Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis in Human Urine for Resource and Energy Recovery: Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites as Co-Existing Anticatalyzers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
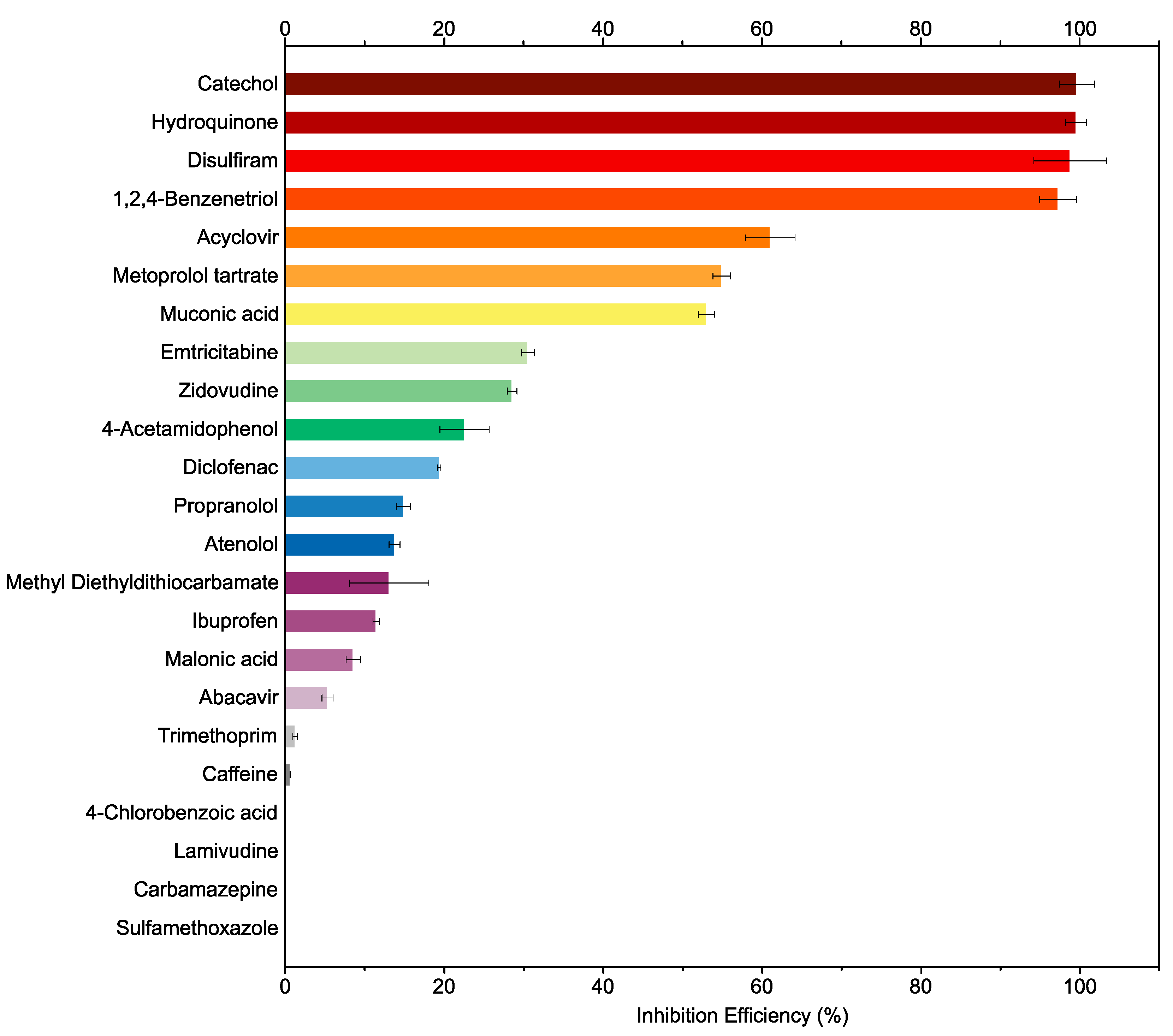
2.1. Survey of Urease Inhibition Efficiencies of Pharmaceuticals
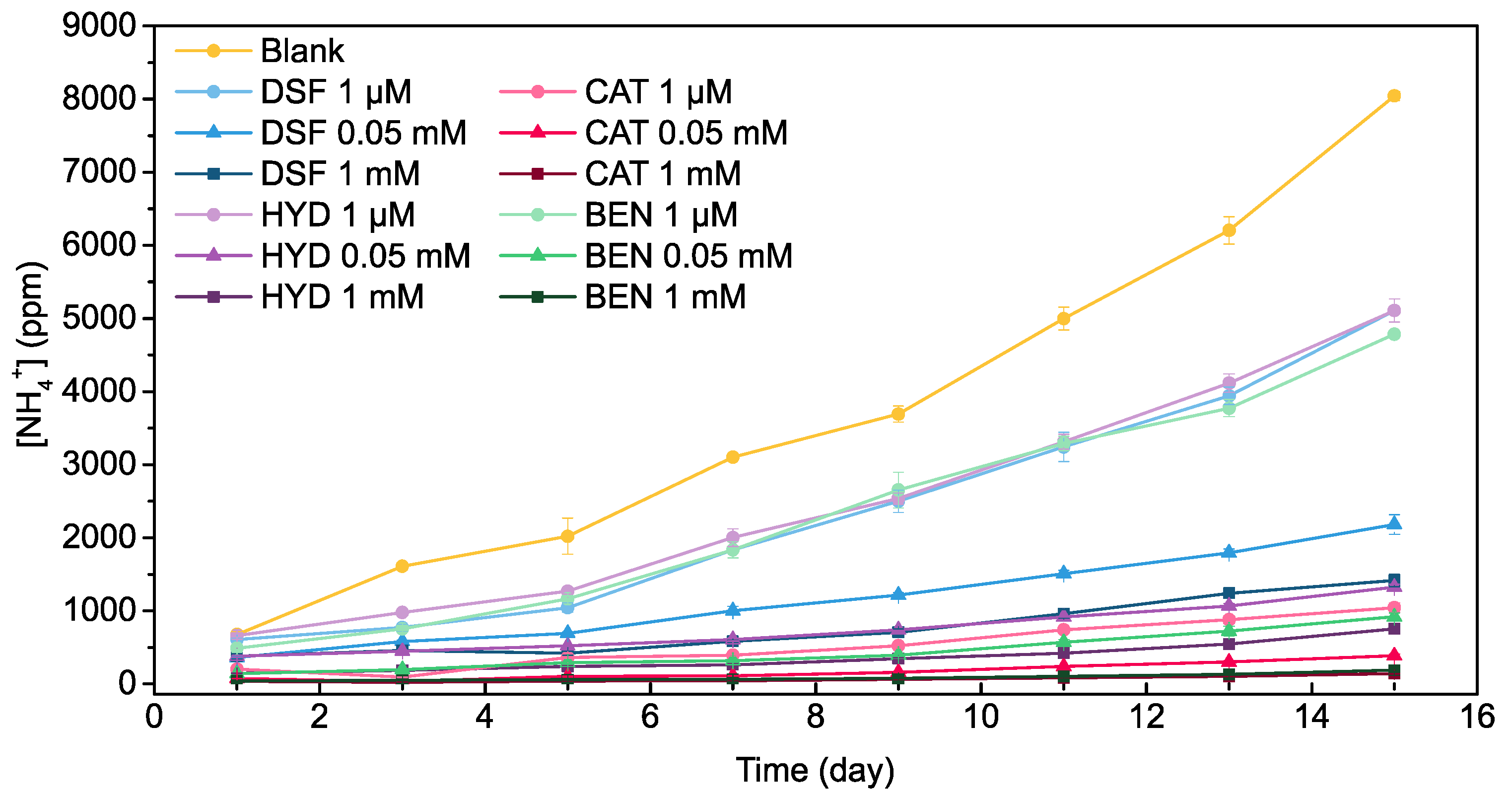
2.2. Long-Term Urine Stabilization Abilities of Pharmaceuticals and Metabolites
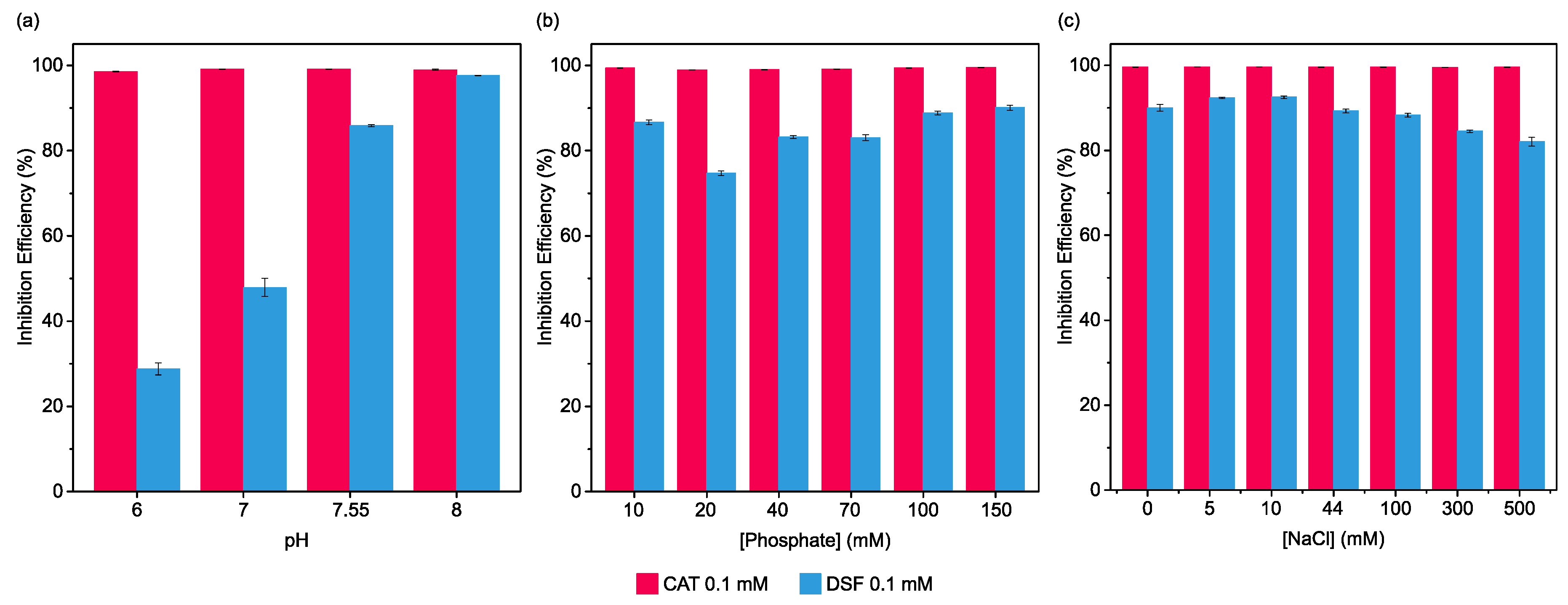
2.3. Influence of pH, Phosphate, and Salinity on Pharmaceuticals’ Urease Inhibition Efficiency
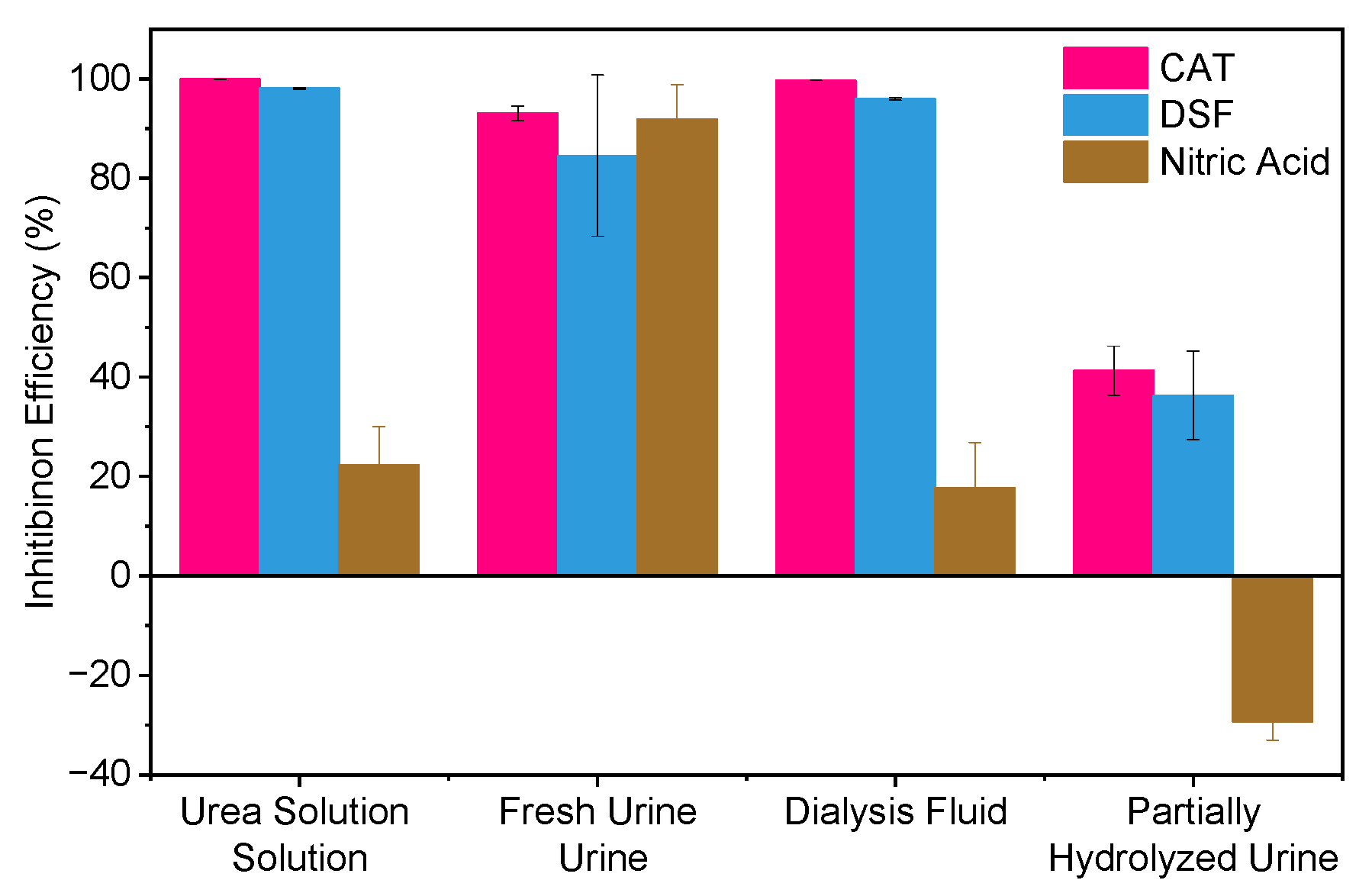
2.4. Impact of Water Matrix Composition on Urease Inhibition Efficiency
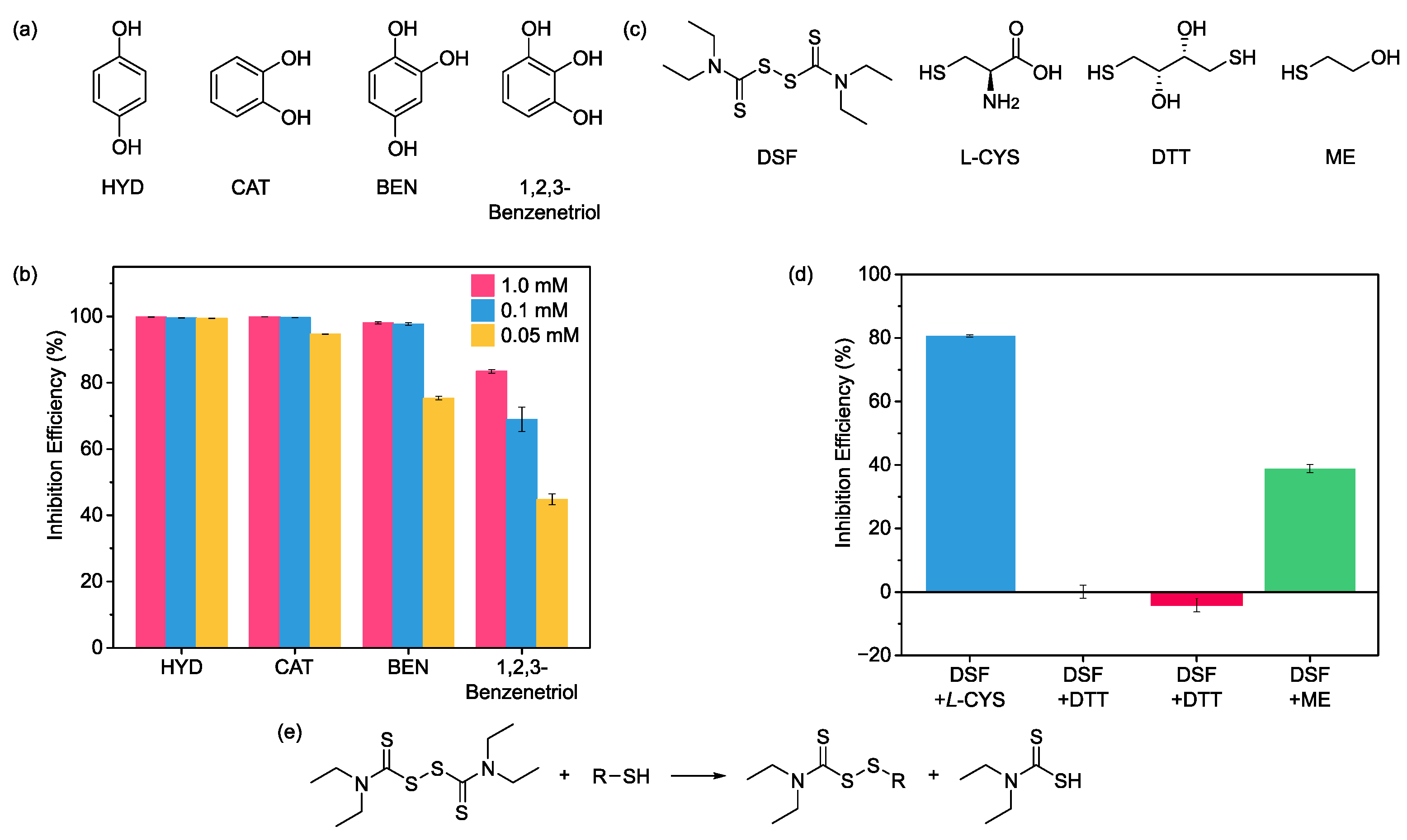
2.5. Mechanism Study of Urease Inhibition for Phenol and Disulfide Functionalities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Concentration of Urease in Stock Solutions
3.4. Preliminary Screening of Pharmaceuticals and Metabolites’ Performance in Inhibition of Urease
3.5. Long-Term Urine Stabilization Experiment
3.6. Impact of pH, Phosphate Concentration, and Salinity on Pharmaceuticals’ Urease Inhibition Efficiencies
3.7. Impact of Water Matrix Composition on Urease Inhibition
3.8. Inhibition Mechanisms
3.9. Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis of CAT and DSF at Low Concentrations
4. Implications for Practical Applications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilsenach, J.A.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effects of Separate Urine Collection on Advanced Nutrient Removal Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarpeh, W.A.; Barazesh, J.M.; Cath, T.Y.; Nelson, K.L. Electrochemical Stripping to Recover Nitrogen from Source-Separated Urine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Jaroniec, M.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S.-Z. Urea Catalytic Oxidation for Energy and Environmental Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1552–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.A.; Alder, A.C.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Maurer, M.; Lienert, J. Source Separation: Will We See a Paradigm Shift in Wastewater Handling? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6121–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.K.L.; Boyer, T.H. Life Cycle Comparison of Centralized Wastewater Treatment and Urine Source Separation with Struvite Precipitation: Focus on Urine Nutrient Management. Water Res. 2015, 79, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.A.; Riechmann, M.E.; Udert, K.M. State of the Art of Urine Treatment Technologies: A Critical Review. Water Res. X 2021, 13, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Pronk, W.; Larsen, T.A. Treatment Processes for Source-Separated Urine. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3151–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udert, K.M.; Larsen, T.A.; Biebow, M.; Gujer, W. Urea Hydrolysis and Precipitation Dynamics in a Urine-Collecting System. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerner, B. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of an Old Enzyme, Urease. Bioorganic Chem. 1991, 19, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, K.; Lee, D.; Qiu, W.; Wang, J. Urea Hydrolysis and Recovery of Nitrogen and Phosphorous as MAP from Stale Human Urine. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, D.; Johansson, E.; Grennberg, K. Storage of Human Urine: Acidification as a Method to Inhibit Decomposition of Urea. Ecol. Eng. 1999, 12, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetta, D.; Padda, A.; Li, X.; Leyva, C.; Mirchandani, P.B.; Boscovic, D.; Boyer, T.H. Real-Time Monitoring and Control of Urea Hydrolysis in Cyber-Enabled Nonwater Urinal System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3187–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, D.; Carrier, C. Comparison of Four Strong Acids on the Precipitation Potential of Gypsum in Brines during Distillation of Pretreated, Augmented Urine: Preliminary Results. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Environmental Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 July 2012; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, H.; Saetta, D.; Boyer, T.H. Characterization of Urea Hydrolysis in Fresh Human Urine and Inhibition by Chemical Addition. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, J.; De Pryck, L.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Rabaey, K.; Clauwaert, P. Electrochemically Induced Precipitation Enables Fresh Urine Stabilization and Facilitates Source Separation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senecal, J.; Vinnerås, B. Urea Stabilisation and Concentration for Urine-Diverting Dry Toilets: Urine Dehydration in Ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, D.G.; Krähenbühl, M.; Köpping, I.; Larsen, T.A.; Udert, K.M. A Novel Approach for Stabilizing Fresh Urine by Calcium Hydroxide Addition. Water Res. 2016, 95, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetta, D.; Boyer, T.H. Mimicking and Inhibiting Urea Hydrolysis in Nonwater Urinals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13850–13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Mahmood, I.B. Stabilization of Source-Separated Human Urine by Chemical Oxidation. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, L. Stabilization of Source-Separated Urine by Heat-Activated Peroxydisulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikematsu, M.; Kaneda, K.; Iseki, M.; Yasuda, M. Electrochemical Treatment of Human Urine for Its Storage and Reuse as Flush Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arve, P.H.; Popat, S.C. Stabilization of Urea for Recovery from Source-Separated Urine Using Electrochemically Synthesized Hydrogen Peroxide. ACS ES T Eng. 2021, 1, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, S.; Funamizu, N. Inhibition Factor of Ammonification in Stored Urine with Fecal Contamination. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahore, M.M.; Ushijima, K.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. Fate of Nitrogen during Volume Reduction of Human Urine Using an On-Site Volume Reduction System. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Xi, Y.; Nazim Uddin, S.M.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on Microbial Inactivation and Urea Decomposition in Human Urine during Thermal Storage. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2017, 7, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svane, S.; Sigurdarson, J.J.; Finkenwirth, F.; Eitinger, T.; Karring, H. Inhibition of Urease Activity by Different Compounds Provides Insight into the Modulation and Association of Bacterial Nickel Import and Ureolysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Melgarejo, A.; Colomer-Lluch, M.; Stoll, C.; Lucena, F.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Sludge As a Potential Important Source of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Both the Bacterial and Bacteriophage Fractions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7602–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The Challenge of Micropollutants in Aquatic Systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 398–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.E.; Thomas, S.M.; Bodour, A.A. Prioritizing Research for Trace Pollutants and Emerging Contaminants in the Freshwater Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T.A. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in the Environment: Agents of Subtle Change? Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. S6), 907–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A Review on the Occurrence of Micropollutants in the Aquatic Environment and Their Fate and Removal during Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, B. Occurrence, Transformation, and Fate of Antibiotics in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 951–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in U.S. Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.R.; Kay, P.; Brown, L.E. Global Synthesis and Critical Evaluation of Pharmaceutical Data Sets Collected from River Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.A.; Lienert, J.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. How to Avoid Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 113, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, M.; Tettenborn, F.; Faika, D.; Gulyas, H.; Otterpohl, R. Comparison of Analytical and Theoretical Pharmaceutical Concentrations in Human Urine in Germany. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3633–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrubini, G.; Calleri, E.; Coccini, T.; Castoldi, A.F.; Manzo, L. Direct Analysis of Phenol, Catechol and Hydroquinone in Human Urine by Coupled-Column HPLC with Fluorimetric Detection. Chromatographia 2005, 62, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillas, S.; Lacasa, E.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Electrolytic and Electro-Irradiated Technologies for the Removal of Chloramphenicol in Synthetic Urine with Diamond Anodes. Water Res. 2018, 128, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojoa-Sierra, S.D.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Herrera-Calderon, E.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Elimination of the Antibiotic Norfloxacin in Municipal Wastewater, Urine and Seawater by Electrochemical Oxidation on IrO2 Anodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendrowski, A.; Boyer, T.H. Phosphate Removal from Urine Using Hybrid Anion Exchange Resin. Desalination 2013, 322, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, Z.; Spendlingwimmer, R. Treatment of Yellow Water by Membrane Separations and Advanced Oxidation Methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronk, W.; Palmquist, H.; Biebow, M.; Boller, M. Nanofiltration for the Separation of Pharmaceuticals from Nutrients in Source-Separated Urine. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, M.B.; Torrejais, J.; Janssens, R.; Luis, P.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Dubey, K.K.; Mandal, M.K.; Bronze, M.R.; Crespo, J.G.; Pereira, V.J. Treatment of Anticancer Drugs in Hospital and Wastewater Effluents Using Nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpeh, W.A.; Udert, K.M.; Nelson, K.L. Comparing Ion Exchange Adsorbents for Nitrogen Recovery from Source-Separated Urine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2373–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, O.; Seiji, K.; Nakatsuka, H.; Watanabe, T.; Yin, S.; Li, G.L.; Cai, S.X.; Jin, C.; Ikeda, M. Excretion of 1,2,4-Benzenetriol in the Urine of Workers Exposed to Benzene. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1989, 46, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesareo, S.D.; Langton, S.R. Kinetic Properties of Helicobacter Pylori Urease Compared with Jack Bean Urease. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 99, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, B.; Zaborska, W. The Effect of Phosphate Buffer in the Range of pH 5.80–8.07 on Jack Bean Urease Activity. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 1999, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, W.T.; Bingham, F.T. Influence of Salinity on Soil Enzyme Activities. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, N.E.; Gazzola, C.; Blakeley, R.L.; Zerner, B. Jack Bean Urease (EC 3.5.1.5). Metalloenzyme. Simple Biological Role for Nickel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 4131–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.J.; Hausinger, R.P. Competitive Inhibitors of Klebsiella Aerogenes Urease: Mechanisms of Interaction with the Nickel Active Site. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15835–15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.L.; Flugga, N.; Boer, J.L.; Mulrooney, S.B.; Hausinger, R.P. Interplay of Metal Ions and Urease. Metallomics 2009, 1, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benini, S.; Rypniewski, W.R.; Wilson, K.S.; Miletti, S.; Ciurli, S.; Mangani, S. A New Proposal for Urease Mechanism Based on the Crystal Structures of the Native and Inhibited Enzyme from Bacillus pasteurii: Why Urea Hydrolysis Costs Two Nickels. Structure 1999, 7, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambelli, B.; Musiani, F.; Benini, S.; Ciurli, S. Chemistry of Ni2+ in Urease: Sensing, Trafficking, and Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciurli, S.; Benini, S.; Rypniewski, W.R.; Wilson, K.S.; Miletti, S.; Mangani, S. Structural Properties of the Nickel Ions in Urease: Novel Insights into the Catalytic and Inhibition Mechanisms. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 190–192, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Su, J.; Wu, D.; Yu, X.; Su, Z.; He, J.; Wu, X.; Kong, S.; Lai, X.; Lin, J.; et al. Kinetics and Mechanism Study of Competitive Inhibition of Jack-Bean Urease by Baicalin. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, e879501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, L.; Cianci, M.; Contaldo, U.; Ciurli, S. Insights into Urease Inhibition by N-(n-Butyl) Phosphoric Triamide through an Integrated Structural and Kinetic Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, F.; Ali, Y.; Ahmad Kiani, F.; Fahad Hassan, S.; Fatima, T.; Khan, A.; Niaz, B.; Hassan, A.; Latif Ansari, F.; Rashid, U. Design, Synthesis, in Vitro Evaluation and Docking Studies on Dihydropyrimidine-Based Urease Inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2017, 74, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, L.; Cianci, M.; Vara, A.G.; Ciurli, S. The Structure of Urease Inactivated by Ag(i): A New Paradigm for Enzyme Inhibition by Heavy Metals. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8240–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, Á.G.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Martínez-Martínez, A.; Aguirre-Reyes, L.; Orozpe-Olvera, J.A.; Ramos-Soto, M.A.; Núñez-Gastélum, J.A.; Alvarado-Tenorio, B.; De la Rosa, L.A. Inhibition of Urease by Disulfiram, an FDA-Approved Thiol Reagent Used in Humans. Molecules 2016, 21, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, B.; Zaborska, W. Jack Bean Urease: The Effect of Active-Site Binding Inhibitors on the Reactivity of Enzyme Thiol Groups. Bioorganic Chem. 2007, 35, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lee, M.H.; Hausinger, R.P.; Clark, P.A.; Wilcox, D.E.; Scott, R.A. Structure of the Dinuclear Active Site of Urease. X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopic Study of Native and 2-Mercaptoethanol-Inhibited Bacterial and Plant Enzymes. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Thiol–Disulfide Exchange Covering Direct Substitution and Thiol Oxidation-Mediated Pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.H. Determination of Blood Urea with P-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quastel, J.H. The Action of Polyhydric Phenols on Urease; the Influence of Thiol Compounds. Biochem. J. 1933, 27, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, D.F. Composition and Concentrative Properties of Human Urine; NASA-CR-1802; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19710023044 (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Drukker, W.; Parsons, F.M.; Gordon, A. Practical Application of Dialysate Regeneration: The Redy System. In Replacement of Renal Function by Dialysis; Drukker, W., Parsons, F.M., Maher, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 244–258. ISBN 978-94-009-9327-3. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, C.; Esposito, R.; Bello, P.; Quarto, E.; Gonzalez, F.M. Cold Carbon Apparatus for Hemodialysis. J. Dial. 1976, 1, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, I.; Wilczek, A. A Rapid Uhplc Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Selected B-Blockers, Nsaids, and Their Metabolites in Human Urine and Water Samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2010, 33, 1776–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, P.; Gaudin, R.; Robert, A.; Francin, J.M.; Maire, C. Improvement in HPLC Analysis of Urinary Trans, Trans-Muconic Acid, a Promising Substitute for Phenol in the Assessment of Benzene Exposure. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1990, 62, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischel, H.N.; Özel Duygan, B.D.; Strande, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Udert, K.M.; Kohn, T. Pathogens and Pharmaceuticals in Source-Separated Urine in EThekwini, South Africa. Water Res. 2015, 85, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cload, P.A. A Review of the Pharmacokinetics of Zidovudine in Man. J. Infect. 1989, 18, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.; Kissinger, P.T. Determination of Acetaminophen Metabolites in Urine by Liquid Chromatography/Electrochemistry. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 125, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.F.; Schneck, D.W.; Hayes, A.H., Jr. Determination of Propranolol and Six Metabolites in Human Urine by High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1979, 162, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, M.E.; Sternberg, M.R.; Pao, C.-I.; Ahluwalia, N.; Pfeiffer, C.M. Urine Excretion of Caffeine and Select Caffeine Metabolites Is Common in the US Population and Associated with Caffeine Intake. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschek, L.D.; Grindel, J.M. Review of the Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Zomepirac in Man and Animals. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1980, 20, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngumba, E.; Gachanja, A.; Nyirenda, J.; Maldonado, J.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Antiretroviral Drugs in Source-Separated Urine, Groundwater, Surface Water and Wastewater in the Peri-Urban Area of Chunga in Lusaka, Zambia. Water SA 2020, 46, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Molecular Weight (g·mol−1) | Concentration (mol·L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea Solution | Fresh Urine | Partially Hydrolyzed Urine | Collected Urine | Dialysis Fluid | ||
| Urea | 60.06 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.00038 |
| Creatinine | 113.10 | - | 0.0012 | - | 0.0097 | 0.0012 |
| Uric acid | 168.11 | - | 0.0021 | - | 0.0021 | 0.000574 |
| NH4OH | 35.04 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.03 | - |
| Na2HPO4 | 141.96 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - |
| NaH2PO4 | 119.98 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.014 | 0.02 | - |
| KCl | 74.55 | - | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | - |
| MgCl2·6H2O | 203.32 | - | 0.0042 | - | - | - |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 147.02 | - | 0.0045 | - | 0.0045 | - |
| Na2SO4 | 142.04 | - | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.0015 | - |
| NH4HCO3 | 79.05 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.00002 | - |
| NaCl | 58.44 | 0.044 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | - |
| pH | - | 6.88 | 5.20 | 7.89 | 9.44 | 6.44 |
| Buffer capacity | 0.0088 | 0.0039 | 0.0135 | 0.0152 | 0.0059 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Guo, L. Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis in Human Urine for Resource and Energy Recovery: Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites as Co-Existing Anticatalyzers. Catalysts 2025, 15, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070630
Chi H, Chen M, Yang W, Li Y, Sun S, Wang H, Yang X, Hoffmann MR, Guo L. Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis in Human Urine for Resource and Energy Recovery: Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites as Co-Existing Anticatalyzers. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070630
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Haoran, Minshu Chen, Wei Yang, Ya Li, Shuhui Sun, Hualin Wang, Xuejing Yang, Michael R. Hoffmann, and Lei Guo. 2025. "Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis in Human Urine for Resource and Energy Recovery: Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites as Co-Existing Anticatalyzers" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070630
APA StyleChi, H., Chen, M., Yang, W., Li, Y., Sun, S., Wang, H., Yang, X., Hoffmann, M. R., & Guo, L. (2025). Inhibition of Urea Hydrolysis in Human Urine for Resource and Energy Recovery: Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites as Co-Existing Anticatalyzers. Catalysts, 15(7), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070630






