Role of the Solvent and Ultrasound Irradiation in the Preparation of TiO2 for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Water
Abstract
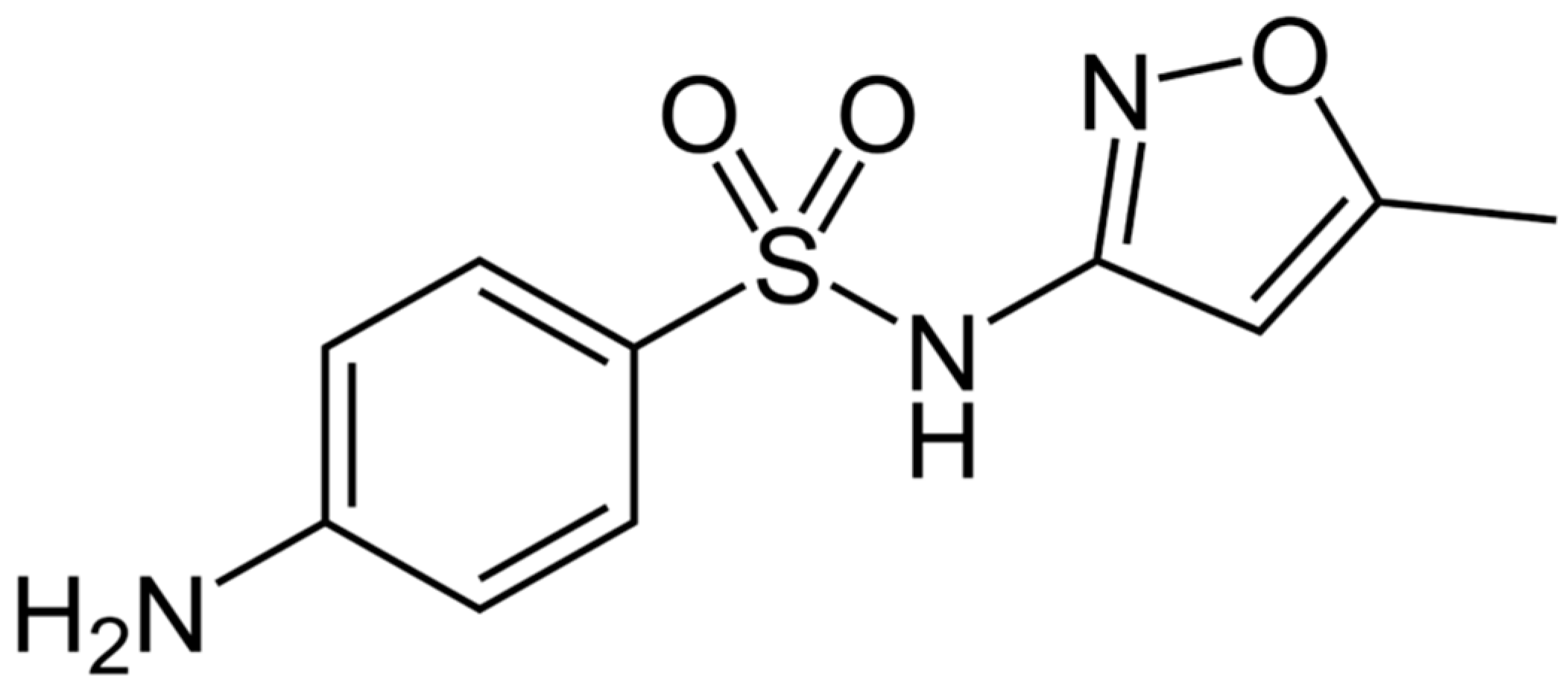
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization Results
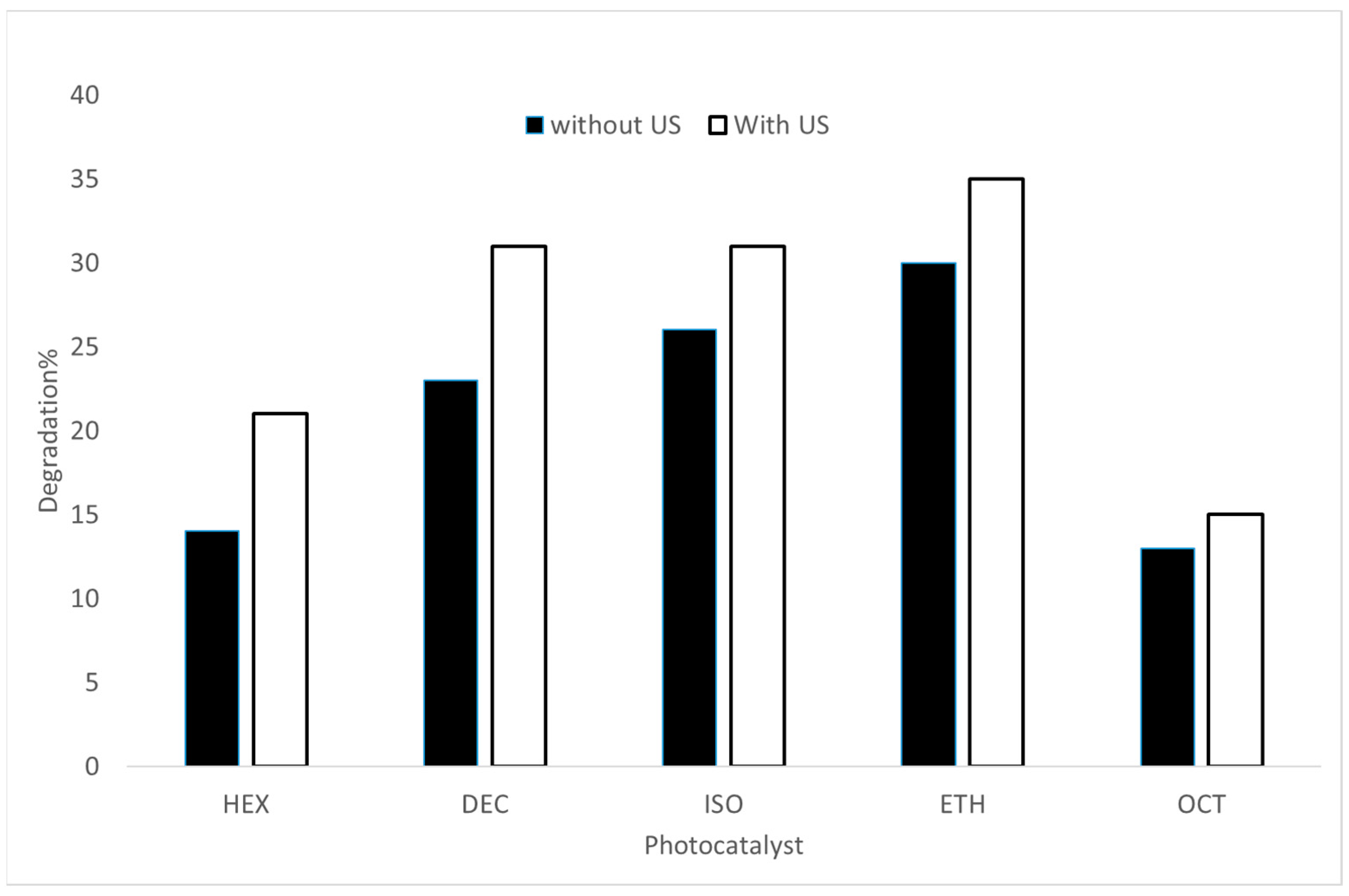
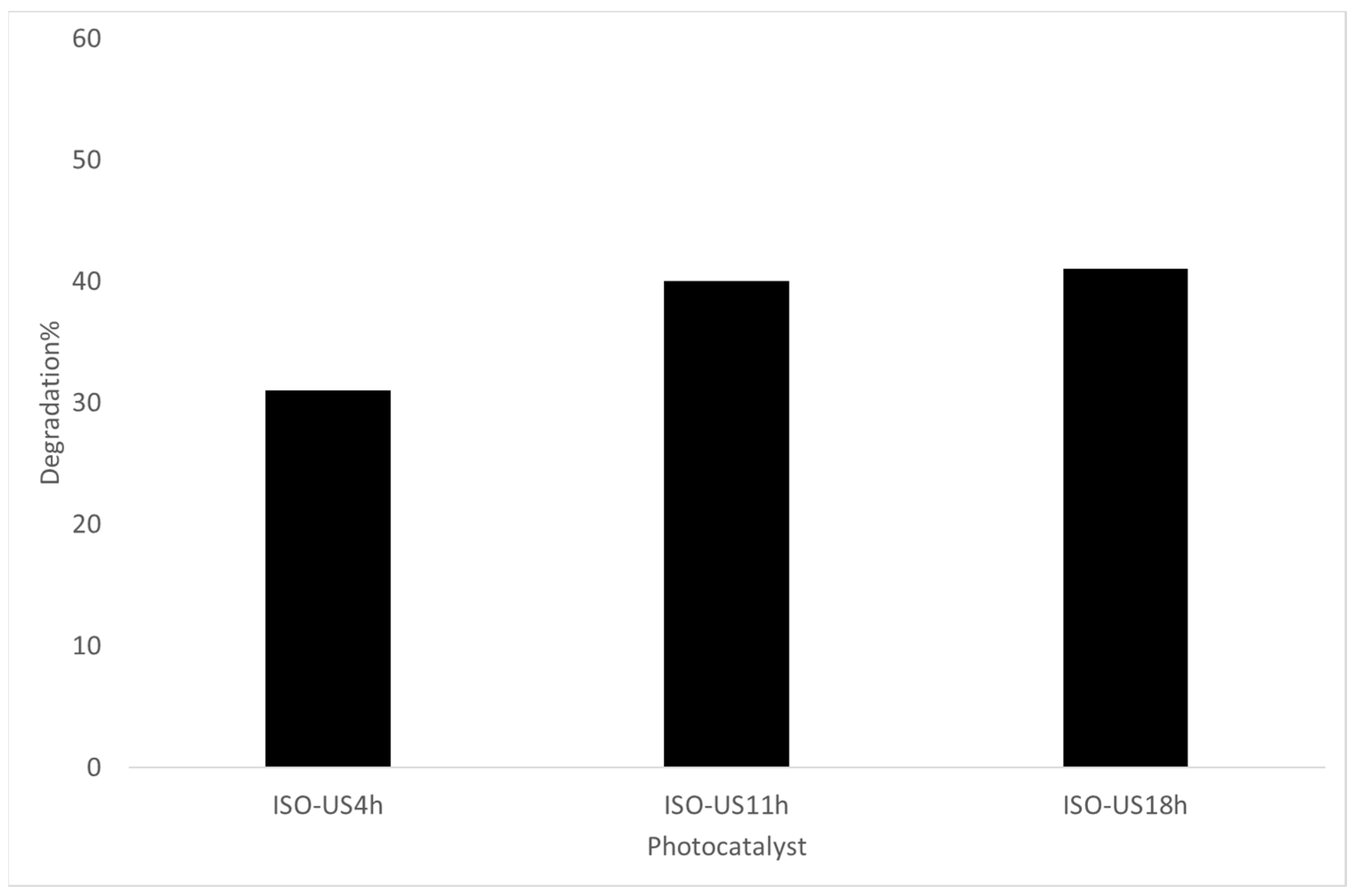
2.2. Experimental Photodegradation Test
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
3.2. SMX Degradation Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levin, R.; Villanueva, C.M.; Beene, D.; Cradock, A.L.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Lewis, J.; Martinez-Morata, I.; Minovi, D.; Nigra, A.E.; Olson, E.D.; et al. US drinking water quality: Exposure risk profiles for seven legacy and emerging contaminants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 34, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance déterminants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Feng, M. Water depollution using metal-organic frameworks-catalyzed advanced oxidation processes: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhuang, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, Z. Sonochemical fabrication of inorganic nanoparticles for applications in catalysis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 71, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatel, G. Sonochemistry in nanocatalysis: The use of ultrasound from the catalyst synthesis to the catalytic reaction. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Hyeon, T.; Fang, M.; Cichowlas, A.A. Sonochemical Preparation of Nanostructured Catalysts. In Advanced Catalysts and Nanostructured Materials; Moser, W.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; Chapter 8; pp. 197–212. ISBN 9780125084604. [Google Scholar]
- Amaniampong, P.N.; Jérôme, F. Catalysis under ultrasonic irradiation: A sound synergy. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 22, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, C.Y.; Wu, T.Y.; Juan, J.C. An application of ultrasound technology in synthesis of titania-based photocatalyst for degrading pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 586–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, M.D.; Sil, S.; Singh, N.; Ray, P.P.; Darbha, G.K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mallick, A.I.; Majumder, T.P. Sonochemical synthesis of nanospherical TiO2 within graphene oxide nanosheets and its application as a photocatalyst and a Schottky diode. FlatChem 2020, 22, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, G. Sonochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline TiO2 by hydrolysis of titanium alkoxides. Microelectron. Eng. 2003, 66, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; Zhang, D. Sonochemical synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles on graphene for use as photocatalyst. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2011, 18, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arami, H.; Mazloumi, M.; Khalifehzadeh, R.; Sadrnezhaad, S.K. Sonochemical preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4559–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiana, L.; Wardoyo, A.Y.P.; Masruroh; Dharmawan, H.A. Synthesis TiO2 using sonochemical method and responses the CO2 gas of the nanoparticle TiO2 layers on the QCM sensor surfaces. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2165, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. Sonochemistry. Science 1990, 247, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Price, G.J. Applications of ultrasound to materials chemistry. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B. Recent developments on ultrasound assisted catalyst-free organic synthesi. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintas, P.; Tagliapietra, S.; Calcio Gaudino, E.; Palmisano, G.; Cravotto, G. Glycerol: A solvent and a building block of choice for microwave and ultrasound irradiation procedures. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeigera, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupacchini, M.; Mascitti, A.; Giachi, G.; Tonucci, L.; D’Alessandro, N.; Martinez, J.; Colacino, E. Sonochemistry in non-conventional, green solvents or solvent-free reactions. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 609–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, M.; Hoang, S.; Suib, S.L.; Gao, P.X. Solvent effects on the heterogeneous growth of TiO2 nanostructure arrays by solvothermal synthesis. Catal. Today 2021, 360, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, I.S.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Lee, W.I.; Dai, S.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Pan, J.H. Nanoporous TiO2 spheres with tailored textural properties: Controllable synthesis, formation mechanism, and photochemical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldas, B.E. Hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide and effects of hydrolytic polycondensation parameters. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Costa, M.E.V.; Otero-Irurueta, G.; Capela, I. Ultrasonic irradiation as a green production route for coupling crystallinity and high specific surface area in iron nanomaterials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominami, H.; Kohno, M.; Kera, Y. Synthesis of brookite-type titanium oxide nano-crystals in organic media. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J. Direct Sonochemical Preparation and Characterization of Highly Active Mesoporous TiO2 with a Bicrystalline Framework. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4647–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.G.; Koteswara Rao, K.S.R. Polymorphic phase transition among the titania crystal structures using a solution-based approach: From precursor chemistry to nucleation process. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11574–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, P.; Paolantoni, M.; Cataliotti, R.S.; Palombo, F.; Morresi, A. Water/Alcohol Mixtures: A Spectroscopic Study of the Water-Saturated 1-Octanol Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19557–19565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuzwayo, Z.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Modelling and simulation of photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of chlorohalogenated substituted phenols in batch systems: Langmuir–Hinshelwood approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, M.N.; Bayarri, B.; Giménez, J.; Costa, J. Photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole in aqueous suspension of TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 74, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B. Effect of wavelengths on photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole in the presence of TiO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, B.; Chen, H. Selective photocatalytic removal of sulfonamide antibiotics: The performance differences in molecularly imprinted TiO2 synthesized using four template molecules. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M.H.; Shaikh, M.A.A.; Gafur, M.A. UV/TiO2 photodegradation of metronidazole, ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole in aqueous solution: An optimization and kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.G.; Van de Lagemaat, J.; Frank, A.J. Comparison of dye-sensitized rutile- and anatase-based TiO2 solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 8989–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainca, A.; Boccalon, E.; Nocchetti, M.; Vivani, R.; Di Michele, A.; Longhi, M.; Pirola, C. Sonochemical and mechanochemical synthesis of iron-based nano-hydrotalcites promoted with Cu and K as catalysts for CO and CO2 Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Fuel 2024, 373, 132303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Michele, A.; Dell’Angelo, A.; Tripodi, A.; Bahadori, E.; Sànchez, F.; Motta, D.; Dimitratos, N.; Rossetti, I.; Ramis, G. Steam reforming of ethanol over Ni/MgAl2O4 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.; Bianchi, C.L.; Di Michele, A.; Diodati, P.; Boffito, D.; Ragaini, V. Ultrasound and microwave assisted synthesis of high loading Fe-supported Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaini, V.; Pirola, C.; Borrelli, S.; Ferrari, C.; Longo, I. Simultaneous ultrasound and microwave new reactor: Detailed description and energetic considerations. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2012, 19, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. Generalized Structure Analysis System (GSAS) LAUR 86-748; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, M.; Schwerdtfeger, C.F.; Meagher, E.P. Refinement of the structure of anatase at several temperatures. Z. Krist. 1972, 136, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, E.P.; Lager, G.A. Polyhedral Thermal Expansion Ln The Tio, Polymofphs: Refinement Of The Crystal Structures Of Rutile And Brookite At High Temperature. Can. Mineral. 1979, 17, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
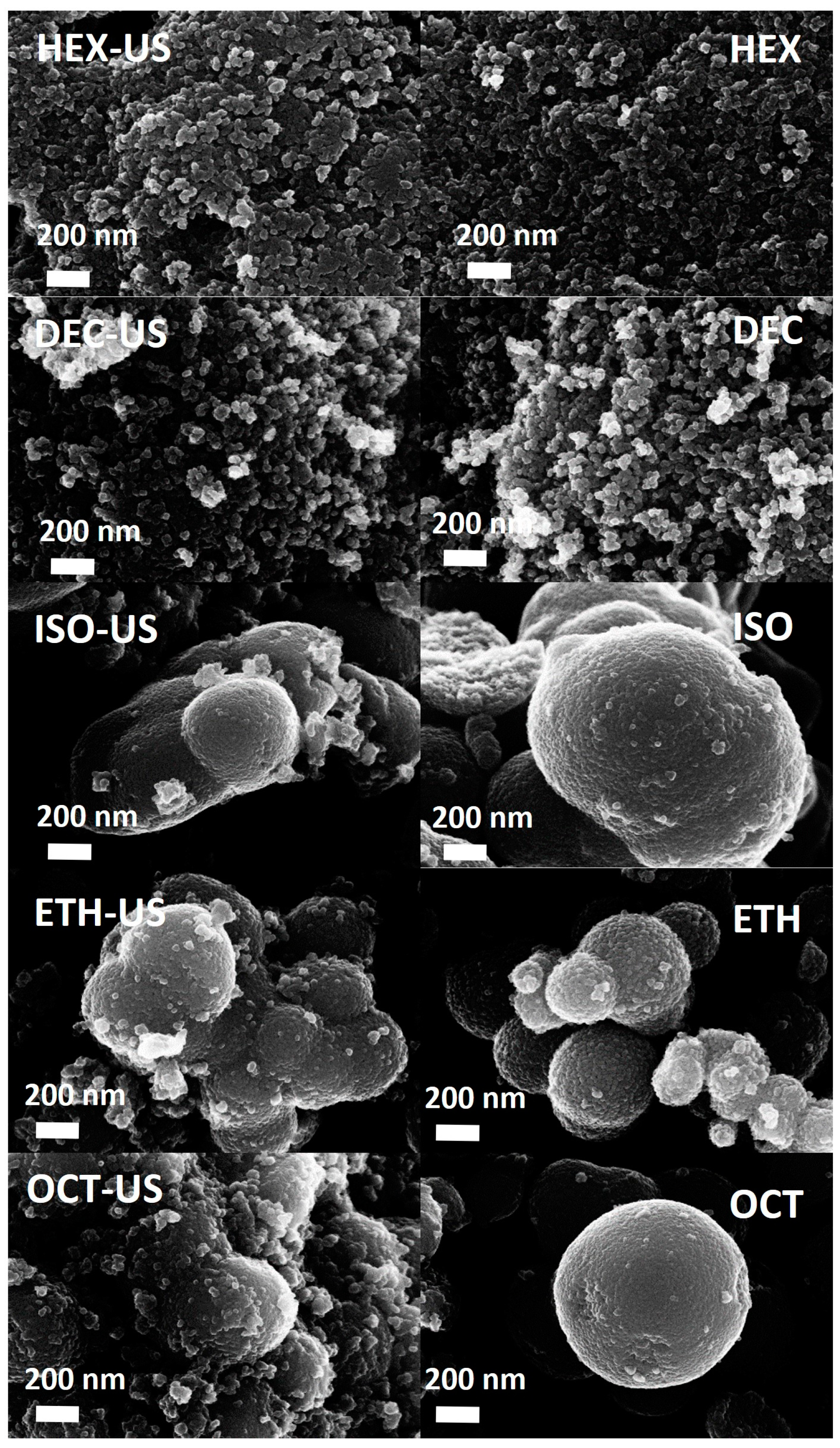

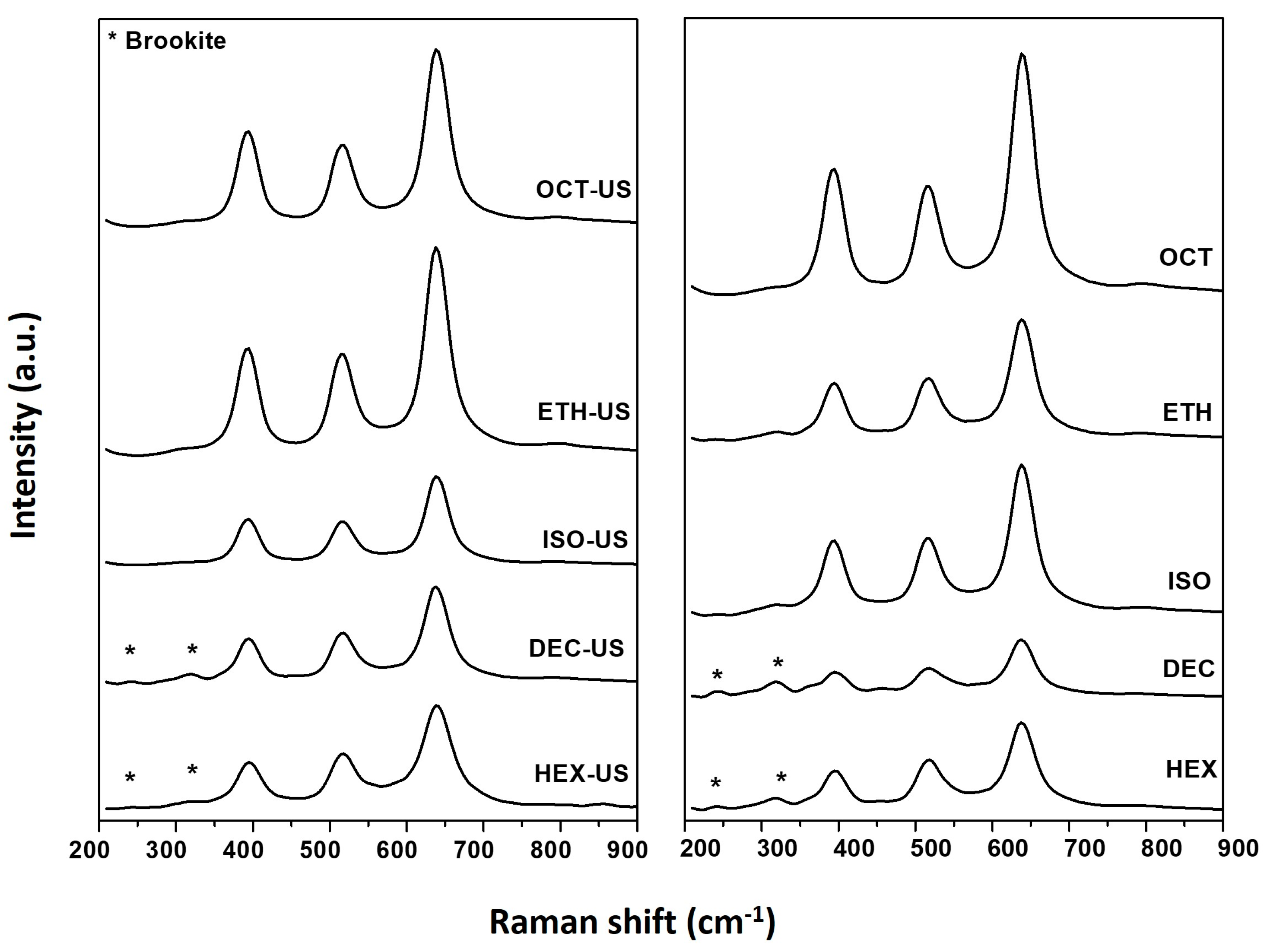

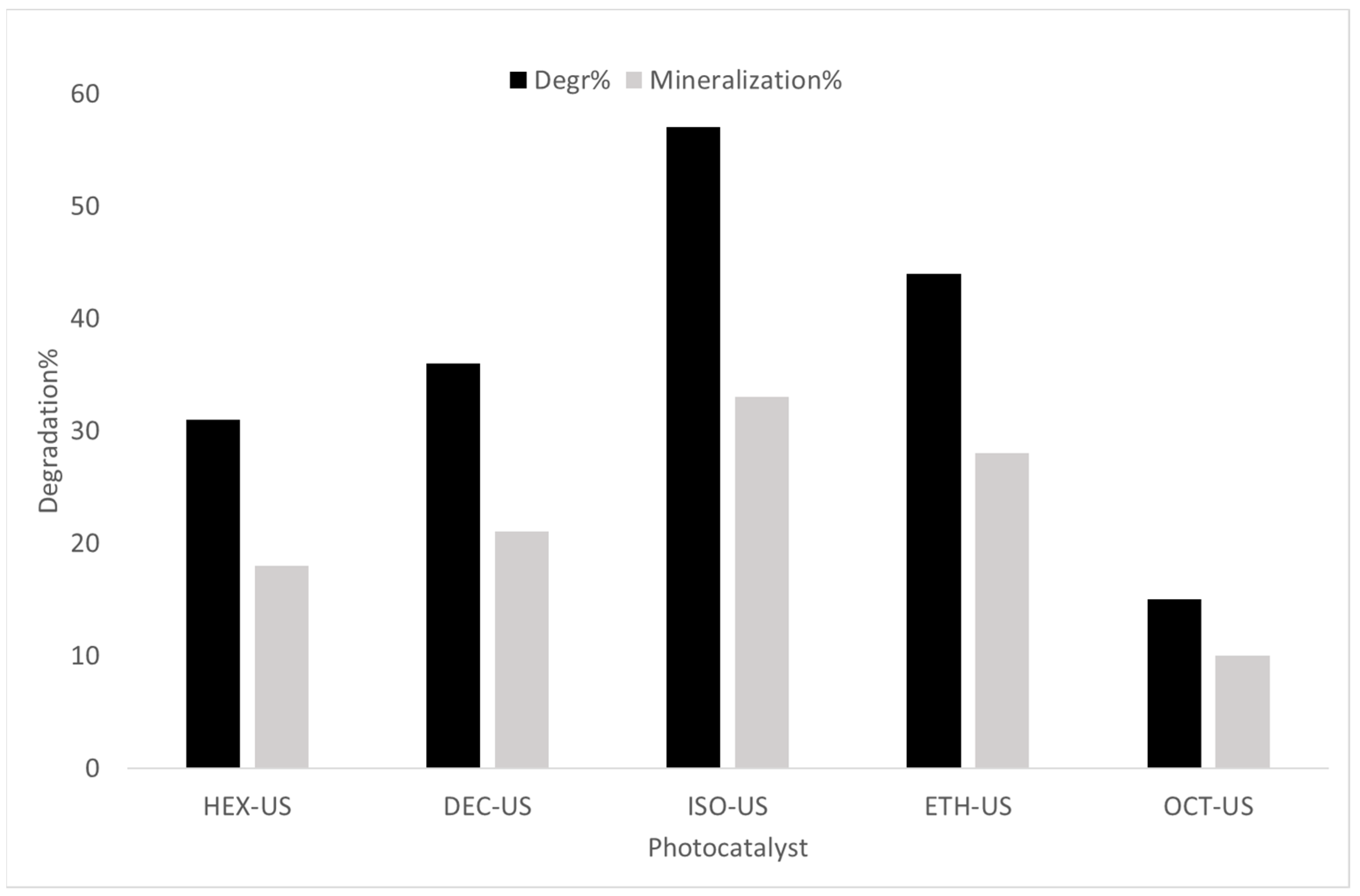
| Sample | Solvent | US | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Phase Composition * A = Anatase B = Brookite R = Rutile | Mean Crystallite Size * (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P25 | - | - | 68 | A(75(2)%)/R(25(2)%) | 25(2) |
| HEX-US | Hexane | On | 78 | A(81(1)%)/B(19(1)%) | 24(2) |
| HEX | Hexane | Off | 75 | A(83(2)%)/B(17(2)%) | 28(2) |
| DEC-US | Decane | On | 68 | A(69(1)%)/B(31(1)%) | 29(3) |
| DEC | Decane | Off | 63 | A(57(1)%)/B(43(1)%) | 19(1) |
| ISO-US | Isopropanol | On | 54 | A(100%) | 27(2) |
| ISO | Isopropanol | Off | 45 | A(100%) | 22(1) |
| ETH-US | Ethanol | On | 60 | A(100%) | 32(2) |
| ETH | Ethanol | Off | 41 | A(100%) | 19(1) |
| OCT-US | 1-Octanol | On | 7 | A(100%) | 27(2) |
| OCT | 1-Octanol | Off | 6 | A(100%) | 27(2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Michele, A.; Sassi, P.; Vivani, R.; Minguzzi, A.; Prati, L.; Pirola, C. Role of the Solvent and Ultrasound Irradiation in the Preparation of TiO2 for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Water. Catalysts 2024, 14, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14120910
Di Michele A, Sassi P, Vivani R, Minguzzi A, Prati L, Pirola C. Role of the Solvent and Ultrasound Irradiation in the Preparation of TiO2 for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Water. Catalysts. 2024; 14(12):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14120910
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Michele, Alessandro, Paola Sassi, Riccardo Vivani, Alessandro Minguzzi, Laura Prati, and Carlo Pirola. 2024. "Role of the Solvent and Ultrasound Irradiation in the Preparation of TiO2 for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Water" Catalysts 14, no. 12: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14120910
APA StyleDi Michele, A., Sassi, P., Vivani, R., Minguzzi, A., Prati, L., & Pirola, C. (2024). Role of the Solvent and Ultrasound Irradiation in the Preparation of TiO2 for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Water. Catalysts, 14(12), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14120910










