Treatment of Textile Wastewater by a Novel Clay/TiO2/ZnO-Based Catalyst, Applying a Synergic Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
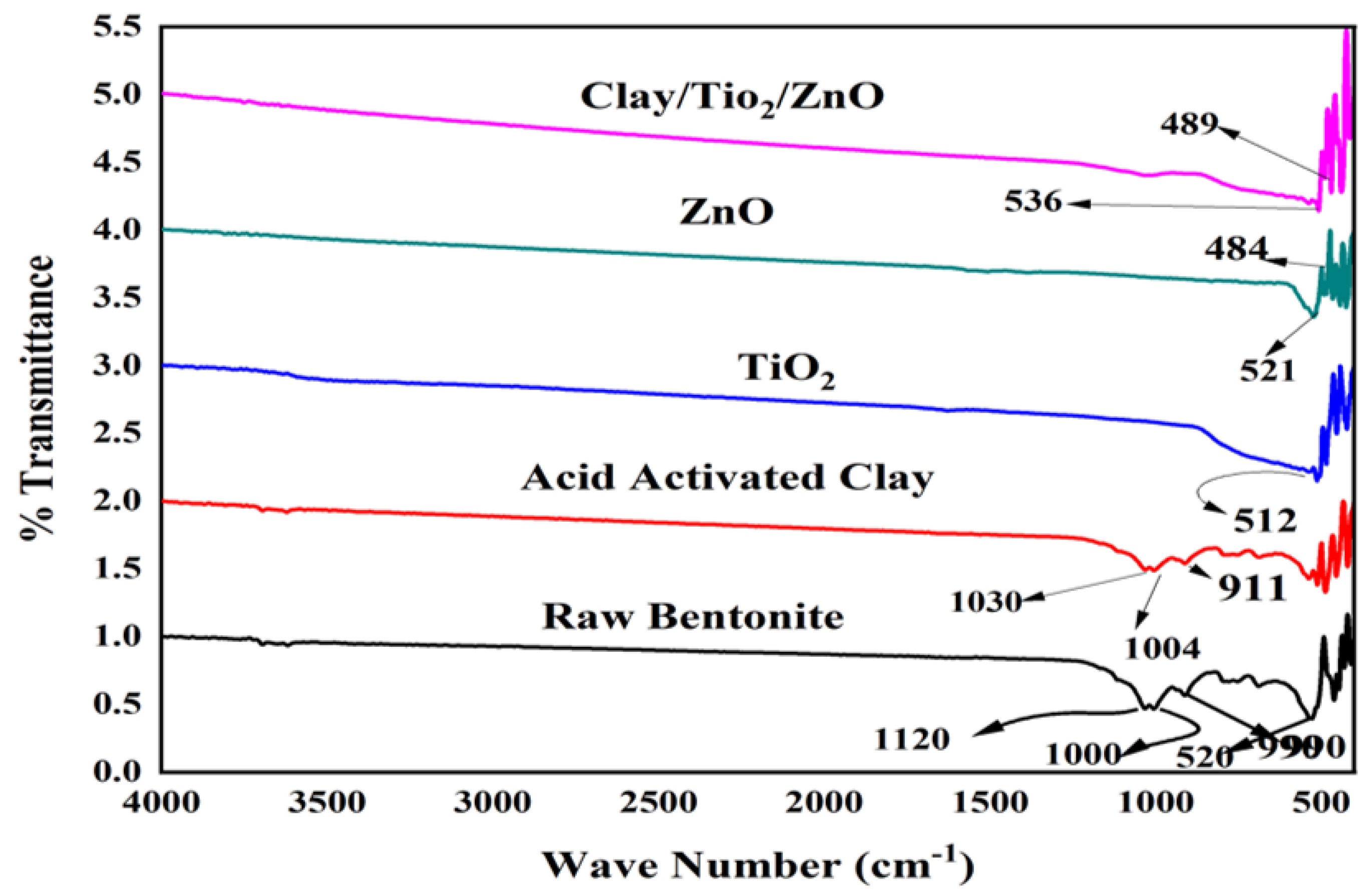
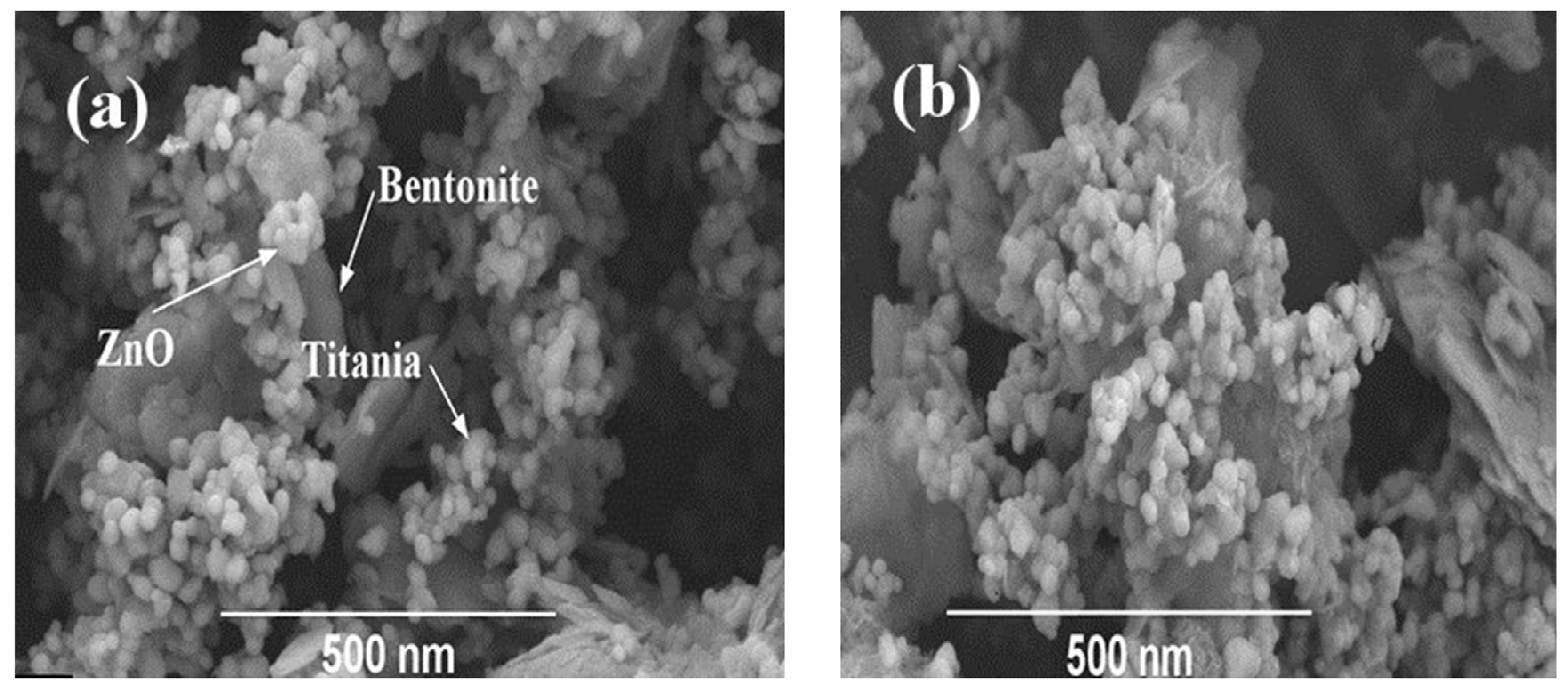
2.1. Characterization
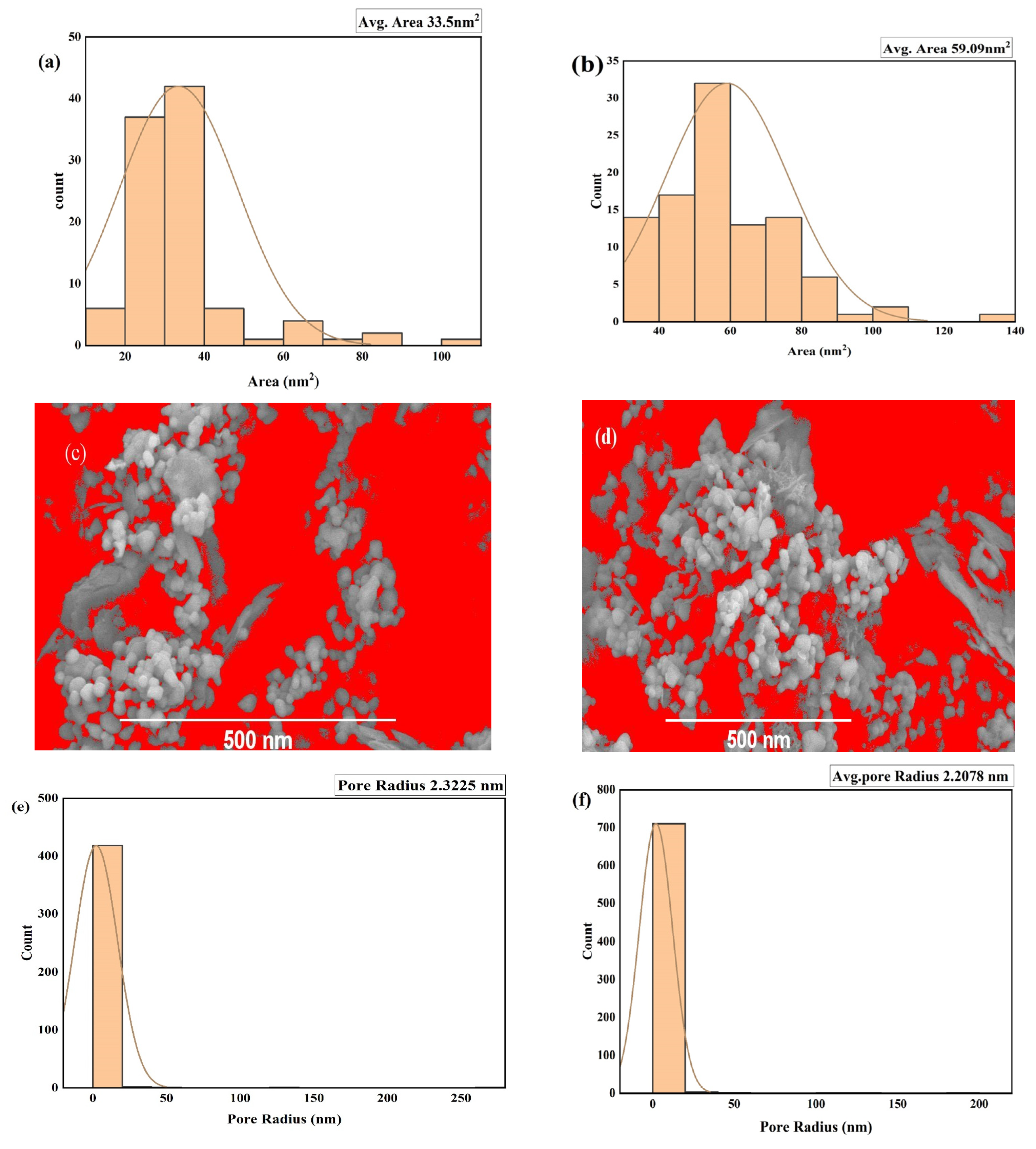
2.2. Surface Area, Porosity, and Pore-Size Distribution
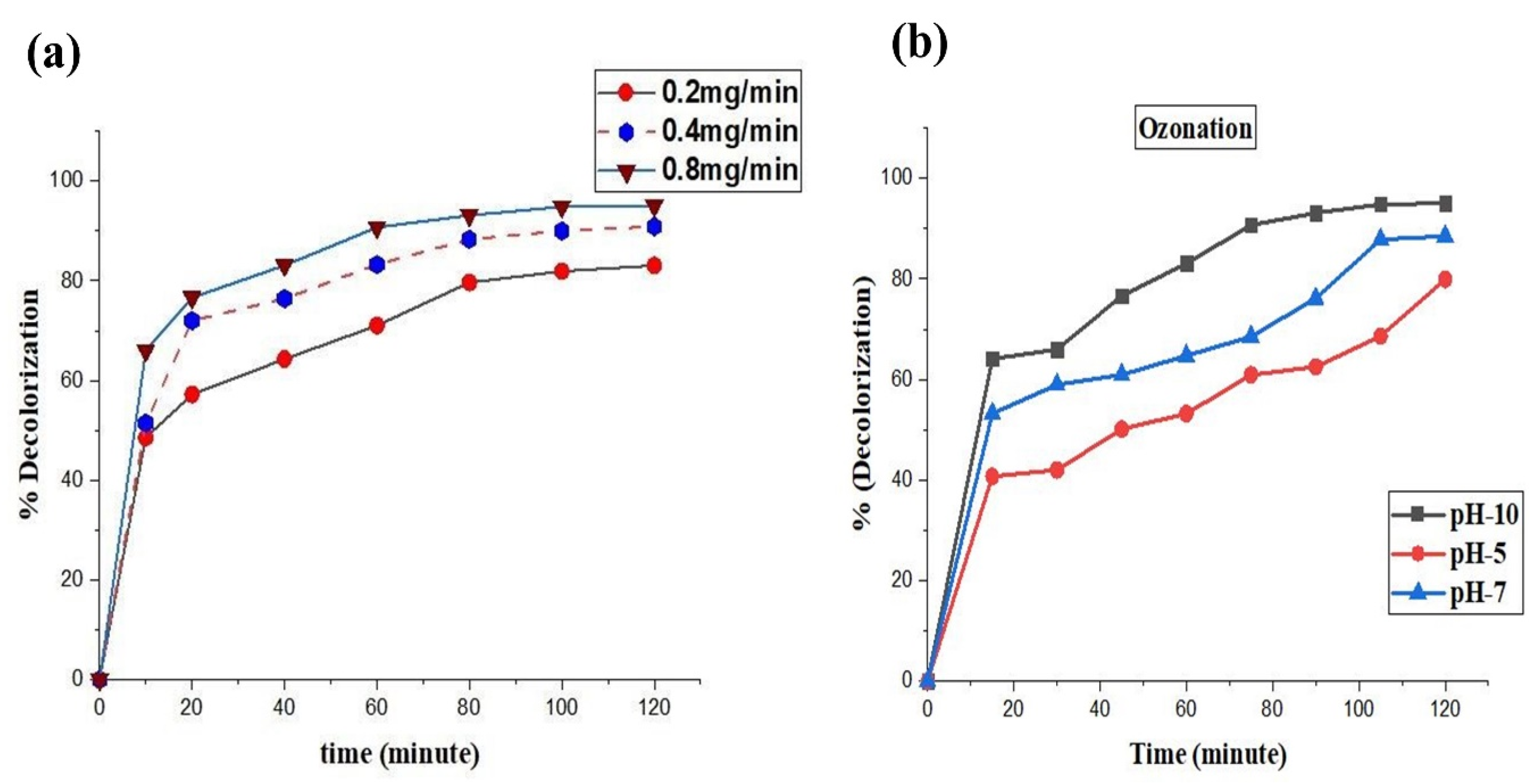
2.3. Ozone Dose Optimization
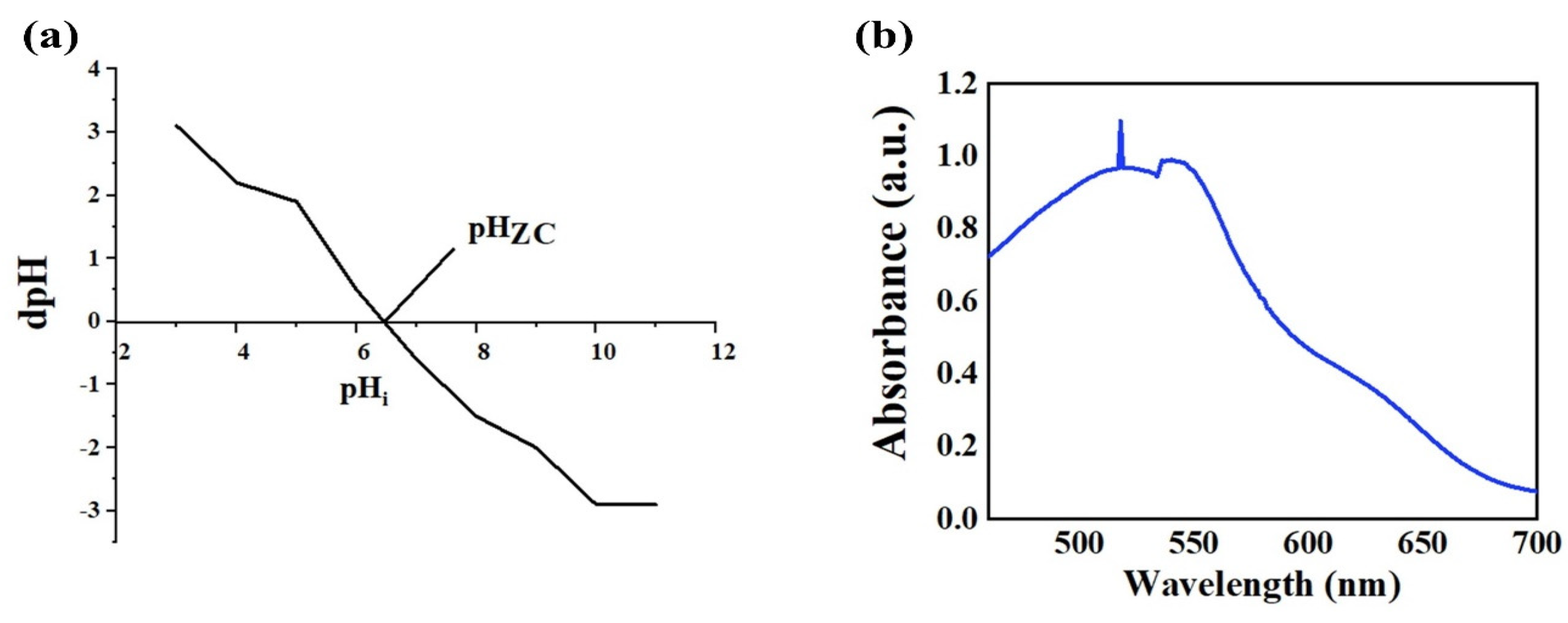
2.4. pH Optimization
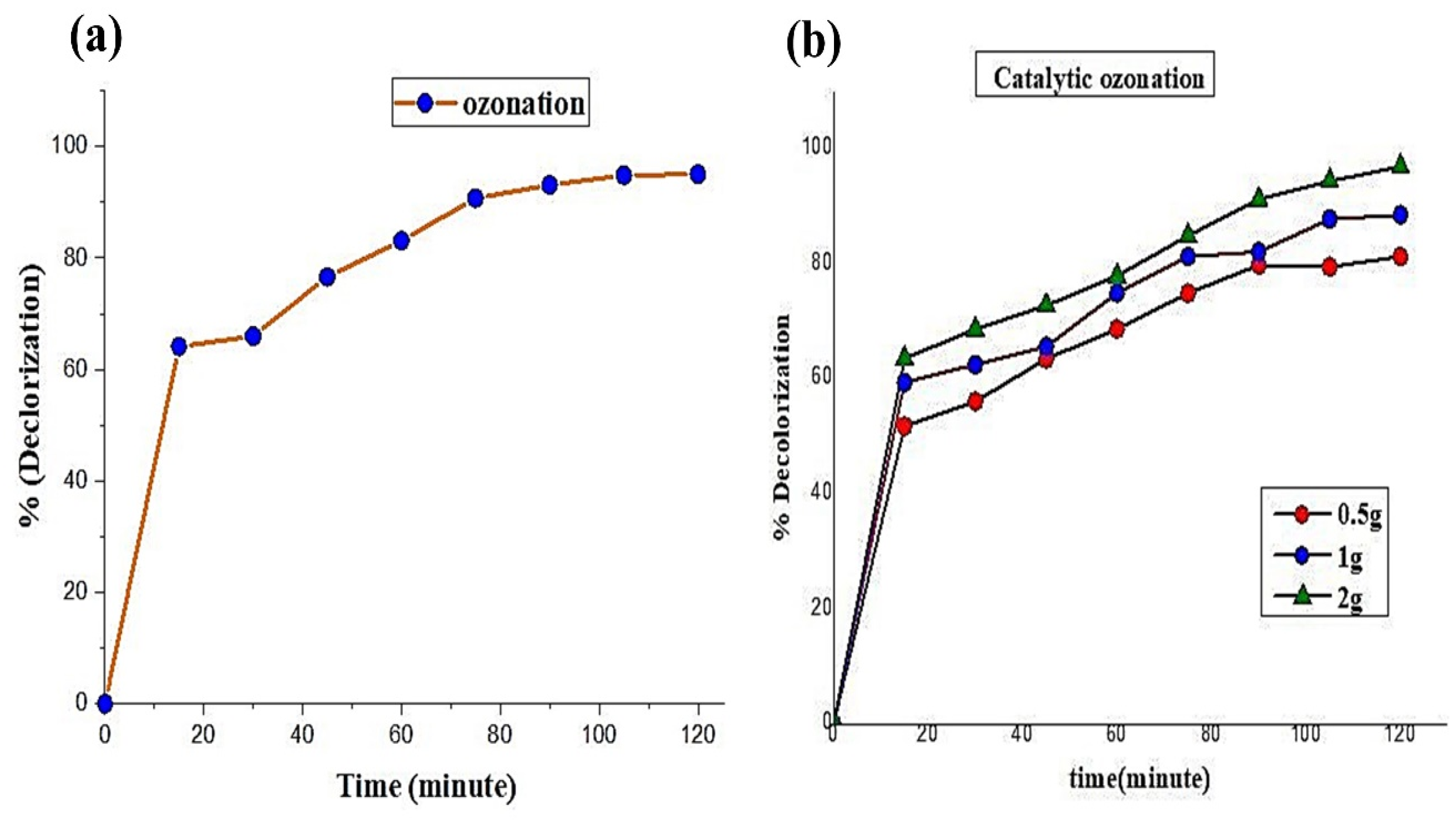
2.5. Time Optimization
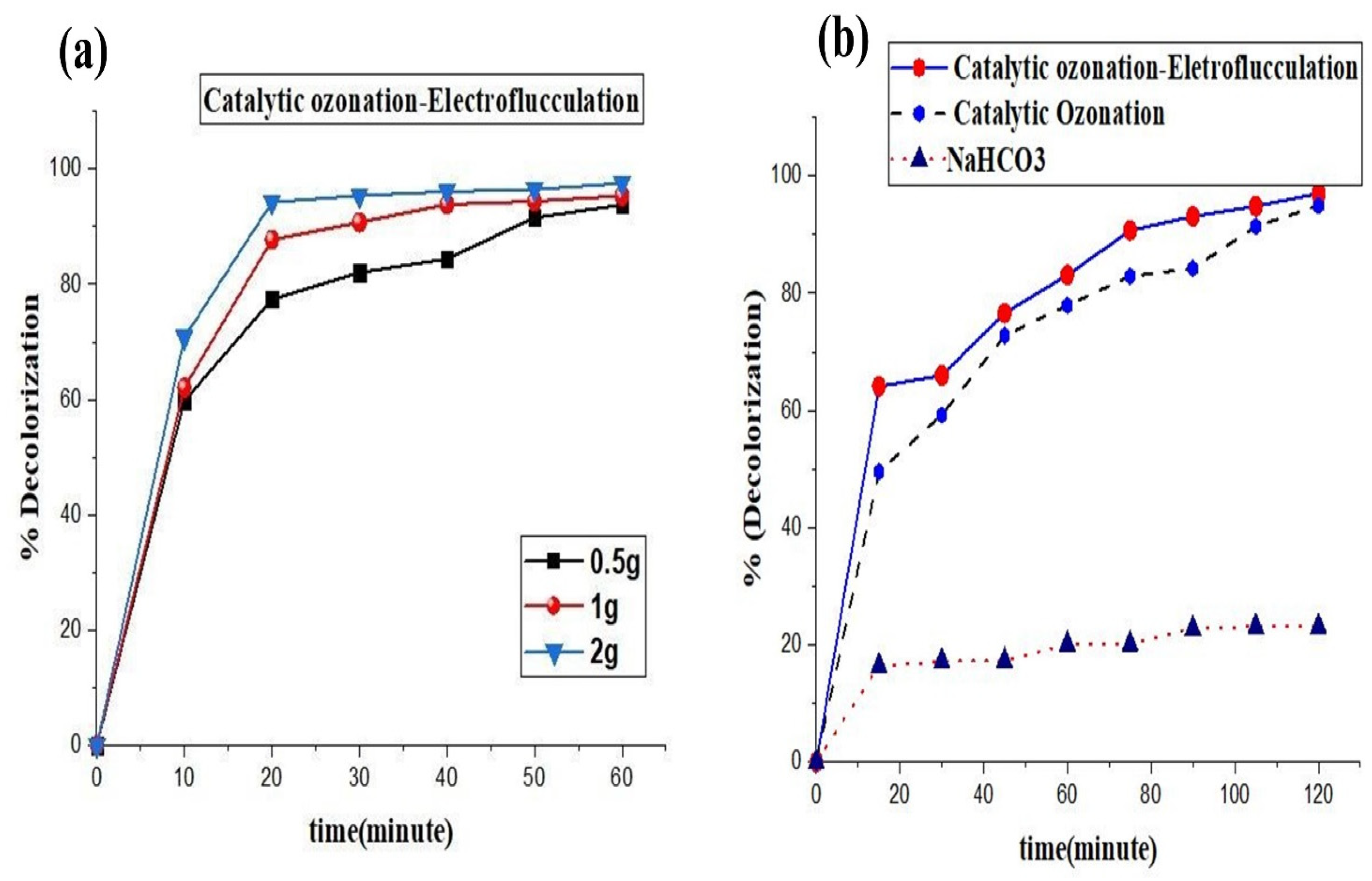
2.6. Catalyst Dose Optimization
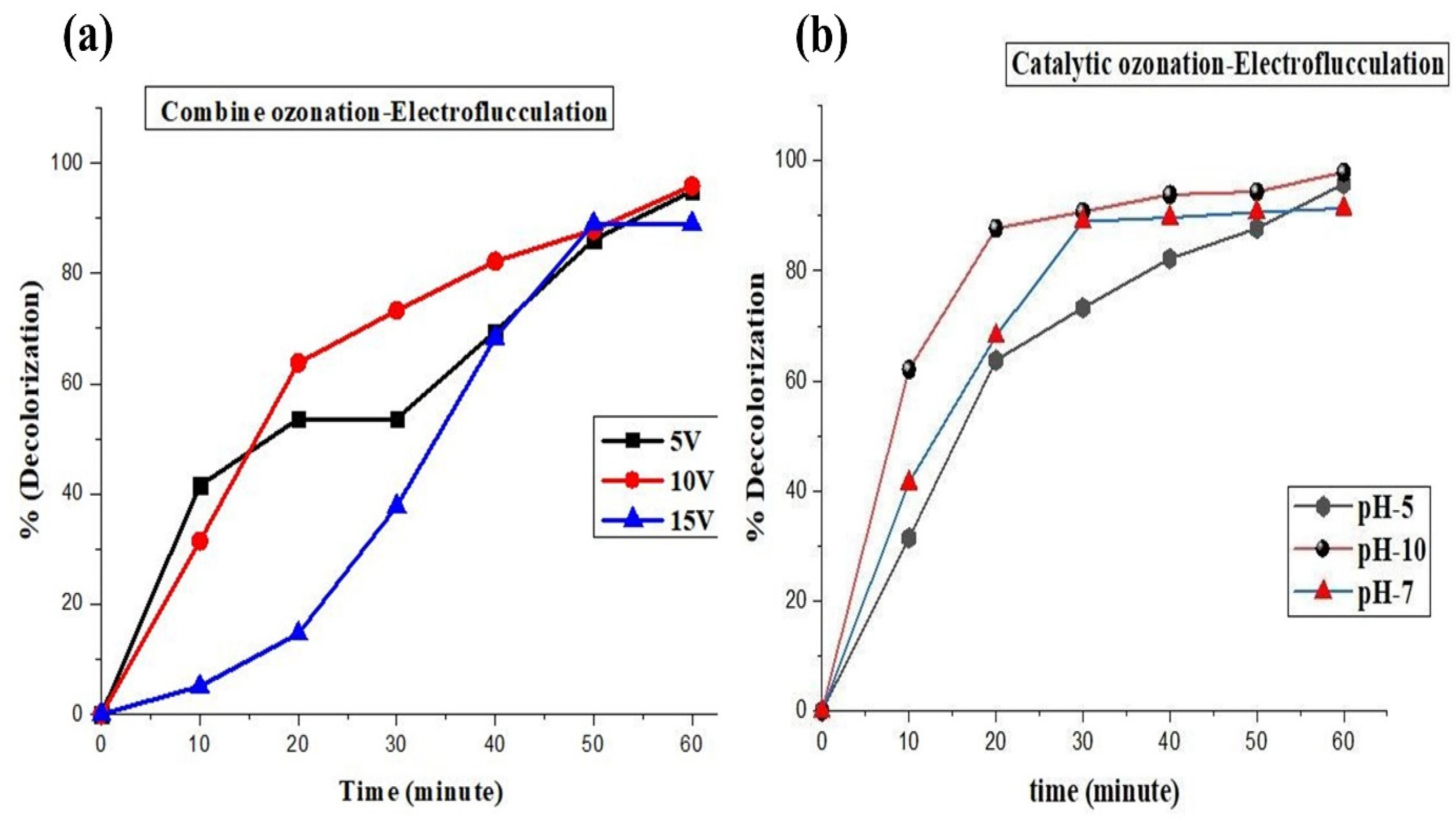
2.7. Voltage Optimization
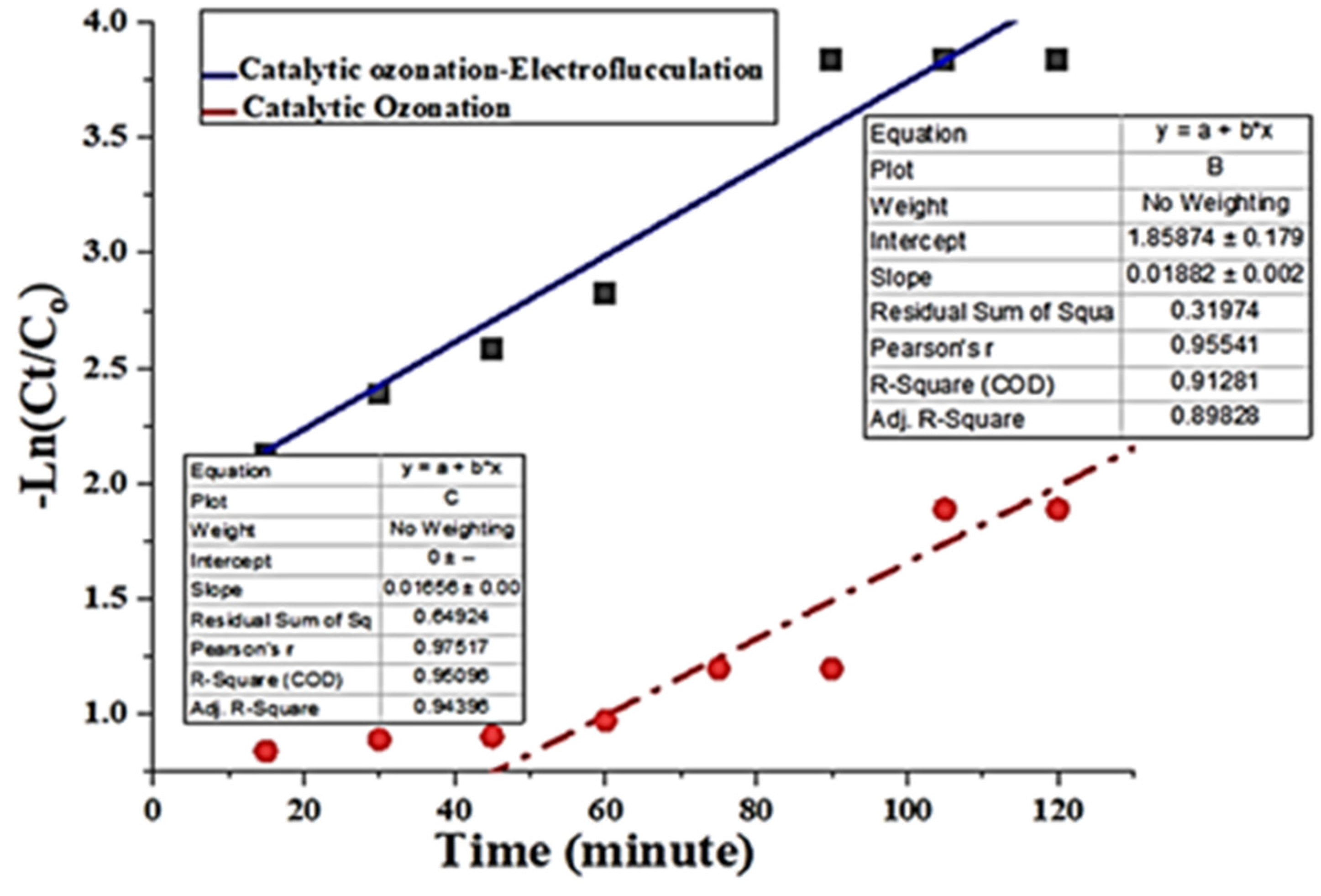
Kinetics Study
2.8. Scavenger Analysis of Catalytic Ozonation and Synergic Process
Effect of NaHCO3 on the Removal Efficiency for Catalytic Ozonation and Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation on Bentonite Clay/TiO2/ZnO
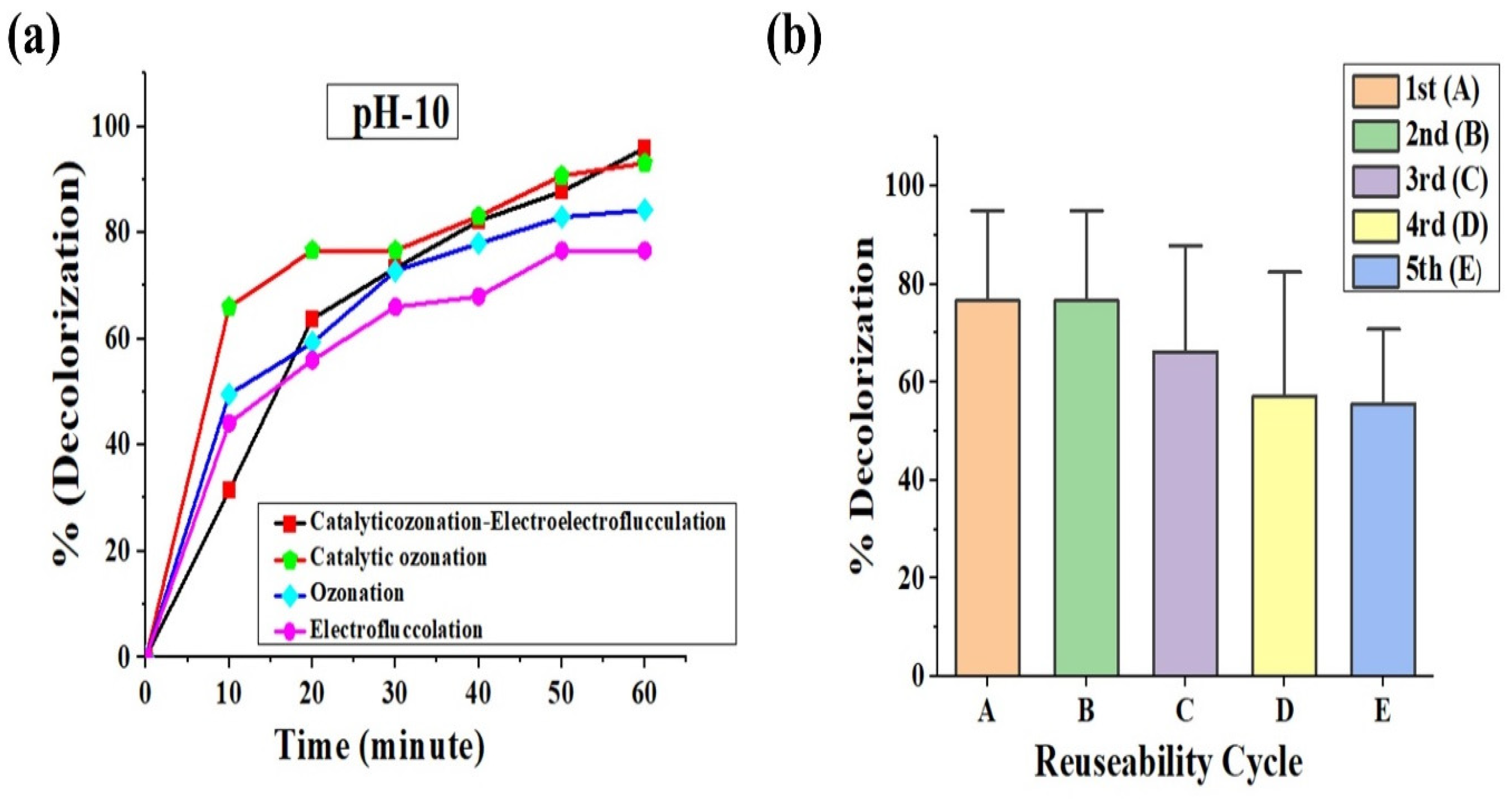
2.9. Catalyst Reuse
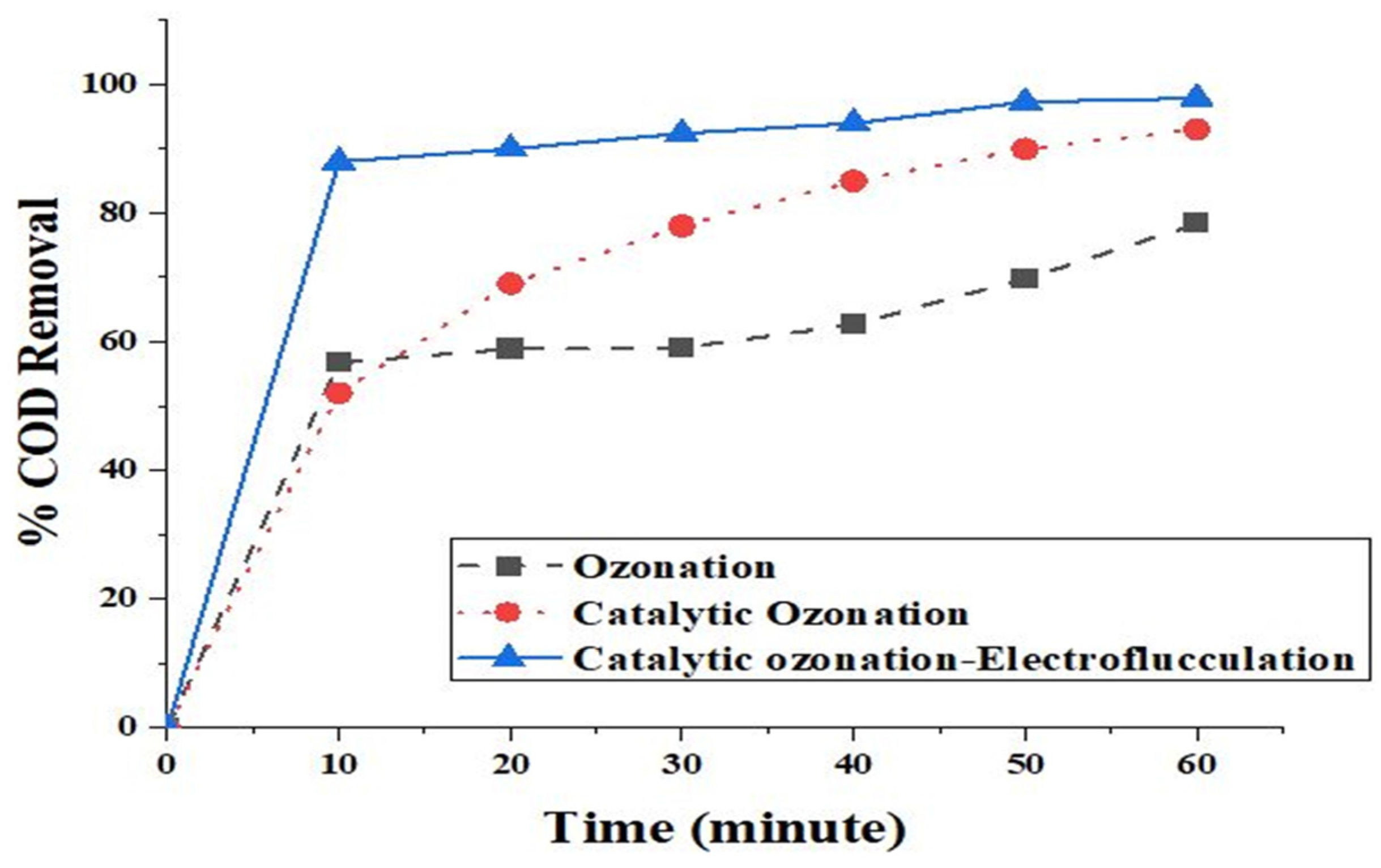
2.10. Comparison of Various Processes
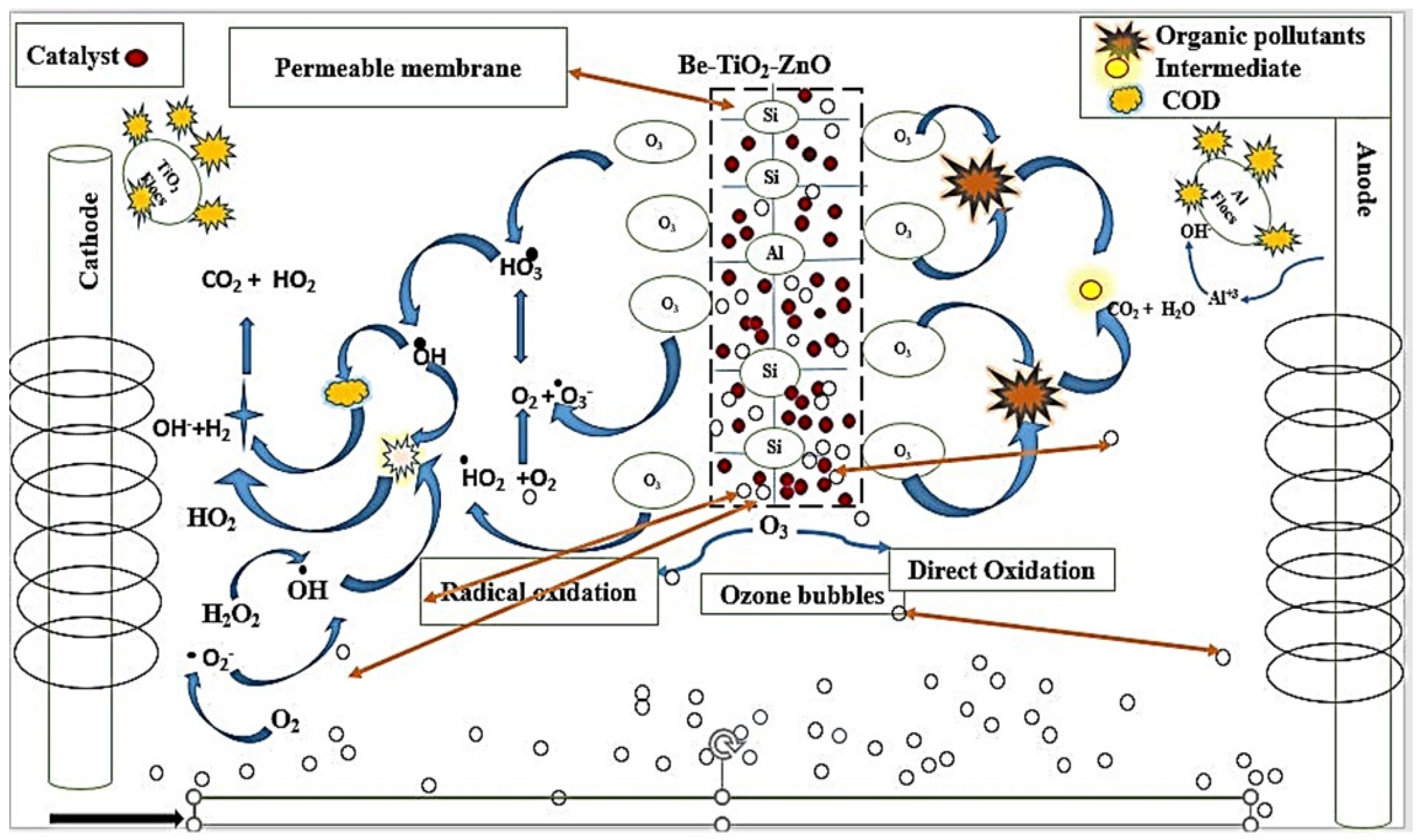
2.11. Proposed Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
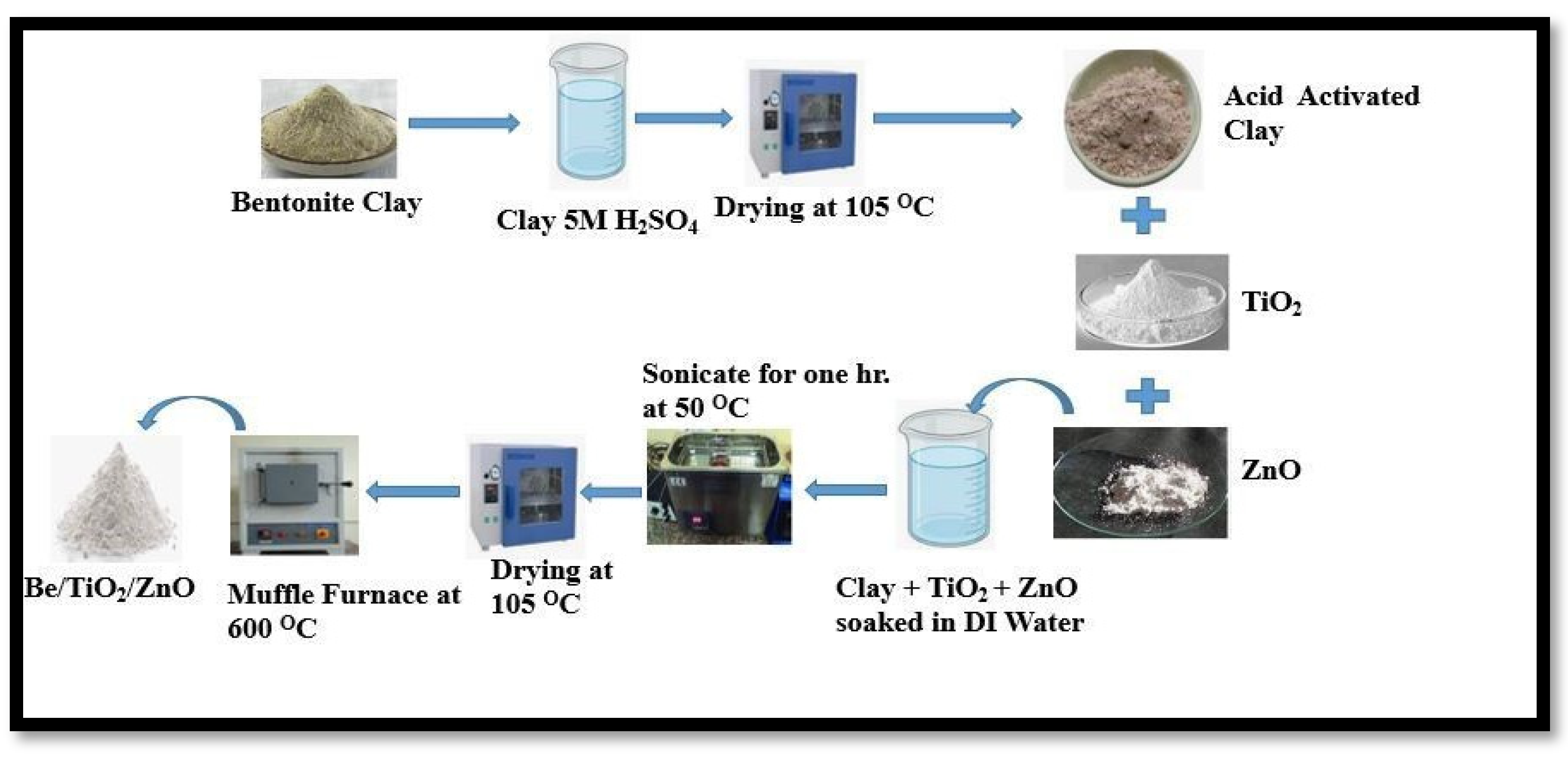
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
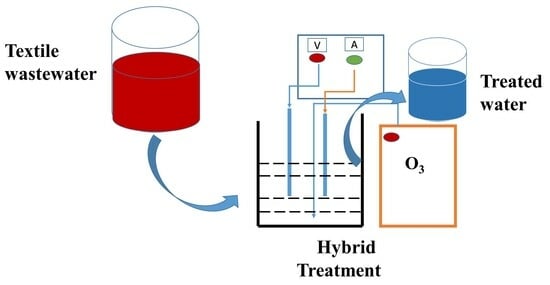
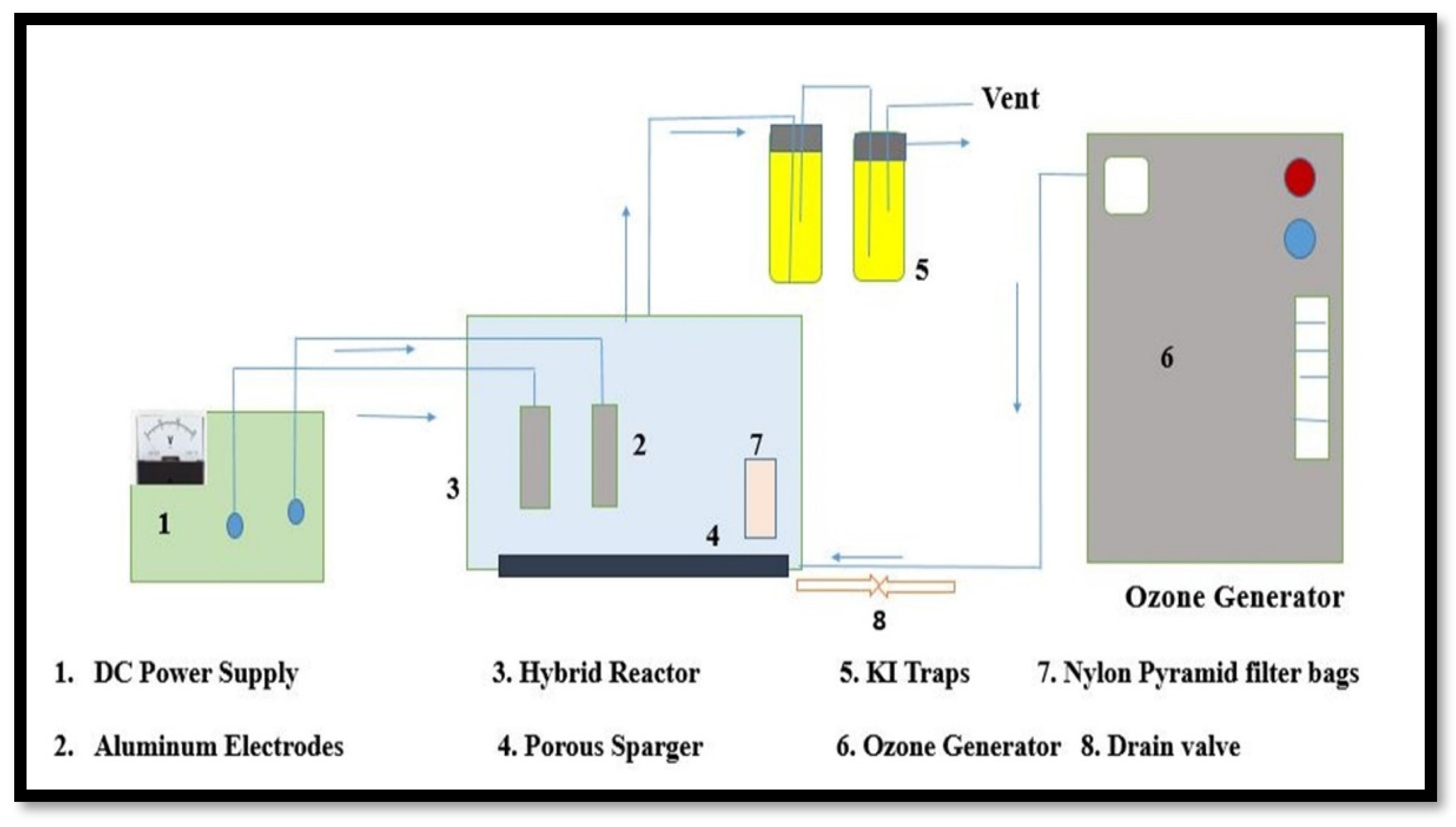
3.3. Experimental Setup
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Experimental Procedure
3.6. Analytical Method
Ozone Dose Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben Slama, H.; Bouket, A.C.; Pourhassan, Z.; Alenezi, F.N.; Silini, A.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Oszako, T.; Luptakova, L.; Golińska, P.; Belbahri, L. Diversity of synthetic dyes from textile industries, discharge impacts and treatment methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgerdi, Z.H.; Meshkat, S.S.; Esrafili, M.D. Enhanced adsorptive removal of Indigo carmine dye performance by functionalized carbon nanotubes based adsorbents from aqueous solution: Equilibrium, kinetic, and DFT study. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2019, 9, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Jadhao, P.; Kumari, K. Clay nano-adsorbent: Structures, applications and mechanism for water treatment. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, K.M.; Hadi, H. Coagulation/Flocculation Process for Produced Water Treatment Coagulation/Flocculation Process for Produced Water Treatment. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 6, 551–555. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, C.J.A.; Avant, J.; Lowther, J.; Till, D.; Lees, D.N. Human norovirus in untreated sewage and effluents from primary, secondary and tertiary treatment processes. Water Res. 2016, 103, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Kazmi, M.; Javed, F.; Joya, K.S.; Anwar, F. Combined catalytic ozonation and electroflocculation process for the removal of basic yellow 28 in wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 127, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Catalytic ozone pretreatment of complex textile effluent using Fe2+ and zero valent iron nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbelge, T.A.; Erol, F. Effects of pH, initiator, scavenger, and surfactant on the ozonation mechanism of an Azo Dye (Acid Red-151) in a batch reactor. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2009, 196, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karat, I. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Removal of COD from Pulp and Paper Mill Effluents. Diva-Portal.Org 2013, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, E.K.; O’Malley, K.N.; Heffron, J.; Huo, J.; Mayer, B.K.; Wang, Y.; McNamara, P.J. Analysis of operational parameters, reactor kinetics, and floc characterization for the removal of estrogens via electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, A.; Russo, C.; Marques, M.R.C. Electroflocculation for textile wastewater treatment. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoie, W.I. Natural Clay Supported Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles as a Potential Coagulant for Ammonia Reduction from Industrial Wastewater Effluents. Mod. Concepts Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Javed, F.; Akram, A.; Rehman, A.; Qi, F.; Javed, M.; Mehdi, M.J.; Waheed, F.; Naveed, S.; Aziz, H.A. Synergic catalytic ozonation and electroflocculation process for the treatment of veterinary pharmaceutical wastewater in a hybrid reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Pan, F.; Sun, P.; Fu, J. An overview of nanomaterials applied for removing dyes from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15882–15904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Zafar, M.; Javed, F.; Yasar, A.; Akram, A.; Shabbir, S.; Qi, F. Catalytic ozonation for the removal of reactive black 5 (RB-5) dye using zeolites modified with CuMn2O4/gC3N4 in a synergic electro flocculation-catalytic ozonation process. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Martínez, L.A.; Barrera-Díaz, C.; Solís-Morelos, C.; Natividad, R. Synergy of electrochemical and ozonation processes in industrial wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Shuaib, D.T.; Ajala, A.O.; Mohammed, A.K. Application of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles Immobilized on Clay in Wastewater Treatment: A Reiew; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 10, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Natural Bentonite Clay and Its Composites for Dye Removal: Current State and Future Potential. Am. J. Chem. Appl. 2016, 3, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yang, Q. Applied Clay Science Magnetization improvement of Fe-pillared clay with application of polyetheramine. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, L.; Sheilatin, P.V.P.; Sepia, N.S. Preparation and characterization of titania/bentonite composite application on the degradation of naphthol blue black dye. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2018, 22, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dinari, A.; Mahmoudi, J. Response surface methodology analysis of the photodegradation of methyl orange dye using synthesized TiO2/Bentonite/ZnO composites. Adv. Environ. Technol. 2022, 8, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kéri, A.; Sápi, A.; Ungor, D.; Sebők, D.; Csapó, E.; Kónya, Z.; Galbács, G. Porosity determination of nano- And sub-micron particles by single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, K.; Krishnan, S.; Ramalingam, S.; Balu, K. Optimization of process variables by the application of response surface methodology for dye removal using a novel adsorbent. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 72, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Shang, S.; Chiu, A.K.L. Removal of Reactive Dyes in Textile Effluents by Catalytic Ozonation Pursuing on-Site Effluent Recycling. Molecules 2019, 24, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.I.; Yuzer, B.; Ongen, A.; Okten, H.E.; Selcuk, H. Comparison of ozonation and coagulation decolorization methods in real textile wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 103, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, M.A.; Roa-Morales, G.; Barrera-Díaz, C.; Miranda, V.M.; Hernández, P.B.; Silva, T.B.P. Integrated advanced oxidation process (Ozonation) and electrocoagulation treatments for dye removal in denim effluents. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 8752–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yoza, B.A.; Li, Q.X.; Kou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Catalytic ozonation of recalcitrant organic chemicals in water using vanadium oxides loaded ZSM-5 zeolites. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Aslam, T.; Zafar, A.M.; Javed, F.; Munir, H.M.S. Combined ozonation and adsorption system for the removal of heavy metals from municipal wastewater: Effect of COD removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 159, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmilin, A.; Sangsirimongkolying, R. Treatment of iron from groundwater by ozonation: Influence of hardness as a scavenger. Appl. Environ. Res. 2021, 43, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raashid, M.; Kazmi, M.; Ikhlaq, A.; Iqbal, T.; Sulaiman, M.; Shakeel, A. Degradation of Aqueous CONFIDOR® Pesticide by Simultaneous TiO2 Photocatalysis and Fe-Zeolite Catalytic Ozonation. Water 2021, 13, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, Z.; Ikhlaq, A.; Farooq, U.; Qi, F.; Javed, F.; Aziz, H.A. Removal of anti-biotics from veterinary pharmaceutical wastewater using combined Electroflocculation and Fe-Zn loaded zeolite 5A based catalytic ozonation process. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Q.; Shaheen, S.; Bilal, M.; Tariq, M.; Zeb, B.S.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, A. Chemical pollutants from an industrial estate in Pakistan: A threat to environmental sustainability. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.K.M.M.; Dey, S.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Zakaria, A.M.; Sarker, M.; Ashaduzzmaman, M.; Shamsuddin, S.M. Kaolinite/TiO2/ZnO Based Novel Ternary Composite for Photocatalytic Degradation of Anionic Azo Dyes. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, N.K.V.; Fu, H. pH effects on catalytic ozonation of carboxylic acids with metal on metal oxides catalysts. Top. Catal. 2005, 33, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati Sani, O.; Navaei fezabady, A.A.; Yazdani, M.; Taghavi, M. Catalytic ozonation of ciprofloxacin using γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles in synthetic and real wastewaters. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.; Do, V.M.; Trinh, V.T. Nano-Catalysts in Ozone-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaab, M.; Bellemin-Laponnaz, S.; Gade, L.H. “Catalysis in a tea bag”: Synthesis, catalytic performance and recycling of dendrimer-immobilised bis- and trisoxazoline copper catalysts. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5450–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngteni, R.; Hossain, M.S.; Kadir, M.O.A.; Asis, A.J.; Tajudin, Z. Kinetics and isotherm modeling for the treatment of rubber processing euent using iron (II) sulphate waste as a coagulant. Water 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
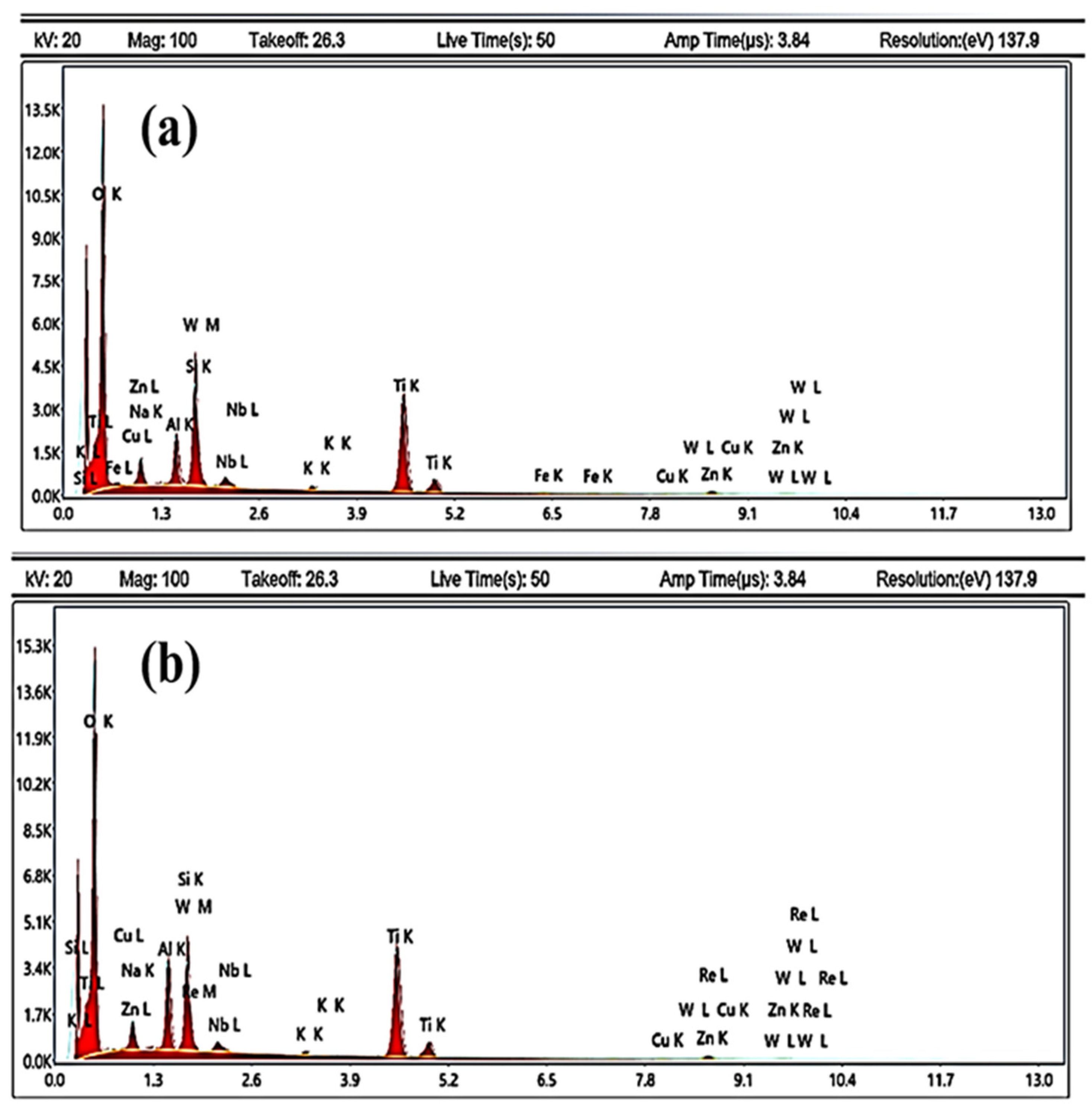
| Elements | Before Process | After Process |
|---|---|---|
| O | 68.46 | 67.25 |
| Na | 3.71 | 4.2 |
| Al | 4.58 | 7.16 |
| Si | 4.97 | 4.11 |
| Nb | 1.63 | 1.44 |
| K | 0.45 | 0.38 |
| Ti | 13.78 | 14.33 |
| Cu | 0.28 | 0.31 |
| W | 0.38 | 0.27 |
| Zn | 1.41 | 0.55 |
| Parameters | Before Treatment | After Treatment | NEQs [32] |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 11 | 7 | 6–9 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1750 | 890 | - |
| Electrical conductivity (µs/cm) | 3550 | 1500 | - |
| Chemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 1200 | 40 | 150 mg/L |
| Biological oxygen demand (BOD) | 510 | 30 | 80 mg/L |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 0.90 | 0.20 | - |
| Maximum wavelength | 518 nm | - | |
| Color | Dark red | Colorless | Colorless |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, T.; Yasin, S.; Ramzan, N.; Aslam, Z.; Ikhlaq, A.; Qazi, U.Y.; Javaid, R. Treatment of Textile Wastewater by a Novel Clay/TiO2/ZnO-Based Catalyst, Applying a Synergic Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation Process. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091315
Jamil T, Yasin S, Ramzan N, Aslam Z, Ikhlaq A, Qazi UY, Javaid R. Treatment of Textile Wastewater by a Novel Clay/TiO2/ZnO-Based Catalyst, Applying a Synergic Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation Process. Catalysts. 2023; 13(9):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091315
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Tayyaba, Saima Yasin, Naveed Ramzan, Zaheer Aslam, Amir Ikhlaq, Umair Yaqub Qazi, and Rahat Javaid. 2023. "Treatment of Textile Wastewater by a Novel Clay/TiO2/ZnO-Based Catalyst, Applying a Synergic Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation Process" Catalysts 13, no. 9: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091315
APA StyleJamil, T., Yasin, S., Ramzan, N., Aslam, Z., Ikhlaq, A., Qazi, U. Y., & Javaid, R. (2023). Treatment of Textile Wastewater by a Novel Clay/TiO2/ZnO-Based Catalyst, Applying a Synergic Catalytic Ozonation–Electroflocculation Process. Catalysts, 13(9), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091315