Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots
Abstract
1. Introduction
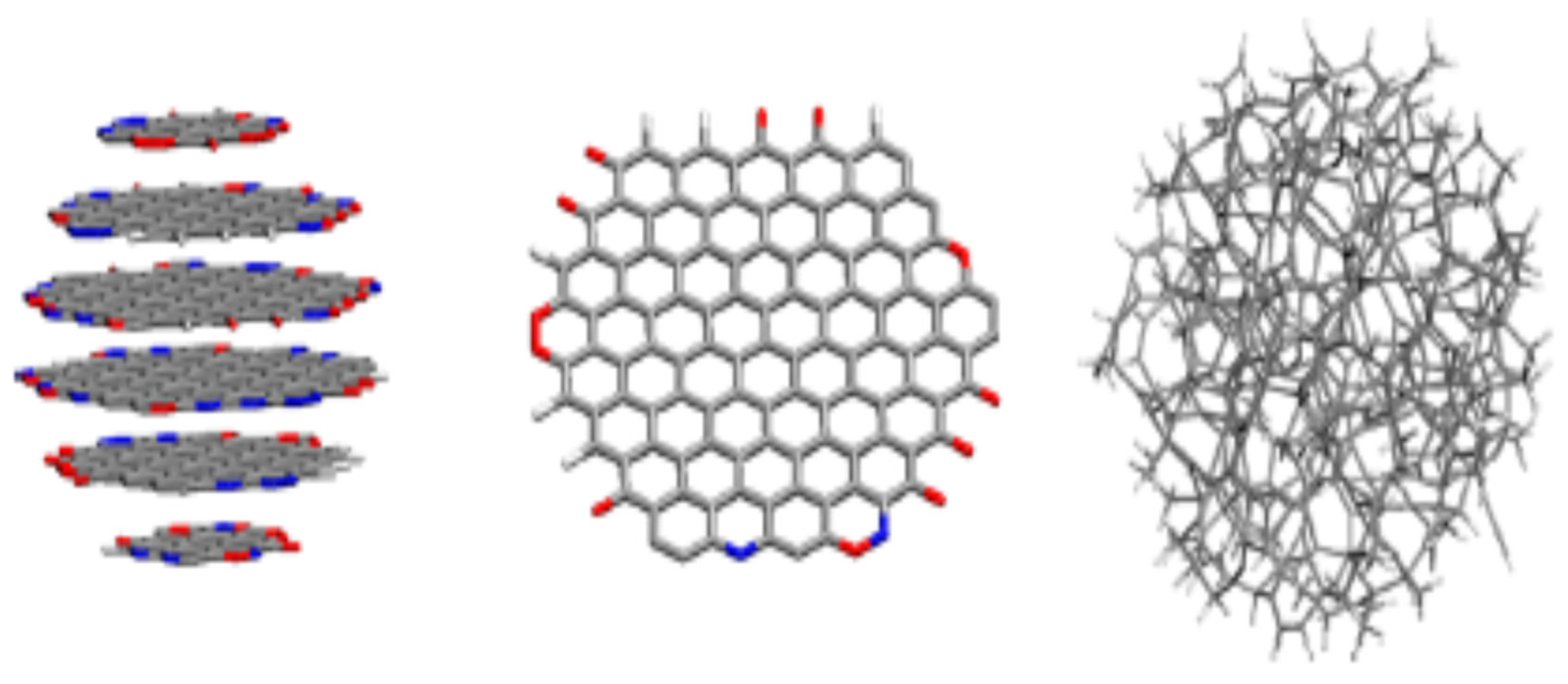
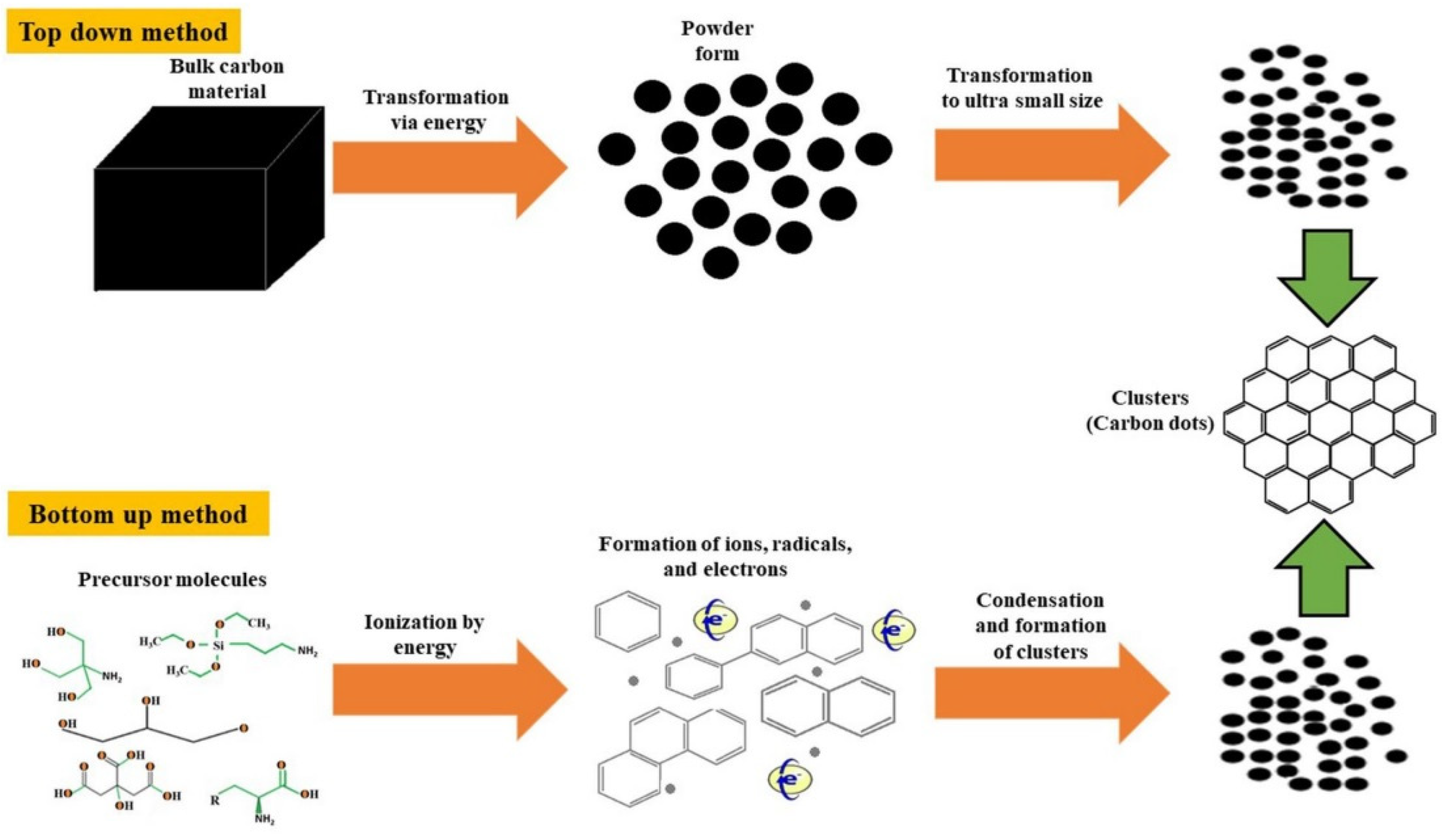
2. Novel Methods for the Synthesis of Carbon Nanodots
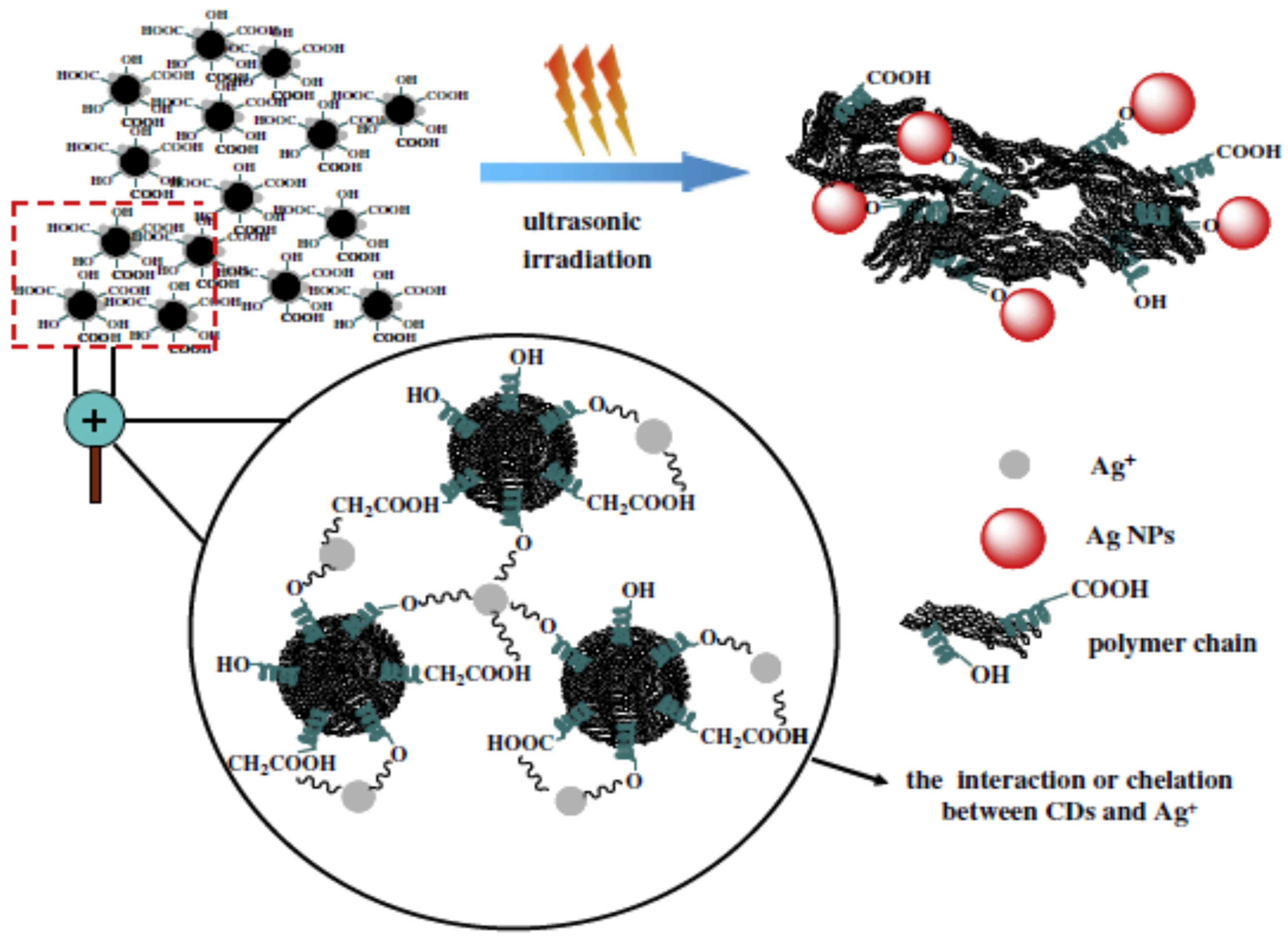
2.1. Sonochemical/Ultra-Sonic Fabrication of CDs
2.2. Hydrothermal Synthesis
2.3. Carbonization/Pyrolysis
2.4. Electrochemical Synthesis
2.5. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis
3. Applications of Carbon Dots (CDs)
3.1. Sensing
3.2. Bio Imaging Probes
3.3. Photodynamic Therapy
3.4. Photocatalysis
3.5. Biological Sensors and Chemical Sensors
3.6. Drug Delivery
3.7. Micro-Fluidic Marker
3.8. Bioimaging
3.9. Carbon Dots Chiral Photonics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.Y.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.L.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. QuantumSized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Chi, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, B. Electrochemiluminescence of Water-Soluble Carbon Nanocrystals Released Electrochemically from Graphite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4564–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: Emergent Nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; He, X.D.; Kang, Z.H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Lian, S.Y.; Tsang, C.C.A.; Yang, X.B.; Lee, S.T. Water-Soluble Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots and Catalyst Design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Ming, H.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.H.; Lee, S.T. Bioinspired Photoelectric Conversion System Based on Carbon Quantum Dot Doped Dye—Semiconductor Complex. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5080–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.W.; Wu, M.X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.M.; Huang, Y.B.; Wang, X.H.; Sun, Q. A sensitive “off-on” carbon dots-Ag nanoparticles fluorescent probe for cysteamine detection via the inner filter effect. Talanta 2021, 221, 121463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Ge, H.; Ren, Z.P.; Huang, Z.J.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.H. Controllable Synthesis of Biocompatible Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Cellulose Hydrogel for the Specific Detection of Hg2+. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 617097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Ni, Y. Facile Microwave Assisted Solid Phase Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Nitrogen Sulfur Co-doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Cellular Imaging Applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13004–13011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Lei, B. Far-Red Carbon Dotsas Efficient Light-Harvesting Agents for Enhanced Photosynthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21009–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.S.; Zhang, H.Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.Z. Highly fluorescent carbon dots as selective and visual probes for sensing copper ions in living cells via an electron transfer process. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, J.; Lee, H.J.; Chung, J.S.; Kim, M.H.; Hur, S.H. Blue emitting nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for nitrite ion sensing and cell-imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1079, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C. Rapid screening and quantitative detection of Salmonella using a quantum dot nanobead-based biosensor. Analyst 2020, 145, 2184–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, Fluorescence Origin and Sensing Applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.H.; Zhang, D.F.; Ding, Y.F.; Zheng, X.D.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Hua, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, X.L.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.L. Applications of hydrothermal synthesis of Escherichia coli derived carbon dots in in vitro and in vivo imaging and p-nitrophenol detection. Analyst 2020, 145, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.T. Graphene plasmon for optoelectronics. Rev. Phys. 2021, 6, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Y.K.; Sharma, G.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, P.; Johnston, A.; Bappi, G.; Fan, J.Z.; Kung, H. Bright High-Colour Purity Deep-Blue Carbon Dot Light-Emitting Diodes via Efficient Edge Amination. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, M.Y.; Qiu, J.S.; Sun, Y.P. Design and fabrication of carbon dots for energy conversion and storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, M.T. Graphene-based SERS for sensor and catalysis. Appl. Spectrosco. Rev. 2021, 58, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Shih, Z.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chang, H.T. Synthesis and analytical applications of photoluminescent carbon nanodots. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Pathan, S.H.; Mitra, S.; Modha, B.H.; Goswami, A.; Pramanik, P. Tuning of photoluminescence on different surface functionalized carbon quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 3602–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, W. Green synthesis of silver nanoclusters supported on carbon nanodots: Enhanced photoluminescence and high catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12558–12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottam, N.; Smrithi, S.P. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Current prospects on synthesis, properties and sensing applications. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2021, 9, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.; He, P.; Ding, G. Carbon-based quantum dots with solid-state photoluminescent: Mechanism, implementation, and application. Small 2020, 16, 2004621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Chen, P.C.; Periasamy, A.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Chang, H.T. Photoluminescent carbon nanodots: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and analytical applications. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mat. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippidis, A.; Stefanakis, D.; Anglos, D.; Ghanotakis, D. Microwave heating of arginine yields highly fluorescent nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, S. Plant leaf-derived fluorescent carbon dots for sensing, patterning and coding. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4925–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, B.; Wang, Y.; Da, P.; Li, J.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Zhao, D.; Gong, X.; Zheng, G. Solar-driven photoelectrochemical probing of nanodot/nanowire/cell interface. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Liu, R.; Koynov, K.; Wu, D.; Best, A.; Kumar, R.; Bonoiu, A.; Prasad, P.N. Photoluminescent carbon dots as biocompatible nanoprobes for targeting cancer cells in vitro. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2010, 114, 12062–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.C.E.; Gonçalves, H.M. Analytical and bioanalytical applications of carbon dots. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K. Quantum dots go large: A small industry could be on the verge of a boom. Nature 2009, 459, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Meziani, J.M.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Luo, P.G.; Lin, Y.; Harruff, B.A.; Veca, L.M.; Murray, D.; et al. Carbon Dots for Multiphoton Bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11318–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.T.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.F.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y.P. Carbon Dots for Optical Imaging in Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Ban, R.; Zhang, P.H.; Wu, G.H.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhu, J.J. Hair Fiber as a Precursor for Synthesizing of Sulfur- and Nitrogen-Codoped Carbon Dots with Tunable Luminescence Properties. Carbon 2013, 64, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Han, K.; Tang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, T.; Cheng, W. Recent advances in carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Boghossian, A.A. Covalent conjugation of proteins onto fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes for biological and medical applications. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.L.; Niu, K.Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, N.Q.; Du, X.W. One-Step Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles by Laser Irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ming, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Ren, S.; Chen, C.; Chi, Y.; Yu, T. Etching Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes into Green and Yellow Single-Layer Graphene Quantum Dots. Carbon 2013, 64, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadranel, A.; Margraf, J.T.; Strauss, V.; Clark, T.; Guldi, D.M. Carbon nanodots for charge-transfer processes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lian, S.; Lee, S.T.; Kang, Z. One-Step Ultrasonic Synthesis of Water-Soluble Carbon Nanoparticles with Excellent Photoluminescent Properties. Carbon 2011, 49, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; He, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Kang, Z.H.; Lee, S.T. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles Directly from Active Carbon via a One-Step Ultrasonic Treatment. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 16, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, H.B.; Guo, C.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based Dots Co-doped with Nitrogen and Sulfur for High Quantum Yield and Excitation-Independent Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaraki, R.; Abdi, O. Microwave assisted synthesis of N-doped carbon dots: Aneasy, fast and cheap sensor for determination of aspartic acid in sport supplements. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for selective detection of picric acid in water samples. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8111–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.B.; Sun, Z.S.; Zhou, W.Y.; Mo, F.W.; Wu, Z.C.; Zhang, X.G. Hydrothermal synthesis of bright blue-emitting carbon dots for bioimaging and fluorescent determination of baicalein. Opt. Mater. 2021, 113, 110796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.L.; Long, B.B.; Xie, D.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, K. Rapid and Green Fabrication of Carbon Dots for Cellular Imaging and Anti-Counterfeiting Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannan, A.; Imae, T. One-Pot Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Orange Waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 15673–15678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, M.P.; Wiguna, P.A.; Susanto-Rosita, N.; Suciningtyas, S.A. Sulhadi Performance of Photocatalyst Based Carbon Nanodots from Waste Frying Oil in Water Purification. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1725, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Achilleos, D.S.; Kasap, H.; Reisner, E. Photocatalytic hydrogen generation coupled to pollutant utilization using carbon dots produced from biomass. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2831–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Saini, D.; Singh, B.; Kaushik, J.; Garg, A.K.; Sonkar, S.K. Bitter apple peel derived photoactive carbon dots for the sunlight induced photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye. Sol. Energy 2020, 197, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Tripathi, K.M.; Singh, N.; Choudhary, S.; Gupta, R.K. Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from lemon peel waste: Applications in sensing and photocatalysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72423–72432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, A.D.; Potasz, P.; Korkusinski, M.; Hawrylak, P. Graphene Quantum Dots; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hawrylak, P.; Peeters, F.; Ensslin, K. Carbononics-integrating electronics, photonics and spintronics with graphene quantum dots. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2016, 10, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, K.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, J.H. Tuning the optical properties of graphene quantum dots for biosensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3219–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisker, G.; Bakh, N.A.; Lee, M.A.; Ahn, J.; Park, M.; O’Connell, E.B.; Strano, M.S. Insulin detection using a corona phase molecular recognition site on single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Lan, J.Y.; Jin, J.C.; Dong, P.; Jiang, F.L.; Liu, Y. Highly Photoluminescent Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots and Their Protective Effects against Oxidative Stress on Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28346–28352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Bian, L.; Wang, X.; Pu, Q. Controlled synthesis of fluorescent carbon materials with the assistance of capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2021, 228, 122224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvali, D.; Narin, I.; Soylak, M.; Yilmaz, E. Green synthesis of magnetic carbon nanodot/graphene oxide hybrid material (Fe3O4@C-nanodot@GO) for magnetic solid phase extraction of ibuprofen in human blood samples prior to HPLC-DAD determination. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, L.; Cao, L.; Chang, Z.; Mei, Q.; Yan, R.; Ge, M.; Jiang, C.; Dong, W.F. Green Synthesis of Lutein-Based Carbon Dots Applied for Free-Radical Scavenging within Cells. Materials 2020, 13, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Cheng, D.; Wu, C.; Lu, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Yin, P.; Liu, M.; Li, H. Group IV nanodots: Synthesis, surface engineering and application in bioimaging and biotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10290–10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. One-step synthesis of a macroporous Cu-g/C3N4 nanofiber electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14087–14090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhong, X.; He, J. Synthesis of Yellow-Fluorescent Carbon Nano-dots by Microplasma for Imaging and Photocatalytic Inactivation of Cancer Cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Seo, Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Oh, H.; Lee, Y.; Park, E. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots to destroy bacteria competing with Campylobacter jejuni in enrichment medium, and development of a monoclonal antibody to detect C. jejuni after enrichment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Bao, L.; Wang, H.; Larson, S.L.; Ballard, J.H.; Knotek-Smith, H.M.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, F. A simple method for the synthesis of biochar nanodots using hydrothermal reactor. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Jiang, X.; Pang, D.W. Carbon Nanoparticles and Nanostructures; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small molecules derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, H. Amino Acids as the Source for Producing Carbon Nanodots: Microwave Assisted One-Step Synthesis, Intrinsic Photoluminescence Property and Intense Chemiluminescence Enhancement. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9634–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzier, D.; Favaro, M.; Agnoli, S.; Silvestrini, S.; Granozzi, G.; Maggini, M.; Moretto, A. Synthesis of Luminescent 3D Microstructures Formed by Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Self Assembly Properties. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6592–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Dallas, P.; Giannelis, E.P. Formation Mechanism of Carbogenic Nanoparticles with Dual Photoluminescence Emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, K.; Wu, L.; Yu, S.-H.; Antonietti, M.; Titirici, M.-M. Engineering Carbon Materials from the Hydrothermal Carbonization Process of Biomass. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenke, A.M.; Hoeppener, S.; Schubert, U.S. Synthesis and Modification of Carbon Nanomaterials Utilizing Microwave Heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4113–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, E.; Giacalone, F.; Prato, M. Non-Conventional Methods and Media for the Activation and Manipulation of Carbon Nanoforms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, E.; Prato, M. Carbon Nanotubes and Microwaves: Interactions, Responses, and Applications. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3819–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Shi, H.; Ji, W.; Guo, X.; Yuan, W.; Hu, Q. One-step microwave synthesis of carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of copper ions in aqueous solution. New, J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Xiong, Y.; von Seckendorff, M.; Susha, A.S.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Molecular fluorescence in citric acid-based carbon dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Valcàrcel, M. Strong luminescence of carbon dots induced by acetone passivation: Efficient sensor for a rapid analysis of two different pollutants. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 804, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðordevi’c, L.; Arcudi, F.; Prato, M. Preparation, functionalization and characterization of engineered carbon nanodots. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2931–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Mauro, N.; Buscarino, G.; Sciortino, L.; and Popescu, R.; Schneider, R.; Giammona, G.; Gerthsen, D.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F. β-C3N4 nanocrystals: Carbon dots with extraordinary morphological, structural, and optical homogeneity. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Yin, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wei, J. Carbon nanodots derived from urea and citric acid in living cells: Cellular uptake and antioxidation effect. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Chai, L.; Ma, J.; Qian, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, H. B-doped carbon quantum dots as a sensitive fluorescence probe for hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Sol-gel chemistry for carbon dots. Chem. Rev. 2018, 18, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðordevi’c, L.; Arcudi, F.; Prato, M. Synthesis, separation, and characterization of small and highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Wu, X.; Hao, Y. The mechanism of blue photoluminescence from carbon nanodots. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2014, 16, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, L.; Yinzi, C.; Chun, L.; Jiali, F.; Weidong, X.; Xiaojuan, L. Carbon nanodots with intense emission from green to red and their multifunctional applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Holá, K.; Sudolská, M.; Kalytchuk, S.; Nachtigallová, D.; Rogach, A.L.; Otyepka, M.; Zboril, R. Graphitic nitrogen triggers red fluorescence in carbon dots. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckmeier, C.J.; Schneider, J.; Xiong, Y.; Häusler, J.; Kasák, P.; Schnick, W.; Rogach, A.L. Aggregated molecular fluorophores in the ammonothermal synthesis of carbon dots. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Pang, D.W. Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: Surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Croy, G.E.; Sonkar, S.K.; Yang, F.; Monica Veca, L.; Wang, P.; Tackett II, K.N.; Yu, J.-J.; Vasile, E.; Qian, H.; Liu, Y. Towards structurally defined carbon dots as ultracompact fluorescent probes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4522–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Carbon dots and graphene quantum dots in electrochemical biosensing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Soriano, M.L.; Sciortino, A.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F.; Cardenas, S. One-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dots and simultaneous nanostructured self-assembly via a novel microwave-assisted method: Impact on triazine removal and efficiency monitoring. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Luo, P.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y.; Shi, G. Large scale preparation of graphene quantum dots from graphite with tunable fluorescence properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Sun, L. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, W.; Lee, G.; Do, S.; Joo, T.; Rhee, S.W. Size-controlled soft-template synthesis of carbon nanodots toward versatile photoactive materials. Small 2014, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.H.; Suslick, K.S. Applications of ultrasound to the synthesis of nanostructured materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukin, D.G.; Radziuk, D.; Möhwald, H. Ultrasonic fabrication of metallic nanomaterials and nanoalloys. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodgopal, K.; Neppolian, B.; Lightcap, I.V.; Grieser, F.; Ashokkumar, M.; Kamat, P.V. Sonolytic design of graphene−Au nanocomposites. Simultaneous and sequential reduction of graphene oxide and Au (III). Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J. Crystal formation and growth mechanism of inorganic nanomaterials in sonochemical syntheses. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 2292–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrabalak, S.E. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of carbon materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedanken, A. Using sonochemistry for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, T. Sonochemical synthesis of SnO2nanobelt/CdS nanoparticle core/shell heterostructures. Chem. Commun. 2004, 22, 2558–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasin, P.; Wu, Y. Sonochemical synthesis of copper hydride (CuH). Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslick, K.S.; Flannigan, D.J. Inside a collapsing bubble: Sonoluminescence and the conditions during cavitation. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Shao, M.; Lee, S.T. Upconversion and downconversion fluorescent graphene quantum dots: Ultrasonic preparation and photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, J.; Ge, Z.; You, Y.; Xu, H. Sonochemical synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon nanodots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52230–52234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Wan, Q.; Wen, Y.Q.; Wei, Y. A one-step ultrasonic irradiation assisted strategy for the preparation of polymer-functionalized carbon quantum dots and their biological imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Park, E.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.W.; Jeong, S.W.; Chi, H.K.; Lee, Y.C.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, J. Photoluminescent Green Carbon Nanodots from Food-Waste-Derived Sources: Large-Scale Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Wan, J.; Chu, H.; Chen, M. Carbon nanodots as reductant and stabilizer for one-pot sonochemical synthesis of amorphous carbon-supported silver nanoparticles for electrochemical nonenzymatic H2O2 sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 728, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, P.; Dhanabalan, S.C.; Alagan, M.; Muthuvijayan, S.; Ponraj, J.S.; Somasundaram, C.K. Facile synthesis and characterisation of green luminescent carbon nanodots prepared from tender coconut water using the acid-assisted ultrasonic route. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.A.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, J.; Huh, Y.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.; An, H.R.; et al. Biocompatible liquid-type carbon nanodots (C-paints) as light delivery materials for cell growth and astaxanthin induction of Haematococcus pluvialis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Endoplasmic reticulum-targeted polymer dots encapsulated with ultrasonic synthesized near-infrared carbon nanodots and their application for in vivo monitoring of Cu2+. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 627, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, R.; Gangapuram, B.R.; Dadigala, R.; Eslavath, R.; Singh, S.S.; Guttena, V. Facile and green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from onion waste and their potential applications as sensor and multicolour imaging agents. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 28633–28639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Gopinath, P. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 2015, 140, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Zhu, X.; Xue, H.; Ng, T.W.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Yang, T.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Green preparation of carbon dots with papaya as carbon source for effective fluorescent sensing of Iron (III) and Escherichia coli. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasibabu, B.S.B.; D’Souza, S.L.; Jha, S.; Singhal, R.K.; Basu, H.; Kailasa, S.K. One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for imaging bacterial and fungal cells. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, G.; Yu, S.H. Scale-up synthesis of fragrant nitrogen-doped carbon dots from bee pollens for bioimaging and catalysis. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latief, U.; ul Islam, S.; Khan, Z.M.; Khan, M.S. A facile green synthesis of functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for a highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 262, 120132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.X.; Dong, M.T.; Huang, C.B. Low-cost synthesis of carbon nanodots from natural products used as a fluorescent probe for the detection of ferrum(III) ions in lake water. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.N.; Jha, S.; Kailasa, S.K. One-pot green synthesis of carbon dots by using Saccharum officinarum juice for fluorescent imaging of bacteria (Escherichia coli) and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 38, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.B.; Qin, X.Y.; Liu, S.; Chang, G.H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Luo, Y.L.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X.P. Economical, Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles and Their Use as Probes for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Mercury(II) Ions. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5351–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C. One step hydrothermal synthesis of carbon nanodots to realize the fluorescence detection of picric acid in real samples. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 258, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, F.; Hu, S.; Wu, B.G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Jiang, B.J.; Fu, H.G. Graphene Quantum-Dot-Modified Hexagonal Tubular Carbon Nitride for Visible-Light Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. RSC Adv. 2018, 10, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Mansoor, F.; Naz, S.; Lei, J.; Kanwal, S. Oxidative synthesis of highly fluorescent boron/nitrogen co-doped carbon nanodots enabling detection of photosensitizer and carcinogenic dye. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10232–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Batra, G.; Kaushik, K.; Rao, C.; Verma, N.C.; Mondal, B.; Yadav, A.; Nandi, C.K. Absorption and emission of light in red emissive carbon nanodots. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3615–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.B.; Wei, J.S.; Xiong, H.M. Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakier, Y.M.; Ghali, M.; Elkun, A.; Beltagi, A.M.; Zahra, W.K. Static interaction between colloidal carbon nano-dots and aniline: A novel platform for ultrasensitive detection of aniline in aqueous media. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 134, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, X.; Peng, Y. A General Solid-State Synthesis of Chemically-Doped Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging and Optoelectronic Applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10162–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lau, S.; Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Yang, P. Multicolour light emission from chlorine-doped graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 7308–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneerad, J.; Neungnoraj, K.; In, I.; Paoprasert, P. Environmentally friendly supercapacitor based on carbon dots from durian peel as an electrode. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 803, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, D.K.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Hong, L.L.; Huang, S.M. One-pot synthesis of N-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 16714–16718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjal, D.B.; Naik, V.M.; Waghmare, R.D.; Patil, C.S.; Shejwal, R.V.; Gore, A.H.; Kolekar, G.B. Sustainable carbon nanodots synthesised from kitchen derived waste tea residue for highly selective fluorimetric recognition of free chlorine in acidic water: A waste utilization approach. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Sánchez, C.; Mediavilla, M.; Guerrero-Esteban, T.; Revenga-Parra, M.; Pariente, F.; Lorenzo, E. Direct covalent immobilization of new nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots by electrografting for sensing applications. Carbon 2020, 159, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, J.P.; Jha, G.; Youn, D.H.; Ziegler, J.M.; Andoni, I.; Choi, E.; Heller, A.; Dunn, B.S.; Weiss, P.S.; Penner, R.M. Electrode Degradation in Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1243–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Tang, Y.; Han, K.; Wang, B. Facile synthesis of carbon nanodots from ethanol and their application in ferric (III) ion assay. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15068–15073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, A.K.; Ashraf, P.M. Carbon nanodots synthesized from chitosan and its application as a corrosion inhibitor in boat-building carbon steel BIS2062. Appl. Nano. 2020, 10, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvapalli, D.M.; Sheardy, A.T.; Alapati, K.C.; Wei, J. High quantum yields fluorescent carbon nanodots for detection of Fe (III) Ions and electrochemical study of quenching mechanism. Talanta 2020, 209, 120538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluta, S.; Lesiak, A.; Cabaj, J. Simple and cost-effective electrochemical method for norepinephrine determination based on carbon dots and tyrosinase. Sensors 2020, 20, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Bai, T.; Li, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, W. Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7955–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Zhai, X.; Liu, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, W. A facile and versatile approach to biocompatible “fluorescent polymers” from polymerizable carbon nanodots. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10431–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescenttwo-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, Z.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of wavelength-tunablephotoluminescent carbon nanodots and their potential applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Gurung, R.B.; Srivastava, R. Graphene quantum dots from mangiferaindica: Application in near-infrared bioimaging and intracellular nanothermometry. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.R.; Santos, C.M.W.; Sousa, R.R.; De Paula, R.C.M.; Cunha, P.L.R.; Feitosa, J.P.A. Novel and Fast Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Raw Cashew Gum. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, S.; Alas, M.O.; Ozbek, B.; Genc, R. Evaluation of the physical properties of fluorescent carbon nanodots synthesized using Nerium oleander extracts by microwave-assisted synthesis methods. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Rapid synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogendoped graphene quantum dots for effective detection of ferric ions and as fluorescent ink. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15842–15848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendao, R.M.S.; Crista, J.D.M.A.; Afonso, A.C.P.; Yuso, M.V.M.; Algarra, M.; Silva, J.C.E.; Silva, L.P. Insight into the hybrid luminescence showed by carbon dots and molecular fluorophores in solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, G.; Bai, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Tang, C.; Kong, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. A versatile platform for colorimetric, fluorescence and photothermal multi-mode glyphosate sensing by carbon dots anchoring ferrocene metal-organic framework nanosheet. J. Hazard. Mat. 2023, 443, 130277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized fluorescent carbon dots: Water stability, pH sensing, and cellular imaging. ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Sahoo, D.; Sarkar, P.; Chakraborty, K.; Das, S. Fluorescence turn-on andturn-off sensing of pesticides by carbon dot-based sensor. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12137–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, N.; Marinovic, A.; Yoshizawa, N.; Goode, A.E.; Fay, M.; Khlobystov, A.; Titirici, M.M.; Sapelkin, A. Structure and solvents effects on the optical properties of sugar-derivedcarbon nanodots. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Violette, K.; Ogunsolu, O.O.; Hanson, K. Metal ion mediated electrontransfer at dye–semiconductor interfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 2679–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Q.; Long, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, R. Enhancing theluminescence of carbon dots with a reduction pathway. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10650–10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Deore, A.; Mondal, S. Ultrafast dynamics in carbon dots as photosensitizers: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 7587–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Madonia, A.; Gazzetto, M.; Sciortino, L.; Rohwer, E.J.; Feurer, T.; Gelardi, F.M.; Cannas, M.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. The interaction of photoexcited carbon nanodotswith metal ions disclosed down to the femtosecond scale. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11902–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, H.; Kong, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, C.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z. Ultra-sensitiveand selective Hg2+ detection based on fluorescent carbon dots. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lv, J.J.; Zhou, D.L.; Bao, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, A.J.; Feng, J.J. One-pot greensynthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21691–21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, W.; Wang, R. Facile synthesis of polyaniline/carbon dotnanocomposites and their application as a fluorescent probe to detect mercury. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 41914–41919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, M.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhang, B.; Pang, D.W. Photoinduced electron transfer mediated by coordination between carboxyl on carbon nanodotsand Cu2+ quenching photoluminescence. J. Phy. Chem. C 2018, 122, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Qu, Q.; Shao, X.; Kong, B.; Tian, Y. Carbon-dot-based dual-emissionnanohybrid produces a ratiometric fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of cellular copperions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7185–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, L.J.; Omer, K.M. Dual functional highly luminescence B, N Co-dopedcarbon nanodots as nanothermometer and Fe3+/Fe2+ sensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, A.; Yadav, R.; Basavaraj, N. Fluorescence quenching mechanism and the application of green carbon nanodots in the detection of heavy metal ions: A review. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 2326–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, H.M.; Duarte, A.J.; da Silva, J.C.E. Optical fiber sensor for Hg (II) based on carbon dots. Biosen. Bioelect. 2010, 26, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharat, P.M.; Pal, H.; Choudhury, S.D. Photophysics and luminescence quenching ofcarbon dots derived from lemon juice and glycerol. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectro. 2019, 209, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karali, K.K.; Sygellou, L.; Stalikas, C.D. Highly fluorescent N-doped carbon nanodotsas an effective multi-probe quenching system for the determination of nitrite, nitrate and ferric ions infood matrices. Talanta 2018, 189, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Liu, D.; Filpponen, I.; Johansson, L.S.; Malho, J.M.; Quraishi, S.; Liebner, F.; Santos, H.A.; Rojas, O.J. Photoluminescent hybrids of cellulose nanocrystals and carbon quantum dots as cytocompatible probes for in vitro bioimaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronican, J.J.; Thompson, D.B.; Beier, K.T.; McNaughton, B.R.; Cepko, C.L.; Liu, D.R. Potent delivery of functional proteins into Mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo using a superchargedprotein. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Behera, B.; Maiti, T.K.; Mohapatra, S. Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: Application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8835–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Jose, J.; Shanavas, M.S.; Marathakam, A.; Uddin, M.; Mathew, B. Silicon quantum dots: Promising theranostic probes for the future. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Tian, F.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Liu, W. One-step synthesis of surfacepassivated carbon nanodots by microwave assisted pyrolysis for enhanced multicolour photoluminescence and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13163–13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Qian, R.C. Rolling “wool-balls”: Rapid live-cell mapping of membrane sialic acids via poly-p-benzoquinone/ethylenediamine nanoclusters. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9681–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Yang, K.; Ma, Z.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Z. In vivo NIR fluorescenceimaging, biodistribution, and toxicology of photoluminescent carbon dots produced from carbonnanotubes and graphite. Small 2012, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.H.; Ryoo, S.R.; Park, J.; Min, D.H.; Kim, B.S. Highly biocompatible carbon nanodots for simultaneous bioimaging and targeted photodynamic therapy invitro and in vivo. Adv. Functional Mater. 2014, 24, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.B.; He, X.W.; Zhang, Y.K. High-yield and high-solubility nitrogen-doped carbon dots: Formation, fluorescence mechanism and imaging application. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Leung, K.C.F.; Wáng, Y.X.J. High performancephotoluminescent carbon dots for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging: Effect of nitrogen dopingratios. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8063–8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankoti, K.; Rameshbabu, A.P.; Datta, S.; Das, B.; Mitra, A.; Dhara, S. Onion derived carbon nanodots for live cell imaging and accelerated skin wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6579–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, F.; Kang, Z. Large scaleelectrochemical synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots and their photocatalytic property. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9526–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, T.; Sun, H.; Shao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Song, K.; Hao, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z. Two-step hydrothermally synthesized carbon nanodots/WO3 photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 15769–15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. Ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor based on water soluble carbon nanodots with multiple sensing capacities. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5514–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedamalai, M.; Periasamy, A.P.; Wang, C.W.; Tseng, Y.T.; Ho, L.C.; Shih, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Carbon nanodots prepared from o-phenylenediamine for sensing of Cu2+ ions in cells. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13119–13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Wen, X.; Zhang, G.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Controllable synthesis of green and blue fluorescent carbon nanodots for pH and Cu2+ sensing in living cells. Biosen. Bioelect. 2016, 77, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhao, C.; Wei, W.; Ren, J.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N.; Qu, X. Aptamer carbon-nanodot sandwich used for fluorescent detection of protein. Analyst 2012, 137, 5483–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Liang, S.; Tan, Y.; Sheng, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.X.A. Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.I.; Wu, W.C.; Periasamy, A.P.; Chang, H.T. Electrochemical synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots from glycine for highly sensitive detection of hemoglobin. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Chowdhury, D. Novel carbon dot coated alginate beads with superior stability, swelling and pH responsive drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4089–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Saha, B.; Ghosh, S.K.; Singh, N.P. Photoresponsivequinoline tethered fluorescent carbon dots for regulated anticancer drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10471–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework materials: Recent progress in synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16811–16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, T.; An, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Wu, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, C. Carbon nanodots@ zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles for simultaneous pH-responsive drug delivery and fluorescence imaging. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2014, 16, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jang, G.; Lee, T.S. New fluorescent metal-ion detection using a paper-based sensor strip containing tethered rhodamine carbon nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15649–15657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, P.; Ehrenberg, B.; Chen, J.Y. Carbon nanodots featuring efficient FRET for two-photon photodynamic cancer therapy with a low fs laser power density. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9372–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Guan, X.; Hu, X.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. Integrating oxaliplatin with highly luminescent carbon dots: An unprecedented theranostic agent for personalized medicine. Adv. Mat. 2014, 26, 3554–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wong, T.; Liow, J.L. Experimental and theoretical investigations of non-Newtonian electro-osmotic driven flow in rectangular microchannels. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6206–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencia, J.; Beebe, D.J. Controlled microfluidic interfaces. Nature 2005, 437, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.P.; Sharei, A.; Ding, X.; Sahay, G.; Langer, R.; Jensen, K.F. In vitro and ex vivo strategies for intracellular delivery. Nature 2016, 538, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, D.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, L.; An, T.; Lim, W.; Wong, T.; Sun, H. Fast dynamic visualizations in microfluidics enabled by fluorescent carbon nanodots. Small 2017, 13, 1700869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Storey, B.D.; Oddy, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Santiago, J.G. Instability of electrokinetic microchannel flows with conductivity gradients. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, 1922–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Luo, P.G.; Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Carbon Dots as Nontoxic and High-Performance Fluorescence Imaging Agents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18110–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Luo, Z.; Ding, C.; Li, B.; Zhou, S.; Wang, R.; Tian, Y. A two-photon “turn-on” fluorescent probe based on carbon nanodots for imaging and selective biosensing of hydrogen sulfide in live cells and tissues. Analyst 2014, 139, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Deshpande, S.; Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K.; Singh, N. Mitigating the cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots and enhancing their applications in bioimaging and drug delivery. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. Fluorescent carbon nanodots conjugated with folic acid for distinguishing folate-receptor-positive cancer cells from normal cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12568–12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, F.P.; Govan, J.; Mukhina, M.V.; Gun’ko, Y.K. The chiral nano-world: Chiroptically active quantum nanostructures. Nano. Hori. 2016, 1, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Tsunega, S.; Jin, R.H. Self-directing chiral information in solid–solid transformation: Unusual chiral-transfer without racemization from amorphous silica to crystalline silicon. Nano. Hori. 2017, 2, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Pociecha, D.; Abberley, J.P.; Martinez-Felipe, A.; Paterson, D.A.; Forsyth, E.; Lawrence, G.B.; Henderson, P.A.; Storey, J.M.; Gorecka, E.; et al. Spontaneous chirality through mixing achiral components: A twist-bend nematic phase driven by hydrogen-bonding between unlike components. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3383–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Nakagawa, M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.; Herranz, M.A.; Martín, N. Chirality transfer from graphene quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Liu, Q.; Geng, L.; Fang, Q.; Gong, J.R. Chiral nanoparticles as a new efficient antimicrobial nanoagent. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017, 6, 1601011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Han, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wei, T.; Yang, D.; Xu, H.; Nie, G. Highly fluorescent chiral N-S-doped carbon dots from cysteine: Affecting cellular energy metabolism. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malishev, R.; Arad, E.; Bhunia, S.K.; Shaham-Niv, S.; Kolusheva, S.; Gazit, E.; Jelinek, R. Chiral modulation of amyloid beta fibrillation and cytotoxicity by enantiomeric carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7762–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
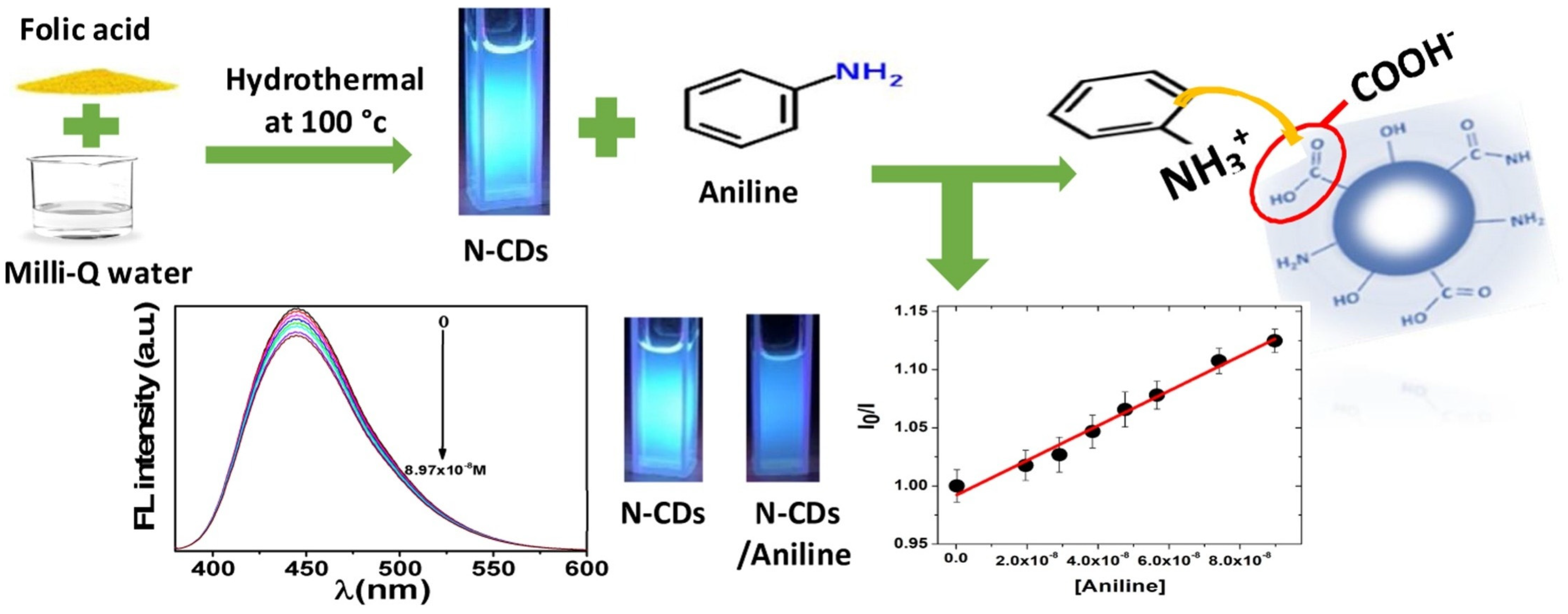
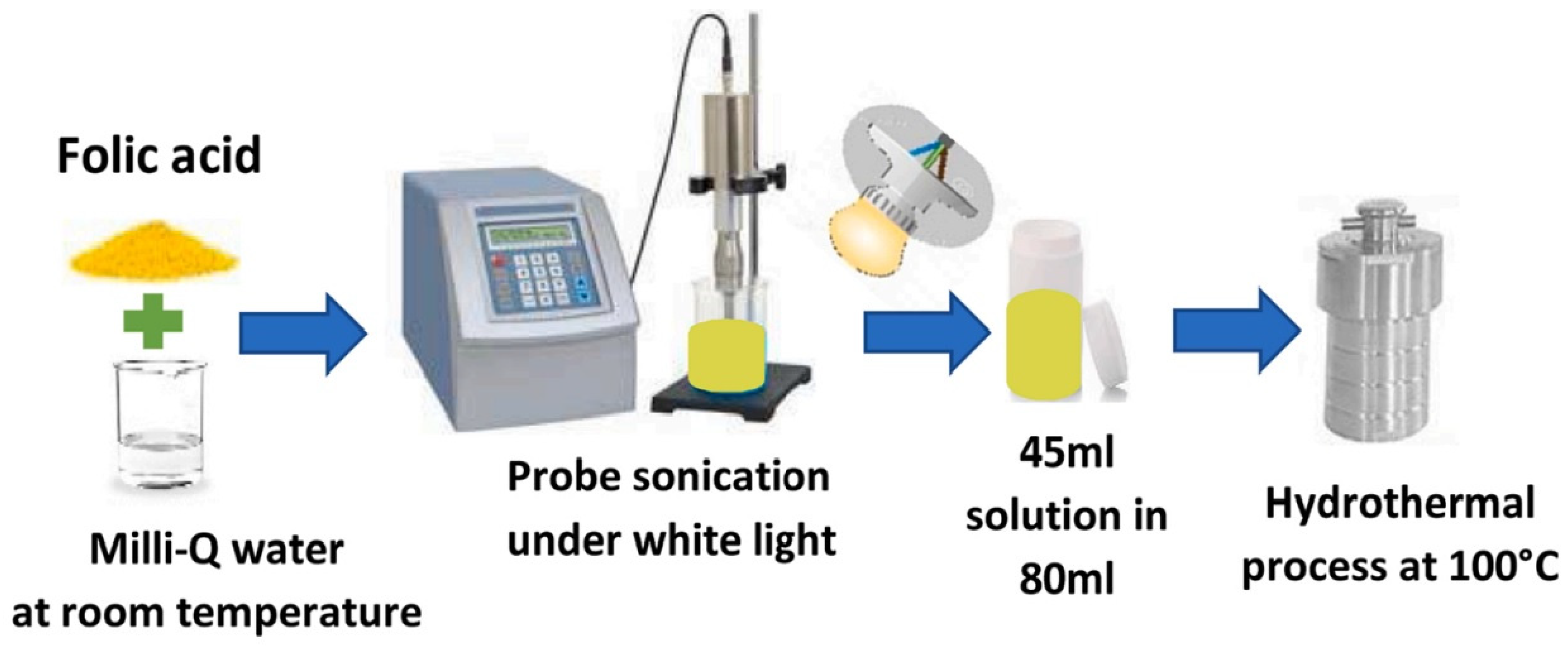

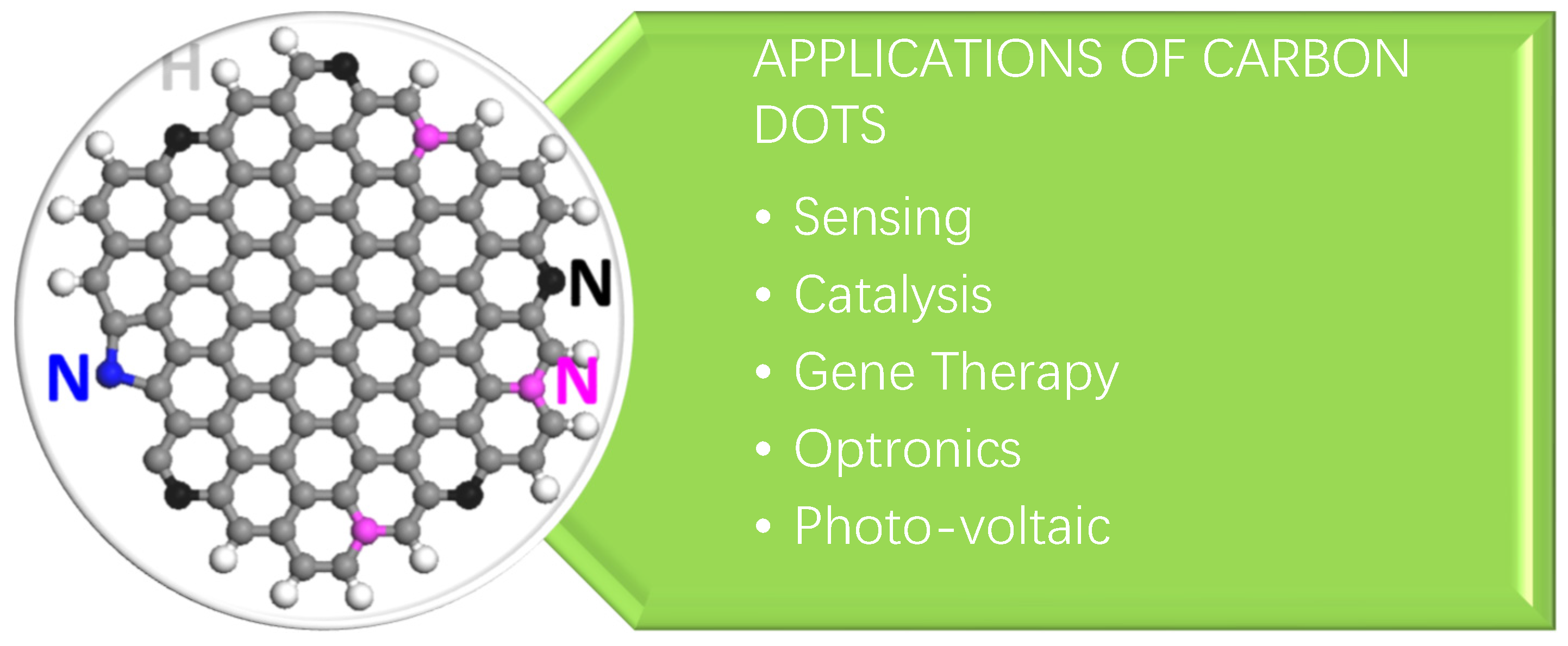
| Synthetic Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sonochemical/Ultra-sonic fabrication | Easy-operation | Expensive cost of energy | [108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116] |
| Hydrothermal synthesis | Cost-effective, environmentally benign, non-toxic | No uniformity in size | [124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131] |
| Carbonization/Pyrolysis | No solvent required, cost-effective, bulk-production | No uniformity in distribution of size | [132,133,134,135,136] |
| Electrochemical synthesis | Easy, cost-effective, environmentally benign | Uniformity in size distribution | [137,138,139,140,141,142] |
| Microwave-assisted synthesis | Fast, cost-effective, environmentally benign | No uniformity in distribution of size | [143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151] |
| Sources | Synthetic Methods | References |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon, Silver nitrate liquid solution | Sonochemical synthesis | [112] |
| Saccharum officinarum (Sugarcane) | Hydrothermal synthesis | [124] |
| Coconut water | Ultrasonication synthesis | [113] |
| o-phenylenediamine | Hydrothermal synthesis | [129] |
| Waste biomass | Carbonization synthesis | [136] |
| Ethanol | Electrochemical carbonization synthesis | [139] |
| Graphene | Sonochemical synthesis | [108] |
| p-phenylenediamine and urea | Hydrothermal synthesis | [130] |
| Mangifera indica (Mango) | Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis | [147] |
| Chitosan | Hydrothermal carbonization synthesis | [140] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banger, A.; Gautam, S.; Jadoun, S.; Jangid, N.K.; Srivastava, A.; Pulidindi, I.N.; Dwivedi, J.; Srivastava, M. Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots. Catalysts 2023, 13, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13050858
Banger A, Gautam S, Jadoun S, Jangid NK, Srivastava A, Pulidindi IN, Dwivedi J, Srivastava M. Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots. Catalysts. 2023; 13(5):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13050858
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanger, Anjali, Sakshi Gautam, Sapana Jadoun, Nirmala Kumari Jangid, Anamika Srivastava, Indra Neel Pulidindi, Jaya Dwivedi, and Manish Srivastava. 2023. "Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots" Catalysts 13, no. 5: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13050858
APA StyleBanger, A., Gautam, S., Jadoun, S., Jangid, N. K., Srivastava, A., Pulidindi, I. N., Dwivedi, J., & Srivastava, M. (2023). Synthetic Methods and Applications of Carbon Nanodots. Catalysts, 13(5), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13050858








