Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalyst with Hierarchical Meso-Macroporous Structure for Hydrodemetallization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
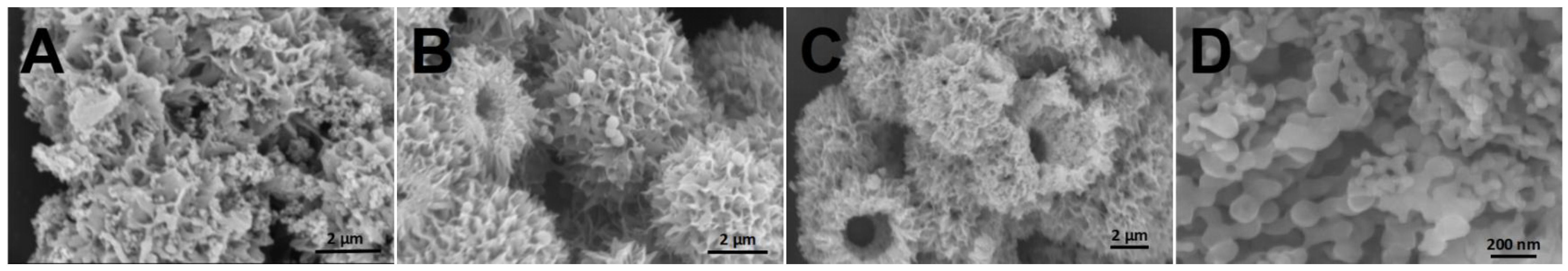
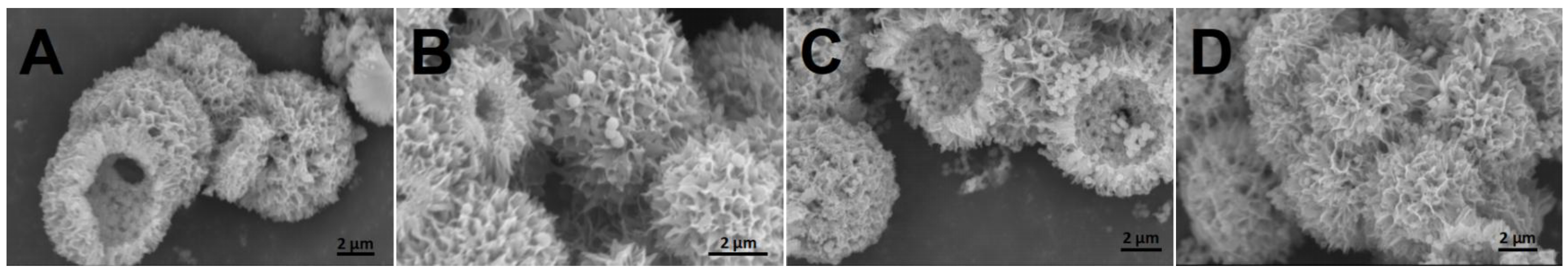
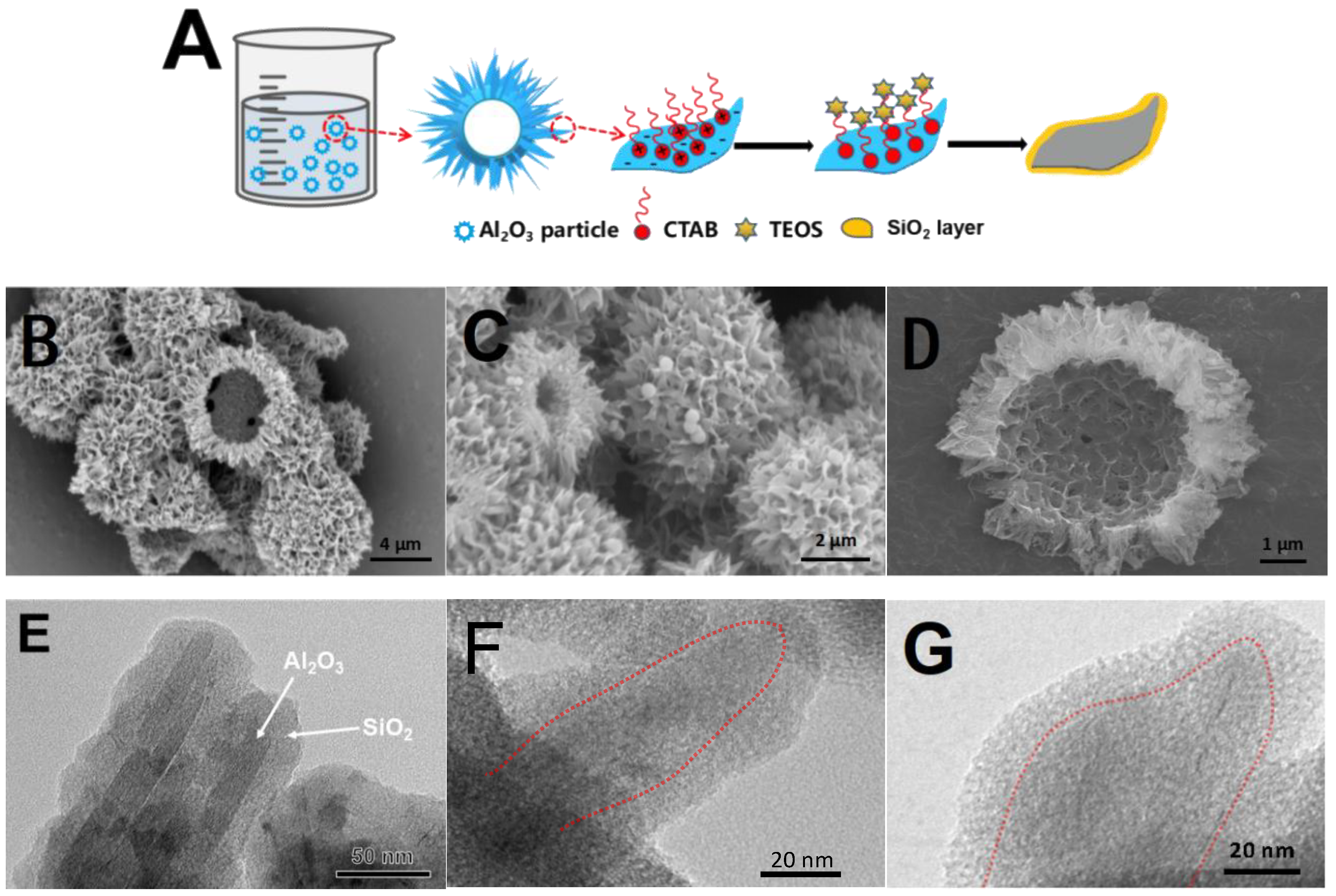
2.1. Morphology and Structure of Al2O3@SiO2
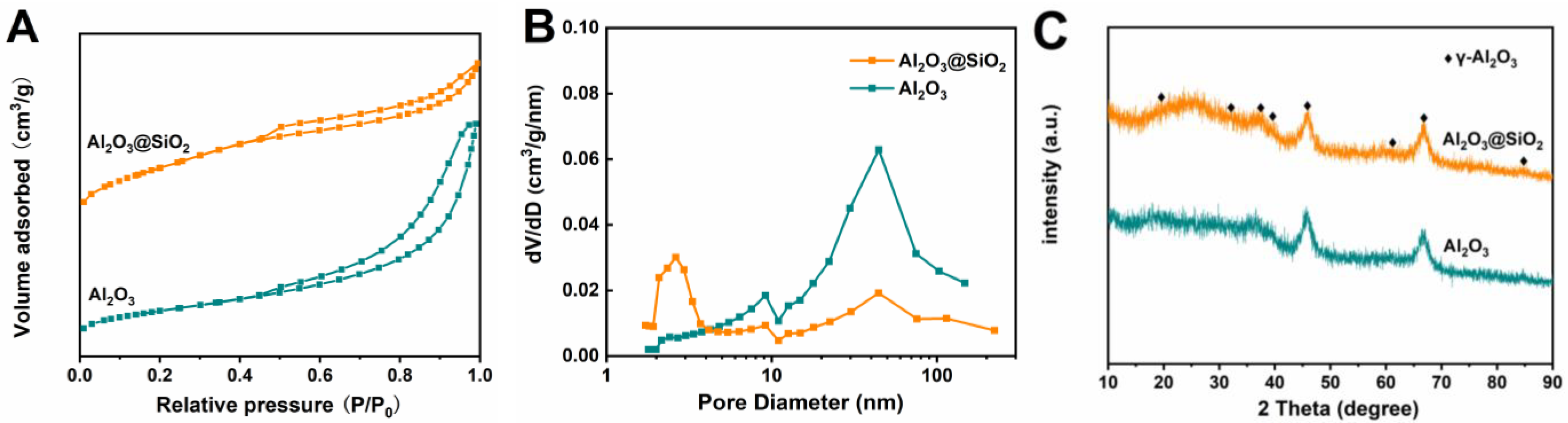
2.2. Physical Properties of Al2O3@SiO2
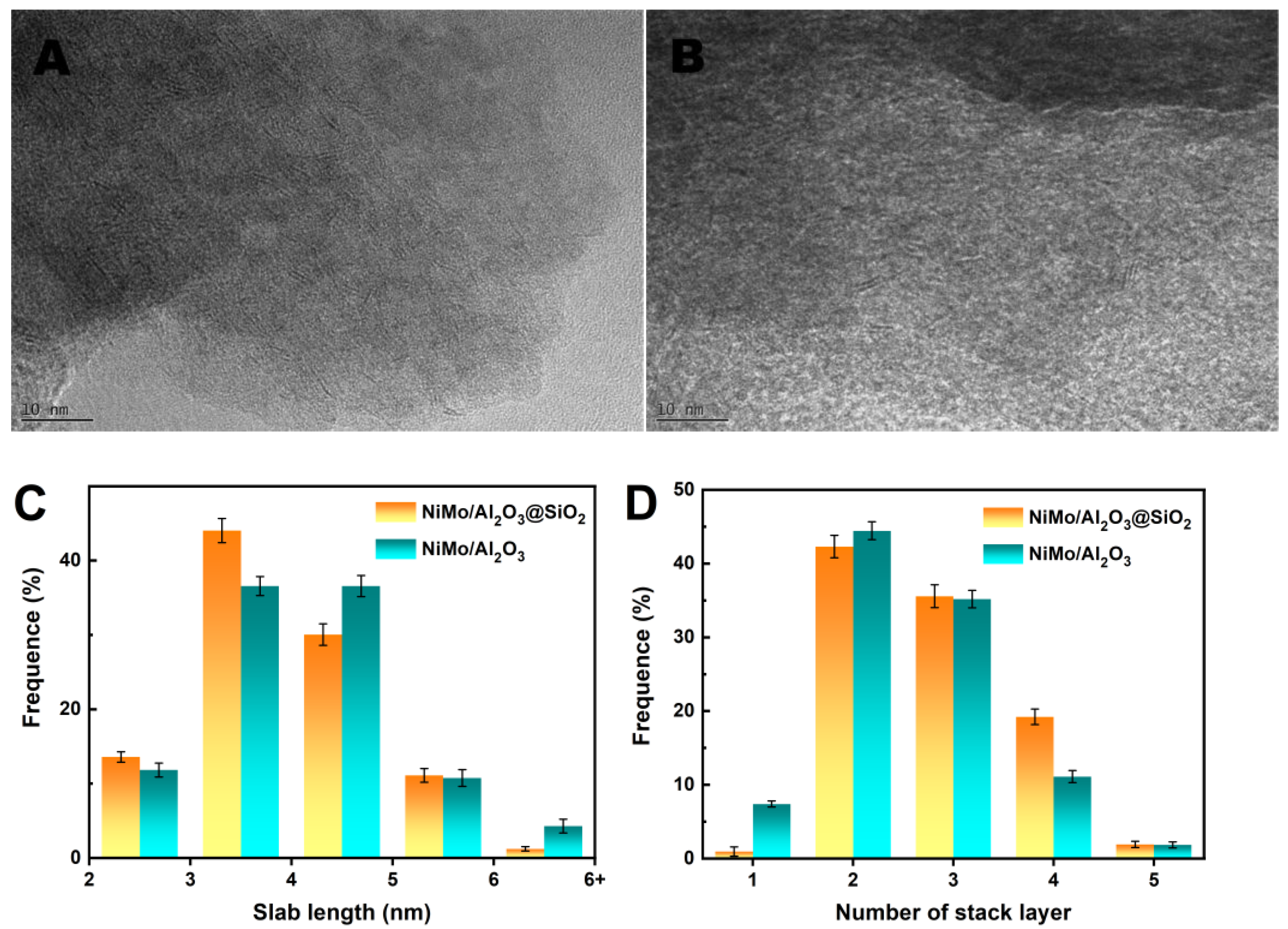
2.3. Physicochemical Properties of NiMo/Al2O3@SiO2 Catalyst
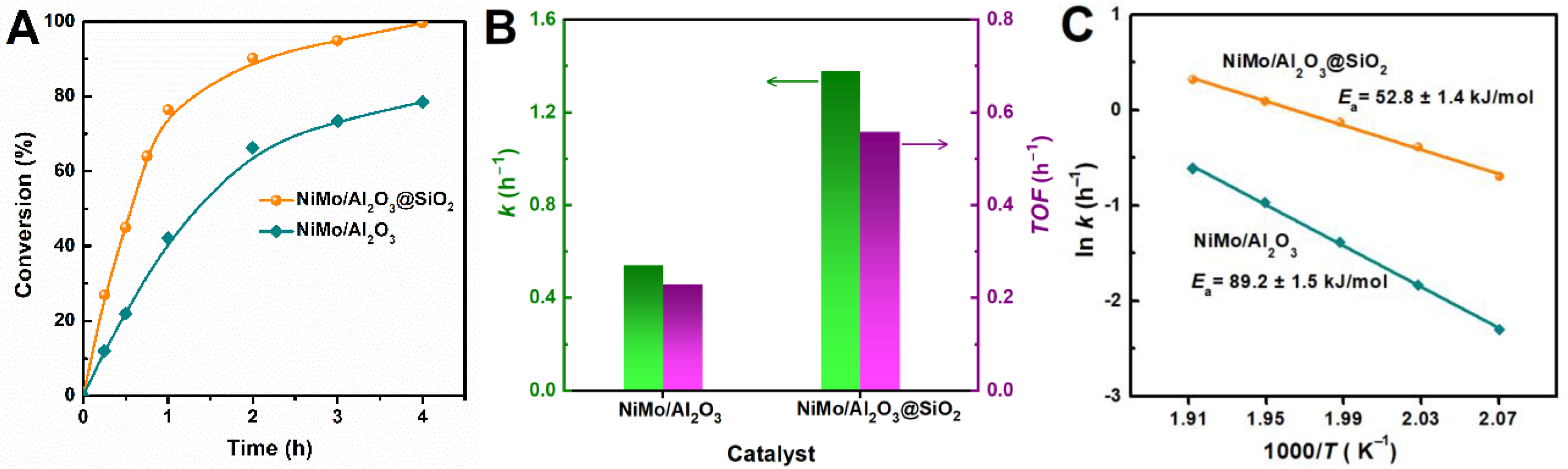
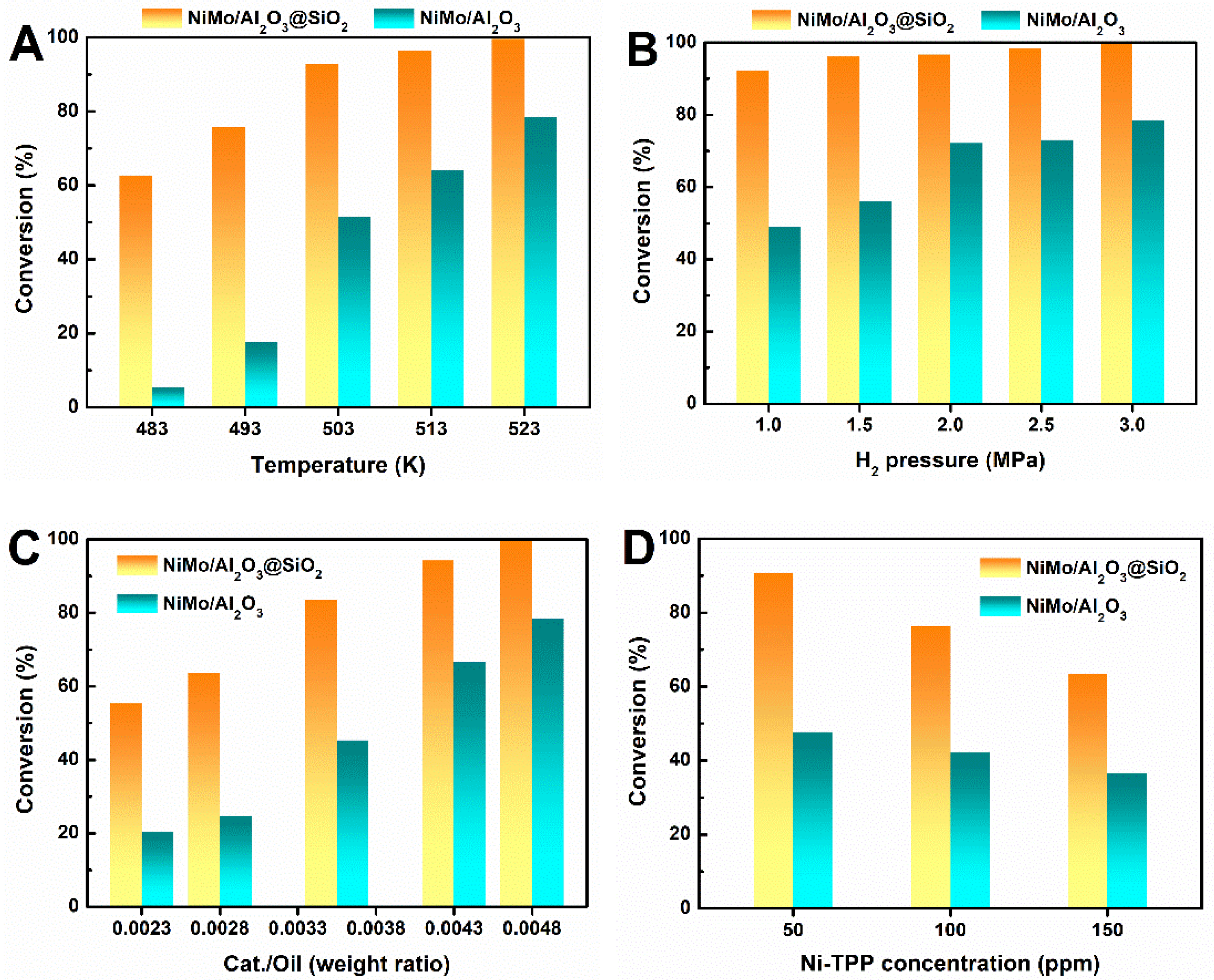
2.4. HDM Performance of NiMo/Al2O3@SiO2 Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.1.2. Preparation of γ-Al2O3 Supports
3.1.3. Preparation of Al2O3@SiO2 Supports
3.1.4. Preparation of Al2O3 and Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalysts
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Catalytic HDM Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Tuning the electrophilicity of vanadium-substituted polyoxometalate based ionic liquids for high-efficiency aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 271, 118936–118943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Gu, B. Impacts of the increasingly strict sulfur limit on compliance option choices: The case study of Chinese SECA. Sustainability 2019, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Characterization, determination and elimination technologies for sulfur from petroleum: Toward cleaner fuel and a safe environment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 25, e00080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Jia, J.; Qi, Z.; Peng, S. Unconventional Oil Ores around the World: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 621, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. In-situ heavy and extra-heavy oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2016, 185, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafi, A.; Albazzaz, H.; Rana, M.S. Hydroprocessing of heavy residual oil: Opportunities and challenges. Catal. Today 2019, 329, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeykina, V.S.; Parkhomchuk, E.V.; Polukhin, A.V.; Parunin, P.D.; Lysikov, A.I.; Ayupov, A.B.; Cherepanova, S.V.; Kanazhevskiy, V.V.; Kaichev, V.V.; Glazneva, T.S.; et al. CoMoNi catalyst texture and surface properties in heavy oil processing. Part I: Hierarchical macro/mesoporous alumina support. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Verma, V.; Khan, A.; Mishra, A.; Anand, M.; Pramod, C.V.; Farooqui, S.A.; Sinha, A.K. Hydrotreating and hydrodemetalation of raw jatropha oil using mesoporous Ni-Mo/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Fuel 2022, 326, 125108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, K.; Prajapati, R.; Maity, S.K.; Sau, M.; Sharma, B.K. Deactivation of a hydrotreating catalyst during hydroprocessing of synthetic crude by metal bearing compounds. Fuel 2019, 243, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas, M.A.; Martínez, M.T.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Rial, C.; Jiménez-Mateos, J.M.; Gómez-García, F.J. Structural and morphological study of metal deposition on an aged hydrotreating catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 220, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelaar, B.M.; Eijsbouts, S.; Bergwerff, J.A.; Heiszwolf, J.J. Hydroprocessing catalyst deactivation in commercial practice. Catal. Today 2010, 154, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Pour, Z.A.; Alnafisah, M.S.; Cortes, P.G.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Elshewy, A.; Sebakhy, K.O. Enhanced catalytic hydrogenation of olefins in sulfur-rich naphtha using molybdenum carbide supported on γ-Al2O3 spheres under steam conditions: Simulating the hot separator stream process. Materials 2024, 17, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, K.; Prajapati, R.; Maity, S.K.; Sharma, B.K. Effect of silica, activated carbon, and alumina supports on NiMo catalysts for residue upgrading. Energies 2020, 13, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.S.; AlHumaidan, F.S.; Navvamani, R. Synthesis of large pore carbon-alumina supported catalysts for hydrodemetallization. Catal. Today 2020, 353, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Fang, W.; Yi, X. Template-free synthesis of hierarchical meso-macroporous γ-Al2O3 support: Superior hydrodemetallization performance. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 168, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Liu, C. NiMo/Al2O3 catalyst containing nano-sized zeolite Y for deep hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrogenation of diesel. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2011, 20, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.K.; Flores, L.; Ancheyta, J.; Fukuyama, H. Carbon-Modified Alumina and Alumina—Carbon-Supported Hydrotreating Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Zeng, H.C. Targeted synthesis of silicomolybdic acid (keggin acid) inside mesoporous silica hollow spheres for Friedel–Crafts alkylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16235–16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y. Self-assembly of cetyl trimethylammonium bromide in ethanol-water mixtures. Front. Chem. China 2006, 1, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidrich, G.; Castagnet, J.F.; Ferkel, H. Dispersion behavior of Al2O3 and SiO2 nanoparticles in nickel sulfamate plating baths of different compositions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.C.; Torres, V.; Popa, M.; Crespo, D.; Calderón-Moreno, J.M. Preparation of core–shell nanospheres of silica–silver: SiO2@Ag. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 5435–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K. The use of nitrogen adsorption for the characterisation of porous materials. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2001, 187, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zuo, T.; Lu, J. Effect of preparation methods on the hydrocracking performance of NiMo/Al2O3 catalysts. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, W.; Hu, D.; Nie, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; Deng, Z.; Yang, Q. Promoting effects of SO42− on a NiMo/γ-Al2O3 hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 5218–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, C.; Rana, M.S.; Ancheyta, J. Surface characterization of Al2O3–SiO2 supported NiMo catalysts: An effect of support composition. Catal. Today 2008, 130, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.E.; Perez-Zurita, M.J.; Carbognani, L.A.; Molero, H.; Vitale, G.; Guzmán, H.J.; Pereira-Almao, P. Preparation of NiMoS nanoparticles for hydrotreating. Catal. Today 2015, 250, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Duan, A.; Xu, C.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Ge, B. Synthesis of NiMo catalysts supported on mesoporous Al2O3 with different crystal forms and superior catalytic performance for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and 4, 6-dimethyldibenzothiophene. J. Catal. 2016, 344, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, J.B. Computerized infrared studies of molybdenum/alumina and molybdenum/silica catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, K.; Legens, C.; Guillaume, D.; Raybaud, P. A rational comparison of the optimal promoter edge decoration of HDT NiMoS vs CoMoS catalysts. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. IFP 2009, 64, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulier, L.; De Beer, V.H.J.; Van Veen, J.A.R.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Correlation between hydrodesulfurization activity and order of Ni and Mo sulfidation in planar silica-supported NiMo catalysts: The influence of chelating agents. J. Catal. 2001, 197, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Yi, X.; Fang, W. NiMoS flower-like structure with self-assembled nanosheets as high-performance hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ekspong, J.; Ashok, A.; Koroidov, S.; Gracia-Espino, E. Solid-state synthesis of few-layer cobalt-doped MoS2 with CoMoS phase on nitrogen-doped graphene driven by microwave irradiation for hydrogen electrocatalysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34323–34332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, K.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Slurry phase hydrocracking of vacuum residue in the presence of presulfided oil-soluble MoS2 catalyst. Fuel 2019, 246, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.D.; Alvarez, C.L.; Beltrán, K.A.; Elguezabal, A.A. Effect of the SiO2 support morphology on the hydrodesulfurization performance of NiMo catalysts. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3646–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Kong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, A.; Kong, L.; Wang, X. Hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene over NiMo supported on yolk-shell silica catalysts with adjustable shell thickness and yolk size. J. Catal. 2022, 410, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Klimova, T. Effect of the support on the high activity of the (Ni)Mo/ZrO2–SBA-15 catalyst in the simultaneous hydrodesulfurization of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT. J. Catal. 2011, 281, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, L.; Barlow, D.E.; Mazur, U.; Hipps, K.W. Scanning tunneling microscopy, orbital-mediated tunneling spectroscopy, and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy of metal (II) tetraphenylporphyrins deposited from vapor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4073–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Catalyst | Al2O3 a (wt.%) | SiO2 a (wt.%) | MoO3 a (wt.%) | NiO a (wt.%) | SBET b (m2·g−1) | Vp c (cm3·g−1) | D c (nm) | LMoS d | NMoS d | fMo d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiMo/Al2O3@SiO2 | 61.64 | 31.19 | 4.33 | 2.84 | 384 | 0.31 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 0.27 |
| NiMo/Al2O3 | 92.86 | / | 4.32 | 2.82 | 177 | 0.35 | 8.9 | 4.1 | 2.9 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Bao, J.; Zeng, S.; Zheng, J.; Fang, W.; Yi, X.; Yang, Q.; Lai, W. Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalyst with Hierarchical Meso-Macroporous Structure for Hydrodemetallization. Catalysts 2025, 15, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070646
Li W, Bao J, Zeng S, Zheng J, Fang W, Yi X, Yang Q, Lai W. Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalyst with Hierarchical Meso-Macroporous Structure for Hydrodemetallization. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weichu, Jun Bao, Shuangqin Zeng, Jinbao Zheng, Weiping Fang, Xiaodong Yi, Qinghe Yang, and Weikun Lai. 2025. "Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalyst with Hierarchical Meso-Macroporous Structure for Hydrodemetallization" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070646
APA StyleLi, W., Bao, J., Zeng, S., Zheng, J., Fang, W., Yi, X., Yang, Q., & Lai, W. (2025). Al2O3@SiO2 Supported NiMo Catalyst with Hierarchical Meso-Macroporous Structure for Hydrodemetallization. Catalysts, 15(7), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070646







