Abstract
Microwave-assisted ionothermal strategies offer an effective pathway for rapid zeolite crystallization under mild conditions, while conventional ionothermal approaches are still constrained by prolonged crystallization cycles that limit their industrial applicability. Herein, we report a microwave-activated, ionic liquid-mediated synthesis strategy that enables the precise modulation of crystallization kinetics and composite assembly. By introducing ZSM-5 seeds into the ionic liquid system, the nucleation and growth of AlPO4-5 were significantly accelerated, reducing crystallization time by up to 75% (optimal condition: 60 min). Among various imidazolium-based ionic liquids, [BMMIm]Br demonstrated an optimal balance of hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions, yielding composite zeolites with high surface area (350 m2·g−1) and large pore volume (0.28 cm3·g−1). Comprehensive characterization (XRD, SEM-EDX, NH3-TPD) confirmed the formation of well-defined ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 core–shell structures and revealed tunable acid site distributions depending on the ionic liquid used. In methanol to olefins (MTO) reactions, the composite catalyst exhibited outstanding selectivity towards light olefins (C2=–C4=: 72.84%), markedly outperforming the individual ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 components. The superior catalytic behavior is primarily attributed to the synergistic effect of hierarchical acid site tuning and the integrated core–shell architecture, which together optimize reaction selectivity. This strategy provides a promising route for the rational design of high-performance zeolites with significant industrial applicability.
1. Introduction
Low-carbon olefins [1], as core feedstocks in the chemical industry, exhibit profound correlations between their production processes and energy infrastructure. The coal-dominated energy landscape presents significant resource compatibility challenges with conventional petroleum-based olefin cracking technologies [2,3], driving the strategic advancement of coal-to-olefin processes. While breakthroughs in MTO technologies have mitigated petroleum scarcity constraints [4,5], existing catalytic systems still face critical bottlenecks, including inadequate selectivity regulation and insufficient dynamic market responsiveness, particularly in precise ethylene/propylene ratio control and byproduct suppression [6,7,8].
Microwave technology has revolutionized zeolite catalyst design through its unique energy transfer mechanisms [9,10]. Unlike conventional thermal conduction requiring layered heating, microwave-induced dielectric polarization enables molecular-level energy transfer [11,12], demonstrating dual advantages in zeolite synthesis: ultra-rapid heating (>10 °C·s−1) and precise temperature modulation [13,14,15]. Studies reveal that microwave-assisted crystallization can enhance AlPO4-5 crystallinity while narrowing particle size distribution by over 40% compared to hydrothermal methods. Significantly, ionic liquids (IL) [16] are widely applied in a broad variety of fields, including catalysis, separations, synthesis, and many others, and the synergy between microwave fields and ionic liquid media enables innovative hierarchical pore engineering. Utchariyajit et al. [17] developed a single-step microwave crystallization of AlPO4-5 with optimized structure-directing agents to enhance crystallinity and particle uniformity [18]. Zhao’s group [19] achieved tunable mesopores (3–30 nm) in SAPO-5 through microwave-assisted ionothermal synthesis by regulating P/Al ratios, F/Al ratios, and thermal parameters in eutectic melts. Subsequent work by Zhao et al. [20] established hierarchical SAPO-5 architectures with adjustable mesopore volumes via supersaturation control and acid substitution strategies. Despite the strong acidity of ZSM-5, which typically promotes side reactions [21], its microwave-synthesized composite with AlPO4-5 demonstrates exceptional functionality. By combining the acid-driven cracking capability inherent in ZSM-5 with the shape-selective diffusion characteristics of AlPO4-5, this hybrid system successfully overcomes the selectivity limitations encountered in the MTO reaction [22,23,24].
This study innovatively developed ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 composite catalysts through ionic liquid-mediated microwave synthesis. Systematic optimization of microwave power [25], crystallization kinetics [26,27,28], and acid site matching achieved breakthrough performance: 18% light olefin yield extension versus conventional ZSM-5 [29]. This study proposes the following catalytic enhancement mechanisms: Microwave-driven non-equilibrium nucleation processes generate sub-200 nm microcrystalline structures, significantly enhancing the accessibility of acidic sites [30]. A gradient acid strength distribution system was innovatively constructed from the strong Brønsted acid sites of ZSM-5 zeolite to the weak acid sites of AlPO4-5 zeolite. This gradient design maintains C-C bond cleavage activity (conversion rate >95%) while suppressing side reactions to below 5%. By establishing a microwave-assisted synthesis optimization model and combining molecular-level studies on the synergy mechanism between acidic site distribution and pore channel mass transfer, the structure-activity relationship between acid strength gradient distribution and mass transfer kinetics in the catalyst system was elucidated. The research outcomes not only deepen the understanding of zeolite catalytic mechanisms but also provide scientifically rigorous foundations with both theoretical depth and engineering applicability for next-generation coal-based olefin catalytic technologies
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Microwave-Assisted Ion-Thermal Process Conditions on the Crystallization of ALPO4-5 Zeolite
The AlPO4-5 zeolite was synthesized using [EMMIm]Br as the solvent via a microwave-assisted ionothermal method, as depicted in Figures S1–S13. A systematic investigation was conducted to evaluate the influence of key synthesis parameters, including crystallization temperature, microwave power, heating rate, and crystallization time. The experimental results revealed that an increase in crystallization temperature promoted the zeolite crystallization process [31]. However, excessively high temperatures resulted in the formation of impure crystals. The optimal crystallization temperature for producing high-purity AlPO4-5 was determined to be 180 °C [32]. The morphology of the crystals was primarily influenced by microwave power, underscoring its critical role in controlling the structural characteristics of the zeolite.
The heating rate was another key factor affecting the relative crystallinity of the AlPO4-5 zeolite. Higher heating rates initially improved relative crystallinity, reaching a maximum at 40 °C·min−1, before declining. This behavior can be attributed to the interplay between heating rate, heating duration, and crystallization kinetics. At lower heating rates, extended heating durations result in suboptimal crystallization rates, reducing crystallinity. Conversely, excessively rapid heating shortens the crystallization period, limiting the time available for proper crystal formation, thus also reducing crystallinity. The microwave-assisted ionothermal synthesis method significantly reduced the required crystallization time to just 90 min [33], a remarkable improvement compared to the 24 h duration typically required in traditional ionothermal synthesis. Increasing crystallization time generally enhanced crystallinity; however, prolonged crystallization led to a decrease in crystallinity, likely due to overgrowth or secondary nucleation effects.
The optimal synthesis conditions for AlPO4-5 zeolites were identified as a microwave crystallization temperature of 180 °C, microwave power of 600 W, a heating rate of 40 °C·min−1, and a crystallization time of 90 min. These parameters provided a balance between crystal growth and structural stability, resulting in zeolites with high crystallinity and purity. The results of this study offer a valuable framework for optimizing zeolite synthesis using microwave-assisted ionothermal techniques.
2.2. Structural Characterization of ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 Zeolite with Different Kinds of Ionic Liquid
The XRD patterns of Z/A-60 min, ZSM-5, and Al-90 min samples synthesized in [EMMIm]Br are shown in Figure 1a. Characteristic diffraction peaks of AlPO4-5 were observed at 2θ = 7.4°, 19.8°, 21.1°, and 22.4°. For Z/A-60 min, diffraction peaks appeared at 2θ = 7.9°, 8.8°, 23°, and 23.8°, while ZSM-5 displayed peaks at 2θ = 7.4°, 7.9°, 8.8°, 19.8°, 21.1°, 22.4°, 23°, and 23.8°. That reveals the simultaneous presence of diffraction peaks corresponding to both ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5, confirming the formation of a dual-phase zeolite structure. Notably, the intensities of the diffraction peaks for Z/A-60 min at similar 2θ angles were significantly lower than those observed for individual ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 zeolites. This reduction in peak intensity suggests interactions between the two phases, potentially indicating partial structural integration or the formation of a composite material.
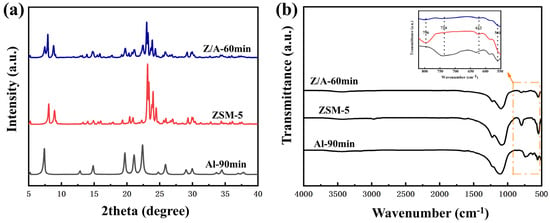
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns of synthesized zeolite in [EMMIM]Br. (b) FT-IR spectra of synthesized zeolite in [EMMIM]Br.
The FT-IR spectra of Z/A-60 min, ZSM-5, and Al-90 min samples are shown in Figure 1b. The FT-IR spectrum of Z/A-60 min displayed absorption bands at 796, 734, 622, and 561 cm−1, corresponding to the characteristic vibrational modes of ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5. The overlap of these bands further corroborates the successful synthesis of the Z/A-60 min composite, integrating the structural features of both zeolites. Specifically, the absorption band at 796 cm−1 is attributed to the symmetric stretching vibration of Si-O-Si in ZSM-5, while the band at 734 cm−1 is related to the bending vibration of Al-O-P in AlPO4-5. The coexistence of these spectral features provides strong evidence of the synergistic integration of the two zeolite frameworks.
The SEM images of the synthesized samples Z/A-60 min, ZSM-5, and Al-90 min are presented in Figure 2. Figure 2a,b reveals that the AlPO4-5 sample (Al-90 min) exhibits a uniform ellipsoidal morphology, indicative of homogeneous crystal growth. In contrast, c and d show that ZSM-5 comprises irregularly shaped agglomerates, reflecting non-uniform nucleation and growth behavior. The e and f demonstrate that the Z/A-60 min composite features a hybrid morphology composed of both spherical particles and irregular agglomerates, suggesting the coexistence and spatial integration of the two distinct zeolitic phases. Specifically, the spherical particles with diameters ranging from 200 to 500 nm are consistent with the characteristic morphology of AlPO4-5, while the larger irregular agglomerates (1–3 μm) align with the polycrystalline nature of ZSM-5. This morphological duality supports the formation of a heterogeneous composite, in agreement with the phase coexistence and interfacial interactions inferred from the corresponding XRD and FT-IR analyses.
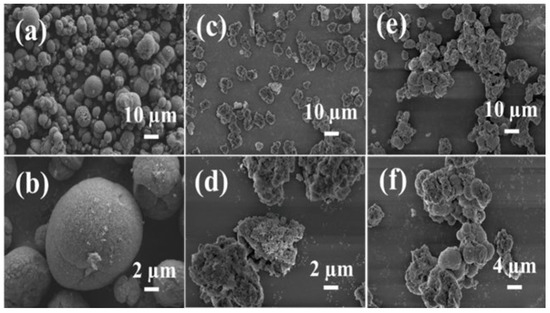
Figure 2.
SEM images of samples Al-90 min (a,b), ZSM-5 (c,d), as well as Z/A-60 min (e,f).
EDX analysis confirms the presence of Si alongside Al and P elements in the composite sample, providing direct evidence for the incorporation of ZSM-5 within the Z/A-60 min system (Table 1). The measured Si/Al atomic ratio of the composite is 68.9, notably lower than the typical ratio of 80 observed in pure ZSM-5. This 13.9% deviation is attributed to the presence of the AlPO4-5 phase, which lacks silicon, thereby diluting the overall Si content and reducing the Si/Al ratio.

Table 1.
EDX analysis of Z/A-60 min.
Furthermore, the relative enrichment of Al in the AlPO4-5 domains is estimated to be approximately 42% higher than in the ZSM-5 phase, suggesting significant elemental redistribution during composite formation. This redistribution, potentially driven by interfacial charge-balancing effects, may contribute to the stabilization of the heterojunction interface. These compositional insights are consistent with previous XRD results indicating lattice distortion and FT-IR spectra revealing overlapping vibrational bands, collectively providing multiscale evidence for the structural integration and synergistic interaction within the Z/A-60 min composite zeolite.
The XRD patterns confirm the successful synthesis of the ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 composite zeolite in the ionic liquid [BMIm]Br (Figure 3a). For the [B]-Al-90 min sample, characteristic diffraction peaks of the AlPO4-5 phase are observed at 2θ = 7.4°, 19.8°, 21.1°, and 22.4°, while ZSM-5 exhibits distinct reflections at 2θ = 7.9°, 8.8°, 23°, and 23.8°. The XRD profile of [B]-Z/A displays a combination of diffraction peaks corresponding to both ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 at 2θ = 7.4°, 7.9°, 8.8°, 19.8°, 21.1°, 22.4°, 23°, and 23.8°, indicating the coexistence of the two crystalline phases. Furthermore, the coexistence of characteristic peaks from both phases in the composite sample, without the emergence of new peaks, confirms that ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 exist as independent crystalline phases rather than forming a solid solution. However, the significantly reduced intensity of the composite’s characteristic peaks compared to the individual components may arise from the formation of defect structure or lattice contraction in the ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 frameworks [34]. The attenuated intensity of these peaks in the [B]-Z/A sample, relative to the individual components, suggests a degree of structural interaction or partial integration between the ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 domains, possibly accompanied by lattice strain or interfacial effects. FT-IR spectroscopy further supports the formation of the composite zeolite (Figure 3b). The spectrum of [B]-Z/A exhibits overlapping absorption bands at 796, 734, 622, and 561 cm−1, corresponding to the characteristic framework vibrations of both ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5. These superimposed features confirm the successful incorporation of structural units from both zeolitic frameworks, evidencing the hybrid nature of the synthesized composite.
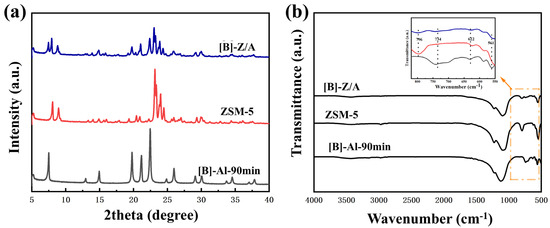
Figure 3.
(a) XRD patterns of synthesized zeolite in [BMMIM]Br. (b) FT-IR spectra of synthesized zeolite in [BMMIM]Br.
The SEM images of the [B]-Z/A, ZSM-5, and [B]-Al-90 min samples (Figure 4) provide insights into their distinct morphological features. As shown in Figure 4a,b, [B]-Al-90 min exhibits a uniform ellipsoidal morphology, the regular morphology is formed through microwave ionothermal synthesis, and its uniformity is attributed to the rapid nucleation and controlled growth mechanism enabled by microwave heating, while ZSM-5 (Figure 4c,d) displays irregular agglomerated particles. And [B]-Z/A exhibits a large irregular block of lamellar ZSM-5 particles scattered on the surface of the AlPO4-5 shell. This dual-phase morphology corroborates the structural features observed in XRD and FT-IR analyses, confirming the successful integration of the two zeolitic components.
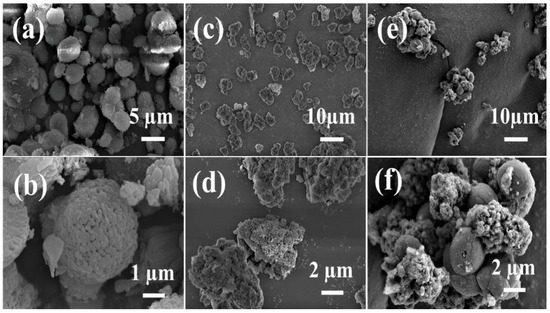
Figure 4.
SEM images of samples [B]-Al-90 min (a,b), ZSM-5 (c,d), and [B]-Z/A (e,f).
The EDX analysis (Table 2) confirms the presence of Al, P, and Si elements in the [H]-Z/A sample. Notably, Si was not present in the raw materials used for synthesizing AlPO4-5, indicating the incorporation of ZSM-5 in the composite. Furthermore, the measured Si/Al ratio of the sample is 72.4, slightly lower than the nominal Si/Al ratio of pure ZSM-5 (80). This deviation is likely due to the contribution of AlPO4-5, which lacks silicon in its framework, thereby diluting the overall silicon content and reducing the Si/Al ratio.

Table 2.
EDX analysis of [B]-Z/A.
The XRD and FT-IR analyses further confirm the composite nature of the synthesized materials. As shown in Figure 5a, the XRD pattern of [H]-Al-90 min exhibits the characteristic diffraction peaks of AlPO4-5 at 2θ = 7.4°, 19.8°, 21.1°, and 22.4°, without any detectable impurity peaks, indicating high phase purity. In contrast, ZSM-5 shows its typical diffraction peaks at 2θ = 7.9°, 8.8°, 23.0°, and 23.8°, consistent with its MFI topology. Notably, the XRD pattern of the composite [H]-Z/A displays diffraction peaks corresponding to both AlPO4-5 and ZSM-5 at 2θ = 7.4°, 7.9°, 8.8°, 19.8°, 21.1°, 22.4°, 23.0°, and 23.8°, confirming the coexistence of both phases. The reduced intensity of the characteristic peaks in [H]-Z/A compared to the individual components suggests structural interaction and mutual influence between the two zeolites. Figure 5b presents the FT-IR spectra of [H]-Z/A, ZSM-5, and [H]-Al-90 min. The composite [H]-Z/A exhibits absorption bands at 813, 749, 628, and 559 cm−1, corresponding to the characteristic vibrations of both ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 frameworks. The superimposed IR features further validate the successful integration of the two zeolitic components in the composite structure.
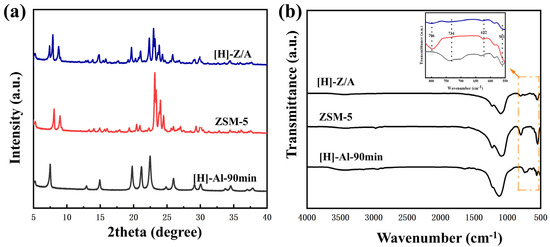
Figure 5.
(a) XRD patterns of synthesized zeolite in [HMMIM]Br. (b) FT-IR spectra of synthesized zeolite in [HMMIM]Br.
The SEM images reveal distinct morphological characteristics among the samples. [H]-Al-90 min (Figure 6a,b) exhibits a uniform ellipsoidal morphology, the regular morphology is formed through microwave ionothermal synthesis, and its uniformity is attributed to the rapid nucleation and controlled growth mechanism enabled by microwave heating, while ZSM-5 (Figure 6c,d) displays irregular agglomerated particles. In contrast, [H]-Z/A (Figure 6e,f) presents a heterogeneous morphology that integrates features of both components, reflecting the effective combination and intergrowth of the ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 phases within the composite structure.
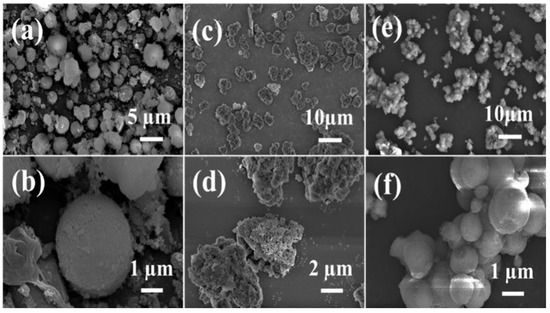
Figure 6.
SEM images of samples [H]-Al-90 min (a,b), ZSM-5 (c,d), and [H]-Z/A (e,f).
Table 3 presents the EDX elemental analysis of the [H]-Z/A composite sample. The data confirm the presence of Al, P, and Si elements. Notably, the presence of Si—despite its absence in the raw materials used for AlPO4-5 synthesis—provides strong evidence for the successful incorporation of ZSM-5 into the composite. Furthermore, the measured Si/Al atomic ratio in the composite is approximately 75, which is slightly lower than that of pure ZSM-5 (Si/Al = 80). This deviation is likely attributed to the introduction of AlPO4-5 into the composite, which contributes additional Al but no Si, thereby lowering the overall Si/Al ratio.

Table 3.
EDX analysis of [H]-Z/A.
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of [H]-Z/A, Z/A-60 min, and [B]-Z/A (Figure 7a) exhibit typical type IV behavior with pronounced hysteresis loops, characteristic of mesoporous and macroporous materials. Corresponding pore size distribution curves (Figure 7b) display broad distributions with prominent peaks in the 30–100 nm range, which can be attributed to intercrystalline voids and macroporous structures. These observations collectively confirm the presence of hierarchical porosity within the composite zeolites.
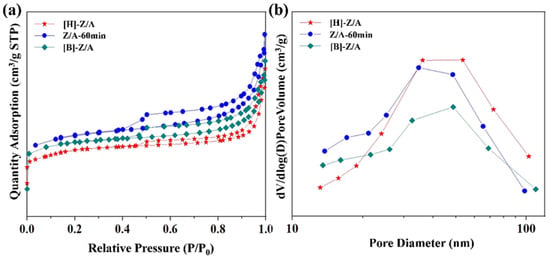
Figure 7.
(a) N2 adsorption and desorption isotherms of composite zeolites synthesized in different ionic liquids. (b) Pore size distribution of composite zeolites synthesized in different ionic liquids.
2.3. Catalyst Reaction Performance Test
As shown in Table S1, the specific surface area of the composite zeolites progressively decreases with increasing alkyl chain length of the ionic liquids, suggesting that different ionic liquids play a pivotal role in tailoring the pore structure during microwave-assisted ionothermal synthesis. The catalytic performance of various samples in the MTO reaction, including methanol conversion and product distribution, is summarized in Table 4 and illustrated in Figure 8a. The ZSM-5 sample yielded higher amounts of alkanes and C5+ hydrocarbons, likely due to its higher acidity and relatively larger pore size, which facilitates enhanced hydrogen transfer. In contrast, AlPO4-5, characterized by weak acidity, exhibited negligible activity for low-carbon olefin production. Among the tested catalysts, [B]-Z/A exhibited the highest selectivity toward light olefins (72.84%), representing improvements of 18%, 3.53%, and 7.29% over Z5, Z/A-60 min, and [H]-Z/A, respectively. Moreover, [B]-Z/A showed a notably lower alkane selectivity, highlighting its superior performance in suppressing hydrogen transfer side reactions. Besides, as shown in Figure S14, Z/A-60 min exhibited significant deactivation after 16 h of operation, whereas [H]-Z/A and [B]-Z/A maintained stable performance with no signs of deactivation even after 31 h.

Table 4.
Catalytic properties of different samples in the MTO reaction.
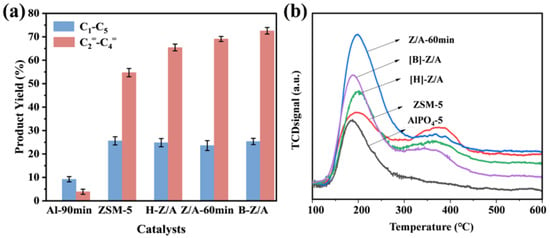
Figure 8.
(a) Product yield of samples. (b) NH3-TPD curves of samples.
NH3-TPD profiles of Z/A-60 min, [B]-Z/A, [H]-Z/A, ZSM-5, and Al-90 min (Figure 8b) further elucidate the acidity characteristics of these materials. Al-90 min displayed only weak acid sites, whereas ZSM-5 exhibited both weak and strong acid sites. Notably, an excessive density of strong acid sites can lead to prolonged interaction between reactants and acid centers, adversely affecting the selectivity towards the desired product. In contrast, a higher proportion of weak acid sites facilitates the selective cracking of bulky intermediates, thereby favoring the formation of light olefins. Accordingly, [B]-Z5/Al5, which features a well-balanced acid profile characterized by reduced strong acidity and enriched weak acid density, outperforms other catalysts in both activity and selectivity (Table 5). And compared with ZSM-5, the composite zeolites demonstrated a downward shift in high-temperature desorption peaks along with decreased peak intensities, while low-temperature desorption peaks were enhanced. These observations indicate a moderated acid strength and a redistribution of acid site types in the composite systems, attributed to the integration of ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 components. The modulated acidity correlates well with the improved olefin selectivity in the MTO reaction, reinforcing the conclusion that composite zeolites enable the fine-tuning of acidity and catalytic behavior through rational structural design.

Table 5.
The acidities over various catalysts.
3. Materials and Methods
The Preparation of ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 composite zeolite in ionic liquids: a certain amount of ionic liquid was added into a 50 mL three-necked flask, and the three-necked flask was connected to a condensing device and placed in a water bath at 75 °C, 1.77 g of phosphoric acid (Tianjin Kaitong Chemical Reagent Co, Ltd. Tianjing, China), 0.02 g of HF (Luoyang Chemical Reagent Factory, Henan, China), and 1.30 g aluminum isopropoxide Sigma–Aldrich, Shanghai Trade Co, Ltd., Shanghai, China) 1.60 g of ZSM-5 seeds (Gongyi Xiangrui Environmental Protection Material Co., Ltd., Henan, China) and 0.14 g of H2O with stirring were added sequentially under stirring, and triethylamine(Xilong Chemical Co, Ltd., Guangdong, China) was added after 30 min of stirring. The molar ratio of the initial gel was 1.0 Al2O3(Macklin, Shanghai, China): 2.4 P2O5: 12 ionic liquids: 1.5 triethylamine 0.1 HF, and after continuous stirring for 1 h, the three-necked flask and the condensing device were transferred to a microwave reactor with a microwave power of 600 W and a heating rate of 40 °C·min−1 to 180 °C for crystallization. After crystallization, the three-necked flask was cooled to room temperature, deionized water was added and ultrasonicated for 10 min, and the product was washed with deionized water to neutralize and then put into an oven at 90 °C for 10 h to dry the product. The product synthesized in [EMMIM]Br is named Z/A-t, where Z/A denotes ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 and t denotes the time taken to synthesize ZSM-5/AlPO4-5. The product synthesized in [BMMIM]Br was named [B]-Z/A, and the sample synthesized in [HMMIM]Br was named [H]-Z/A.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we successfully pioneered a microwave-assisted ionothermal strategy for the rapid and controllable synthesis of ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 composite zeolites using various ionic liquid systems. Compared with conventional oven-heating methods, this approach significantly reduced the crystallization time—most notably for AlPO4-5, from 24 h to just 90 min—while maintaining high phase purity and structural integrity. Detailed characterization revealed that the ionic liquids not only promoted strong interfacial integration between ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 domains but also enabled fine-tuning of the acid site distribution within the composite framework. Moreover, the resulting composite exhibits a substantially higher density of weak acid sites compared to individual ZSM-5 or AlPO4-5 molecular sieves, along with a reduced concentration of strong acid sites relative to standalone ZSM-5. This optimized acid site distribution directly contributes to enhanced light olefin selectivity in MTO catalysis. The structural evolution exhibited a clear dependence on the alkyl chain length of the ionic liquids: longer chains resulted in decreased specific surface area, micropore area, and external surface area, accompanied by an increase in average pore diameter. Catalytic testing in the methanol-to-olefins reaction demonstrated that all three composite zeolites synthesized with different ionic liquids outperformed the individual ZSM-5 and AlPO4-5 counterparts in terms of light olefin selectivity. These findings underscore the unique advantages of microwave-assisted ionothermal synthesis in engineering multifunctional composite zeolites with tunable physicochemical properties, offering a promising pathway for tailoring catalytic behavior and enhancing product selectivity in MTO and related tandem catalytic processes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15060605/s1, Figure S1: XRD patterns of the samples obtained at different crystallization temperatures. Figure S2: Relative crystallinity of the samples obtained at different crystallization temperatures. Figure S3: XRD patterns of the samples obtained at different microwave powers. Figure S4: XRD patterns of composite zeolites obtained at different crystallization times. Figure S5: Relative crystallinity of the samples obtained at different microwave powers. Figure S6: SEM images of the samples obtained at different microwave powers (a,b) Al-200W (c,d), Al-400W (e, f), Al-600W (g, h), Al-800W. Figure S7: XRD patterns of the samples obtained at different heating rates. Figure S8: Relative crystallinity of the samples obtained at different heating rates. Figure S9: XRD patterns of the samples obtained at different crystallization times. Figure S10: Relative crystallinity of samples obtained at different crystallization times. Figure S11: TG-DTA diagram of the sample Al-90 min. Figure S12: FT-IR patterns of the sample Al-90 min. Figure S13: Relative crystallinity of the composite zeolites obtained at different crystallization times. Figure S14: Catalytic performances of different catalysts in MTO. Table S1: Pore structure parameters of ZSM-5/AlPO4-5 synthesized in different ionic liquids.
Author Contributions
L.H.: writing—original draft, supervision, funding acquisition; M.Z.: writing—reviewing and editing; H.L.: writing—reviewing and editing; J.F.: writing—reviewing and editing, supervision; Z.P.: writing—reviewing and editing, funding acquisition; H.D.: formal analysis; J.Z.: formal analysis. Y.Z.: formal analysis; L.W.: formal analysis; C.J.: formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program (No. 2022YFE0208300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22278380), and the Excellent Youth of Henan Province (242300421122).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, L.; Gao, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Jun, K.W.; Kim, S.K.; Zhao, T.; Wan, H.; Guan, G. Carbon-neutral light olefins production for energy decarbonization: Process development and techno-econo-environmental analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Co2C nanoprisms for syngas conversion to lower olefins with high selectivity. Chin. J. Cat. 2017, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Li, P.; Yuan, X. Process optimization, exergy efficiency, and life cycle energy consumption-GHG emissions of the propane-to-propylene with/without hydrogen production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Song, X.; Yan, W.; Yu, J. Low-energy adsorptive separation by zeolites. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis of low-silica SAPO-34 at lower hydrothermal temperature by additional pressure and its enhanced catalytic performance for methanol to olefin. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 323, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, N.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. Conversion of methanol to propylene over SAPO-14: Reaction mechanism and deactivation. Chin. J. Cat. 2022, 43, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, P.; Ren, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Peng, H.; Jiang, J.-G.; Guan, Y.; Wu, P. New CHA-Type aluminoborosilicates as efficient catalysts for MTO and NH3-SCR of NOx reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Qian, Y. Comprehensive energy analysis and integration of coal-based MTO process. Energy 2021, 214, 119060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanchao, W.; Yapeng, L.; Dongsheng, L.; Qiuju, H.; Yi, P.; Chengcheng, J.; Lei, L.; Jin, L.; Jian, H. Pyrolysis of Oil Shale Based on Electromagnetic Heating Technology—A Review. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2023, 58, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khaled, D.; Novas, N.; Gazquez, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Microwave dielectric heating: Applications on metals processing. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 82, 2880–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makova, A.S.; Timofeeva, M.N.; Tkachenko, O.P.; Panchenko, V.N.; Leonov, A.V.; Kapustin, G.I.; Davshan, N.A.; Kalmykov, K.B.; Kustov, A.L.; Ter-Akopyan, M.N.; et al. Effect of microwave irradiation on the synthesis of zeolite with ferrierite structure: Study of acid and catalytic properties. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 703, 135321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Hu, X.; Song, H.; Xia, G.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Yu, R.; Moskovits, M. Microwave synthesis of zeolites and their related applications. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 323, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Lin, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Bai, L.; Hu, D.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of all-silica DDR zeolite by microwave heating. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2016, 219, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W. Microwave synthesis of zeolite membranes: A review. J. Membrance. Sci. 2008, 316, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.; Ibrahim, D.; Komarneni, S. Microwave-assisted versus conventional synthesis of zeolite A from metakaolinite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 115, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Doert, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ruck, M. Inorganic Synthesis Based on Reactions of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22148–22165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utchariyajit, K.; Wongkasemjit, S. Structural aspects of mesoporous AlPO4-5 (AFI) zeotype using microwave radiation and alumatrane precursor. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 114, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Lv, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, P. Synthesis EMT-type zeolite by microwave and hydrothermal heating. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2019, 278, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Kang, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Ionothermal synthesis of mesoporous SAPO-5 zeolites by microwave heating and using eutectic solvent as structure-directing agent. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2012, 151, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wen, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, A.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Hierarchically structured SAPO-5 zeolite catalysts with tailored mesoporosity for alkylation reaction. J. Porous. Mat. 2015, 22, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Asahina, S.; Asano, N.; Zhang, G.; Qian, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Mintova, S. The inner heterogeneity of ZSM-5 zeolite crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2021, 9, 4203–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savu, S.V.; Marin, R.C.; David, A.; Olei, A.B.; Dumitru, I.; Tarnita, D.; Maternova, A.; Savu, I.D. Reducing NOx Emissions through Microwave Heating of Aftertreatment Systems for Sustainable Transport in the Inland Waterway Sector. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Wen, J.; Li, A.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Microwave synthesis of AFI-type aluminophosphate zeolite under solvent-free conditions. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2015, 213, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Sang, X.; Yang, G. Synthesis of a phosphomolybdic acid-modified AlPO4-5/SAPO-34 composite catalyst and its catalytic performance in the MTO reaction. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2024, 669, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmani, F.M.; Halladj, R.; Askari, S. Effect of contributing factors on microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized SAPO-34 zeolites. Powder Technol. 2012, 221, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin-yan, Z.; Ting-ting, D.; Yao, W.; Jing-yue, Y.; Xue, W.; Yan-yan, G.; Qun, S.; Xin, Z.; Shao-qing, Z. Green synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 zeolite by seed-assisted route for effective reduction of nitric oxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhung, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, J.-S. Crystal size control of transition metal ion-incorporated aluminophosphate zeolites: Effect of ramping rate in the syntheses. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 112, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Sun, A.; Wu, X.; Hai, G.; Hu, J.; Li, T.; Li, G. The preparation of nano-sized H[Zn, Al]ZSM-5 zeolite and its application in the aromatization of methanol. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2011, 143, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, W. Strategies to Enhance the Catalytic Performance of ZSM-5 Zeolite in Hydrocarbon Cracking: A Review. Catalysts 2017, 7, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, R.; Wu, J.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Miao, Z.; Meng, X. Research on double template agents to regulate the grain growth behavior of SAPO-34. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2023, 349, 112428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Dong, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Facile synthesis of FeAlPO-5 zeolite in eutectic mixture via a microwave-assisted process. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2012, 151, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Chang, P.; Geng, S. Crystal morphology control of AlPO4-11 zeolites by microwave irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Song, X.; Liang, Z. Ultrafast synthesis of SAPO-17 zeolites with excellent CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 separation performance. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 4519–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Jiang, X.-G.; Lu, T.-L.; Wang, B.-S.; Xu, J.; Zhan, Y.-Z.; Wang, J.-F.; Rawal, A.; Zhao, C. Preparation of composite zeolites in polymer hydrogels and their catalytic performances in the methanol-to-olefin reaction. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 165, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).