Enhancing Biomedical and Photocatalytic Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Copper–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Co-Precipitation Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
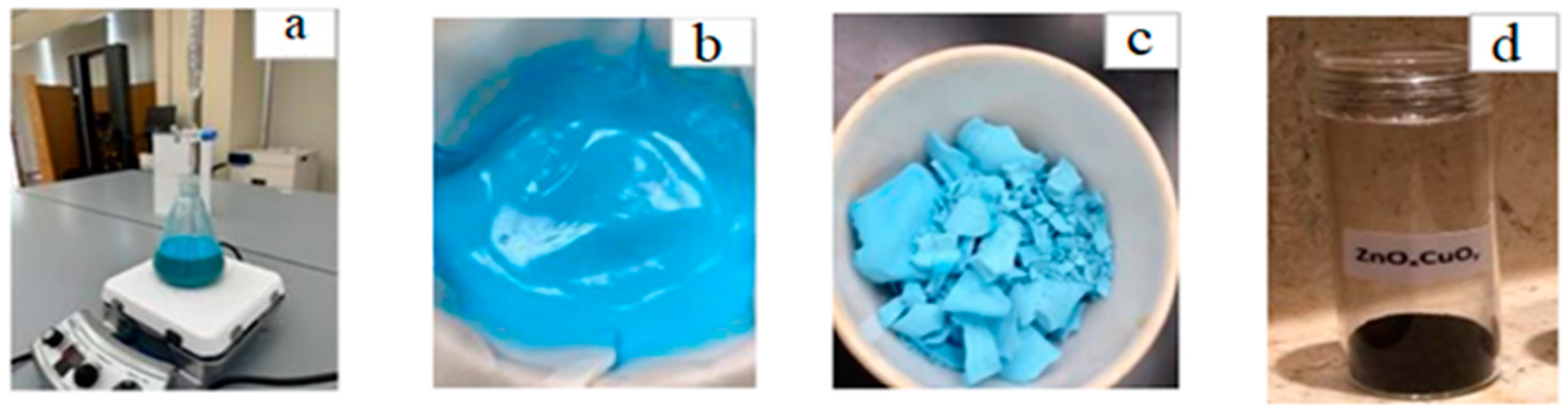
2.2. Preparation of Cu-Doped ZnO NPs
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX)
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.5. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy (UV-Vis)
2.3.6. Fluorescence
2.3.7. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
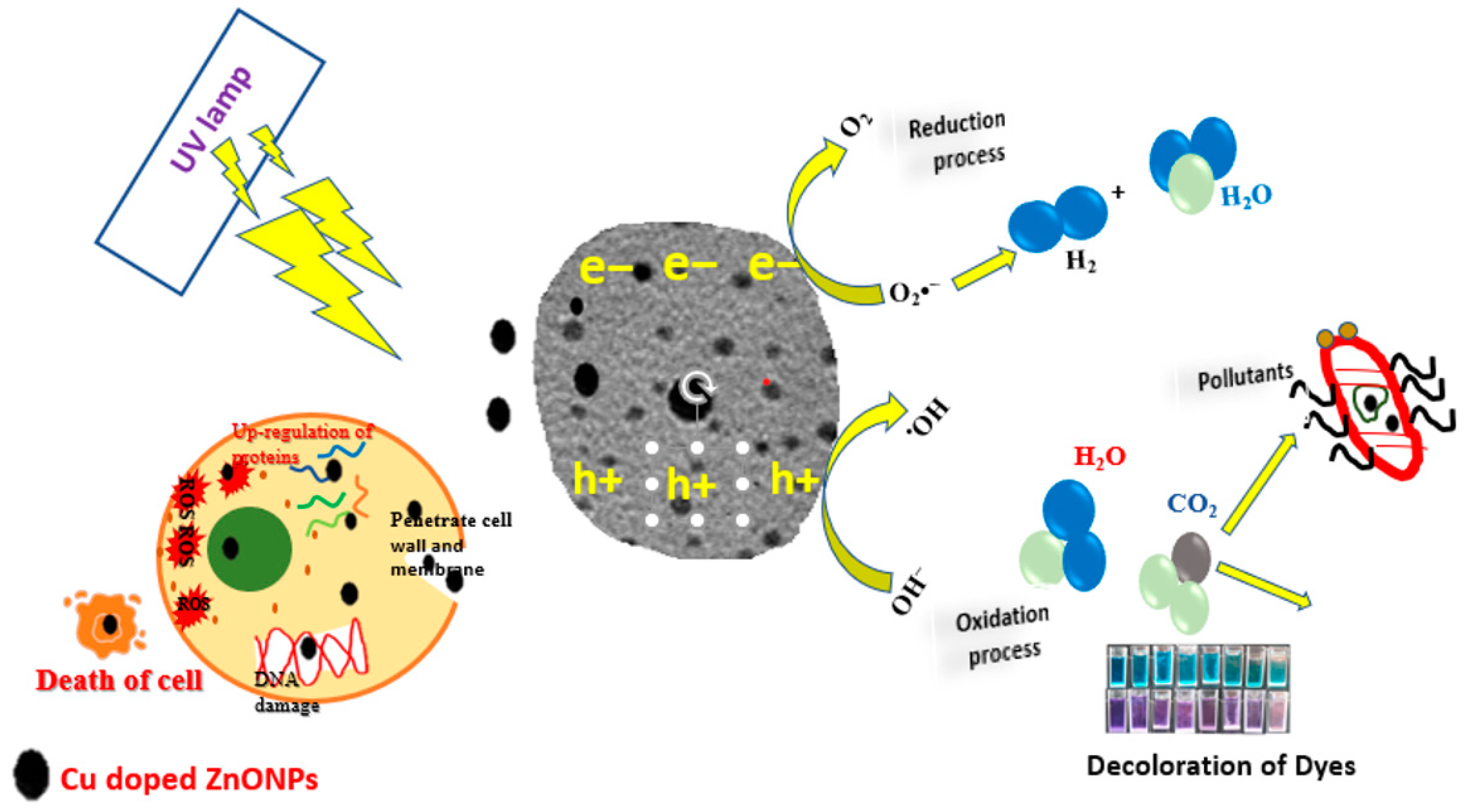
2.4. Photocatalytic Process
2.5. Biological Studies
3. Results and Discussion
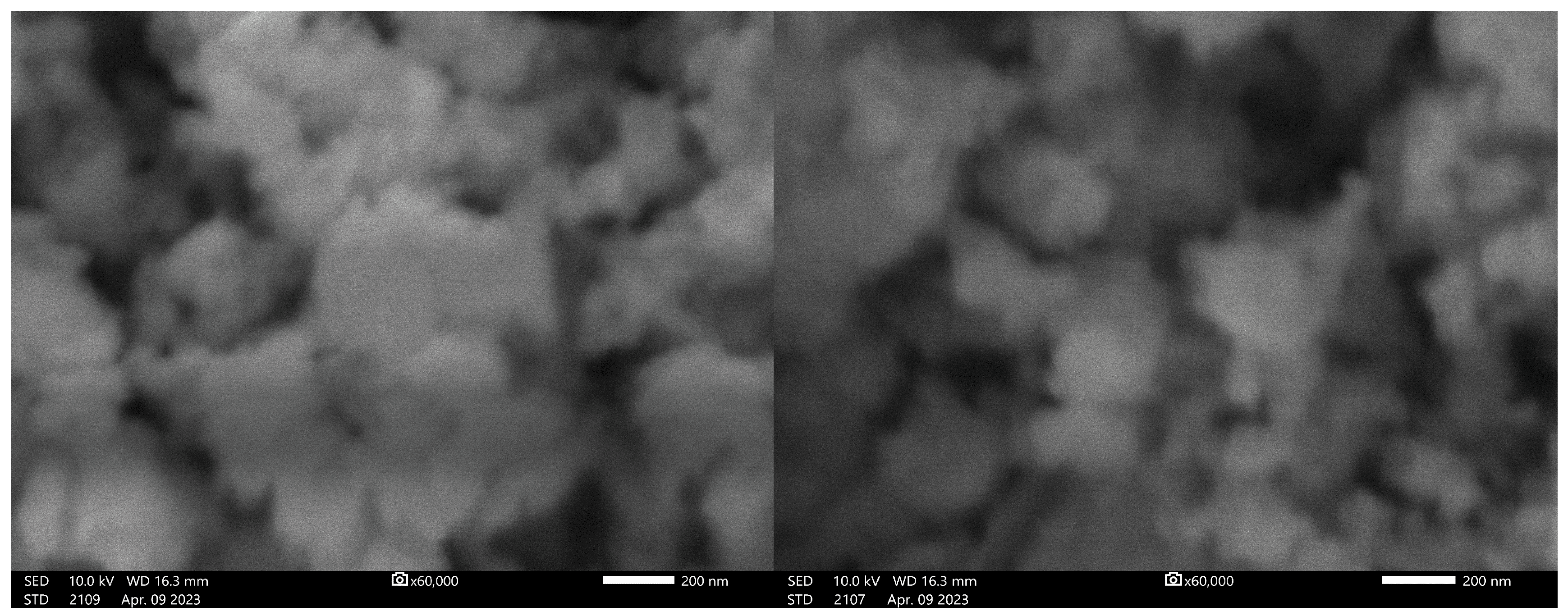
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Studies
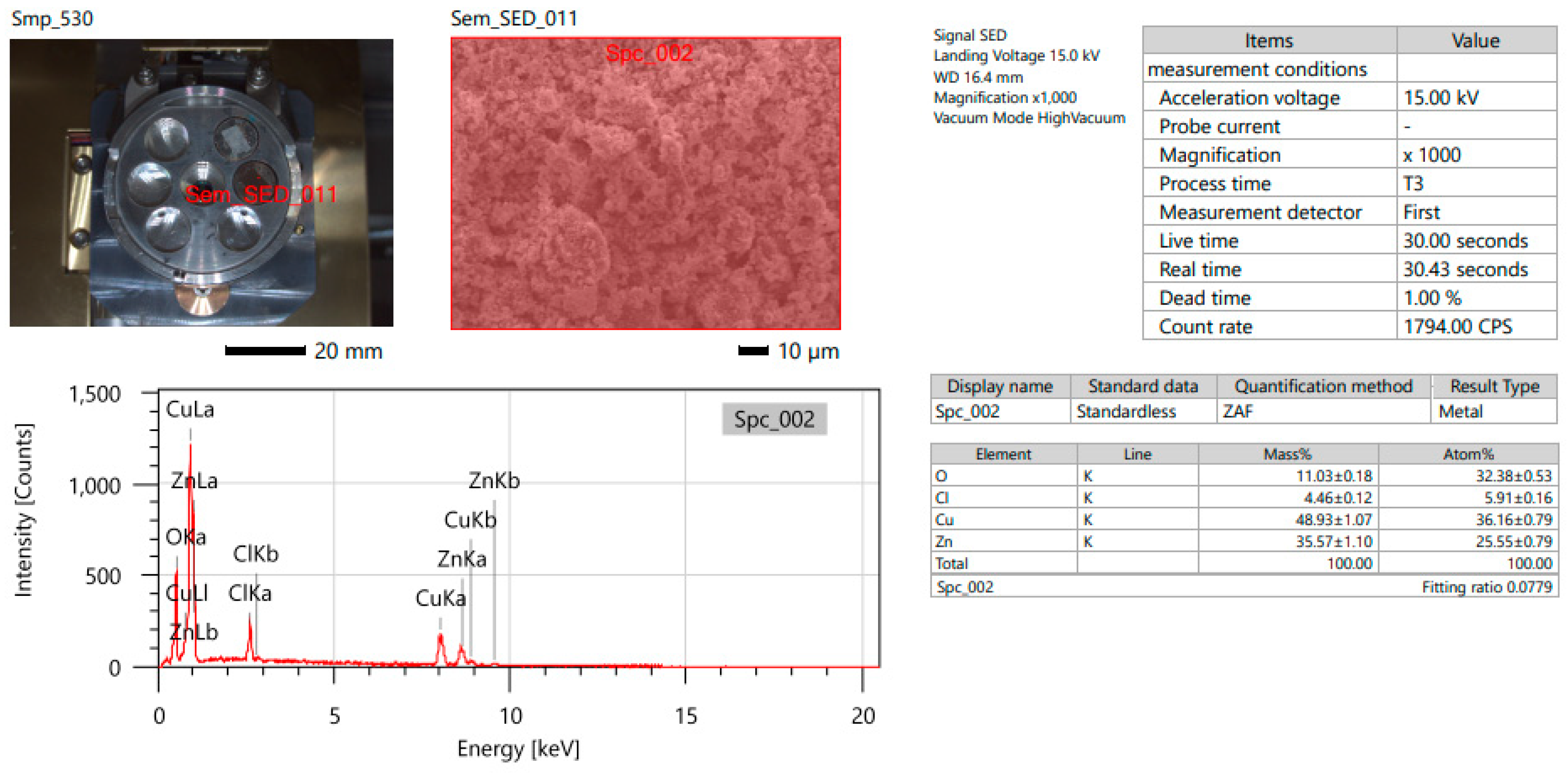
3.2. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX) Analysis
3.3. XRD Results
3.4. TEM Results
3.5. FTIR Results
3.6. UV-Vis Results
3.7. Fluorescence Emission
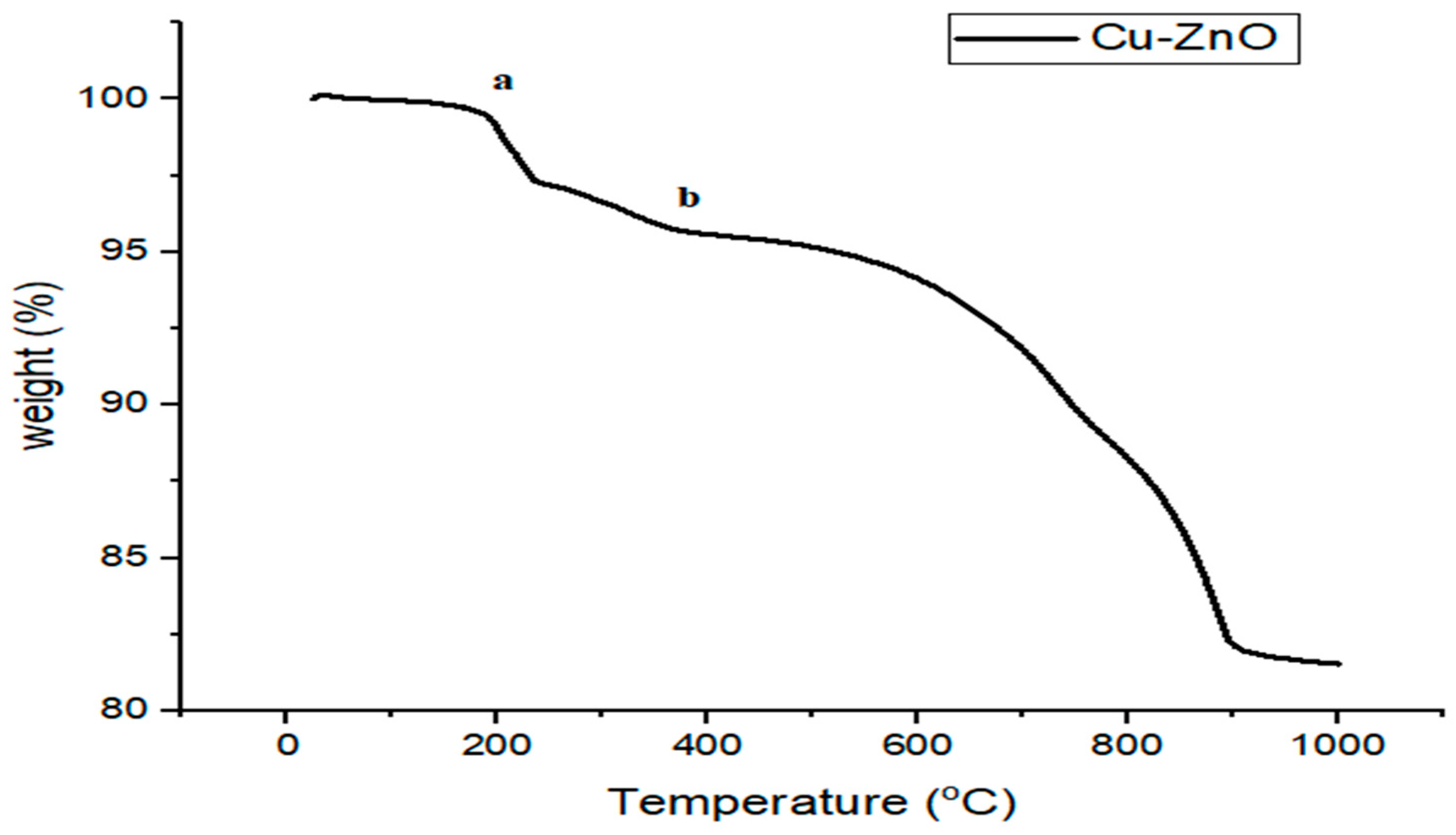
3.8. Cu-ZnO TGA Analysis
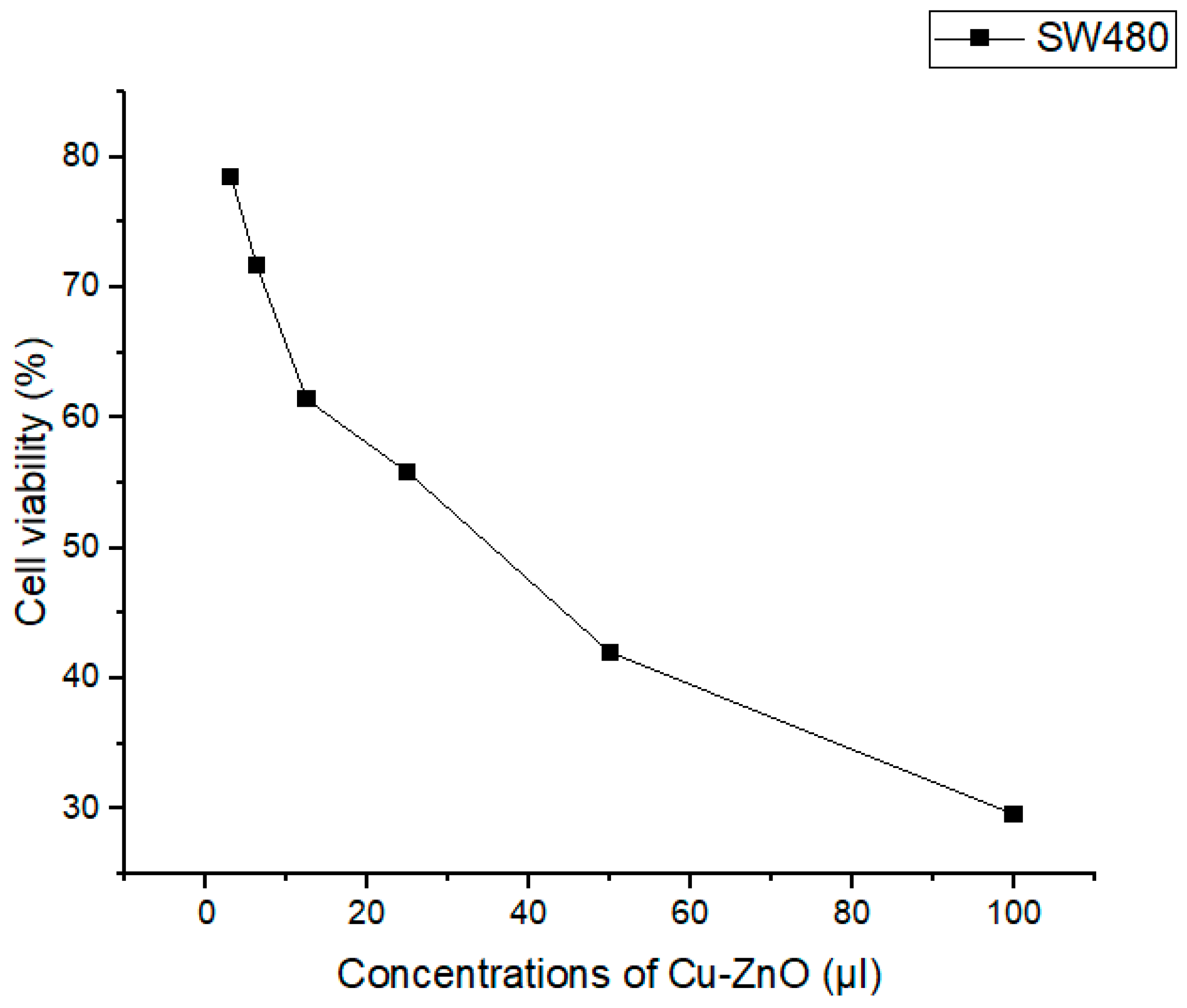
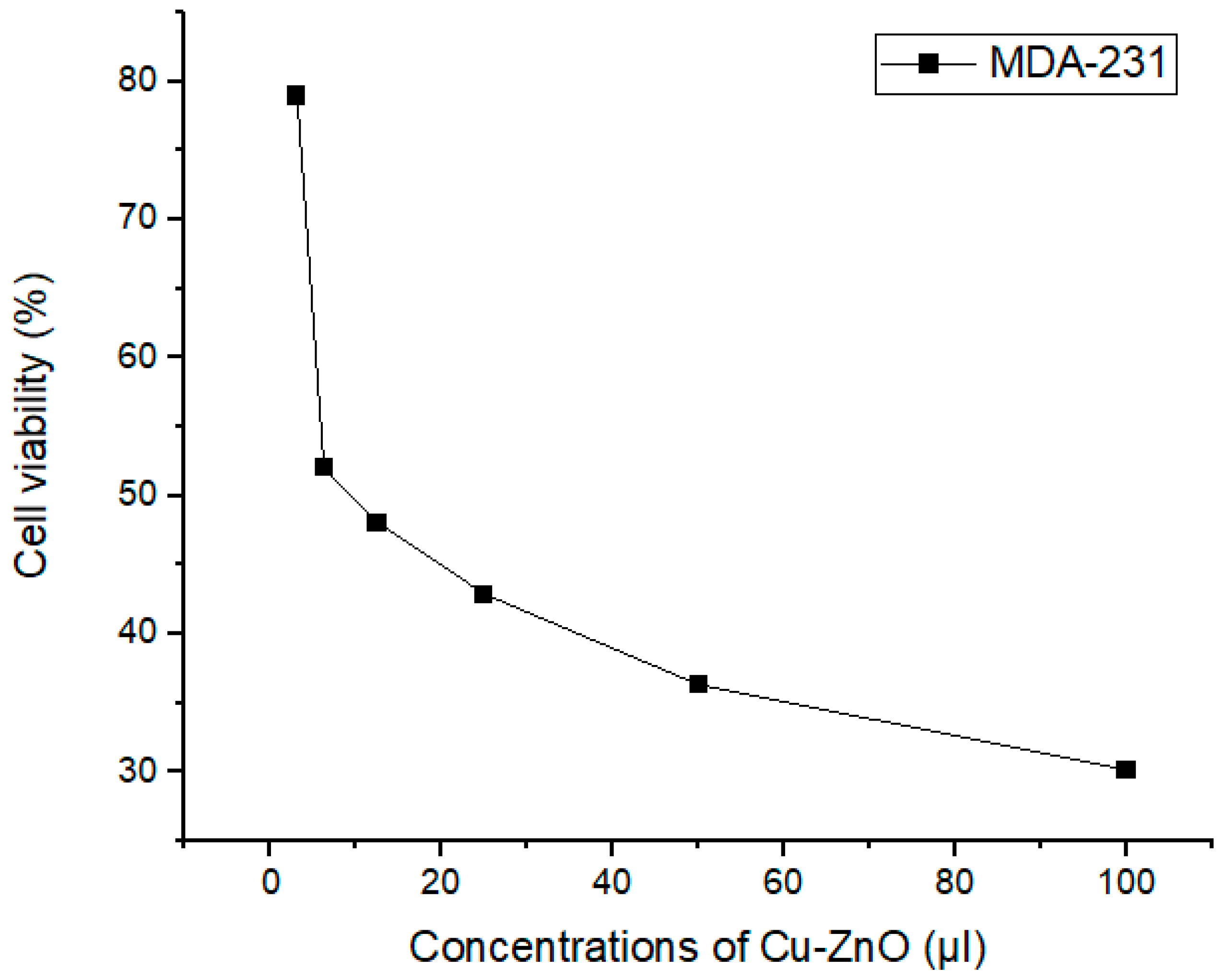
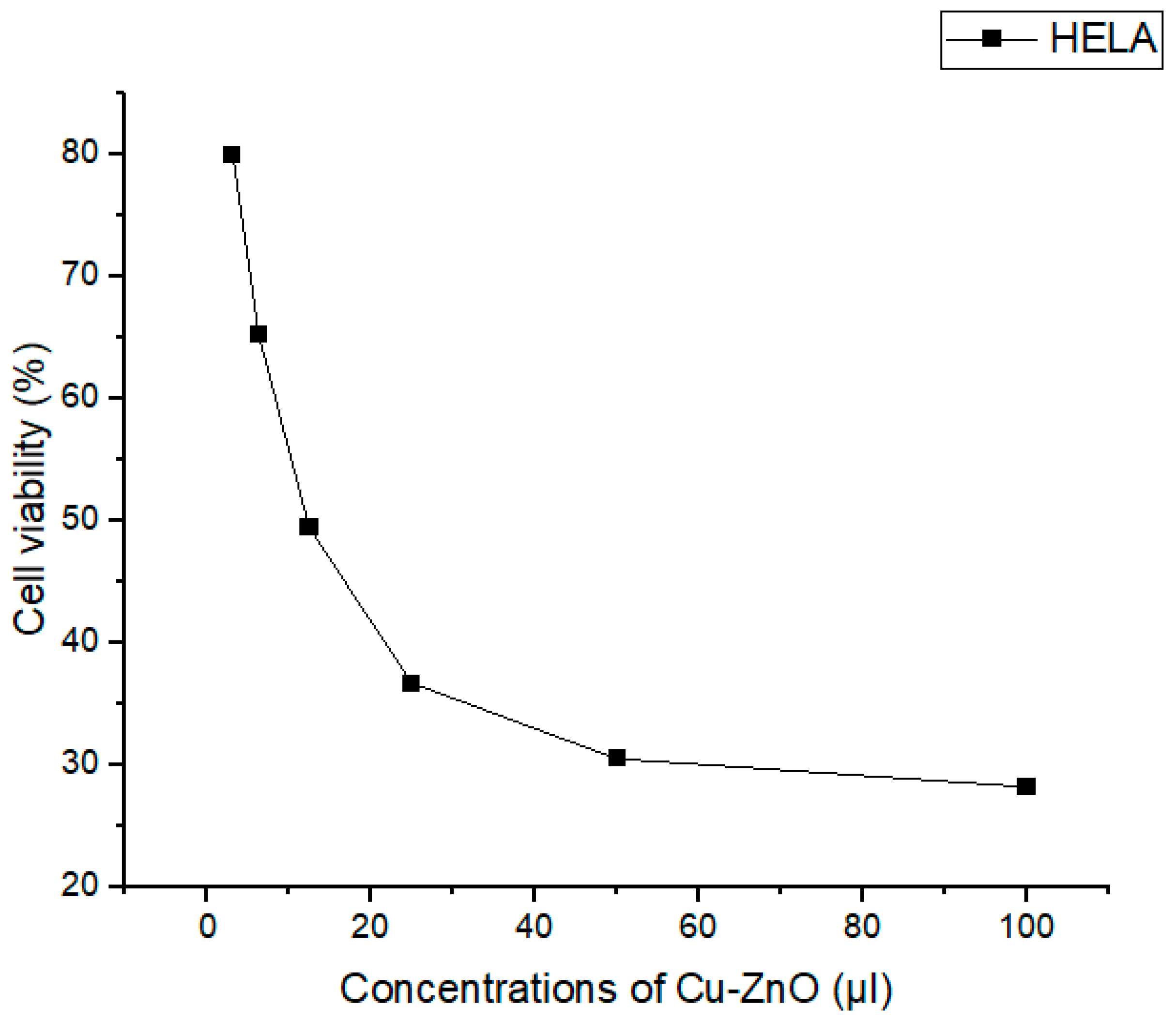
3.9. Anticancer Activity
3.10. Antibacterial Activity
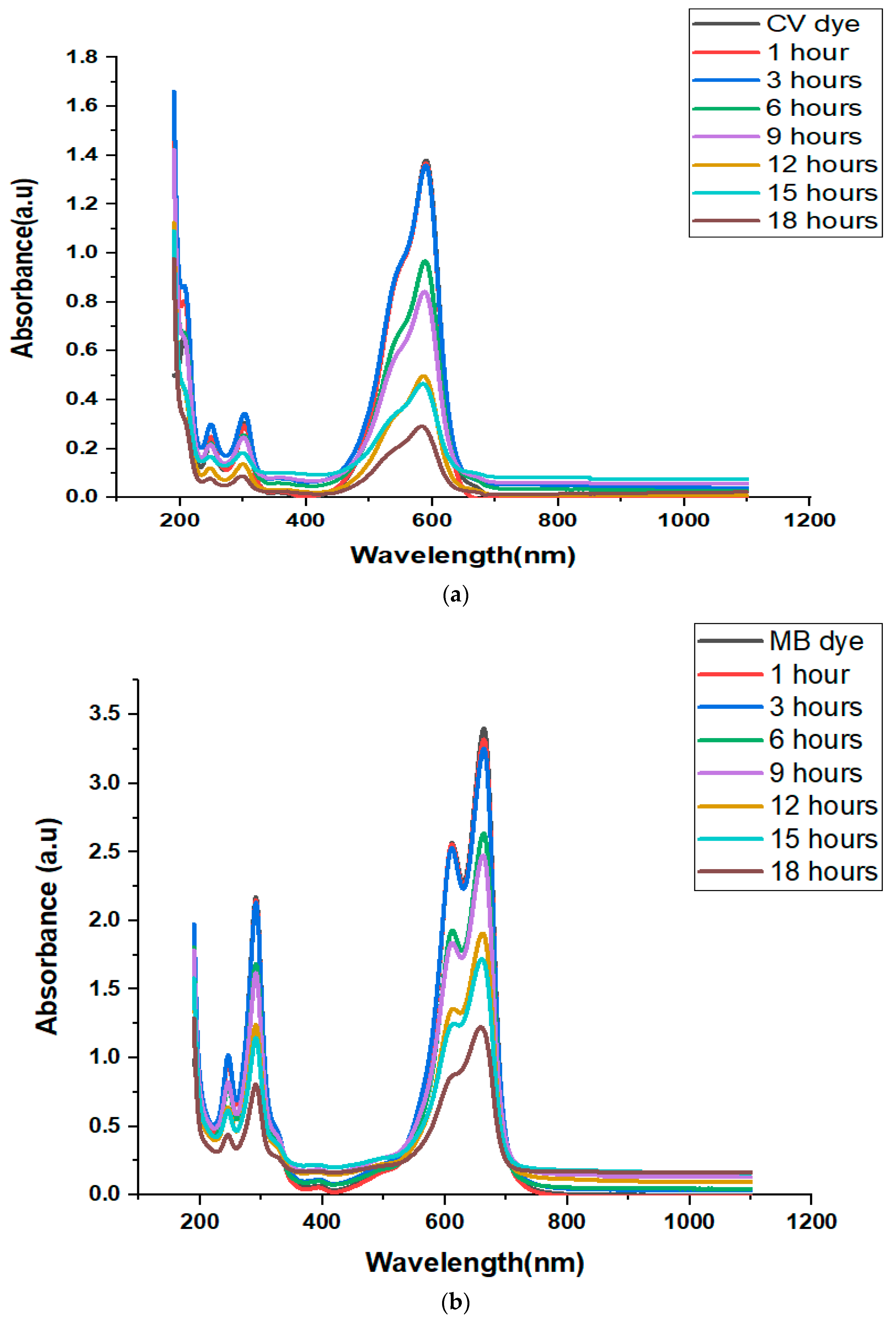
3.11. Photocatalytic Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Noreen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, G. Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, P.V. Photophysical, photochemical, and photocatalytic aspects of metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7729–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikprabhu, D.; Lingappa, K. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the Streptomyces coelicolor klmp33 pigment: An antimicrobial agent against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, F.C.; Barbante, C. Nanoscience, nanotechnology, and spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2013, 86, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, I.; Narayanan, T.S.; Stephen, A. Pulsed electrodeposition of nanocrystalline Cu–Ni alloy films and evaluation of their characteristic properties. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, M.F.; Kaji, N.; Habuchi, S.; Bianco, A.; Baba, Y. Nanobiotechnology meets plant cell biology: Carbon nanotubes as organelle targeting nanocarriers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4856–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyraz, S.; Cerkez, I.; Huang, T.S.; Liu, Z.; Kang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X. One-step synthesis and characterization of polyaniline nanofiber/silver nanoparticle composite networks as antibacterial agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20025–20034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Billone, P.S.; Mullett, W.M. Nanomedicine in action: An overview of cancer nanomedicine on the market and in clinical trials. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 629681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, S.E. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.J.; Alhadlaq, H.A.; Alshamsan, A.; Majeed Khan, M.A.; Ahamed, M. Aluminum doping tunes band gap energy level and oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in MCF-7 cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.W.; Martinez, E.; Louka, P.; Wingett, D.G. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishikesh, S.; Basha, M.A.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant & Anticancer Activities of Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Acta Chim. Slov. 2020, 67, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, C.; Layne, J.; Punnoose, A.; Reddy, K.; Coombs, I.; Coombs, A.; Feris, K.; Wingett, D. Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 295103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Shohag, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Islam, M.R.; Nafady, M.H.; Akter, A.; Mitra, S.; Roy, A.; Emran, T.B.; Cavalu, S. Exploring the journey of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) toward biomedical applications. Materials 2022, 15, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Noreen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Hussain, G. Comparative synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and photocatalytic dye degradation activities. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2017, 12, 877–889. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantar, E.; Kabir, K.; Gharibi, F.; Hatami, S.; Maleki, A. Effect and properties of surface-modified copper doped ZnO nanoparticles (Cu: ZnO NPs) on killing curves of bacterial pathogens. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2013, 2, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, R.P. Synthesis and characterization of copper-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Glaspell, G.; Dutta, P.; Manivannan, A. A room-temperature and microwave synthesis of M-doped ZnO (M = Co, Cr, Fe, Mn & Ni). J. Clust. Sci. 2005, 16, 523–536. [Google Scholar]
- Mallika, A.N.; RamachandraReddy, A.; SowriBabu, K.; Reddy, K.V. Synthesis and optical characterization of aluminum-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12171–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, S.; Joy, P.A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanowires. Solid State Commun. 2007, 142, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, R.; Djaja, N.F. Transition-metal-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity under U.V. light. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, O.D.; Salunke, H.G.; Kadam, R.M.; Mohapatra, M.; Yaswant, G.; Kulshreshtha, S.K. Magnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by a co-precipitation method. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalizadeh, L.; Shohany, B.G.; Abrishami, M.E. Effects of Mn doping on electrical properties of ZnO thin films. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 30, 1650024–1650044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.H.; Cho, K.; Yun, J.; Suh, K.S.; Kim, T.; Kim, S. Enhancement of electrical characteristics of electrospun polyaniline nanofibers by embedding the nanofibers with Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Org. Electron. 2008, 9, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Muthukumar, S.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ng, H.M.; Jiang, W.; Garfunkel, E.L. Ga-doped ZnO single-crystal nanotips grown on fused silica by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3401–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Chandrappa, K.G.; Hamid, S.B.A. Facile synthesis of nano-sized ZnO by direct precipitation method. Pharma Chem. 2013, 5, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pung, S.Y.; Ong, C.S.; Isha, K.M.; Othman, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakamavalli, J.; Pandiselvi, K.; Park, K.; Kwak, I.S. Garcinia cambogia assisted synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles coupled with chitosan for antibacterial, antibiofilm, cytotoxic, anticancer, and ecotoxicity assessment. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 33, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Interactions of zinc oxide nanostructures with mammalian cells: Cytotoxicity and photocatalytic toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitha, D.; Latha, H.K.; Lalithamba, H.S.; Jeppu, Y.V. Impact of Al and Mn doping on structural and Electrical properties of the Green synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Systems for Applications in Electrical Sciences (ICSSES), Tumakuru, India, 7–8 July 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffarian, H.R.; Saiedi, M.; Sayyadnejad, M.A.; Rashidi, A.M. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by spray pyrolysis method. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2011, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.O.; Evans, I.R. Beyond classical applications of powder diffraction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salavati-Niasari, M.; Davar, F.; Khansari, A. Nanosphericals and nanobundles of ZnO: Synthesis and characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvezdanović, J.; Marković, D. Bleaching of chlorophylls by U.V. irradiation in vitro: The effects on chlorophyll organization in acetone and n-hexane. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2008, 73, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoneef, M.; Awad, M.; Aldosari, H.; Hendi, A.; Aldehish, H.; Merghani, N.; Alshammari, S. Exploring the multi-faceted potential: Synthesized ZnO nanostructure—Characterization, photocatalysis, and crucial biomedical applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32714–e32729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidyasagar, C.C.; Naik, Y.A.; Venkatesh, T.G.; Viswanatha, R. Solid-state synthesis and effect of temperature on optical properties of Cu–ZnO, Cu–CdO, and CuO nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Suri, P.; Shishodia, P.K.; Mehra, R.M. Synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnO powder via sol-gel route for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, P.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Shim, M.S. Photo-triggered antibacterial and anticancer activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 4852–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaani, M.; Rahaiee, S.; Zare, M.; Jafari, S.M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using loquat seed extract; Biological functions and photocatalytic degradation properties. Lwt 2020, 134, 110133–110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, A.H.; Mansour, S.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Rashad, M. Direct precipitation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Oyedeji, A.O. Biogenic synthesis of CuO, ZnO, and CuO–ZnO nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Dovyalis caffra and their biological properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Tsegaye, D.; Sori, C.; Renuka Prasad, R.C.K.; Murthy, H.A. Cu/CuO-doped ZnO nanocomposites via solution combustion synthesis for catalytic 4-nitrophenol reduction. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 9597–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, I.Y. Facile synthesis of highly oriented p-type aluminum co-doped zinc oxide film with aqua ammonia. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riter, R.E.; Kimmel, J.R.; Undiks, E.P.; Levinger, N.E. Novel reverse micelles partition nonaqueous polar solvents in a continuous hydrocarbon phase. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 8292–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riter, R.E.; Undiks, E.P.; Levinger, N.E. Impact of counterion on water motion in aerosol O.T. reverse micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, D.M.; Riter, R.E.; Levinger, N.E. Dynamics of polar solvation in lecithin/water/cyclohexane reverse micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4151–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riter, R.E.; Willard, D.M.; Levinger, N.E. Water immobilization at surfactant interfaces in reverse micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. (Ed.) Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Oves, M.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, I.; Amir, S.; Ahmed, J.; Rehman, M.T.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Ali, I. Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: Anticancer and antimicrobial activities. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15357–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-González, S.C.; Sánchez-Valdés, S.; Ramírez-Barrón, S.N.; Loera-Arias, M.J.; Bernal, J.; Meléndez-Ortiz, H.I.; Betancourt-Galindo, R. Effects of different surface modifying agents on the cytotoxic and antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 37, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Mahalakshmi, S. Effect of triethanolamine on zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Focus 2013, 2, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmann, N.; Tremel, W.; Brieger, J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for therapeutic purposes in cancer medicine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 4973–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Ullah, N.; Haroon, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Optical, morphological, and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29541–29548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.; Khan, S.T.; Dwivedi, S.; Ahamed, M.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Effective inhibition of bacterial respiration and growth by CuO microspheres composed of thin nanosheets. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Marzoog, T.R.; Jabir, M.S. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles’ antibacterial, anti-parasitic, and anticancer activities. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandy, M.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Muneeswaran, T.; Song, J.M.; Manoharan, N. Biologically synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nano antibiotics against ESBLs producing gram harmful bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, E.; Musevi, S.J.; Aslani, A. Antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and characterization of ZnO and ZnO–Al2O3 mixed oxide nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S230–S235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.S.; Madrigal, B.M.; Riascos, H.; Avila, Y.P. Colloidal metal oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation technique and their antibacterial test. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, R.; Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M. Preparation and characterization of graphene sheet prepared by laser ablation in liquid. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 20, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, K.S.; Jabir, M.S.; Abdulameer, F.A. Preparation and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles decorated carbon nanoparticles using laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1003, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.R.A.; Alam, M.M.; Momin, M.A.; Mamur, H. Characterization of Al doped ZnO nanostructures via an electrochemical route. Int. J. Energy Appl. Technol. 2017, 4, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Singh, J.; Jolly, S.S.; Rawat, R.; Kukkar, D.; Kumar, S.; Basu, S.; Rawat, M. Fructose modified synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and its application for removal of industrial pollutants from water. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 7364–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, V.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M. Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using plant extract and its prodigious potential for photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108569–108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabri, S.; Dhara, A.; Show, B.; Adak, D.; Sinha, A.; Mukherjee, N. Mesoporous CuO–ZnO p–n heterojunction based nanocomposites with high specific surface area for enhanced photocatalysis and electrochemical sensing. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3238–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Gao, Z. Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elilarassi, R.; Chandrasekaran, G. Effect of annealing on structural and optical properties of zinc oxide films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.Y.; Ng, A.M.C.; Liu, F.; Djurisic, A.B.; Chan, W.K.; Su, H.; Wong, K.S. Effect of native defects on photocatalytic properties of ZnO. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 11095–11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.K.; Sadasivam, R.; Packirisamy, G.; Saravanan, P. Nanoremediation: Sunlight mediated dye degradation using electrospun PAN/CuO–ZnO nanofibrous composites. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitkari, G.; Chowdhary, P.; Kumar, V.; Singh, S.; Motghare, A. Potential of Copper-Zinc Oxide nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of congo red dye. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.K.; Abrishami, M.E.; Majid, W.A.; Yousefi, R.; Hosseini, S.M. Effects of annealing temperature on some structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by a modified sol–gel combustion method. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Karthick, K. High quality ZnO/CuO nanocomposites synthesized by microwave assisted reaction. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qin, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D.; Feng, W.; Chen, S. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of p (BaSnO3)-n (anatase/rutile/brookite TiO2) heterojunction composites by efficient interfacial charge transfer. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1294, 136440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Kim, S.C.; Yun, K.; Choong, C.E.; Nah, I.W.; Jeon, B.H.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, M. Understanding the potential band position and e–/h+ separation lifetime for Z-scheme and type-II heterojunction mechanisms for effective micropollutant mineralization: Comparative experimental and DFT studies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 273, 119034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Chemicals | Chemical’s Structure | Manufacturer Company | Purity % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | Loba Chemie, Mumbai, India | 98% |
| Zinc (II) chloride | ZnCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany | 99.95% |
| Copper (II) chloride | CuCl2 | VWR Chemicals, Leuven, Belgium | 99.99% |
| Distilled water | H2O | VWR chemicals | - |
| 2θ (°) | d (Å) | h | k | l | Lattice Constant a (Å) | Lattice Constant b (Å) | Lattice Constant c (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.67° | 2.82 Å | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2.82 | 0 | 0 |
| 34.35° | 2.61 Å | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5.22 |
| 67.94° | 1.38 Å | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5.05 |
| 53.51° | 1.71 Å | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3.42 | 0 |
| 72.41° | 1.30 Å | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 5.22 |
| 75.01° | 1.27 Å | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 5.06 |
| Peak Position (2θ) | FWHM (ꞵ) | Crystallite Size D (nm) | D (nm) (Average) Cu-ZnO NPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31.67 | 0.22 | 38.38 | 26.48 |
| 34.35 | 0.21 | 40.36 | |
| 36.18 | 0.24 | 34.99 | |
| 38.71 | 0.47 | 17.73 | |
| 47.49 | 0.25 | 34.05 | |
| 48.61 | 0.47 | 18.36 | |
| 56.54 | 0.30 | 30.02 | |
| 58.24 | 0.40 | 22.73 | |
| 53.51 | 0.46 | 19.23 | |
| 61.49 | 0.39 | 23.59 | |
| 62.82 | 0.32 | 29.05 | |
| 66.12 | 0.72 | 13.16 | |
| 67.94 | 0.44 | 21.57 | |
| 69.04 | 0.35 | 27.45 |
| Bacteria | Sample ID | mm (Zone Inhibition) |
|---|---|---|
| Salmonella enterica | Cu-doped ZnO1 (5 µg/mL) | 0.0 |
| Cu-doped ZnO2 (10 µg/mL) | 0.0 | |
| Shigella sonnei | Cu-doped ZnO1 (5 µg/mL) | 0.0 |
| Cu-doped ZnO2 (10 µg/mL) | 0.0 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Cu-doped ZnO1 (5 µg/mL) | 0.7 |
| Cu-doped ZnO2 (10 µg/mL) | 0.8 | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Cu-doped ZnO1 (5 µg/mL) | 0.0 |
| Cu-doped ZnO2 (10 µg/mL) | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almoneef, M.M.; Awad, M.A.; Aldosari, H.H.; Hendi, A.A.; Aldehish, H.A.; Merghani, N.M.; Alshammari, S.G.; Alsuliman, L.M.; Alghareeb, A.A.; Ahmed, M.S. Enhancing Biomedical and Photocatalytic Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Copper–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Co-Precipitation Approach. Catalysts 2024, 14, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090641
Almoneef MM, Awad MA, Aldosari HH, Hendi AA, Aldehish HA, Merghani NM, Alshammari SG, Alsuliman LM, Alghareeb AA, Ahmed MS. Enhancing Biomedical and Photocatalytic Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Copper–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Co-Precipitation Approach. Catalysts. 2024; 14(9):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090641
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmoneef, Maha M., Manal A. Awad, Haia H. Aldosari, Awatif A. Hendi, Horiah A. Aldehish, Nada M. Merghani, Saad G. Alshammari, Latifah M. Alsuliman, Alhanouf A. Alghareeb, and Magd S. Ahmed. 2024. "Enhancing Biomedical and Photocatalytic Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Copper–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Co-Precipitation Approach" Catalysts 14, no. 9: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090641
APA StyleAlmoneef, M. M., Awad, M. A., Aldosari, H. H., Hendi, A. A., Aldehish, H. A., Merghani, N. M., Alshammari, S. G., Alsuliman, L. M., Alghareeb, A. A., & Ahmed, M. S. (2024). Enhancing Biomedical and Photocatalytic Properties: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Copper–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Co-Precipitation Approach. Catalysts, 14(9), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090641





