Ru Nanoparticle Assemblies Modified with Single Mo Atoms for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Seawater Electrocatalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
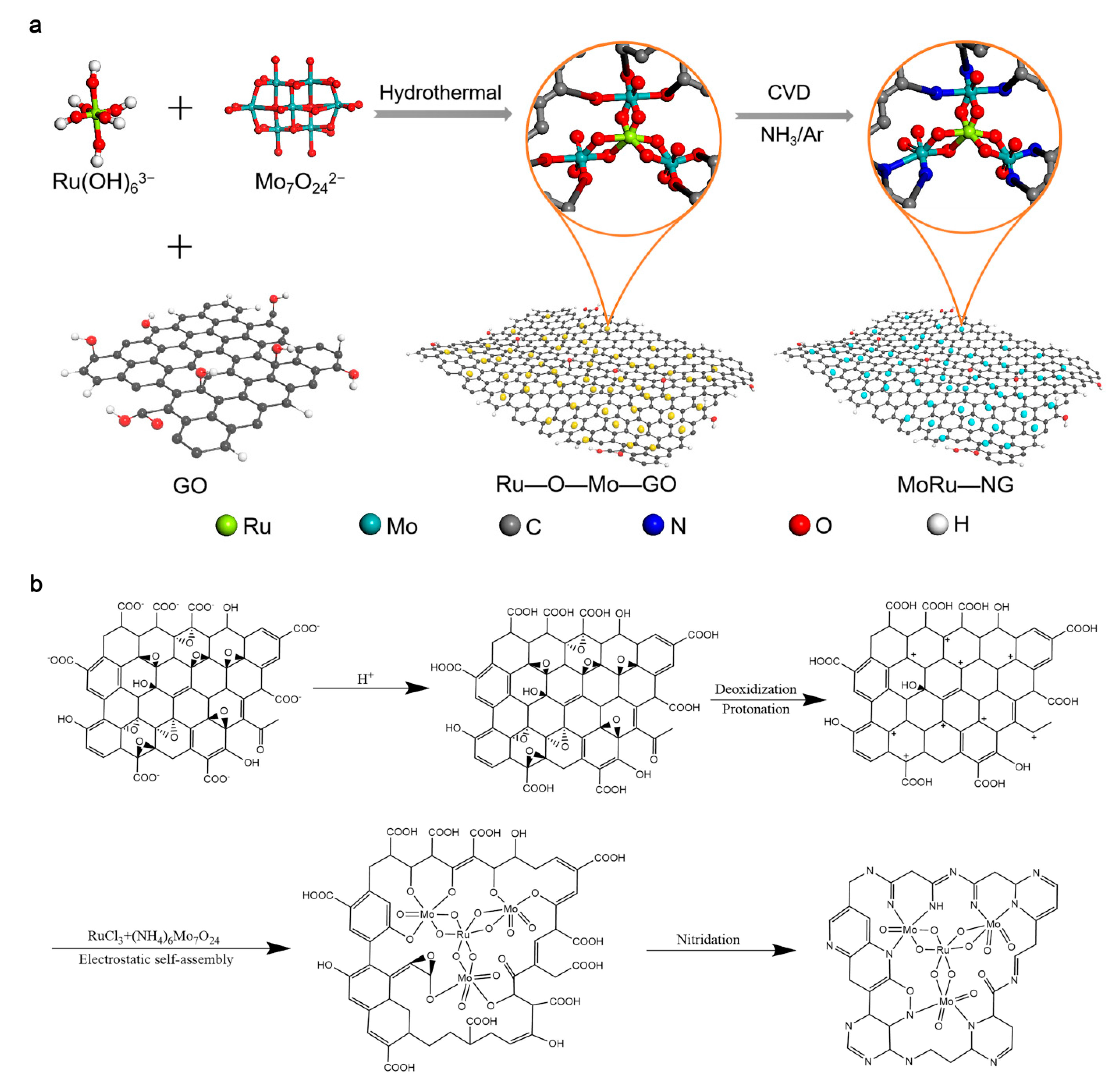
2.1. Synthesis of MoRu-NG
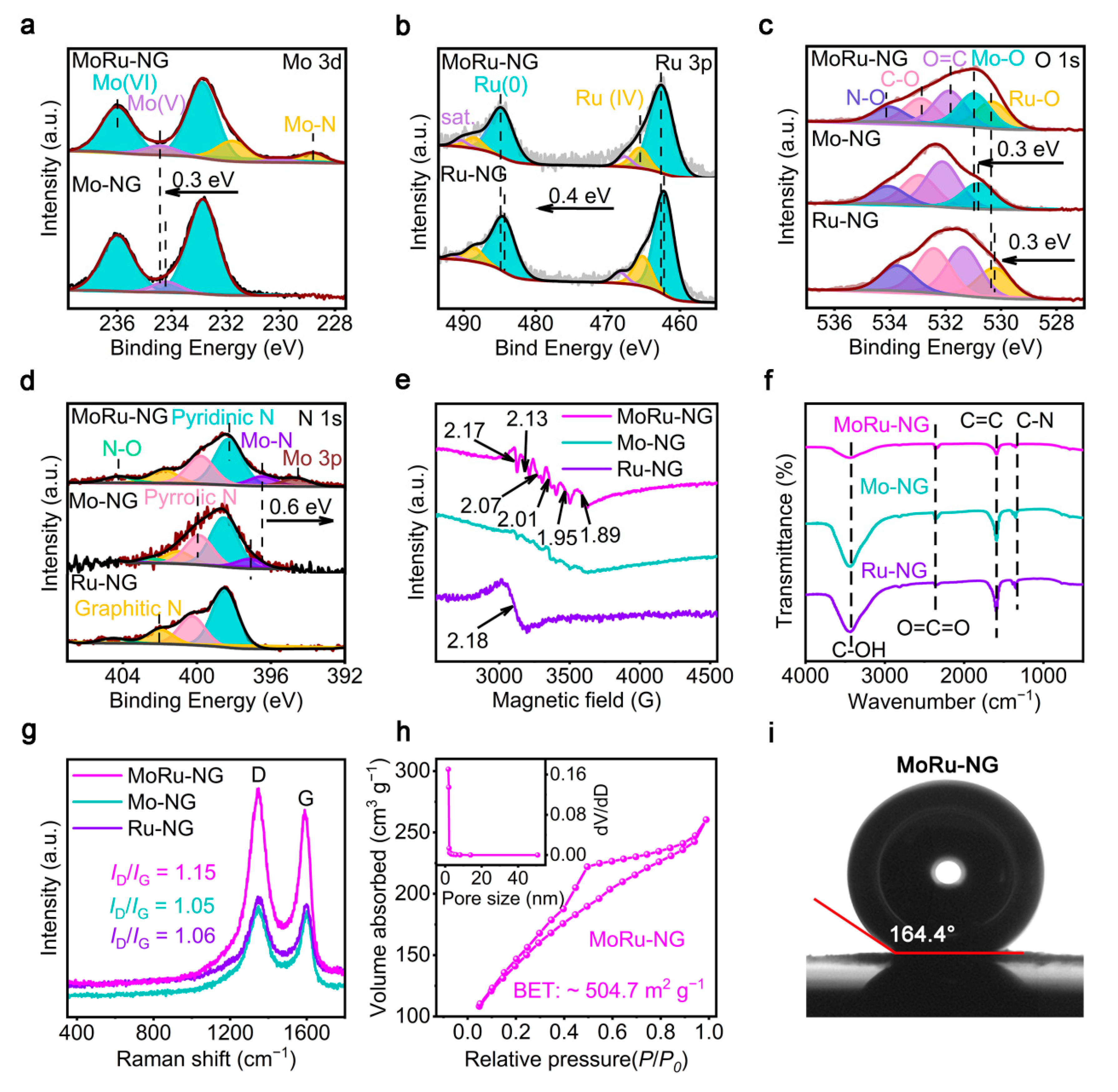
2.2. Structural Characterization of MoRu-NG
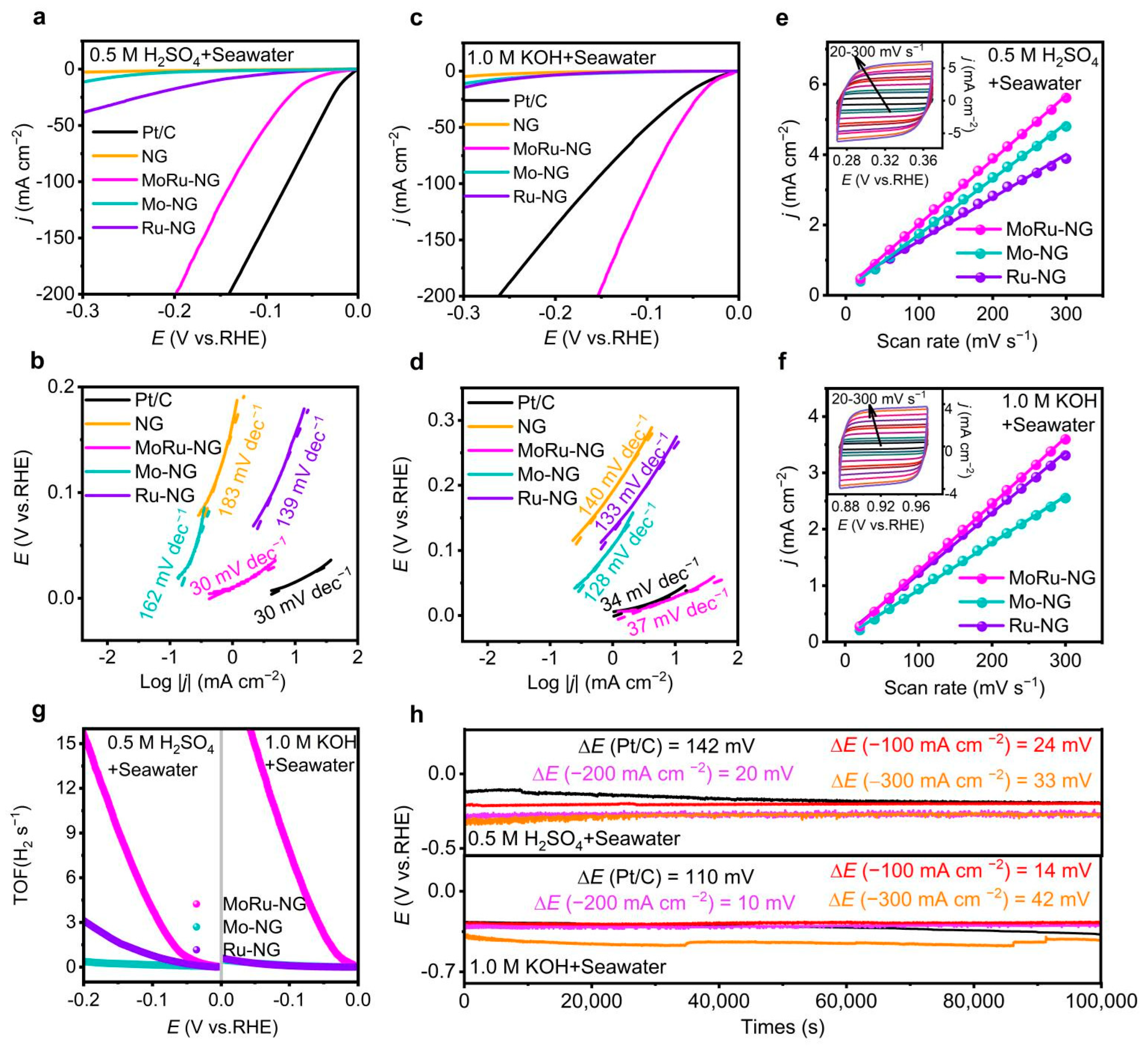
2.3. Electrocatalytic HER Performance
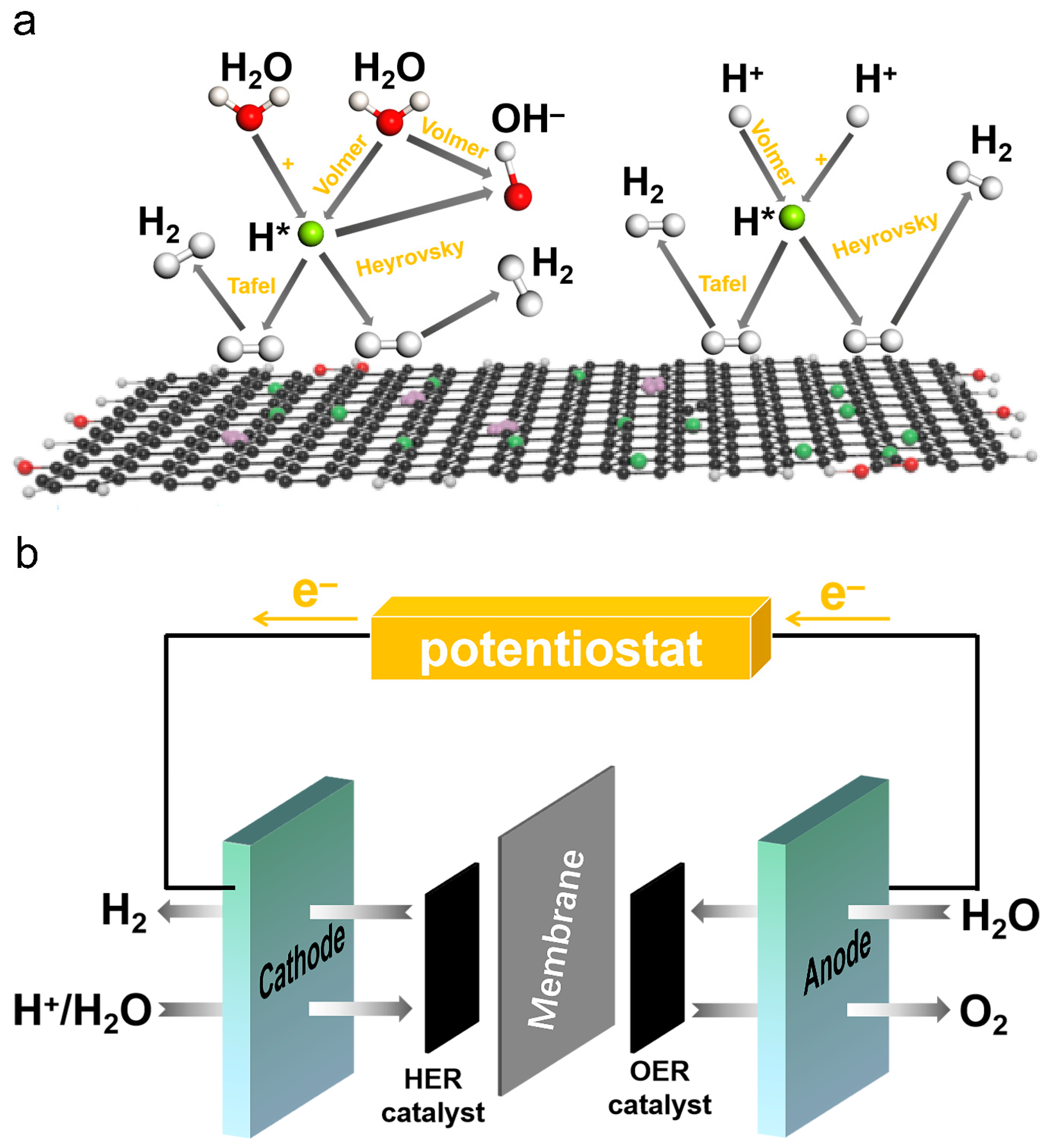
2.4. Mechanism of HER and Schematic Representation of Seawater Electrocatalysis
3. Experiments
3.1. Preparation of the MoRu-NG Composite
3.2. Preparation of Mo-NG and Ru-NG Composites
3.3. Preparation of A-MR, B-MR, and C-MR Composites
3.4. Material Characterization
3.5. HER Electrochemical Setup
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, X.; Sha, Q.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Yu, E.; Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Dynamic chloride ion adsorption on single iridium atom boosts seawater oxidation catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Bu, L.; Huang, B.; Wang, P.; Shen, C.; Bai, S.; Chan, T.S.; Shao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Huang, X. Compensating Electronic Effect Enables Fast Site-to-Site Electron Transfer over Ultrathin RuMn Nanosheet Branches toward Highly Electroactive and Stable Water Splitting. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2105308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Setzler, B.P.; Zhu, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhuang, Z. A highly-active, stable and low-cost platinum-free anode catalyst based on RuNi for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Luo, W. Phosphorus-Induced Activation of Ruthenium for Boosting Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Electrocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 11751–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xiao, D.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X.; Gong, M.; Deng, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D. Boosting alkaline hydrogen electrooxidation on an unconventional fcc-Ru polycrystal. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 61, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; He, Q.; Ding, W.; Wei, Z. Lattice-confined Ru clusters with high CO tolerance and activity for the hydrogen oxidation reaction. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C. Ru-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: Recent research advances and perspectives. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 15, 100274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionigi, F.; Reier, T.; Pawolek, Z.; Gliech, M.; Strasser, P. Design Criteria, Operating Conditions, and Nickel-Iron Hydroxide Catalyst Materials for Selective Seawater Electrolysis. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, C.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Synthesis of Ru-Doped VN by a Soft-Urea Pathway as an Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, T.; Haik, Y. Strategies of Anode Design for Seawater Electrolysis: Recent Development and Future Perspective. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2200030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Yoon, H.; Ju, B.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-W. Electrocatalytic Selective Oxygen Evolution of Carbon-Coated Na2Co1–xFexP2O7 Nanoparticles for Alkaline Seawater Electrolysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Song, S.; McElhenny, B.; Wang, D.; Wu, C.; Qin, Z.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Non-noble metal-nitride based electrocatalysts for high-performance alkaline seawater electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, H.T.; Sidra, S.; Hoa, V.H.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Mai, M.; Tran, P.K.L.; Kim, D.H. In situ growth and interfacial reconstruction of Mo-doped Ni3S2/VO2 as anti-corrosion electrocatalyst for long-term durable seawater splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 365, 124925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ren, G.; Qin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Meng, X. Reconstruction Co-O-Mo in amorphous-crystalline MoOx/Co(OH)2 interface for industry-level active and stable electrocatalytic seawater hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2024, 121, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Jiao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, C. Construction of Heterojunction-Rich Metal Nitrides Porous Nanosheets Electrocatalyst for Alkaline Water/Seawater Splitting at Large Current Density. Small 2024, 20, 2310535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pang, D.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Jia, B.; Guo, Z.; Fan, X.; et al. Vacancy and Dopant Co-Constructed Active Microregion in Ru–MoO3−/Mo2AlB2 for Enhanced Acidic Hydrogen Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202504084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, R.; Jia, W.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; Jiao, L. Suppressing lattice oxygen oxidation in ruthenium oxide via equivalent substitution for sustainable oxygen evolution reaction in PEMWEs. Chem Catal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hung, S.-F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Bi, S.; Li, S.; Ma, J.-J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Modulating the covalency of Ru-O bonds by dynamic reconstruction for efficient acidic oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Sakthivel, T.; Guo, Z.; Dai, Z. Intensifying the Supported Ruthenium Metallic Bond to Boost the Interfacial Hydrogen Spillover Toward pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Hu, L.; Lv, X.; Dang, J. Significantly enhanced OER and HER performance of NiCo-LDH and NiCoP under industrial water splitting conditions through Ru and Mn bimetallic co-doping strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, J.; Yang, M.; Niu, Z. Simultaneous Manipulation of Anions and Water Molecules by Lewis Acid–Base for Highly Stable Zn Anodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202501327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Ding, R.; Zeng, Z.-W.; Liu, B.-W.; Zeng, F.-R.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhao, H.-B. Satellite-like shielding for dual single-atom catalysis, boosting ampere-level alkaline seawater splitting. Matter 2024, 7, 3189–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Ge, S.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. A corrosion-resistant RuMoNi catalyst for efficient and long-lasting seawater oxidation and anion exchange membrane electrolyzer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Aoki, T.; Pattengale, B.; Huang, J.; He, X.; Bian, W.; Younan, S.; Williams, N.; et al. Atomically engineering activation sites onto metallic 1T-MoS(2) catalysts for enhanced electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Urrego-Ortiz, R.; Liao, N.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Luo, J. Rationally designed Ru catalysts supported on TiN for highly efficient and stable hydrogen evolution in alkaline conditions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, L.R.; Bockrath, B. On the Chemical Nature of Graphene Edges: Origin of Stability and Potential for Magnetism in Carbon Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5917–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Pei, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; An, P.; Huang, H.; Zheng, L.; et al. Selective Activation of Lattice Oxygen Site Through Coordination Engineering to Boost the Activity and Stability of Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Peters, F.; Pope, M.T.; Gatteschi, D. Polyoxometalates: Very Large ClustersNanoscale Magnets. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 239–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, R.; Mallojjala, S.C.; Wheeler, S.E. Electrostatic Interactions in Asymmetric Organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhan, S.; Chen, L.; Tian, Q.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, B.; Ahlquist, M.S.G. Electrostatic Interactions Accelerating Water Oxidation Catalysis via Intercatalyst O–O Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2484–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Wang, N.N.; Zou, Y.H.; Qin, X.; Wang, P.; Lu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, W.Y.; Lu, Y. N, N′-bidentate ligand anchored palladium catalysts on MOFs for efficient Heck reaction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, S.; Sun, N.; Li, M.; Sheng, H.; Hu, S.; Yao, T.; et al. Matching Bidentate Ligand Anchoring: An Accurate Control Strategy for Stable Single-Atom/ZIF Nanocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Kuang, T.; Wei, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.J.N.R. Design and construction of size-controlled CoO/CS catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Nano Res. 2023, 17, 2520–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Meng, F.; Peng, H.; Lyu, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Lin, T.; et al. Unveiling Strong Ion–Electron–Lattice Coupling and Electronic Antidoping in Hydrogenated Perovskite Nickelate. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2300617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Li, J.Y.; Qin, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, W.W.; Xu, K.; Yan, H.; Xiao, D.; Jia, C.J.; Fu, Q.; et al. Pt(n)-O(v) synergistic sites on MoO(x)/γ-Mo(2)N heterostructure for low-temperature reverse water-gas shift reaction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Qin, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Meng, X. Engineering active and robust alloy-based electrocatalyst by rapid Joule-heating toward ampere-level hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Tan, G.; Duan, X.; Yuan, B.; Sendeku, M.G.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, F.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Single atomic Ru in TiO2 boost efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation to hydrogen peroxide. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhuansun, M.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Meira, D.; Sun, H.; Wei, J.; et al. Enriched electrophilic oxygen species facilitate acidic oxygen evolution on Ru-Mo binary oxide catalysts. Nano Res. 2023, 17, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Meng, P.; Yang, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zong, C.; et al. Local Charge Transfer Unveils Antideactivation of Ru at High Potentials for the Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 16619–16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratanov, N.; Yurkov, G.; Fionov, A.; Koksharov, Y.; Popkov, O.; Kolesov, V. Creation and physical properties of the molybdenum-containing polyethylene-based nanomaterials. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2009, 54, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.; Qu, J.; Liu, H. Tungsten-Assisted Phase Tuning of Molybdenum Carbide for Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Shu, Y.; Bao, X.; Xu, Y. Methane Dehydro-aromatization under Nonoxidative Conditions over Mo/HZSM-5 Catalysts: EPR Study of the Mo Species on/in the HZSM-5 Zeolite. J. Catal. 2000, 189, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wei, W.; Wu, Z.-S.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Mesoporous Metal–Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Electrocatalysts for Highly Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16002–16005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, K.; Hu, M.; Li, Q.-K.; Han, Y.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G. Cooperative Nitrogen Activation and Ammonia Synthesis on Densely Monodispersed Mo–N–C Sites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 3962–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xuan, H.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Cheng, L. Nanoporous nonprecious multi-metal alloys as multisite electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 97, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, P.; Tan, W.; Ma, K.; Zou, W.; Tang, C.; Dong, L. Enhanced low-temperature NH3-SCR performance of CeTiOx catalyst via surface Mo modification. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Guan, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xu, B.; Ma, J.; Chu, W.; Zhang, R.; Giambastiani, G.; Liu, Y. Synergizing Mon Clusters and Mo2C Nanoparticles on Oxidized Carbon Nanotubes Boosting the CO2 Reduction Activity. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 10939–10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Xu, F.; Hu, J.; Zhu, D.; Yu, Q.; Shi, C. Geopolymer composites for marine application: Structural properties and durability. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 152, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, S.; Ortíz-Ledón, C.A.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Phosphorus Vacancies that Boost Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution by Two Orders of Magnitude. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 8258–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Wen, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Recycling Spent Ternary Cathodes to Oxygen Evolution Catalysts for Pure Water Anion-Exchange Membrane Electrolysis. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 22454–22464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Anjum, M.; Lee, M.; Lee, B.-J.; Lee, J. Activating MoS2 Basal Plane with Ni2P Nanoparticles for Pt-Like Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Acidic Media. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1809151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N.; Pan, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Tan, M.-Y.; Cui, R.; Shi, Z.; et al. Doping Ruthenium into Metal Matrix for Promoted pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Sk, M.A.; Thia, L.; Ge, X.; Lim, R.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Lim, K.H.; Wang, X. Molybdenum phosphide as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2624–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, R.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Huang, W.J. A nanohybrid consisting of NiPS3 nanoparticles coupled with defective graphene as a pH-universal electrocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 23536–23542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Sun, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, B.; Al-Hilo, A.; Benamara, M.; Zhu, H.; Watanabe, F.; Cui, J.; Chen, T. Pure and stable metallic phase molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Maiti, U.N.; Lim, J.; Choi, D.S.; Lee, W.J.; Oh, Y.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, S.O. Molybdenum Sulfide/N-Doped CNT Forest Hybrid Catalysts for High-Performance Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Duan, Z.; Wen, X.; Si, R.; Zhang, Q.; Guan, J. Highly Dispersed Ruthenium-Based Multifunctional Electrocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9897–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, D. Nitrogen-doped RuS(2) nanoparticles containing in situ reduced Ru as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 17862–17868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, K.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Qu, P.; Liu, D. Ru(x)Se@MoS(2) hybrid as a highly efficient electrocatalyst toward hydrogen evolution reaction. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13486–13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.J. Hierarchical CoS/MoS2 and Co3S4/MoS2/Ni2P nanotubes for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25410–25419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Pohl, D.; Rellinghaus, B.; Dong, R.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X. Interface Engineering of MoS2/Ni3S2 Heterostructures for Highly Enhanced Electrochemical Overall-Water-Splitting Activity. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Santra, S.; Nanda, K.K. In Situ Fabrication of a Nickel/Molybdenum Carbide-Anchored N-Doped Graphene/CNT Hybrid: An Efficient (Pre)catalyst for OER and HER. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35025–35038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wu, M.; Tang, Z.; Tse, J.S.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Single Atom Ruthenium-Doped CoP/CDs Nanosheets via Splicing of Carbon-Dots for Robust Hydrogen Production. Angew. Chem. 2021, 60, 7234–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Dong, M. An efficient ruthenium-based dual-electrocatalyst towards hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 16, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zheng, K.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Xu, C. Ultralow Ru-Induced Bimetal Electrocatalysts with a Ru-Enriched and Mixed-Valence Surface Anchored on a Hollow Carbon Matrix for Oxygen Reduction and Water Splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51437–51447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Carbon quantum dots enhanced the activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction in ruthenium-based electrocatalysts. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Liao, F.; Li, Y.; Shao, M. Silicon monoxide assisted synthesis of Ru modified carbon nanocomposites as high mass activity electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11817–11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Jeong, H.Y.; Lee, M.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.S. Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Catalysis in Alkaline Media by All-in-One MoS2 with Multifunctional Active Sites. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1707105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, P.; Lv, W.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Du, S.; Huang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Ultrastable Ruthenium-Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction in High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. CCS Chem. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, D.; Bai, J.; Han, C.; Li, X.; Zhuang, L.; Song, P.; Xu, W. Ru-MnO Heterostructure Clusters Toward Efficient and CO-Tolerant Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 15, 2404266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chuanqi, C.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y. Unveiling the Aggregation of M-N-C Single Atoms into Highly Efficient MOOH Nanoclusters during Alkaline Water Oxidation. Angew. Chem. 2024, 137, e202413308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.J. Carbon-Based Double-Metal-Site Catalysts: Advances in Synthesis and Energy Applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 11749–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Niu, R.; Liu, J.; Guo, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Electrostatic self-assembly of 2D/2D CoWO4/g-C3N4 p–n heterojunction for improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution: Built-in electric field modulated charge separation and mechanism unveiling. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6987–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, Y.; Do, D.; Zhou, B.; Dong, J.; Yan, W.; Qin, Y.; et al. O-coordinated W-Mo dual-atom catalyst for pH-universal electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, S.; Yan, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.-M.; Fan, X. Tuning Binding Strength of Multiple Intermediates towards Efficient pH-universal Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution by Mo8O26-NbNxOy Heterocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, H.-L.; Yan, W.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Qin, Y.; Long, R.; Zhang, X.-M.; Fan, X. Covalently Connected Nb4N5–xOx–MoS2 Heterocatalysts with Desired Electron Density to Boost Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4925–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yan, W.; Zhou, H.; Fan, X. Ru Nanoparticle Assemblies Modified with Single Mo Atoms for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Seawater Electrocatalysis. Catalysts 2025, 15, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050475
Wang S, Qin J, Zhang Y, Chen S, Yan W, Zhou H, Fan X. Ru Nanoparticle Assemblies Modified with Single Mo Atoms for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Seawater Electrocatalysis. Catalysts. 2025; 15(5):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050475
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuhan, Jiani Qin, Yong Zhang, Shuai Chen, Wenjun Yan, Haiqing Zhou, and Xiujun Fan. 2025. "Ru Nanoparticle Assemblies Modified with Single Mo Atoms for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Seawater Electrocatalysis" Catalysts 15, no. 5: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050475
APA StyleWang, S., Qin, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, S., Yan, W., Zhou, H., & Fan, X. (2025). Ru Nanoparticle Assemblies Modified with Single Mo Atoms for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Seawater Electrocatalysis. Catalysts, 15(5), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050475






