Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Using Leaf Extract of Azadirachta indica: Characterizations and In Silico and Nematicidal Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Biosynthesized-ZnO NSs
2.2. Nematicidal Effect of Biosynthesized-ZnO NS on J2 Mortality of M. incognita In Vitro
2.3. Nematicidal Effect of Biosynthesized ZnO NS on Egg Hatching of M. incognita In Vitro
2.4. Effect of Biosynthesized ZnO NS on J2 Penetration in Roots of Tomato Seedlings
2.5. Molecular Docking of Hsp90-ZnO Complex
2.6. Molecular Docking of ODR1-ZnO Complex
3. Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties of Biosynthesized ZnO NS
3.2. Morphological Nature of Biosynthesized ZnO NS
3.3. Optical Characteristics of Biosynthesized ZnO NS
3.4. Chemical Bonding and Functional Groups in ZnO NS
3.5. Zeta Potential and Stability in ZnO NS
3.6. Aspect Format of Biosynthesized ZnO NS
3.7. Nematicidal Efficacy of Biosynthesized ZnO NS
3.8. Comparative Discussion of ZnO NS Binding to Hsp90 and ODR1
4. Materials and Techniques
4.1. Materials and Instrumentations
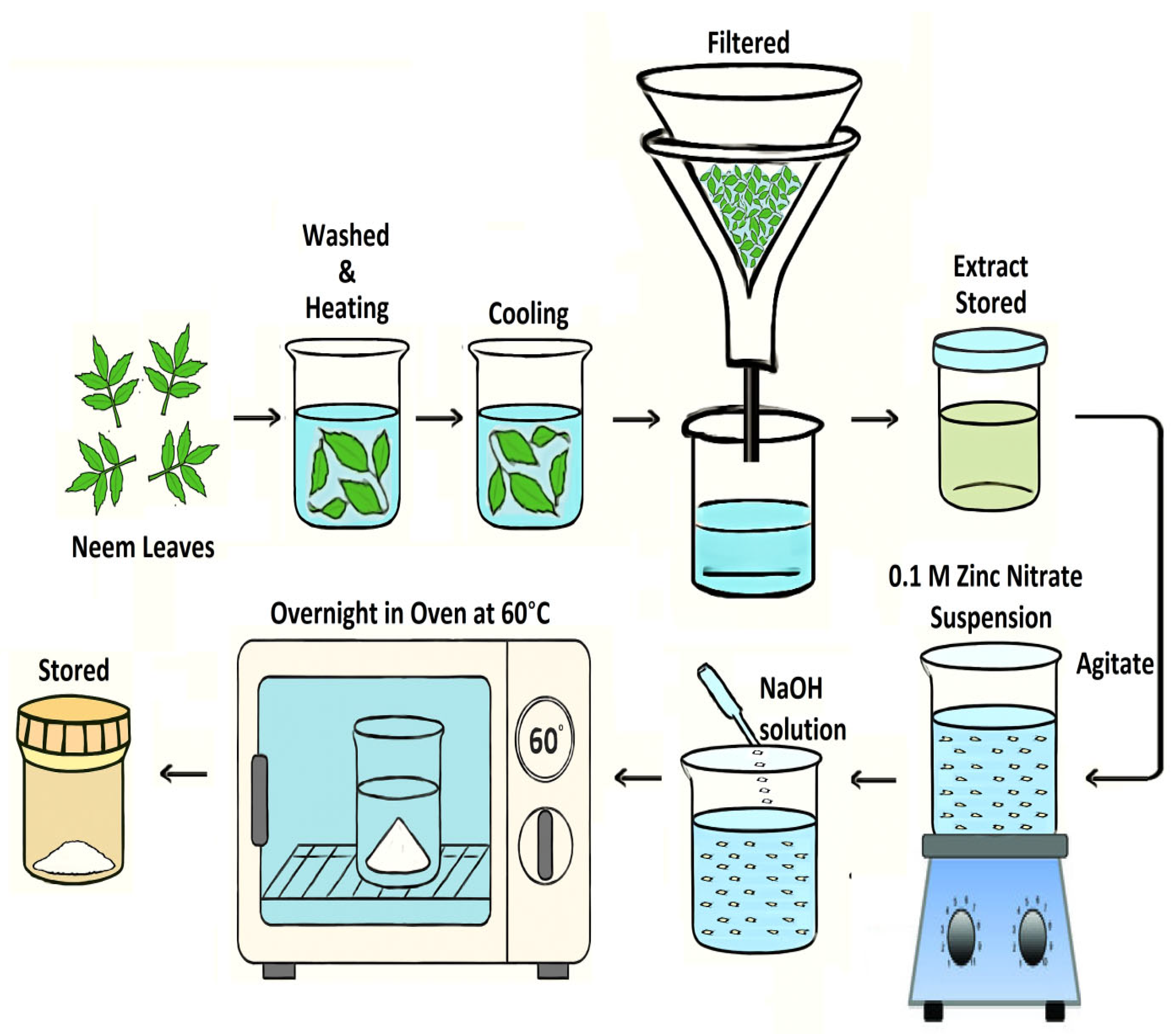
4.2. Extraction of Leaf Extract and Green Synthesis of ZnO NS
4.3. Characterization of Biosynthesized-ZnO NS
4.4. Gathering and Multiplying the Inoculum (J2s) of M. incognita
4.5. Mortality Test
4.6. Hatching Bioassay
- C0 = Count of J2s Emerged in DDW (Control);
- Tα = Count of Emerged J2s in each concentration of synthesized ZnO NS.
4.7. J2s Infection Bioassay
4.8. In Silico Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelkhalek, A.A.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Behiry, S.I. Bacillus licheniformis strain POT1 mediated poly-phenol biosynthetic pathways genes activation and systemic resistance in potato plants against Alfalfa mosaic virus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Zaid, G.A.; Matar, S.M.; Abdelkhalek, A. Induction of plant resistance against tobacco mosaic virus using the biocontrol agent Streptomyces cellulosae isolate Actino 48. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Mukhtar, T.; Kayani, M.Z. Reproduction of Meloidogyne incognita on resistant and susceptible okra cultivars. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Khalil, O.S.; Osman, A.; Alshilawi, M.S.; Taha, A.E.; Aboelenin, S.M.; Saad, A.M. Bioactive peptides supplemented raw buffalo milk: Biological activity, shelf life and quality properties during cold preservation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4581–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, A.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Sayed, S.; Moustafa, M.A.; Taha, A.E.; Ramadan, M.M. Polyphenolic extracts from pomegranate and watermelon wastes as substrate to fabricate sustainable silver nanoparticles with larvicidal effect against Spodopteralittoralis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5674–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromwell, W.; Yang, J.; Starr, J.; Jo, Y.K. Nematicidal effects of silver nanoparticles on root-knot nematode in bermudagrass. J. Nematol. 2014, 46, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelkhalek, A.; Salem, M.Z.M.; Hafez, E.; Behiry, S.I.; Qari, S.H. The phytochemical, antifungal, and first report of the antiviral properties of Egyptian Haplophyllumtuberculatum extract. Biology 2020, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliyamoorthy, T.S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Renganathan, S.; Elavarasan, V.; Ravi, J.; Prabhakaran Kala, P.; Vijayakumar, S. Sustainable Environmental-Based ZnO Nanoparticles Derived from Pisonia grandis for Future Biological and Environmental Applications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulab, H.; Fatima, N.; Tariq, U.; Gohar, O.; Irshad, M.; Khan, M.Z.; Hanif, M.B. Advancements in Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, and Diverse Applications. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2024, 39, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortella, G.; Rubilar, O.; Pieretti, J.C.; Fincheira, P.; de Melo Santana, B.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Seabra, A.B. Nanoparticles as a Promising Strategy to Mitigate Biotic Stress in Agriculture. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish, M.; Shahid, M.; Farah, M.A.; Al-Anazi, K.M.; Ahmed, S.M.; Mohamed, H.I.; Ahamad, L. CuO–ZnO Nanocomposites Mitigate Root-Knot Nematode Stress in Vigna radiata by Enhancing Physiological and Antioxidant Defense Responses. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 139, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Ragab, M.; Osman, A.; El-Masry, R.A.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Althagafi, H.; El-Saber, M.M. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Neem Extract and Their Anticancer and Antibacterial Activities. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Dwivedi, G.K.; Dey, P.; Praharaj, S. Green Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles for Sustainable Production and Nutritional Biofortification of Green Gram. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Bhat, A.H.; Raja, V.; Ahmad, S.S.; Hussain, M.A.; Ataya, F.S.; Fouad, D. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Achillea millefolium: Multifunctional Applications in Plant Growth and Nematode Control. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 136, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Parveen, G.; Bhat, A.H.; Reshi, Z.A.; Ataya, F.S.; Handoo, Z.A. Harnessing Walnut-Based Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Sustainable Approach to Combat the Disease Complex of Meloidogyne arenaria and Macrophomina phaseolina in Cowpea. Plants 2024, 13, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, F.; Bwatanglang, I.B.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Shaik, J.P.; Al-Tilasi, H.H.; Soleiman, A.A. Influence of Surface Coating towards the Controlled Toxicity of ZnO Nanoparticles In Vitro. Coatings 2023, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Ahmed, S.; Rehman, B.; Ali, S.K.; Azooz, R.E.; Hassan, K.F.; Khan, A.; Ranjan, P.; Negi, D.S. A synergistic effect of ZnO low dimensional rods/PEDOT:PSS hybrid structure for UV radiation detection. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ansari, A.; Bishwanathan, S.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Tailor, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Negi, D.S.; Ranjan, P. Electronic tongue based on ZnO/ITO@glass for electrochemical monitoring of spiciness levels. Langmuir 2024, 40, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutaleb, A.; Ahmed, S.; Imran, M. Synergistic photocatalysis: Harnessing WSe2-ZnOnanocomposites for efficient malachite green dye degradation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghdari, M.; Saboor, F.H.; Babapoor, A.; Karve, V.V.; Asgari, M. Recent Advances in MOF-Based Adsorbents for Dye Removal from the Aquatic Environment. Energies 2022, 15, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaka, V.R.; Ravi, P.; Reddy, M.C.; Thummala, C.; Mandal, T.K. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Modern Science and Technology: Multifunctional Roles in Healthcare, Environmental Remediation, and Industry. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandhan, K.; Harish, S.; Tilak Kumar, R. Effect of Morphology on the Formation of CdO Nanostructures for Antibacterial and Hemolytic Studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 489, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharsini, N.; Bhuvaneswari, N.; Joshy, J. Plant Mediated Synthesis of ZnO and Mn Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Using Carica papaya Leaf Extract for Antibacterial Application. Asian J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 5, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Sonbol, F.I.; Sun, J.; Hussein, M.A.; Hafez, A.-E.E.; Abdelkarim, E.A.; Kornaros, M.; Ali, A.; Azab, M. Molecular Characterization of Virulence and Drug Resistance Genes-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Chicken Meat: Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Novel Antibacterial Agents. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.S.; Moawad, M.S.; Hussein, M.A.; Azab, M.; Abdelkarim, E.A.; Badr, A.; Sun, J.; Khalil, M. Efficacy of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Novel Antimicrobial Agents against Multi-Drug and Multi-Virulent Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken Meat and Giblets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 344, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.N.; Prasad, L.; Suyal, U. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Trichoderma harzianum and Its Bio-Efficacy on Alternaria brassicae. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1506695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, K.D.; Davis, T.Z.; Van Eden, M.E.; Aust, S.D. Deleterious iron-mediated oxidation of biomolecules. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftab, Z.-e.-H.; Mirza, F.S.; Anjum, T.; Rizwana, H.; Akram, W.; Aftab, M.; Ali, M.D.; Li, G. Antifungal Potential of Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Controlling Cercospora Leaf Spot in Mung Bean. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannai, Z.; Bouslama, W.; Karkouch, I.; Bouslama, L.; Khlifi, K.; Aouadi, K.; Nouira, F. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO and CuO Coatings for Antibacterial and Antiviral Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 329, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bharati, R.; Kubes, J.; Popelkova, D.; Praus, L.; Yang, X.; Severova, L.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Application Alleviates Salinity Stress by Modulating Plant Growth, Biochemical Attributes and Nutrient Homeostasis in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1432258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freinbichler, W.; Colivicchi, M.A.; Stefanini, C.; Bianchi, L.; Ballini, C.; Misini, B.; Weinberger, P.; Linert, W.; Varešlija, D.; Tipton, K.F.; et al. Highly reactive oxygen species: Detection, formation, and possible functions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, C.; Ding, N.; Pan, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y. The degradation pathways of contaminants by reactive oxygen species generated in the Fenton/Fenton-like systems. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.S.; Muhammad, F.; Farooq, M.; Aslam, M.U.; Akhter, N.; Toleikienė, M.; Iqbal, R. ZnO-Nanoparticles and Stage-Based Drought Tolerance in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Effect on Morpho-Physiology, Nutrient Uptake, Grain Yield and Quality. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, Z.; Fan, K. ZnO Nanoparticles: Improving Photosynthesis, Shoot Development, and Phyllosphere Microbiome Composition in Tea Plants. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.P.; Hirota, K.; Kato, M.; Tsukagoshi, K.; Yamada, H.; Terabe, A.; Mizutani, H. Addition Dependence of Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Powders on Their Physico-chemical Properties. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 2019, 66, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, P.; Antonoglou, O.; Vourlias, G.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Tailoring Ca-based nanoparticles by polyol process for use as nematicidals and pH adjusters in agriculture. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3870–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Argawy, E.; Rahhal, M.; El-Korany, A.; Elshabrawy, E.; Eltahan, R. Efficacy of some nanoparticles to control damping-off and root rot of sugar beet in El-Behiera Governorate. Asian J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 11, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Kim, D. CRDS: Consensus reverse docking system for target fishing. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Uchida, K. Protein adductomics: A comprehensive analysis of protein modifications by electrophiles. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathi, A.; Roopan, S.M.; Vasavi, C.S.; Munusami, P.; Gayathri, G.A.; Gayathri, M. In silico molecular docking and in vitro antidiabetic studies of dihydropyrimido [4,5-a]acridin-2-amines. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 971569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kundu, A.; Dutta, A.; Mandal, A.; Negi, L.; Malik, M.; Puramchatwad, R.; Antil, J.; Singh, A.; Rao, U.; Saha, S.; et al. A comprehensive in vitro and in silico analysis of nematicidal action of essential oils. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 614143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadwal, N.; Ben Mrad, R.; Behdinan, K. Review of Zinc Oxide Piezoelectric Nanogenerators: Piezoelectric Properties, Composite Structures and Power Output. Sensors 2023, 23, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, A.T.; Ahmadipour, M.; Pung, S.Y. A Review on ZnO-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators: Synthesis, Characterization Techniques, Performance Enhancement and Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, A.H.; Rouby, W.M.E.; Ismail, N.; Farghali, A.A. Morphology transition engineering of ZnO nanorods to nanoplatelets grafted Mo8O23-MoO2 by polyoxometalates: Mechanism and possible applicability to other oxides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, K.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Bendary, E.S.; Ali, H.M. Experimental Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Thyme and Basil Essential Oils and Their Phenolic Constituents: Theoretical Antioxidant Evaluation. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, K.M.A.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Mohamed, H.I.; Shalaby, T.A.; Galal, A.; Mansour, A.T.; Aboul Fotouh, M.M.; Bendary, E.S.A. Antioxidant, Anti-Cancer Activity and Phytochemicals Profiling of Kigelia pinnata Fruits. Separations 2022, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Prasad, M.; Sah, N.K. Anticancer Biology of Azadirachta indica L. (Neem): A Mini Review. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Saiqali, M.; Tangutur, A.D.; Banoth, C.; Bhukya, B. Antimicrobial and Anticancer Potential of Low Molecular Weight Polypeptides Extracted and Characterized from Leaves of Azadirachta indica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, D.G.; Godin, A.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Nogueira, R.D.; Brito, A.M.S.; Melo, I.S.F.; Machado, R.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Azadirachtin in Mice. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, M.M.; Upadhyay, C.; Pandya, G.; Jana, A.M. Inhibitory Potential of Neem (Azadirachta indica Juss) Leaves on Dengue Virus Type-2 Replication. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasanth, S.; Hamsaveni Gopal, R.; Rao, R.B. Plant Anti-Malarial Agents. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1990, 49, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lokanadhan, S.; Muthukrishnan, P.; Jeyaraman, S. Neem Products and Their Agricultural Applications. J. Biopestic. 2012, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Anukrati, K.; Paul, P.K. Anti-Phytopathogenic and SAR Inducing Properties of Neem: A Review. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 9, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, R.F.; Patel, R.L.; Chaudhari, S.M.; Pandey, S.K.; Brajesh, S. In Vitro Evaluation of Different Plant Extracts against Alternaria alternata Causing Early Blight of Potato. J. Indian Potato Assoc. 2003, 30, 141–142. [Google Scholar]
- Narde, J.; Ahmed, N.; Maiti, S.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Ganapathy, D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Aloe vera and Neem Leaf Extract and Their Cytotoxic Effect Evaluation. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis Miller Leaf Extract: Structure and Optical Properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.N.; Abaker, Z.M.; Makawi, S.Z.A. Phytochemical Substances Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs). Inorganics 2023, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltak, N.A.; Gniedy, N.A.; Abdel-Haleem, D.R.; Farag, S.M. Based on GC-MS Analysis: An Evaluation Activity of Some Algal Extracts against Culex pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2023, 27, 461–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.F.; Rehman, M.; Hussain, S.Z.; Huma, Z.E.; Shahnaz, G.; Qureshi, O.S.; Qandeel, K.; Shaper, M.; Irshad, H.; Webster, T.J. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles by Neem Extract as Multi-Facet Therapeutic Agents. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, F. Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) from Leaves of Some Plants. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor 2023, 61, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, T.; Peng, H.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, W. Optimization of Fenton-like reaction pathways using O v-containing ZnO@ nitrogen-rich porous carbon: The electron transfer and 1O2 triggered non-radical process. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Rizvi, T.F. Nanotechnology: Scope and Application in Plant Disease Management. Plant Pathol. J. 2014, 13, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogamalar, N.R.; Bose, A.C. Absorption–Emission Study of Hydrothermally Grown Al:ZnO Nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8493–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashry, R.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; El-Sobki, A.E.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Al-Otaibi, S.; El-Shehawi, A.M.; Saad, A.M.; Elshaer, N. Biological Silicon Nanoparticles Maximize the Efficiency of Nematicides Against Biotic Stress Induced by Meloidogyne incognita in Eggplant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 29, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, M.; Choudhary, A.K.; Kumar, R. Nanotechnology in Agricultural Diseases and Food Safety. J. Phytol. 2010, 2, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Vu, V.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Tran, V.K.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Antibacterial Activity of TiO2- and ZnO-Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Posgai, R.; Gorey, T.J.; Nielsen, M.; Hussain, S.M.; Rowe, J.J. Silver Nanoparticles Induced Heat Shock Protein 70, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 242, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammini-Premachandra, W.T.C.; Mampitiyarachchi, H.; Ebssa, L. Nemato-Toxic Potential of Betel (Piper betle L.) (Piperaceae) Leaf. J. Crop Prot. 2014, 65, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Saini, I.; Kaushik, P.; Aldawsari, M.M.; Al Balawi, T.; Alam, P. Mycorrhizal fungi and Pseudomonas fluorescens application reduces root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne javanica) infestation in eggplant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Qi, G.; Yin, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, X. Bacillus cereus Strain S2 Shows High Nematicidal Activity Against Meloidogyne incognita by Producing Sphingosine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Elsharabasy, S.F.; Abdulsamad, D. Evaluation of In Vitro Nematicidal Efficiency of Copper Nanoparticles against Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita. S. Asian J. Parasitol. 2019, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, S. “Traditional” Sol-Gel Chemistry as a Powerful Tool for the Preparation of Supported Metal and Metal Oxide Catalysts. Materials 2019, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serov, D.A.; Gritsaeva, A.V.; Yanbaev, F.M.; Simakin, A.V.; Gudkov, S.V. Review of Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyiukwu, D.N.; Ononuju, C.C.; Okeke, C.; Chukwu, L.A. Plant Parasitic Nematodes, Serious but Most Trivialized Biotic Challenge against Food Security: A Spotlight on Their Management for Sustainable Agriculture and Public Health. Direct Res. J. Public Health Environ. Technol. 2021, 6, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, I.; Khan, M.S.; Ansari, M.R.; Bari, M.N. Exploring the potential of Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss.) as a sustainable biopesticide: Opportunities in Sudan. Ann. Phytomed. 2024, 13, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.; Hussain, A.; Ahmed, A. Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss)—A Nature’s Drugstore: An Overview. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenback, J.D.; Hunt, D.J. General Morphology. In Root-Knot Nematodes; Starr, J.L., Moens, M., Perry, R.N., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 18–54. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rokiek, K.G.; El-Nagdi, W.M. Dual Effects of Leaf Extracts of Eucalyptus citriodora on Controlling Purslane and Root-Knot Nematode in Sunflower. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2011, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissani, N.; Urgeghe, P.P.; Oplos, C.; Saba, M.; Tocco, G.; Petretto, G.L. Nematicidal Activity of the Volatilome of Eruca sativa on Meloidogyne incognita. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6120–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, M. Probit Analysis of Preference Data. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 33, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behreus, A.S.; Karbeur, L. Determination of LD50. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1953, 28, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Almutairi, F.M.; Khan, A.; Ajmal, M.R.; Khan, R.H.; Khan, M.F.; Lal, H.; Ullah, M.F.; Ahmad, F.; Ahamad, L.; Khan, A. Phytochemical Analysis and Binding Interaction of Cotton Seed Cake Derived Compounds with Target Protein of Meloidogyne incognita for Nematicidal Evaluation. Life 2022, 12, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridge, J.; Page, S.; Jordan, S. An Improved Method for Staining Nematodes in Roots. Rothamsted Exp. Stn. Annu. Rep. 1982, 1, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Tameem, M.; Amir, M.; Muslim, M.; Ahmed, R.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, F.; Javed, S. Multispectral Analysis and Molecular Docking of a Zinc (II) Complex Interaction with Bovine Serum Albumin and Studies on Antibacterial Properties, and Catecholase Mimicry of the Complex. Biophys. Chem. 2025, 317, 107355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, M.; Nabi, F.; Zaheer, S.M.F.; Khan, R.H.; Javed, S. Exploring the Molecular Basis of Tucatinib Interaction with Human Serum Albumin: A Spectroscopic and Computational Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; Qureshi, M.A.; Khan, A.; Nayeem, S.M.; Malik, W.A.; Javed, S. Exploring the Interaction of Tepotinib with Calf Thymus DNA Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Multispectroscopic Techniques. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 308, 123678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Akbar, M.; Amir, M.; Javed, S. Molecular Interactions of Esculin with Bovine Serum Albumin and Recognition of Binding Sites with Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 2630–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, M.; Javed, S. Elucidation of Binding Dynamics of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Tepotinib to Human Serum Albumin Using Spectroscopic and Computational Approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Amir, M.; Khan, R.H.; Musarrat, J.; Javed, S. Glycation Reduces the Binding Dynamics of Aflatoxin B1 to Human Serum Albumin: A Comprehensive Spectroscopic and Computational Investigation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 14797–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheoran, O.P.; Tonk, D.S.; Kaushik, L.S.; Hasija, R.C.; Pannu, R.S. Statistical Software Package for Agricultural Research Workers. In Recent Advances in Information Theory, Statistics & Computer Applications; Hooda, D.S., Hasija, R.C., Eds.; Department of Mathematics Statistics, CCS HAU: Hisar, India, 1998; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]













| Treatment | Concentrations (ppm) | Average Number of Dead J2s at Various Time Intervals (Hours) (Mean ± SE) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 48 | 72 | ||
| ZnO NS | 150 | 8 ± 1.15 (11.42%) | 13 ± 1 (18.57%) | 20 ± 1.15 (28.57%) | 26 ± 1.73 (37.14%) |
| 300 | 15 ± 1 (21.42%) | 21 ± 1.15 (30%) | 28 ± 1.52 (40%) | 34 ± 1.73 (48.57%) | |
| 450 | 21 ± 1.52 (30%) | 29 ± 1.52 (41.42%) | 35 ± 1.73 (50%) | 42 ± 2.08 (60%) | |
| 600 | 30 ± 1.52 (45.71%) | 37 ± 1.73 (52.85%) | 45 ± 2.08 (64.28%) | 53 ± 1.73 (75.71%) | |
| DW | 0 ± 0 (0%) | 0 ± 0 (%) | 0 ± 0 (%) | 0 ± 0 (%) | |
| Degrees of freedom | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Sum of Squares | 783 | 960 | 1014 | 1196.25 | |
| Mean Squares | 261 | 320 | 338 | 398.75 | |
| F-Calculated | 49.71 | 55.65 | 40.97 | 33.93 | |
| Significance | 0.00002 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00007 | |
| Treatment | Exposure Period (Hours) | LC50 Value in ppm (95% CL) |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 842.15 | |
| 24 | 585.723 | |
| 48 | 397.683 | |
| 72 | 270.33 |
| Treatment | Concentrations (ppm) | Number of Penetrated J2s (Mean ± SE) in Roots After 5 Days of Inoculation |
|---|---|---|
| 5 days | ||
| ZnO NS | 150 | 33 ± 1.52 (37.77%) |
| 300 | 27 ± 1.52 (51.11%) | |
| 450 | 23 ± 1.73 (60%) | |
| 600 | 18 ± 1.15 (71.11%) | |
| DW | 45 ± 1.52 (11.11%) | |
| Degrees of freedom | 4 | |
| Sum of Squares | 362.25 | |
| Mean Squares | 120.75 | |
| F-Calculated | 17.88 | |
| Significance | 0.00066 | |
| S.N. | Amino Acids of Hsp90 Protein | Atoms of ZnO NS | Type of Bonds Involved | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ILE87 | Oxygen | Conventional H-Bond | 3.12449 |
| 2. | TRP90 | Oxygen | Pi-Donor H-Bond | 3.26606 |
| 3. | TRP90 | Oxygen | Pi-Donor H-Bond | 3.76018 |
| 4. | TYR57 | Zinc | Pi-Alkyl | 5.00853 |
| 5. | PHE67 | Zinc | Pi-Alkyl | 5.03625 |
| 6. | PHE130 | Zinc | Pi-Alkyl | 4.75283 |
| S.N. | Amino Acid of ODR1 Protein | Atoms of ZnO NS | Type of Bonds Involved | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | PHE123 | Oxygen | Conventional H-Bond | 3.22606 |
| 2. | HIS121 | Oxygen | Conventional H-Bond | 3.27704 |
| 3. | PHE123 | Oxygen | Pi-Donor H-Bond | 3.72806 |
| 4. | HIS111 | Zinc | Pi-Alkyl | 5.06967 |
| Method | Synthesis Approach | Advantages | Limitations | Effectiveness | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Synthesis | Traditional chemical methods (e.g., precipitation, sol-gel) | High purity, controlled particle size | Expensive, hazardous, complex process | Moderate efficacy, environmental concerns | [71,72] |
| Other Nanomaterials (e.g., AgNPs, TiO2) | Nanoparticles of silver, titanium dioxide | Broad antimicrobial activity, well-studied | High cost, environmental risk (e.g., silver) | Effective, but can be toxic and expensive | [73,74] |
| Synthetic Nematicides | Chemical pesticides (e.g., carbofuran) | Fast acting | Toxic to environment, expensive | High efficacy but harmful to non-target species | [75] |
| Green Synthesis (Neem Extract) | Biosynthesis using neem leaf extract | Eco-friendly, low cost, sustainable | Limited scalability | High nematicidal efficacy, low toxicity | Present Study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khuwaja, G.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Mashlawi, A.M.; Alamri, A.A.; Alfifi, F.; Anjum, K.; Alam, M.S.; Alam, M.I.; Ali, S.K.; Raza, N.; et al. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Using Leaf Extract of Azadirachta indica: Characterizations and In Silico and Nematicidal Potentials. Catalysts 2025, 15, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070693
Khuwaja G, Chaudhary AA, Mashlawi AM, Alamri AA, Alfifi F, Anjum K, Alam MS, Alam MI, Ali SK, Raza N, et al. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Using Leaf Extract of Azadirachta indica: Characterizations and In Silico and Nematicidal Potentials. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070693
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhuwaja, Gulrana, Anis Ahmad Chaudhary, Abadi M. Mashlawi, Abdullah Ali Alamri, Faris Alfifi, Kahkashan Anjum, Md Shamsher Alam, Mohammad Intakhab Alam, Syed Kashif Ali, Nadeem Raza, and et al. 2025. "Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Using Leaf Extract of Azadirachta indica: Characterizations and In Silico and Nematicidal Potentials" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070693
APA StyleKhuwaja, G., Chaudhary, A. A., Mashlawi, A. M., Alamri, A. A., Alfifi, F., Anjum, K., Alam, M. S., Alam, M. I., Ali, S. K., Raza, N., Ali, M. A. M., & Imran, M. (2025). Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Using Leaf Extract of Azadirachta indica: Characterizations and In Silico and Nematicidal Potentials. Catalysts, 15(7), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070693







