Enhanced Sulfamethazine Degradation over a Wide pH Range by Cost-Effective Zero-Valent Iron-Based Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
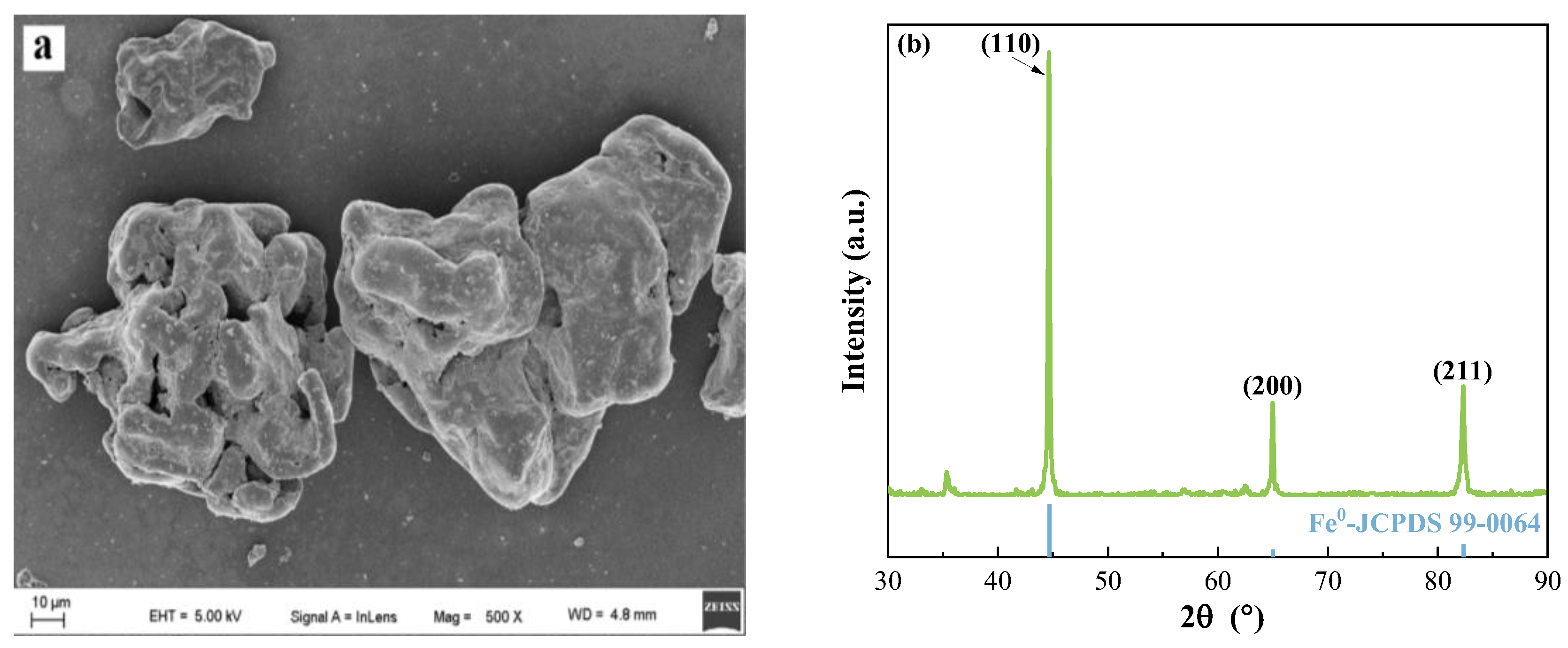
2.1. Characterization of Fe0
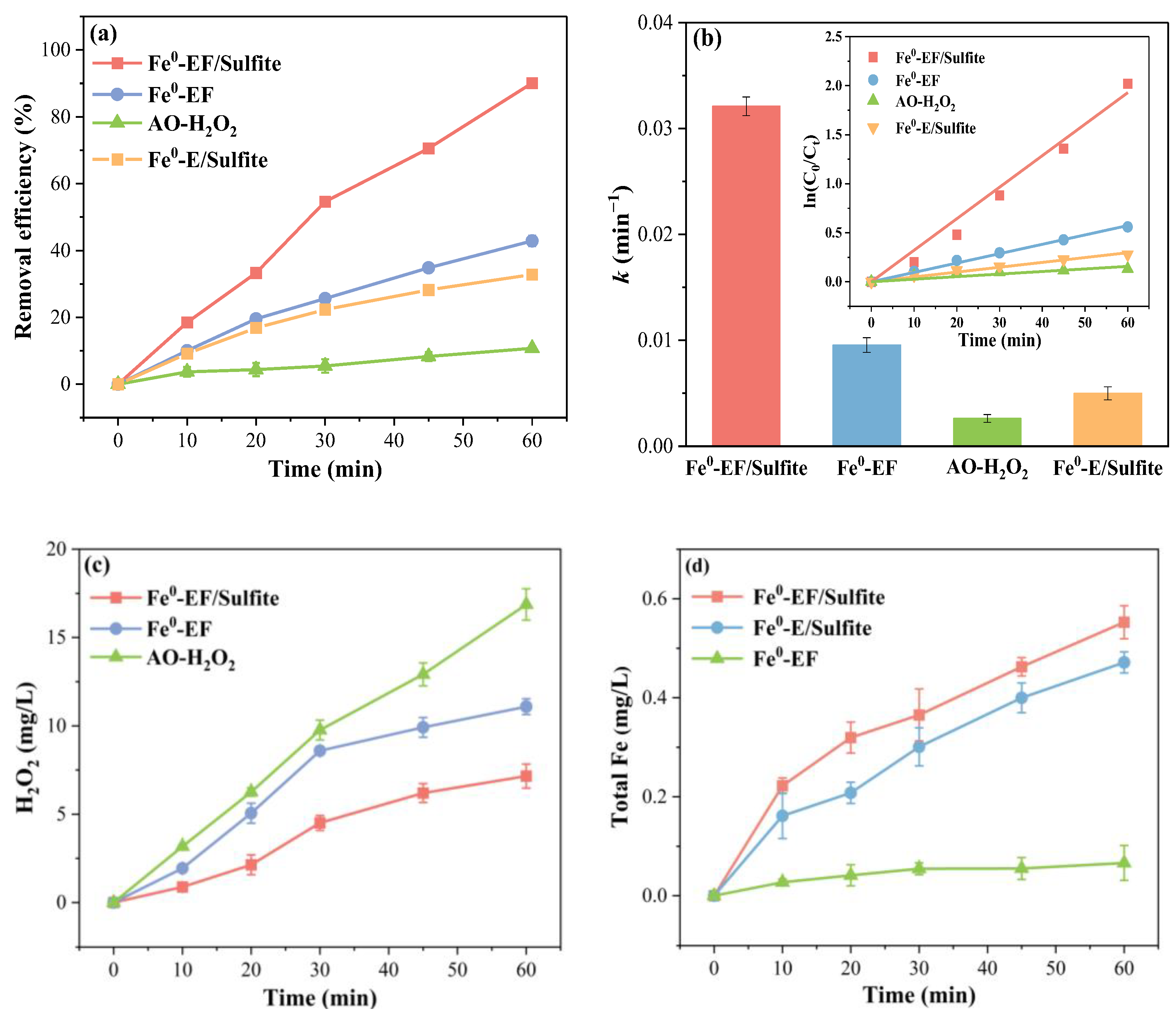
2.2. Elimination of SMT in Different Systems
2.3. Impacts of Key Factors
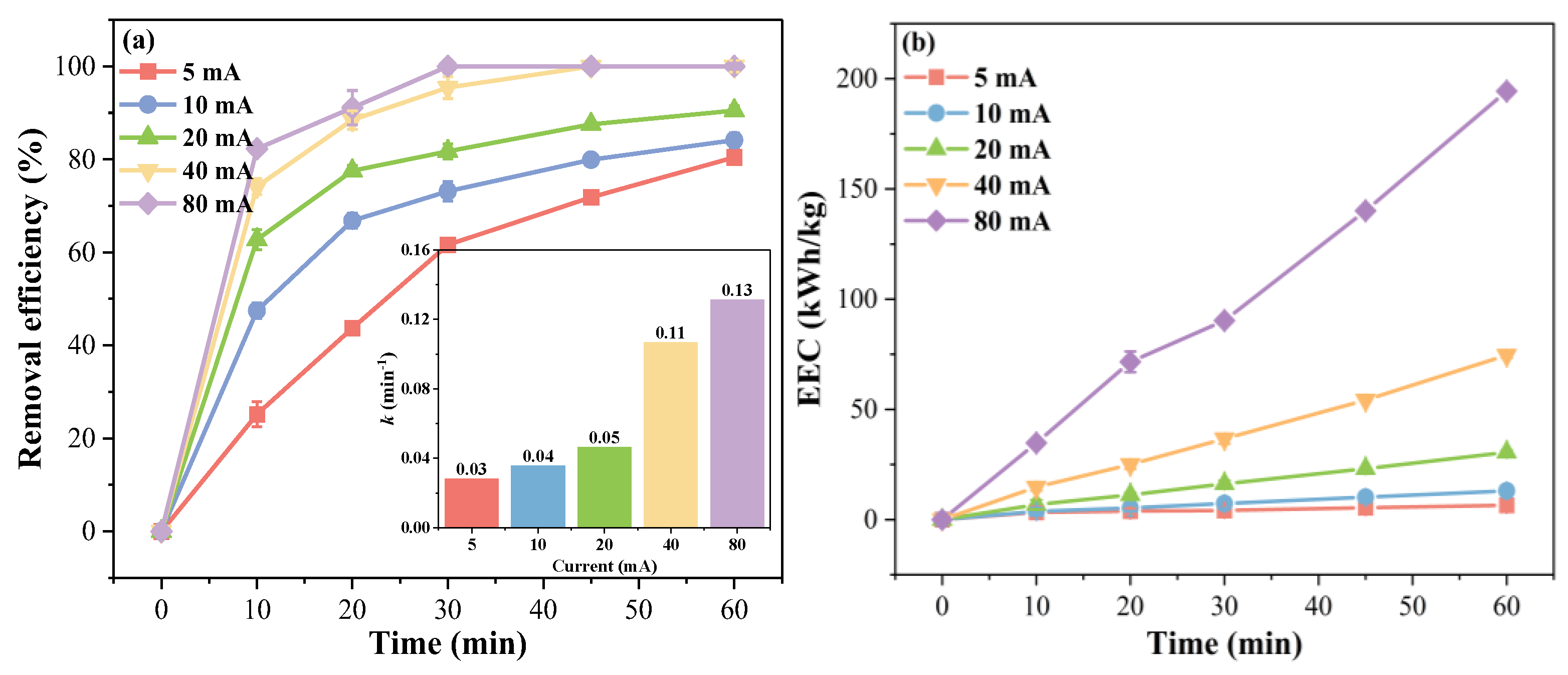
2.3.1. Effect of Current
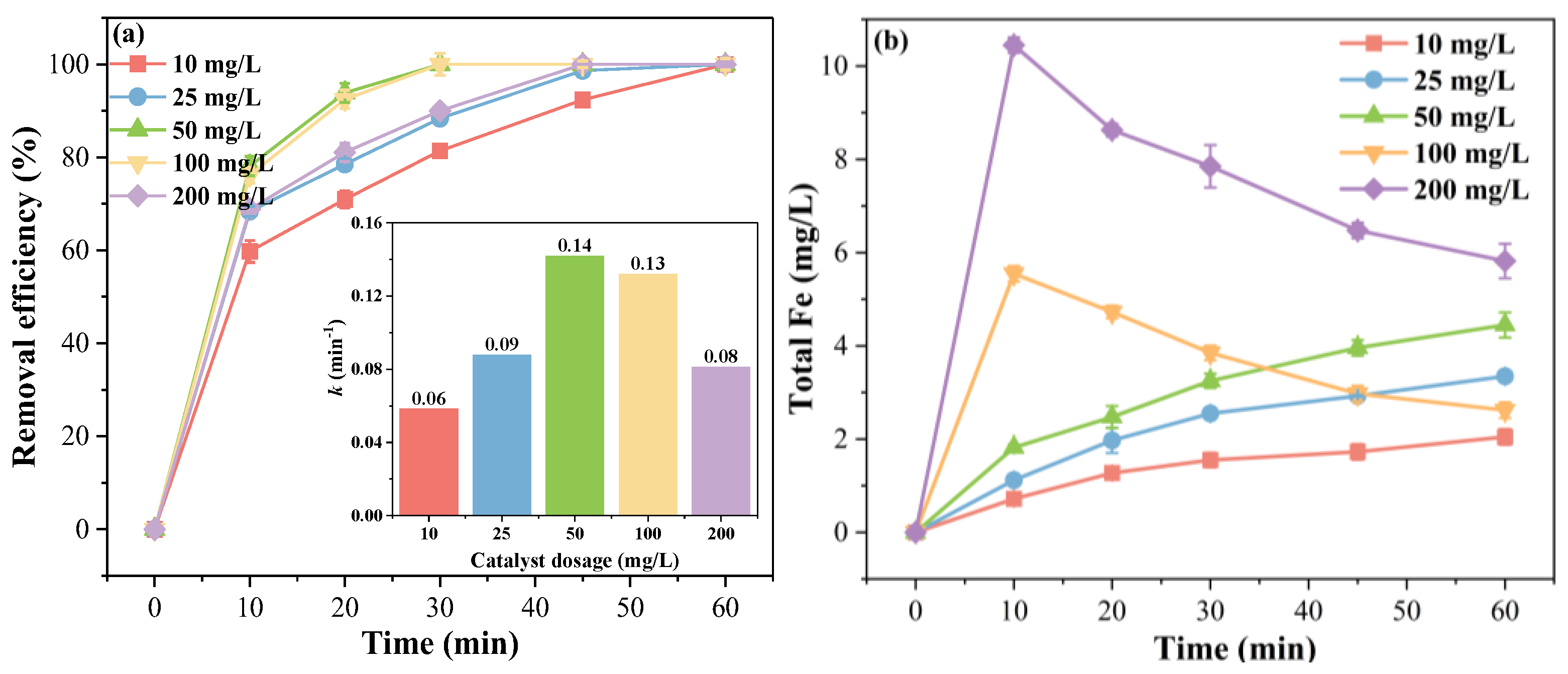
2.3.2. Effect of Catalyst Dosage
2.3.3. Effect of Sulfite Dosage
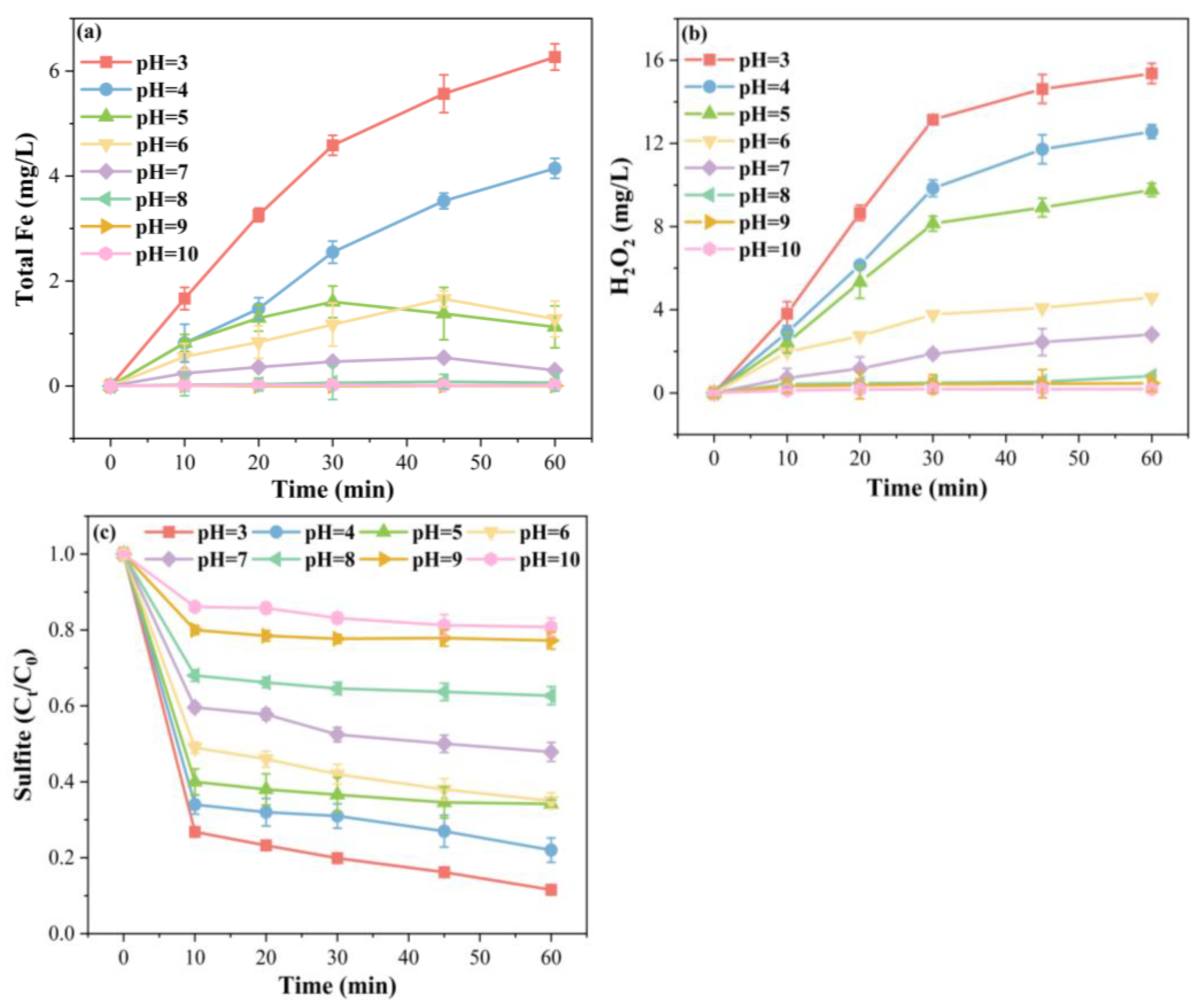
2.3.4. Effect of Initial pH
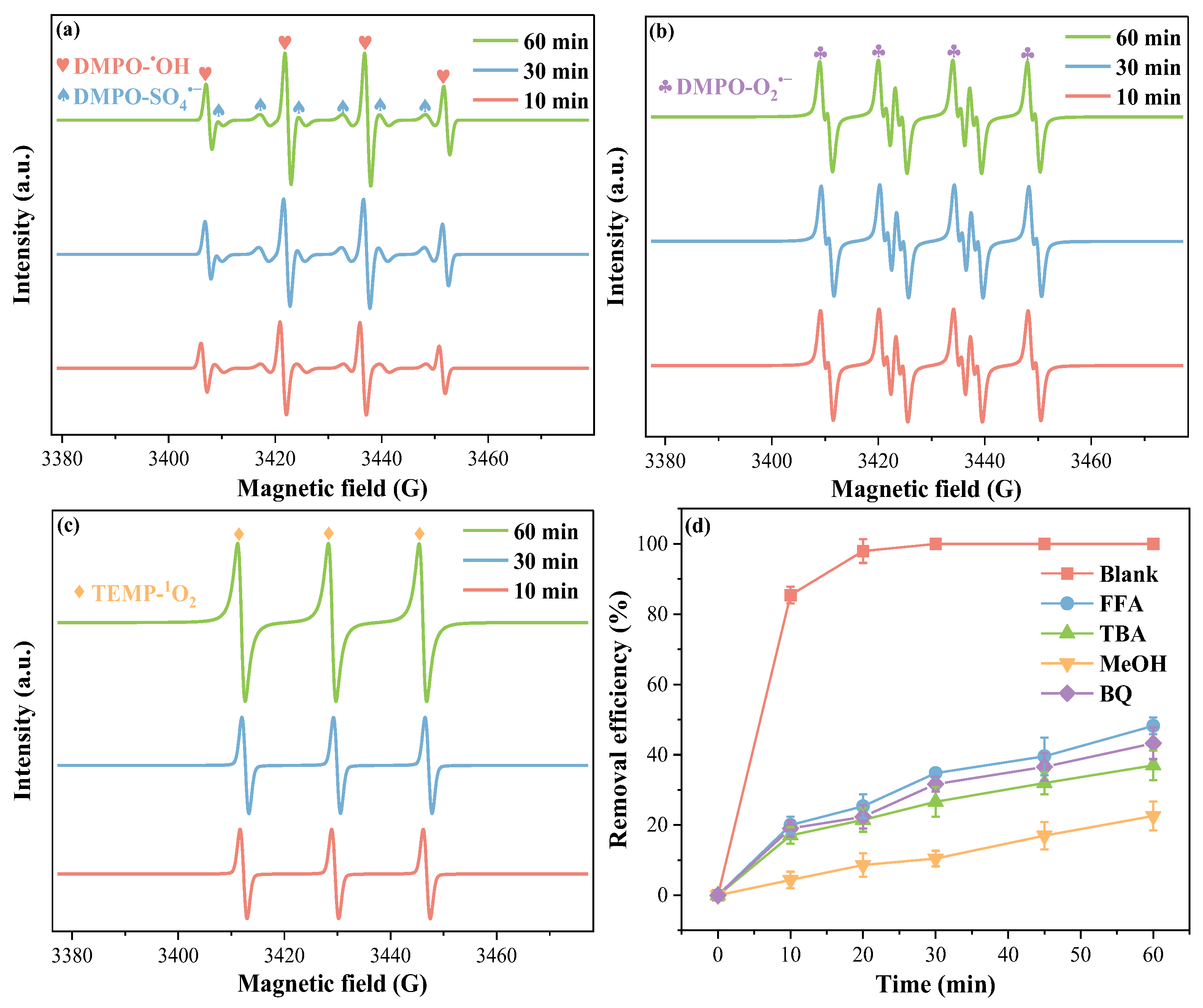
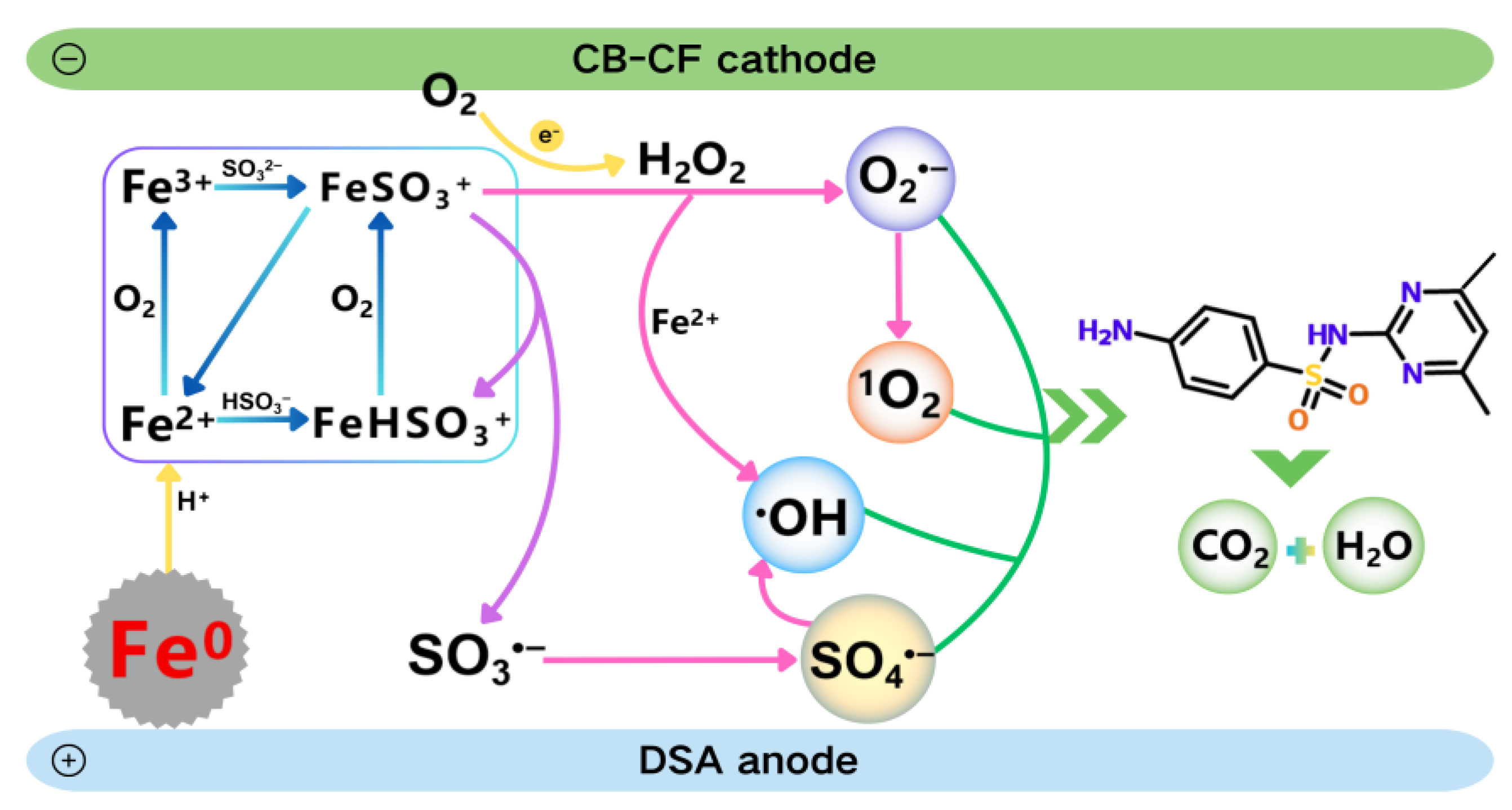
2.4. Mechanism of the Fe0-EF/Sulfite System
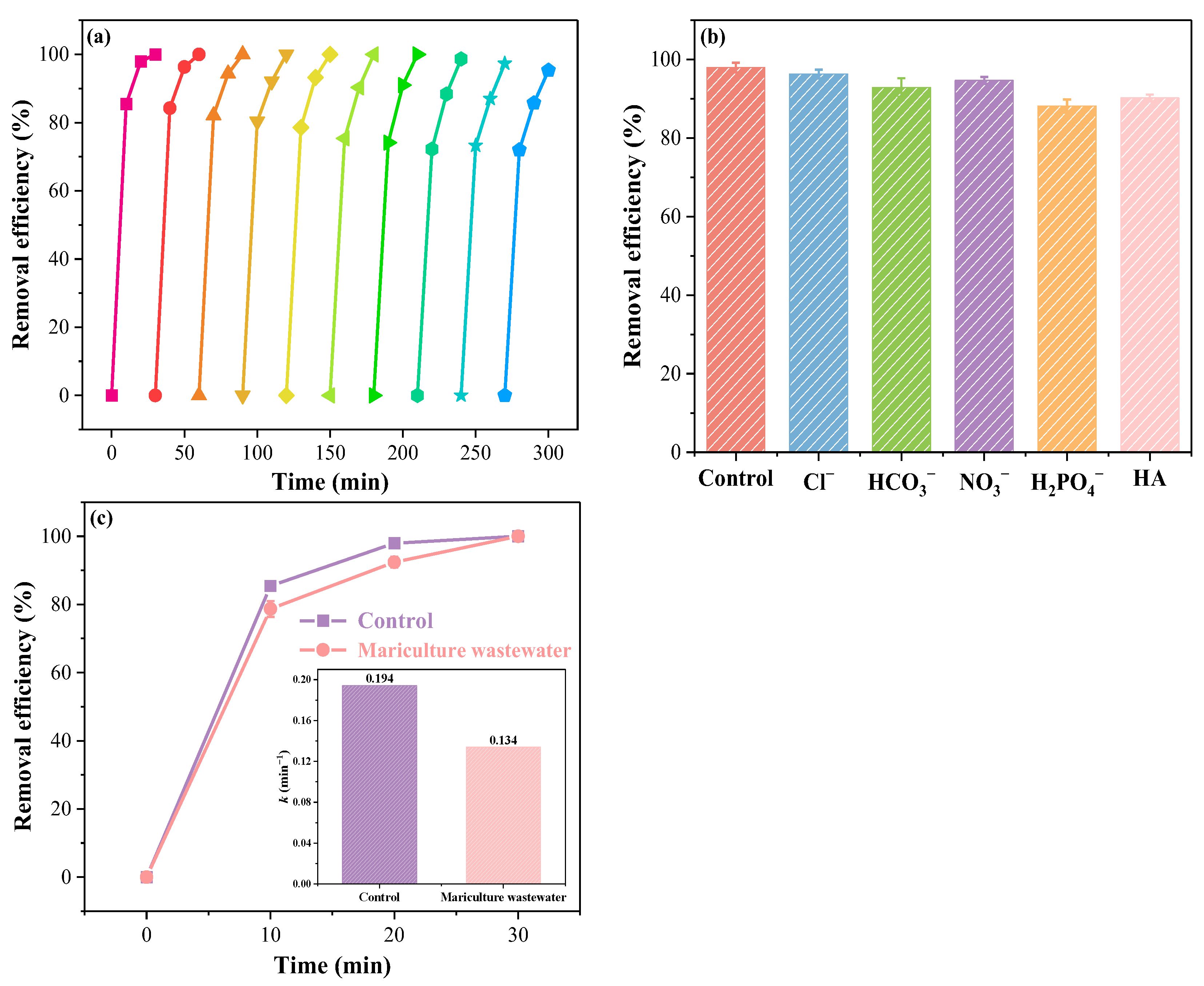
2.5. Environmental Applications
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Experimental Procedure
3.3. Characterization and Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Pang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Huang, D.; Dong, J.; Li, L. Highly Efficient Activation of Peracetic Acid Via Zero-Valent Iron-Copper Bimetallic Nanoparticles (nZVIC) for the Oxidation of Sulfamethazine in Aqueous Solution under Neutral Condition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 340, 123183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, J. Degradation of Sulfamethazine by Vacuum Ultraviolet-Activated Sulfate Radical-Advanced Oxidation: Efficacy, Mechanism and Influences of Water Constituents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Review of Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Influenced by Dissolved Organic Matter and Iron Oxides. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and Ecotoxicity of Sulfonamides in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.T.; Wang, J.L. Metal Organic Framework with Coordinatively Unsaturated Sites as Efficient Fenton-Like Catalyst for Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethazine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shang, R.; Wang, S.; Ding, J.; Wan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Ma, J. Application of a Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Using Sulfite and Zero-Valent Iron in Treatment of Organic Pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qin, X.; Cao, P.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Quan, X. High-Efficiency Refractory Organic Pollutants Removal Boosted by Combining Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton with Electrochemical Anodic Oxidation over a Broad pH Range. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xiang, Q.; Lei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. Ferric Iron Reduction Reaction Electro-Fenton with Gas Diffusion Device: A Novel Strategy for Improvement of Comprehensive Efficiency in Electro-Fenton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Zhou, M.; Du, X.; Su, P.; Guo, J. Mechanistic Insight into the Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process for Ultraefficient Degradation of Pollutants over a Wide pH Range. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Pan, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Boosting Active Sites of Protogenetic Sludge-Based Biochar by Boron Doping for Electro-Fenton Degradation Towards Emerging Organic Contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, M.; Pan, Y.; Cai, J.; Ren, G. Pre-Magnetized Fe0 as Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Catalyst for the Degradation of P-Nitrophenol at Neutral pH. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Zhou, M.; Martinez-Huitle, C.A. Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton and Photoelectro-Fenton Processes: A Critical Review of Fundamental Principles and Application for Water/Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 235, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Dong, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xiang, S.; Hou, X.; Chu, D. Degradation of Sulfamethazine in Water by Sulfite Activated with Zero-Valent Fe-Cu Bimetallic Nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohantorabi, M.; Moussavi, G.; Giannakis, S. A Review of the Innovations in Metal- and Carbon-Based Catalysts Explored for Heterogeneous Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) Activation, with Focus on Radical vs. Non-Radical Degradation Pathways of Organic Contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 127957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.N.; Chen, L.; Li, J.J.; Wu, F. Transition Metal Catalyzed Sulfite Auto-Oxidation Systems for Oxidative Decontamination in Waters: A State-of-the-Art Minireview. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peng, X.Z.; Liu, J.H.; Li, J.J.; Wu, F. Decolorization of Orange II in Aqueous Solution by an Fe(II)/Sulfite System: Replacement of Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13632–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ding, W.; Wu, F.; Mailhot, G.; Zhou, D.N.; Hanna, K. Rapid Catalytic Oxidation of Arsenite to Arsenate in an Iron(III)/Sulfite System under Visible Light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 186, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Effect of Inorganic, Synthetic and Naturally Occurring Chelating Agents on Fe(II) Mediated Advanced Oxidation of Chlorophenols. Water Res. 2009, 43, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.H.; Sun, Y.K.; Qin, H.J.; Li, J.X.; Lo, I.M.C.; He, D.; Dong, H.R. The Limitations of Applying Zero-Valent Iron Technology in Contaminants Sequestration and the Corresponding Countermeasures: The Development in Zero-Valent Iron Technology in the Last Two Decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 75, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.W.; Zhou, M.H.; Wang, Q.; Cai, J.J.; Tian, Y.S.; Zhang, Y. EDTA, Oxalate, and Phosphate Ions Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Sulfamethazine Removal by Zero-Valent Iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Enhanced Oxidation of 4-Chlorophenol Using Sulfate Radicals Generated from Zero-Valent Iron and Peroxydisulfate at Ambient Temperature. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Sun, L.; Tu, Y.; Teng, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Xie, X.; Gu, X. Highly stable carbon-coated nZVI composite Fe0@RF-C for efficient degradation of emerging contaminants. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 22, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Du, X.; Zheng, Y.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, M. A Novel Electro-Fenton Process Coupled with Sulfite: Enhanced Fe3+ Reduction and TOC Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tan, W.; Feng, X. Rapid Oxidative Dissolution of Zerovalent Iron Induced by Sulfite for Efficient Removal of Arsenate and Arsenite: Selective Formation of Scorodite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 16225–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wang, L.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y.; Xie, F. Porous Amorphous High Entropy Oxide Coated Dimensionally Stable Anode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Acidic Media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 684, 161882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, L.; Lin, Y.; Yin, K.; Yang, C. Sulfite-Based Advanced Oxidation and Reduction Processes for Water Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, H. New Insight into the Mechanism of Electro-Assisted Pyrite Minerals Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects, Activation Sites and Electron Transfer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Gou, J.; Cheng, X. Activation of Sulfite by Micron-Scale Iron-Carbon Composite for Metronidazole Degradation: Theoretical and Experimental Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wu, D.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xu, A.; Li, X. Activation of Sulfite by Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Cobalt Nanoparticles for Organic Pollutants Removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhu, S.; Jin, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Wen, Q.; Ma, F. Sorption mechanisms of antibiotic sulfamethazine (SMT) on magnetite-coated biochar: pH-dependence and redox transformation. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xue, Y.; Luo, T.; Wu, F.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Electrolysis-assisted UV/sulfite oxidation for water treatment with automatic adjustments of solution pH and dissolved oxygen. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, A. The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, G.; Zhou, M. Highly Dispersed FeN-CNTs Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Catalyst for Carbamazepine Removal with Low Fe Leaching at Wide pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. The Influence of Structure and Surface Chemistry of Carbon Materials on the Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide. Carbon 2013, 62, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, N.; Lai, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Li, J. A Critical Review of Environmental Remediation Via Iron-Mediated Sulfite Advanced Oxidation Processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, M.; Pan, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, Q. MoS2 as Highly Efficient Co-Catalyst Enhancing the Performance of Fe0 Based Electro-Fenton Process in Degradation of Sulfamethazine: Approach and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Feng, M.; Guo, L.; Zhai, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sharma, V.K. Nitrogen-Sulfur Co-Doped Industrial Graphene as an Efficient Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Singlet Oxygen-Dominated Catalytic Degradation of Organic Contaminants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 251, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wu, H.; Jing, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Song, G.; Liang, R.; Ren, X.; Zhou, M. Amorphous Cosx in Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton: A 1O2-Mediated System for Efficient and Selective Water Decontamination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 359, 124501. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.F.; Llanos, J.; Saez, C.; Lopez, C.; Canizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. The Jet Aerator as Oxygen Supplier for the Electrochemical Generation of H2O2. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.F.; Sun, X.P.; Sun, Z.R. Fabrication of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Black Co-Modified Graphite Felt Cathode for Amoxicillin Removal by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes under Mild pH Condition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8231–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lei, X.; Liang, X.; Cheng, S.; Ouyang, G.; Yang, X. Assessing the Use of Probes and Quenchers for Understanding the Reactive Species in Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malefane, M.E.; Managa, M.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Kuvarega, A.T. S-Scheme3d/3d Bi0/Biobr/P Doped G-C3N4 with Oxygen Vacancies (Ov) for Photodegradation of Pharmaceuticals: In-Situ H2O2 Production and Plasmon Induced Stability. Chemsuschem 2025, 18, 145053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.Y.; Wei, G.F.; Yin, D.Q.; Guan, X.H. Mechanistic Insight into the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Sulfite Activation with Fe(III) for Contaminants Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonette, J.E.; Templeton, J.C. Improvements to the Quantitative Assay of Nonrefractory Minerals for Fe(II) and Total Fe Using 1,10-Phenanthroline. Clays Clay Miner. 1998, 46, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Song, G.; Islam, A.; Zhou, M. Enhanced Sulfamethazine Degradation over a Wide pH Range by Cost-Effective Zero-Valent Iron-Based Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process. Catalysts 2025, 15, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070680
He J, Song G, Islam A, Zhou M. Enhanced Sulfamethazine Degradation over a Wide pH Range by Cost-Effective Zero-Valent Iron-Based Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070680
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiayi, Ge Song, Akhtar Islam, and Minghua Zhou. 2025. "Enhanced Sulfamethazine Degradation over a Wide pH Range by Cost-Effective Zero-Valent Iron-Based Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070680
APA StyleHe, J., Song, G., Islam, A., & Zhou, M. (2025). Enhanced Sulfamethazine Degradation over a Wide pH Range by Cost-Effective Zero-Valent Iron-Based Electro-Fenton/Sulfite Process. Catalysts, 15(7), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070680








