, A. Surface species in CO2 methanation over amorphous palladium/zirconia catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. 1991, 69, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, J.J.; Carrizosa, I.; Odriozola, J.A. HCOOH hydrogenation over lanthanide-oxide-promoted Rh/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Surf. 1993, 68, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Morimoto, K.; Ishizawa, N.; Yoshimura, M. Diffusionless Tetragonal–Cubic Transformation Temperature in Zirconia–Ceria Solid Solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 2865–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Morimoto, K.; Ishizawa, N.; Yoshimura, M. Zirconia–Ceria Solid Solution Synthesis and the Temperature–Time–Transformation Diagram for the 1:1 Composition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 76, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Ohtake, K.; Arashi, H.; Kakihana, M.; Yoshimura, M. Determination of cubic-tetragonal phase boundary in Zr1−xYxO2−x/2 solid solutions by Raman spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 7603–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Arashi, H.; Kakihana, M.; Yoshimura, M. Raman Scattering Study of Cubic–Tetragonal Phase Transition in Zr1−xCexO2 Solid Solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Sun, T.; Gao, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. CO2 methanation on Ni/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 catalysts for the production of synthetic natural gas. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2014, 123, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.I.; Kim, D.H.; Yezerets, A.; Andersen, P.; Kung, H.H.; Kung, M.C. Effect of Preparation Method and Redox Treatment on the Reducibility, and Structure of Supported Ceria-Zirconia Mixed Oxide. J. Catal. 2002, 209, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Reverse water gas shift reaction over Co-precipitated Ni-CeO2 catalysts. J. Rare Earth 2008, 26, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.S.; Potdar, H.S.; Jun, K.W.; Kim, J.W.; Oh, Y.S. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni incorporated into Ce-ZrO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 276, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Shinomiya, H.; Izumiya, K.; Kumagai, N.; Habazaki, H.; Hashimoto, K. CO2 methanation of Ni catalysts supported on tetragonal ZrO2 doped with Ca2+ and Ni2+ ions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 8347–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkas, N.; Amirian, G.; Zhong, Z.; Teo, J.; Gofer, Y.; Gedanken, A. Methanation of Carbon Dioxide on Ni Catalysts on Mesoporous ZrO2 Doped with Rare Earth Oxides. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wen, J.; Chu, W.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni/ZrO2-Al2O3 catalysts: Effects of ZrO2 promoter and preparation method of novel ZrO2-Al2O3 carrier. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2011, 20, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Wang, K.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Han, C.; Liu, J.; Tong, M.; Liang, X.; et al. Mesoporous zirconia-modified clays supported nickel catalysts for CO and CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18894–18907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, S.; Mebrahtu, C.; Giglio, E.; Deorsola, F.; Bensaid, S.; Perathoner, S.; Pirone, R.; Centi, G. Catalytic performance of γ-Al2O3-ZrO2-TiO2-CeO2 composite oxide supported Ni-based catalysts for CO2 methanation. Int. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4451–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Qian, G.; Xu, Z.P.; Chen, C.; Liu, Q. Reinvestigation of dehydration and dehydroxylation of hydrotalcite-like compounds through combined TG-DTA-MS analyses. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 10768–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, S.; Barbera, K.; Giglio, E.; Deorsola, F.; Bensaid, S.; Perathoner, S.; Pirone, R.; Centi, G. Synthesis, characterization and activity pattern of Ni-Al Hydrotalcite catalysts in CO2 methanation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8299–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y. Unique catalysis of Ni-Al hydrotalcite derived catalyst in CO2 methanation: Cooperative effect between Ni nanoparticle and a basic support. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrovska, M.; Edreva-Kardjieva, R.; Crisan, D.; Tzvetkov, P.; Shopska, M.; Shtereva, I. Ni-Al layered double hydroxides as catalyst precursors for CO2 removal by methanation. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2012, 105, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, D.; Debek, R.; Motak, M.; Grzybek, T.; Galvez, M.E.; Da Costa, P. Novel Ni-La-hydrotalcite derived catalysts for CO2 methanation. Catal. Commun. 2016, 83, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Chu, W. Cerium promoted nano nickel catalysts Ni-Ce/CNTs and Ni-Ce/Al2O3 for CO2 methanation. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2014, 151, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Dai, Y.; He, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y. A novel W-doped Ni-Mg mixed oxide catalysts for CO2 methanation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 196, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkache, R.; Fechete, I.; Maamache, M.; Bernard, M.; Turek, P.; Al-Dalama, K.; Garin, F. 3D ordered mesoporous Fe-KIT-6 catalysts for methylcyclopentane (MCP) conversion and carbon dioxide (CO2) hydrogeneation for energy and environmental applications. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 504, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Kodama, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Tamaura, Y. Preparation and CO2 Methanation Activity of an ultrafine Ni(II) Ferrite Catalyst. J. Catal. 1996, 164, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, K.; Kodama, T.; Tabata, M.; Yoshida, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Adsorption of CO2 on oxygen-deficient magnetite: Adsorption enthalpy and adsorption isotherm. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 2771–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nishizawa, K.; Tabata, M.; Abe, H.; Kodama, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Methanation of CO2 with H2-reduced magnetite. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, K.; Kato, H.; Mimori, K.; Yoshida, T.; Hasegawa, N.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Methanation of carbon deposited directly from CO2 on rhodium-bearing activated magnetite. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Nishizawa, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tamaura, Y. Methanation reactivity of carbon deposited directly from CO2 on to the oxygen-deficient magnetite. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 5481–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Kato, H.; Kodama, T.; Chang, S.G.; Hesegawa, N.; Tamaura, Y. Methanation of CO2 on H2-reduced Ni(II)-or Co(II)-bearing ferrites at 200 °C. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 6227–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Sano, T.; Wada, Y.; Tamaura, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Tsuji, T.; Miyazaki, S. Methanation of CO2 with the oxygen-deficient Ni(II)-ferrite under dynamic conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 6350–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Methanation of CO2 using ultrafine NixFe3−xO4. Energy 1997, 22, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y.; Hurue, T.; Hayashida, T.; Ogawa, K. Carbon recycling system through methanation of CO2 in flue gas in LNG power plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 1997, 38, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligaard, T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Dahl, S.; Matthiesen, J.; Christensen, C.H.; Sehested, J. The Brønsted–Evans–Polanyi relation and the volcano curve in heterogeneous catalysis. J. Catal. 2004, 224, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.P.; Bligaard, T.; Kustov, A.; Larsen, K.E.; Greeley, J.; Johannessen, T.; Christensen, C.H.; Nørskov, J.K. Toward computational screening in heterogeneous catalysis: Pareto-optimal methanation catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 239, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehesteda, J.; Larsen, K.E.; Kustov, A.L.; Frey, A.M.; Johannessen, T.; Bligaard, T.; Andersson, M.P.; Nørskov, J.K.; Christensen, C.H. Discovery of technical methanation catalysts based on computational Screening. Top. Catal. 2007, 45, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, A.L.; Frey, A.M.; Larsen, K.E.; Johannessen, T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Christensen, C.H. CO methanation over supported bimetallic Ni-Fe catalysts: From computational studies towards catalyst optimization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 320, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, G.; Knozinger, H.; Schüth, F.; Weitkamp, J. Handbook of Heterogenous Catalysis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dumesic, J.A.; Rudd, D.F.; Aparicio, L.M.; Rekoske, J.E.; Treviño, A.A. The Microkinetics of Heterogeneous Catalysis; ACS Professional Reference Book; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Boudart, M.; Djega-Mariadassou, G. Kinetics of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions; Pricenton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Nørskov, J.K.; Bligaard, T.; Logadottir, A.; Bahn, S.; Hansen, L.B.; Bollinger, M.; Bengaard, H.; Hammer, B.; Sljivancanin, Z.; Mavrikakis, M.; et al. Universality in Heterogeneous Catalysis. J. Catal. 2002, 209, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linic, S.; Barteau, M.A. Control of Ethylene Epoxidation Selectivity by Surface Oxametallacycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4034–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, K.; Frenkel, D.; Scheffler, M. The Steady State of Heterogeneous Catalysis, Studied by First-Principles Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 116105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honkala, K.; Hellman, A.; Remediakis, I.N.; Logadottir, A.; Carlsson, A.; Dahl, S.; Christensen, C.H.; Nørskov, J.K. Ammonia Synthesis from First-Principles Calculations. Science 2005, 307, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareto, V.; Montesano, A.; Zanni, A.; Bruni, L.; Chipman, J.S.; McLure, M. Manual of Political Economy: A Critical and Variorum Edition, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bligaard, T.; Jóhannesson, G.H.; Ruban, A.V.; Skriver, H.L.; Jacobsen, K.W.; Nørskov, J.K. Pareto-optimal alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 4527–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Xu, W.C.; Ishidzuki, T.; Ogasawara, N.; Imai, J.; Kobayashi, K. Mechanochemical activation of catalysts for CO2 methanation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 137, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaccato, K.; Carhart, R.; Hagemeyer, A.; Lesik, A.; Strasser, P.; Volpe, A.F., Jr.; Turner, H.; Weinberg, H.; Grasselli, R.K.; Brooks, C. Competitive CO and CO2 methanation over supported noble metal catalysts in high throughput scanning mass spectrometer. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 296, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, Z. Insights into the mechanisms of CO2 methanation on Ni(111) surfaces by density functional theory. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, D.J. Methanation of Carbon Dioxide. Mc.S. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus, A.L.; Gaidai, N.A.; Nekrasov, N.V.; Tishkova, L.A.; Agafonov, Y.A.; Myshenkova, T.N. The mechanism of carbon dioxide hydrogenation on copper and nickel catalysts. Pet. Chem. 2007, 47, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Ma, S.S.K.; Wang, X.; Su, H.; Chan, S.H. Catalysis mechanism of CO2 and CO methanation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4048–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.J.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.B.; Park, D.H.; Huh, D.S. Adsorbed carbon formation and carbon hydrogenation for CO2 methanation on the Ni(111) surface: ASED-MO study. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, 26, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Mechanistic aspects of the selective methanation of CO over Ru/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Today 2012, 181, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medsforth, S. CLXIX—Promotion of catalytic reactions: Part I. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1923, 123, 1452–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, C.; Wokaun, A.; Baiker, A. On the mechanism of CO and CO2 hydrogenation reactions on zirconia-supported catalysts: A diffuse reflectance FTIR study: Part II. Surface species on copper/zirconia catalysts: Implications for methanoi synthesis selectivity. J. Mol. Catal. 1990, 63, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, S.J.; Yoo, Y.D.; Prasad, P.S.S.; Lim, H.J.; Byun, C.D. Co-methanation of CO and CO2 on the Nix-Fe1−x/Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of Fe contents. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 2282–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, J.; Hong, U.G.; Jung, J.C.; Koh, D.J.; Lim, H.; Byun, C.; Song, I.K. Hydrogenation of carbon monoxide to methane over mesoporous nickel-M-alumina (M = Fe, Ni, Co, Ce, and La) xerogel catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Hong, U.G.; Lee, J.; Seo, J.G.; Baik, J.H.; Koh, D.J.; Lim, H.; Song, I.K. Methanation of carbon dioxide over mesoporous Ni-Fe-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by a coprecipitation method: Effect of precipitation agent. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, J.; Hong, U.G.; Baik, J.H.; Koh, D.J.; Lim, H.; Song, I.K.S. Methanation of carbon dioxide over mesoporous Ni-Fe-Ru-Al2O3 xerogel catalysts: Effect of ruthenium content. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyscinski, J.; Schildhauer, T.J.; Biollaz, S.M.A. Employing Catalyst Fluidization to Enable Carbon Management in the Synthetic Natural Gas Production from Biomass. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Selective methanation of CO over supported Ru catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.D.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.C. Recent progress in selective CO removal in a H2-rich stream. Catal. Today 2009, 139, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snel, R. Supported iron catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Influence of the preparation method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Wada, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Sano, T.; Tamaura, Y. CO2 decomposition by metallic phase on oxygen-deficient Ni(II)-bearing ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1996, 15, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, J.W.; Xu, Z. Role of complexing agents in ferrite formation under ambient conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 4689–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondinone, A.J.; Samia, A.C.S.; Zhang, Z.J. A chemometric approach for predicting the size of magnetic spinel ferrite nanoparticles from the synthesis conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 7919–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Yue, Z.X.; Zhou, J. Synthesis and high-frequency magnetic properties of sol-gel derived Ni-Zn ferrite forsterite composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 210, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaura, Y.; Tahata, M. Complete reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon using cation-excess magnetite. Nature 1990, 346, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Kodama, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Decomposition of carbon dioxide to carbon by hydrogen-reduced Ni(II)-bearing ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 5689–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Nishida, Y.; Kodama, T.; Mimori, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tamaura, Y. CO2 decomposition with oxygen-deficient Mn(II) ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Akanuma, K.; Nishizawa, K.; Mimori, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Reactivity of oxygen-deficient Mn(II)-bearing ferrites (MnxFe3−xO4−δ, 0 ≤ x ≥ δ > 0) toward CO2 decomposition to carbon. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 6753–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Tabata, M.; Sano, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. XRD and Mössbauer Studies on Oxygen-Deficient Ni(II)-Bearing Ferrite with a High Reactivity for CO2 Decomposition to Carbon. J. Solid State Chem. 1995, 120, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.S.; Adhikari, A.K.; Tsai, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Chien, T.T.; Tsai, H.B. Synthesis and characterization of nickel ferrite nanocatalysts for CO2 decomposition. Catal. Today 2011, 174, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Akanuma, K.; Togawa, T.; Tsuji, M.; Tamaura, Y. Mössbauer study of oxygen-deficient ZnII-bearing ferrites (ZnxFe3−xO4−δ, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1) and their reactivity toward CO2 decomposition to carbon. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, P.P.; Vadera, S.R.; Patra, M.K.; Ghosh, N.N. Synthesis and characterization of pure single phase Ni-Zn ferrite nanopowders by oxalate based precursor method. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Choi, S.C.; Jung, K.D.; Han, S.H. Mechanism of M Ferrites (M = Cu and Ni) in the CO2 decomposition reaction. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhei, C.; Mathisen, K.; Safonova, O.; van Beek, W.; Nicholson, D.G. Decomposition of Carbon Dioxide at 500 °C over Reduced Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, and Zinc Ferrites: A Combined XANES−XRD Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19568–19577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhei, C.; Mathisen, K.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Nicholson, D. Decomposition of Carbon Dioxide over the Putative Cubic Spinel Nanophase Cobalt, Nickel, and Zinc Ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 6531–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C. Nickel supported on iron-bearing olivine for CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 12910–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczynski, D.; Courson, C.; Bedel, L.; Kiennemann, A.; Guille, J. Characterization of Ni-Fe/MgO/Olivine catalyst for fluidized bed steam gasification of biomass. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. Nickel supported on modified olivine catalyst for steam reforming of biomass gasification tar. Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Wang, J.; Han, C.; Liang, X.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Metal (Fe, Co, Ce or La) doped nickle catalyst supported on ZrO2 modified mesoporous clays for CO and CO2 methanation. Fuel 2016, 183, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Deo, G. Effect of support on the catalytic activity of Ni-Fe catalysts for CO2 methanation reaction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project Homepage—HELMETH. Available online: http://www.helmeth.eu/index.php/project (accessed on 16 December 2016).
- Project Homepage—BioCat Project, Electrochaea. Available online: http://www.electrochaea.com/technology/ (accessed on 16 December 2016).
- Kristjanpoller, F.; Crespo, A.; Barbera, L.; Viveros, P. Biomethanation plant assessment based on reliability impact on operational effectiveness. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).