Design of Highly Efficient Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Molybdenum (NCMM) Nano-Catalysts Supported on Activated Carbon for Desulfurization Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Performance Evaluation of the Designed Nano-Catalysts
2.1.1. Chemical Composition
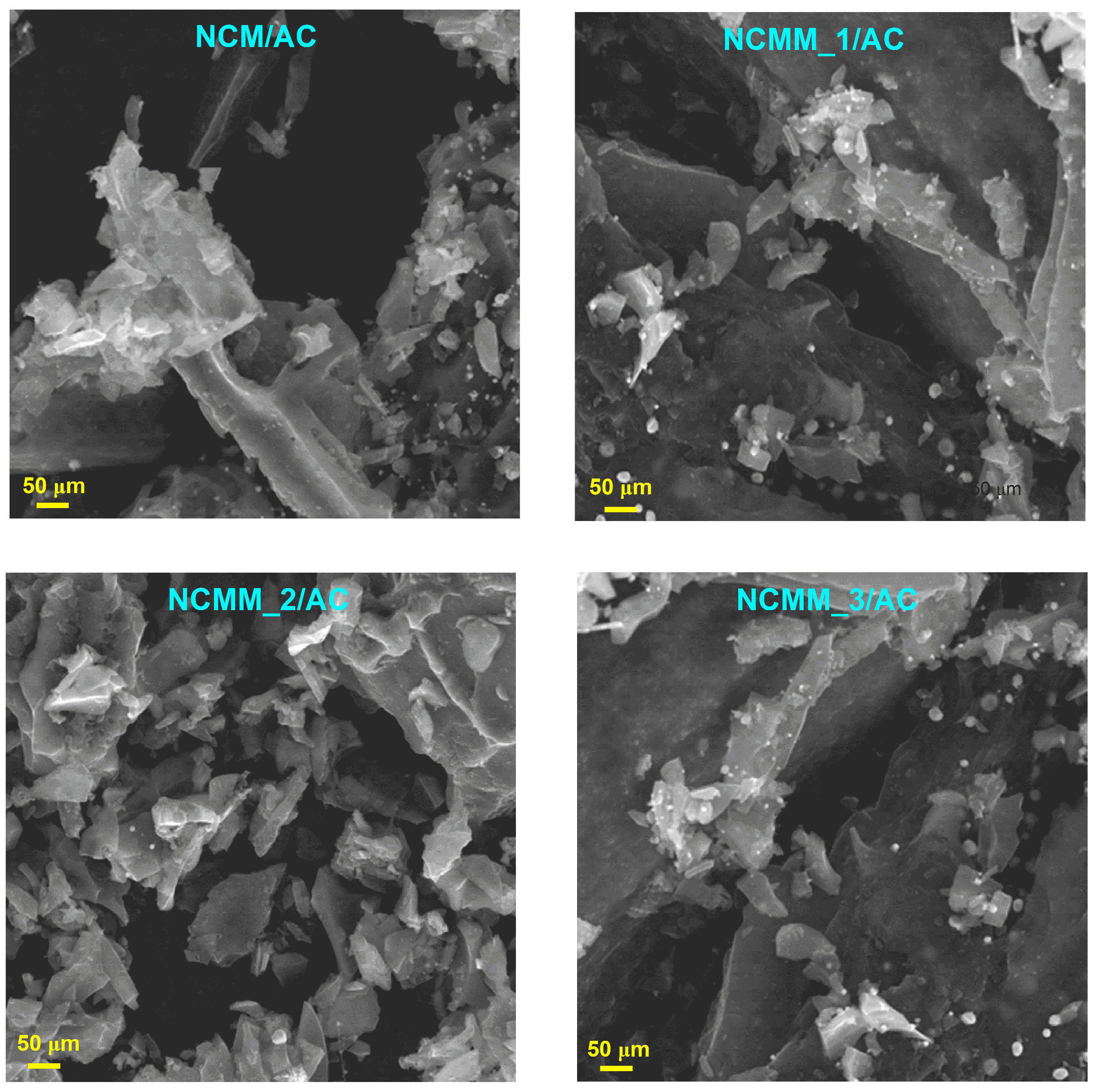
2.1.2. SEM Analysis
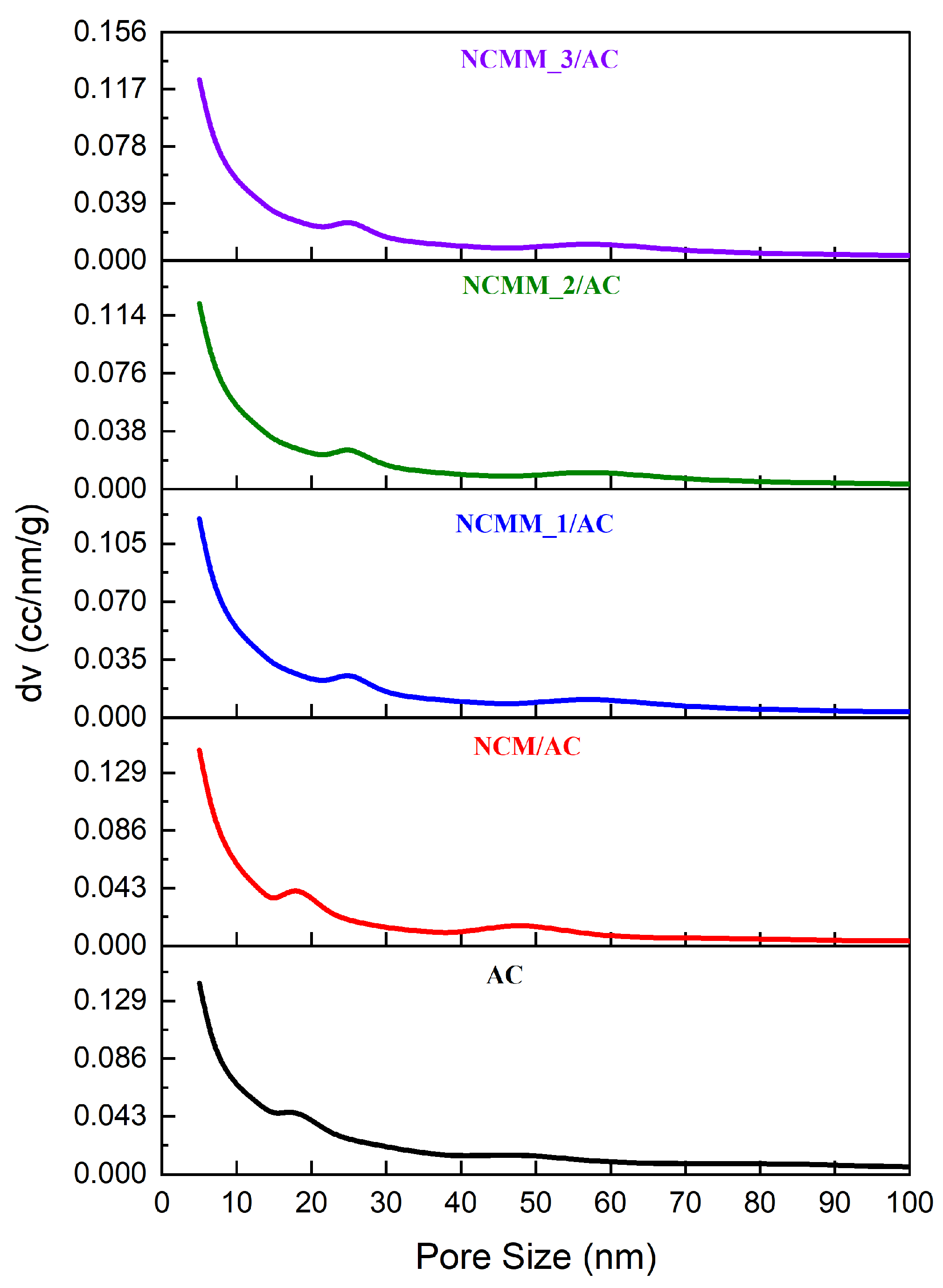
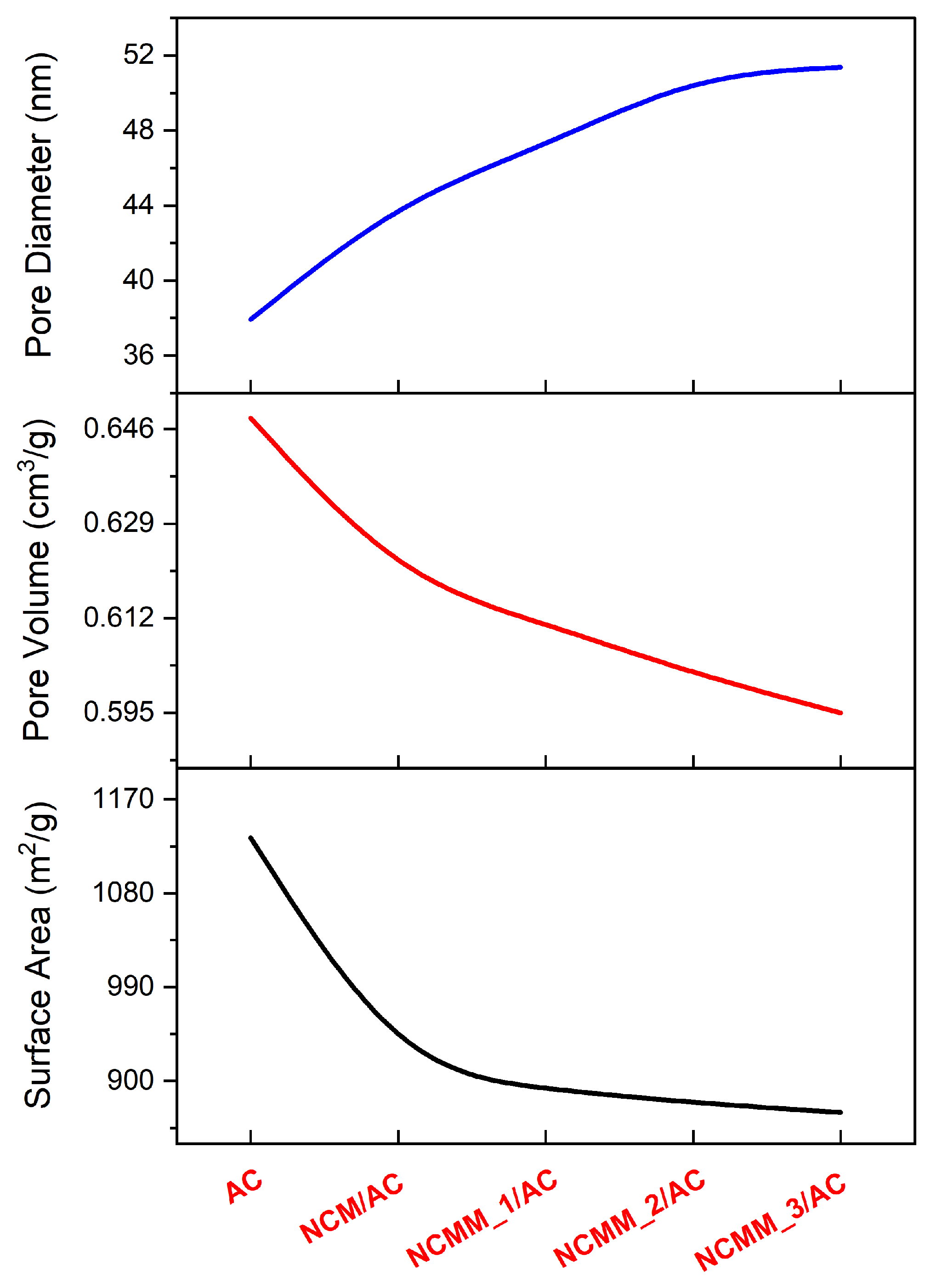
2.1.3. Pore Size Distribution Evaluation
2.1.4. Thermographic Analysis (TGA)
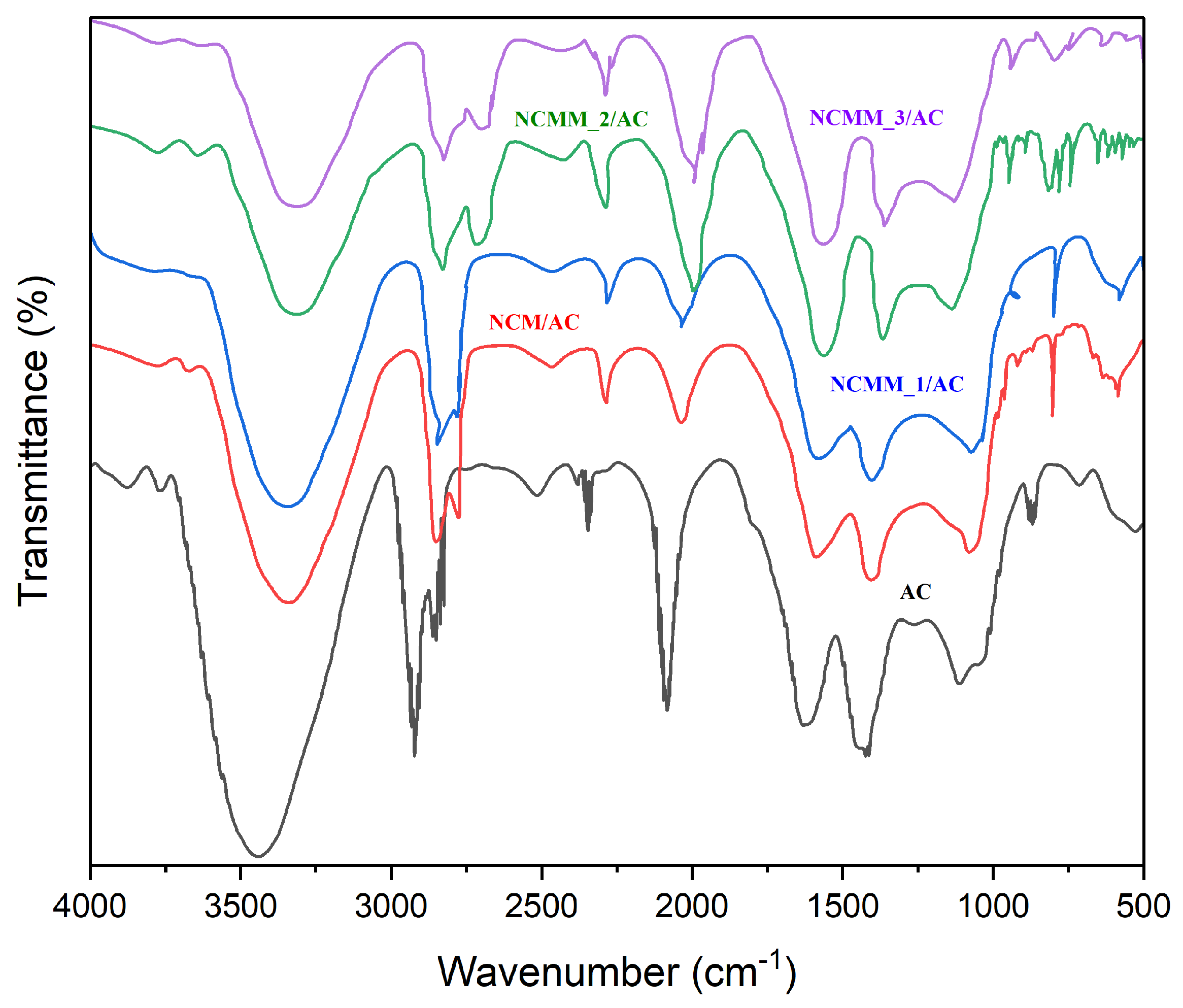
2.1.5. FTIR Analysis
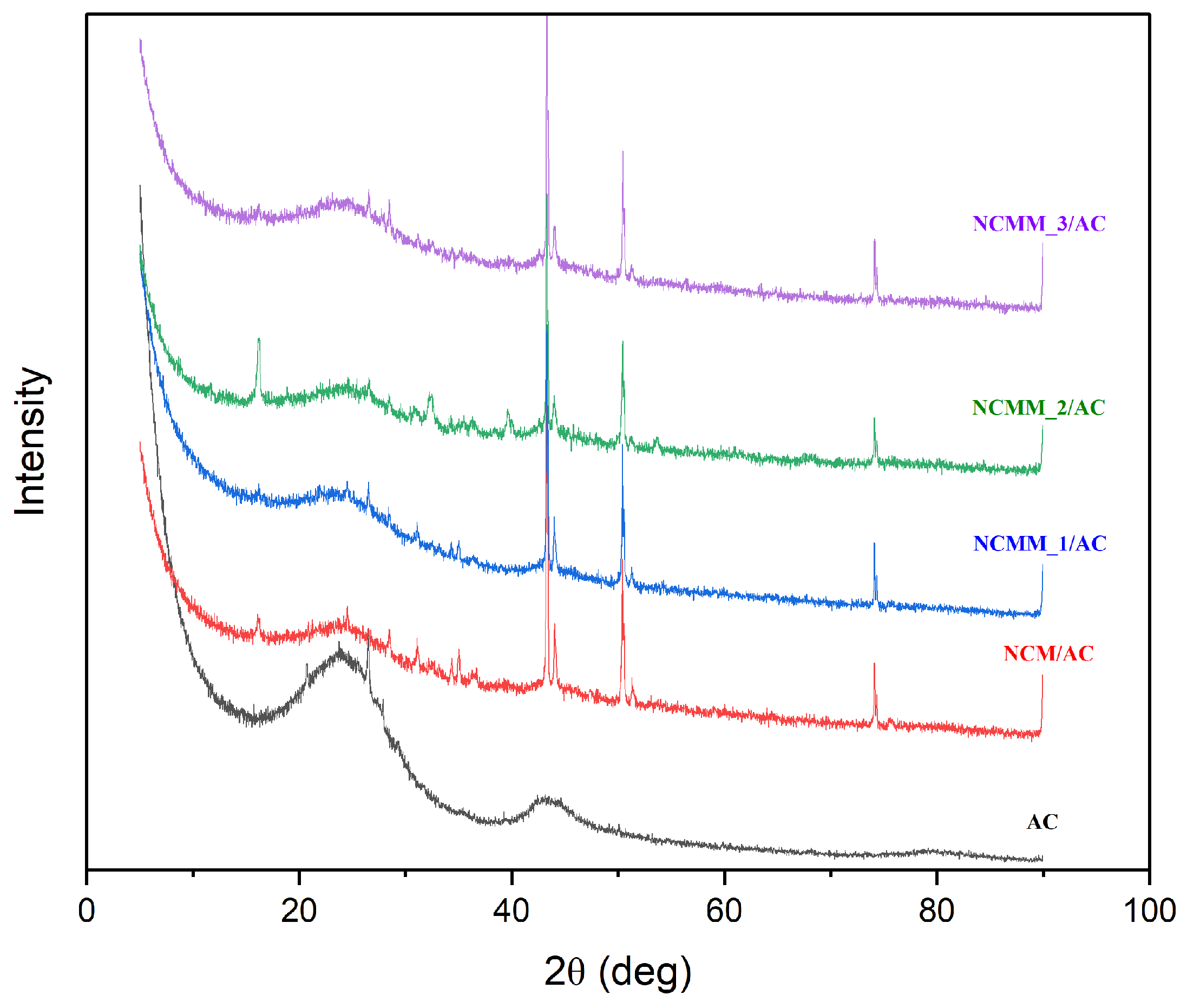
2.1.6. XRD Analysis
2.1.7. Surface Area and Pore Volume
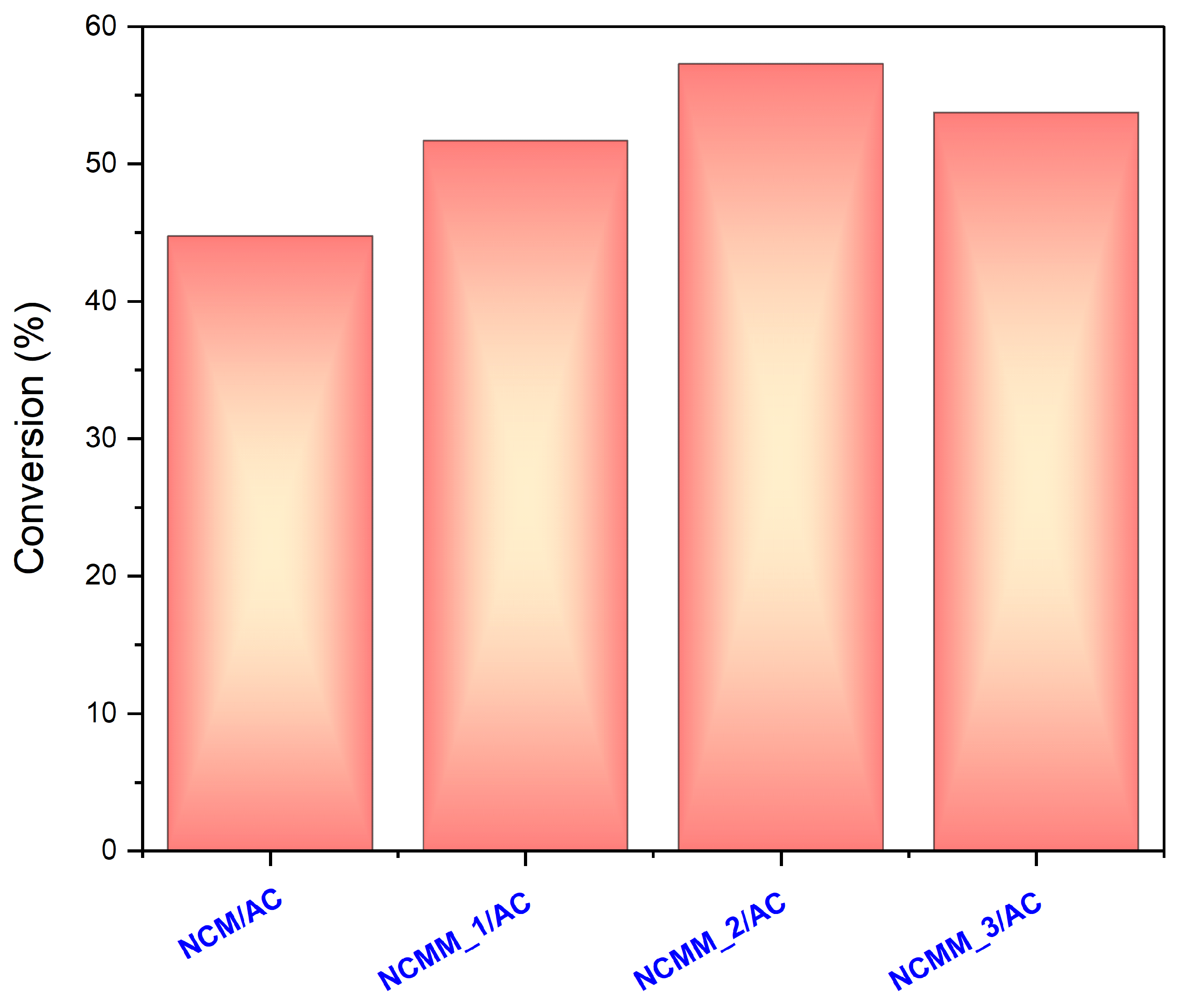
2.2. Evaluation of the Catalysts Using Batch Reactor
3. Experiment
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
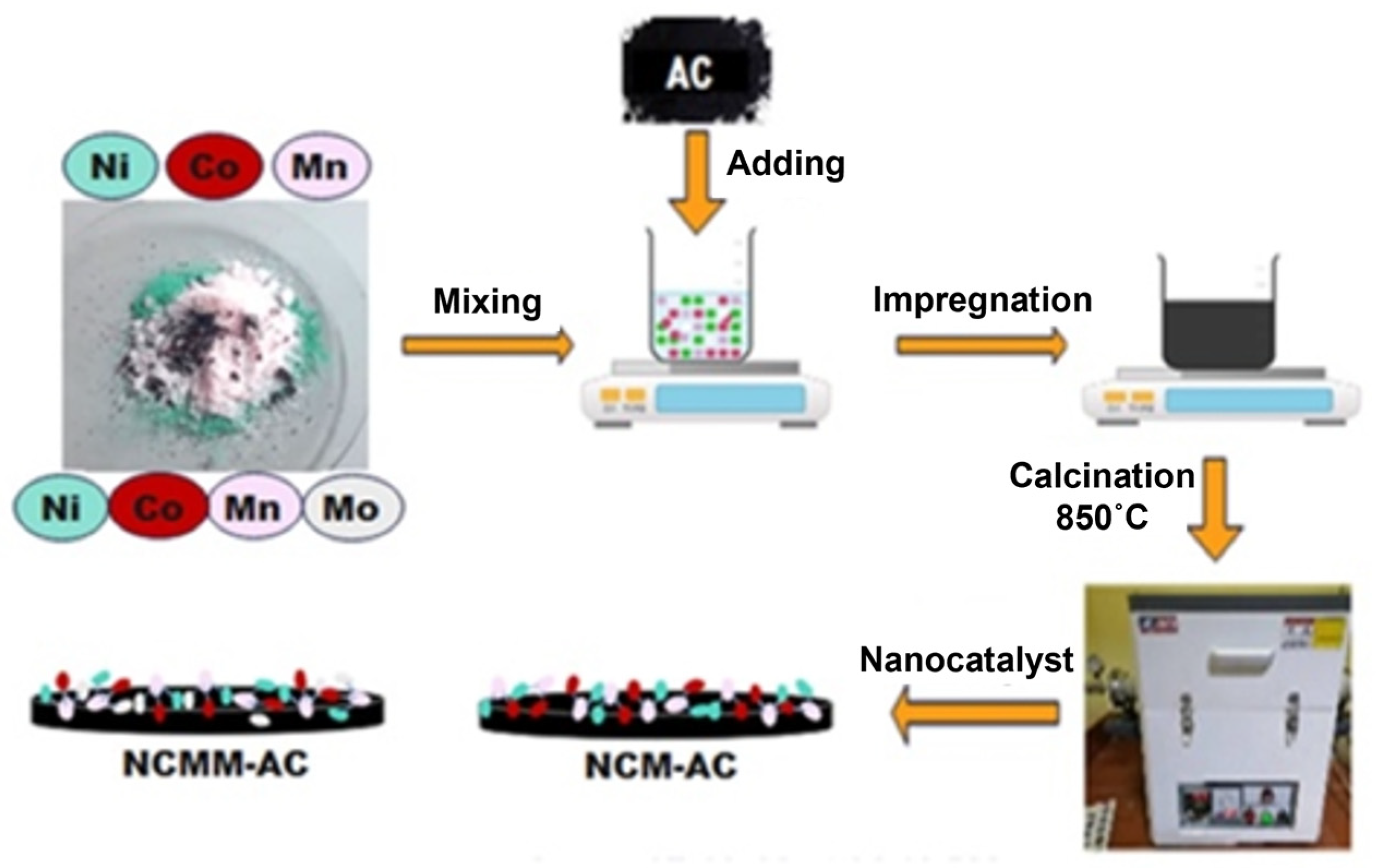
3.2. Nano-Catalysts Preparation
3.2.1. Activated Carbon Preparation
3.2.2. Metals Loading and Chemical Activation
3.3. Evaluation of the Catalysts Performances
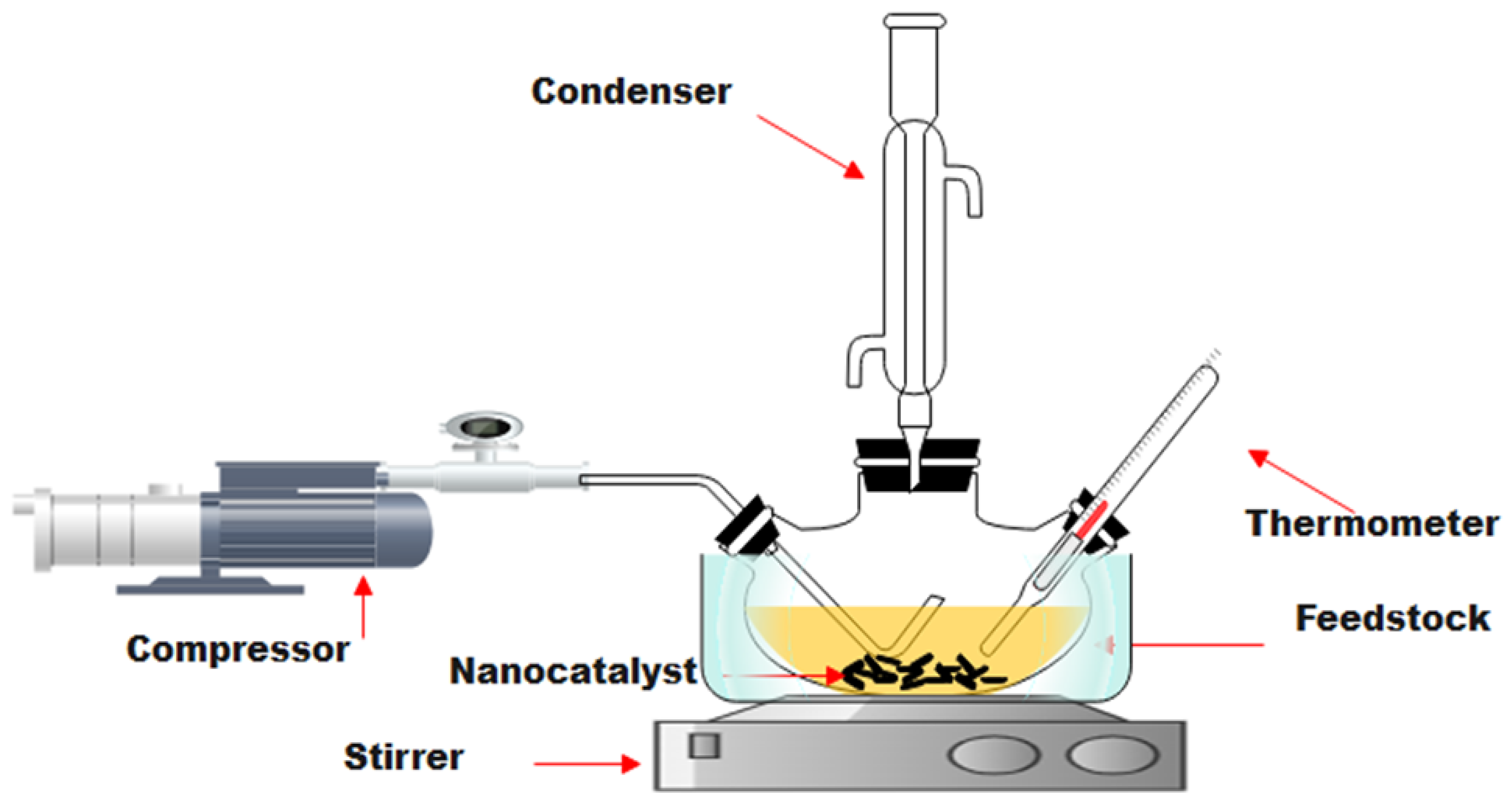
3.3.1. Batch Reactor
3.3.2. Conditions of Process
3.3.3. Sulfur Compound Oxidation (ODS Reaction)
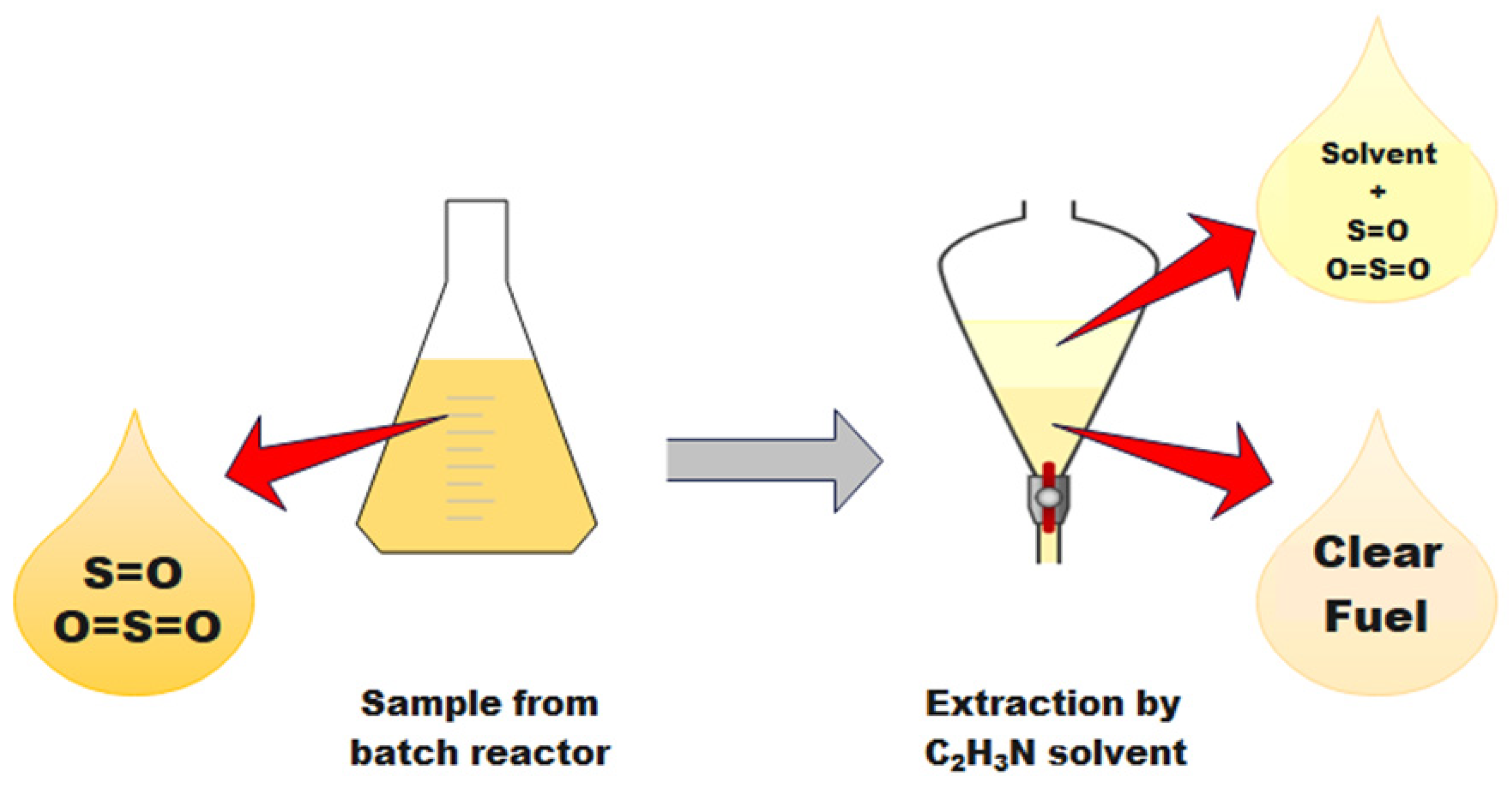
3.3.4. Extraction
3.3.5. Sample Examination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, V.C. An evaluation of desulfurization technologies for sulfur removal from liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal–organic frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sakanishi, K.; Isoda, T.; Mochida, I. Hydrodesulfurization reactivities of narrow-cut fractions in a gas oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 34, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sakanishi, K.; Mochida, I. Hydrodesulfurization reactivities of various sulfur compounds in diesel fuel. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 33, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancheyta, J. Handbook of Deactivation of Heavy Oil Hydroprocessing Catalysts: Fundamentals and Modeling, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bakar, W.A.W.A.; Ali, R.; Kadir, A.A.A.; Mokhtar, W.N.A.W. The Role of Molybdenum Oxide Based Catalysts on Oxidative Desulfurization of Diesel Fuel. Mod. Chem. Appl. 2015, 3, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Rang, H.; Kann, J.; Oja, V. Advances in Desulfurization Research of Liquid Fuel. Oil Shale 2006, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannikos, F.; Lois, E.; Stournas, S. Desulfurization of petroleum fractions by oxidation and solvent extraction. Fuel Process. Technol. 1995, 42, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, S.; Nonaka, T.; Takashima, N.; Qian, W.; Ishihara, A.; Imai, T.; Kabe, T. Oxidative Desulfurization of Light Gas Oil and Vacuum Gas Oil by Oxidation and Solvent Extraction. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Martin, J.M.; Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Perez-Presas, P.; Fierro, J.L.G. Oxidative processes of desulfurization of liquid fuels. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houda, S.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchar, P.; Poinel, L.; Lamonier, C. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Oils with High Sulfur Content: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, L.J.; Han, Y.Z.; Leyshon, D.W. Organosulfur Oxidation Process. U.S. Patent 2,004,178,122, 16 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kocal, J.A.; Branvold, T.A. Removal of Sulfur-Containing Compounds from Liquid Hydrocarbon Streams. U.S. Patent 6,368,495, 9 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jarullah, A.T.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hussein, H.M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Mohammed, H.J. Evaluation of synthesized Pt/HY-H-Mordenite composite catalyst for Isomerization of Light Naphtha. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2023, 30, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Degs, Y.S.; Khalili, F.I. Minimisation of organosulphur compounds by activated carbon from Diesel fuel: Mechanistic study. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedzeki, N.S.; Ali, S.M.; Al-Karkhi, S.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Tri-Composite Activated Carbon. Iraqi J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2017, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheety, M.A.; Al-Jibori, S.A.; Karadağ, A.; Akbaş, H.; Ahmed, M.H. A novel synthesis of MnO2, nanoflowers as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of thiophenes. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 20, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarda, K.K.; Bhandari, A.; Pant, K.K.; Jain, S. Deep desulfurization of diesel fuel by selective adsorption over Ni/Al2O3 and Ni/ZSM-5 extrudates. Fuel 2012, 93, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; He, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zeng, G.; Kang, L.; Qian, H.; Zhu, C. Preparation, characterization, and catalytic performances of cobalt catalysts supported on KIT-6 silicas in oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Fuel 2017, 200, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, P.; Arun Kumar, U.K.; Gosu, V.; Subbaramaiah, V. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of DBT using green catalyst (Mo/MCM-41) derived from coal fly ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Xie, W.; Sun, S.; Wu, G.M.; Zheng, L.; Chu, S.; Gao, C.; Bao, J. Activated-carbon-supported K–Co–Mo catalyst for synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarullah, A.T.; Ahmed, A.N.; Ban, A.A.; Ahmed, A.M. Design of New Composites Nano-Catalysts for Naphtha Reforming Process: Experiments and Process Modeling. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2023, 30, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, S.; Sobrinho, E.V.; da Silva, T.; Pergher, S.B.C. V or Mn zeolite catalysts for the oxidative desulfurization of diesel fractions using dibenzothiophene as a probe molecule: Preliminary study. Mol. Catal. 2020, 482, 100495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, B.; Budinova, T.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Kochkodan, V.; Shkavro, Z.; Petrov, N. Removal of aromatic hydrocarbons from water by activated carbon from apricot stones. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkhalil, M.; Moghaddam, A.; Rashidi, A.; Towfighi, J.; Mortazavi, Y. Preparation of highly active manganese oxides supported on functionalized MWNTs for low temperature NOx reduction with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haw, K.; Abu Bakar, W.; Ali, R.; Chong, J.; Kadir, A. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of diesel utilizing hydrogen peroxide and functionalized-activated carbon in a biphasic diesel– acetonitrile system. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, E.; Chen, A. Volatile production from pyrolysis of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contescu, I.; Adhikari, P.; Gallego, C.; Evans, D.; Biss, E. Activated Carbons Derived from High-Temperature Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass. C J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchalala, R.; El-Demellawi, K.; Abou-Hamad, E. Hybrid electrolytes based on ionic liquids and amorphous porous silicon nanoparticles: Organization and electrochemical properties. Appl. Mater. 2017, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A. The influence of treatment temperature on the acidity of MWCNT oxidized by HNO3 or a mixture of HNO3/H2SO4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7746–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, A.; Hajati, S.; Ghaedi, M. Synthesis of regenerable Zn(OH)2 nanoparticleloaded activated carbon for the ultrasound-assisted removal of malachite green: Optimization, isotherm and kinetics. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79119–79128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Kadhim, W.; Deraman, M.; Abdullah, S.; Tajuddin, S.; Yusoff, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.; Rahim, M. Efficient and reusable iron-zinc oxide catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of model fuel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A. Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on Hg (II) adsorption fromaqueous solution by silica-multiwall carbon nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16721–16731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamin, J.M.; Aysar, T.J.; Ban, A.A.; Hala, M.H. Preparation of synthetic composite nano-catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of kerosene. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Jarullah, A.T.; Aldulaimi, S.K.; Al-Tabbakh, B.A.; Mujtaba, I.M. A new synthetic composite nano-catalyst achieving an environmentally Friendly fuel by batch oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.; Huixiang, W.; Ruimin, D.; Liancheng, W.; Zhong, L.; Baoliang, L. Highly efficient oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene using Ni modified MoO3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 589, 117308. [Google Scholar]
- Iovik, Y.A.; Krivtsov, E.B. Thermal Transformations of Sulfur-Containing Components of Oxidized Vacuum Gas Oil. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, A.V.; Plotnikov, D.A.; Polikarpova, P.D.; Kedalo, A.A.; Egazar’yants, S.V.; Anisimov, A.V.; Karakhanov, E.A. Deep Purification of Vacuum Gas Oil by the Method of Oxidative Desulfurization. Pet. Chem. 2019, 59, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WanXin, Y.; Guoqing, G.; Zhihong, M.; Yinghao, Y. Deep oxidative desulfurization of model fuels catalysed by immobilized ionic liquid on MIL100(Fe). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21804. [Google Scholar]


| Component (wt%) | NCM/AC | NCMM_1/AC | NCMM_2/AC | NCMM_3/AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 73.1 | 72.2 | 71.7 | 70.9 |
| Oxygen (O) | 14.2 | 18.3 | 17.4 | 17.8 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 3.89 | 3.17 | 3.19 | 3.18 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 1.95 | 1.49 | 1.48 | 1.51 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 3.91 | 3.11 | 3.06 | 3.08 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.0 | 0.96 | 1.91 | 2.97 |
| Chemicals | Formula | Purity% | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel acetate tetra hydrate | (CH3COOH)2Ni·4H2O | 99 | Thomas Baker, London, UK |
| Manganese (III) acetate hydrate | (CH3COO)2 Mn·2H2O | 99 | Thomas Baker, London, UK |
| Cobalt Chloride hexa hydrate | CoCl2·6H2O | 99 | Thomas Baker, London, UK |
| Ammonium Molybdate tetra hydrate | (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O | 99 | Thomas Baker, London, UK |
| Deionized water | H2O | pH = 7.0 TDS = 0.0 | Analytical chemicals lab—Chemical Engineering Department/Tikrit, Tikrit, Iraq |
| Acetonitrile | C2H3N | 99.9 | Concord Technology, Ramtekdi, India |
| Factors | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Sp.gr @ 15.6 C | 0.7708 |
| Sulfur content | 4826 ppm |
| Initial boiling point | 29 °C |
| End boiling point | 345 °C |
| API | 52.08 |
| Sample | Metal | Weight (%) | Salt (g) | Total Deionized Water (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCM | Ni | 4.0 | 16.96 | 1748.91 |
| Co | 2.0 | 8.07 | ||
| Mn | 4.0 | 19.52 | ||
| NCMM_1/AC | Ni | 3.6 | 15.30 | 1678.63 |
| Co | 1.8 | 7.30 | ||
| Mn | 3.6 | 17.60 | ||
| Mo | 1.0 | 1.20 | ||
| NCMM_2/AC | Ni | 3.2 | 13.60 | 1607.85 |
| Co | 1.6 | 6.50 | ||
| Mn | 3.2 | 15.60 | ||
| Mo | 2.0 | 2.40 | ||
| NCMM_3/AC | Ni | 2.8 | 11.88 | 1537.12 |
| Co | 1.4 | 5.65 | ||
| Mn | 2.8 | 13.67 | ||
| Mo | 3.0 | 3.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hameed, S.A.; Amar, R.B.; Hamad, K.I.; Jarullah, A.T.; Mujtaba, I.M. Design of Highly Efficient Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Molybdenum (NCMM) Nano-Catalysts Supported on Activated Carbon for Desulfurization Process. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081196
Hameed SA, Amar RB, Hamad KI, Jarullah AT, Mujtaba IM. Design of Highly Efficient Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Molybdenum (NCMM) Nano-Catalysts Supported on Activated Carbon for Desulfurization Process. Catalysts. 2023; 13(8):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081196
Chicago/Turabian StyleHameed, Shymaa A., Raja Ben Amar, Khaleel I. Hamad, Aysar T. Jarullah, and Iqbal M. Mujtaba. 2023. "Design of Highly Efficient Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Molybdenum (NCMM) Nano-Catalysts Supported on Activated Carbon for Desulfurization Process" Catalysts 13, no. 8: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081196
APA StyleHameed, S. A., Amar, R. B., Hamad, K. I., Jarullah, A. T., & Mujtaba, I. M. (2023). Design of Highly Efficient Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese-Molybdenum (NCMM) Nano-Catalysts Supported on Activated Carbon for Desulfurization Process. Catalysts, 13(8), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081196








