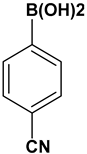
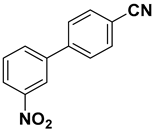
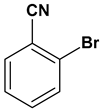
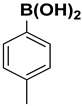
Abstract
A nanocatalyst comprising ultra-small palladium nanoparticles supported on nanodiamonds (ultra-small Pd/rNDs) was fabricated via a reduction of palladium (II) salt on oxidized nanodiamond. The prepared catalyst was characterized using XRD, XPS, ICP-MS, AAS, and TEM/HRTEM techniques, including STEM-EDS chemical mapping, which revealed that the modified material is a combination of reduced nanodiamond decorated with palladium nanoparticles. The as-prepared and well-characterized ultra-small Pd supported on rNDs displayed superb catalytic activity for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions at low temperature without any toxic solvents, to obtain the respective products in good-to-excellent yields (75–98%). The catalyst was easily separated from the reaction solution and was reused four times without loss of catalytic activity or chemical stability.
1. Introduction
Over the last thirty years, cross-coupling reactions mediated by palladium named after Suzuki, Heck, Negishi, Miyaura, Kumada, Stille, Mizoroki, and Sonogashira have transformed synthetic organic chemistry from a sequential pattern of slow, consecutive reaction steps with protected substrates to the parallel production of vital precursors which are linked jointly at a later stage in the procedure [1,2]. This is achievable because, in addition to their broad adaptability, these reactions are typically tolerant of the existence of functional groups in the coupling partners, avoiding the need for tedious procedures to protect and deprotect functional groups in the reagents. A homogeneous Pd catalyst, in general, facilitates the reaction between different carbon nucleophiles and a less reactive organic electrophile, usually aryl halides [3]. However, homogeneous cross-coupling processes have significant drawbacks, including poor reusability of the costly catalyst, and contamination of palladium in the end product [4]. Removing palladium residual from a pharmaceutical material in order to reduce its amount to the maximum accepted concentration limit requires a time-consuming and expensive purifying process [5]. Effective heterogenization of the palladium catalytic species is obviously needed to produce selective and reusable solid catalysts. This is necessary to avoid or limit product contamination that results from using costly, non-reusable homogeneous Pd catalysts and their undesirable propensity to persist in the end products.
As a synthetic approach, transition metal-catalysis is important in the development of industrial reactions, particularly in the synthesis of fine chemicals. One of the most beneficial reactions in the organic synthesis, along with double bond hydrogenation, is the catalytic creation of C-C bonds. Pd is the preferred metal for these processes, and since the 1970s, numerous homogeneous catalytic systems based on Pd (II) or Pd (0) have been explored, turning Pd into a crucial tool for complete synthesis and organic transformations [6,7]. As a result, industrial interest in Pd-catalyzed C-C bond formation has increased recently, leading to the issuance of several patents [8].
A new trend in heterogeneous catalysis is the modification of a neutral substrate with an active catalytic center to observe new possible materials with high catalytic performance [9]. Different forms of nanocarbon materials (fullerenes, nanotubes, nanodiamonds (NDs) and graphene) deliver the possibility to combine functions of ligand and substrate [10,11,12,13].
Carbon–carbon bond forming reactions, including Heck, Suzuki, Sonogashira, and many others, have rapidly become one of the most effective tools in organic synthesis for the assembly of highly-functionalized molecules [14,15,16,17,18,19]. These organic reactions are generally performed under homogeneous conditions, which involve ligands to increase the catalyst’s stability and range of reactivity [20,21]. Homogeneous catalysis in cross-coupling reaction shows many disadvantages in large scale industrial and pharmaceutical synthesis due to low reusability issues, possible contamination of metal components in the products of the reaction, and complexity in catalyst separation from the reaction mixture [5,22,23]. To overcome these issues, a promising solution is to use solid support for metal deposition to employ an efficient catalyst providing unique stability, reactivity, and recyclability [24,25,26].
Cross-coupling reactions are extremely significant transformations with numerous applications, including pharmaceutical synthesis and medicinal chemistry [27,28]. The Suzuki–Miyaura reaction is the most commonly used cross-coupling reaction in industry [29,30]. In the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction, organic electrophiles including triflates, aryl, and alkenyl or alkynyl halides are combined with organoboron compounds in the presence of a base [31]. Akira Suzuki and co-workers first reported the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction in 1979, and it is now among the most extensively utilized cross-coupling reactions for the synthesis of biphenyls because it is scalable and has high functional group tolerance for application in industrial processes [29,32]. Most of the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling processes use palladium catalysts, which are extremely reactive but costly due to palladium scarcity [15,21]. Palladium salts are more expensive, and natural reserves will ultimately run out because palladium is a non-abundant platinum group metal [33]. Palladium content should ideally be recovered at the end of the reaction to improve the sustainability and environmental friendliness of palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling processes [34]. To reduce the high costs, extensive research has been conducted on strategies for recovering palladium content from used catalysts [35]. Palladium-catalyzed processes may become more sustainable and “greener” with the use of catalyst recycling techniques [36]. Recycling palladium catalysts is highly desirable since it allows for the recovery and reuse of “active” Pd species. Moreover, separate “heterogeneous” and immobilized Suzuki catalysts have been reported in earlier research [37].
To date, numerous studies have been undertaken to develop new nanocatalysts for organic coupling reactions in which supports are based on polymers [38], cellulose [39,40], zeolites [41], inorganic oxides [42,43,44], and activated carbons [45,46]. Additionally, in recent years, carbon composites such as graphene [47,48,49], nanotubes [50,51], and NDs [52,53,54,55] have attracted attention due to their specific properties for advanced catalytic applications, especially their good thermal stability and high surface area. Due to their high surface area, nanosized particles, high chemical stability, different carbonyl functional groups, unsaturated bonds on their surface, and superhardness, diamond nanoparticles (NDs) are intriguing candidates for numerous applications. In particular, they have attracted a lot of attention as a promising catalyst material [55,56]. The NDs as a unit contain diamond nanocrystal 4–5 nm in diameter and possess an onion-like carbon shape with many functional groups [57,58]. Recently, many interesting research works have been published that show the important role of NDs in catalysis fields [59,60].
Notably, NDs have been found as a catalyst in a variety of gas and liquid phase reactions, where NDs have been used as a catalyst with or without supported metal [61]. In this context, metal deposition on NDs significantly improves catalytical activity and provides other promising values for these materials. The use of NDs as a heterogeneous catalyst is infrequent in comparison with other carbon materials (graphene, nanotubes, carbon dots etc.) [62,63]. Consequently, nanodiamond supported metal nanoparticles including platinum, palladium, nickel, iron, copper, and gold have been described. These catalysts exhibited high catalytic activity in oxidative dehydrogenation [64,65], nitrobenzene reduction [66], aldol condensation [67], dehydration of alcohols [68], and hydrochlorination reactions [69,70].
Nanodiamond supported Palladium nanoparticles demonstrated promising catalytic activity in several important reactions, such as a hydrogenation deamination [55], hydrogenation [71], C=C and C≡C bonds, and hydroamination [72,73], where metal or surface groups perform important role as active sites of reactions. A detailed study of the literature shows that NDs are highly suitable as a robust support for the deposition of transition metal nanoparticles [74]. NDs have the ability to restrict agglomeration on the surface, with uniform dispersion of particles even via high temperature (600 °C) hydrogen reduction processes [75], and demonstrate high activity due to surface arrangement, and the nearly absolute absence of micropores [76,77].
Based on our continuing study examining carbon materials as substrates for chemical transformations, especially nanodiamond as a support with excellent properties, we describe the preparation of Pd/rNDs based on palladium nanoparticles (0) on oxidized nanodiamond and its superior catalytic activity in the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of aryl halide under benign conditions. This catalytic technique is an effective multistep synthetic processes utilizing toxic and complex compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
Typically, in the synthesis of Pd/rNDs, the nanodiamond support was first oxidized, and Pd nanoparticles were then immobilized via a reduction using PdCl2 salt. The as-prepared Pd/rNDs catalyst’s structural and morphological nature were investigated using several characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), microscopic techniques including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and high-angle annular dark-field scanning electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). (See SI for details of techniques).
Figure 1 displays the XRD pattern of a Pd/rND composite compared with a cubic XRD pattern of basic nanodiamond corresponding to the crystal planes of (111), (220), and (311). Pd NPs dispersed on NDs show other diffraction peaks at 2θ = 46.9°, 54.8°, 81.1°, and 99.4° assigned to (111), (200), (220), and (311) crystal planes of Pd [78].
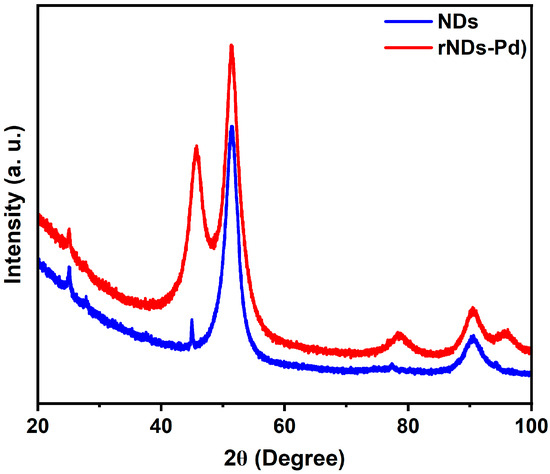
Figure 1.
XRD analysis of NDs support and Pd/rNDs.
As shown in the wide-scan XPS spectra of Pd/rNDs in Figure 2a, we can observe sharp peaks corresponding to carbon and oxygen. Notably, an oxidized and reduced nanodiamond are compared in Figure 2b,c, which show the sp2 and sp3 ratio of C-C bonds of nanodiamond, and Figure 2c displays the peak of O=C-O at 288.3 eV. Figure 2d shows the 3d line of Pd0 and PdO [79,80,81]. XPS data clearly indicate the presence of Pd0, with characteristic peaks at 334.42 and 339.69 eV, and for PdO at 336.67 and 341.93 eV. The Pd3d binding energy for pure Pd is approximately 334.4. When Pd is oxidized, the Pd3d moves from 335.42 to 336.67 eV; such an upward shift of more than 1 eV has also been found elsewhere [79,82]. The relative intensities of the Pd 3d lines indicate that approximately 83% of Pd corresponds to Pd0 and 17% to PdO. The majority of Pd interacts with the surface of NDs in the Pd0 form. The Pd0 species are obtained during the reduction of Pd (II) to Pd0 [81,83].
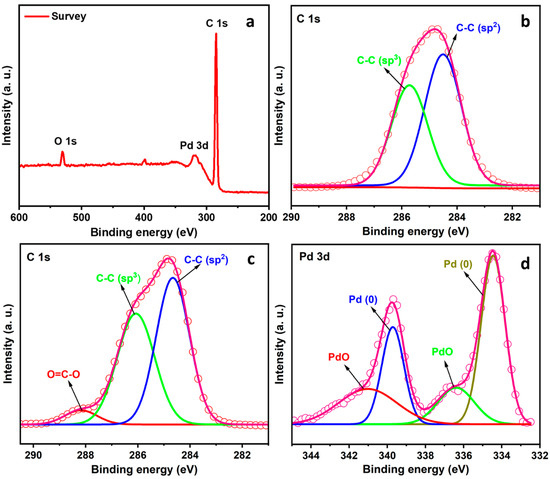
Figure 2.
XPS spectra: (a) Survey spectrum of Pd/rNDs; (b) C 1s spectrum of ND (hollow nanodiamond as support); (c) C 1s spectrum of Pd/rNDs; and (d) Pd 3d spectrum.
TEM/HRTEM reveals that Pd NPs are homogenously dispersed on the nanodiamond surface (Figure 3a–c). Spherical nanodiamond nanoparticles are small, <10 nm, and the size of Pd NPs was found to be 5.3 ± 0.6 nm, homogenously distributed on the nanodiamond surface without any agglomeration. The high-resolution image of the Pd/rNDs nanocomposite confirmed the oriented lattice of Pd NPs (Figure 3c). Along with TEM analysis, scanning electron microscopy with EDS analysis confirmed the structure, morphology, and elemental composition (see Figure S1). The HAADF-STEM analysis confirmed the presence of Pd, C, and O (Figure 3d–h). Pd NPs dominate in the form of Pd0 on the surface; globular nanodiamond nanoparticles were also confirmed via XRD, TEM, HRTEM-HAADF, and XPS.
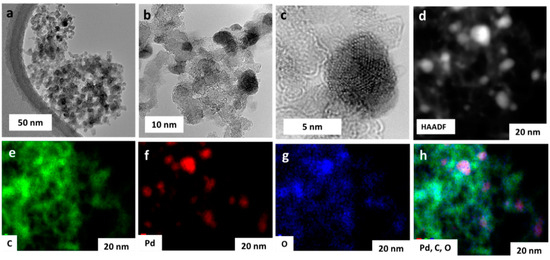
Figure 3.
(a–c) TEM/HRTEM images of Pd/rNDs with gradual details of nanocomposite showing palladium nanoparticles; (d) HAADF-STEM image and corresponding EDS elemental mapping for (e) carbon, (f) palladium, (g) oxygen, and (h) carbon, palladium, and oxygen overlap.
The wt% palladium in Pd/rNDs nanocomposite was confirmed via ICP-MS, and the palladium content was valued as 6.5 wt%.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Diamond (nanopowder, <10 nm particle size) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich modified via PdCl2 (Reagent Plus) by Sigma-Aldrich. In synthesis, acids were used (H2SO4: HNO3, sulphuric acid, 96% G.R. Lach: ner; nitric acid, 65% + pure, Penta, HCl, 35% G.R., Lach: ner). Acetone was purchased from Penta. Reducing agents (sodium borohydride and hydrazine) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louise, USA. All other chemicals and solvents (aryl halide, potassium carbonate, boronic acid) used for organic reactions were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and were used without any further purifications.
3.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Oxidized NDs
A sample of 45 mg of diamond (commercially available nanopowder, 636428-1g, Sigma-Aldrich) was suspended in a mixture of acids (H2SO4 (96%): HNO3 (65%), 4:1, 20 mL). This suspension was sonicated for 15 min and stirred for 24 h at 130 °C. The resulting oxidized nanodiamond was centrifuged in glass vessels and washed many times with DI water and acetone. The obtained product was dried at 60 °C in a vacuum oven.
3.3. Synthesis of rNDs/Palladium Composite
A 50 mg sample of rNDs was added to 20 mL of distilled water and sonicated for 20 min, and then 1.5 mL of an aqueous solution of PdCl2 (10 mg. mL−1) was added. After 30 min of stirring the mixture, 3 mL of an aqueous NaBH4 solution (15 mg. mL−1) was added dropwise. The mixture was vigorously stirred for 30 min. The resulting solution of composite was centrifuged and washed with water and acetone and dried in vacuum.
3.4. Preparation of Palladium Nanoparticles
Pd/NPs were synthesized via the reduction of Pd ions using hydrazine hydrate. The palladium precursor (H2PdCl4) was synthesized by adding 0.25 mmol of PdCl2, 3 mL of 0.2 M HCl, and diluting to 125 mL with DI water. A 15 mL solution of Pd NPs was synthesized via the reduction of H2PdCl4 (2 mM, 4.2 mL), using hydrazine hydrate solution as a reducing agent (10 mM, 9.6 mL) in presence of polypyrrolidone (PVP, 1 wt%, 1.2 mL). The resulting reaction mixture was then magnetically stirred for 1.5 h to obtain a final sample of Pd NPs. Following that, the catalyst was filtered from the solution, washed with ethanol and distilled water in order to remove the remaining NaBH4, and dried at 70 °C under vacuum overnight.
3.5. General Procedure for Suzuki–Miyaura Reaction of Aryl Halide and Boronic Acid
A reaction mixture containing aryl halide (0.5 mmol), boronic acid (0.6 mmol), and potassium carbonate (2 mmol) in solvent (water; water and ethanol mixture, 1:1; 5 mL) was degassed for 10 min with N2, and the Pd/rNDs composite was added to the reaction mixture under a reflux system. The reaction mixture was stirred continually at 100 °C for an adequate reaction time (Table 1). Thin layer chromatography (TLC; silica gel; n-hexane/ethyl acetate) was used to monitor the progress of the reaction. After the desired time, the volatiles were extracted under low pressure and the residual material was analyzed via gas chromatography and compared with standard samples.

Table 1.
Optimization study of the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction between iodobenzene and phenyl boronic acid catalyzed via Pd/rNDs.
4. Catalytic Activity
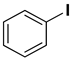
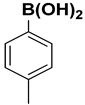
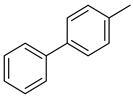
The catalytic activity of a Pd/rNDs nanocomposite for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction was investigated. Initially, 1-iodo-benzene and phenylboronic acid were chosen as model starting reactants in the presence of a base, K2CO3, and solvent system, H2O: EtOH, at 100 °C (Table 1). After optimizing the reaction conditions, the range of catalytic activity was investigated for various substituted aryl halides and boronic acid.
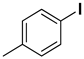
At first, the optimizing conditions show that the reaction without a catalyst or with a non-metal nanodiamond did not proceed (Table 1). The ideal amount for quantitative conversion of 1-iodo-4-methylbenzene was revealed as 0.025 mmol of Pd/rNDs catalyst (Table 1, entry 7). The catalytic reaction, performed under described conditions with only palladium NPs, demonstrated comparatively lower conversion (Table 1, entry 5). These results indicate the importance of NDs as a substrate for palladium NPs deposition.
A detailed study of further substrate range was explored for substituted iodobenzene, bromobenzene, and fluorobenzene with phenylboronic acid to obtain excellent yields of corresponding products (Table 2). It was shown that, in comparison to other functional groups of substrates such as methyl- and methoxy- (Table 2, entries 2–6), electron-withdrawing groups like nitro- and hydroxy- (Table 2, entries 7–11) showed slightly lower yields and had longer reaction times. A high yield was obtained from all substrates with an electron-donating and -withdrawing group at various ortho and para positions. Aryl bromides interacted well with p-tolylboronic acid, resulting in an excellent yield of the desired product. All results are compared with other heterogeneous catalysts (nanocomposites) applied in Suzuki–Miyaura reactions (Table S1).

Table 2.
The catalytic activity of Pd/rNDs in the Suzuki reaction between aryl halides and boronic acid.
4.1. Recyclability Studies
After completion of the model catalytic reaction (phenyl iodide (0.5 mmol), phenylboronic acid (0.6 mmol), K2CO3 (2 mmol), 10 mg Pd/rNDs, water: EtOH (1:1; 5 mL), 100 °C) the catalyst was centrifuged and further washed with ethanol four times to eliminate organics and dried at 50 °C under vacuum. The well-dried catalyst was furthermore included in the next cycle of the reusability study.
4.2. Reusability of the Pd/rNDs Catalyst
The reusability of a nanocatalyst is the main factor for its effective and environmentally friendly value in heterogeneous catalysis. In general, for Pd and Pt containing catalytic reactions, a special condition (mainly nitrogen atmosphere) during separation is needed to avoid the danger of fire. On the other hand, in case of Pd/rNDs, we observed that the process of catalysis was highly stable, and it was possible to separate through centrifugation, could be dried and applied multiple times without losing catalytic activity. Figure 4 shows that the Pd/rNDs nanocatalyst could be recycled up to five times without losing its selectivity during the tested catalytic reaction mentioned in the optimizing section. Additionally, TEM images (Figure S2b) of the recycled nanocatalyst revealed that the stability of the composition and morphology of palladium NPs on a nanodiamond support remained stable after five cycles. The AAS analysis showed only minimal (less than 0.01 mmol) palladium leaching.
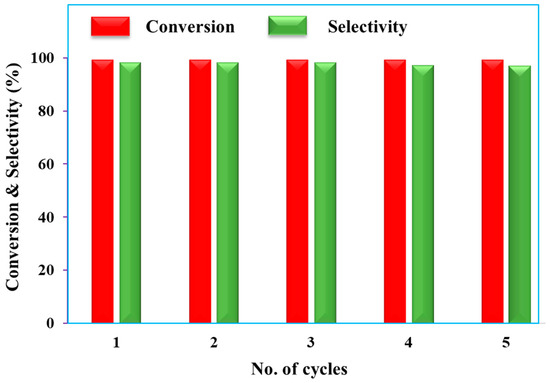
Figure 4.
Reusability study of Pd/rNDs nanocatalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling reaction.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we effectively synthesized ultra-small Pd nanoparticles (~5 nm) supported on nanodiamond, applicable for organic transformations such as Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions, for excellent yields with low catalyst loading. The demonstrated system displays various superior properties in contrast to other methods, including high yield, selectivity, short reaction time, and ideal recyclability of the catalyst: up to five cycles without losing efficiency or selectivity. The reactions were carried out in a very simple manner at ambient conditions, a low reaction temperature, without any toxic solvents, and no inert atmosphere was needed; as well, this methodology is likely to find applications in other important organic transformations. This environmentally conscious procedure facilitates easy reusability and uses a benign reaction system which could lead to new future exploration in heterogeneous C-C bond catalysis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal14010053/s1, Figure S1: SEM images with EDS mapping of (a) oxidized nanodiamond and (b) catalyst Pd/rNDs; Figure S2: TEM analysis of (a) fresh prepared Pd/rNDs catalyst and (b) Pd/rNDs catalyst after five cycles of Suzuki reaction; Table S1: Comparison of selected heterogenous Pd catalysts used for Suzuki reactions [84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93].
Author Contributions
Data curation, R.P. (Robert Prucek), A.B., I.R.W. and L.K.; formal analysis, R.P. (Radka Pocklanova), R.P. (Robert Prucek), A.B., A.P., I.R.W. and R.G.K.; investigation, A.P., L.K. and M.B.G.; methodology, R.P. (Radka Pocklanova) and R.P. (Robert Prucek); project administration, R.P. (Radka Pocklanova); supervision, M.B.G.; writing—original draft, R.P. (Radka Pocklanova); writing—review and editing, M.B.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work is also funded by the Palacky University Institutional support and IGA grant (Project No. IGA-PrF-2023-029). M.B.G. gratefully acknowledges the DST-SERB Core Research Grant (CRG/2021/001738) for funding support.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jana Stráská and Klara Čépe for microscopic analyses, and Josef Kašlík and Martin Petr for XRD and XPS spectroscopic determinations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Barnard, B.C. Palladium-catalysed C-C coupling: Then and now. Platin. Met. Rev. 2008, 52, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, M.; Pandarus, V.; Ciriminna, R.; Béland, F.; Demma Carà, P. Heterogeneous versus homogeneous palladium catalysts for cross-coupling reactions. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-F.; Anbarasan, P.; Neumann, H.; Beller, M. From noble metal to nobel prize: Palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions as key methods in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9047–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhi Maureen, A. Suzuki-coupling chemistry takes hold in commercial practice, from small-scale synthesis of screening compounds to industrial production of active ingredients. Chem. Eng. News 2004, 82, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C.E.; Prasad, K. The art of meeting palladium specifications in active pharmaceutical ingredients produced by Pd-catalyzed reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Bulger, P.G.; Sarlah, D. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions in total synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4442–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, C.M.; Kwong, F.Y. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of aryl mesylates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, J.-P.; Mignani, G. Selected patented cross-coupling reaction technologies. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2651–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Liu, Q.; Tang, D.; Li, X.; Bi, J.; Gao, D. Nanodiamond supported Ru nanoparticles as an effective catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Z.; Schlögl, R.; Su, D. Stabilization of palladium nanoparticles on nanodiamond-graphene core-shell supports for CO oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15823–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Truong-Phuoc, L.; Liu, Y.; Duong-Viet, C.; Nhut, J.-M.; Nguyen-Dinh, L.; Granger, P.; Pham-Huu, C. Hierarchical carbon nanofibers/graphene composite containing nanodiamonds for direct dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene. Carbon 2016, 96, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodubtseva, E.V.; Vinogradov, M.G.; Turova, O.V.; Bumagin, N.A.; Rakov, E.G.; Sokolov, V.I. Palladium(0) supported on carbon nanotubes as an efficient catalyst of the C≡C bond hydrogenation. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubina, E.V.; Lokteva, E.S.; Erokhin, A.V.; Veligzhanin, A.A.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Likholobov, V.A.; Lunin, V.V. The role of metal-support interaction in catalytic activity of nanodiamond-supported nickel in selective phenylacetylene hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2016, 344, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamaki, A.R.; Lin, Y.; Woodberry, K.; Connell, J.W.; Gupton, B.F. Palladium nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes from solventless preparations: Versatile catalysts for ligand-free Suzuki cross coupling reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12909–12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Buchwald, S.L. Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions employing dialkylbiaryl phosphine ligands. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathi, A.K.; Gawande, M.B.; Pechousek, J.; Tucek, J.; Aparicio, C.; Petr, M.; Tomanec, O.; Krikavova, R.; Travnicek, Z.; Varma, R.S.; et al. Maghemite decorated with ultra-small palladium nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3-Pd): Applications in the heck-mizoroki olefination, Suzuki reaction and allylic oxidation of alkenes. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Dutta, S.; Sharma, S.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S.; Gawande, M.B. Fe3O4 (iron oxide)-supported nanocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and applications in coupling reactions. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3184–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Yadav, M.; Gaur, R.; Gupta, R.; Adholeya, A.; Gawande, M.B. Synthesis of iron oxide palladium nanoparticles and their catalytic applications for direct coupling of acyl chlorides with alkynes. ChemPlusChem 2016, 81, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Yadav, S.; Dutta, S.; Kale, H.B.; Warkad, I.R.; Zbořil, R.; Varma, R.S.; Gawande, M.B. Silver nanomaterials: Synthesis and (electro/photo) catalytic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11293–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.F. Palladium-catalyzed reactions of organic halides with olefins. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979, 12, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butters, M.; Catterick, D.; Craig, A.; Curzons, A.; Dale, D.; Gillmore, A.; Green, S.P.; Marziano, I.; Sherlock, J.-P.; White, W. Critical assessment of pharmaceutical processes-a rationale for changing the synthetic route. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3002–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, C.J.; Albaneze-Walker, J.; Leonard, W.R.; Biba, M.; DaSilva, J.; Henderson, D.; Laing, B.; Mathre, D.J.; Spencer, S.; Bu, X.; et al. Adsorbent screening for metal impurity removal in pharmaceutical process research. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2005, 9, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Vorobyeva, E.; Mitchell, S.; Fako, E.; Ortuño, M.A.; López, N.; Collins, S.M.; Midgley, P.A.; Richard, S.; Vilé, G.; et al. A heterogeneous single-atom palladium catalyst surpassing homogeneous systems for Suzuki coupling. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptal, V.B.; Saptal, M.V.; Mane, R.S.; Sasaki, T.; Bhanage, B.M. Amine-functionalized graphene oxide-stabilized Pd nanoparticles (Pd@APGO): A novel and efficient catalyst for the Suzuki and carbonylative Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Ao, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, H.; Zhou, L.; Suvorova, A.; Saunders, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, S. Surface-tailored nanodiamonds as excellent metal-free catalysts for organic oxidation. Carbon 2016, 103, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuloja, N.; Kylmälä, T.; Xu, Y.; Franzén, R. Synthesis of Xenbucin using Suzuki reaction catalyzed by Pd/C in water. Open Chem. 2008, 6, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.K.; Brar, A.; Li, G.; Findlater, M. Homogeneous and recyclable palladium catalysts: Application in Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. Organometallics 2023, 42, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, A. A new stereospecific cross-coupling by the palladium-catalyzed reaction of 1-alkenylboranes with 1-alkenyl or 1-alkynyl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3437–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, S.E.; Heidari, B.; Sedghi, R.; Varma, R.S. Recent advances in the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction using efficient catalysts in eco-friendly media. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A. Organoborates in new synthetic reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 1982, 15, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. Stereoselective synthesis of arylated (E)-alkenes by the reaction of alk-1-enylboranes with aryl halides in the presence of palladium catalyst. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 19, 866–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genkin, A.D.; Evstigneeva, T.L. Associations of platinum-group minerals of the Noril’sk copper-nickel sulfide ores. Econ. Geol. 1986, 81, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K. Chemistry: It’s not easy being green. Nature 2011, 469, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardis, F.L.; Grant, R.A.; Sherrington, D.C. A review of methods of separation of the platinum-group metals through their chloro-complexes. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 65, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, Á. Efficient, selective, and recyclable palladium catalysts in carbon-carbon coupling reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2251–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z. Diatomite-supported Pd nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for Heck and Suzuki reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7485–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kann, N. Recent applications of polymer supported organometallic catalysts in organic synthesis. Molecules 2010, 15, 6306–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhepe, P.L.; Fukuoka, A. Cellulose conversion under heterogeneous catalysis. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Hrapovic, S.; Majid, E.; Chong, J.H.; Luong, J.H.T. Catalysis using gold nanoparticles decorated on nanocrystalline cellulose. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djakovitch, L.; Koehler, K. Heck reaction catalyzed by Pd-modified zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5990–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Johnson, M.; Veinot, J.G.C. Iron/iron oxide nanoparticles: A versatile support for catalytic metals and their application in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. ChemComm 2010, 46, 2411–2413. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Ruthenium on chitosan: A recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for aqueous hydration of nitriles to amides. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hankari, S.; El Kadib, A.; Finiels, A.; Bouhaouss, A.; Moreau, J.J.; Crudden, C.M.; Brunel, D.; Hesemann, P. SBA-15-type organosilica with 4-mercapto-N,N-bis-(3-Si-propyl)butanamide for palladium scavenging and cross-coupling catalysis. Chemistry 2011, 17, 8984–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.-C.; Choi, J.; Nahm, K.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, P. One-step synthesis of carbon-supported Pd@Pt/C core-shell nanoparticles as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts and their enhanced activity and stability. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4038–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 46 Köhler, K.; Heidenreich, R.G.; Soomro, S.S.; Pröckl, S.S. Supported palladium catalysts for Suzuki reactions: Structure-property relationships, optimized reaction protocol and control of palladium leaching. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.; Siamaki, A.R.; Gupton, B.F.; El-Shall, M.S. Pd-partially reduced graphene oxide catalysts (Pd/PRGO): Laser synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on PRGO nanosheets for carbon-carbon cross coupling reactions. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Hajizadeh, Z.; Abbasi, H. Surface modification of graphene oxide by citric acid and its application as a heterogeneous nanocatalyst in organic condensation reaction. Carbon Lett. 2018, 27, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, A.; Kadam, R.G.; Tuček, J.; Sofer, Z.; Bouša, D.; Varma, R.S.; Gawande, M.B.; Zbořil, R. Fe(0)-Embedded thermally reduced graphene oxide as efficient nanocatalyst for reduction of nitro compounds to amines. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 382, 122469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.A.; Flanagan, K.A.; Hain, H. Suzuki coupling activity of an aqueous phase Pd nanoparticle dispersion and a carbon nanotube/Pd nanoparticle composite. Catal. Today 2009, 145, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gualdrón, D.A.; McKenzie, G.D.; Alvarado, J.F.J.; Balbuena, P.B. Dynamic evolution of supported metal nanocatalyst/carbon structure during single-walled carbon nanotube growth. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, A. Beyond the shine: Recent progress in applications of nanodiamond. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12571–12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Z. Sulfate surfactant assisted approach to fabricate sulphur-doped supported nanodiamond catalyst on carbon nanotube with unprecedented catalysis for ethylbenzene dehydrogenation. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, X.; Peng, M.; Jia, Z.; Xie, J.; Xiao, D.; Wen, X.; Wang, N.; et al. Anchoring Cu1 species over nanodiamond-graphene for semi-hydrogenation of acetylene. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Ding, Y.; Feng, Z.; Su, D. Palladium supported on nanodiamonds as an efficient catalyst for the hydrogenating deamination of benzonitrile and related compounds. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, A. Diamond nanoparticles: Jewels for chemistry and physics. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondon, N.; Raehm, L.; Charnay, C.; Boukherroub, R.; Durand, J.-O. Nanodiamonds for bioapplications, recent developments. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10878–10896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, G.; Zhao, L.; Bianco, A.; Komatsu, N. Chemical functionalization of nanodiamonds: Opportunities and challenges ahead. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17918–17929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, L.; Cazzanelli, M.; Orlandi, M.; Miotello, A. Nanodiamonds: Synthesis and application in sensing, catalysis, and the possible connection with some processes occurring in space. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Wang, Q.; Wen, G.; Su, D. Nanodiamonds for catalytic reactions. In Nanodiamonds; Chapter 18; Arnault, J.-C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 439–463. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Chu, P.K. Group IV nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and biological applications. Small 2010, 6, 2080–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiuk, E.V.; Basiuk, V.A. Green chemistry of carbon nanomaterials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 644–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Holmen, A.; Sui, Z.; Zhou, X. Carbon mediated catalysis: A review on oxidative dehydrogenation. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 824–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, D.S.; Blume, R.; Schlögl, R.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Gajović, A. Surface chemistry and catalytic reactivity of a nanodiamond in the steam-free dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8640–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obraztsova, I.I.; Eremenko, N.K.; Velyakina, Y.N. Reaction kinetics of nitrobenzene hydrogenation on a palladium catalyst supported on nanodiamonds. Kinet. Catal. 2008, 49, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.-W.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Cai, S.-J.; Cheng, C.-L.; Chen, C. Organic functionalization of ultradispersed nanodiamond: Synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8432–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Su, D. Fabrication of nitrogen-modified annealed nanodiamond with improved catalytic activity. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7823–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykov, P.A.; Magdalinova, N.A.; Gruzdev, M.S.; Lysenok, A.A.; Belkina, E.G.; Klyuev, M.V. Tetrachloromethane hydrodechlorination over palladium-containing nanodiamonds. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveritinova, E.A.; Zhitnev, Y.N.; Kulakova, I.I.; Cherkasov, N.; Maslakov, K.I.; Nesterova, E.A.; Ivanov, A.S.; Savilov, S.V.; Lunin, V.V. The role of structure and surface chemistry of carbon nanomaterials in catalytic conversion of 1,2-dichloroethane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turova, O.V.; Starodubtseva, E.V.; Vinogradov, M.G.; Sokolov, V.I.; Abramova, N.V.; Vul, A.Y.; Alexenskiy, A.E. Palladium supported on detonation nanodiamond as a highly effective catalyst of the C=C and C≡C bond hydrogenation. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalinova, N.A.; Klyuev, M.V.; Vershinin, N.N.; Efimov, O.N. Pt- and Pd-containing nanodiamonds in hydrogenation and hydroamination reactions. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, D.S.; Proskurnin, M.A.; Korobov, M.V. Elemental analysis of nanodiamonds by inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Carbon 2014, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, J.T.; Man, H.B.; Saha, B.; Ho, D.; Schatz, G.C. Understanding the surfaces of nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 17256–17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, O.S.; Nosova, L.V.; Ryndin, Y.A. Formation and properties of dispersed Pd particles over graphite and diamond. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Guczi, L., Solymosi, F., Tétényi, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 75, pp. 837–847. [Google Scholar]
- Piña-Salazar, E.-Z.; Kukobat, R.; Futamura, R.; Hayashi, T.; Toshio, S.; Ōsawa, E.; Kaneko, K. Water-selective adsorption sites on detonation nanodiamonds. Carbon 2018, 139, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piña-Salazar, E.-Z.; Sakai, T.; Ōsawa, E.; Futamura, R.; Kaneko, K. Unusual hygroscopic nature of nanodiamonds in comparison with well-known porous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 549, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylet, A.; Marécot, P.; Duprez, D.; Castellazzi, P.; Groppi, G.; Forzatti, P. In situ Raman and in situ XRD analysis of PdO reduction and Pd° oxidation supported on γ-Al2O3 catalyst under different atmospheres. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4607–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, M.; Berthet, A.; Bertolini, J.C. XPS, AES and auger parameter of Pd and PdO. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1999, 104, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, M.A.; Moncea, O.; Poinsot, D.; Keskes, M.; Domenichini, B.; Heintz, O.; Chassagnon, R.; Herbst, F.; Carlson, R.M.K.; Dahl, J.E.P.; et al. Nanodiamond-palladium core-shell organohybrid synthesis: A mild vapor-phase procedure enabling nanolayering metal onto functionalized sp3-carbon. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burueva, D.B.; Sviyazov, S.V.; Huang, F.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Bukhtiyarov, A.V.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I.; Liu, H.; Koptyug, I.V. Pd on nanodiamond/graphene in hydrogenation of propyne with parahydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 27221–27229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Gossmann, A.F.; Winograd, N. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of palladium oxides and the palladium-oxygen electrode. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csákai, Z.; Skoda-Földes, R.; Kollár, L. NMR investigation of Pd(II)–Pd(0) reduction in the presence of mono- and ditertiary phosphines. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 286, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Lin, A.; Adly, M.S.; El-Shall, M.S. Enhancement of the catalytic activity of Pd nanoparticles in Suzuki coupling by partial functionalization of the reduced graphene oxide support with p-phenylenediamine and benzidine. J. Catal. 2020, 385, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Maddila, S.; Yalagala, K.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. Organo functionalized graphene with Pd nanoparticles and its excellent catalytic activity for Suzuki coupling reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 505, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; He, J. Facile deposition of Pd nanoparticles on carbon nanotube microparticles and their catalytic activity for Suzuki coupling reactions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8172–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Chokkalingam, A.; Cha, W.S.; Lakhi, K.S.; Su, X.; Lawrence, G.; Vinu, A. Pd nanoparticles embedded in mesoporous carbon: A highly efficient catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. Catal. Today 2015, 243, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, S.; Mahanta, A.; Kakati, D.; Rashid, M.H. Green chemical synthesis of Pd nanoparticles for use as efficient catalyst in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.; Das, P. Phosphine-stabilized Pd nanoparticles supported on silica as a highly active catalyst for the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenegger, G.J.; Maier, M.; Hackl, M.; Khinast, J.G.; Gössler, W.; Griesser, T.; Kumar, V.S.P.; Gruber-Woelfler, H.; Deshpande, P.A. Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions using novel metal oxide supported ionic palladium catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2017, 426, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Di, J.-Q.; Zhao, A.-D.; Zhang, Z.-H. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of palladium supported on pyridine-based covalent organic polymer for Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, D.; Sekar, G. Palladium nanoparticles stabilized by metal-carbon covalent bond: An efficient and reusable nanocatalyst in cross-coupling reactions. Catal. Commun. 2013, 39, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Sarkar, A. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on chemically modified silica gel: Efficient heterogeneous catalyst for Suzuki, Stille and Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).