Abstract
To address the technical challenges in bisphenol A (BPA) pollution control, this research introduced a novel synthetic approach combining co-precipitation with subsequent thermal treatment to engineer layered double hydroxides (LDHs) with a spinel-structured CoMn-LDO catalyst. Systematic material characterizations such as a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an X-ray diffractometer (XRD), a transmission electron microscope (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were employed to analyze the structural and chemical properties of the synthesized CoMn-LDO calcined at 500 °C. The catalytic performance was evaluated under optimized conditions (35 °C, pH 7.0, 2.0 mM PMS, 0.3 g/L catalyst), and mechanistic studies were conducted to identify the dominant reactive oxygen species. The CoMn-LDO exhibited exceptional peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation performance, achieving 96.75% BPA degradation within 90 min and 58.22% TOC removal. The synergistic redox cycling between Co2+/Co3+ and Mn3+/Mn4+ promoted the generation of ·OH (72.3% contribution) and SO4·−. The catalyst demonstrated superior stability, maintaining 89% degradation efficiency after five cycles. These results provide theoretical and practical insights for developing high-efficiency persulfate-activating catalysts.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution and the energy crisis have emerged as two of the most pressing global challenges in the 21st century, driving extensive research into sustainable technologies for pollutant degradation and resource recovery [1,2,3]. As an environmentally persistent compound with slow degradation rates, bisphenol A (BPA) can bioaccumulate through food webs, significantly increasing both ecosystem disturbances and human exposure risks [4,5,6,7]. The treatment of BPA-containing wastewater has consequently emerged as a critical research focus in environmental engineering. Conventional wastewater treatment processes often fail to effectively remove BPA due to its recalcitrance to biological degradation, necessitating the development of advanced treatment technologies. Advanced oxidation utilizing sulfate radicals (SO4·−) exhibits superior efficacy in BPA decomposition, attributable to the radical species’ elevated redox potential (E0 = 2.5–3.1 V) and target-specific reaction pathways [8,9,10].
Transition metal-based catalysts demonstrate exceptional persulfate (PS) activation performance owing to their unique electronic structures. Among these, cobalt (Co)- and manganese (Mn)-based materials have emerged as research hotspots due to their combined advantages of high catalytic activity and excellent recyclability [11,12,13]. As a class of two-dimensional materials with tunable interlayer structures, layered double hydroxides (LDHs) exhibit three key merits: (1) precisely adjustable metal composition in the laminates, (2) large specific surface areas (typically >100 m2/g), and (3) facile synthesis via coprecipitation methods [14,15,16,17]. These characteristics make LDHs particularly valuable for PS activation applications, with the CoMn-LDHs/PS system having been extensively validated for organic wastewater treatment [18,19,20]. However, current studies reveal three critical limitations of LDH materials: (1) structural collapse of the laminates during recycling, (2) high metal leaching rates (generally >15%), and (3) inadequate long-term stability [21,22]. These drawbacks significantly hinder their practical implementation, thereby making the development of modified LDHs with enhanced stability both scientifically meaningful and technologically imperative.
In this study, spinel-type CoMn bimetallic oxides (CoMn-LDO) were synthesized via a co-precipitation–calcination method using cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O) and manganese(II) nitrate tetrahydrate (Mn(NO3)2·4H2O) as precursors. The material’s microstructure and structural characteristics were systematically characterized by SEM, XRD, TEM, and XPS techniques. Critical process variables including calcination temperature (300–700 °C), PMS concentration (0.1–2 mM), reaction temperature (25–55 °C), and solution pH (3–11) were systematically assessed to optimize BPA removal efficiency. Additionally, the mechanistic pathways underlying catalytic BPA decomposition in the CoMn-LDO/PMS system were elucidated through radical quenching experiments combined with XPS analysis. This work provides valuable insights into developing efficient and stable persulfate-activated catalysts and offers practical references for the remediation of BPA-containing wastewater.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Composition and Structural Analysis of CoMn-LDO
2.1.1. SEM/EDS Characterization
Figure 1 presents the SEM image and corresponding EDS analysis of the CoMn-LDO catalyst. The SEM micrograph reveals a highly porous structure formed after calcination, exhibiting loosely aggregated nanoparticles with abundant void spaces. Furthermore, the calcined sample possesses a relatively large specific surface area and a uniform pore size distribution, which is likely to facilitate the catalytic reaction. EDS elemental mapping (Figure 1b–d) demonstrates the homogeneous distribution of cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), and oxygen (O) throughout the catalyst matrix. Quantitative EDS analysis (Figure 1e) indicates atomic percentages of 35.25% for Co and 16.88% for Mn, yielding a Co/Mn atomic ratio of approximately 2:1-consistent with the designed stoichiometry for optimized catalytic performance. Figure 1f displays the particle size distribution statistics of CoMn-LDO, indicating that the particle sizes are predominantly within the range of 100–300 nm, with a calculated average particle size of 210 nm. Such a relatively narrow size distribution contributes to a high specific surface area, thereby providing an increased number of catalytically active sites.
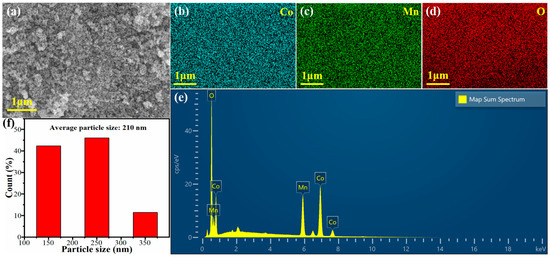
Figure 1.
(a) SEM image of CoMn-LDO; (b–e) Corresponding EDS elemental mapping of CoMn-LDO demonstrating (b) cobalt, (c) manganese, (d) oxygen distributions, and (e) map sum spectrum; (f) particle size distribution of CoMn-LDO.
2.1.2. XRD Characterization and Analysis
Figure 2 shows the XRD pattern of CoMn-LDO. The peak positions at 18.79–75.62° demonstrate perfect indexing with cubic crystal system planes, sequentially representing (111), (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511), (440), and (533) lattice orientations. These diffraction features match well with the standard reference pattern for MnCo2O4 (PDF#23–1237) [23], confirming the formation of hexagonal-structured MnCo2O4 after high-temperature calcination of CoMn-LDH. Additionally, the sharp and narrow diffraction peaks with high intensity indicate that the CoMn-LDO catalyst possesses high crystallinity and a well-defined crystal structure. To further quantify the crystallite size, the average crystallite dimension was calculated to be approximately 57.5 nm using the Scherrer equation (Equation (1)) [24]. This nanocrystalline size is consistent with the particle morphology observed by SEM (Figure 1a) and TEM (Figure 3a), wherein the catalyst exhibits loosely aggregated nanoparticles with sizes predominantly in the range of 100–300 nm. The discrepancy between the crystallite size and the particle size indicates that each particle is composed of multiple crystallites, which is typical for polycrystalline materials formed via calcination. The high crystallinity and small crystallite size contribute to the large specific surface area and abundant active sites of CoMn-LDO, thereby enhancing its catalytic performance.
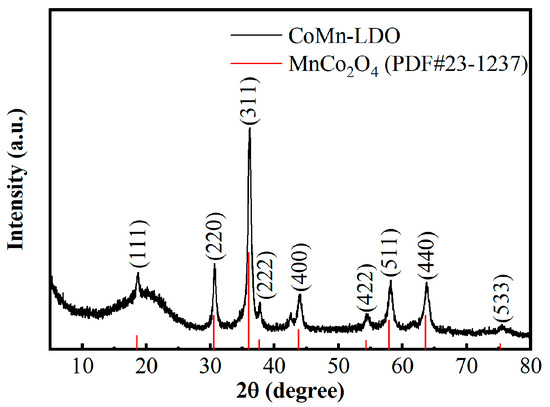
Figure 2.
XRD pattern of the CoMn-LDO catalyst.
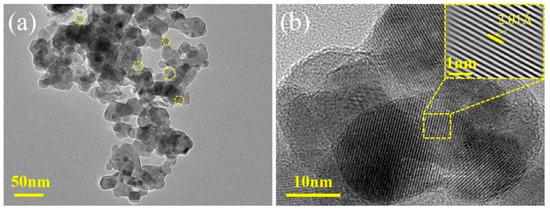
Figure 3.
(a) TEM and (b) HRTEM images of CoMn-LDO.
2.1.3. TEM/HRTEM Characterization and Analysis
The nanostructure morphology was characterized through Figure 3, which displays representative TEM images along with corresponding HRTEM analyses. As clearly observed in Figure 3a, the CoMn-LDO catalyst exhibits a hexagonal nanosheet morphology. Well-ordered atomic planes are resolved with 2.01 Å separation distances (Figure 3b), systematically corresponding to the (311) plane according to crystallographic databases (consistent with the XRD results in Figure 2).
Combined characterization techniques, including SEM-EDS, XRD, and TEM, conclusively confirm the successful synthesis of CoMn-LDO.
2.1.4. FT-IR Characterization Analysis
The functional groups of CoMn-LDO were characterized by FT-IR as shown in Figure 4. Compared to CoMn-LDH [10], the significant decrease in the infrared absorption peak at 3416.9 cm−1, corresponding to −OH stretching modes of hydrogen-bonded interlamellar water molecules [25], indicates substantial water evaporation during calcination. The absorption peak at 1631.6 cm−1 corresponds to the bending vibration of −OH groups from interlayer water molecules [26]. The peak at 1384.1 cm−1 arises from the vibration of NO3− ions in the interlayers of CoMn-LDO [27]. The spectral features between 400 and 700 cm−1 originate from characteristic vibrational modes, including both metal-hydroxyl bending (M–OH) and metal-oxygen stretching (M=O) excitations [28]. FT-IR analysis confirms the presence of NO3−, −OH groups, and H2O molecules in CoMn-LDO.
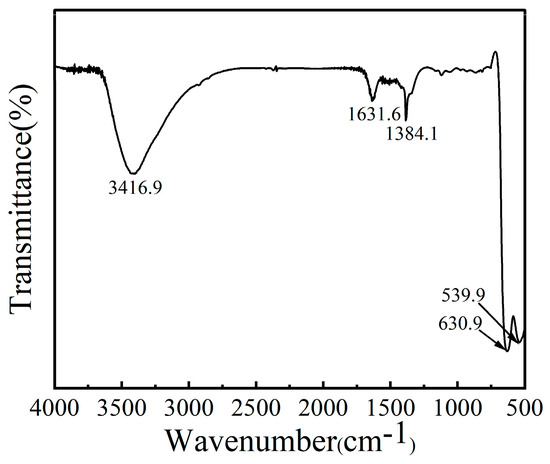
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectrum of CoMn-LDO.
2.1.5. BET Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution
Figure 5 presents the characterization results for CoMn-LDO: (a) low-pressure N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms (77 K) and (b) differential pore volume distribution by the BJH method. Adsorption/desorption branch divergence in the 0.4–0.9 relative pressure range generates the characteristic H3-type hysteresis, concomitant with the Type IV isotherm profile that suggests multilayer adsorption followed by pore filling [29], confirming the mesoporous structure of the material. Quantitative analysis reveals that CoMn-LDO possesses a BET specific surface area of 34.17 m2/g, with pore sizes predominantly distributed in the 2–40 nm range (average pore diameter: 35.81 nm) and a total pore volume of 0.31 cm3/g. These results unambiguously demonstrate the typical mesoporous nature of CoMn-LDO.
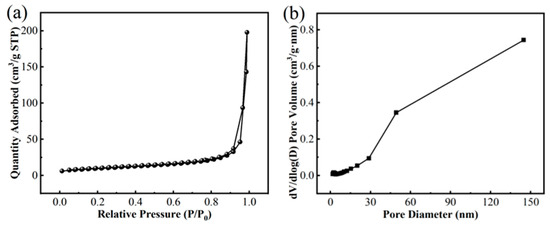
Figure 5.
(a) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution of CoMn-LDO.
2.2. Degradation Behavior of BPA via CoMn-LDO-Activated PMS
2.2.1. The Effect of Calcination Temperature on CoMn-LDO Activated PMS for BPA Degradation
As shown in Figure 6a, the five CoMn-LDO samples exhibited comparable BPA degradation trends, with the 400 °C-calcined sample showing faster initial degradation kinetics, while the 500 °C-calcined sample achieved the highest degradation efficiency (96.24%). XRD analysis (Figure 6b) revealed progressively intensified diffraction peaks with increasing calcination temperature, indicating enhanced crystallinity. Notably, the 600 °C sample demonstrated maximum peak intensity but developed impurity phases. Therefore, 500 °C was selected as the optimal calcination temperature for subsequent studies.
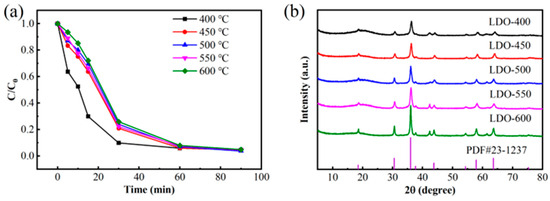
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of calcination temperature on BPA degradation efficiency; (b) XRD patterns of catalysts prepared at different calcination temperatures (conditions: PMS dosage = 2 mmol/L, CoMn-LDO loading = 0.3 g/L, T = 25 °C, pH = 7.0, reaction volume = 100 mL of 50 mg/L BPA solution).
2.2.2. Operational Parameters Affecting PMS Activation by CoMn-LDO for BPA Degradation
As evidenced by the comparative degradation performance of different catalytic systems (Figure 7a), CoMn-LDO exhibited limited adsorption capacity, maintaining an adsorption–desorption equilibrium state within 90 min. The degradation efficiencies of BPA reached 2.00%, 77.67%, and 96.24% when using H2O2, PDS, and PMS as oxidants, respectively, with the CoMn-LDO/PMS system achieving the highest degradation efficiency.
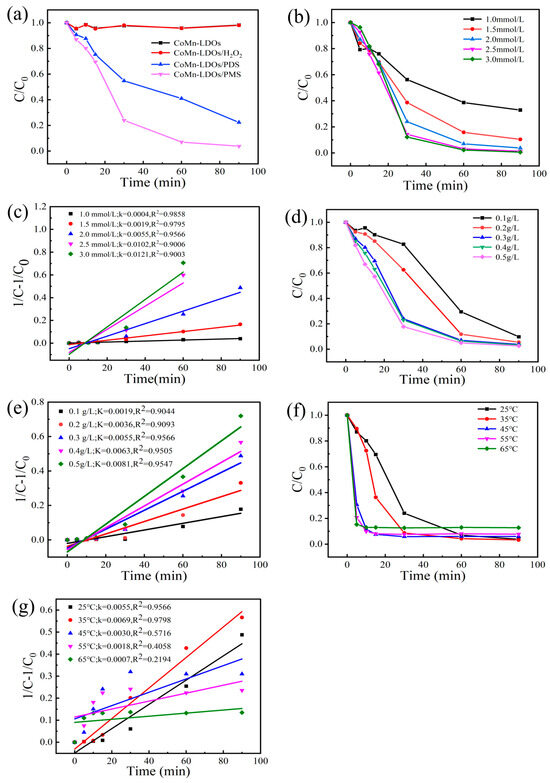
Figure 7.
(a) Comparative evaluation of BPA degradation performance across various catalytic systems; (b) Effect of PMS dosage on BPA degradation performance; (c) Pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves for BPA degradation under varying PMS dosages; (d) Effect of CoMn-LDO loading on BPA degradation efficiency; (e) Pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves of BPA degradation under different CoMn-LDO loadings; (f) Effect of temperature on BPA degradation performance; (g) Pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves of BPA degradation at different temperatures (Standard conditions: [PMS] = 2 mmol/L, [CoMn-LDO] = 0.3 g/L, T = 25 °C, pH 7.0, 0.1 L of BPA solution with concentration of 50 mg/L unless otherwise specified).
Figure 7b demonstrates the influence of PMS dosage on BPA degradation efficiency, while Figure 7c presents the corresponding pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves. As illustrated in Figure 7b, BPA removal efficiency showed a concentration-dependent enhancement with PMS dosage. As PMS concentration rose from 1.0 to 2.0 mmol/L, the degradation efficiency at 90 min improved from 67.14% to 96.24%, while the apparent rate constant (k) surged from 0.0004 to 0.0055 min−1—a 13-fold enhancement. However, further increasing the PMS concentration to 2.5 and 3.0 mmol/L only marginally improved degradation efficiencies (98.77% and 99.44%, respectively) with k values rising to 0.0102 and 0.0121 min−1. The observed plateau phenomenon stems from active site saturation, wherein surplus PMS competitively scavenges critical radicals (·OH and SO4·−), thus reducing their availability for BPA degradation. Based on the optimal trade-off between degradation efficiency and reaction kinetics, 2.0 mmol/L was identified as the most effective PMS dosage in the CoMn-LDO/PMS system.
Figure 7d presents the BPA degradation efficiency under varying catalyst loadings, while Figure 7e displays the corresponding pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves. Experimental data showed that elevating catalyst loading from 0.1 g/L to 0.3 g/L improved BPA degradation efficiency from 90.28% to 96.24%, accompanied by a 2.89-fold increase in the rate constant (k: 0.0019 → 0.0055 min−1). Further increases in catalyst loading to 0.4 g/L and 0.5 g/L yielded only marginal improvements, achieving degradation efficiencies of 96.72% (k = 0.0063 min−1) and 97.40% (k = 0.0081 min−1), respectively. This trend suggests that while higher catalyst concentrations provide additional active sites, the enhancement becomes less pronounced beyond 0.3 g/L. Consequently, 0.3 g/L CoMn-LDO is identified as the optimal dosage, balancing catalytic performance and resource efficiency.
The thermal activation effect on BPA degradation was quantified in Figure 7f,g. When the temperature increased from 25 °C to 35 °C, the degradation efficiency of BPA at 90 min rose from 96.24% to 96.75%. However, further elevating the temperature to 65 °C led to a gradual decline in BPA degradation to 81.62%, and the reaction no longer followed second-order reaction kinetics. Although elevated temperature enhances the molecular activity of reactants, it also induces desorption of reactants from the catalyst surface, resulting in insufficient utilization of the catalyst and ultimately impairing the catalytic degradation performance. From the perspective of degradation rate, higher temperatures improved the degradation efficiency of BPA. Through comprehensive evaluation of both reaction kinetics and thermodynamic efficiency, 35 °C emerged as the Pareto-optimal temperature for the CoMn-LDO/PMS catalytic system.
Figure 8a,b present the BPA degradation profiles and corresponding pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting results under different pH conditions, respectively. Notably, pH significantly influenced the degradation efficiency of BPA but had minimal impact on the ultimate degradation extent. When the pH increased from acidic to alkaline conditions, the degradation efficiency was enhanced, while the final degradation percentage remained relatively constant (~95%) after 60 min treatment. The optimal performance was achieved at pH 9, with maximum degradation percentage (99.44%) and apparent rate constant (0.0443 min−1). This phenomenon originates from the chain propagation reaction: SO4·− + OH− → SO4·2− + ·OH (k = 6.5 × 107 M−1s−1), where sulfate radical oxidation induces sustained ·OH production via oxygen-centered radical conversion. However, the transition to a highly alkaline environment (pH 11) led to a reduction in the degradation percentage and a decrease in the rate constant, likely due to the suppressed PMS activation efficiency.
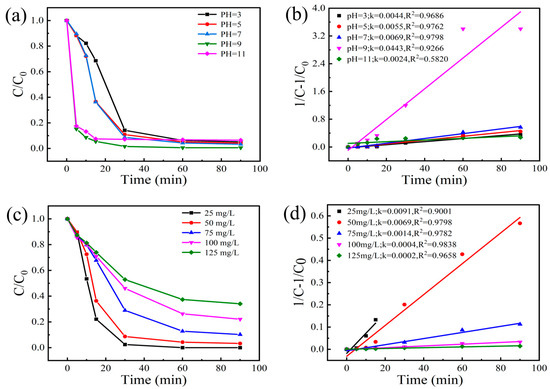
Figure 8.
(a) Effect of reaction pH on BPA degradation efficiency; (b) Pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves for BPA degradation under different pH conditions; (c) Influence of initial BPA concentration on degradation efficiency; (d) Pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting curves for BPA degradation at different initial concentrations. (Experimental conditions: PMS dosage = 2 mmol/L, CoMn-LDO dosage = 0.3 g/L, T = 35 °C, initial pH = 7, reaction volume = 100 mL of 50 mg/L BPA solution).
The degradation profile (Figure 8c) exhibited concentration-dependent behavior, with 25 mg/L BPA achieving >99% removal within 60 min. Elevated concentrations required extended treatment durations, demonstrating removal efficiencies of 96.75% (50 mg/L), 89.80% (75 mg/L), 77.92% (100 mg/L), and 65.94% (125 mg/L) after 90 min reactions. The pseudo-second-order kinetic fitting results (Figure 8d) showed that the k values decreased from 0.0091 to 0.0002 min−1. This reduction can be attributed to the limited and constant amount of reactive species generated by fixed dosages of catalyst and oxidant in the system, while the BPA concentration increased, consequently leading to lower degradation rates.
2.3. Mechanism Analysis of PMS-Catalyzed BPA Degradation
Figure 9a–c systematically compares the XPS spectral features of CoMn-LDO catalysts in pristine and reacted states, and Figure 9d shows the quenching experimental results. The XPS survey spectrum of CoMn-LDO (Figure 9a) exhibits four principal peaks corresponding to Co 2p, Mn 2p, O 1s, and C 1s.
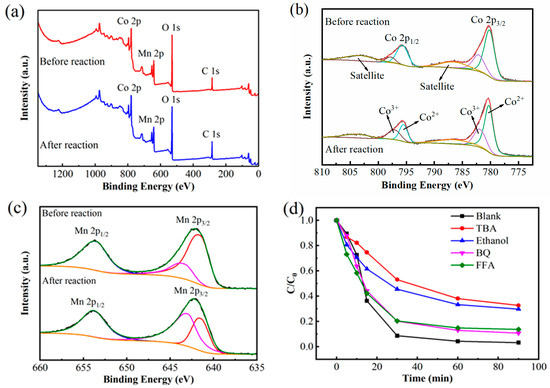
Figure 9.
(a) XPS survey spectrum, (b) Co 2p, and (c) Mn 2p high-resolution spectra of CoMn-LDO; (d) Effects of quenching agents on BPA degradation efficiency. (Reaction conditions: [PMS] = 2 mmol/L, [CoMn-LDO] = 0.3 g/L, T = 35 °C, initial pH = 7, V = 100 mL of 50 mg/L BPA solution).
High-resolution XPS measurements of the Co 2p and Mn 2p core levels are, respectively, displayed in Figure 9b,c, providing insights into the metal oxidation states. Before the reaction, the Co 2p spectrum (Figure 9b) displayed two major peaks at 795.7 eV (Co 2p1/2) and 780.2 eV (Co 2p3/2), along with satellite peaks at 786.5 eV and 803.2 eV, indicating the dominant presence of Co2+ [30]. After the reaction, the binding energies of the two main peaks slightly shifted to 795.4 eV and 780.5 eV. Conversely, the peak area representing Co3+ (781.9 eV and 797.1 eV) increased significantly, indicating an increase in Co3+ content after the reaction [31]. Similarly, the Mn 2p spectrum (Figure 9c) before the reaction contained characteristic peaks for Mn 2p1/2 (653.5 eV) and Mn 2p3/2, which were further resolved into two components at 641.6 eV (Mn3+) and 643.40 eV (Mn4+) [32], confirming Mn3+ as the dominant oxidation state. Post-reaction, the Mn 2p1/2 peak shifted to 653.8 eV, while the Mn 2p3/2 peaks shifted to 641.5 eV (Mn3+) and 643.0 eV (Mn4+), indicating an increase in Mn4+ content.
As evidenced by the quenching tests (Figure 9d), the introduction of tert-butanol (TBA, a hydroxyl radical scavenger) or ethanol (EtOH, a dual scavenger for both ·OH and SO4·−) in the CoMn-LDO/PMS system led to significant inhibition of BPA degradation, achieving only 67.38% and 70.31% removal efficiency after 90 min, respectively. In contrast, when benzoquinone (BQ, a superoxide radical scavenger) or furfuryl alcohol (FFA, a singlet oxygen quencher) was added, the degradation efficiencies remained relatively high at 89.26% and 86.33%, respectively, suggesting minimal involvement of non-radical pathways. These findings confirm the critical role of hydroxyl (·OH) and persulfate (SO4·−) radicals in facilitating the catalytic degradation, with ·OH being the predominant reactive oxygen species.
Building upon the XPS analysis and radical trapping experiments, a schematic illustration of the proposed catalytic mechanism for BPA degradation in the CoMn-LDO/PMS system is presented in Figure 10. The redox cycling between Co2+/Co3+ and Mn3+/Mn4+ facilitates the continuous activation of PMS to generate reactive radicals, with ·OH playing the dominant role in the oxidative degradation of BPA molecules. BPA produces by-products such as phenylethanol, p-isopropylphenol, phenol, benzoquinone, benzaldehyde, styrene, hydroxyphenylethanone, p-ethylstyrene, and 4-isopropylphenol under the attack of SO4·− and ·OH, and the formed by-products were further mineralized into CO2 and H2O [9,33]. The specific reaction equations involved are as follows:
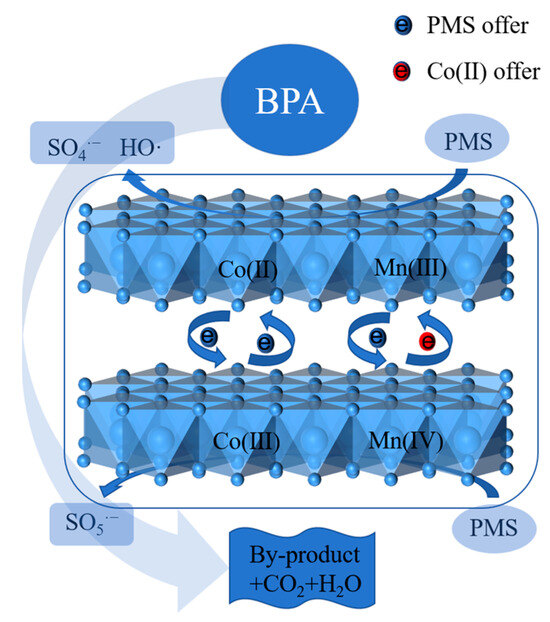
Figure 10.
Proposed mechanism of PMS activation by CoMn-LDO for BPA degradation.
2.4. Performance Comparison Between CoMn-LDO and CoMn-LDH
The comparative evaluation of CoMn-LDO and our previously synthesized CoMn-LDH was conducted using two key metrics: (1) TOC removal efficiency during BPA degradation and (2) cycling stability, with the results presented in Figure 11. Figure 11 demonstrates a progressive increase in TOC removal efficiency with extended reaction time. At 30 min of reaction, TOC removal rates reached 54.50% and 55.15% for CoMn-LDH and CoMn-LDO, respectively, followed by a gradual increase to 62.41% (CoMn-LDH) and 67.61% (CoMn-LDO) after 180 min. Interestingly, at 60 min of reaction, the TOC removal rates of CoMn LDH and CoMn LDO were significantly higher than previously reported for Fe-Co LDH [34]. Throughout the degradation process, CoMn-LDO exhibited both superior TOC removal efficiency and faster mineralization kinetics compared to CoMn-LDH. Notably, while previous results confirmed >95% BPA removal under identical conditions, more than 30% of initial TOC remained unresolved. This observation strongly supports the proposed two-stage degradation mechanism: (1) rapid oxidative cleavage of BPA molecules into smaller organic intermediates, followed by (2) slower complete mineralization to CO2 and H2O.
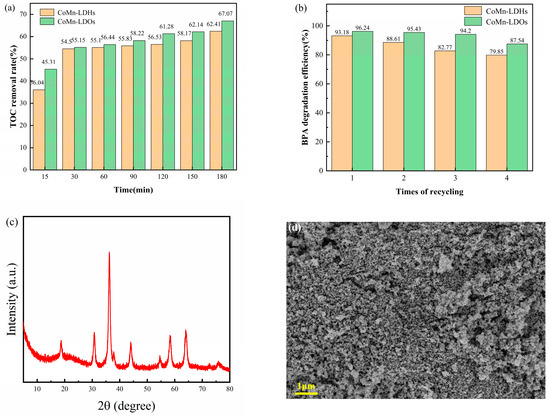
Figure 11.
(a) TOC removal and (b) recycling performance. (Conditions: [PMS] = 2 mmol/L, [catalyst] = 0.3 g/L, T = 35 °C, pHinitial = 7, 100 mL of 50 mg/L BPA solution). (c) XRD and (d) SEM images of CoMn-LDO after cyclic testing.
As shown in the cycling tests, the BPA degradation efficiency gradually decreased with increasing catalyst reuse cycles, though CoMn-LDO consistently outperformed CoMn-LDH. After four successive cycles (90 min each), CoMn-LDH retained 79.85% degradation efficiency, while CoMn-LDO maintained significantly higher activity (87.54%)—demonstrating a 7.99-percentage-point advantage. These results confirm that the calcined CoMn-LDO catalyst exhibits superior catalytic activity and structural stability relative to its CoMn-LDH precursor. To further evaluate the structural stability, the CoMn-LDO catalyst after cycling tests was characterized by XRD and SEM (Figure 11c,d). The diffraction patterns and surface morphology remained largely unchanged compared to those of the fresh catalyst, further confirming its high structural stability. Furthermore, compared with previous reports on the degradation of bisphenol A by the PMS system, the CoMn LDO/PMS system in this study exhibited higher catalytic activity (as shown in Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of degradation results of BPA.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis of CoMn-LDO
The CoMn-LDO catalyst was prepared via a combined precipitation and calcination method. The detailed procedure is described as follows:
A homogeneous solution was prepared by dissolving 0.4656 g of Co(NO3)2·6H2O, 0.4656 g of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, 0.3264 g of NaNO3, and 0.7112 g of NH4F in 800 mL of deionized water with continuous stirring at a constant temperature of 25 ± 1 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, 500 μL of 30 wt% H2O2 was introduced into the reaction system, followed by pH titration with 0.08 M NaOH(aq) under N2 protection until the endpoint pH of 10.0 was achieved. After 20 h of static aging at ambient temperature, the colloidal suspension was processed through a Büchner funnel (0.45 μm PTFE membrane), thoroughly washed with ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ·cm), and subsequently dried in a vacuum oven (60 °C, 10 kPa) for 12 h to isolate the precursor. Finally, the as-synthesized precursor was subjected to thermal treatment with a controlled heating gradient (5 °C min−1) in a nitrogen-rich environment (N2 flow rate = 50 sccm) until the predetermined calcination temperature was achieved, and maintained for 5 h to produce the CoMn-LDO catalyst.
All chemicals were of analytical grade (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and ultrapure water used in the experiments was prepared in the laboratory.
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of CoMn-LDO
A comprehensive characterization of CoMn-LDO was conducted using multiple analytical techniques. Microstructural characterization was performed using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (Zeiss Sigma 300, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic system (Oxford X-Max 50, Oxford Instruments, Oxford, UK), enabling simultaneous topography examination and elemental distribution mapping. Microstructural analysis was conducted using a field-emission transmission electron microscope (FEI Tecnai F20, Hillsboro, OR, USA). The phase composition was analyzed using a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer (Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.5406 Å) operating at 40 kV and 40 mA, with a scanning rate of 2° min−1 in the 2θ range of 10–80°. Chemical functionalization of surfaces was characterized using an FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker Vertex 70, Bruker Optics, Ettlingen, Germany). Porous characteristics were evaluated by N2 sorption analysis at 77 K (Micromeritics ASAP 2460, Norcross, GA, USA), calculating specific surface area by the BET method and pore size distribution via NLDFT modeling. Oxidative stability was examined by thermogravimetric analysis coupled with differential thermal analysis (NETZSCH STA449 F3, Netzsch, Selb, Germany) in synthetic air. Surface speciation was probed by high-resolution XPS (Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, Waltham, MA, USA) with adventitious carbon referencing at 284.8 eV.
3.3. Catalytic Performance Evaluation
3.3.1. Catalytic Degradation of BPA
The catalytic degradation experiments were conducted using the following procedure: 100 mL of standard BPA solution (50 mg/L) was transferred into a 250 mL amber conical flask. Predetermined concentrations of catalyst (0.1–0.5 g/L) and PMS (1–3 mM) were added to the solution. The reaction system was then placed in a constant-temperature oscillating incubator (HZQ-X300, Shanghai, China, temperature control accuracy ±0.5 °C) and maintained at specified temperatures (25–65 °C) with continuous shaking at 180 rpm.
At specified time points, 5 mL samples were withdrawn and promptly filtered using 0.45 μm hydrophilic membrane filters. To terminate the reaction, each filtrate was treated with 1 mL of methanol. The filtrate was analyzed for remaining BPA levels by UV-Vis spectrophotometry, with absorbance measurements recorded at 278 nm, and the concentration was calculated using standard curve fitting equations (as displayed in Figure 12). The BPA degradation efficiency was then calculated according to Equation (1). Important experimental notes: all operations were conducted under light-protected conditions, and each experiment was performed in triplicate.
where C0 and C are defined as the initial and current BPA concentrations (mg/L), respectively.
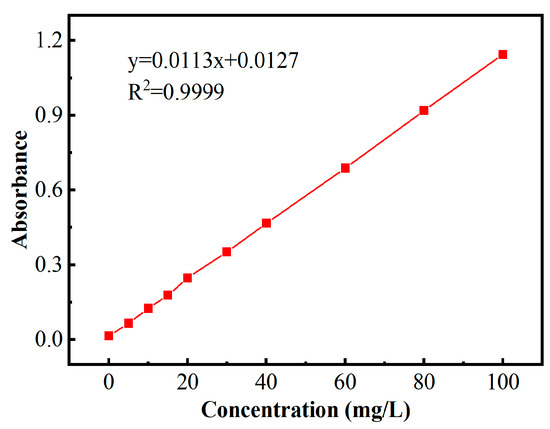
Figure 12.
Calibration curve for BPA quantification.
3.3.2. Radical Scavenging Experiments
The key reactive species involved in BPA degradation were investigated using radical scavengers including tert-butanol (TBA), ethanol (EtOH), p-benzoquinone (BQ), and furfuryl alcohol (FFA). While both TBA and EtOH scavenge hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and sulfate radicals (SO4·−), their distinct kinetic preferences were utilized for discrimination: TBA (with reaction rate constants of (3.8–7.6) × 108 M−1s−1 for ·OH and (4.0–9.1) × 105 M−1s−1 for SO4·− [44]) was employed as the ·OH indicator due to its significantly higher selectivity toward ·OH, whereas EtOH ((1.2–2.8) × 109 M−1s−1 for ·OH and (1.6–7.7) × 107 M−1s−1 for SO4·− [45]) served as the SO4·− probe given its comparable reactivity with both radicals. Additionally, BQ and FFA were applied as specific scavengers for superoxide radicals (O2−) and singlet oxygen (1O2), respectively.
3.3.3. Catalyst Stability Evaluation
The stability of a catalyst is a crucial parameter in assessing its catalytic performance. In this research, the reusability of the catalyst was systematically evaluated through the following procedure: After completing the BPA degradation experiments (Section 3.3.1), the recovered catalyst was subjected to three consecutive washing cycles using deionized water and ethanol under vacuum filtration. Following thorough washing, the catalyst underwent vacuum drying at 60 °C for a 12 h duration. Finally, the regenerated catalyst was reused under identical degradation conditions (Section 3.3.1) to evaluate its catalytic stability and reusability.
4. Conclusions
A well-crystallized CoMn-LDO catalyst with hexagonal flake-like morphology and mesoporous structure was successfully synthesized via thermal calcination of a CoMn-LDH precursor. Through systematic parameter screening, optimal performance was obtained with a 500 °C-calcined catalyst at reaction conditions of 35 °C, neutral pH (7.0), 0.3 g/L catalyst loading, and 2.0 mmol/L PMS dosage. Under these optimized parameters, 96.75% BPA degradation and 58.22% TOC removal rates were achieved within 90 min.
The CoMn-LDO catalyst exhibits exceptional capability for activating PMS, demonstrating significantly superior catalytic efficiency compared to its uncalcined CoMn-LDH precursor as well as other similar catalysts. Compared to the pristine CoMn-LDH, the calcined CoMn-LDO exhibited superior catalytic activity and cycling stability, confirming its potential for practical wastewater treatment applications.
Mechanistic investigations demonstrated that the activation of PMS by CoMn-LDO primarily generated hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and sulfate radicals (SO4·−), with ·OH identified as the dominant reactive oxygen species. XPS analysis elucidated the synergistic redox cycling between Co and Mn, where efficient electron transfer between Co2+/Co3+ and Mn3+/Mn4+ pairs significantly enhanced radical generation.
This study reveals the catalytic mechanism of BPA degradation in the CoMn- LDO/PMS system through XPS analysis and free radical quenching experiments, thereby providing a theoretical basis and practical guidance for the development of high-efficiency persistent sulfate-activated catalysts. Although CoMn-LDO exhibits excellent catalytic performance under laboratory conditions, the complex water quality conditions that may exist in actual wastewater treatment (e.g., high salinity, coexistence of multiple pollutants, etc.) might affect the efficiency and stability of the catalyst. Future studies need to further explore the performance of the catalyst under different water quality conditions.
Author Contributions
G.W.: Conceptualization; Methodology; Experimental; Testing; Writing—original. M.J.: Experimental, Supervision; Data curation; Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund Project of China Coal Science and Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. (2023CX-II-01), and the project leader was Guanyu Wang.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and are also available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Guanyu Wang was employed by China Coal Research Institute Corporation Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, W.; Su, X.; Wu, Y.; Yi, G.; Guo, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. A comprehensive review of PbO2 electrodes in electrocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Environ. Res. 2025, 279, 121885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Su, X.; Wu, Y.; Yi, G.; Guo, X.; Oderinde, O.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances in tungsten-based photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation: A comprehensive review. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1036, 181624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Su, X.; Liu, W.; Yi, G.; Shi, S.; Oderinde, O.; Zeng, H.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, C.; et al. GO/Bi2O2CO3/NiWO4 with Z-scheme heterojunction: Efficiently enhanced degradation of organic pollutants under visible light and DFT studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, X.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, fate and risk assessment of BPA and its substituents in wastewater treatment plant: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yun, J.; Zhang, H.; Si, J.; Fang, X.; Shao, L. Degradation of Bisphenol A by ozonation in rotating packed bed: Effects of operational parameters and co-existing chemicals. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cao, X.; Fu, M.; Zeng, G. Magnetic porous carbon nanopolyhedron modified rGO composites as recyclable sorbent for effective removal of bisphenol A from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Show, P.L.; Ivanets, A.; Luo, D.; Wang, C. MXenes as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysts for removal of organic pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-B.; Do, Q.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, W.-H.; Bui, X.-T.; Dong, C.-D. Decoration of marigold flower-like CoMo LDH on reinforced cow manure-derived biochar as an effective peroxymonosulfate activator for degradation of Bisphenol A in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; She, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hong, J. High-efficiency degradation of bisphenol A by heterogeneous Mn–Fe layered double oxides through peroxymonosulfate activation: Performance and synergetic mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Facile preparation of porous Mn/Fe3O4 cubes as peroxymonosulfate activating catalyst for effective bisphenol A degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguzie, K.L.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, X.; Oguzie, E.E.; Njoku, V.O.; Obodo, G.A. Oxidative degradation of Bisphenol A in aqueous solution using cobalt ion-activated peroxymonosulfate. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Xi, S.; Miao, S.; Ding, J.; Cai, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; et al. Single Cobalt Atoms Anchored on Porous N-Doped Graphene with Dual Reaction Sites for Efficient Fenton-like Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12469–12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Alzaharani, Y.; Alshehri, S.M. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A with g-C3N4/MoS2-PANI nanocomposite: Kinetics, main active species, intermediates and pathways. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. H-TiO2-NTs/CoMn-LDO/MoSe2-Ce electrodes for selective extraction of lead ions via capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 367, 132895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adim, S.; Eddahmi, M.; Boussetta, A.; Mansori, M.; Essoumhi, A.; Bouissane, L. Green four-component reaction and dye adsorption studies of new ZnCoAl-LDH and ZnCoCr-LDH materials. J. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 1036, 123719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-Y.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, H.-J.; Oh, J.-M. Development of Mesopore Structure of Mixed Metal Oxide through Albumin-Templated Coprecipitation and Reconstruction of Layered Double Hydroxide. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Bonab, M.; Aber, S.; Salari, D.; Khodam, F. Water treatment with CoZnAl-LDH and its mixed metal oxide. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Wen, G. Recent advance of layered double hydroxides materials: Structure, properties, synthesis, modification and applications of wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, Z.P.; Erbas, Z.; Soylak, M. Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs) for the Treatment and Determination of Pollutants in Water and Wastewater. Anal. Lett. 2023, 57, 1646–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B.; Yi, G.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z. Peroxymonosulfate activation by cobalt–manganese layered double hydroxide for bisphenol A degradation. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2024, 26, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Upadhyay, C. Layered double hydroxides for industrial wastewater remediation: A review. Catal. Today 2025, 445, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Huo, P.; Liu, X. A Short Review of Layered Double Oxide-Based Catalysts for NH3-SCR: Synthesis and NOx Removal. Catalysts 2024, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, T.; Dong, S. Tetracycline hydrochloride degradation over manganese cobaltate (MnCo2O4) modified ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheet through the highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate under visible light irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 600, 449–462. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Yi, G.; Guo, X.; Yin, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, H.; Xing, B.; et al. Carbonized nitrogen doped carbon dots functionalized PbO2 electrode for efficient degradation of organic pollutants. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1319, 139453. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Sui, M.; Yuan, B.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y. Efficient degradation of nitrobenzene by Cu-Co-Fe-LDH catalyzed peroxymonosulfate to produce hydroxyl radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, Y. Simultaneous removal of arsenate and antimonate in simulated and practical water samples by adsorption onto Zn/Fe layered double hydroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalagedara, M.N.; Samaraweera, M.; Dharmarathna, S.; Kuo, C.-H.; Pahalagedara, L.R.; Gascón, J.A.; Suib, S.L. Removal of Azo Dyes: Intercalation into Sonochemically Synthesized NiAl Layered Double Hydroxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 17801–17809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Luo, K.; Yao, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe-Co layered doubled hydroxide for efficient catalytic degradation of Rhoadmine B. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 321, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, M.; Li, B.; Lin, Q.; Liao, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, C. 3-D hierarchical micro/nano-structures of porous Bi2WO6: Controlled hydrothermal synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performances. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 313, 110830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunpandian, M.; Oh, T.H. Nitrogen-Doped Hollow Carbon Spheres-Decorated Co2SnO4/WS2 Heterostructures with Improved Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye. Molecules 2025, 30, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; You, H.; Wu, G.; Huang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Co/Fe co-doped ZIF-8 derived hierarchically porous composites as high-performance electrode materials for Cu2+ ions capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Shao, M.; Yan, D.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. CoMn-layered double hydroxide nanowalls supported on carbon fibers for high-performance flexible energy storage devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Niu, W.; Yang, S.; Chen, M.; Rehman, S.; Zhu, N. Enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation of Fe-Al layered double hydroxide by dissolved organic matter: Performance and mechanism. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, C.; Lu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, D.; Ma, J. Oxygen Vacancy-Induced Nonradical Degradation of Organics: Critical Trigger of Oxygen (O2) in the Fe–Co LDH/Peroxymonosulfate System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15400–15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shao, P.; Gao, S.; Bai, Z.; Tian, J. Benzoquinone-assisted heterogeneous activation of PMS on Fe3S4 via formation of active complexes to mediate electron transfer towards enhanced bisphenol A degradation. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kong, L.; Xie, M.; Lu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Feng, Z.; Zhan, J. Carbon aerogel from forestry biomass as a peroxymonosulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, J.; Jie, H.; Wu, W.; Jiang, F. Highly Efficient Copper Doping LaFeO3 Perovskite for Bisphenol A Removal by Activating Peroxymonosulfate. Catalysts 2023, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Wu, W.; Jie, H.; Jiang, F. La2CoO4+δ perovskite-mediated peroxymonosulfate activation for the efficient degradation of bisphenol A. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, J. Micro-nano structured CoS: An efficient catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation for removal of bisphenol A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Cao, S.; Liu, R.; Tang, R.; Chen, H.; Jiang, F. Preparation of nitrogen-containing carbon using a one-step thermal polymerization method for activation of peroxymonosulfate to degrade bisphenol A. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Meng, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Roles of naturally occurring biogenic iron-manganese oxides (BFMO) in PMS-based environmental remediation: A complete electron transfer pathway. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 155, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, H. Understanding oxygen-deficient La2CuO4-δ perovskite activated peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol A degradation: The role of localized electron within oxygen vacancy. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 284, 119732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of bimetallic crednerite nanosheet as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst in Fenton-like degradation of bisphenol A. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2025, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, X.; Shi, C.; Yang, S. Decolorization of Acid Orange 7 with peroxymonosulfate oxidation catalyzed by granular activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 232, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Niu, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Wen, X.; Liang, C.; Zeng, G. Co-Mn layered double hydroxide as an effective heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of organic dyes by activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).