Study on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis of Dioxins in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Using Water-Washed Synergistic Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of Water-Washed Fly Ash
2.1.1. Physicochemical Properties of Water-Washed Fly Ash
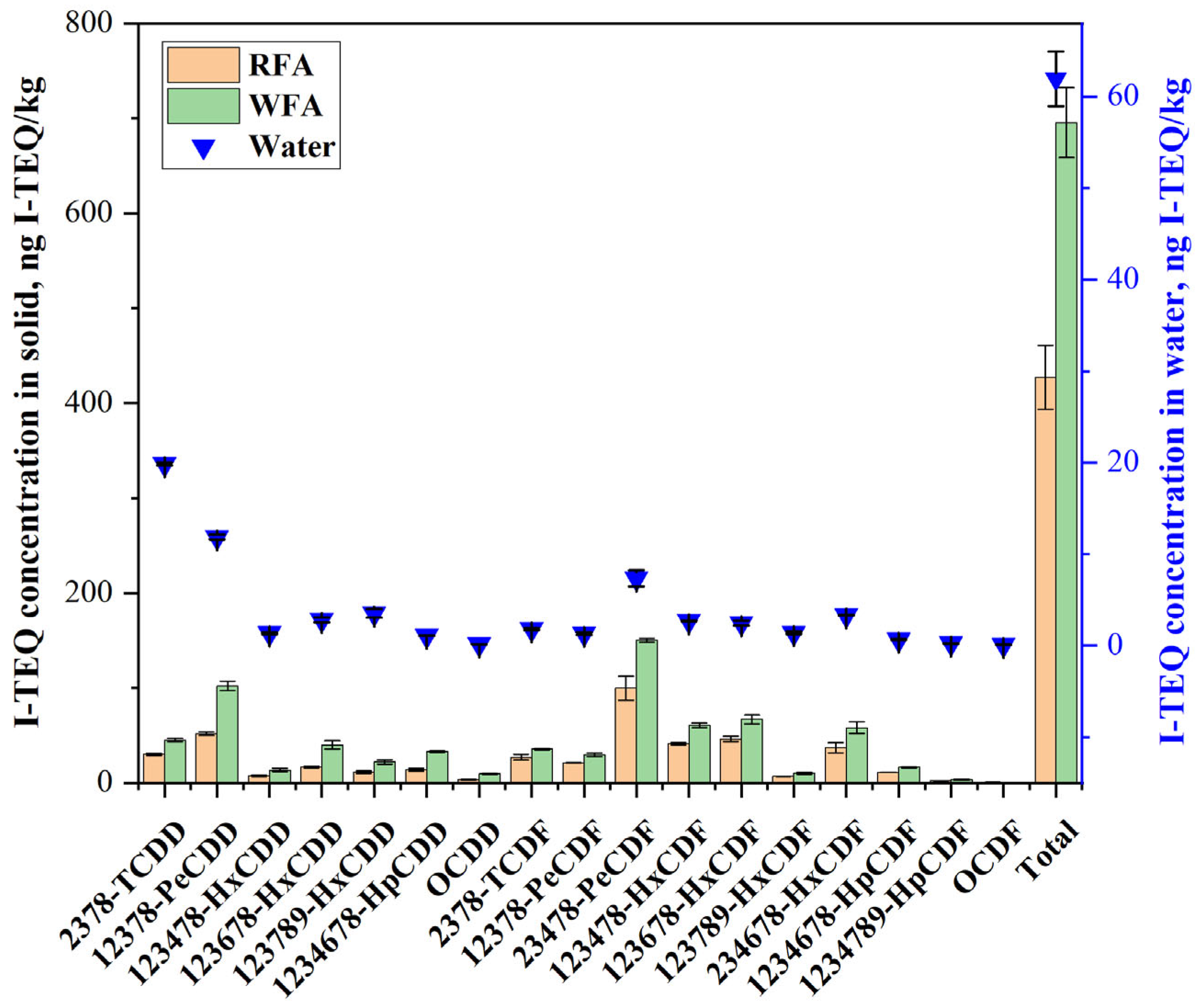
2.1.2. The Migration of Dioxins During the Water-Washing Process
2.2. Degradation Characteristics of Dioxins in WFA
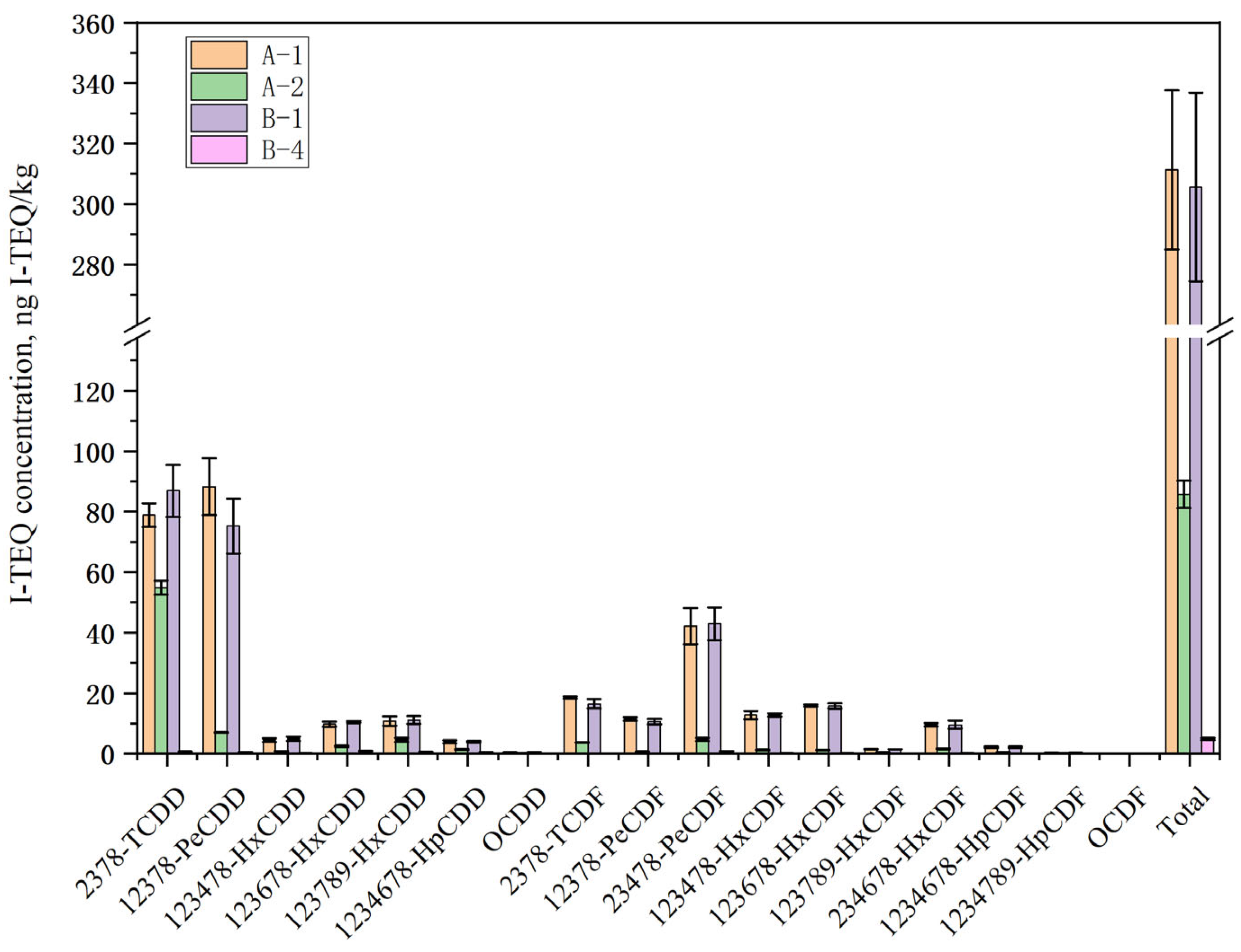
2.2.1. Effect of Water-Washing Treatment on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis
2.2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature on Degradation Characteristics of Dioxins in WFA
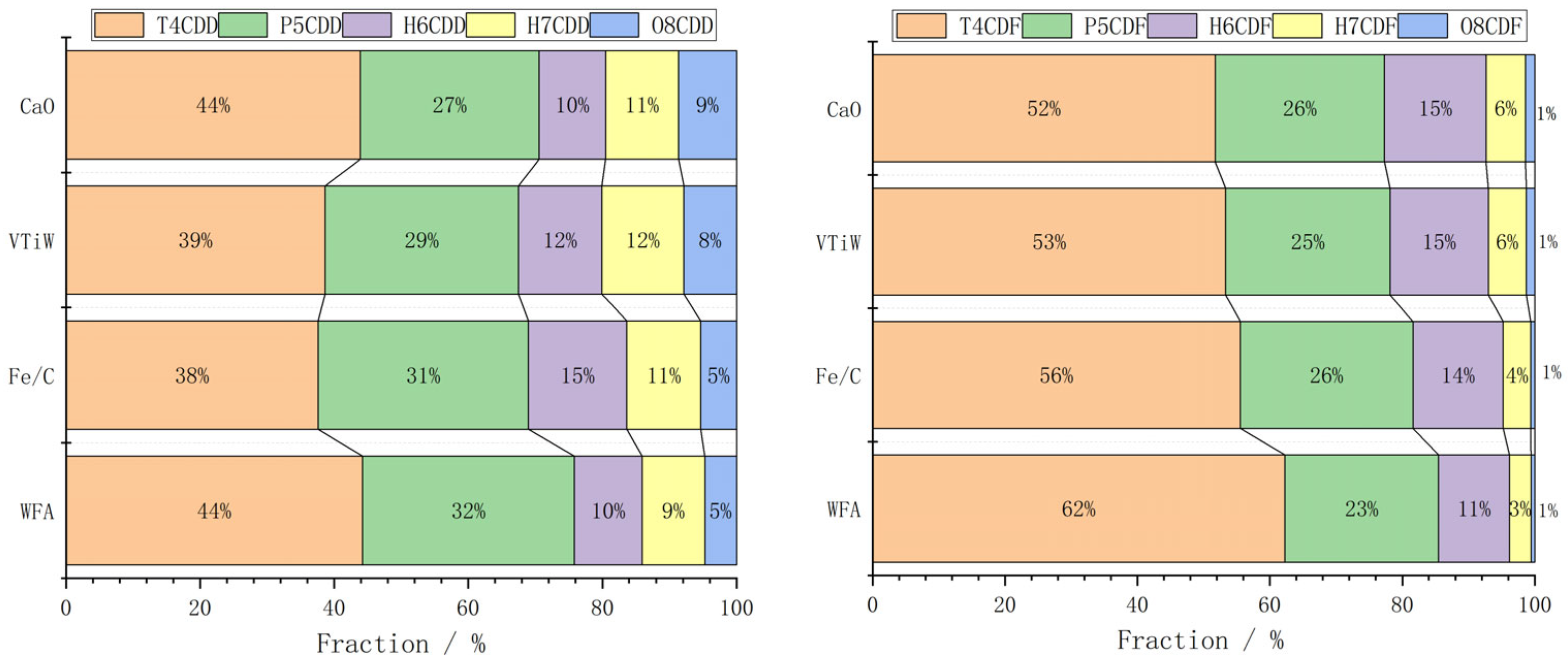
2.2.3. Analysis of Degradation Characteristics of 136 Dioxins
2.3. Low-Temperature Catalytic Pyrolysis of Dioxins
2.3.1. The Degradation Effects of Different Catalysts on Dioxins
2.3.2. Effect of CaO Catalyst Addition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
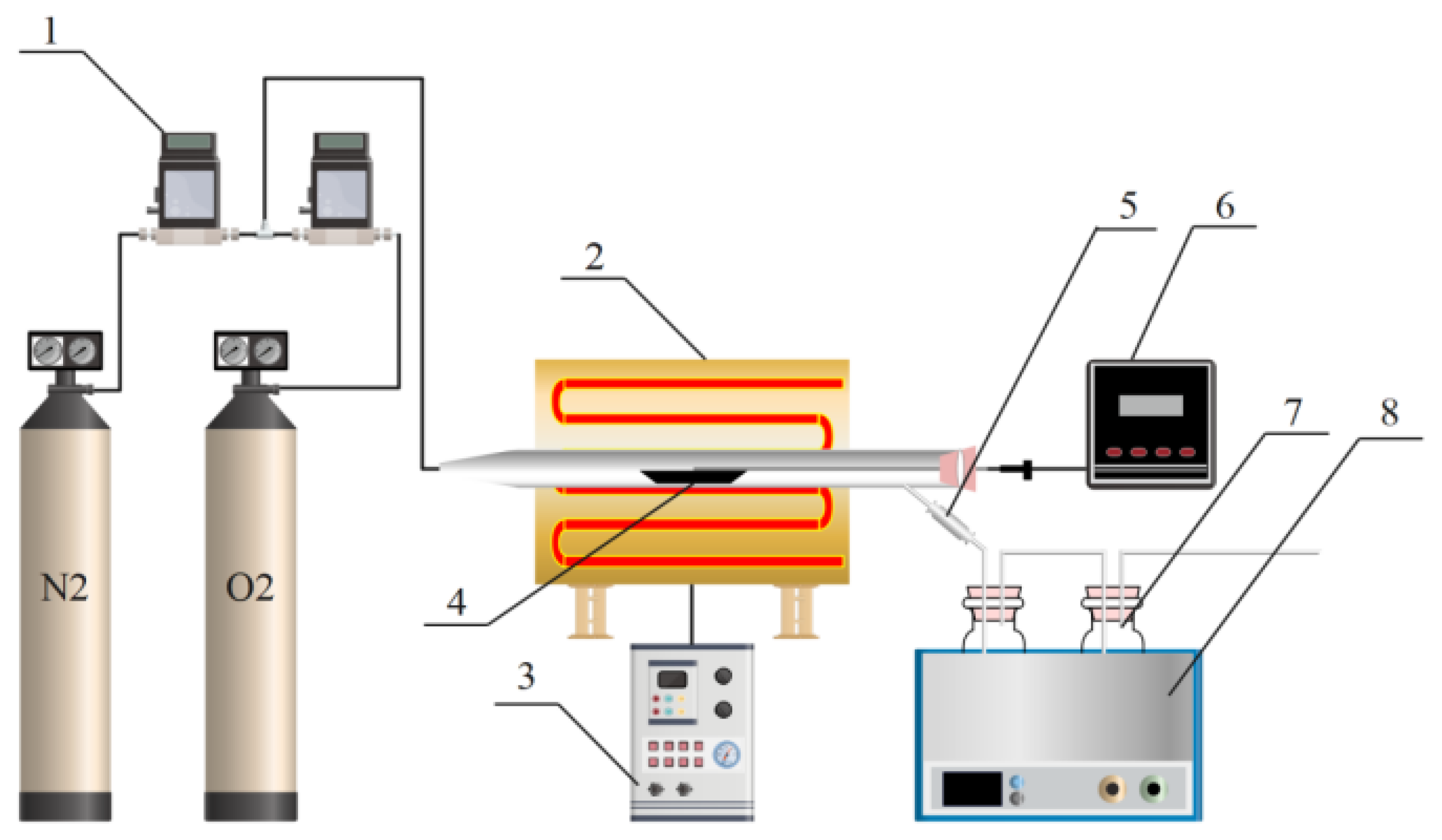
3.2. Experiment Design
3.3. Water-Washing Treatment
3.4. Experimental Conditions
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, D.H.; Peng, Z.; Yu, L.F.; Sun, Y.Z.; Yong, R.; Karstensen, K.H. Characterization of heavy metals and PCDD/Fs from water-washing pretreatment and a cement kiln co-processing municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Weber, R.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.W.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, L.F. Characterization of PCDD/Fs and heavy metal distribution from municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash sintering process. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ 1134-2020; Technical Specification for Pollution Control of Fly-Ash from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Hagenmaier, H.; Kraft, M.; Brunner, H.; Haag, R. Catalytic effects of fly ash from waste incineration facilities on the formation and decomposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ. Sci. Technol 1987, 21, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunda, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J. Disposal technology and new progress for dioxins and heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Long, J.; Yue, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Qian, G. Degradation and regeneration inhibition of PCDD/Fs in incineration fly ash by low-temperature thermal technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Li, X. Decomposition and reformation pathways of PCDD/Fs during thermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, L.; Marklund, S. Thermal degradation of PCDD/F in municipal solid waste ashes in sealed glass ampules. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3872–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Sakurai, T.; Hagenmaier, H. Formation and destruction of pcdd/pcdf during heat treatment of fly ash samples from fluidized bed incinerators. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Lu, S.Y.; Yan, J.H.; Li, X.D.; Chen, T. Thermal removal of PCDD/Fs from medical waste incineration fly ash-effect of temperature and nitrogen flow rate. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Wang, L.Z.; Yin, R.H.; Luo, Y.H. Alteration in formation behaviors of chloroaromatic precursors of PCDD/Fs: An ex-perimental study on the effect of extrinsic and intrinsic oxygen on chlorination. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addink, R.; Govers, H.A.; Olie, K. Kinetics of formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans from carbon on fly ash. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 3549–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G. Dioxin characterisation, formation and minimisation during municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 86, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Dai, X.X.; Wu, Z.B.; Weng, X.L. Unveiling the secondary pollution in the catalytic elimination of chlorinated organics: The formation of dioxins. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.X.; Ni, Y.W.; Zhan, F.Q.; Song, B.Y.; Ren, Y.; Sunn, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Mechanistic aspects of polychlorinated dibenzo-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) formation from chlorine bleaching of non-wood pulp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.M.; Chang, M.B. Catalytic pyrolysis: New approach for destruction of POPs in MWIs fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hung, P.C.; Lu, S.; Chang, M.B. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous PCDD/Fs over V2O5/TiO2-CNTs catalyst: Effect of NO and NH3 addition. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, M.; Peng, Y.; Du, C.; Lu, S. Ozone assisted oxidation of gaseous PCDD/Fs over CNTs-containing composite catalysts at low temperature. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.F.; Li, W.W.; Li, X.D.; Lin, X.Q.; Chen, T.; Yan, J.H. Development of new transition metal oxide catalysts for the destruction of PCDD/Fs. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.F.; Lin, X.Q.; Yan, M.; Li, X.D.; Chen, T.; Yan, J.H. Low temperature destruction of PCDD/Fs over V2O5-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with ozone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 17563–17570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.X.; Yu, M.F.; Zhang, G.; Chen, T.; Li, X.D.; Buekens, A. Low temperature degradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans over a VOx-CeOx/TiO2 catalyst with addition of ozone. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, R.; Budin, R.; Hartl, H.; Stock, M.; Wurst, F. PCDD-destruction and PCDF-destruction by a SCR-unit in a municipal waste incinerator. Chemosphere 1992, 25, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.M.; Chang, M.B. Transformation of mono- to octa- chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in MWI fly ash during catalytic pyrolysis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Yao, G.; Zhu, X.; Hu, S.; Qiu, J.; Chen, P.; Lyu, X. Characterization of the mechanical properties and microcosmic mechanism of Portland cement prepared with soda residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 117994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.T.; Ottosen, L.M.; Ribeiro, A.B. Assessing fly ash treatment: Remediation and stabilization of heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S110–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M.; Zhou, J.; Qian, G. Rapid evaluation of leaching potential of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Takaoka, M.; Takeda, N. Influence of Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn Chlorides and Oxides on Formation of Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds in MSWI Fly Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addink, R.; Altwicker, E.R. Role of copper compounds in the de novo synthesis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans. Environ. Eng. Sci. 1998, 15, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, L.; Aurell, J.; Marklund, S. The behavior of PCDD and PCDF during thermal treatment of waste incineration ash. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lai, J.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Li, L.; Jing, H.; Liu, T.; Yan, J. Field study on PCDD/F decomposition over VOx/TiO2 catalyst under low-temperature: Mechanism and kinetics analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, L.; Qian, K.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, R. MSW pyrolysis volatiles’ reforming by incineration fly ash for both pyrolysis products upgrading and fly ash stabilization. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Emission Characteristics of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans from the Co-combustion of Municipal Solid Waste in a Lab-Scale Drop-Tube Furnace. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5396–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
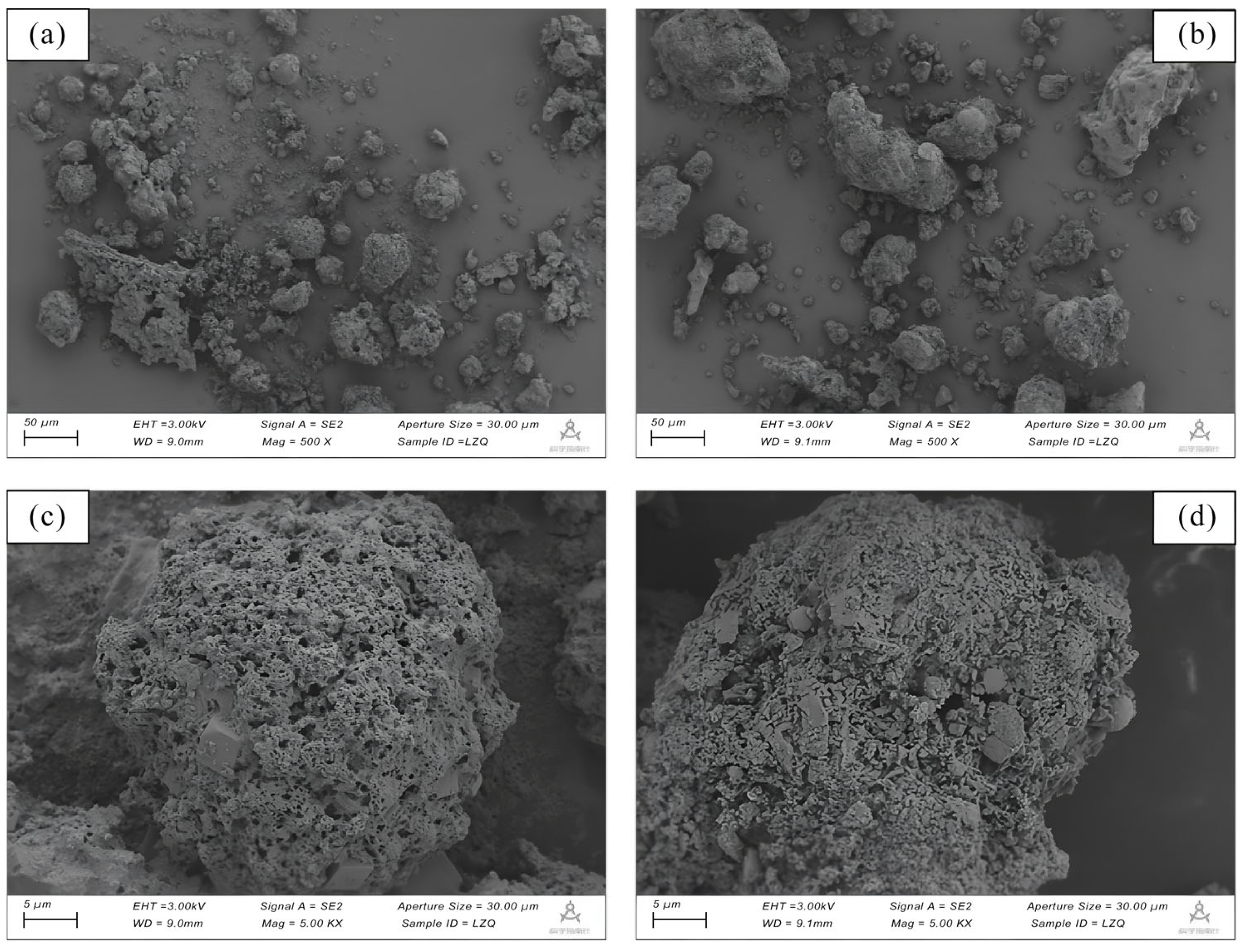

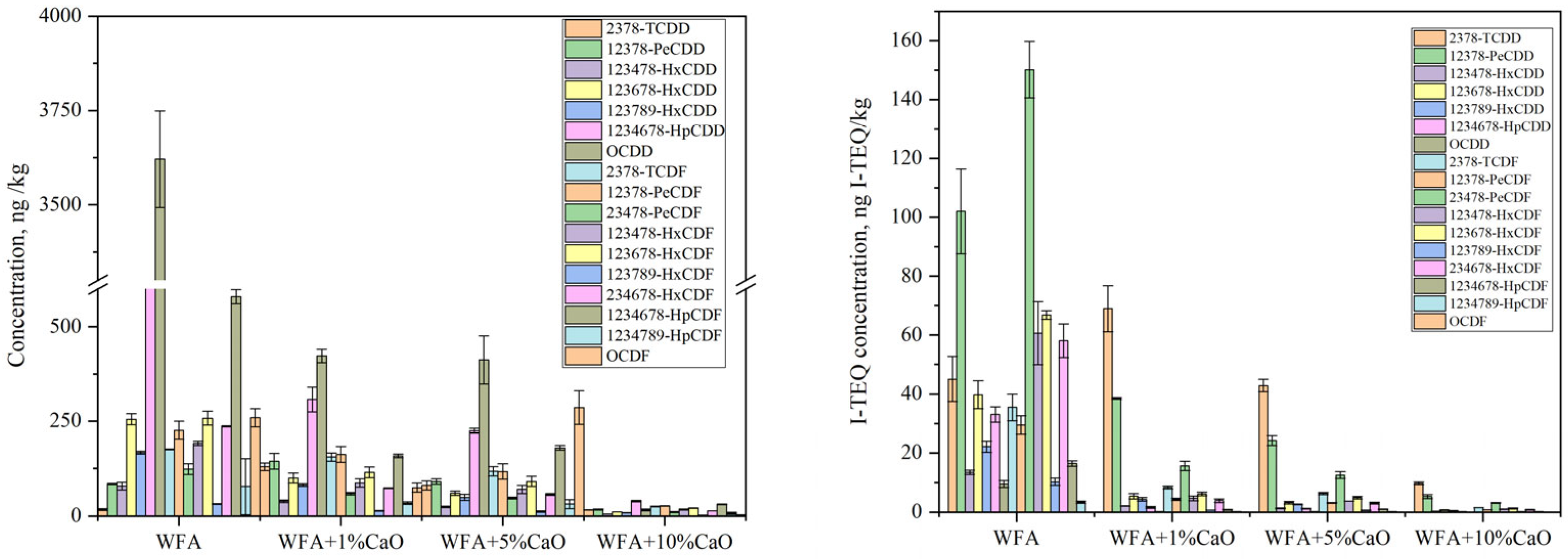
| Element | Ca | Cl | Na | K | Si | S | Fe | Mg | Al | Zn | F | P | Pb | LOI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFA | 25.94 | 21.14 | 9.71 | 4.29 | 4.05 | 2.27 | 1.51 | 1.34 | 1.25 | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 25.6% |
| WFA | 34.14 | 0.62 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 9.07 | 2.10 | 3.43 | 3.43 | 2.97 | 1.36 | 2.38 | 0.85 | 0.23 | 18.9% |
| Compound | Isomer | TEF | Temperatures (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 250 | |||
| T4CDD | 2378 | 1 | 45.03 | 86.92 | 205.05 | 5.83 | 0.66 |
| P5CDD | 12378 | 0.5 | 102.02 | 75.24 | 119.76 | 2.91 | 0.58 |
| H6CDD | 123478 | 0.1 | 13.45 | 4.95 | 5.38 | 0.20 | 0.12 |
| H6CDD | 123678 | 0.1 | 39.74 | 10.53 | 12.40 | 0.44 | 0.86 |
| H6CDD | 123789 | 0.1 | 22.06 | 11.16 | 13.41 | 0.41 | 0.59 |
| H7CDD | 1234678 | 0.01 | 33.06 | 4.00 | 3.58 | 0.15 | 0.45 |
| O8CDD | 12346789 | 0.001 | 9.46 | 0.43 | 0.098 | 0.0063 | 0.029 |
| T4CDF | 2378 | 0.1 | 35.41 | 16.52 | 34.11 | 0.76 | 0.066 |
| P5CDF | 12378 | 0.05 | 29.51 | 10.62 | 16.11 | 0.41 | 0.060 |
| P5CDF | 23478 | 0.5 | 150.17 | 42.90 | 43.96 | 0.90 | 0.87 |
| H6CDF | 123478 | 0.1 | 60.64 | 12.80 | 10.78 | 0.40 | 0.10 |
| H6CDF | 123678 | 0.1 | 66.79 | 15.83 | 15.58 | 0.50 | 0.14 |
| H6CDF | 234678 | 0.1 | 10.24 | 1.53 | 1.42 | 0.081 | 0.044 |
| H6CDF | 123789 | 0.1 | 58.06 | 9.61 | 8.35 | 0.35 | 0.20 |
| H7CDF | 1234678 | 0.01 | 16.44 | 2.13 | 1.65 | 0.083 | 0.038 |
| H7CDF | 1234789 | 0.01 | 3.30 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.020 | 0.013 |
| O8CDF | 12346789 | 0.001 | 0.077 | 0.055 | 0.012 | 0.00035 | 0.00072 |
| TOTAL (ng I-TEQ/kg) | 695.51 | 305.62 | 492.01 | 13.51 | 4.85 | ||
| Compound | Temperatures (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 210 | 220 | 250 | |
| PCDDs (ng/kg) | 6032.59 | 4183.39 | 282.34 | 31.09 |
| PCDFs (ng/kg) | 7064.22 | 5251.16 | 312.92 | 52.54 |
| PCDD/Fs (ng/kg) | 13,096.81 | 9434.55 | 595.27 | 83.63 |
| PCDDs/PCDFs | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.59 |
| Cl-PCDD | 4.85 | 4.99 | 5.21 | 5.78 |
| Cl-PCDF | 4.85 | 4.57 | 4.73 | 5.51 |
| TEQ (ng I-TEQ/kg) | 305.62 | 492.01 | 13.51 | 4.85 |
| Compound | Fe/C | VWTi | CaO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 °C | 210 °C | 200 °C | 210 °C | 200 °C | 210 °C | |
| PCDDs (ng/kg) | 5295.06 | 1324.21 | 2995.02 | 520.95 | 2749.04 | 232.36 |
| PCDFs (ng/kg) | 6428.02 | 2004.71 | 2858.97 | 559.41 | 2532.74 | 336.97 |
| PCDD/Fs | 11,723.09 | 3328.91 | 5853.99 | 1080.35 | 5281.78 | 569.33 |
| PCDDs/PCDFs | 0.82 | 0.66 | 1.05 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 0.69 |
| Cl-PCDD | 5.31 | 5.15 | 5.27 | 5.22 | 5.12 | 5.14 |
| Cl-PCDF | 4.76 | 4.68 | 4.76 | 4.77 | 4.73 | 4.80 |
| TEQ (ng I-TEQ/kg) | 578.82 | 145.29 | 316.39 | 54.42 | 346.91 | 25.67 |
| Condition | Reactant | Temperature/°C | Time/mins | Atmosphere | Flow Rate mL/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-1 | RFA | 200 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| A-2 | RFA | 250 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| B-1 | WFA | 200 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| B-2 | WFA | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| B-3 | WFA | 220 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| B-4 | WFA | 250 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-1 | WFA + 10 wt.% Fe/C | 200 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-2 | WFA + 10 wt.% VWTi | 200 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-3 | WFA + 10 wt.% CaO | 200 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-4 | WFA + 10 wt.% Fe/C | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-5 | WFA + 10 wt.% VWTi | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| C-6 | WFA + 10 wt.% CaO | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| D-1 | WFA + 5 wt.% CaO | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
| D-2 | WFA + 1 wt.% CaO | 210 | 10 | N2 | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Ding, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, S. Study on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis of Dioxins in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Using Water-Washed Synergistic Catalysts. Catalysts 2025, 15, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030274
Zhao X, Ding J, Xiao X, Zhang C, Lu S, Zhu Z, Sun S. Study on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis of Dioxins in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Using Water-Washed Synergistic Catalysts. Catalysts. 2025; 15(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xinglei, Jiamin Ding, Xin Xiao, Chengbo Zhang, Shengyong Lu, Zhanheng Zhu, and Sheng Sun. 2025. "Study on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis of Dioxins in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Using Water-Washed Synergistic Catalysts" Catalysts 15, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030274
APA StyleZhao, X., Ding, J., Xiao, X., Zhang, C., Lu, S., Zhu, Z., & Sun, S. (2025). Study on Low-Temperature Pyrolysis of Dioxins in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Using Water-Washed Synergistic Catalysts. Catalysts, 15(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030274








