Abstract
The large-scale production of soybean proteins results in the generation of a significant volume of wastewater, containing a substantial amount of valuable β-amylase. The β-amylase enzyme was purified from the soybean whey wastewater using a three-step process, including alcohol precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography, and gel filtration chromatography. The specific activity of the purified β-amylase was 29,700 U/mg, with an enzyme activity recovery of 17.3% and purification fold of 16.5. The β-amylase had a molecular mass of around 56 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) value of 4.8. The β-amylase exhibited optimal activity at 55 °C and reasonable stability between 30 °C and 40 °C. The enzyme demonstrated an optimum pH of 6.0 and relative stability in the pH range of 5.0–8.0. Furthermore, the β-amylase activity was stimulated by PMSF, Tween-20, Tween-40, Tween-60, Tween-80, and Triton X-100. In terms of substrate preference, the enzyme hydrolyzed potato starch worked most effectively, followed by amylose, amylopectin, soluble starch, maltose, and pullulan. The purified β-amylase showed Km and Vmax values of 3.62 μM and 1.04 μM/ (g protein min), respectively. The purification process was simple and yielded high purification and recovery. The β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater has potential applications in the food and beverage industries.
1. Introduction
Soybean proteins and peptides are highly nutritious proteins that contain eight essential amino acids and no cholesterol [1,2]. The rising consumption of soybean protein isolate (SPI) in China has led to the generation of millions of tons of soybean whey annually. It is noteworthy that the production process also generates a substantial volume of soybean whey wastewater, with an average generation of 20 tons of soybean whey wastewater per ton of soybean protein isolate produced [3,4]. The wastewater from soybean whey contains high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as having significantly high biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) values (>16,000 mg/L) [5]. Therefore, disposing of it directly into the environment would result in serious pollution and a significant loss of nutrients. Despite the common use of conventional aerobic or anaerobic biological processes for treating soybean whey wastewater in SPI-producing factories, the nutrients in the wastewater are not recovered [6]. In addition, whilst the treatment is relatively efficient, the process is complicated, requires professional equipment, and has a high operating cost [7]. Thus, the effective treatment of soybean whey wastewater has emerged as a bottleneck hindering the healthy and sustainable development of soybean deep processing enterprises.
Soybean whey wastewater is recognized as a potential source of valuable nutrients such as simple sugars, oligosaccharides, isoflavone, saponin, and soybean whey proteins [2]. The recovery of these functional substances from soybean protein wastewater could have significant environmental benefits, as it may help to reduce the BOD and COD levels in the wastewater. Zhou et al. recovered a soybean trypsin inhibitor from the soybean whey wastewater using both ammonium sulfate salting and ethanol precipitation [8]. Niteo-Veloza et al. extracted lunasin, a naturally occurring bioactive peptide, from tofu whey wastewater [9]. Jiang et al. reported a technology of protein separation in soybean whey wastewater by two-stage foam separation [10]. Several techniques have been reported for separating isoflavones from soybean whey wastewater, including precipitation, resin adsorption, membrane separation [11], and two-stage batch foam fractionation [12]. Guan et al. used the ceramic membrane filtration, ultrafiltration, and an organic solvent precipitation methods to recover water-soluble polysaccharides from soybean whey wastewater [13]. Zhang et al. investigated the method of soybean trypsin inhibitor isolation and purification from soybean whey wastewater [14]. Liu et al. successfully extracted whey soy protein from whey wastewater using a novel foam column in a foam fractionation process [15].
β-Amylase (α-1,4-glucan maltohydrolase; E.C:3.2.1.2) is an exo-enzyme that hydrolyzes the α-1,4-glucosidic linkages in polysaccharides in order to release β-maltose units from the non-reducing ends of starch, glycogen, amylose, amylopectin, and other malto-oligosaccharides [16]. β-Amylase, when combined with pullulanase, has been discovered to effectively convert starch into a high-maltose syrup [17], which is widely used in food fields [18]. β-Amylase, which is found in higher plants and microorganisms, has been reported to exhibit high thermo- and pH stability in plant-derived sources, suggesting promising prospects [19]. β-Amylase has been purified and characterized from fenugreek seeds [20], sweet potatoes, barley, malt [21], and peas [22]. The molecular evolution and structural dynamics of β-amylase were studied in sweet potatoes [23] and barley [24].
Soybean whey wastewater, which contains up to 4 g/L protein [10] and constitutes approximately 9~15.3% of the soybean seed protein, is mainly composed of lipoxygenase, soybean agglutinin, trypsin inhibitors, and β-amylase [14]. Through the use of a continuous technology of successive foaming and defoaming processes to precipitate whey soy protein, Li et al. found that the concentration of β-amylase in soybean whey wastewater was 0.4 mg/L [25].
However, further investigation is needed to understand the purification and characteristics of β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater. In this study, we developed a method to purify β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater and characterized the purified β-enzyme. The experimental flow chart is shown in Figure 1. The results of this study are beneficial for the recovery of the β-enzyme from soybean whey wastewater and for the potential application of the β-enzyme in the food industry.
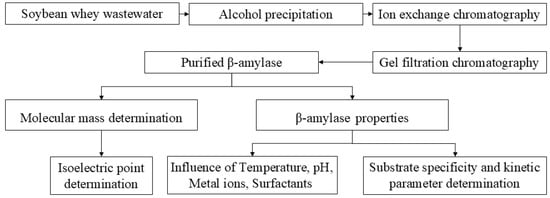
Figure 1.
Experimental flow chart.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of β-Amylase
The β-amylase enzyme was purified from soybean whey wastewater through a three-step process, which included alcohol precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography on a HiTrap QFF column, and gel filtration chromatography on a Sephacryl S-200HR column. Table 1 provides a summary of the purification process of β-amylase, revealing that the use of alcohol precipitation in soybean whey wastewater resulted in a purification fold of 4.0 and a yield of 59.4% (Table 1). Following the initial extraction, the crude extract containing β-amylase underwent anion-exchange chromatography and was eluted from the column using a one-step linear gradient of NaCl. Monitoring the absorbance at 280 nm revealed three primary protein peaks, with the second peak containing the majority of the β-amylase (Figure 2a). Subsequently, the specific activity of the enzyme increased by 11.6 fold, from 7200 to 20,890 U/mg, with a yield of 33.4% (Table 1). The active fractions obtained from the anion-exchange chromatography were further separated using a gel filtration chromatography column (as shown in Figure 2b). Notably, the enzymatic activity was eluted in a single peak that coincided with the protein peak. Fractions from this peak were collected and concentrated, resulting in a purification fold of 16.5, a recovery of 17.3%, and a specific activity of 29,700 U/mg of protein (Table 1). Previous studies have also demonstrated the successful use of ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration chromatography for the purification of β-amylase from various sources, including potato leaves [19], tubers of Curculigo pilosa [26], rhizomes of hedge bindweed (Calystegia sepium) [27], and malted African finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds [28]. The purification process presented in this study is straightforward and simple, making it easily adaptable for large-scale purification.

Table 1.
Purification summary of β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater.
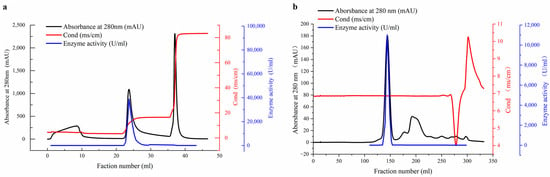
Figure 2.
Elution profiles of β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater on an anion-exchange column and a gel filtration chromatography column. (a) The crude β-amylase obtained from the soybean whey wastewater was loaded on a HiTrap QFF anion-exchange column and eluted with a linear salt gradient. (b) Pooled active fractions from the ion-exchange column were applied on the Sephacryl S-200HR (26/60) column previously equilibrated in 50mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 6.0). The enzyme activity (—), absorbance at 280 nm (—), and the conductance of the eluent (—) are shown.
2.2. Molecular Mass Determination
The purification of β-amylase in different steps was evaluated using SDS-PAGE gels (Figure 3). The results demonstrated that the band corresponding to β-amylase was intensified after ethanol precipitation, and further enhanced after ion-exchange chromatography. The final step of β-amylase purification using gel filtration chromatography resulted in a single sharp band, indicating that the enzyme was successfully purified from soybean whey wastewater. The molecular mass of the purified β-amylase was estimated to be approximately 56 kDa using SDS-PAGE (as depicted in Figure 3).
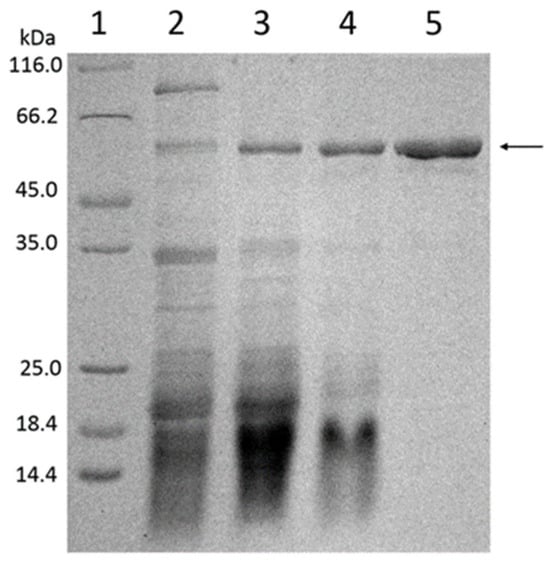
Figure 3.
The determination of the purity and molecular mass of β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater on SDS–PAGE. Lane 1: standard protein markers. Lane 2: crude enzyme extract. Lane 3: ethanol precipitated enzyme. Lane 4: purified enzyme from HiTrap QFF column. Lane 5: purified β-amylase from Sephacryl S-200HR column.
The molecular mass of the purified β-amylase, estimated to be approximately 56 kDa by SDS-PAGE (Figure 3), was comparable to that of common β-amylases obtained from plant sources such as potato leaves, [29] rhizomes of hedge bindweed (Calystegia sepium) [27], and malted African finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds [28]. However, β-amylase from soybeans purified using superparamagnetic particles and soybean flour exhibited a molecular mass of 70 kDa and 61.7 kDa, respectively, indicating that the molecular mass of β-amylase may vary depending on the plant’s origin, species, and developmental stage [30].
2.3. Isoelectric Point Determination
Isoelectric focusing of the purified β-amylase resulted in a single band with an isoelectric point (pI) of approximately 4.8 (Figure 4), which was consistent with the pI value reported for β-amylase from hedge bindweed [27]. This pI value was similar to those of β-amylase from pea epicotyls [31] and African finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds [28], which had pI values of 4.35 and 5.2, respectively. Notably, the pI value of β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater was lower than that of soybean flour β-amylase, which had a pI of 5.85 [32]. This suggests that the two β-amylases may have different amino acid sequences.
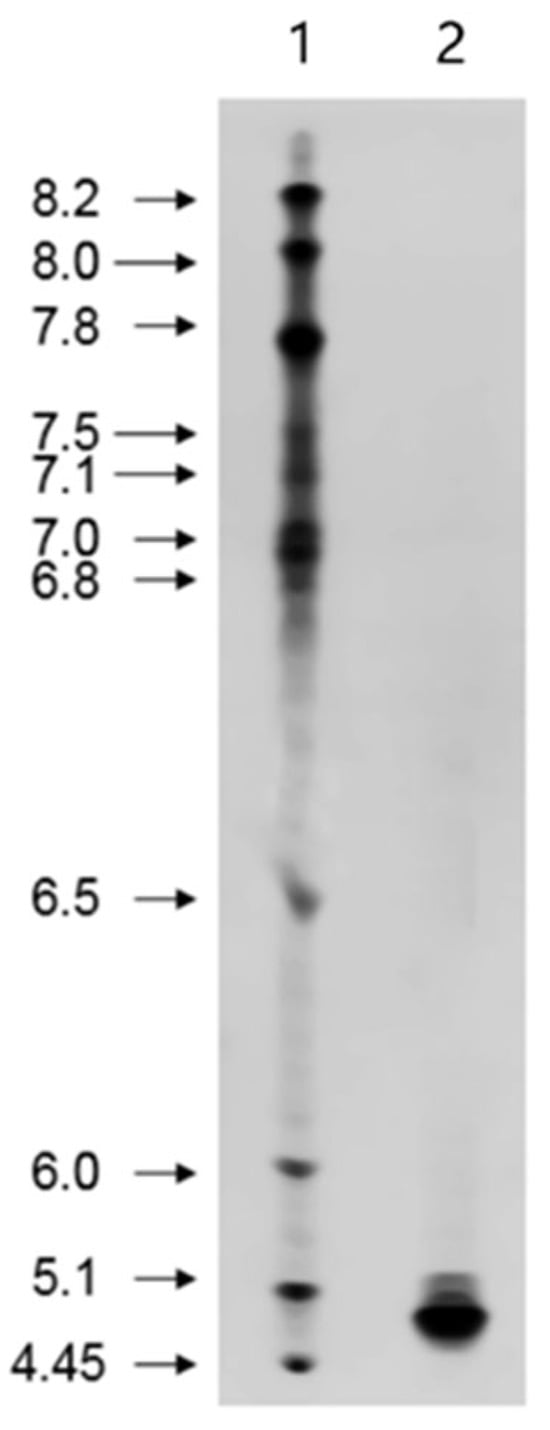
Figure 4.
Isoelectric focusing analysis of purified β-amylase. Lane 1, pI markers (pI range 3–9), and lane 2, purified β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater.
2.4. Effect of Temperature on Activity and Stability of Purified β-Amylase
The optimum temperature of β-amylase was determined by measuring its activity at various temperatures. As shown in Figure 5a, the enzyme exhibited activity over a wide temperature range (between 40 °C and 70 °C). The highest enzymatic activity was observed at 55 °C, which was higher compared to other sources. For instance, the optimum temperatures for β-amylase obtained from malted seeds of African finger millet and leaves of potatoes were reported to be 50 °C and 40 °C, respectively [28].
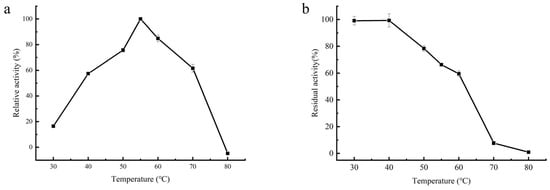
Figure 5.
The effect of temperature on β-amylase activity and thermal stability was investigated. (a) The temperature profiles range from 30 to 80 °C. Relative activity is expressed as a percentage of the maximum temperature activity of the enzyme. (b) The thermostability of β-amylase was determined by measuring β-amylase activity after pre-incubation of the enzyme at different temperatures (30–80 °C) for 1 h. The activity of an unheated enzyme sample was defined as 100%.
The impact of temperature on the stability of the purified β-amylase is illustrated in Figure 5b. The enzyme exhibited reasonable stability between 30 °C and 40 °C, retaining approximately 70% of its initial activity after 1 h of incubation at 50 °C. However, the enzyme was nearly inactive after 1 h of incubation at 80 °C due to denaturation at high temperatures [33]. The thermal stability of the β-amylase was similar to β-amylases isolated from other plant sources [28,33]. The notable thermal stability of the β-amylase purified from soybean whey wastewater makes it suitable for various biotechnological applications.
2.5. Effect of pH on Activity and Stability of Purified β-Amylase
The activity of the purified β-amylase was assessed in various pH buffer systems, and the results are presented in Figure 6a. The enzyme displayed significant activity over a wide pH range, from 3 to 10, with the highest activity observed at pH 6.0. The enzyme retained approximately 80% of its activity within the pH range of 5.0–8.0, with pH 6.0 being the optimum pH for the enzyme (Figure 6a). Plant β-amylases are typically reported to have an optimum of pH between 5.0 and 6.0. For instance, soybean β-amylase has been reported to have an optimum pH ranging from 5 to 6 [34,35], Termitomyces clypeatus amylase has an optimum pH of 5.5, and sweet potato β-amylase has an optimum pH range of 5.0 to 6.0 [16]. Similarly, finger millet malt amylase has an optimum pH of 5.0 to 5.5 [36]. In contrast, the optimum pH range of β-amylase from Aspergillus carbonarius is 6.0 to 7.0 [37].
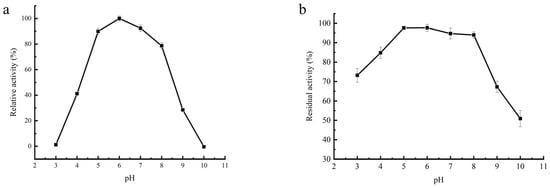
Figure 6.
The effect of pH on the activity and stability of purified β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater. (a) The enzyme’s activity was determined under various pH conditions. Relative activity is expressed as a percentage of the maximum pH activity of the enzyme. (b) The pH stability of the amylase was studied by pre-incubating the enzyme at different pH levels for 24 h at 4 °C. The values of residual activities are shown as percentages of the original activity, which was taken as 100%.
The β-amylase was found to be highly stable in the pH range of 3.0 to 8.0, with approximately 95% of its initial activity retained after 24 h of incubation at 4 °C. However, at pH values above 8.0, the residual activity of the enzyme sharply decreased, with only 50% activity retained at pH 10.0 (Figure 6b). This pH stability profile of the purified β-amylase was similar to that of potato β-amylase [29]. Importantly, the β-amylase from soybean whey wastewater demonstrated stability over a wide pH range, suggesting its potential utility in diverse pH conditions.
2.6. Effects of Metal Ions and Surface-Active Agents on β-Amylase Activity
The impact of various metal ions on the activity of the purified β-amylase was examined (Table 2). The activity of β-amylase was not significantly (p > 0.05) impacted by K+, Na+, Mn2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Li+, Ba2+, Ca2+, or Zn2+. Nevertheless, the enzyme retained only 38.4% of its activity in the presence of 10mM Cu2+. Previous reports have suggested that the inactivation of the enzyme by metal ions may result from their binding to the catalytic residues of the enzyme [36]. Most of the amylases were metalloenzymes that required calcium ions (Ca2+) for their activity, structural integrity, and stability [38]. The β-amylase purified from soybean whey wastewater exhibited a Ca2+-independent behavior, similar to the amylases produced by Bacillus sp. [39].

Table 2.
Effect of metal ions on β-amylase activity.
The β-amylase activity was dramatically enhanced in the presence of most surfactant agents (Table 3). The PMSF, Tween-20, Tween-40, Tween-60, Tween-80 and Triton X-100 increased its activity by 52%, 58%, 48%, 151%, 50%, and 58%, respectively. The stimulatory effect of surfactants on amylase activity was controversial. Arnesene et al. reported that the amylase activity from Thermomyces lanuginosus was slightly inhibited by Triton X-100 [40].

Table 3.
Effect of surfactant agents on β-amylase activity.
The presence of several surfactant agents significantly enhanced the activity of β-amylase, as shown in Table 3. Specifically, PMSF, Tween-20, Tween-40, Tween-80, and Triton X-100 increased the enzyme’s activity by 52%, 58%, 48%, 50%, and 58%, respectively, with the greatest enhancement observed with Tween-20 at 158%. However, Triton X-100 was reported to slightly inhibit amylase activity from Thermomyces lanuginosus by Arnesene et al. [40]. Triton X-100 has been reported to activate or stabilize starch-degrading enzymes [33], while Oberoi et al. found that SDS (6%) and Tween-80 (1%) had stimulatory effects on the activity and stability of amylase from Bacillus sp. [41]. The enzyme’s slight inhibition by EDTA suggests that metallic ions are not required for its activity. However, when treated with β-mercaptoethanol and SDS, the β-amylase retained only 11.79% and 20.49% of its original activity, respectively, indicating its susceptibility to denaturation under reducing and denaturing conditions. The inhibitory and stimulatory effects of metal ions and surface-active agents may be crucial factors in the commercial utilization of the enzyme, where enzyme stability and activity are of the utmost importance [41].
2.7. Substrate Specificity and Kinetics Studies
The substrate specificity and kinetic parameters of purified β-amylase were determined. The enzyme exhibited the highest activity towards potato starch, with only 95%, 83%, and 35.6% of its maximum activity observed for amylose, soluble starch, amylopectin, and glycogen, respectively (Figure 7a). Furthermore, the purified enzyme showed lower activity when applied to maltose and almost no activity when used on pullulan, indicating its specificity for cleaving long chains, and confirming that it was β-amylase and not glucoamylase. These findings were consistent with those of a study on β-amylase from malted African finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds [28].
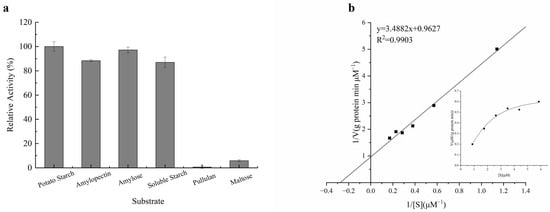
Figure 7.
Substrate specificity and kinetic properties of purified β-amylase. (a) The substrate specificity of the amylase was measured in the presence of 2% potato starch, amylose, soluble starch, amylopectin, pullulan, and maltose. (b) A Lineweaver–Burk plot was studied in the presence of different concentrations of potato starch.
The Km and Vmax values of the purified enzyme were determined using different concentrations of potato starch (0.1–2.0 mg/mL) as the substrate (Figure 7b). The Km and Vmax values of the enzyme, calculated from a Lineweaver–Burk plot, were approximately 3.62 μM and 1.04 μM/ (g protein min), respectively. The Km value was higher than those of other β-amylases, such as pea epicotyl β-amylase (4.88 mg/mL) [31], β-amylase from rice (3 mg/mL) [42], and β-amylase from malted African finger millet (2.1 mM) [28], indicating the distinctness of soybean β-amylase and its higher affinity for potato starch, which confirms its physiological role in amylolytic activity [43].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
The soybean whey wastewater was obtained from TianJing Vegetable Proteins Industry Co. Ltd. (Pingdingshan, Henan, China), and had a whey soybean protein concentration of 2.0 ± 0.3 g/L and a pH of 4.6. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was purchased from Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All other chemicals were of an analytical grade, and purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
3.2. Enzyme Activity Assay
The method described by Biazus et al. was used to measure the activity of β-amylase, with potato starch used as the substrate [44]. The reaction mixture, consisting of 0.5 mL of an appropriately diluted enzyme solution and 0.75 mL of 2% (w/v) potato starch prepared in a 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0), was incubated at 60 °C for 3 min. The reaction was terminated by adding 0.75 mL of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS), and the released reducing sugar was analyzed using the DNS method as reported by Miller [45]. One unit of β-amylase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that released 1 mg of reducing sugar as glucose equivalents per hour under the assay conditions.
3.3. Protein Determination
The protein concentration was determined using the Bradford method, with bovine serum albumin (BSA) being used as the standard protein. The protein concentration during purification studies was determined by measuring the absorbance at 595 nm.
3.4. Extraction of the Crude β-Amylase
The extraction and purification of the enzymes were conducted at 4 °C, unless stated otherwise. The wastewater was first fractionated by adding half the volume of chilled absolute ethyl alcohol dropwise, and then centrifuged at 6738× g for 10 min. The supernatant liquid was then removed and precipitated with two volumes of absolute ethyl alcohol, followed by another round of centrifugation. The pellet obtained was resuspended in one-fifthof the original volume of 100 mM acetate buffer (pH 6.0), and subsequently filtered through a 0.22 μm cellulose acetate membrane to obtain the crude extract of β-amylase.
3.5. Purification of the β-Amylase
The β-amylase was purified from the crude extract using a combination of anion-exchange and gel filtration column chromatography. Initially, the crude extract was loaded onto a 1 mL HiTrap QFF column (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) that had been equilibrated with 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.0) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. Following a 15 mL wash with an equilibration buffer, the enzyme bound to the anion-exchange column was eluted using a linear gradient of 0 to 1.0 M NaCl in the same buffer. Fractions of 1 mL each were collected and assayed for their enzyme activity.
The β-amylase’s activity fractions were subsequently combined and underwent further purification via gel filtration chromatography using a pre-equilibrated Sephacryl S-200HR (26/60) column (GE Healthcare) with a 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 6.0). Elution was conducted at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min, with 0.5 mL fractions collected, and their protein concentration was monitored at 280 nm via absorbance measurement. The resulting fractions displaying the β-amylase’s activity were then combined.
3.6. SDS-PAGE for Purity and Molecular Mass Determination
The β-amylase’s purity and molecular mass were estimated using sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE), following Laemmli’s protocol [46]. The resolving gel consisted of 12% acrylamide, while the stacking gel had 3.75% acrylamide. Then, the gel was stained with Coomassie Blue R-250 for 1 h and destained with 7% acetic acid for 3 h. Pre-stained protein molecular mass markers were also included in the same gel.
3.7. Isoelectric Focusing of Purified β-Amylase
Isoelectric focusing was performed using a Multiphor II device (GE Healthcare) using the method of Vesterberg and Svensson [47]. Electrophoresis was conducted in two steps, with the first step lasting 20 min at 500 V, followed by an additional 90 min at 2000 V. After the electrophoresis was completed, the gel was treated with 10% trichloroacetic acid for a minimum of 30 min, and then stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue for another 30 min. To determine the isoelectric point (pI) of the purified β-amylase, IEF standards (pI range 4.45–9.6; BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) were included in the same gel, and the pI values were plotted against the migration distance.
3.8. Effect of Temperature on β-Amylase Activity and Stability
To investigate the effect of temperature on β-amylase activity, the enzyme activities were measured at various temperatures ranging from 30 to 80 °C using a 50 mM sodium acetate buffer at pH 5.0. The relative activity was expressed as a percentage of the maximum β-amylase activity. The thermal stability of β-amylase was determined by pre-incubating the purified enzyme at different temperatures (30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 °C) for 1 h, followed by rapid cooling in an ice bath, and measuring the remaining activity under the same conditions as described above, with the initial activity considered as 100%.
3.9. Effect of pH on β-Amylase Activity and Stability
To assess the impact of pH on the activity of purified β-amylase, buffers with concentrations of 0.1 M (sodium acetate, sodium phosphate, and Tris-HCl) were utilized within a pH range of 3 to 10 at room temperature. The reaction was then conducted according to the β-amylase assay method mentioned above, and the activity at the optimal pH was set as 100%. For the assessment of pH stability, the enzyme was subjected to pre-incubation at various pH values for 24 h at 4 °C. The remaining activity was determined, and the initial activity was considered as 100%.
3.10. Effects of Metal Ions, Inhibitors, and Surfactants on β-Amylase Activity
To investigate the impact of various metal ions on the activity of β-amylase, the purified enzyme was pre-incubated with 10 mM concentrations of different metal ions (MnCl2, FeCl3, LiCl, BaCl2, CuSO4, CaCl2, KCl, ZnCl2, and NaCl) individually for an hour at 37 °C. The residual activity was evaluated, with the enzyme’s activity in the absence of metal ions considered as 100%, and the relative activities were then calculated.
The impact of different inhibitors and surfactants on purified β-amylase activity was investigated. The assay mixture was supplemented with phenylmethyl sulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (10%), EDTA (10%), β-mercaptoethanol (10%), Tween 20 (2%), Tween 40 (2%), Tween 60 (2%), Tween 100 (2%), and SDS (2%) individually. The relative activity (%) was determined with respect to the control sample without any additives.
3.11. Substrate Specificity
To assess the enzyme’s activity against various substrates, six different polymers—potato starch, amylose, soluble starch, amylopectin, pullulan, and maltose—were employed. These substrates were individually prepared by dissolving 2% (w/w) in a 100 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 6.0). Potato starch was used as the reference substrate and taken as 100% to compare enzyme activity.
3.12. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
The purified enzyme was incubated with varying concentrations of soluble potato starch (0.1–2 mg/mL) in a sodium acetate buffer (100 mM, pH 6.0), and the activity was measured. Initial velocities (V0) were determined for all substrate concentrations, and the Lineweaver–Burk plot was used to calculate the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) and maximum reaction velocity (Vmax) values.
3.13. Statistical Analysis
All the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. The data from the experiments were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to assess the significance of the differences between the data on GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., Boston, MA, USA, 2018). The value of p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, β-amylase was successfully purified from soybean whey wastewater using a three-step process involving alcohol precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography, and gel filtration chromatography. The purified enzyme displayed a high purification fold, recovery, and specific activity, indicating the effectiveness of the purification procedure. Temperature had the strongest influence on enzyme activity, with the highest activity occurring at 55 °C. In the pH range of 5 to 7, pH had a relatively small impact on enzyme activity. Cu2+ markedly inhibited the enzyme, whereas Tween-20 significantly enhanced its activity. The enzyme exhibited excellent thermal stability and a broad range of pH activity and stability, making it a valuable resource with potential applications in the food industry. The analysis of substrate specificity and kinetic parameters revealed the enzyme’s preference for long chains and its distinctness from other β-amylases, with a higher affinity for potato starch. This study emphasizes the potential of β-amylase from industrial waste liquids as a valuable commodity, with promising applications in the food industry. The findings indicate that β-amylase purified from soybean whey wastewater has potential industrial uses. Further research can investigate the potential industrial applications of purified β-amylase, such as its use in food processing and other biotechnological processes.
Author Contributions
B.Y.: experimentation, data processing, manuscript writing, funding acquisition; C.J.: experimentation, data processing, manuscript writing; Y.G.: experimentation, data processing, manuscript writing; Z.C.: conceptualization, data curation, supervision; Q.L.: methodology, data curation, revision; H.G.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, revision, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by the Shanghai Municipal Natural Science Foundation (22ZR141200) (Shanghai, China); the Ningxia Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2023AAC03735); the Ningxia Association for Science and Technology Youth Talent Support Program Ning Kexie (2024) No.6; the Ningxia technology-benefiting-people program (2024CMG03049); and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Ningxia Market Supervision and Administration Department (2024SJKY0005).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study area are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hu, M.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, F.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Li, S. The Aggregation Behavior between Soybean Whey Protein and Polysaccharides of Diverse Structures and Their Implications in Soybean Isoflavone Delivery. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. The Investigation of Soybean Protein Isolates and Soybean Peptides Assisting Lactobacillus plantarum K25 to Inhibit Escherichia coli. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Soy Whey: More than Just Wastewater from Tofu and Soy Protein Isolate Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, F.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L. Recovery of Soy Whey Protein from Soy Whey Wastewater at Various Cavitation Jet Pretreatment Time and Their Structural and Emulsifying Properties. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Tian, J.; Shi, J.; Linhardt, R.J.; Ye, T.D.X.; Chen, S. Recovery of High Value-added Nutrients from Fruit and Vegetable Industrial Wastewater. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgentini, D.A.; Wagner, J.R. Comparative Study of Structural Characteristics and Thermal Behavior of Whey and Isolate Soybean Proteins. J. Food Biochem. 1999, 23, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Serventi, L. Sustainability of Dairy and Soy Processing: A Review on Wastewater Recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Enrichment of Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater Using Different Precipitating Agents and Analysis of Their Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Veloza, A.; Zhong, Q.; Kim, W.-S.; D’Souza, D.; Krishnan, H.B.; Dia, V.P. Utilization of Tofu Processing Wastewater as a Source of the Bioactive Peptide Lunasin. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, Q. Technology of Protein Separation from Whey Wastewater by Two-Stage Foam Separation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Study on Separation and Purification of Genistein in the Soybean Residue Using Macroporous Resin Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Z.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, W.C.; Yu, Y. Recovery of Isoflavones from the Soy Whey Wastewater Using Two-Stage Batch Foam Fractionation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13761–13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, Q.; Lin, B.; Sun, M.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, J.; Lai, G. Structural Characterization of a Soluble Polysaccharide SSPS1 from Soy Whey and Its Immunoregulatory Activity in Macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, N.; Wu, Z. Foam Fractionation for Recovering Whey Soy Protein from Whey Wastewater: Strengthening Foam Drainage Using a Novel Internal Component with Superhydrophobic Surface. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Kainuma, K. Partial Hydrolysis of Sweet-Potato Starch with β-Amylase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.-C.; Zhang, G.-P.; Zhou, M.-X. Protein and Hordein Content in Barley Seeds as Affected by Nitrogen Level and Their Relationship to β-Amylase Activity. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folasade, M.O.; Folasade, M.A. Production, Purification and Partial Characterization of Moderately Thermostable β-Amylase from Bacillus polymyxa BWB-01. Curr. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Vajravijayan, S.; Pletnev, S.; Mani, N.; Pletneva, N.; Nandhagopal, N.; Gunasekaran, K. Structural Insights on Starch Hydrolysis by Plant β-Amylase and Its Evolutionary Relationship with Bacterial Enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.C.; Dwevedi, A.; Kayastha, A.M. Biochemical and Thermodynamic Characterization of de Novo Synthesized β-Amylase from Fenugreek. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zheng, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Process Optimization of the Extraction Condition of β-amylase from Brewer’s Malt and Its Application in the Maltose Syrup Production. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2018, 65, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amylase Research Society of Japan. Handbook of Amylases and Related Enzymes: Their Sources, Isolation Methods, Properties and Applications; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Obe, D.A.; Fatoki, T.H. In Silico Evaluation of the Structural Dynamics β-Amylase from Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas). Asian J. Biotechnol. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stewart, D.C.; Eglinton, J.K.; Logue, S.J.; Langridge, P.; Evans, D.E. Comparative Enzyme Kinetics of Two Allelic Forms of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) β-Amylase. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 31, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ji, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, J. Precipitation of Proteins from Soybean Whey Wastewater by Successive Foaming and Defoaming. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 128, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicko, M.H.; Searle-van Leeuwen, M.J.F.; Beldman, G.; Ouedraogo, O.G.; Hilhorst, R.; Traoré, A.S. Purification and Characterization of β-Amylase from Curculigo pilosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Hu, J.; Barre, A.; Hause, B.; Baggerman, G.; Rougé, P.; Peumans, W.J. Purification, Characterization, Immunolocalization and Structural Analysis of the Abundant Cytoplasmic β-amylase from Calystegia sepium (Hedge Bindweed) Rhizomes. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 6263–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Ajele, J.O.; Sirdeshmukh, R. Purification and Characterization of Alkaline-Stable β-Amylase in Malted African Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana) Seed. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2178–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viksø-Nielsen, A.; Christensen, T.M.I.E.; Bojko, M.; Marcussen, J. Purification and Characterization of β-amylase from Leaves of Potato (Solanum tuberosum). Physiol. Plant. 1997, 99, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Y.-S.; Kuo, S.-T.; Jiang, C.-M.; Wu, M.-C. Purification of Soybean Amylase by Superparamagnetic Particles. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, P.A.; Henson, C.A.; Duke, S.H. Purification and Characterization of Pea Epicotyl β-Amylase. Plant Physiol. 1990, 92, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Duan, C.; Liu, Z.; Qin, L. Properties of β-Amylase from China Soybean Core Collection. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2006, 21, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Robyt, J.F. Activation and Stabilization of 10 Starch-Degrading Enzymes by Triton X-100, Polyethylene Glycols, and Polyvinyl Alcohols. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2005, 37, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.S.; Vishwanath, K.S.; Singh, S.A.; Rao, A.G.A. Entrapment of α-Amylase in Alginate Beads: Single Step Protocol for Purification and Thermal Stabilization. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, A.; Birk, Y. Purification and Characterization of a β-Amylase from Soya Beans. Biochem. J. 1965, 95, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmala, M.; Muralikrishna, G. Three α-Amylases from Malted Finger Millet (Ragi, Eleusine Coracana, Indaf-15)—Purification and Partial Characterization. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, B.N.; Ire, F.S.; Ezeogu, L.I.; Anyanwu, C.U.; Odibo, F.J. Purification and Some Properties of a Novel Raw Starch-Digesting Amylase from Aspergillus carbonarius. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, D.S.; Sticher, L.; Van Huystee, R.; Wagner, D.; Jones, R.L. The Calcium Requirement for Stability and Enzymatic Activity of Two Isoforms of Barley Aleurone α-Amylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 19392–19398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Quan, S.; Liu, D.; Ma, H.; Li, F.; Zhou, F.; Chen, G. Purification and Characterization of a Novel α-Amylase from a Newly Isolated Bacillus methylotrophicus Strain P11-2. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnesen, S.; Havn Eriksen, S.; Olsen, J.; Jensen, B. Increased Production of α-Amylase from Thermomyces lanuginosus by the Addition of Tween 80. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1998, 23, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, R.; Beg, Q.K.; Puri, S.; Saxena, R.K.; Gupta, R. Characterization and Wash Performance Analysis of an SDS-Stable Alkaline Protease from a Bacillus sp. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Chiba, S.; Shimomura, T. Purification and Some Properties of Active β-Amylase in Rice. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1977, 41, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, T.; Thorneycroft, D.; Chapple, A.; Messerli, G.; Chen, J.; Zeeman, S.C.; Smith, S.M.; Smith, A.M. A Cytosolic Glucosyltransferase Is Required for Conversion of Starch to Sucrose in Arabidopsis Leaves at Night. Plant J. 2004, 37, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biazus, J.P.M.; Souza, R.R.D.; Márquez, J.E.; Franco, T.T.; Santana, J.C.C.; Tambourgi, E.B. Production and Characterization of Amylases from Zea mays Malt. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterberg, O.; Svensson, H. Isoelectric Fractionation, Analysis, and Characterization of Ampholytes in Natural pH Gradients. Acta Chem. Scand. 1966, 20, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).