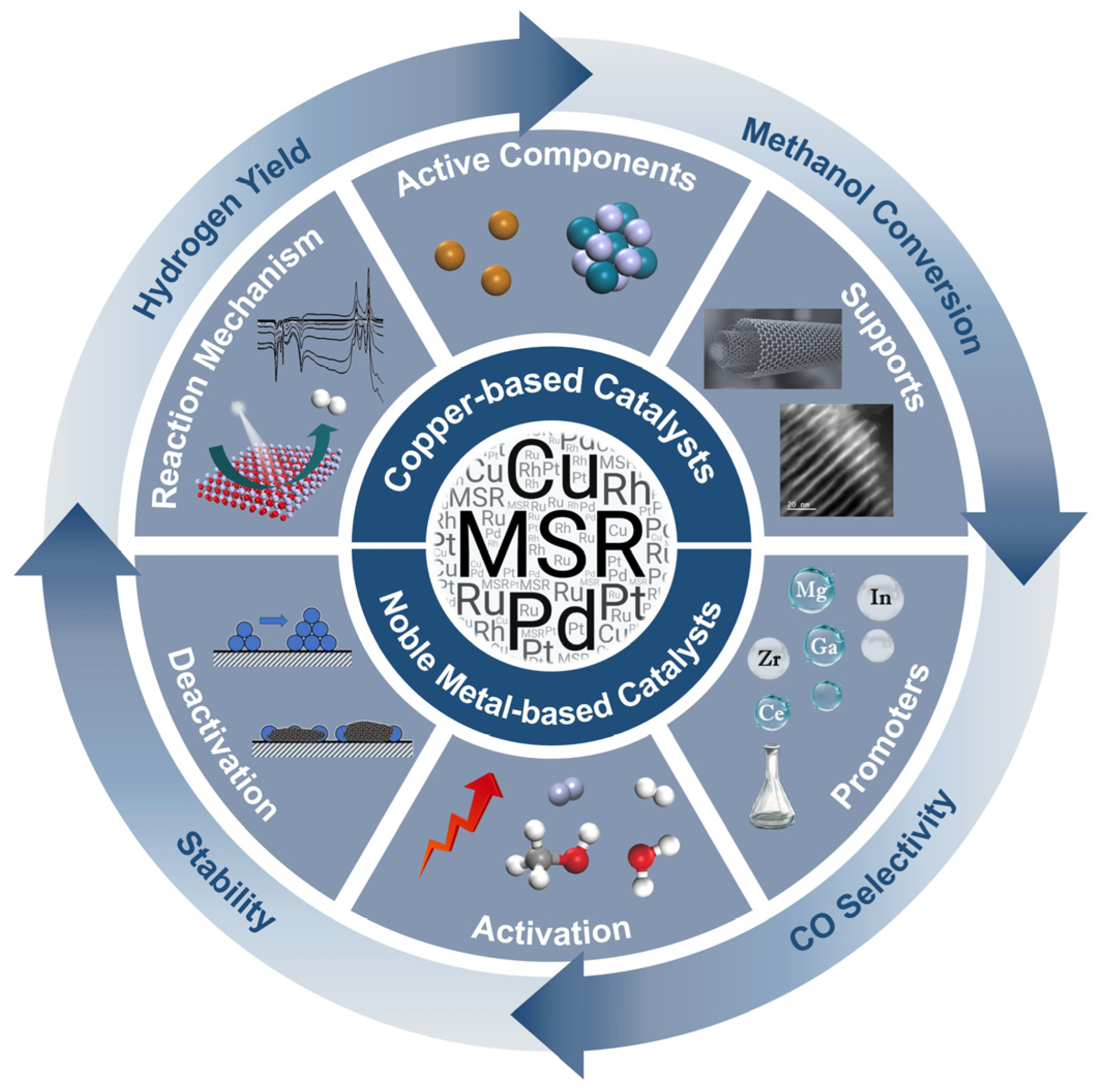
Recent Advances in Methanol Steam Reforming Catalysts for Hydrogen Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Copper-Based Catalysts
2.1. Performance
2.1.1. Active Sites
2.1.2. Supports
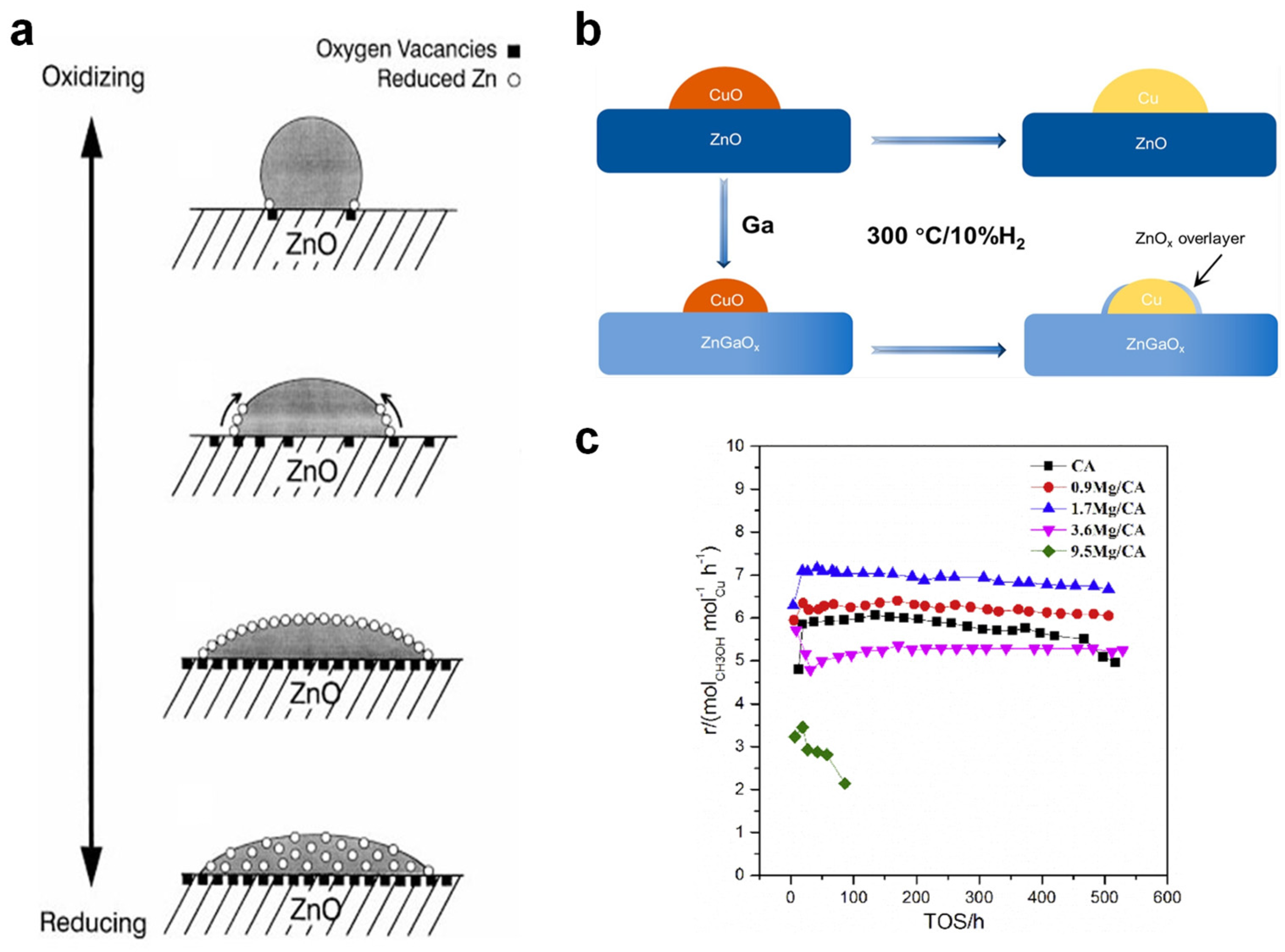
2.1.3. Promoters
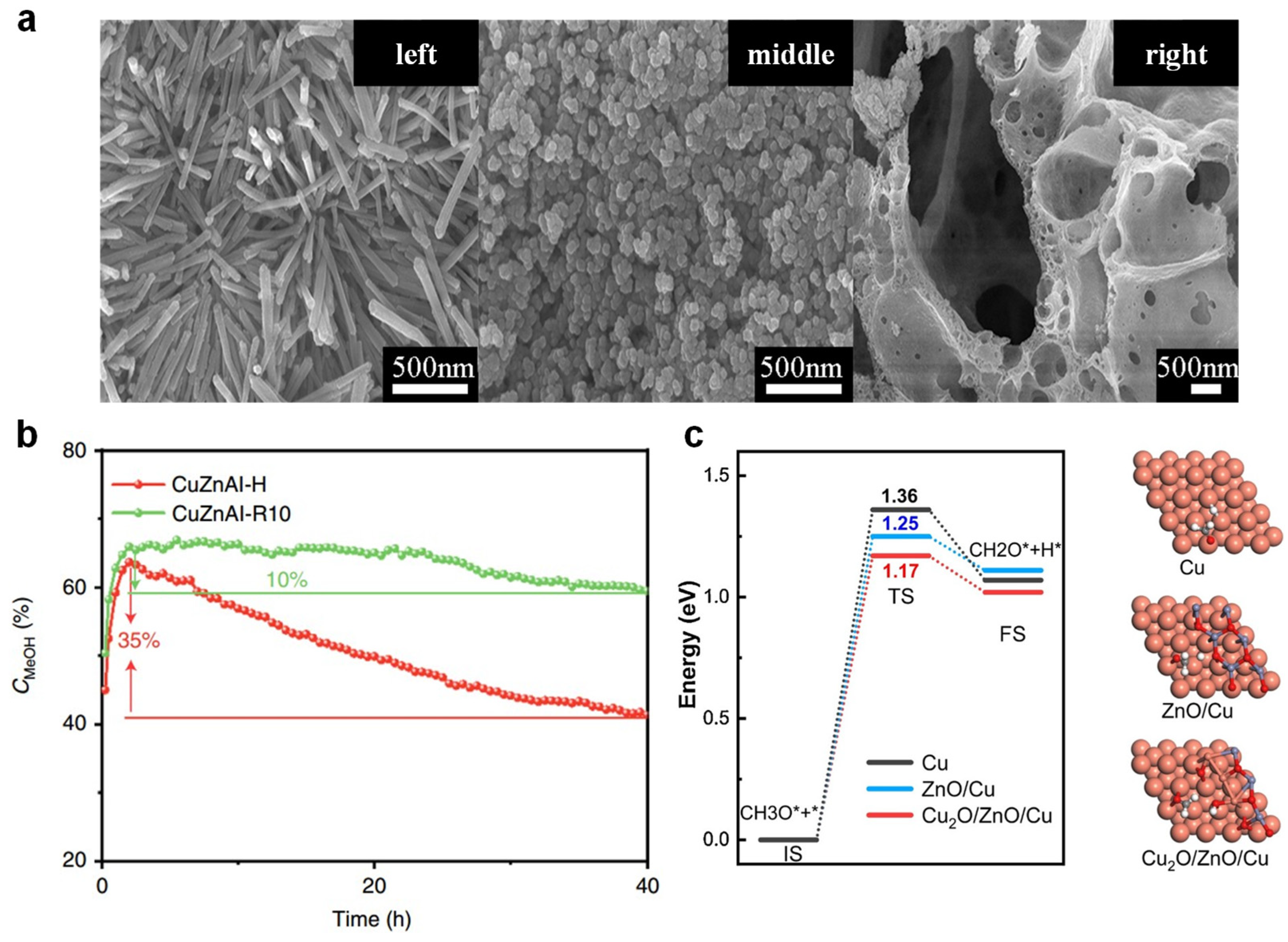
2.1.4. Preparation and Activation
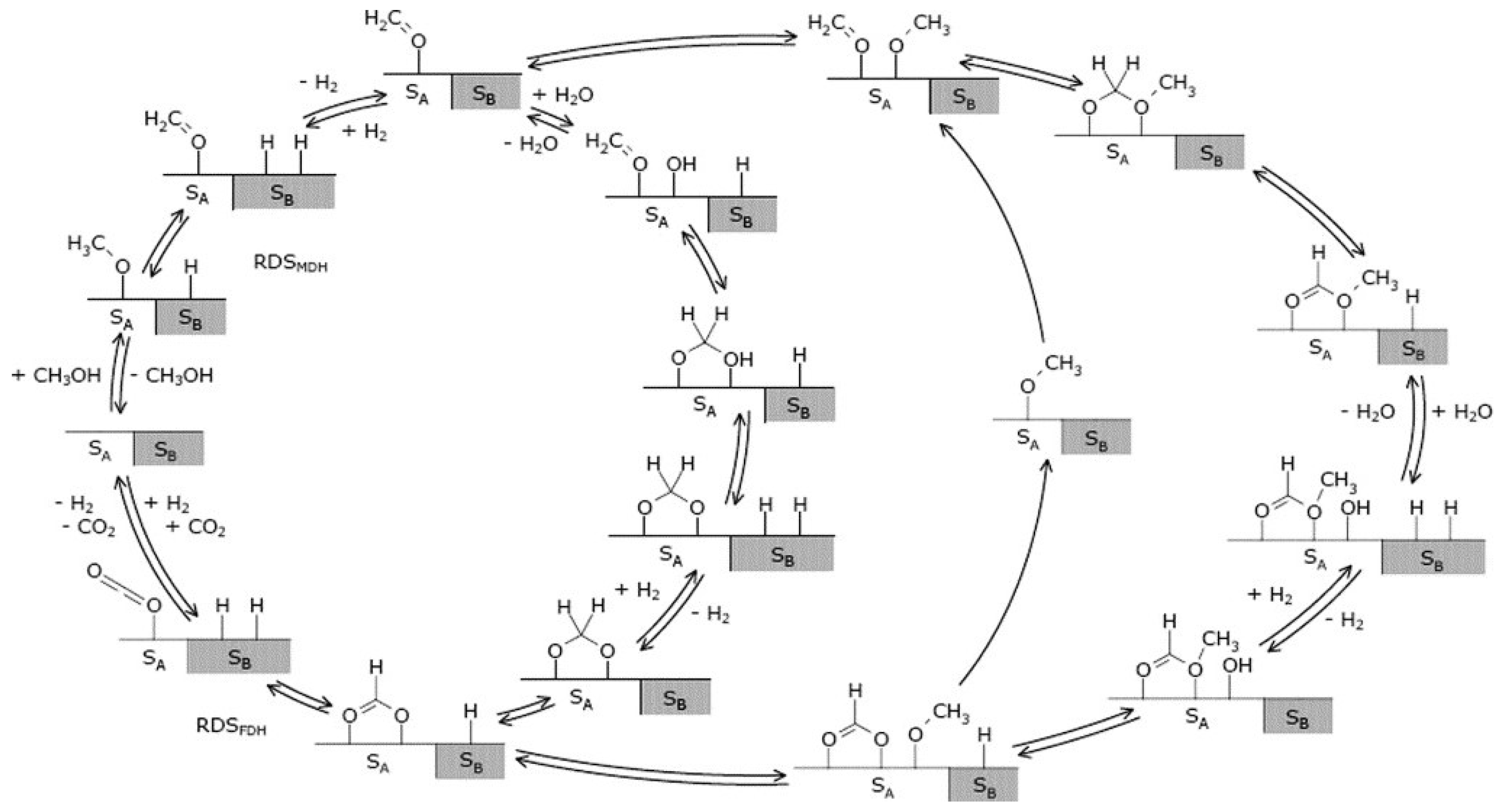
2.2. Reaction Mechanism
2.3. Deactivation
3. Noble Metal-Based Catalysts
3.1. Palladium-Based Catalysts
3.1.1. Alloys
3.1.2. Supports and Promoters
3.1.3. Reaction Mechanism
3.1.4. Deactivation
3.2. Other Catalysts
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSR | methanol steam reforming |
| MD | methanol decomposition |
| WGS | water-gas shift |
| LOHCs | liquid organic hydrogen carriers |
| PEMFCs | polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells |
| CCU | carbon capture and utilization |
| WHSV | weight hourly space velocity |
| GHSV | gas hourly space velocity |
| TOF | turnover frequency |
| SMSIs | strong metal–support interactions |
| OR | Ostwald ripening |
| PMC | particle migration and coalescence |
| SEA | strong electrostatic adsorption |
| SAA | single-atom alloy |
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Qu, Y. Sustainable production of hydrogen with high purity from methanol and water at low temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Lin, H.; Wang, Q.; Ren, X.; Hernández-Pinilla, D.; Nagao, T.; Xie, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, S.; Song, H.; et al. Triggering water and methanol activation for solar-driven H2 production: Interplay of dual active sites over plasmonic ZnCu alloy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12145–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Song, H.; Ichihara, F.; Oshikiri, M.; Lu, W.; Tang, D.-M.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Davin, P.; et al. Light-induced dynamic restructuring of Cu active sites on TiO2 for low-temperature H2 production from methanol and water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 20530–20538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuster, P.; Papp, C.; Wasserscheid, P. Liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs): Toward a hydrogen-free hydrogen economy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjekar, A.M.; Yadav, G.D. Steam reforming of methanol for hydrogen production: A critical analysis of catalysis, processes, and scope. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshan, C.; Stadlmayr, W.; Penner, S.; Lorenz, H.; Memmel, N.; Hävecker, M.; Blume, R.; Teschner, D.; Rocha, T.; Zemlyanov, D.; et al. Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming on copper boosted by zinc-assisted water activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Lan, T.; Zhao, G.; Nie, Q.; Jiang, F.; Lu, Y. Interface-hydroxyl enabling methanol steam reforming toward CO-free hydrogen production over inverse ZrO2/Cu catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 334, 122839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Song, Y.; Kim, T.; Kim, S. Recent trends in the development of reactor systems for hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 3587–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Deng, D. Numerical investigation of a multichannel reactor for syngas production by methanol steam reforming at various operating conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14790–14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, X.; Tang, X.; Dou, P.; Yang, Y.; He, Y. Review on developments of catalytic system for methanol steam reforming from the perspective of energy-mass conversion. Fuel 2023, 345, 128234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Hirose, A.; Shimokawabe, M.; Takahashi, K. Steam reforming of methanol on copper-silica catalysts—Effect of copper loading and calcination temperature on the reaction. Appl. Catal. 1982, 4, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yang, Y.; Shen, T.; Yin, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Yin, P.; Ren, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Designing Cu0−Cu+ dual sites for improved C−H bond fracture towards methanol steam reforming. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, G.; He, H. Mechanistic insights into methanol steam reforming on copper catalysts: Dynamics of active sites and reaction pathway. J. Catal. 2025, 442, 115922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D. The Cu–Al2O3 interface: An unignorable active site for methanol steam reforming hydrogen production. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 3448–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, M.; Gennequin, C.; Aboukaïs, A.; Abi-Aad, E. Cu/Zn-based catalysts for H2 production via steam reforming of methanol. Catal. Today 2011, 176, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, X. Enhancing activation and stability of core-shell CuZn catalyst by ZnOx oxygen vacancies for methanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2024, 678, 119652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, F.; Tang, X.; Dai, S.; Pu, T.; Liu, X.; Tian, P.; Xuan, F.; Xu, Z.; Wachs, I.E.; et al. Induced activation of the commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for the steam reforming of methanol. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrani, R.; Haghighi, M.; Jodeiri, N.; Ajamein, H.; Abdollahifar, M. Fuel cell grade hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming over CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 nanocatalyst with various oxide ratios synthesized via urea-nitrates combustion method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 13141–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pérez, M.A.; Moya, J.; Serrano-Ruiz, J.C.; Faria, J. Interplay of support chemistry and reaction conditions on copper catalyzed methanol steam reforming. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15268–15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, V.G.; Abrokwah, R.Y.; Kuila, D. Synthesis of stable Cu-MCM-41 nanocatalysts for H2 production with high selectivity via steam reforming of methanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 10439–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Kiadehi, A.D. Effects of catalyst preparation route and promoters (Ce and Zr) on catalytic activity of CuZn/CNTs catalysts for hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 8906–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varmazyari, M.; Khani, Y.; Bahadoran, F.; Shariatinia, Z.; Soltanali, S. Hydrogen production employing Cu(BDC) metal–organic framework support in methanol steam reforming process within monolithic micro-reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D. Morphology effect of ceria on the performance of CuO/CeO2 catalysts for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7252–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, T.; Haghighi, M.; Ajamein, H. Fuel cell-grade hydrogen production from methanol over sonochemical coprecipitated copper based nanocatalyst: Influence of irradiation power and time on catalytic properties and performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 126, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, S.G.; Flores, J.H.; da Silva, M.I.P. Cu/ZnO and Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalysts used for methanol steam reforming. Mol. Catal. 2018, 454, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Mao, L.; Du, H.; Zhong, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Tracking the critical roles of Cu+ and Cu0 sites and the optimal Cu+/Cu0 ratio for CH3OH steam reforming (MTSR) to manufacture H2. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, L.; Ni, C.; Sun, T.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, A.; Hu, Y. CeO2–ZrO2-promoted CuO/ZnO catalyst for methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4397–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajrishi, O.Z.; Taghizadeh, M.; Kiadehi, A.D. Methanol steam reforming in a microchannel reactor by Zn-, Ce- and Zr-modified mesoporous Cu/SBA-15 nanocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 14103–14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.M.K.; Tong, W.; West, A.; Cheung, K.; Li, T.; Smith, G.; Guo, Y.; Tsang, S.C.E. Non-syngas direct steam reforming of methanol to hydrogen and carbon dioxide at low temperature. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yan, H.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, M. Gallium-promoted strong metal-support interaction over a supported Cu/ZnO catalyst for methanol steam reforming. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 9511–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Toyir, J.; Ramírez de la Piscina, P.; Homs, N. Hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming over Al2O3- and ZrO2-modified CuOZnOGa2O3 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13704–13711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyar, N.; Khani, Y.; Amini, M.M.; Bahadoran, F.; Safari, N. Copper-based catalysts over A520-MOF derived aluminum spinels for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming: The role of spinal support on the performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 21341–21353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Qing, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Y. Enhancing effect of MgO modification of Cu–Al spinel oxide catalyst for methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Lan, G.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y. High-performance Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol steam reforming with enhanced Cu-ZnO synergy effect via magnesium assisted strategy. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 63, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongboonchoo, Y.; Thouchprasitchai, N.; Pongstabodee, S. Hydrogen production with a low carbon monoxide content via methanol steam reforming over CuxCeyMgz/Al2O3 catalysts: Optimization and stability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 12220–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shen, Q.; Andersson, M.; Li, S.; Yuan, J. Surface of high-entropy perovskite catalyst La(CoCuFeAlCe)0.2O3 (100): Experimental study of methanol steam reforming for hydrogen production and DFT mechanism research. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 684, 161917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, G.; Cen, Y.; Deng, T.; Yan, W.; Gao, J.; Zhu, S.; Olsbye, U.; et al. A highly stable copper-based catalyst for clarifying the catalytic roles of Cu0 and Cu+ species in methanol dehydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Cheng, Q.; Ding, T.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Abe, T.; Tsubaki, N.; et al. Achieving efficient and robust catalytic reforming on dual-sites of Cu species. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. In-situ self-assembled Cu2O/ZnO core-shell catalysts synergistically enhance the durability of methanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 616, 118072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhu, M. Dynamics of the Cu/CeO2 catalyst during methanol steam reforming. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 7003–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Golunski, S.E.; Spencer, M.S. The role of copper and zinc oxide in methanol synthesis catalysts. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwaldt, J.D.; Molenbroek, A.M.; Topsøe, N.Y.; Topsøe, H.; Clausen, B.S. In situ investigations of structural changes in Cu/ZnO catalysts. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Choi, Y.; Fujitani, T. On the issue of the active site and the role of ZnO in Cu/ZnO methanol synthesis catalysts. Top. Catal. 2003, 22, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Morioka, H.; Takehira, K. Production of hydrogen from methanol over Cu/ZnO and Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared by homogeneous precipitation: Steam reforming and oxidative steam reforming. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 268, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurr, P.; Kasatkin, I.; Girgsdies, F.; Trunschke, A.; Schlögl, R.; Ressler, T. Microstructural characterization of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol steam reforming—A comparative study. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 348, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Sun, X.; Lan, G.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y. Tuning lattice strain of copper particles in Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for methanol steam reforming. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 15611–15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, K.; Onodera, H.; Takezawa, N. Highly active copper catalysts for steam reforming of methanol. catalysts derived from Cu/Zn/Al alloys. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1994, 53, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Tong, Q.; Ouyang, G. Polydopamine modified ordered mesoporous carbon for synergistic enhancement of enrichment efficiency and mass transfer towards phenols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1095, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Mohamed, F.; Ashraf, A.M.; Shaban, M.; Aslam Parwaz Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M. Enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting activity of carbon nanotubes@TiO2 nanoribbons in different electrolytes. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chiang, K.; Burke, N. Porous carbon-supported catalysts for energy and environmental applications: A short review. Catal. Today 2011, 178, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, Y.; Tahay, P.; Bahadoran, F.; Safari, N.; Soltanali, S.; Alavi, A. Synergic effect of heat and light on the catalytic reforming of methanol over Cu/x-TiO2(x=La, Zn, Sm, Ce) nanocatalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 594, 117456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Dai, H.X.; Au, C.T. Defective structure, oxygen mobility, oxygen storage capacity, and redox properties of RE-based (RE = Ce, Pr) solid solutions. Catal. Today 2004, 90, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Graciani, J.; Evans, J.; Stacchiola, D.; Senanayake, S.D.; Barrio, L.; Liu, P.; Sanz, J.F.; Hrbek, J.; Rodriguez, J.A. Gold, copper, and platinum nanoparticles dispersed on CeOx/TiO2(110) surfaces: High water-gas shift activity and the nature of the mixed-metal oxide at the nanometer level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Pant, K.K. Activity and stability enhancement of copper–alumina catalysts using cerium and zinc promoters for the selective production of hydrogen via steam reforming of methanol. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Gnaser, H.; Zapf, R.; Hessel, V.; Ziegler, C. Parallel screening of Cu/CeO2/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for steam reforming of methanol in a 10-channel micro-structured reactor. Catal. Commun. 2004, 5, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, X.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Yin, C.; Wang, Y. Methanol steam reforming using Ce and La modified low-Cu catalysts for on-board hydrogen production. Mol. Catal. 2025, 570, 114663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrell, J.; Birgersson, H.; Boutonnet, M.; Melián-Cabrera, I.; Navarro, R.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Production of hydrogen from methanol over Cu/ZnO catalysts promoted by ZrO2 and Al2O3. J. Catal. 2003, 219, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, T.H.; Ko, C.H.; Park, H.C.; Song, I.K. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of methanol in a micro-channel reactor coated with Cu/ZnO/ZrO2/Al2O3 catalyst. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1296–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-S.; Mao, D.-S.; Lu, G.-Z.; Cao, Y.; Fan, K.-N. The role of the promoters in Cu Based Catalysts for methanol steam reforming. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, B.; Pettersson, L.J. Steam reforming of methanol over copper-based monoliths: The effects of zirconia doping. J. Power Sources 2002, 106, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; West, A.; Cheung, K.; Yu, K.-M.; Tsang, S.C.E. Dramatic effects of gallium promotion on methanol steam reforming Cu–ZnO catalyst for hydrogen production: Formation of 5 Å Copper Clusters from Cu–ZnGaOx. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Kang, H.-F.; Hou, X.-N.; Qing, S.-J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.-X.; Xiang, H.-W. Sustained release catalysis: Dynamic copper releasing from stoichiometric spinel CuAl2O4 during methanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 323, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Liu, Y.K.; Kong, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Guo, K.; Liu, D. Hydrolysis precipitation method for the preparation of Cu-ZnO@Al2O3 catalyst in methanol steam reforming. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Haghighi, M.; Ajamein, H. Sonochemically coprecipitation synthesis of CuO/ZnO/ZrO2/Al2O3 nanocatalyst for fuel cell grade hydrogen production via steam methanol reforming. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 421, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-R.; Wang, L.-C.; Yao, C.-Z.; Cao, Y.; Dai, W.-L.; He, H.-Y.; Fan, K.-N. A highly efficient Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst via gel-coprecipitation of oxalate precursors for low-temperature steam reforming of methanol. Catal. Lett. 2005, 102, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Morioka, H.; Takaki, K.; Takehira, K. Active Cu/ZnO and Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared by homogeneous precipitation method in steam reforming of methanol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 263, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lian, C.; Zhu, M. Alcohol-induced strong metal-support interactions in a supported copper/ZnO catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, B.; Jentoft, F.C.; Soerijanto, H.; Kröhnert, J.; Schlögl, R.; Schomäcker, R. Steam reforming of methanol over copper-containing catalysts: Influence of support material on microkinetics. J. Catal. 2007, 246, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Takezawa, N. On the difference in reaction pathways of steam reforming of methanol over copper-silica and platinum-silica catalysts. Chem. Lett. 1985, 14, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, N.; Iwasa, N. Steam reforming and dehydrogenation of methanol: Difference in the catalytic functions of copper and group VIII metals. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Johnson, R.S.; Smith, G.K.; Xie, D.; Guo, H. Pathways for methanol steam reforming involving adsorbed formaldehyde and hydroxyl intermediates on Cu(111): Density functional theory studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 9622–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Xie, D.; Guo, H. Methyl formate pathway in methanol steam reforming on copper: Density functional calculations. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahachi, K.; Takezawa, N.; Kobayashi, H. The mechanism of steam reforming of methanol over a copper-silica catalyst. Appl. Catal. 1982, 2, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Takezawa, N.; Kobayashi, H. Mechanism of formation of methyl formate from formaldehyde over copper catalysts. Chem. Lett. 1983, 12, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, W.-X. Sabatier principle of metal-support interaction for design of ultrastable metal nanocatalysts. Science 2021, 374, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Lu, P.; Cao, Z.; Campbell, C.T.; Xia, Y. The physical chemistry and materials science behind sinter-resistant catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4314–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, G.; Tüysüz, H.; Duyckaerts, N.; Knossalla, J.; Wang, G.-H.; Schüth, F. Hollow Nano- and Microstructures as Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14056–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriruang, C.; Charojrochkul, S.; Toochinda, P. Hydrogen production from methanol-steam reforming at low temperature over Cu–Zn/ZrO2-doped Al2O3. Monatsh. Chem.-Chem. Mon. 2016, 147, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thattarathody, R.; Artoul, M.; Digilov, R.M.; Sheintuch, M. Pressure, Diffusion, and S/M ratio effects in methanol steam reforming kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3175–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowik, G.; Rotko, M.; Ryczkowski, J.; Greluk, M. Hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming over Fe-modified Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Molecules 2024, 29, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.; Gorriz, O.; Tarditi, A.; Cornaglia, L.; Arrúa, L.; Cristina Abello, M. Activity and stability of a CuO/CeO2 catalyst for methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 13379–13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Meng, K.; Sun, S. The study of strong metal-support interaction enhanced PdZn alloy nanocatalysts for methanol steam reforming. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 986, 174006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, S.; Du, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.-h.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. ZnAl2O4 spinel-supported PdZnβ catalyst with parts per million Pd for methanol steam reforming. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 2714–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cai, F. Promoting effect of Zn on Pd/MoC catalyst for the hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 4768–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ouyang, M.; Li, M.; Lee, S.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Low-coordinated Pd catalysts supported on Zn1Zr1Ox composite oxides for selective methanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 580, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, R.; Avendaño, A.D.; Rubio, E.; Rodríguez-Lugo, V. Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming over Pd/ZrO2-TiO2 catalysts. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Men, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; An, W. Morphology effect of Pd/In2O3/CeO2 catalysts on methanol steam reforming for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczynski, P.; Vasilev, K.; Mierczynska, A.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Maniecki, T.P. Highly selective Pd–Cu/ZnAl2O4 catalyst for hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 479, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azenha, C.; Lagarteira, T.; Mateos-Pedrero, C.; Mendes, A. Production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming using CuPd/ZrO2 catalysts—Influence of the catalytic surface on methanol conversion and CO selectivity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 17490–17499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Men, Y.; Wang, J.; He, R.; Wang, Y. Remarkable support effect on the reactivity of Pt/In2O3/MOx catalysts for methanol steam reforming. J. Power Sources 2017, 364, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, V.; Neuberg, S.; Zapf, R.; Pennemann, H.; Kolb, G. Hydrogen production over highly active Pt based catalyst coatings by steam reforming of methanol: Effect of support and co-support. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guan, G.; Shi, C.; Zhu, A.; Hao, X.; Wang, Z.; Kusakabe, K.; Abudula, A. Low-temperature steam reforming of methanol to produce hydrogen over various metal-doped molybdenum carbide catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Ibrahim, J.J.; Fu, Y.; Kong, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Low-temperature hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming on Zn-modified Pt/MoC catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 264, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-K.; Qiao, B.; Huang, C.; Ding, W.; Sun, K.; Zhan, E.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Li, W.-X. Supported single Pt1/Au1 atoms for methanol steam reforming. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3886–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, H.; Huang, C.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y. Maximizing the synergistic effect between Pt0 and Ptδ+ in a confined Pt-based catalyst for durable hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 316, 121669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahay, P.; Khani, Y.; Jabari, M.; Bahadoran, F.; Safari, N. Highly porous monolith/TiO2 supported Cu, Cu-Ni, Ru, and Pt catalysts in methanol steam reforming process for H2 generation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 554, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouad, S.; Gennequin, C.; Mrad, M.; Tidahy, H.L.; Estephane, J.; Aboukaïs, A.; Abi-Aad, E. Steam reforming of methanol over ruthenium impregnated ceria, alumina and ceria-alumina catalysts. Int. J. Energy Res. 2016, 40, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qi, Z.; Peng, X.; Chen, J.-L.; Pao, C.-W.; Zhang, X.; Dun, C.; Young, M.; Prendergast, D.; Urban, J.J.; et al. Insights into the mechanism of methanol steam reforming tandem reaction over CeO2 supported single-site catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12074–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Kudo, S.; Takahashi, H.; Masuda, S.; Takezawa, N. Highly selective supported Pd catalysts for steam reforming of methanol. Catal. Lett. 1993, 19, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Masuda, S.; Ogawa, N.; Takezawa, N. Steam reforming of methanol over Pd/ZnO: Effect of the formation of PdZn alloys upon the reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1995, 125, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Ogawa, N.; Masuda, S.; Takezawa, N. Selective PdZn alloy formation in the reduction of Pd/ZnO catalysts. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 71, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Mayanagi, T.; Nomura, W.; Arai, M.; Takezawa, N. Effect of Zn addition to supported Pd catalysts in the steam reforming of methanol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 248, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Nomura, W.; Mayanagi, T.; Fujita, S.; Arai, M.; Takezawa, N. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of methanol. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2004, 37, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevi, B.; Peterson, E.J.; DeLaRiva, A.; Jeroro, E.; Lebarbier, V.M.; Wang, Y.; Vohs, J.M.; Kiefer, B.; Kunkes, E.; Havecker, M.; et al. Aerosol-Derived Bimetallic Alloy Powders: Bridging the Gap. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 17181–17190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.J.; Halevi, B.; Kiefer, B.; Spilde, M.N.; Datye, A.K.; Peterson, J.; Daemen, L.; Llobet, A.; Nakotte, H. Aerosol synthesis and Rietveld analysis of tetragonal (β1) PdZn. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevi, B.; Peterson, E.J.; Roy, A.; DeLariva, A.; Jeroro, E.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Vohs, J.M.; Kiefer, B.; Kunkes, E.; et al. Catalytic reactivity of face centered cubic PdZnα for the steam reforming of methanol. J. Catal. 2012, 291, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Dagle, V.L.; Halevi, B.; Datye, A.K.; Wang, Y. Influence of ZnO facets on Pd/ZnO catalysts for methanol steam reforming. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föttinger, K.; van Bokhoven, J.A.; Nachtegaal, M.; Rupprechter, G. Dynamic structure of a working methanol steam reforming catalyst: In situ Quick-EXAFS on Pd/ZnO nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Interaction between Pd and ZnO during reduction of Pd/ZnO catalyst for steam reforming of methanol to hydrogen. Chin. J. Catal. 2006, 27, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Bai, X. Reduction of Pd/ZnO catalyst and its catalytic activity for steam reforming of methanol. Chin. J. Catal. 2007, 28, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Conant, T.; Datye, A. The role of PdZn alloy formation and particle size on the selectivity for steam reforming of methanol. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagle, R.A.; Chin, Y.-H.; Wang, Y. The effects of PdZn crystallite size on methanol steam reforming. Top. Catal. 2007, 46, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Chen, Z.-X.; Neyman, K.M.; Rösch, N. Comparative theoretical study of formaldehyde decomposition on PdZn, Cu, and Pd surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 14890–14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, D.; Ma, D. Ensemble effect for single-atom, small cluster and nanoparticle catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghofer, A.; Föttinger, K.; Girgsdies, F.; Teschner, D.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Schlögl, R.; Rupprechter, G. In situ study of the formation and stability of supported Pd2Ga methanol steam reforming catalysts. J. Catal. 2012, 286, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azenha, C.S.R.; Mateos-Pedrero, C.; Queirós, S.; Concepción, P.; Mendes, A. Innovative ZrO2-supported CuPd catalysts for the selective production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, D.; Pabón, B.M.; Azenha, C.; Mateos-Pedrero, C.; Mendes, A.; Pérez-Dieste, V.; Concepción, P. Influence of the ZrO2 crystalline phases on the nature of active sites in PdCu/ZrO2 catalysts for the methanol steam reforming reaction—An in situ spectroscopic study. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y. Enhancement in activity of Pd-Zn catalyst for methanol steam reforming by coprecipitation on zirconia support. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 468, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.E.; Bosco, M.V.; Baltanás, M.A.; Bonivardi, A.L. Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming: Catalytic performance of supported-Pd on zinc-cerium oxides’ nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, S.; Lorenz, H.; Jochum, W.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Wang, D.; Rameshan, C.; Klötzer, B. Pd/Ga2O3 methanol steam reforming catalysts: Part I. morphology, composition and structural aspects. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 358, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, H.; Penner, S.; Jochum, W.; Rameshan, C.; Klötzer, B. Pd/Ga2O3 methanol steam reforming catalysts: Part II. catalytic selectivity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 358, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föttinger, K.; Rupprechter, G. In situ spectroscopy of complex surface reactions on supported Pd-Zn, Pd-Ga, and Pd(Pt)-Cu nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshan, C.; Lorenz, H.; Armbrüster, M.; Kasatkin, I.; Klötzer, B.; Götsch, T.; Ploner, K.; Penner, S. Impregnated and Co-precipitated Pd-Ga2O3, Pd-In2O3 and Pd-Ga2O3-In2O3 catalysts: Influence of the microstructure on the CO2 selectivity in methanol steam reforming. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 3062–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Mayanagi, T.; Ogawa, N.; Sakata, K.; Takezawa, N. New catalytic functions of Pd-Zn, Pd-Ga, Pd-In, Pt-Zn, Pt-Ga and Pt-In alloys in the conversions of methanol. Catal. Lett. 1998, 54, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Barteau, M.A. Spectroscopic identification of alkoxide, aldehyde, and acyl intermediates in alcohol decomposition on Pd(111). Surf. Sci. 1990, 235, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, N.; Takezawa, N. New supported Pd and Pt alloy catalysts for steam reforming and dehydrogenation of methanol. Top. Catal. 2003, 22, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, T.; Karim, A.M.; Lebarbier, V.; Wang, Y.; Girgsdies, F.; Schlogl, R.; Datye, A. Stability of bimetallic Pd–Zn catalysts for the steam reforming of methanol. J. Catal. 2008, 257, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-X.; Neyman, K.M.; Lim, K.H.; Rösch, N. CH3O decomposition on PdZn(111), Pd(111), and Cu(111). A Theoretical Study. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8068–8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-X.; Lim, K.H.; Neyman, K.M.; Rösch, N. Effect of steps on the decomposition of CH3O at PdZn alloy surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4568–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-K.; Li, W.-X. First-principles study on the origin of the different selectivities for methanol steam reforming on Cu(111) and Pd(111). J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21539–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeroro, E.; Vohs, J.M. Zn modification of the reactivity of Pd(111) toward methanol and formaldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10199–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, Y.; Ito, S.-i.; Kameoka, S.; Tomishige, K.; Kunimori, K. Comparative study between Zn–Pd/C and Pd/ZnO catalysts for steam reforming of methanol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 267, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Takahashi, K.; Fuchigami, K.; Uematsu, K. Hydrogen production by oxidative methanol reforming on Pd/ZnO: Catalyst deactivation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 299, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, S.; Jenewein, B.; Gabasch, H.; Klötzer, B.; Wang, D.; Knop-gericke, A.; Schlögl, R.; Hayek, K. Growth and structural stability of well-ordered PdZn alloy nanoparticles. J. Catal. 2006, 241, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Men, Y.; Wang, J.; Kolb, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q. Highly active and durable Pt/In2O3/Al2O3 catalysts in methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21990–21999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Men, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Miao, X. Unravelling the morphology effect of Pt/In2O3 catalysts for highly efficient hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming. Fuel 2024, 372, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ge, Y.; Xu, M.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, D.; Yao, S.; Ma, D. Molybdenum carbide: Controlling the geometric and electronic structure of noble metals for the activation of O-H and C-H bonds. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3372–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Gao, R.; Yao, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Li, Y.-W.; et al. Low-temperature hydrogen production from water and methanol using Pt/α-MoC catalysts. Nature 2017, 544, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D. The nature of interfacial catalysis over Pt/NiAl2O4 for hydrogen production from methanol reforming reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhang, R.-X.; Gao, Z.-H.; Huang, W.; Liu, L.; Zuo, Z.-J. Theoretical insight into hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming on Pt(111). Mol. Catal. 2022, 532, 112745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Diskin-Posner, Y.; Ben-David, Y.; Milstein, D. Reusable homogeneous catalytic system for hydrogen production from methanol and water. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Alberico, E.; Baumann, W.; Drexler, H.-J.; Junge, H.; Gladiali, S.; Beller, M. Low-temperature aqueous-phase methanol dehydrogenation to hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Nature 2013, 495, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lugo, R.E.; Trincado, M.; Vogt, M.; Tewes, F.; Santiso-Quinones, G.; Grützmacher, H. A homogeneous transition metal complex for clean hydrogen production from methanol-water mixtures. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.H.; Agapova, A.; Junge, H.; Haumann, M. Immobilization of a selective Ru-pincer complex for low temperature methanol reforming–Material and process improvements. Catal. Today 2020, 342, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytkina, A.A.; Mironova, E.Y.; Orekhova, N.V.; Ermilova, M.M.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Ru-Containing catalysts for methanol and ethanol steam reforming in conventional and membrane reactors. Inorg. Mater. 2019, 55, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytkina, A.A.; Orekhova, N.V.; Ermilova, M.M.; Petriev, I.S.; Baryshev, M.G.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Ru-Rh based catalysts for hydrogen production via methanol steam reforming in conventional and membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 13310–13322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytkina, A.A.; Orekhova, N.V.; Ermilova, M.M.; Belenov, S.V.; Guterman, V.E.; Efimov, M.N.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Bimetallic carbon nanocatalysts for methanol steam reforming in conventional and membrane reactors. Catal. Today 2016, 268, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


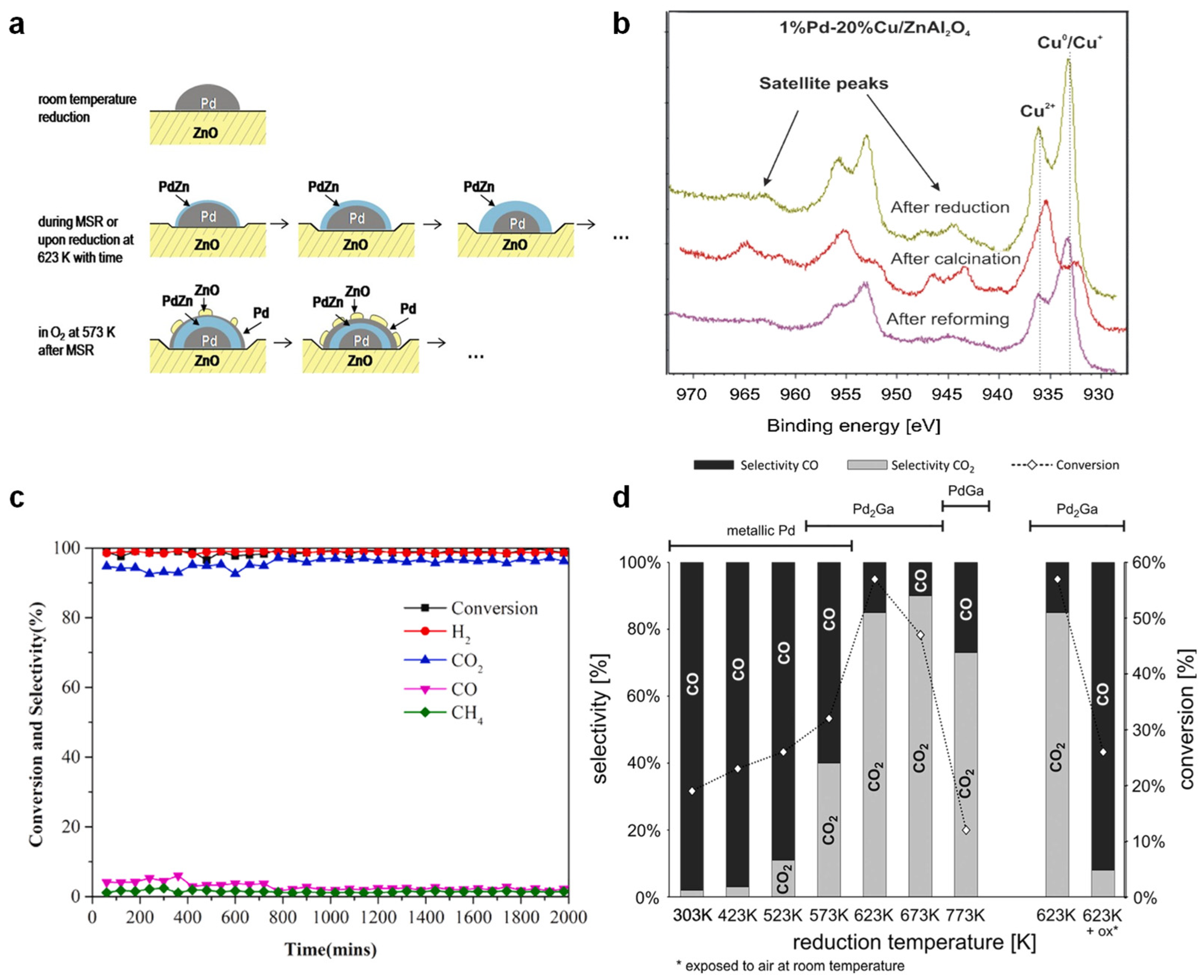
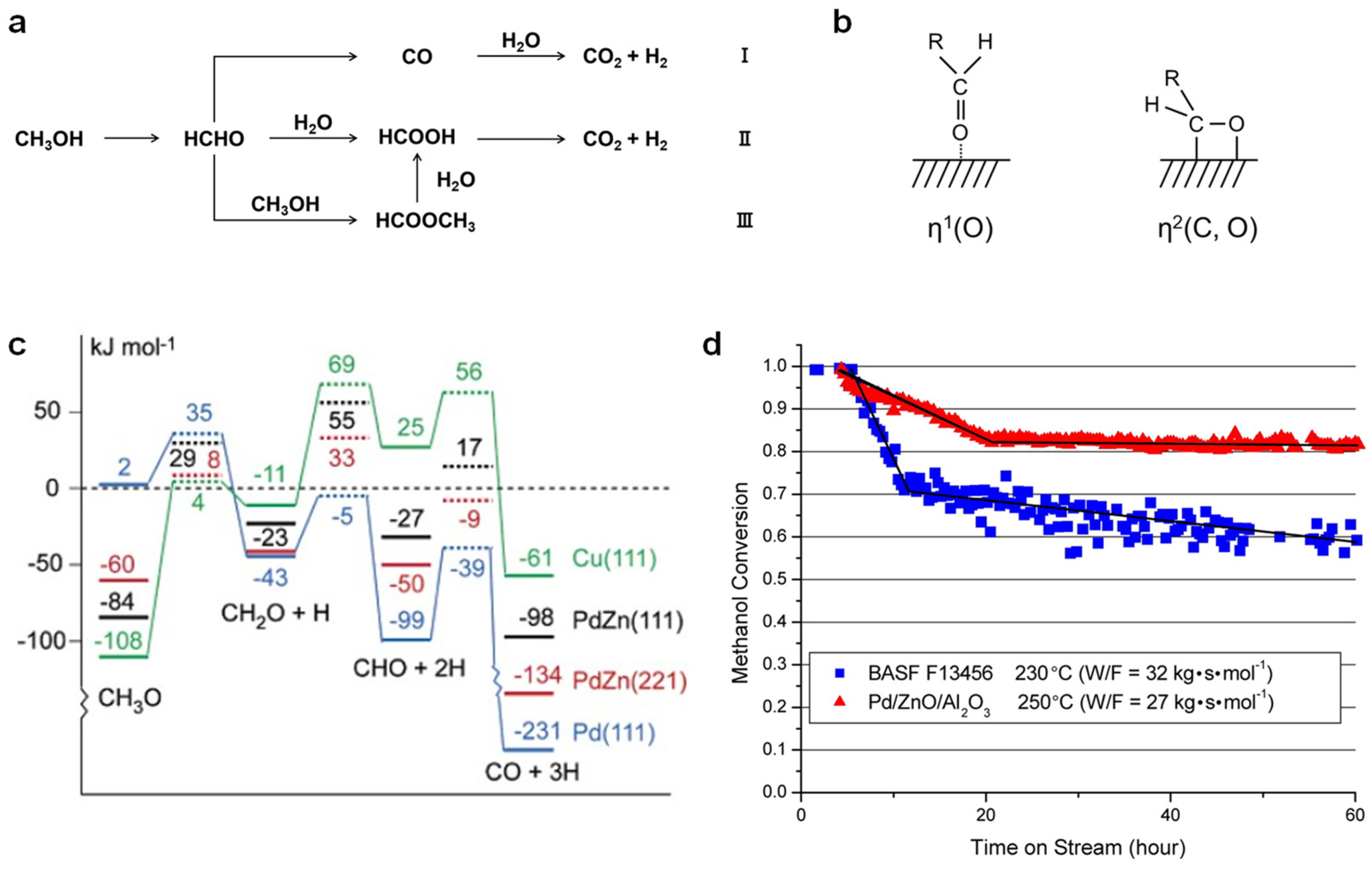

| Catalysts | Temperature (°C) | CH3OH Conversion (%) | CO Selectivity (%) | H2 Yield (mmol g−1 h−1) | Reaction Conditions | Stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu5-Al | 240 | 98 | 1.3 b | 187.2 | H2 pretreatment; feed rate = 0.048 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | \ | [13] |
| Cu/Cu(Al)Ox | 240 | 99.5 | 1 b | 398.88 | H2 pretreatment; feed rate = 2.4 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 240 °C, 100 h, 14% drop in CH3OH conversion | [12] |
| Cu/Al2O3 | 250 | 89.7 | 0.9 a | 531.36 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 10.56 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 200 °C, 100 h, 10% drop in H2 production rate | [14] |
| CuZnAl | 350 | 98 | 0 | 60.02 | GHSV = 15,500 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | \ | [15] |
| CuZnO/γ-Al2O3/Al | 275 | 100 | 3.34 a | 3580 | GHSV = 4000 mL g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 275 °C, 100 h, 10% drop in CH3OH conversion | [16] |
| Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 | 225 | 67 | 0.07 a | \ | CH3OH/H2O/H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 6 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.3 | 225 °C, 40 h, 10% drop in CH3OH conversion | [17] |
| Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 | 240 | 90 | 0 | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 10,000 cm3 g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | 240 °C, 90 h, 30% drop in CH3OH conversion | [18] |
| Cu/SiO2 | 280 | 80 | \ | 105 | GHSV = 300 kg L−1 s−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | \ | [19] |
| Cu-MCM-41 | 250 | 72.3 | 0.8 b | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 2838 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | 250 °C, 48 h, no drop | [20] |
| CeCuZn/CNTs | 300 | 94.2 | 2.6 a | H2 yield = 98.2% | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 7.5 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 300 °C, 48 h, 7% drop in CH3OH conversion | [21] |
| Cu/Ce-Cu(BDC) | 250 | 99 | 2 a | H2 yield = 97% | WHSV = 9.2 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 250 °C, 32 h, 7% drop in CH3OH conversion | [22] |
| CuO/CeO2 | 260 | 100 | 2.4 a | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 800 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.2 | \ | [23] |
| CuO/ZnO/CeO2/ Al2O3 | 200 | 100 | 0 | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 10,000 cm3 g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | 200 °C, 24 h, no drop | [24] |
| ZrO2/Cu | 200 | 32 | 0 | 190 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 10 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.0 | 200 °C, 200 h, no drop | [7] |
| Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 | 250 | 88.6 | 0 | 12,600 mmol gCu−1 h−1 | H2 pretreatment; H2O/CH3OH = 1.0 | \ | [25] |
| Cu/Ce1−xZrxO2 | 240 | 23 | 0 | 316 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 27 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | 240 °C, 90 h, no drop | [26] |
| CuO/ZnO/CeO2-ZrO2 | 240 | 95 | 0.46 a | 1836 mL g−1 h−1 | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 1200 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.2 | 230–260 °C, 360 h, no drop | [27] |
| Cu/ZnO/CeO2/ ZrO2/SBA-15 | 300 | 95.2 | 1.4 b | H2 yield = 90% | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 43.68 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 300 °C, 60 h, 12% drop in CH3OH conversion | [28] |
| CuZnGaOx | 150 | 22.5 | 0 | 393.6 mL g−1 h−1 | H2 pretreatment; feed rate = 6 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | \ | [29] |
| CuGaZn | 200 | \ | 0.2 a | 118.1 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 6 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.3 | 200 °C, 24 h, no drop | [30] |
| CuZnGaZr | 250 | 42.9 | 0.3 | 10,620 mL g−1 h−1 | GHSV = 2200 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 275 °C, 44 h, 7% drop in CH3OH conversion | [31] |
| Cu/MgAl2O4 | 300 | 96 | 2.8 b | \ | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 8.5 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 200 °C, 30 h, 4% drop in CH3OH conversion | [32] |
| Mg/Cu-Al spinel | 255 | 96.5 | 3.8 a | H2 yield = 96.54% | WHSV = 2.28 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2.27 | 255 °C, 500 h, no drop | [33] |
| CuZnAlMg | 200 | 68.5 | 0.88 a | 172 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 3.84 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 350 °C, 8 h, 18% drop in CH3OH conversion | [34] |
| CuCeMg/Al | 250 | 100 | 0.29 c | H2 yield = 29.1% | H2 pretreatment; feed rate = 1 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 250 °C, 72 h, no drop | [35] |
| La(CoCuFeAlCe)0.2O3 | 600 | 98.9 | 8 c | 436.8 | LHSV = 20 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 4 | 600 °C, 50 h, no drop | [36] |
| Catalysts | Temperature (°C) | CH3OH Conversion (%) | CO Selectivity (%) | H2 Yield (mmol g−1 h−1) | Reaction Conditions | Stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/ZnO | 400 | 94 | 0.5 a | 1628 | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 12,000 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.2 | \ | [82] |
| Pd/ZnAl2O4 | 250 | 35 | 3.0 a | 41.04 | H2 pretreatment; Pmethanol = 6.4 mol%; H2O/CH3OH = 1.1 | 250 °C, 100 h, no drop | [83] |
| ZnPd/MoC | 160 | 40.3 | 0.9 b | 68.9 | CH4/H2 pretreatment; feed rate = 1.2 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | 240 °C, 170 h, initial deactivation only | [84] |
| Pd/Zn1Zr1Ox | 330 | 46 | 0 | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 17,000 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.3 | 330 °C, 30 h, no drop | [85] |
| Pd/ZrO2-TiO2 | 300 | 98 | 37 c | \ | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 30,000 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 0.16 | \ | [86] |
| Pd/In2O3/CeO2 | 375 | 96 | 1.3 c | 250 | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 13,809.6 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.4 | 400 °C, 30 h, no drop | [87] |
| Pd-Cu/ZnAl2O4 | 240 | 100 | \ | H2 yield = 84% | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 2400 h−1 | \ | [88] |
| CuPd/ZrO2 | 220 | 63 | 5 a | 86.3 | H2 pretreatment; GHSV = 295 mol g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.4 | 240 °C, 80 h, no drop | [89] |
| Pt/In2O3/CeO2 | 325 | 98.7 | 2.6 a | 333 | feed rate = 1.2 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.4 | 325 °C, 32 h, no drop | [90] |
| Pt/In2O3/CeO2 | 350 | 99.9 | 2.5 c | H2 yield = 64.7% | WHSV = 99,500 mL g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.4 | 350 °C, 100 h, 8% drop in CH3OH conversion | [91] |
| Pt/MoC | 200 | 100 | 3 c | \ | CH4/H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 9000 cm3 g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1 | 200 °C, 20 h, no drop | [92] |
| Zn-Pt/MoC | 160 | 65.9 | \ | 106.9 | Carburizing treatment; feed rate = 1.2 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | 120 °C, 25 h, 4% drop in CH3OH conversion | [93] |
| Pt1/ZnO | 390 | 43 | \ | \ | WHSV = 55,200 cm3 g−1 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.5 | \ | [94] |
| Pt-K@S-1 | 250 | 15 | <1.9% c | 4308 | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 45 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | 400 °C, 50 h, no drop | [95] |
| Ru/TiO2 | 300 | 98.9 | 5.4 b | \ | H2 pretreatment; WHSV = 1.8 h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 1.2 | \ | [96] |
| RuCe | 400 | 98 | 0.13 c | 882 mmol cm−3 h−1 | feed rate = 3.47 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 2 | 400 °C, 115 h, no drop | [97] |
| Ru1/CeO2 | 350 | 25.6 | 2.2 a | 139.6 | feed rate = 3 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | 350 °C, 72 h, no drop | [98] |
| Rh1/CeO2 | 350 | 21 | 36 a | 100 | feed rate = 3 mL h−1; H2O/CH3OH = 3 | \ | [98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Recent Advances in Methanol Steam Reforming Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Catalysts 2025, 15, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010036
Zhang M, Liu D, Wang Y, Zhao L, Xu G, Yu Y, He H. Recent Advances in Methanol Steam Reforming Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Catalysts. 2025; 15(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mengyuan, Diru Liu, Yiying Wang, Lin Zhao, Guangyan Xu, Yunbo Yu, and Hong He. 2025. "Recent Advances in Methanol Steam Reforming Catalysts for Hydrogen Production" Catalysts 15, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010036
APA StyleZhang, M., Liu, D., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Xu, G., Yu, Y., & He, H. (2025). Recent Advances in Methanol Steam Reforming Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Catalysts, 15(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010036









