Reductive Amination of Cyclohexanone via Bimetallic Rh-Ni Catalysts: A Pathway to Improved Catalytic Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
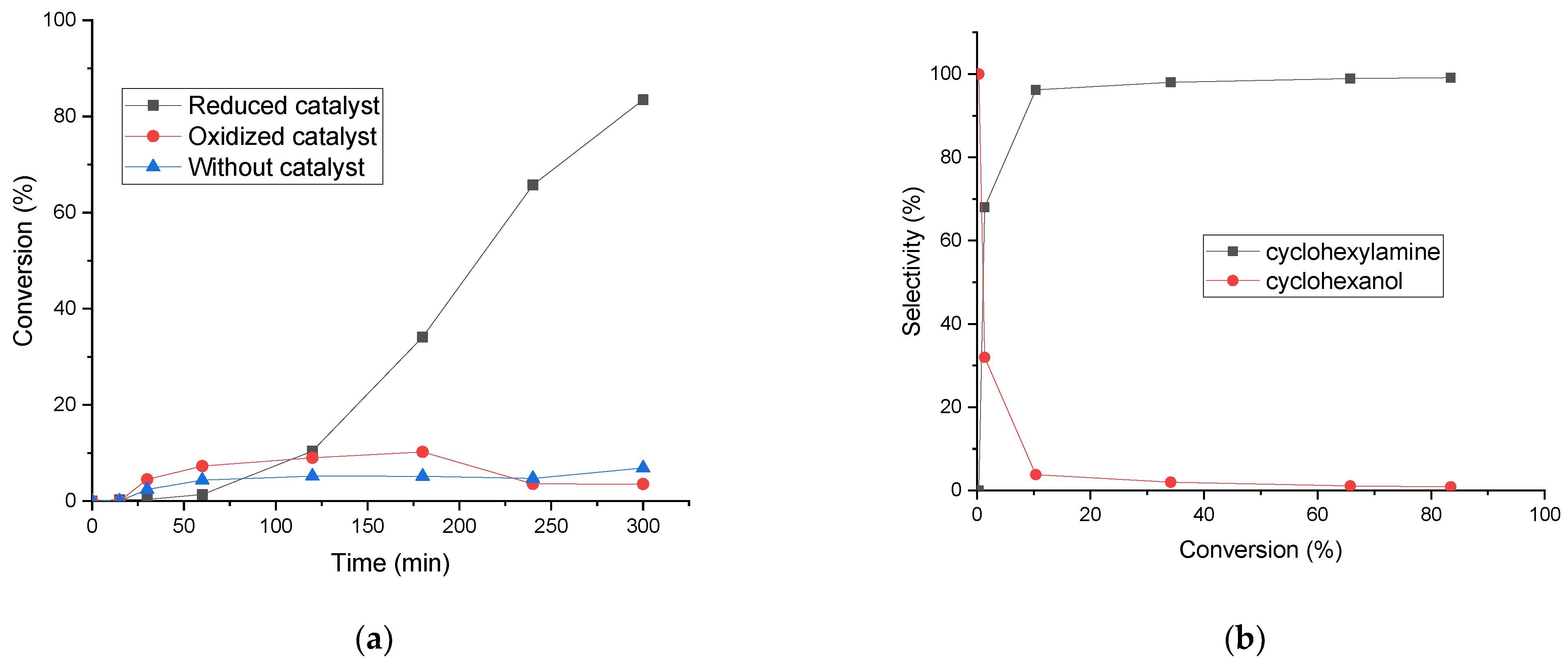
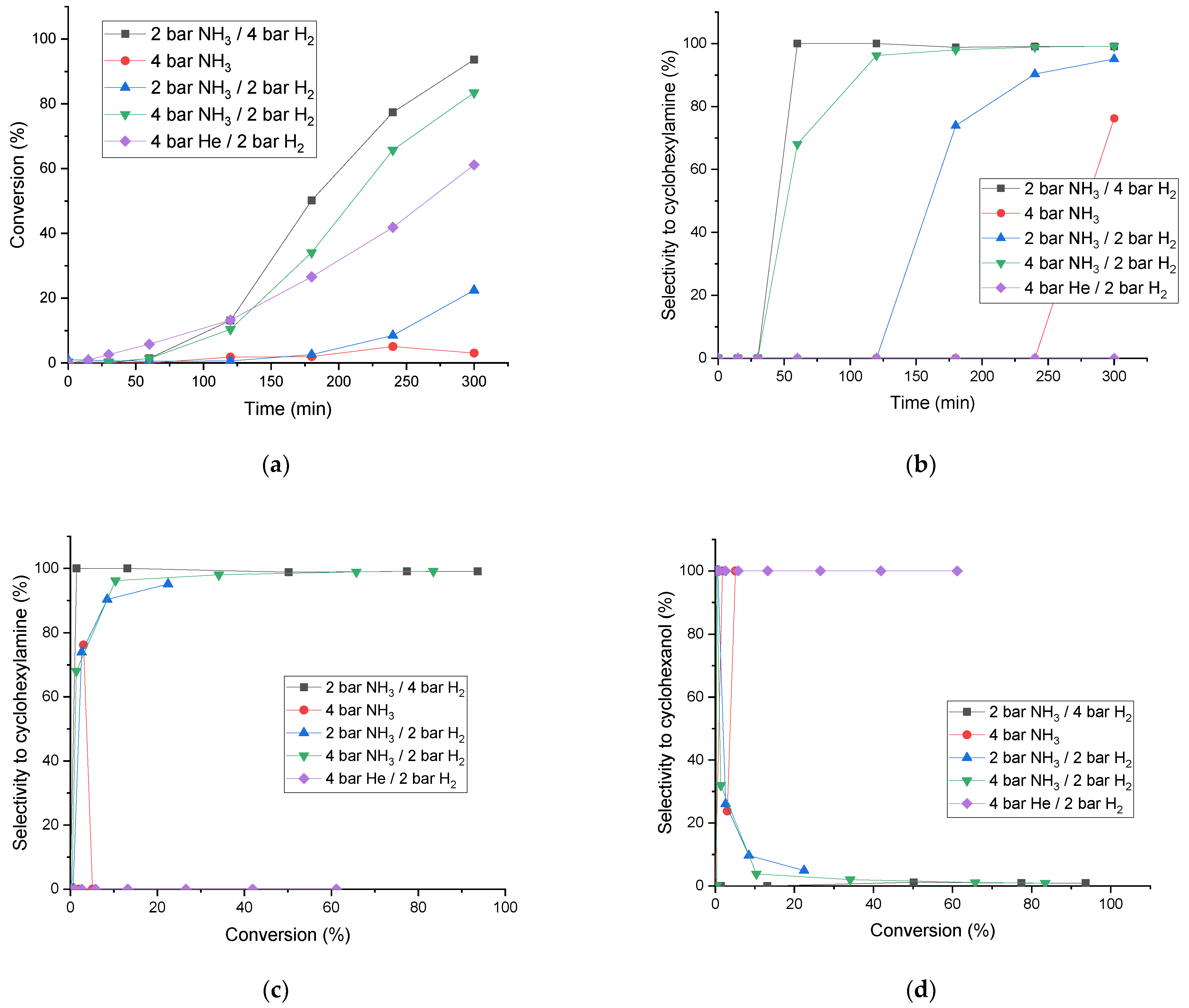
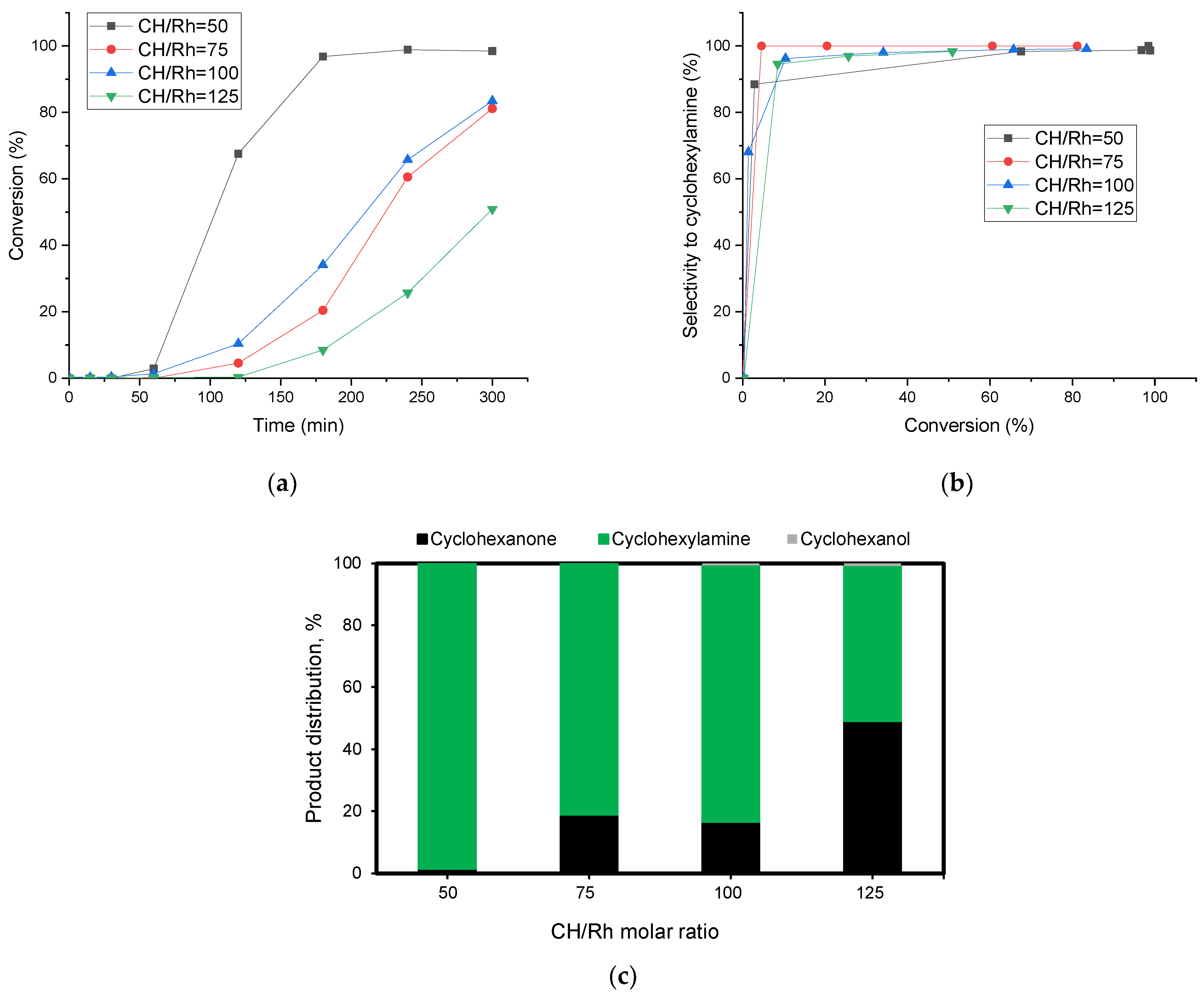
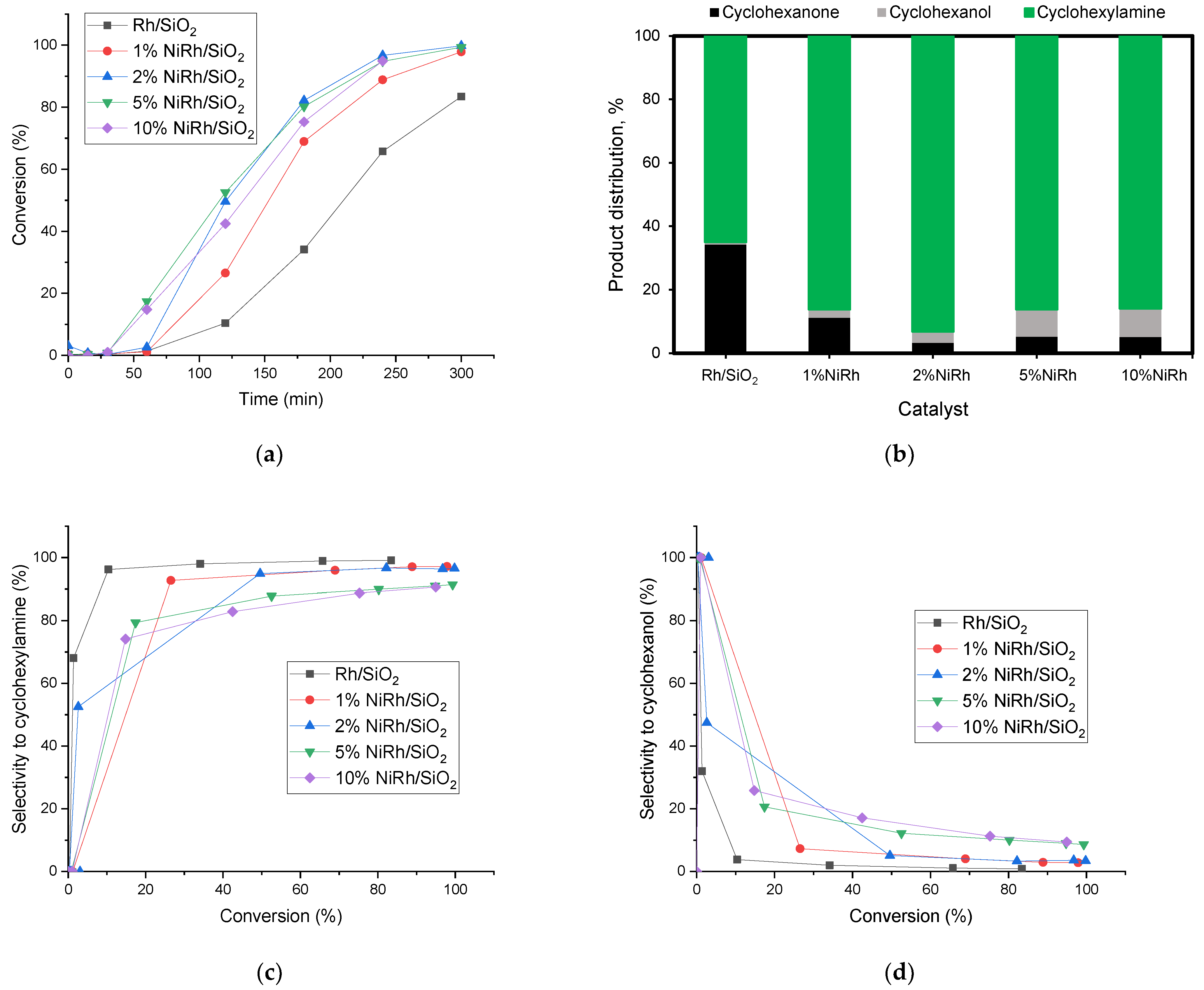
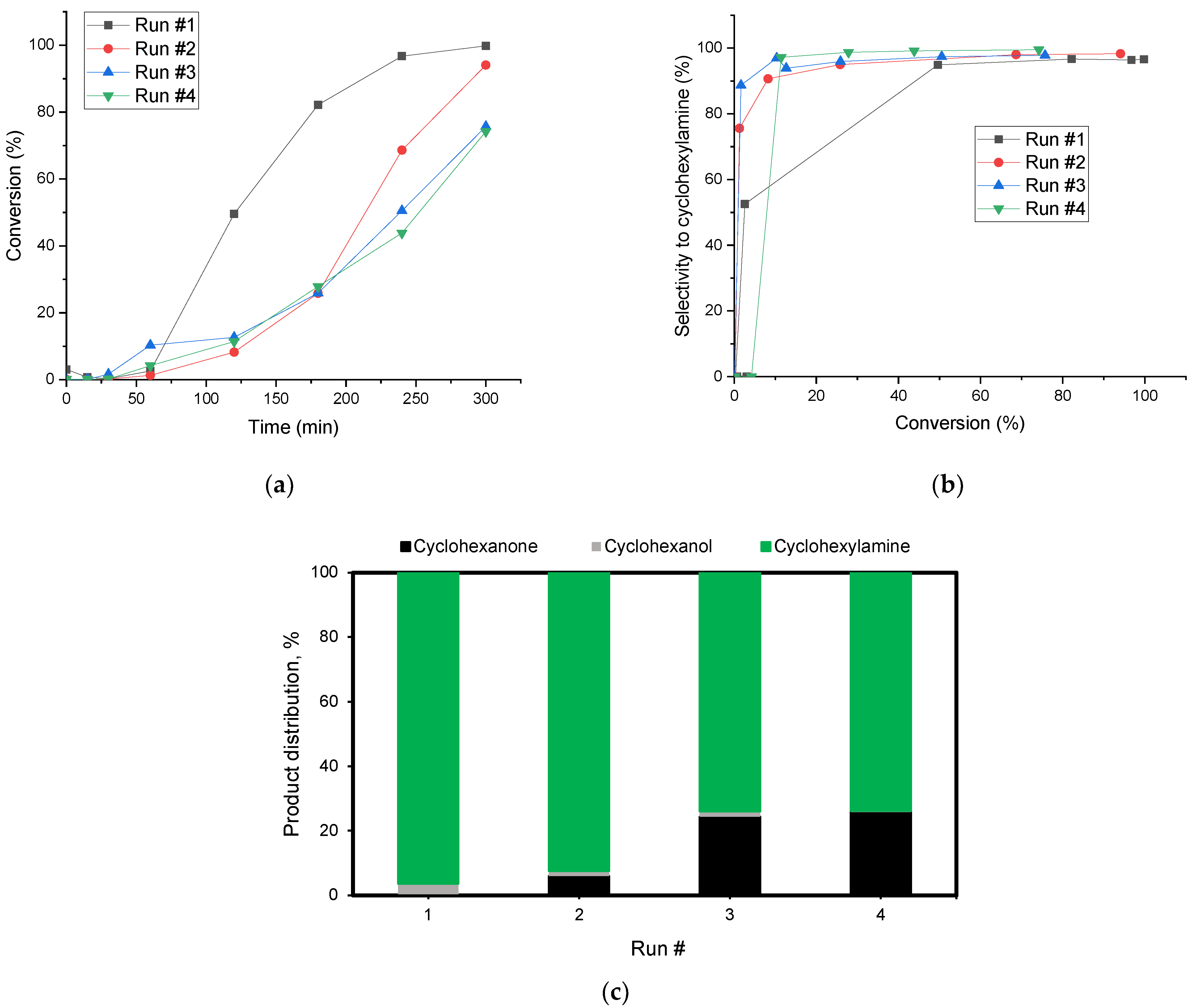
2.2. Reductive Amination
3. Materials and Methods
Characterization of Catalysts and Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CH | Cyclohexanone |
| XPS | X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| NH3-TPD | Temperature-Programmed Desorption of Ammonia |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| HAADF | High-Angle Annular Dark-Field Imaging |
| STEM | Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| H2-TPR | Temperature-Programmed Reduction Using H2 |
| B.E.T. | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| BJH | Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda |
References
- Konofal, E. From past to future: 50 years of pharmacological interventions to treat narcolepsy. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2024, 241, 173804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhao, D.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y. Advances in biosynthesis of chiral amide herbicides and the key enzymes: Dimethenamid-P and S-metolachlor as case studies. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2025, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, M.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Ma, X.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y. Portable fluorogenic probe for monitoring volatile amine vapour and food spoilage. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, T.M.; Furtado, I. Expression of carotenoid pigments of haloarchaeal cultures exposed to aniline. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Dhanda, T. Cyclohexylamine an effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 0.1 N H2SO4: Experimental and theoretical study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Direct catalytic asymmetric synthesis of α-chiral primary amines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6141–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, G.; Kunnas, P.; de Jonge, N. General synthesis of primary amines via reductive amination employing a reusable nickel catalyst. Nat. Catal. 2018, 2, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.; Seayad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Beller, M. Synthesis of primary amines: First homogeneously catalyzed reductive amination with ammonia. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, K.; Wei, Z.; Chandrashekhar, V.; Jiao, H.; Beller, M.; Jagadeesh, R. General and selective synthesis of primary amines using Ni-based homogeneous catalysts. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; He, J.; Oishi, T.; Mizuno, N. The ‘borrowing hydrogen strategy’ by supported ruthenium hydroxide catalysts: Synthetic scope of symmetrically and unsymmetrically substituted amines. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 7199–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, A.; Claes, L.; Geukens, I.; Stassen, I.; De Vos, D.E. Alcohol amination with heterogeneous ruthenium hydroxyapatite catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 469, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingen, D.; Lutz, M.; Vogt, D. Mechanistic study on the ruthenium-catalyzed direct amination of alcohols. Organometallics 2014, 33, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähn, S.; Imm, S.; Neubert, L.; Zhang, M.; Neumann, H.; Beller, M. The catalytic amination of alcohols. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Aho, A.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kumar, N.; Oliva, H.; Murzin, D.Y. Direct amination of dodecanol over noble and transition metal supported silica catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12878–12887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, H.; Tang, C.; Xia, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Effective synthesis of 5-amino-1-pentanol by reductive amination of biomass-derived 2-hydroxytetrahydropyran over supported Ni catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coeck, R.; Meeprasert, J.; Li, G.; Altantzis, T.; Bals, S.; Pidko, E.A.; De Vos, D.E. Gold and silver-catalyzed reductive amination of aromatic carboxylic acids to benzylic amines. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 7672–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Honjo, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Mitsudome, T.; Mizugaki, T. Reductive amination of carboxylic acids under H2 using a heterogeneous Pt–Mo catalyst. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y. Atomically dispersed co–s–n active sites anchored on hierarchically porous carbon for efficient catalytic hydrogenation of nitro compounds. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 5786–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, D.; Ferretti, F.; Scharnagl, F.; Beller, M. Reduction of nitro compounds using 3d-non-noble metal catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2611–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, S.; Peters, J.; Maschmeyer, T. The Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones and the Hydrogenation of Nitriles: Mechanistic Aspects and Selectivity Control. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2002, 344, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal, D.; Bhanage, B. Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed hydrogenation of nitriles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jv, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Q.; Du, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Efficient and mild reductive amination of carbonyl compounds catalyzed by dual-function palladium nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianga, J.; Kopplin, N.; Hülsmann, J.; Vogt, D.; Seidensticker, T. Rhodium-catalysed reductive amination for the synthesis of tertiary amines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschtowski, S.; Kadar, C.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Hamel, C. Kinetic modeling of rhodium-catalyzed reductive amination of undecanal in different solvent systems. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2020, 92, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.S. Industrial processes for manufacturing amines. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 221, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhu, C.; Aneeja, T.; Anilkumar, G. Advances and perspectives in the rhodium catalyzed reductive amination reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2022, 965–966, 122332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; You, K.; Li, W.; Xu, W.; Zhao, F.; Yan, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, H. Highly-dispersed Ni3Fe alloy nanoparticles anchored on MgAl-LDO for efficient catalytic amination of KA-oil to cyclohexylamine. J. Catal. 2024, 430, 115315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Niederer, J.; Keller, M.; Hölderich, W. Amination of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol/cyclohexanone in the presence of ammonia and hydrogen using copper or a group VIII metal supported on a carrier as the catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 197, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beepala, S.; Mitta, H.; Sk, H.; Balla, P.; Chary, K. Reductive amination of cyclohexanol/cyclohexanone to cyclohexylamine using SBA-15 supported copper catalysts. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirumakki, S.; Papadaki, M.; Chary, K.; Nagaraju, N. Reductive amination of cyclohexanone in the presence of cyclohexanol over zeolites Hβ and HY. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 321, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Manrique, R.; Ortega, M.; Castillo-Puchi, F.; Fraile, J.E.; Jiménez, R. One-pot amination of cyclohexanone-to-secondary amines over carbon-supported Pd: Unraveling the reaction mechanism and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N. A remarkable solvent effect on reductive amination of ketones. Mol. Catal. 2018, 454, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Manrique, R.; Castillo-Puchi, F.; Ortega, M.; Bertiola, C.; Jiménez, R.; Pérez, A.J. Experimental protocol for the study of One-pot amination of Cyclohexanone-to-secondary amines over Carbon-supported Pd. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobova, E.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Pestryakov, A.; Pakrieva, E.; Pascual, L.; Smeds, A.; Rahkila, J.; Sandberg, T.; Peltonen, J.; Murzin, D.Y. Reductive Amination of Ketones with Benzylamine Over Gold Supported on Different Oxides. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 3432–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, T.; Kempe, R. Transition-metal-catalyzed reductive amination employing hydrogen. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9583–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coeck, R.; De Vos, D.E. One-pot reductive amination of carboxylic acids: A sustainable method for primary amine synthesis. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5105–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Morales, K.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Chimentão, R.; Murzin, D. direct reductive amination of hmf to 5-(aminomethyl)-2-furanmethanol using supported iridium-based catalysts. ChemPlusChem 2024, 89, e202400453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.; Cui, X.; Shi, F.; Deng, Y. Palladium catalyzed N-alkylation of amines with alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Takamura, R.; Takei, T.; Akita, T.; Haruta, M. Support effects of metal oxides on gold-catalyzed one-pot N-alkylation of amine with alcohol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 413–414, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.R.; Touchy, A.S.; Rashed, N.; Ting, K.W.; Siddiki, H.; Toyao, T.; Maeno, Z.; Shimizu, K. N-Methylation of amines and nitroarenes with methanol using heterogeneous platinum catalysts. J. Catal. 2019, 371, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Xu, G. Selective N-Monomethylation of amines and nitroarenes using methanol over an encapsulated iridium nanocatalyst. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2019, 8, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Xie, S.; Bahri, M.; Ersen, O.; Yan, Z.; Kusema, B.T.; Pera-Titus, M.; Khodakov, A.Y.; Ordomsky, V.V. Catalyst deactivation for enhancement of selectivity in alcohols amination to primary amines. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 5986–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, T.; Tomkins, P.; De Vos, D.E. Direct liquid-phase phenol-to-aniline amination using Pd/C. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2519–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.P.; Han, P.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, S.; Yan, N. Insight into the roles of ammonia during direct alcohol amination over supported Ru catalysts. J. Catal. 2021, 399, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Dong, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. From cyclohexanol to aniline: A novel dehydrogenation-amination-dehydrogenation strategy based on Pt-based catalyst. J. Catal. 2024, 429, 115233, Erratum in J. Catal. 2025, 446, 116085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.I.; Imaiida, N.; Kon, K.; Siddiki, H.; Satsuma, A. Heterogeneous Ni catalysts for N-alkylation of amines with alcohols. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, K.V.R.; Seela, K.K.; Naresh, D.; Ramakanth, P. Characterization and reductive amination of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone over Cu/ZrO2 catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zeng, Y.; Yao, E.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y. One-step reductive amination of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-bis(aminomethyl)furan over Raney Ni. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 2308–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mizuno, N. Selective synthesis of secondary amines via N-alkylation of primary amines and ammonia with alcohols by supported copper hydroxide catalysts. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 1182–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lou, X.B.; Ni, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; He, H.Y.; Fan, K.N. Efficient and clean gold-catalyzed one-pot selective N-alkylation of amines with alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 13965–13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, P.; Eller, K.; Henkes, E.; Rossbacher, R.; Höke, H. Amines, aliphatic. Ullmann’s Encycl. Ind. Chem. 2015, 1, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Williams, R.T. Physisorption Hysteresis Loops and the Characterization of Nanoporous Materials. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2004, 22, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Santo, V.; Gallo, A.; Naldoni, A.; Guidotti, M.; Psaro, R. Bimetallic heterogeneous catalysts for hydrogen production. Catal. Today 2012, 197, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguero-Márquez, G.A.; Lunagómez-Rocha, M.A.; Cervantes-Uribe, A.; Del Angel, G.; Rangel, I.; Torres-Torres, J.G.; González, F.; Godavarthi, S.; Arevalo-Perez, J.C.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.E.; et al. Photodegradation of 2,4-D (dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) with Rh/TiO2: Comparative study with other noble metals (Ru, Pt, and Au). RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25711–25721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, E.-H.; Ke, W. Effects of thiosulfate and dissolved oxygen on crevice corrosion of Alloy 690 in high-temperature chloride solution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Aho, A.; Saloranta, T.; Eränen, K.; Warna, J.; Leino, R.; Murzin, D.Y. Direct amination of dodecanol with NH3 over heterogeneous catalysts. Catalyst screening and kinetic modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wang, P.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, X. An Efficient Method for the Production of Cyclohexylamine from Cyclohexanone and Ammonia over Cu-Cr-La/γ-Al2O3. J. Korean Chem. Soc. 2015, 59, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

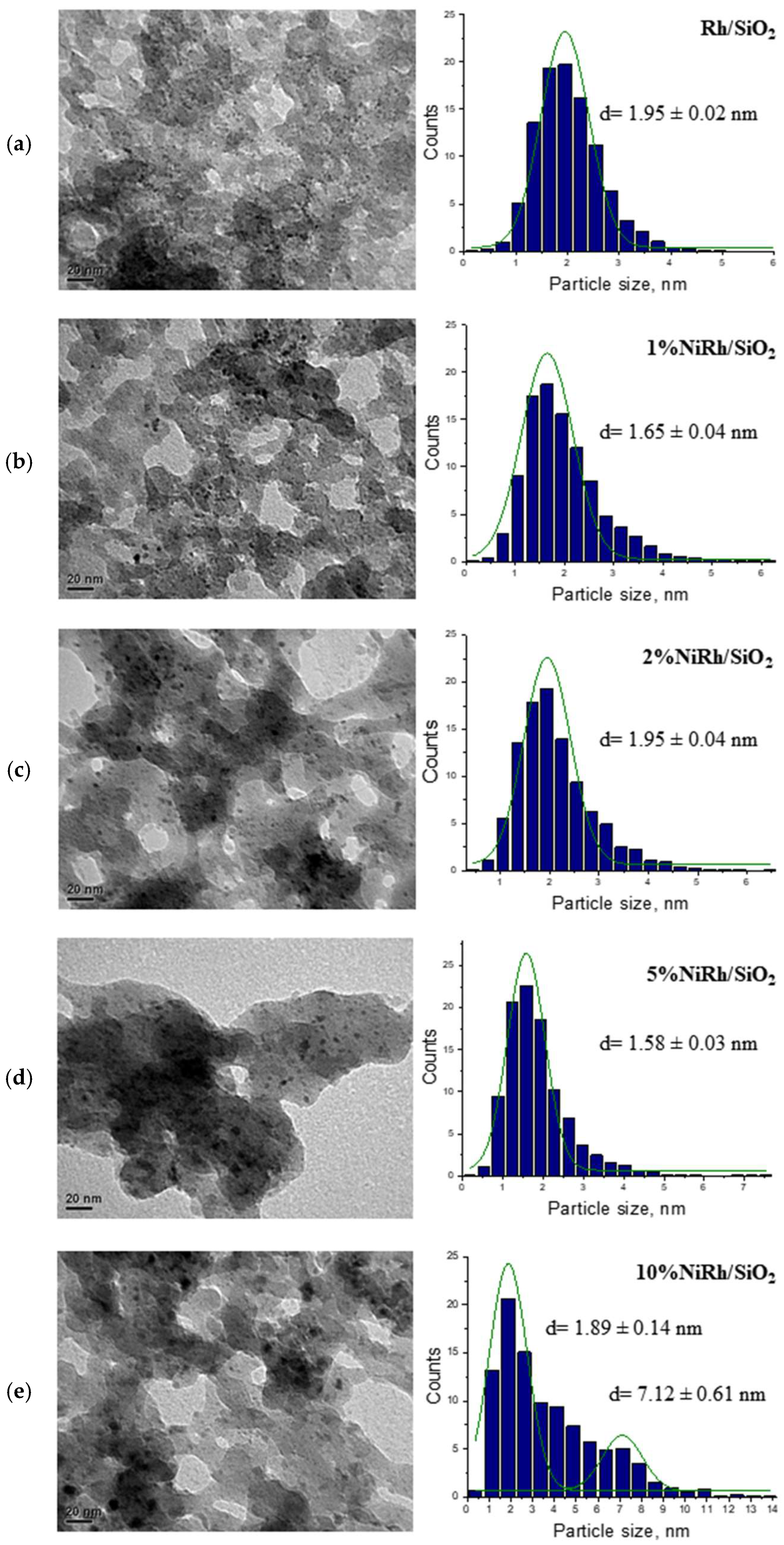
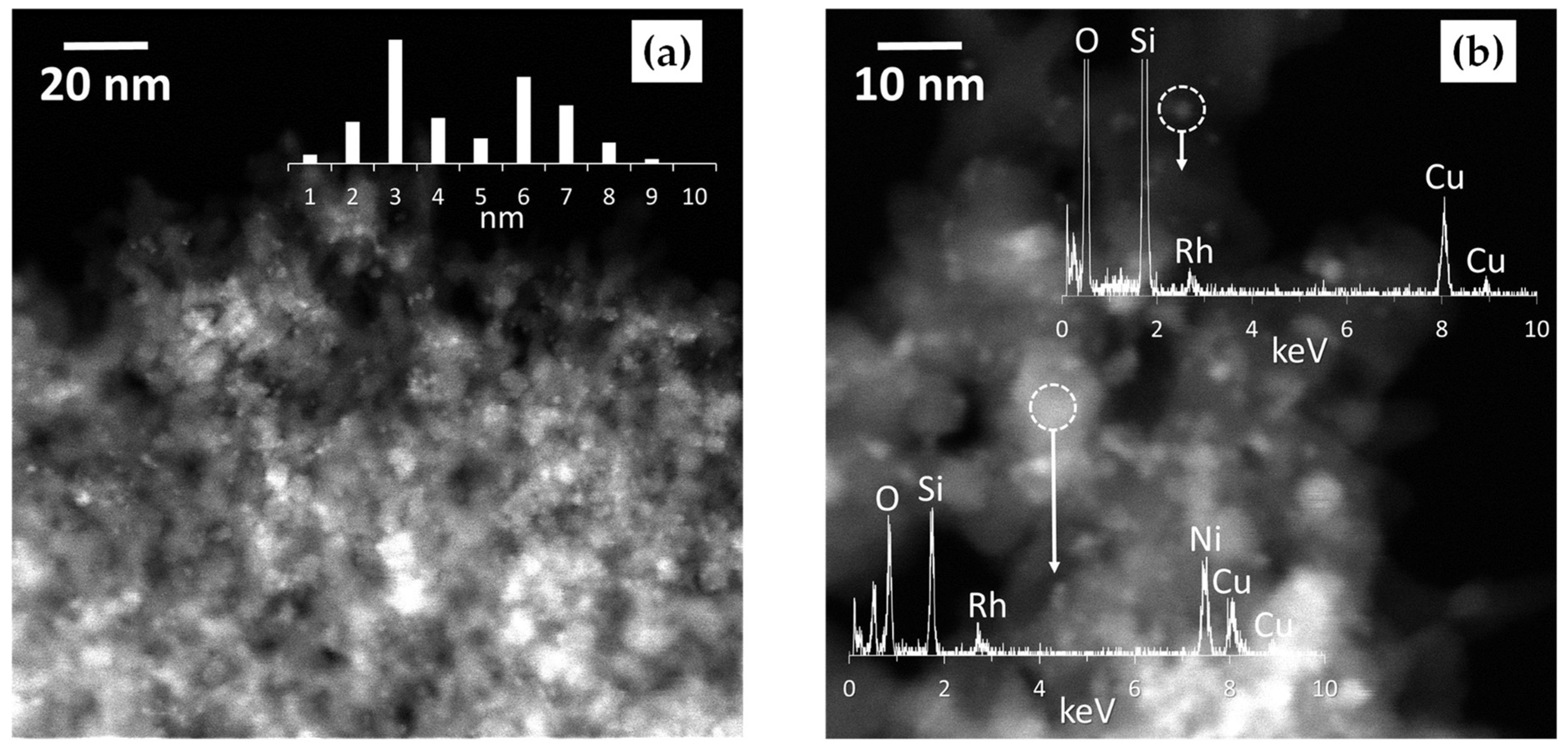
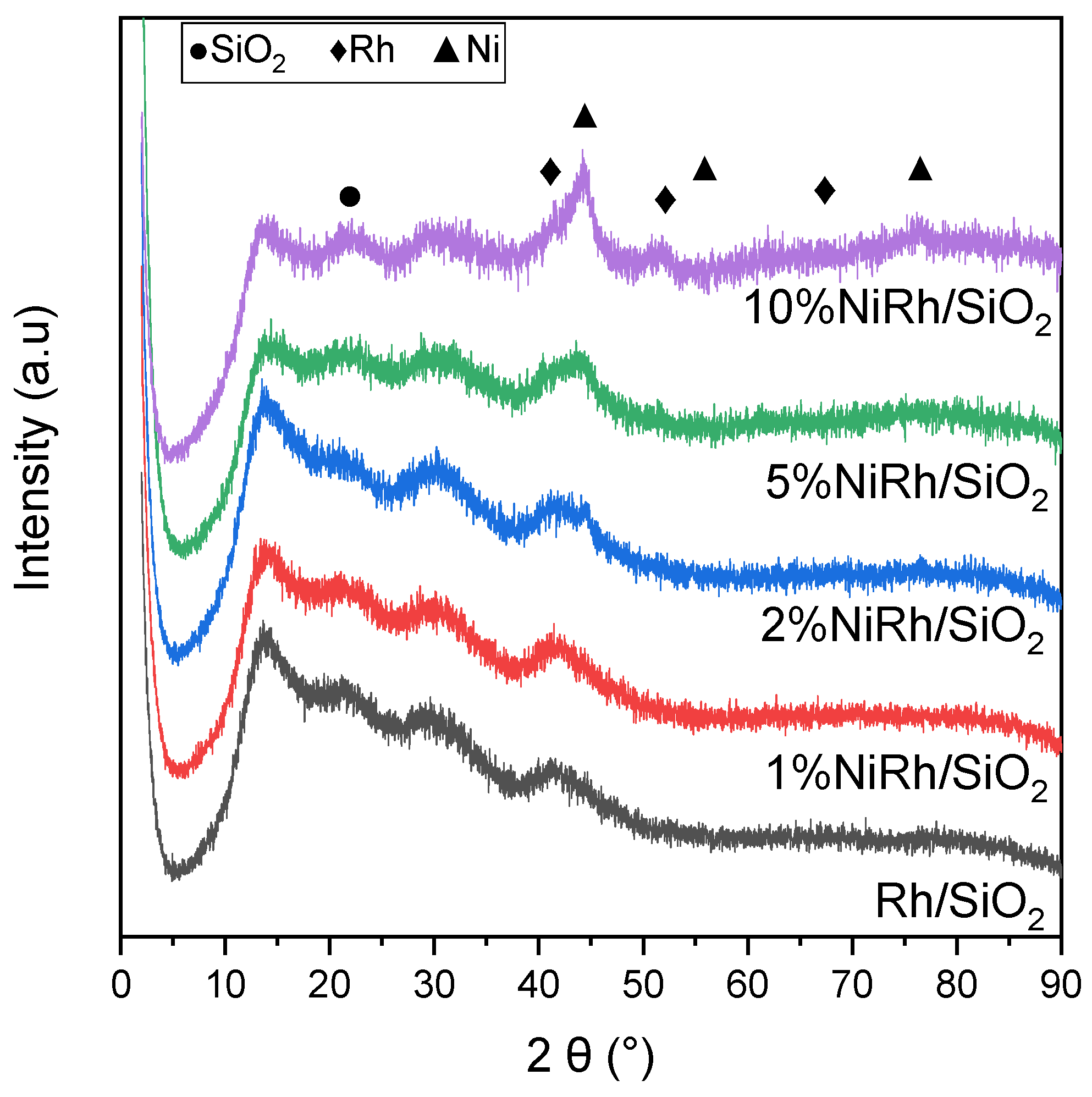
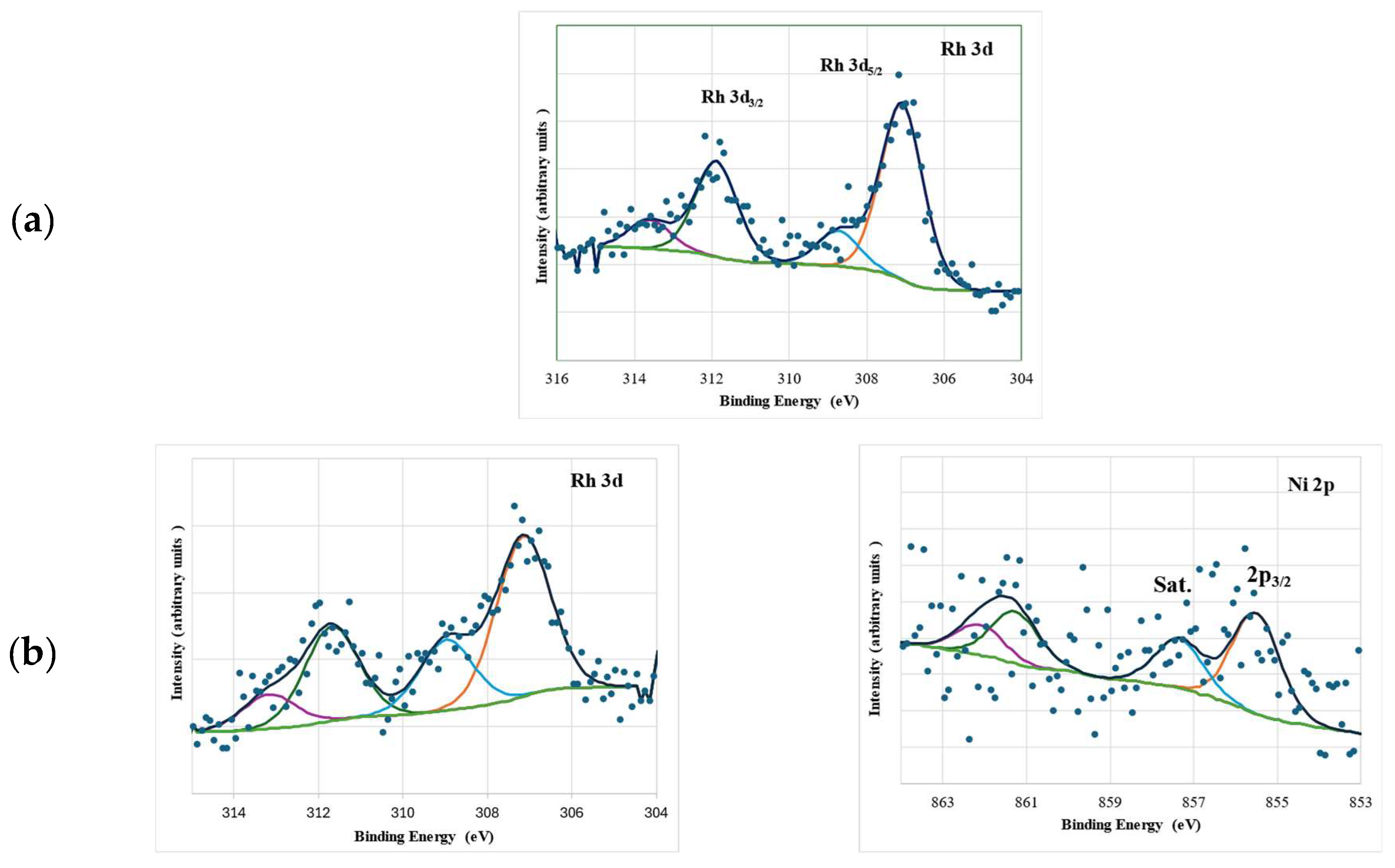
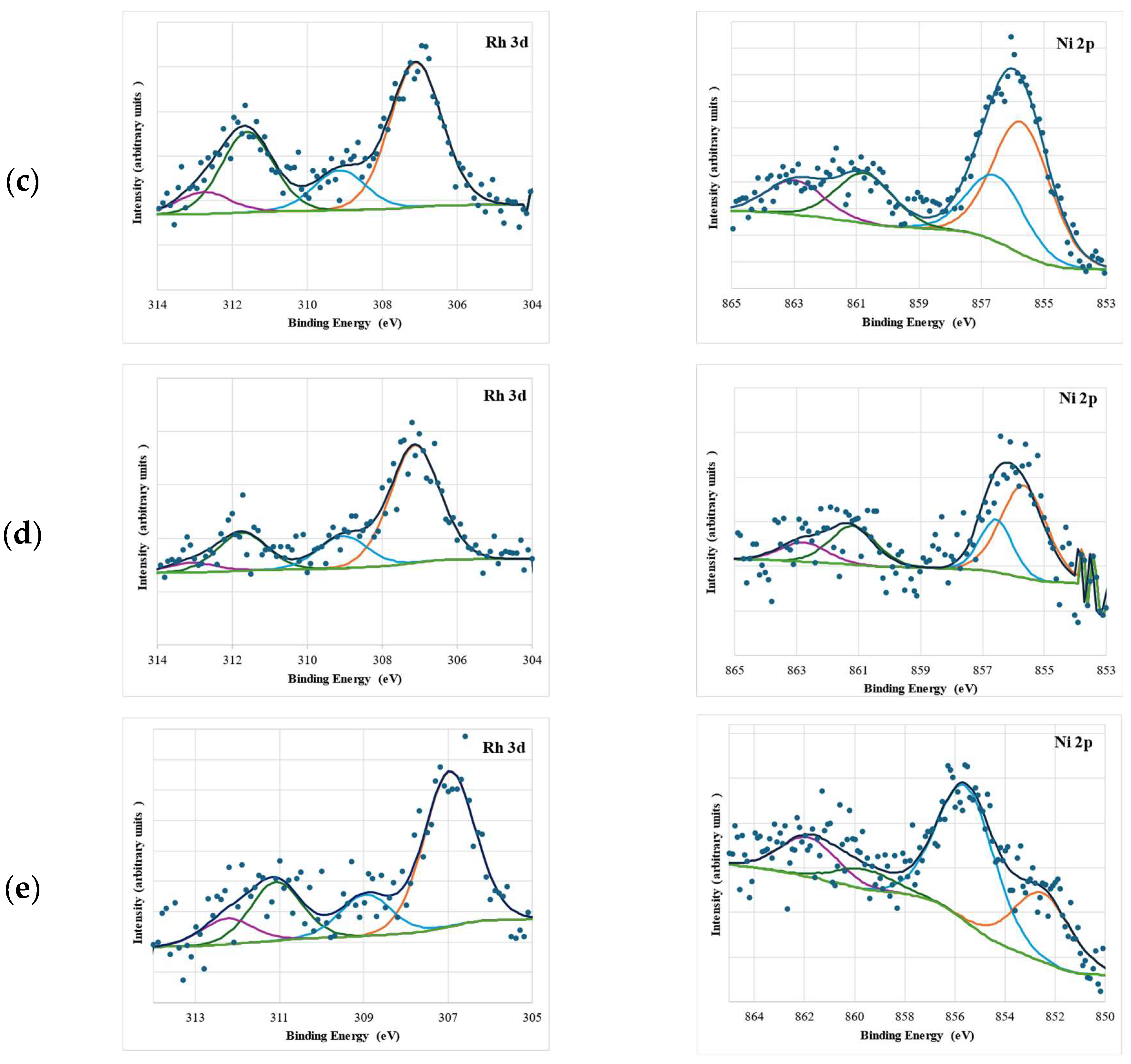
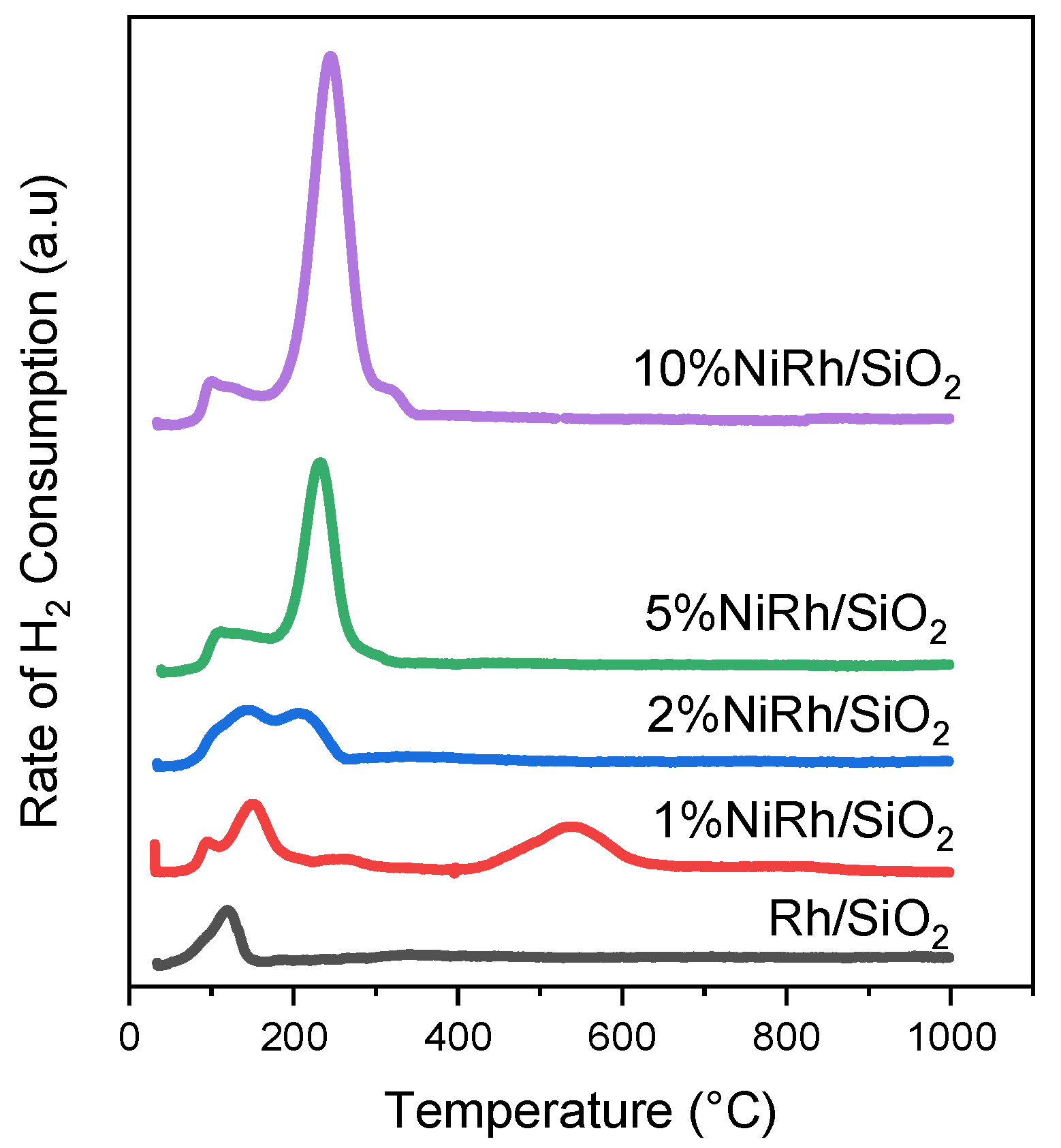

| Catalyst * | SB.E.T (m2 g−1) a | dpore (nm) b | Vpore (cm3 g−1) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 319 | 10.6 | 0.85 |
| Rh/SiO2 | 291 | 11.4 | 0.82 |
| 1 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 280 | 10.9 | 0.77 |
| 2 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 304 | 10.9 | 0.84 |
| 5 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 272 | 10.5 | 0.72 |
| 10 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 263 | 10.1 | 0.67 |
| Catalyst | dTEM (nm) | DTEM (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Rh/SiO2 | 1.95 | 46.8 |
| 1 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 1.65 | 55.3 |
| 2 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 1.95 | 46.8 |
| 5 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 1.58 | 58.1 |
| 10 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 1.88–7.12 | 48.6 |
| Catalyst | Rh | Si | Ni | Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE(eV) 3d5/2 | Rh° Rh3+ | BE(eV) 2p | BE(eV) 2p3/2 | (Ni/Si)at | (Rh/Si)at | (Rh/Ni)at | |
| Rh/SiO2 | 307.1 | 81.0 | 103.5 | - | - | 0.0040 | - |
| 308.7 | 19.0 | ||||||
| 1 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 307.2 | 70.8 | 103.6 | 855.5 ± 5.8 † | 0.0024 | 0.0036 | 1.5286 |
| 309.0 | 29.2 | ||||||
| 2 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 307.1 | 78.4 | 103.4 | 855.7 ± 5.1 † | 0.0171 | 0.0056 | 0.3254 |
| 309.1 | 21.6 | ||||||
| 5 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 307.1 | 78.8 | 103.4 | 855.7 ± 5.5 † | 0.0074 | 0.0032 | 0.4378 |
| 309.1 | 21.2 | ||||||
| 10 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 307.0 | 84.1 | 103.4 | 855.5 ± 5.5 † 852.5 * | 0.0068 | 0.0029 | 0.4236 |
| 309.2 | 15.9 | ||||||
| Catalyst | H2 Consumption (mmol gcat−1) | NH3 Desorption (mmol gcat−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Rh/SiO2 | 0.469 | 0.514 |
| 1 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 1.421 | 0.214 |
| 2 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 0.766 | 0.132 |
| 5 wt.%NiRh/SiO2 | 0.396 | 0.261 |
| 10 wt.% NiRh/SiO2 | 2.732 | 0.328 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales, K.; Sandoval, C.; Peixoto, A.; Chimentão, R.; Llorca, J.; Ruiz, D. Reductive Amination of Cyclohexanone via Bimetallic Rh-Ni Catalysts: A Pathway to Improved Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts 2025, 15, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090803
Morales K, Sandoval C, Peixoto A, Chimentão R, Llorca J, Ruiz D. Reductive Amination of Cyclohexanone via Bimetallic Rh-Ni Catalysts: A Pathway to Improved Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts. 2025; 15(9):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090803
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales, Karen, Camila Sandoval, Andreia Peixoto, Ricardo Chimentão, Jordi Llorca, and Doris Ruiz. 2025. "Reductive Amination of Cyclohexanone via Bimetallic Rh-Ni Catalysts: A Pathway to Improved Catalytic Efficiency" Catalysts 15, no. 9: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090803
APA StyleMorales, K., Sandoval, C., Peixoto, A., Chimentão, R., Llorca, J., & Ruiz, D. (2025). Reductive Amination of Cyclohexanone via Bimetallic Rh-Ni Catalysts: A Pathway to Improved Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts, 15(9), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090803










